Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Abdelzaher E. Rosette forming glioneuronal tumor (RGNT). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorRGNT.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Low grade glioneuronal neoplasm with neurocytic and glial components
- CNS WHO grade 1
- Established as a distinct disease entity by Komori et al. (2002) and later endorsed by WHO classification (2007) (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:582, Acta Neuropathol 2007;114:97)
Essential features
- Rare, slow growing glioneuronal neoplasm (Neurooncol Adv 2020;2:vdaa116)
- Preferentially affects young adults, adolescents and children
- Occurs throughout CNS with predilection for fourth ventricle region
- 2 distinct histological components: neurocytic with distinctive rosettes and glial areas
- Recently, rosette forming glioneuronal tumors (RGNTs) with malignant behavior have been reported (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
Terminology
- Rosette forming glioneuronal tumor of the fourth ventricle (Acta Neuropathol 2007;114:97)
- The 2016 WHO classification modified its description of RGNT and omitted the location qualifier "of the fourth ventricle" (Acta Neuropathol 2016;131:803)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9509/1 - rosette forming glioneuronal tumor
- ICD-11: 2A00.21 & XH2JU8 - mixed neuronal glial tumors & rosette forming glioneuronal tumor
Epidemiology
- Rare; specific population based incidence rates are not available
- Preferentially affects young adults, adolescents and children; mean age at diagnosis is 28 years (range: 2 - 81 years) (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- No gender predilection (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
Sites
- Typically arises in midline and involves posterior fossa with predilection for fourth ventricle (38.3%) and cerebella (31.4%) (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- Recently, it was reported to be present nearly throughout the CNS at both supratentorial and infratentorial sites (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- Sites reported include pineal region / tectum, third ventricle, aqueduct, lateral ventricle, spinal cord, thalamus, suprasellar region, basal ganglia, brain stem, septum pellucidum, frontal lobe, temporal lobe and optic chiasm (Quant Imaging Med Surg 2012;2:227, Cureus 2016;8:e857, Interdiscip Neurosurg 2020;19:1, Surg Neurol Int 2020;11:138, Radiol Case Rep 2021;16:3982, Neurochirurgie 2016;62:60, Oncotarget 2017;8:109175, Childs Nerv Syst 2020;36:2867, Neurooncol Adv 2020;2:vdaa116, Neurosurgery 2009;64:E771)
Pathophysiology
- Histogenesis is unclear; it has been postulated to arise from pluripotent cells of the subependymal plate or the internal granule cell layer of cerebellum or from periventricular stem cell origin with biphenotypic differentiation (J Pediatr Neurosci 2017;12:168, Neurosurgery 2008;62:E1162, Clin Neuropathol 2013;32:370, Virchows Arch 2012;461:581)
- Synergistic interaction between the MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways seem to be involved in the formation of RGNTs; the constitutive activation of the FGFR signaling likely plays a role in a large portion of these tumors together with frequent PIK3CA mutation (Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:497, Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud 2016;2:a001057, Neurooncol Adv 2020;2:vdaa116)
Etiology
- A few cases have been reported in association with neurofibromatosis type 1 and Noonan syndrome, suggesting a genetic susceptibility (Neurosurgery 2009;64:E771, Clin Neuropathol 2011;30:297)
Clinical features
- Nonspecific and site related
- Headache is the most common symptom (60.6%), followed by nausea / vomiting (29%), ataxia (27%) and vertigo / dizziness (20%) (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- Rarely, asymptomatic (7.7%) (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
Diagnosis
- Neuroimaging: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred modality, computed tomography (CT) (Br J Neurosurg 2012;26:668)
- Biopsy
- WHO essential and desirable diagnostic criteria
- Essential diagnostic criteria (presence of the following 3 characteristics)
- Biphasic histomorphology with a neurocytic component and a glial component
- Uniform neurocytes forming rosettes or perivascular pseudorosettes associated with synaptophysin expression
- (For unresolved lesions) small biopsies showing only 1 tumor component (neurocytic or glial) and a methylation profile of rosette forming glioneuronal tumor
- Desirable diagnostic criteria
- FGFR1 mutation with co-occurring PIK3CA or NF1 mutation
- Essential diagnostic criteria (presence of the following 3 characteristics)
Radiology description
- CT (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- Hypodense midline mass
- Calcification (< 25%)
- MRI (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
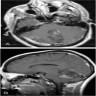
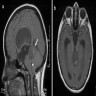
- Relatively circumscribed midline mass, solid or cystic - solid pattern (47%), cystic pattern (35%) and mixed cystic solid pattern (18%)
- T1 hypointense, T2 hyperintense
- Variable contrast enhancement
- Heterogeneous (44.7%), rim (23.7%) or focal (7.9%) enhancement
- No enhancement (25%)
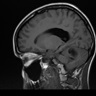
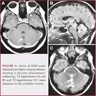
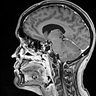
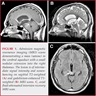
Radiology images
Contributed by Eman Abdelzaher, M.D., Ph.D.
