Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: Jameel Z, Rosa M. Papillary. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantpapillary.html. Accessed October 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- A rare subtype of invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) (J Surg Res 2021;261:105)
- Comprises about 0.5 - 0.7% of all invasive breast cancers (J Surg Res 2021;261:105, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2013;139:77)
Essential features
- A rare subtype of invasive ductal carcinoma with infiltrative papillary growth
- Imperative to distinguish it from other invasive and noninvasive mammary lesions, as well as extramammary tumors metastasizing to the breast
Terminology
- Invasive papillary carcinoma (IPC)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Most commonly seen in non-Caucasian postmenopausal women in their sixth to eighth decade of life (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2013;139:77, J Surg Res 2021;261:105)
- More common in lower economic status and lower household income (J Surg Res 2021;261:105)
Sites
- No specific location in the breast
Etiology
- Insufficient clinicopathological data on this tumor (Mod Pathol 2021 Jan 18 [Epub ahead of print])
- Much of the published literature about IPC in fact describes variants of encapsulated or solid papillary carcinoma with invasion (Mod Pathol 2021 Jan 18 [Epub ahead of print])
Clinical features
- Due to the rarity of this tumor, specific clinical features have not been described
- Typically presents with bloody nipple discharge, an abnormal mass or radiographic abnormalities
- However, it is not clear if these features refer to true IPC or other types of papillary carcinomas misdiagnosed as IPC (J Surg Res 2021;261:105)
