Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Detection methodologies | Common drugs of abuse | Diagrams / tables | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Amaram Samara V, Kelly KA. Drugs of abuse. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/chemistrydrugsofabuse.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Drug abuse is a global major public health problem
- Includes prescription and nonprescription drugs that are either overdosed or illicitly abused for pleasure
- Testing is performed for patient compliance in pain management and for addiction management
Essential features
- Drugs of abuse are commonly analyzed in urine because of the longer window period for detection; less commonly analyzed in serum or plasma
- Drugs are excreted in urine, either in their native form or as their metabolites
- Absence of drugs in the urine indicates inappropriate specimen collection, diversion (i.e. not taking the prescribed dose), diluted urine or adulterated urine
- Dilution of urine samples can be confirmed by measuring the urine creatinine levels (normal 24 hour urine creatinine: 500 - 2000 mg/day; random urine creatinine: 20 - 300 mg/dL)
- Identification of drugs of abuse in pregnant women / neonates during antenatal testing can have serious consequences
- For neonates, meconium can be used to detect drug abuse by the pregnant mother for up to 4 - 5 months before delivery; results are reported as ng/g (Clin Chem 2018;64:1671)
- Cutoff levels for urine testing of drugs of abuse are established in ng/ml for both the screen and confirmation
Terminology
- Meconium
- Kinetic interaction of microparticles in solution (KIMS)
- Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS / MS)
- Gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: F01-F99 - mental, behavioral and neurodevelopmental disorders
Detection methodologies
- Immunoassay screening for drugs of abuse is performed mostly by the kinetic interaction of microparticles in solution (KIMS) method
- Other immunoassay methods, such as enzyme multiplied immunoassay technique (EMIT) and cloned enzyme donor immunoassay (CEDIA), are also performed for drugs of abuse testing
- Results are provided as positive or negative based on the cutoff concentration detection limits
- Immunoassays recognize or detect only 1 or certain drugs in a class and cannot differentiate between the main drug and their metabolites
- Confirmation of drugs of abuse is carried out by quantitative measurement by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS / MS) or gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS) methods
- These methods are highly sensitive and specific to the drugs of interest
- Can also detect the parent drug and its metabolite
- Current trend for toxicology laboratories to convert from GC-MS to LC-MS / MS due to the higher throughput and improved cost savings of the latter (AACC: Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry [Accessed 22 February 2021])
- Point of care testing (POCT) methods / assays are available for some drugs of abuse testing
- However, they should be used only for emergency purposes and the results should be confirmed by more specific and sensitive methods (Ann Clin Biochem 2021 Feb 1 [Epub ahead of print])
Common drugs of abuse
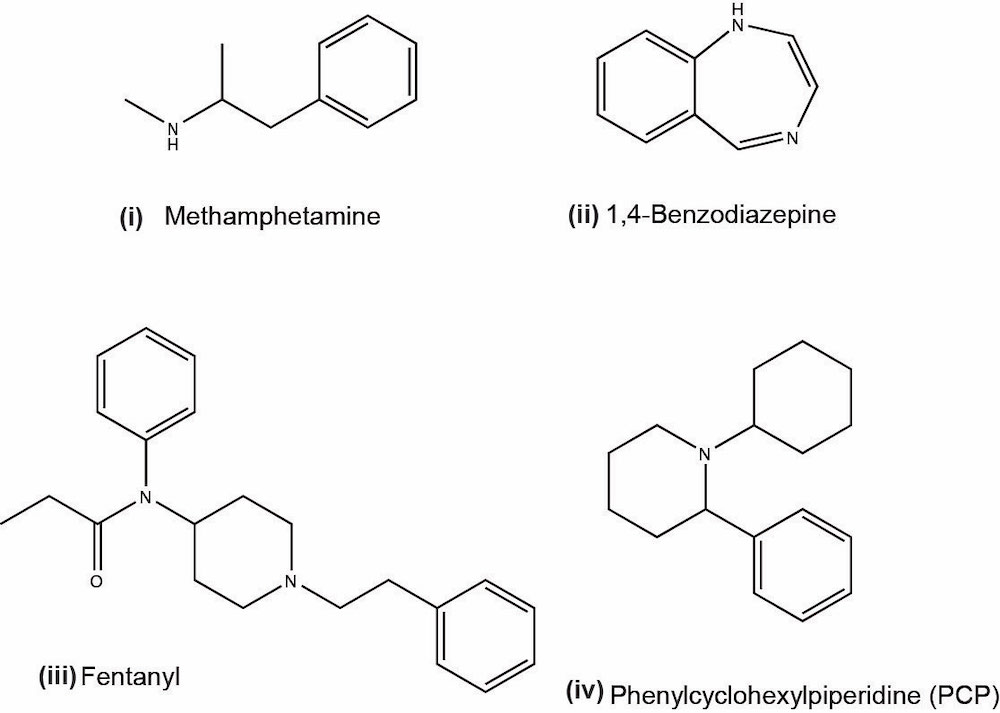
- Amphetamines:
- Belong to phenylethylamine class of drugs and stimulate central nervous system (CNS)
- Pharmacologically used for the treatment of narcolepsy, obesity and ADHD
- High doses and frequent heavy use can create an amphetamine induced psychosis
- Forms of amphetamines used in abuse include crystal methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), also referred to as ecstasy
- Amphetamines are metabolized by liver and eliminated in urine with an average detection window of 3 days
- Quantitative LC-MS / MS based detection cutoff concentrations for amphetamine is 50 ng/ml and for all others, such as methamphetamine and MDMA (ecstasy), is 200 ng/ml
- Barbiturates:
- Class of sedative drugs
- CNS depressants used in treatment of insomnia and seizures
- Short acting sedative barbiturates, such as pentobarbital, secobarbital and amobarbital, are more subjected to abuse compared to long acting phenobarbital that is rarely abused
- Withdrawal symptoms include agitation, anxiety, insomnia, nausea and vomiting
- Detection window for barbiturates ranges from 24 hours to 4 days (for long acting phenobarbital)
- Quantitative analysis by GC-MS can detect individual barbitals with positive cutoff of 50 ng/ml
- Benzodiazepines:
- Include a wide range of compounds that consist of a benzene ring, phenyl ring and a diazepine ring, with a common molecular structure
- LC-MS / MS quantitative detection positive cutoff for most benzodiazepines is 20 ng/ml
- LC-MS / MS can also identify individual derivatives, including lorazepam, oxazepam and flurazepam
- Cocaine:
- Cocaine or coke is a strong, addictive CNS stimulant, chemically an alkaloid made from the leaves of the coca plant
