Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Choschzick M. Condyloma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/vulvacondyloma.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Condyloma acuminatum is an HPV associated wart-like lesion of squamous epithelium
Essential features
- Benign HPV related lesion of the anogenital region with warty appearance and histologically bland papillomatous hyperplasia of squamous epithelium
- Giant condyloma (Buschke-Löwenstein tumor) develops over confluence of longstanding condyloma acuminata with the propensity to transform into invasive carcinoma
Terminology
- Acceptable: condylomatous low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL), genital wart
ICD coding
- ICD-11: 1A95.1 - genital warts
Epidemiology
- Sexually active adults (1%), peak incidence between 20 - 29, HIV predisposing
- Buschke-Löwenstein tumor is observed mostly in the fifth decade after median condyloma diagnosis for 5 years
Sites
- Labia majora, vestibule, perineum, vagina, perianal, rare extragenital
Etiology
- Low risk HPV types 6 and 11 most common (Sex Transm Dis 2013;40:123, Acta Derm Venereol 2013;93:223)
- High risk HPV types in up to 42% (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1513)
Clinical features
- Range from only colposcopically visible lesions to small papules to large masses with cauliflower-like appearance, often multiple (Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2014;28:1063)
- Buschke-Löwenstein tumor shows clinically expansive and destructive growth; there is no sharp criterion for size to differentiate it from large condyloma
Diagnosis
- Clinical appearance, punch biopsy
Prognostic factors
- Benign process, frequent recurrence, spontaneous regression possible (Sex Transm Dis 2011;38:949)
- Buschke-Löwenstein tumor shows focal development of invasive carcinoma in up to 50%, rarely metastasizes; mortality 20%; relapse in up to 50% after therapy (Dis Colon Rectum 1994;37:950)
Case reports
- 25 year old pregnant woman with large condyloma acuminatum in the vagina (Int J STD AIDS 2011;22:534)
- 29 year old woman with giant condyloma during pregnancy (Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2007;86:762)
- 32 year old pregnant woman with disseminated condyloma acuminata (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2019;62:310)
Treatment
- Local excision or laser ablation, imiquimod
Microscopic (histologic) description
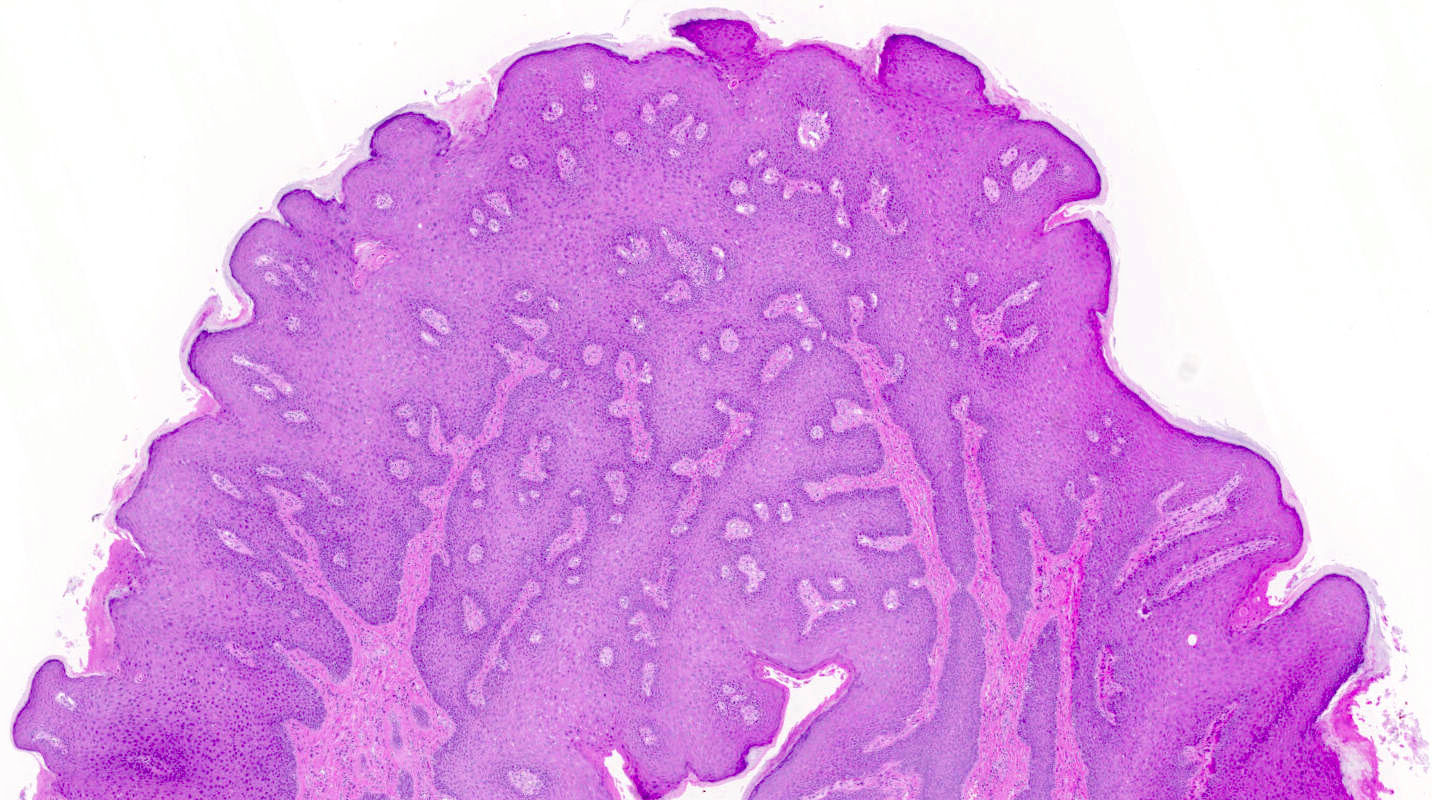
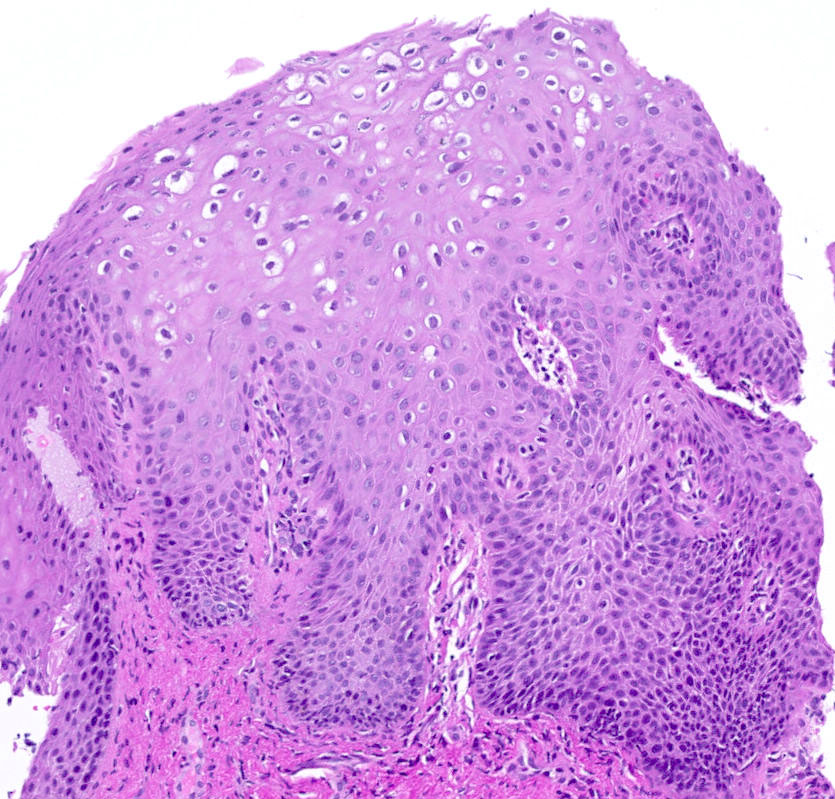
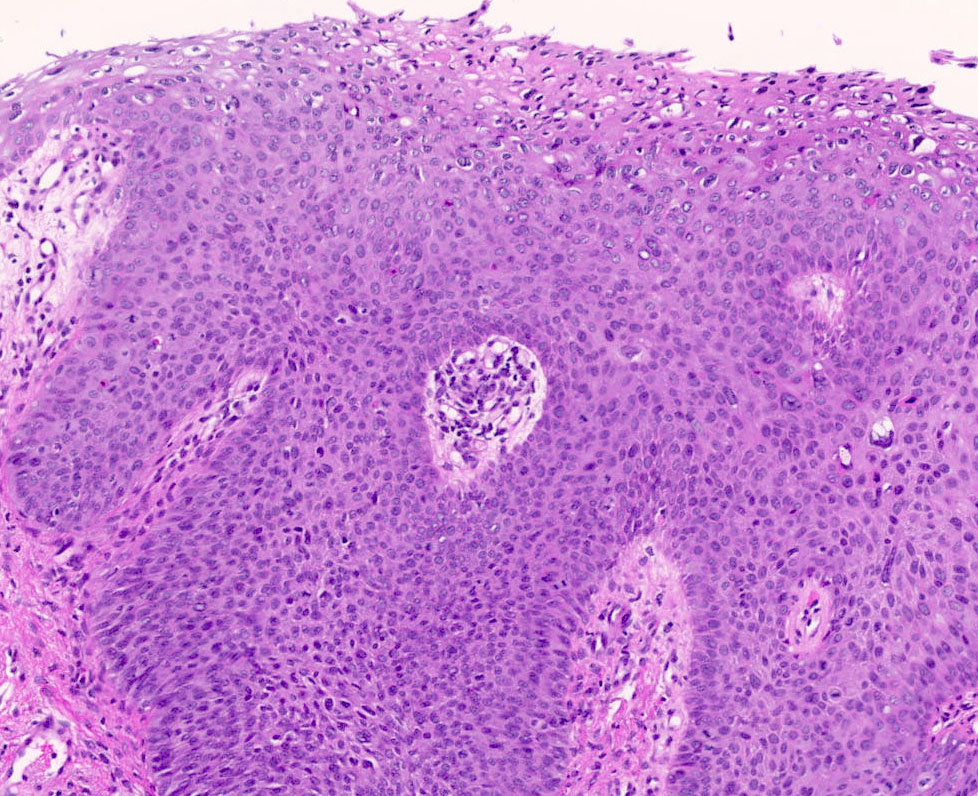
- Overall verrucous or warty architecture (Adv Anat Pathol 2005;12:20)