Diagnosis
- Mammogram
- Breast ultrasound (US)
- Breast MRI
Radiology description
- Solitary mass, solid, solid and cystic, round, oval, lobulated or irregular (Clin Radiol 1997;52:865, Curr Probl Diagn Radiol 2019;48:348)
- Hypoechoic solid, smooth walled abnormalities, with good sound transmission on ultrasound (Cureus 2020;12:e11026)
Prognostic factors
- Tumors should be graded according to the Nottingham grading system (Histopathology 1991;19:403)
- Tumors should be staged according to their pathological size and axillary lymph node status
- Poor prognostic factors include old age, advanced pathologic stage and patients without radiation (J Surg Res 2021;261:105)
- Conflicting data; some report favorable prognosis when compared with invasive ductal carcinoma (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2013;139:77)
- Others report similar prognosis (J Surg Res 2021;261:105)
Case reports
- 45 year old woman with a right breast lump (J Cancer Res Ther 2015;11:1029)
- 52 year old woman with a right nipple lump (BMJ Case Rep 2018;2018:bcr2017222817)
- 61 year old woman with a painless breast mass (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2012;55:543)
- 79 year old woman with an irregular 9 mm right breast mass (Pathol Int 2019;69:183)
Treatment
- Surgical excision followed by adjuvant radiation and systemic therapy based on the predictive and prognostic factors (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2013;139:77)
Gross description
- Size ranging from less than 2 cm to more than 5 cm (Cureus 2020;12:e11026)
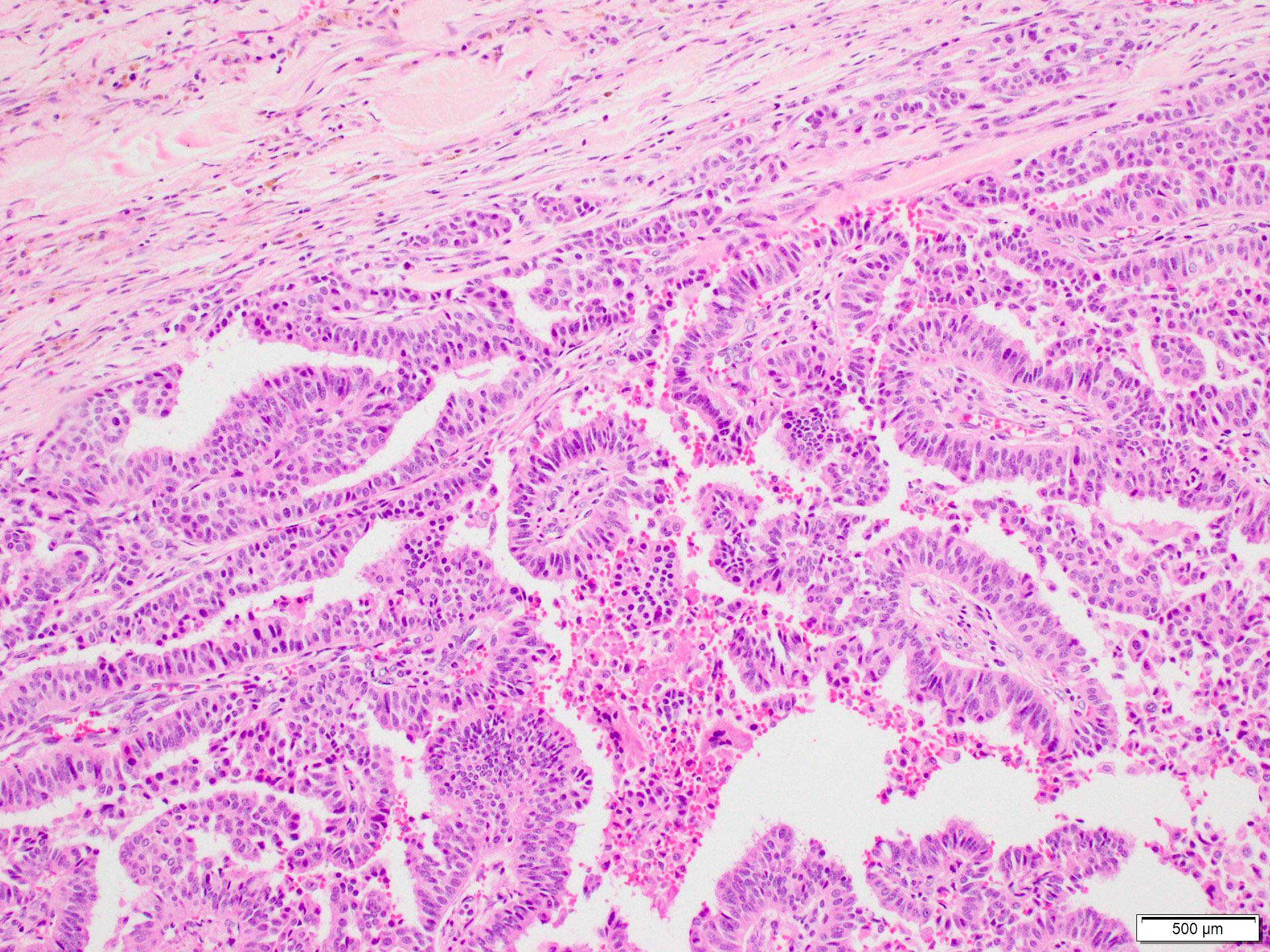
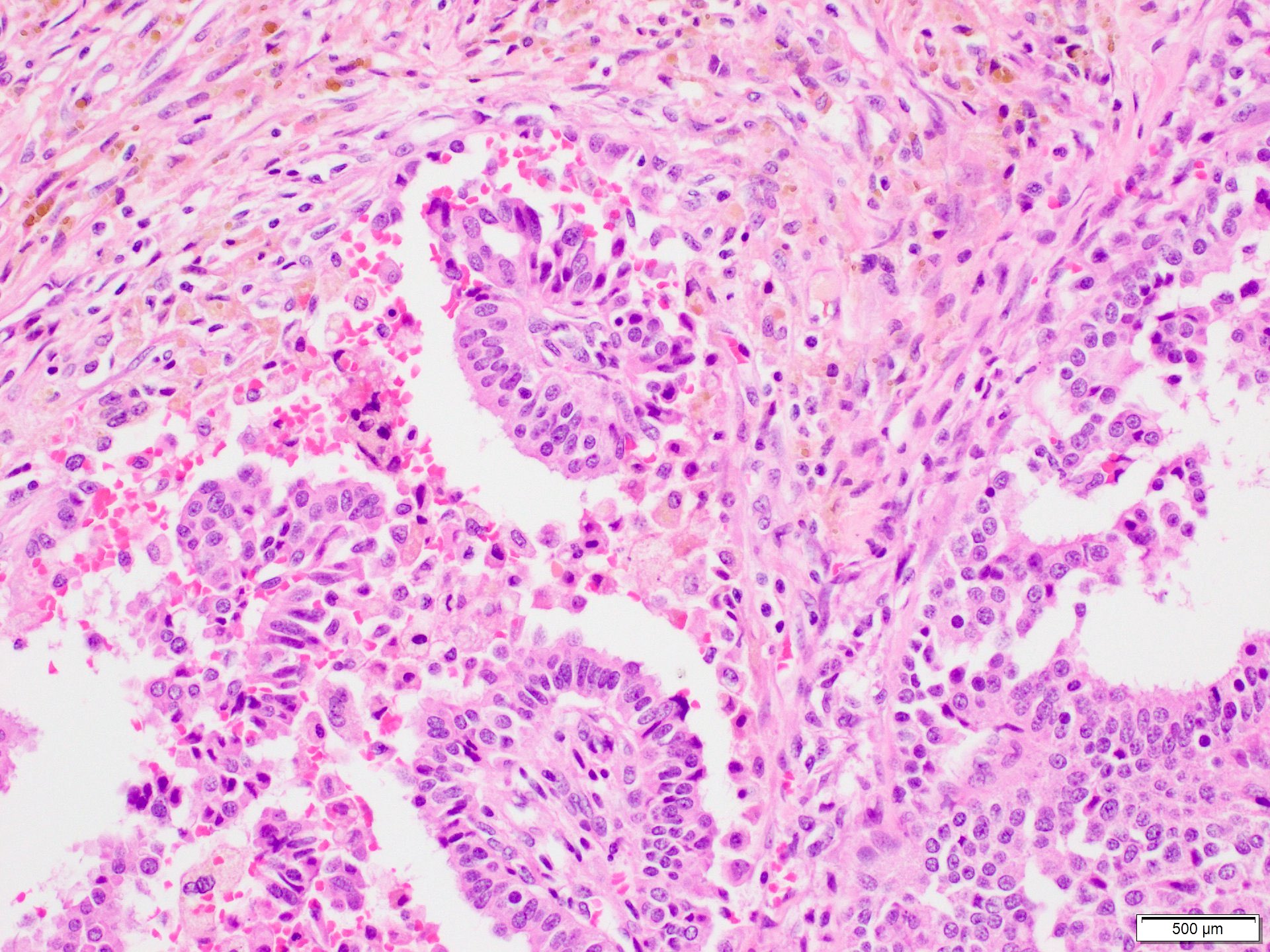