- Cocaine salt form is most commonly abused through snorting (intranasal delivery) or by intravenous injection
- Base form, also known as crack, is consumed as smoke after heating
- Cocaine is metabolized to benzoylecgonine, norcocaine or ecgonine methyl ester and excreted in urine, mostly as benzoylecgonine that can be detectable for 1 - 3 days
- Both oral fluid and urine samples can be tested for detection of cocaine or its metabolite benzoylecgonine; however, because of the short half life of cocaine, benzoylecgonine is the most common analyte measured for cocaine (J Appl Lab Med 2020;5:935)
- Side effects of cocaine abuse cause heart attack, stroke, headache and seizures
- Quantitative GC-MS detection in urine can identify cocaine and its metabolite benzoylecgonine with a positive cutoff of 50 ng/ml
- Cannabinoids:
- Cannabinoids are the products of the plant Cannabis sativa or indica and the most highly consumed drugs of abuse
- Commonly known or available as marijuana, pot and weed; consumed as smoke
- Consumption of cannabinoids results in euphoria, relaxation and mood changes, including psychosis and panic attacks
- Marijuana withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, insomnia and anorexia
- Major psychoactive component of cannabinoids is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which gets deposited in the adipose tissue after consumption
- THC is mainly metabolized to 11-hydroxy-delta-9-THC by the liver CYP450 enzymes
- THC has a longer detection window ranging from 3 to 90 days, depending on the usage
- Quantitative LC-MS / MS detects THC metabolite, 11-Nor-9-carboxy-THC, with cutoff concentration of 15 ng/ml
- Opioids:
- Opioids are a group of compounds that bind to the opioid receptors
- Natural alkaloids opioids, also called opiates, are morphine and codeine and are derived from the opium plant
- Other opioids include semisynthetic heroin, hydrocodone, oxycodone and synthetic opioids such as fentanyl, methadone and tramadol
- Opioids are used as analgesics and are highly addictive, causing nausea, sedation, physical dependence and breathlessness
- Opioid withdrawal symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea, muscle and joint pain, restlessness
- Morphine is metabolized majorly to morphine-3-glucuronide and minorly to hydromorphone when used longterm
- Immunoassay screening for opiates can detect morphine and codeine but not the semisynthetic and synthetic opioids
- Quantitative LC-MS / MS detects hydrocodone, oxycodone and their metabolites, including morphine and codeine, with cutoff concentration of 20 ng/ml
- Fentanyl:
- Synthetic opioid that is 50 - 100 times more potent than morphine
- Prescription drug for management of severe pain or postsurgery
- Illicitly synthesized and sold as China Girl, China White and Dance Fever
- Severe respiratory distress is a common display of fentanyl overdose
- Half life of fentanyl in blood is 3 - 10 hours and in urine is 2 - 3 days
- In a suspected case of fentanyl abuse or overdose, the urine opioid screening results will be negative and a targeted analysis of fentanyl testing is necessary (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68:687)
- Metabolized by CYP450 enzyme in a CYP3A4 mediated N-dealkylation to norfentanyl (major) and less than 1% to hydroxyfentanyl and hydroxynorfentanyl
- Quantitative LC-MS / MS detects hydrocodone, oxycodone and their metabolites, including morphine and codeine, with cutoff concentration of 20 ng/ml
- Phencyclidine (PCP):
- Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP) is a synthetic drug that was originally developed as an anesthetic and now is a Schedule II controlled substance
- Mind altering drug; belongs to the class of hallucinogens and its recreational use has been increasing in recent years (J Med Toxicol 2015;11:321)
- PCP is most commonly taken by smoking; street name is angel dust
- Serious effects of PCP abuse include agitation, anxiety, coma and death (with high doses of more than 20 mg)
- Quantitative LC-MS / MS detection cutoff for PCP is 10 ng/ml
Diagrams / tables
Contributed by Vishnu Amaram Samara, Ph.D.
Images hosted on other servers:
General cutoff limit concentrations of common drug classes by immunoassay screening and LC-MS / MS quantitative confirmation
| | typical cutoff limits (ng/mL) | limits using LC-MS / MS (ng/mL) |
| Amphetamine | ||
| Barbiturates | ||
| Benzodiazepines | ||
| Cannabinoids | ||
| Cocaine | ||
| Opiates | ||
| Phencyclidine |
Additional references
Board review style question #1
In highly suspected cases of drug abuse where the urine results are negative, the dilution of urine samples can be confirmed by measuring which of the following?
- Serum creatinine
- Serum electrolytes
- Urine creatinine
- Urine electrolytes
- Urine volume
Board review style answer #1
C. Urine creatinine. A random urine average creatinine concentration is 20 - 300 mg/dL and if the creatinine concentration is less than 20 mg/dL, the urine is diluted leading to negative drug results.
Comment Here
Reference: Drugs of abuse
Comment Here
Reference: Drugs of abuse