Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - not malignant | Positive staining - tumors | Negative staining | Electron microscopy imagesCite this page: Pernick N. CD1a. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd1a.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- T cell surface antigen (gene on #1q22-23, not MHC linked)
- CD1a+ T cells are normal component of T cell repertoire (Nat Immunol 2010;11:1102), important in dendritic cell presentation of glycolipids and lipopeptide antigens, particularly those that traffic through early endocytic and recycling pathways (J Immunol 2010;184:1235)
- Also called Leu6
- Activin A, a TGFβ family member induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines and involved in skin morphogenesis and wound healing, induces the differentiation of human monocytes into Langerhans cells in absence of TGFβ (PLoS One 2008;3:e3271)
Clinical features
- May identify myeloid dendritic cells that produce IL12 and Th1 CD4+ T cell polarization (Clin Exp Immunol 2009;155:523)
- May activate intrathyroidal T cells in Hashimoto thyroiditis and Grave disease (J Immunol 2005;174:3773)
- CD1A and CD1E polymorphisms contribute to polygenic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis (Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2011;24:175)
Uses by pathologists
- Interpretation: membranous staining
- Used to diagnose Langerhans cell histiocytosis and to exclude other entities that are CD1a negative
- Used to identify Langerhans cells in inflammatory or neoplastic disorders (Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:527, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2011;19:239, Colorectal Dis 2011;13:768)
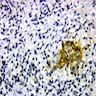
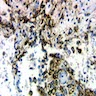
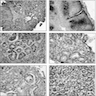
Microscopic (histologic) images
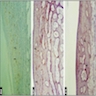
Positive staining - normal
- Cortical thymocytes
- Immature dendritic cells (Langerin-, CD86-, HLA-DR low, CD40 low)
- Indeterminate cells (resemble Langerhans cells but no Birbeck granules on EM)
- Langerhans cells (Langerin+, CD86+)
Positive staining - not malignant
- Actinic cheilitis exhibiting epithelial dysplasia (J Mol Histol 2010;41:357)
- Barretts metaplasia of esophagus (Br J Cancer 2005;92:888)
- Dendritic cells in dermis / epidermis of benign inflammatory skin disorders including pseudolymphomatous folliculitis (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:1313)
- Periodontitis (gingiva, Oral Dis 2012;18:778, but see Indian J Dent Res 2010;21:396
- Primary biliary cirrhosis (up to 79%, Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:732)
- Psoriasis (J Cutan Pathol 1995;22:223)
- Sickle cell anemia-monocytes (Hum Immunol 2004;65:1370)
- Spongiotic dermatitis and lichen planus (Arch Dermatol Res 2002;294:297)
Positive staining - tumors
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis (fairly specific)
- Cutaneous T cell lymphoma
- Myeloid leukemia
- Mycosis fungoides (variable)
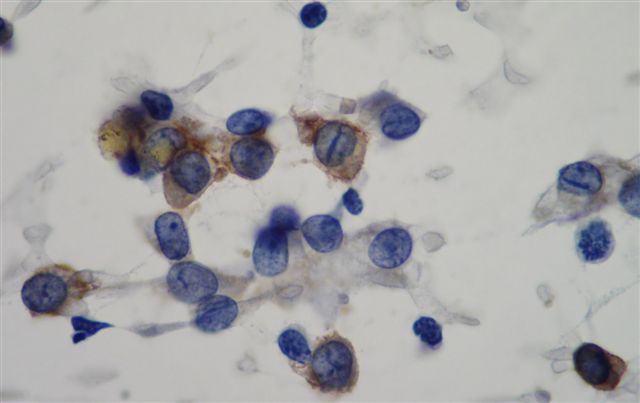
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma (FNA, Cancer Cytopathol 2013;121:206)
- T-ALL (Am J Clin Pathol 2002;117:252)
- Thymoma (Histopathology 2002;40:152)
Negative staining
- B cells, follicular dendritic cells
- Dendritic cells in most cutaneous B cell lymphomas (or weak staining, Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:72), dendritic cell neurofibroma, Erdheim-Chester disease, follicular dendritic cell tumor, histiocytic lymphoma / sarcoma, histiocytoma, interdigitating dendritic cell sarcoma, juvenile xanthogranuloma, sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy
- PECOmas: CD1a negative, but may show aberrant cytoplasmic staining due to endogenous biotin (Hum Pathol 2011;42:369); prior report of CD1a+ PEComas at Pathol Int 2008;58:169