- Acanthosis, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis and hypergranulosis of squamous epithelium
- Broad papillae with rounded ends which are fused at the base
- Viral cytopathic effects: variable koilocytosis (may be absent or inconspicuous), binuclear cells
- Usually no stromal inflammation
- Giant condyloma Buschke-Löwenstein shows the same histological changes with more endophytic growth but without invasion
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
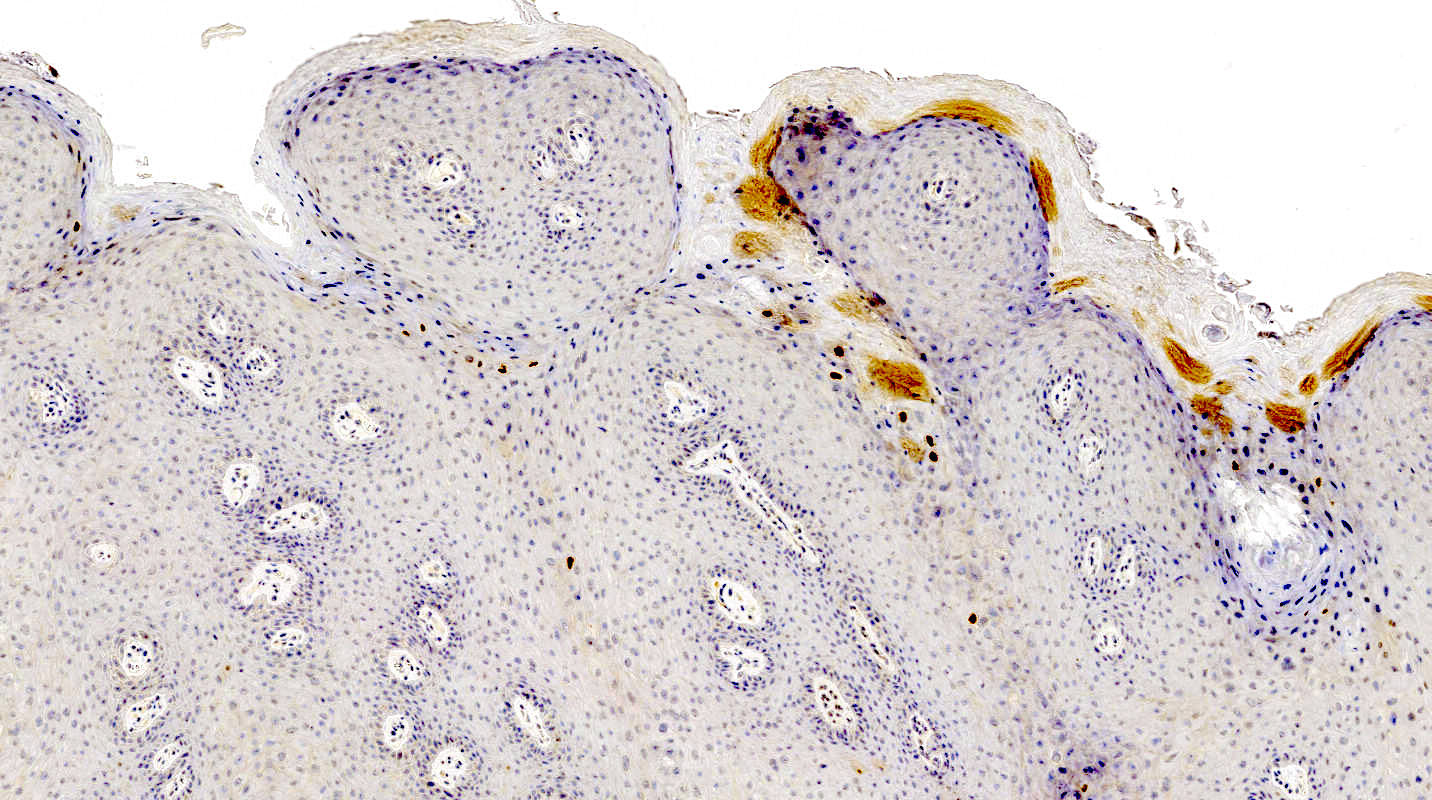
- HPV detection by RNA in situ hybridization or immunohistochemical demonstration of L1 capsid protein
Negative stains
- p16 stains in patchy / nonblock type pattern or is negative
Sample pathology report
- Labium minora, biopsy:
- Condyloma acuminatum
Differential diagnosis
- Seborrheic keratosis:
- Horn pearls, squamous eddies, minimal hypergranulosis
- HPV negative
- Vestibular papillomatosis:
- Branching delicate papillae without keratinization, no cytopathic viral effects
- HPV ISH negative
- Squamous papilloma:
- Minimal branching, fibrovascular core, no cytopathic viral effects
- HPV ISH negative
- Condyloma with HSIL:
- Verrucous carcinoma:
- Unequivocal pushing border invasion, stromal inflammation, no koilocytosis / no HPV association (as seen in giant condyloma Buschke Löwnstein)
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. HPV6
HPV6 is a low risk HPV and is most often found in condyloma as shown in several studies. The frequency of HPV16 is lower than that of HPV6. HIV is only predisposing, not found in the epithelium. There is no association with HHV8 and HSV. (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1513)
Comment Here
Reference: Condyloma
HPV6 is a low risk HPV and is most often found in condyloma as shown in several studies. The frequency of HPV16 is lower than that of HPV6. HIV is only predisposing, not found in the epithelium. There is no association with HHV8 and HSV. (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1513)
Comment Here
Reference: Condyloma
Board review style question #2
Which diagnostic test is useful to differentiate between verrucous carcinoma and a large condyloma?
- HPV IHC
- HPV ISH
- Ki67
- p16
- p53 IHC
Board review style answer #2
B. HPV ISH
HPV ISH has high sensitivity and specificity while HPV IHC has low sensitivity. Both entities are p53 wildtype, p16 patchy / negative and have elevated Ki67 indices.
Comment Here
Reference: Condyloma
HPV ISH has high sensitivity and specificity while HPV IHC has low sensitivity. Both entities are p53 wildtype, p16 patchy / negative and have elevated Ki67 indices.
Comment Here
Reference: Condyloma