Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology / etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Gyure K.A. Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnspontine.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis are complications of treatment of marked hyponatremia
Terminology
- Also termed osmotic demyelination syndrome
Epidemiology
- Occurs most commonly in setting of chronic alcoholism (~40% of cases)
- Hyperosmolar state and other electrolyte imbalances are common
- Other associated conditions are hepatic dysfunction / liver transplantation, malnutrition
Sites
- Most commonly central pons
- Extrapontine sites are cerebellum and lateral geniculate, regions of extensive gray white matter apposition
Pathophysiology / etiology
- Associated with rapid correction of hyponatremia, due to disruption of blood brain barrier with edema and myelinolysis
Clinical features
- Abrupt onset of encephalopathy following recovery from hyponatremia
- Followed by dysarthria, dysphagia, quadriparesis, possible "locked in" syndrome, neurobehavioral deficits
Diagnosis
- Typical imaging findings in an appropriate clinical scenario
Radiology description
- "Trident" or "bat wing" shaped area of restricted diffusion in central pons
- Symmetric T2 weighted signal abnormalities in cases with extrapontine involvement
Prognostic factors
- Outcome (death, residual disability or complete recovery) is not predicted by clinical features or extent of radiologic abnormalities
Case reports
- 5 year old girl with central pontine myelinolysis following pediatric living donor liver transplantation (Pediatr Transplant 2014;18:E120)
- Osmotic demyelination syndrome associated with hypophosphataemia (Acta Paediatr 2013;102:e164)
Treatment
- Prevention is most important
- Once it occurs, corticosteroids and supportive care
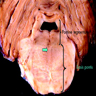
Gross description
- Triangular, T shaped or diamond shaped area of discoloration which may be centrally cavitated in basis pontis
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Myelin / oligodendrocyte loss with relative preservation of neurons / axons
- Macrophages may be present but no significant lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate
Differential diagnosis
- Other causes of demyelination