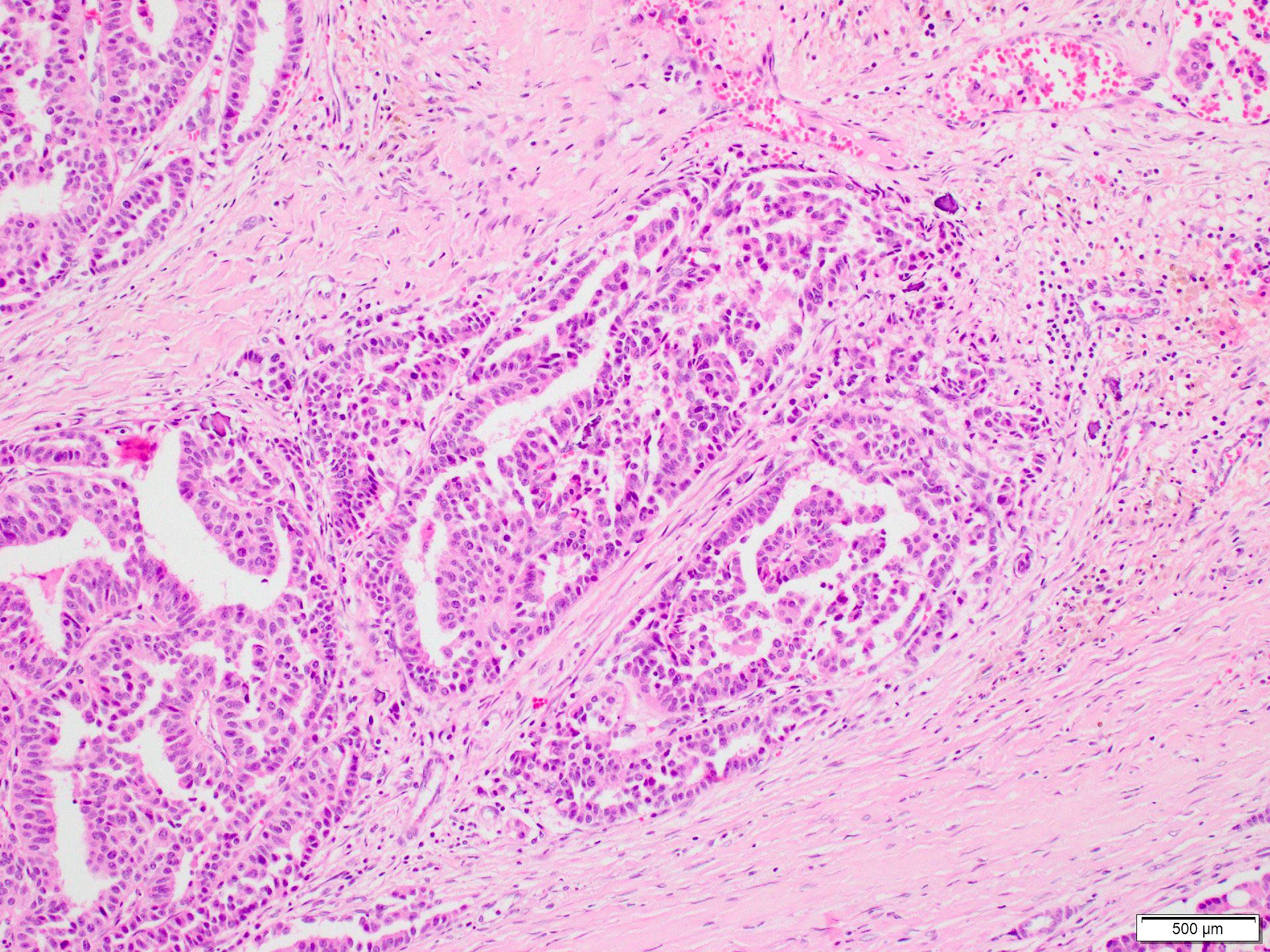
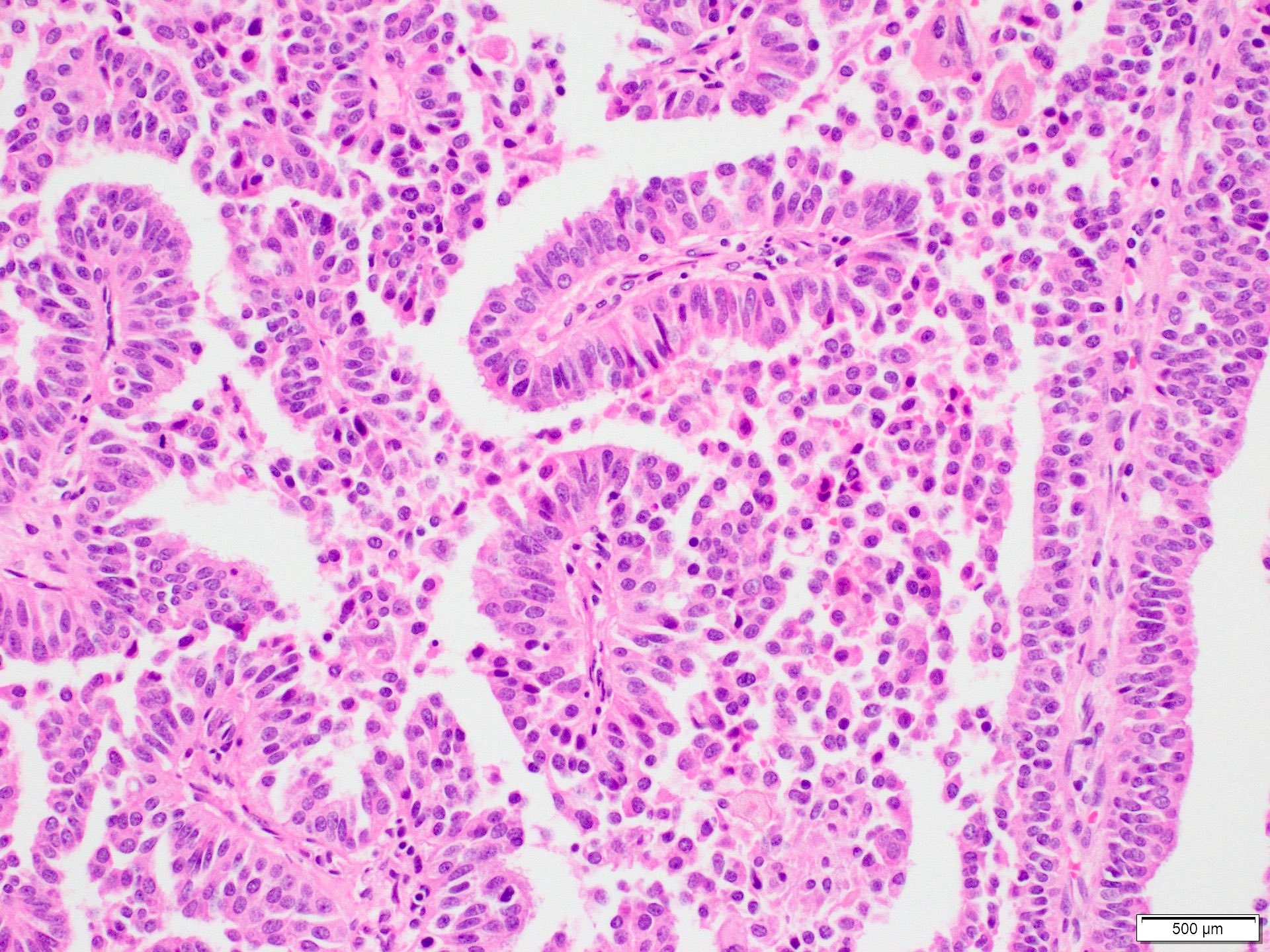
Microscopic (histologic) description
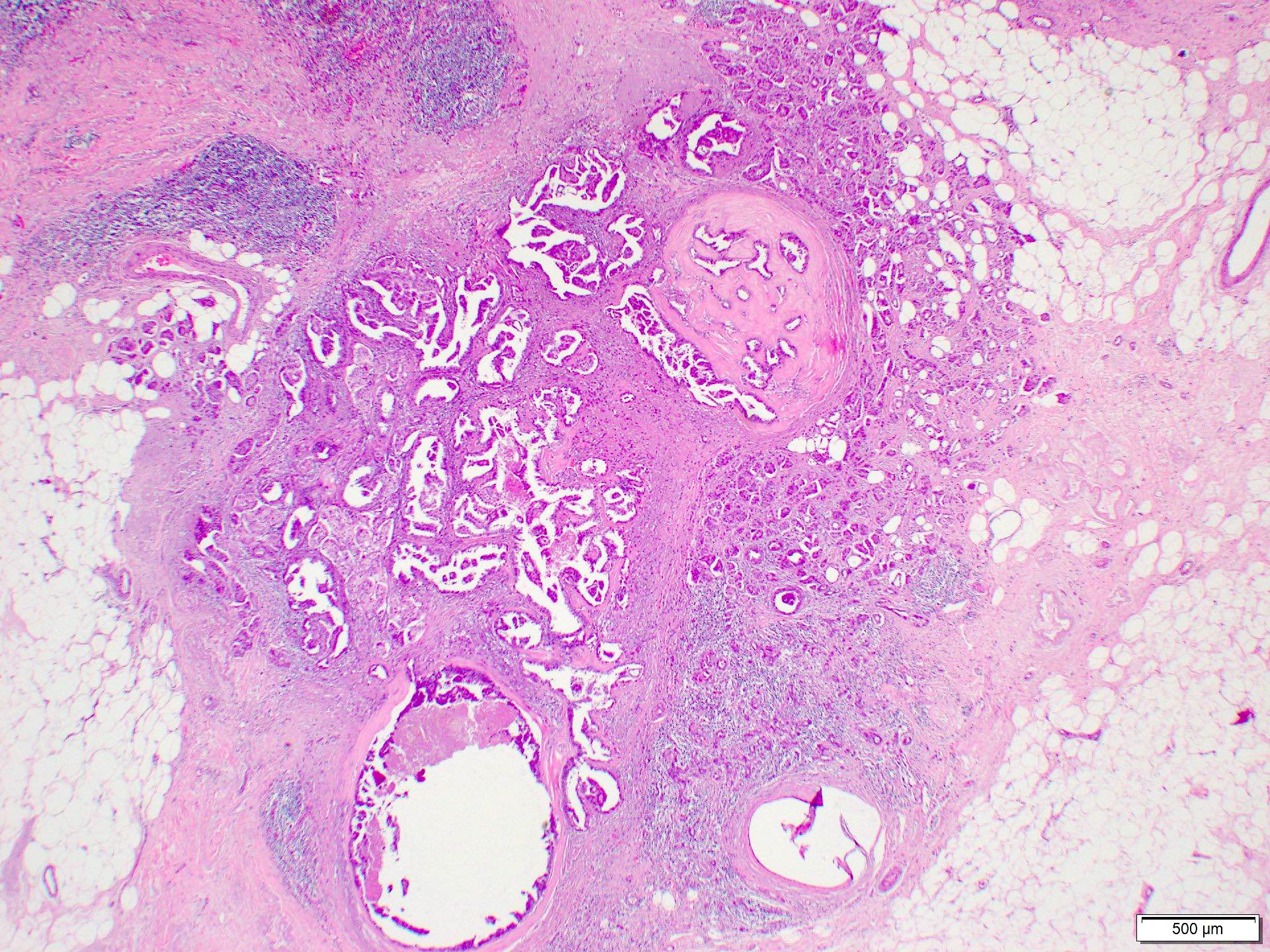
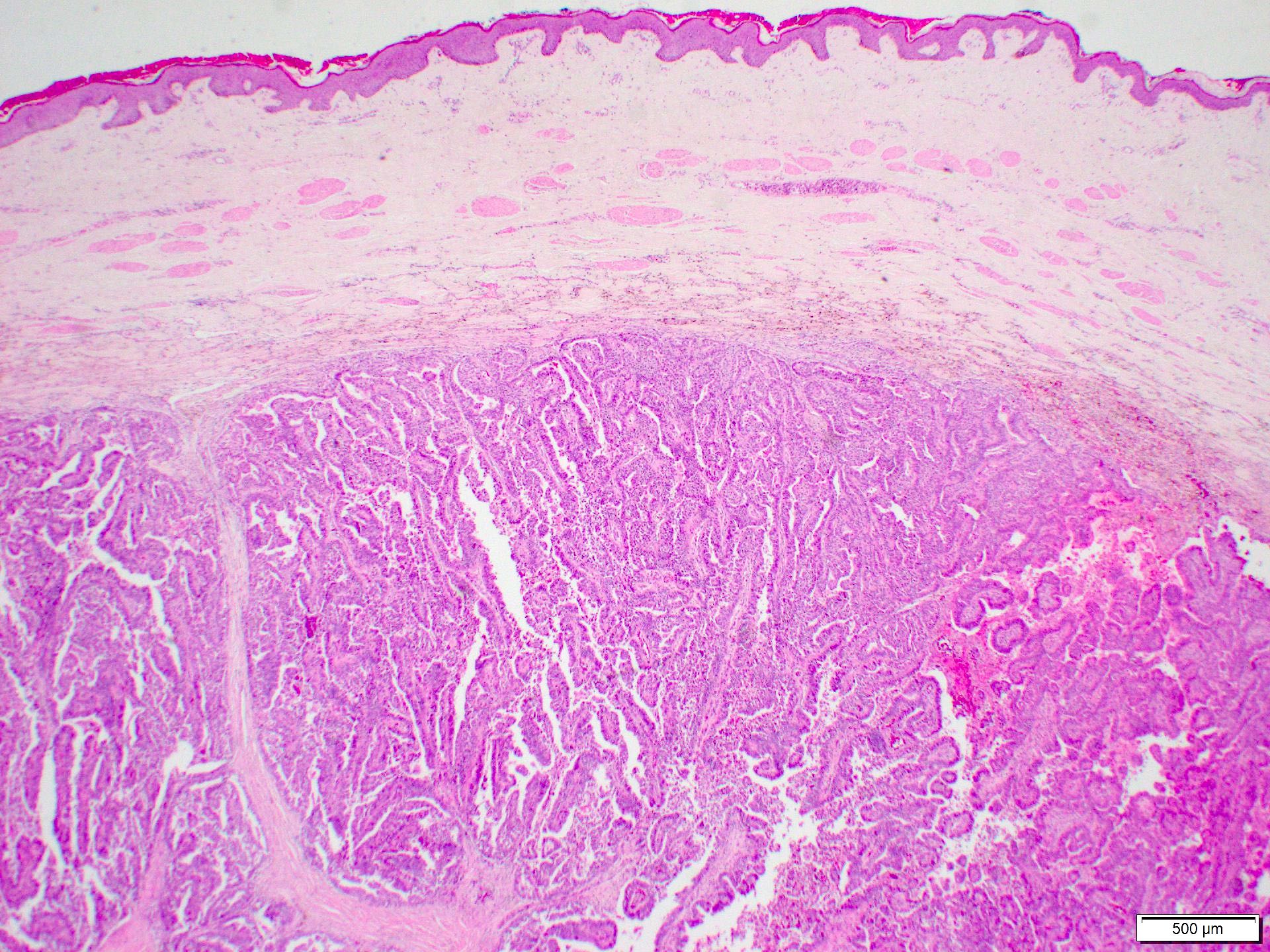
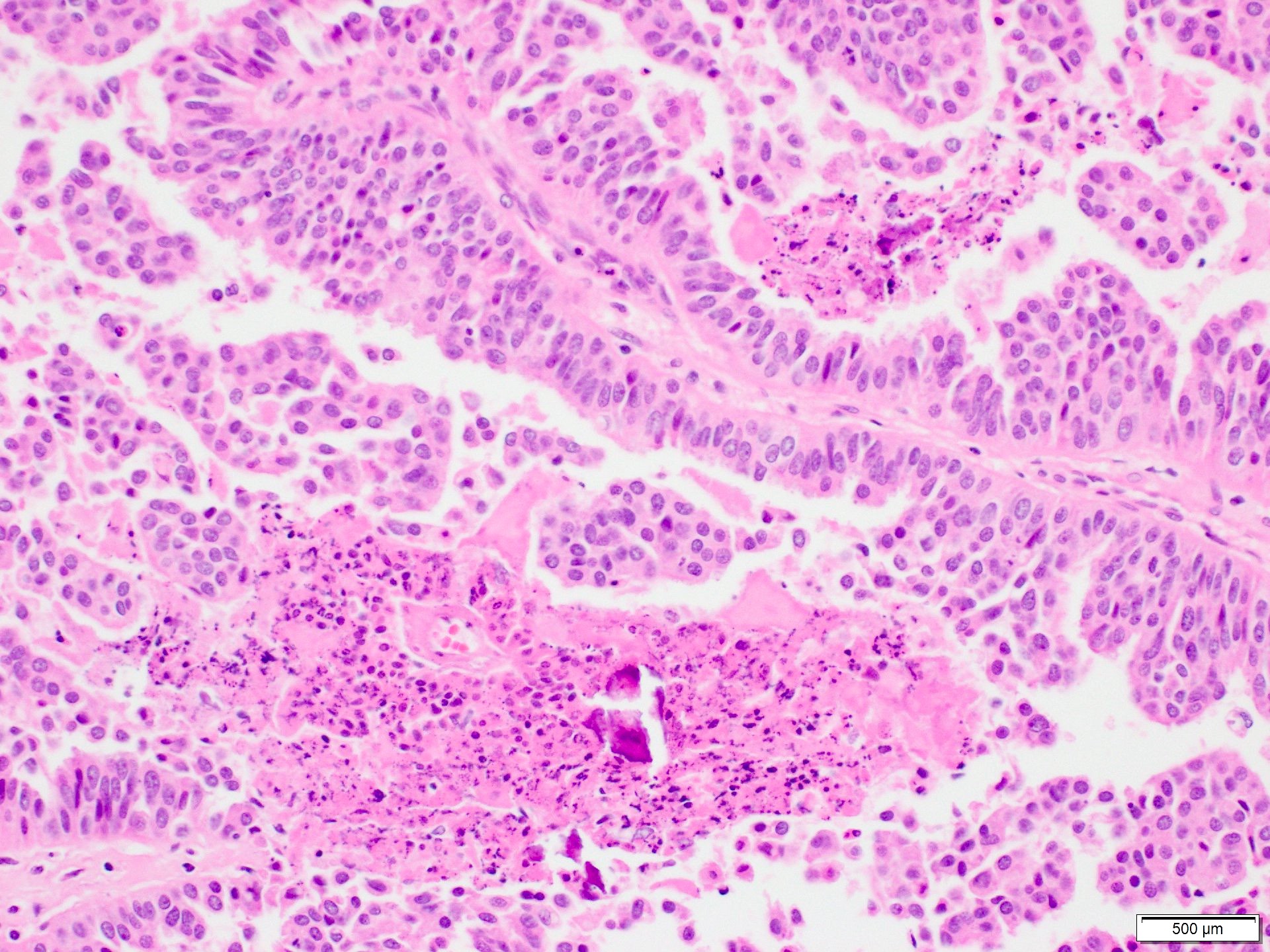
- Invasive carcinoma with > 90% papillary architecture (Mod Pathol 2021 Jan 18 [Epub ahead of print])
- Frankly invasive growth pattern without surrounding fibrous capsule (Mod Pathol 2021;34:78)
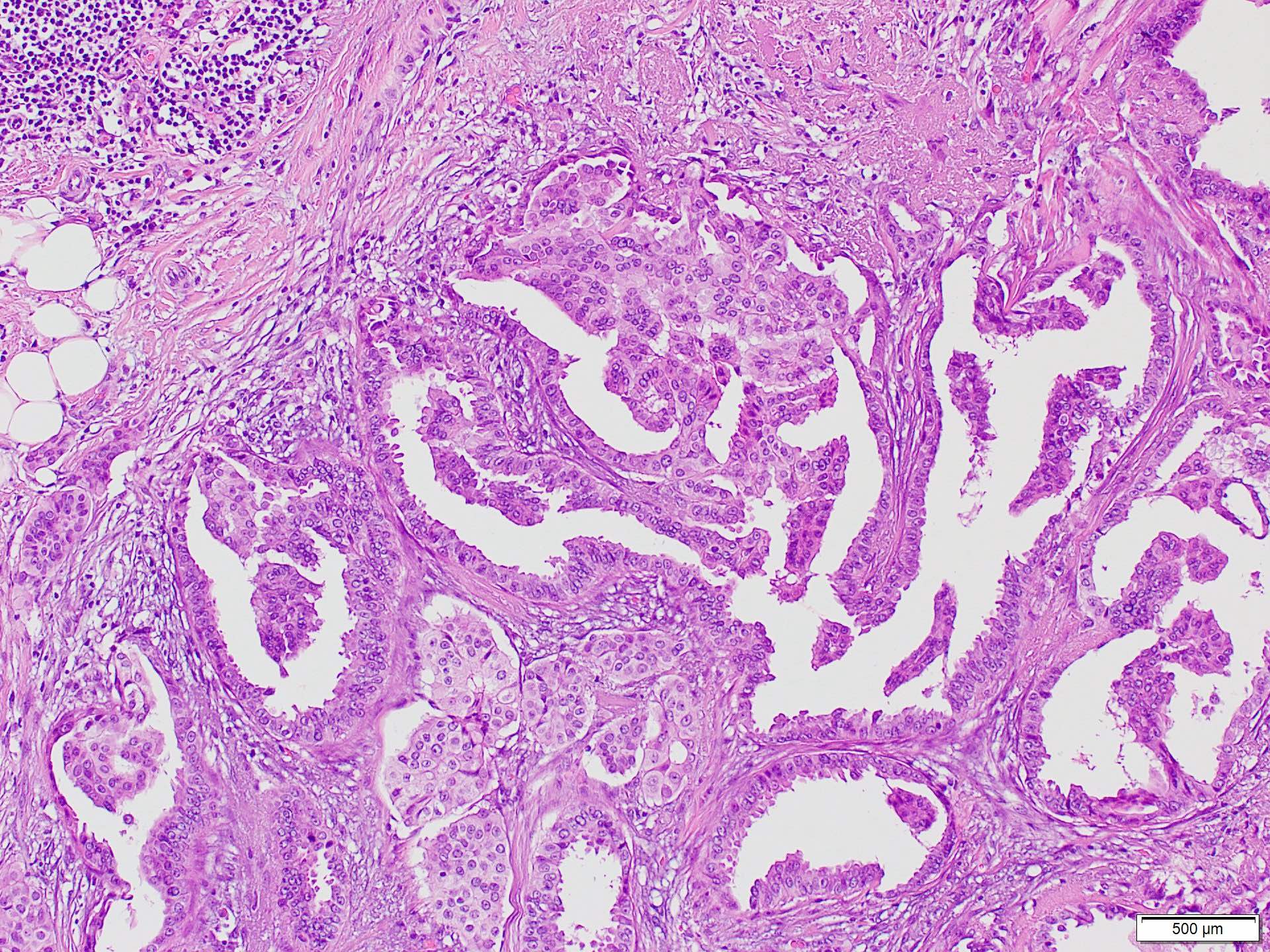
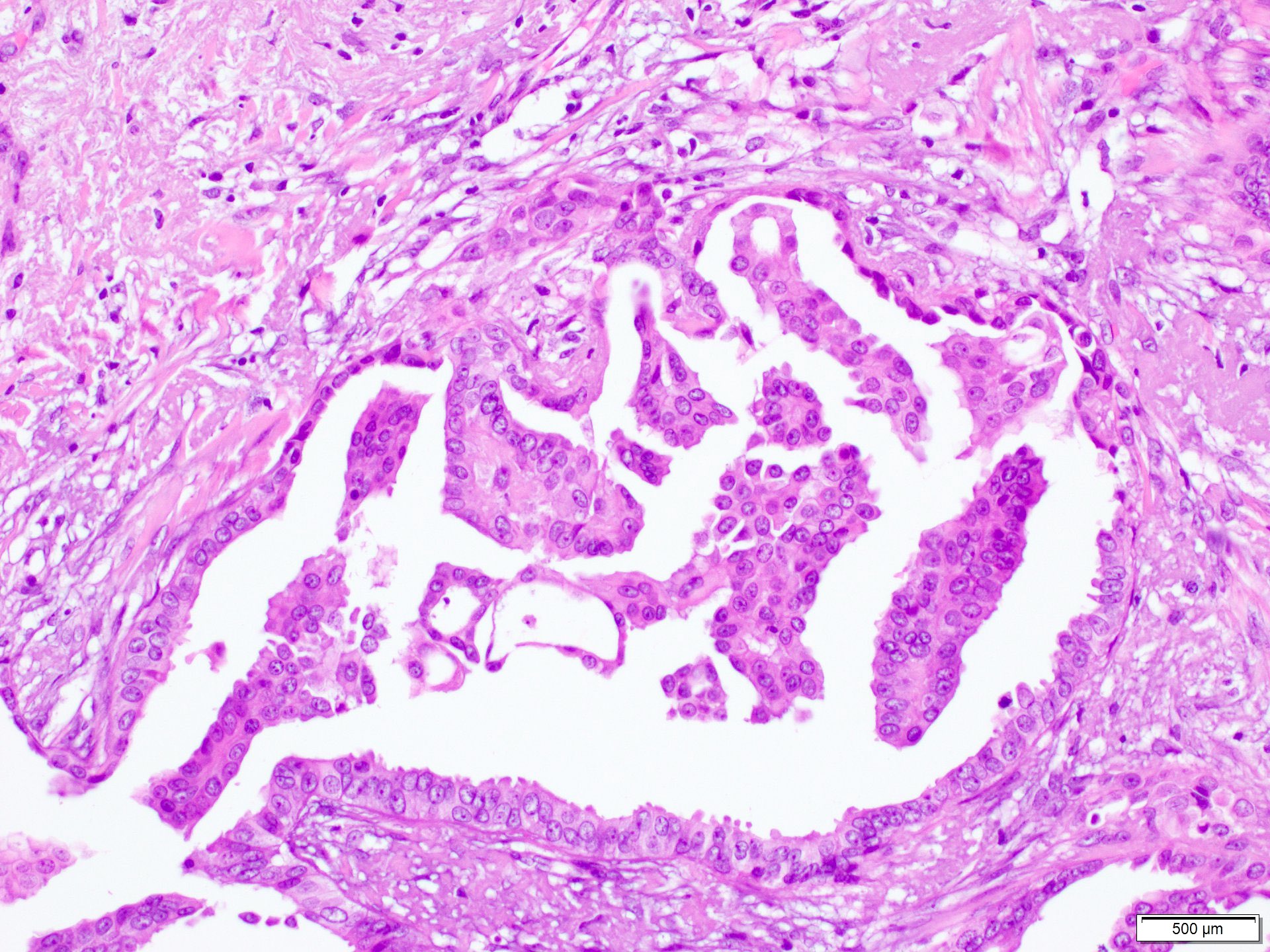
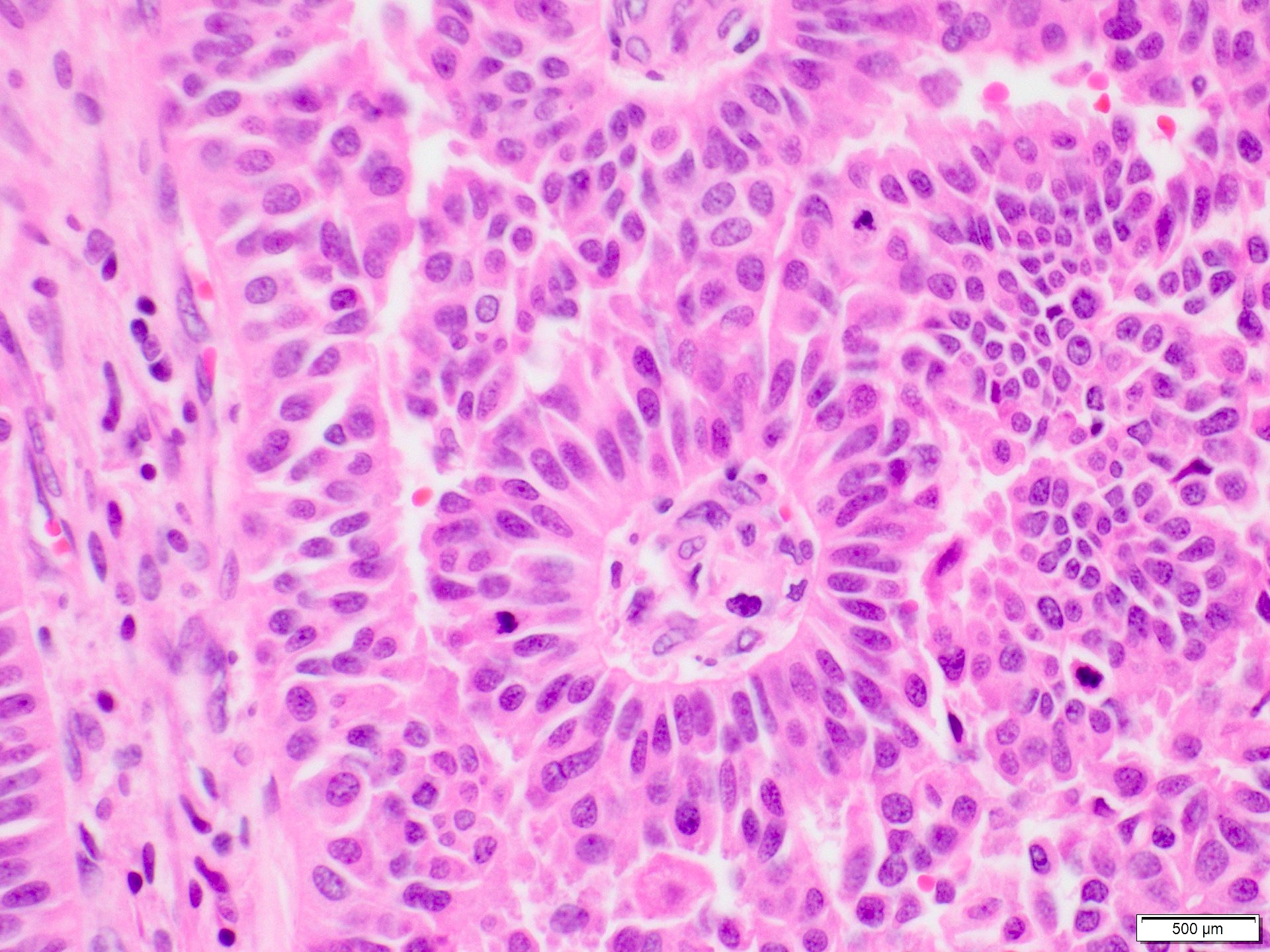
- Growth pattern is characterized by arborizing fibrovascular stalks lined by epithelial cells (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2013;139:77)
- Mitotic figures and necrosis are not common (Sci Rep 2016;6:24037)
