Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Sunassee A, Askeland R. Adenoid basal carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cervixadenoidbasal.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Very rare indolent tumor with favorable clinical course and excellent prognosis
- Affects older postmenopausal women, often non white
- Usually diagnosed retrospectively on surgical specimens
- Rare metastases
Essential features
- Very rare indolent tumor with favorable clinical course and excellent prognosis
- Affects postmenopausal women, often non white
- Important to distinguish from adenoid cystic carcinoma due to different clinical behavior
- Associated with squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL)
Terminology
- The term adenoid basal epithelioma has been proposed due to its indolent nature - not widely accepted (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:965)
Epidemiology
- < 1% of all cervical malignancies (J Menopausal Med 2013;19:154, Balkan Med J 2012;29:453)
- Post-menopausal African American and some Asian women (J Pathol Transl Med 2015;49:396)
Pathophysiology
- Linked to high risk HPV infection - HPV16 (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2016;35:82, Hum Pathol 2005;36:82)
- TP53 gene alterations including wild type hyperexpression and p53 point mutation damage have been noted
Etiology
- Derived from the multipotent cells of the basal layer or reserve cells of cervical epithelium (J Menopausal Med 2013;19:154)
Clinical features
- 80 - 90% are asymptomatic but have an abnormal pap smear - usually high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
- May have vaginal bleeding
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis with low potential for metastasis and recurrence
- Morphologically pure lesions usually have favorable outcome
Case reports
- 20 and 22 year old women (Diagn Pathol 2006;1:20, J Menopausal Med 2013;19:154)
- 55 year old woman with adenoid basal carcinoma combined with invasive squamous cell carcinoma (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014;55(3 Suppl):1225)
- 79 year old woman with high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:485)
Treatment
- Conservative - LEEP, conization
Gross description
- Cervix with no gross abnormality, rarely ulceration
Microscopic (histologic) description
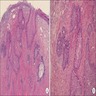
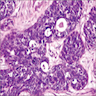
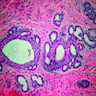
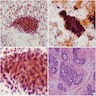
- Solid basaloid tumor nests with peripheral palisading or cord like arrangement and some microcyst formation (Diagn Pathol 2006 Aug 16;1:20)
- May form acini structures without hyaline material
- Uniform, round to oval cells with scant cytoplasm, small hyperchromatic nuclei with inconspicuous nucleoli and minimal nuclear atypia (J Pathol Transl Med 2015;49:396)
- No desmoplastic stroma (J Menopausal Med 2013;19:154)
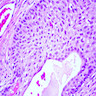
- Associated with SIL (usually HSIL)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Often no findings or unrecognized on cytology, as many cases do not involve surface
- Usually associated with HSIL and hence detected on Pap, HPV 16+
- Three dimensional, somewhat dyscohesive groups of intact small and uniform cells with overlapping nuclei (Acta Cytol 1995;39:563)
- Occasional peripheral palisading
- No glandular formation
- Scant cytoplasm (Diagn Cytopathol 1996;14:172)
- Dense basophilic, hyperchromatic nuclei with fine granular chromatin (J Pathol Transl Med 2015;49:396) and small / inconspicuous nucleoli
- "Windswept appearance" when compared to reactive atypia (Acta Cytol 1995;39:563)
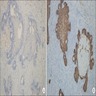
Negative stains
- CD117, laminin, collagen IV (positive in adenoidcystic carcinoma)
Differential diagnosis
- Adenoid basal hyperplasia: absence of deep invasion into stroma
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma: Collagen IV, laminin, CD117+, cribriform nests with hyaline material, coarse granular chromatin, more aggressive
- Invasive squamous cell carcinoma: tumor diathesis, single cells, variation in size of nuclei