- Carcinoma cells show cytologic atypia and stratification (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2013;139:77)
- Nuclear grade ranges from low to high (Sci Rep 2016;6:24037)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Marilin Rosa, M.D.
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Myoepithelial cell stains, such as p63, calponin and smooth muscle myosin heavy chain (Mod Pathol 2021 Jan 18 [Epub ahead of print])
- HER2 (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2013;139:77)
- PAX8, WT1, TTF1, Napsin A and thyroglobulin (Mod Pathol 2021 Jan 18 [Epub ahead of print])
Sample pathology report
- Right / left breast, mastectomy:
- Invasive papillary carcinoma, Nottingham histologic grade (X), measuring (X) cm (please see detailed synoptic report)
- Associated ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), (X) nuclear grade, (X) patterns, comprising X% of tumor (if present).
- Lymphovascular invasion (is / is not) identified.
- Biopsy site changes are identified.
- Margins are (involved / uninvolved).
Differential diagnosis
- Encapsulated papillary carcinoma:
- Rounded pushing border
- Typically surrounded by a fibrous capsule
- Frank invasion may be present when tumor cells infiltrate beyond the fibrous capsule
- Solid papillary carcinoma, invasive and noninvasive:
- Expansile nodules with solid pattern and delicate fibrovascular cores
- Extracellular mucin may be present
- Invasive micropapillary carcinoma (an aggressive form of mammary carcinoma):
- More than 90% of tumor consists of morula-like epithelial clusters
- Tumor clusters are surrounded by empty spaces, devoid of fibrovascular cores and show reverse polarity
- Extramammary carcinoma metastatic to the breast, such as ovarian carcinoma, lung carcinoma with papillary features or thyroid papillary carcinoma (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2013;139:77, J Surg Res 2021;261:105):
- Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1114):
- Carcinoma cells arranged in solid, papillary and glandular structures, resembling thyroid follicles
- Carcinoma glands contain colloid-like material
- Tumor cells are columnar or cuboidal
- Many of the nuclei sit near the luminal membranes, hence the term reversed polarity
- Most tumors are negative for ER and PR
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
C. It may mimic metastases from other organs (metastases to the breast from other organs such as ovary, lung and thyroid must be excluded)
Comment Here
Reference: Invasive papillary carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Invasive papillary carcinoma