Images hosted on other servers:
Prognostic factors
- Mostly indolent course with stable disease in 88% of cases (Clin Case Rep 2021;9:e04355, Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- Favorable prognosis in terms of survival but location may complicate surgical removal with a significant risk of neurologic injury
- RGNTs have the potential for aggressive behavior with tumor dissemination, recurrence, progression or death reported in 12% of cases (Neurooncol Adv 2020;2:vdaa116, Oncotarget 2017;8:109175
- Risk factors for progression: pediatric age, purely solid tumors and inadequate resection (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
Case reports
- 4 year old girl with spinal RGNT (Radiol Case Rep 2021;16:3982)
- 23 year old woman with diffusely invasive supratentorial RGNT (J Neurosurg Case Lessons 2023;6:CASE23435)
- 24 year old man with highly aggressive RGNT (Brain Tumor Pathol 2015;32:124)
- 41 year old woman with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) and tectal plate RGNT (Cureus 2016;8:e857)
- 49 year old man with disseminated aggressive RGNT and spinal drop metastasis (World Neurosurg 2019;132:7)
- 75 year old woman with a thalamic RGNT and third ventricle dissemination (Neurochirurgie 2016;62:60)
Treatment
- Surgery is the mainstay of treatment (Neurooncol Adv 2020;2:vdaa116)
- Long term, close follow up is needed
- Effectiveness of chemotherapy and radiotherapy remains unclear (Neurooncol Adv 2020;2:vdaa116, Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- Future perspective: targeted therapy with inhibitors of FGFR1, PI3K and MAPK pathways (Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:497)
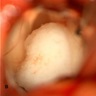
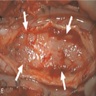
Clinical images
Gross description
- Well demarcated, soft, gelatinous
Frozen section description
- Variable cellularity
- Small, bland and uniform nuclei with circle‐like arrangement (Clin Case Rep 2021;9:e04355)
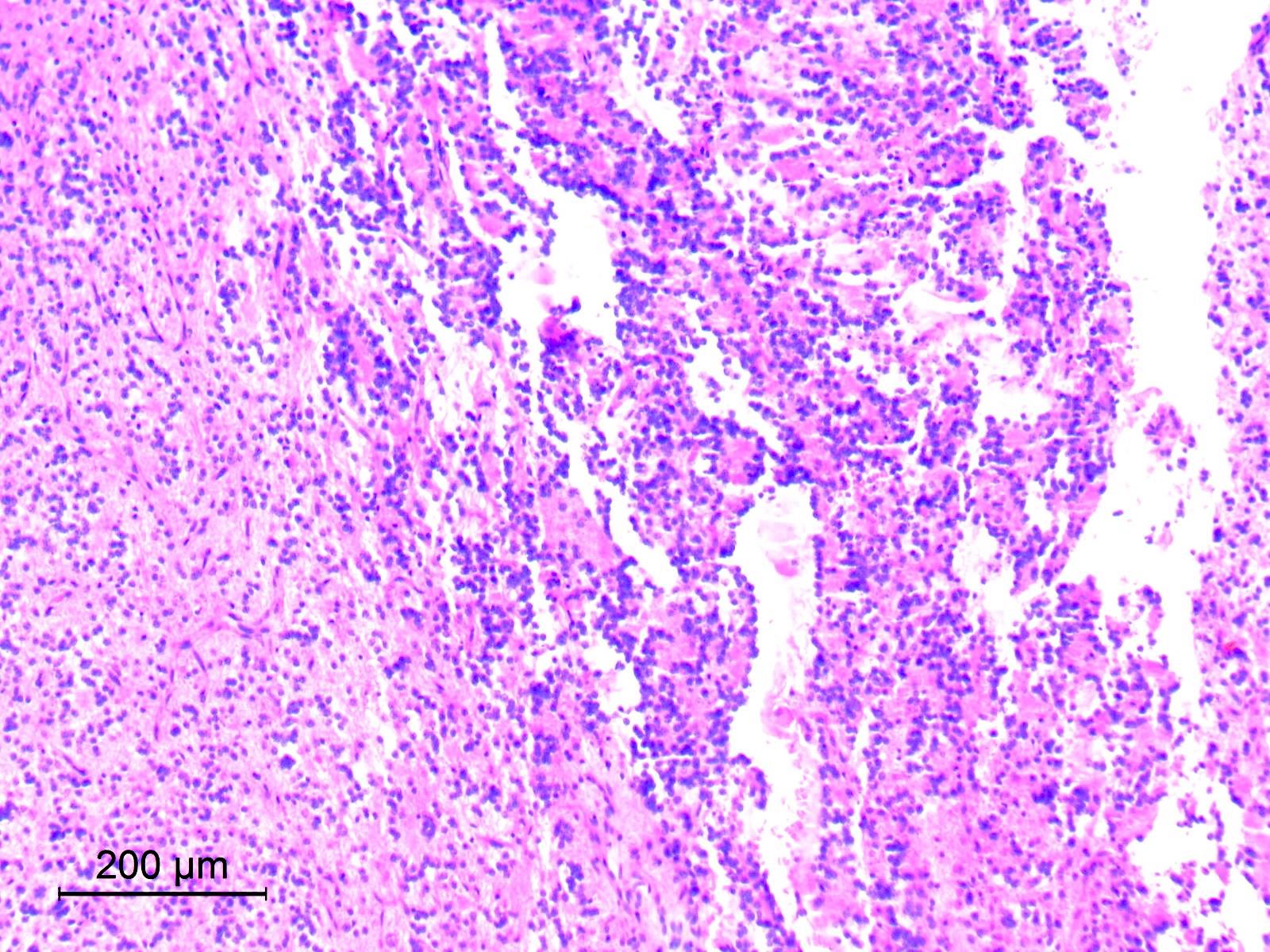
Microscopic (histologic) description
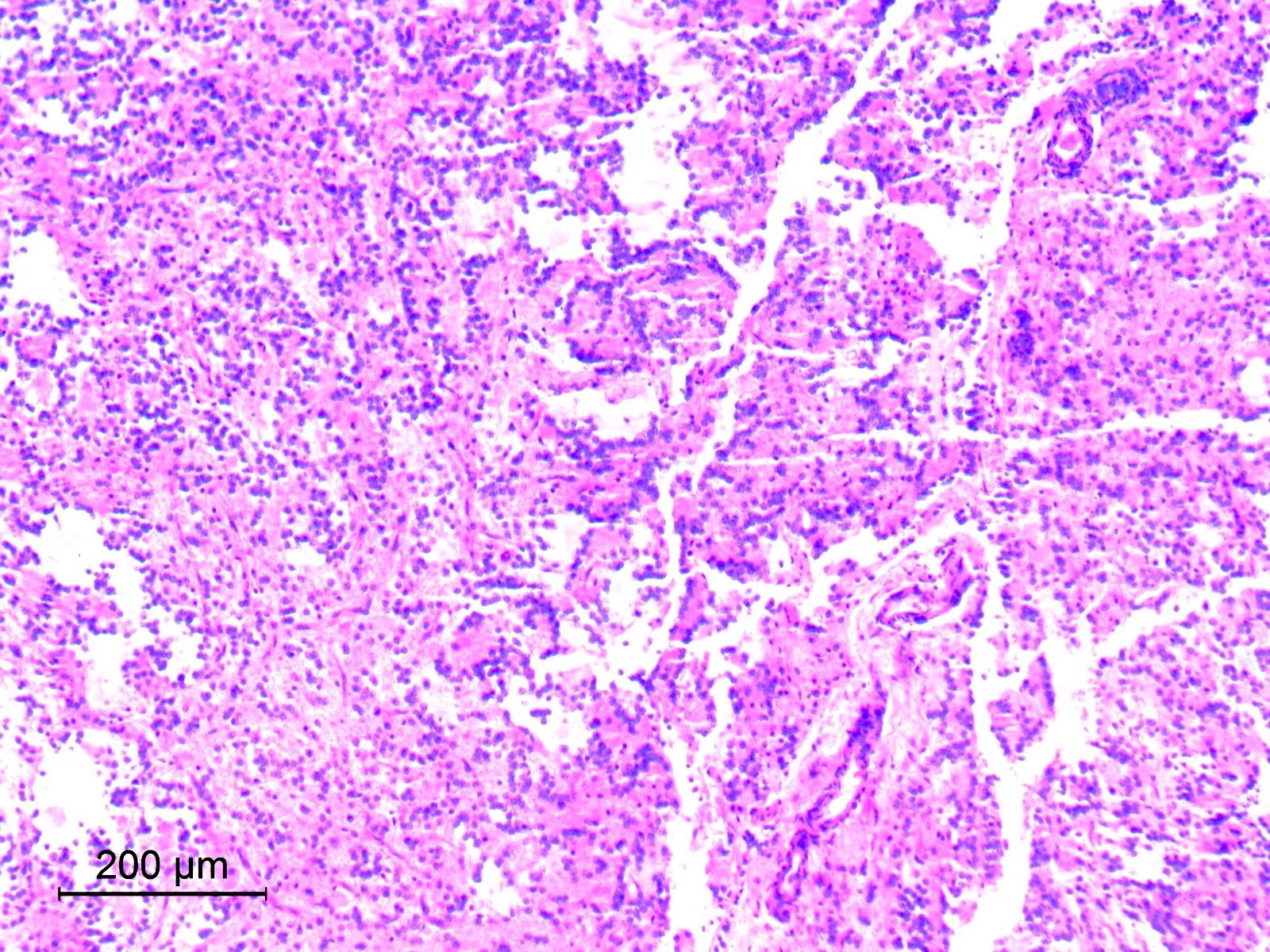
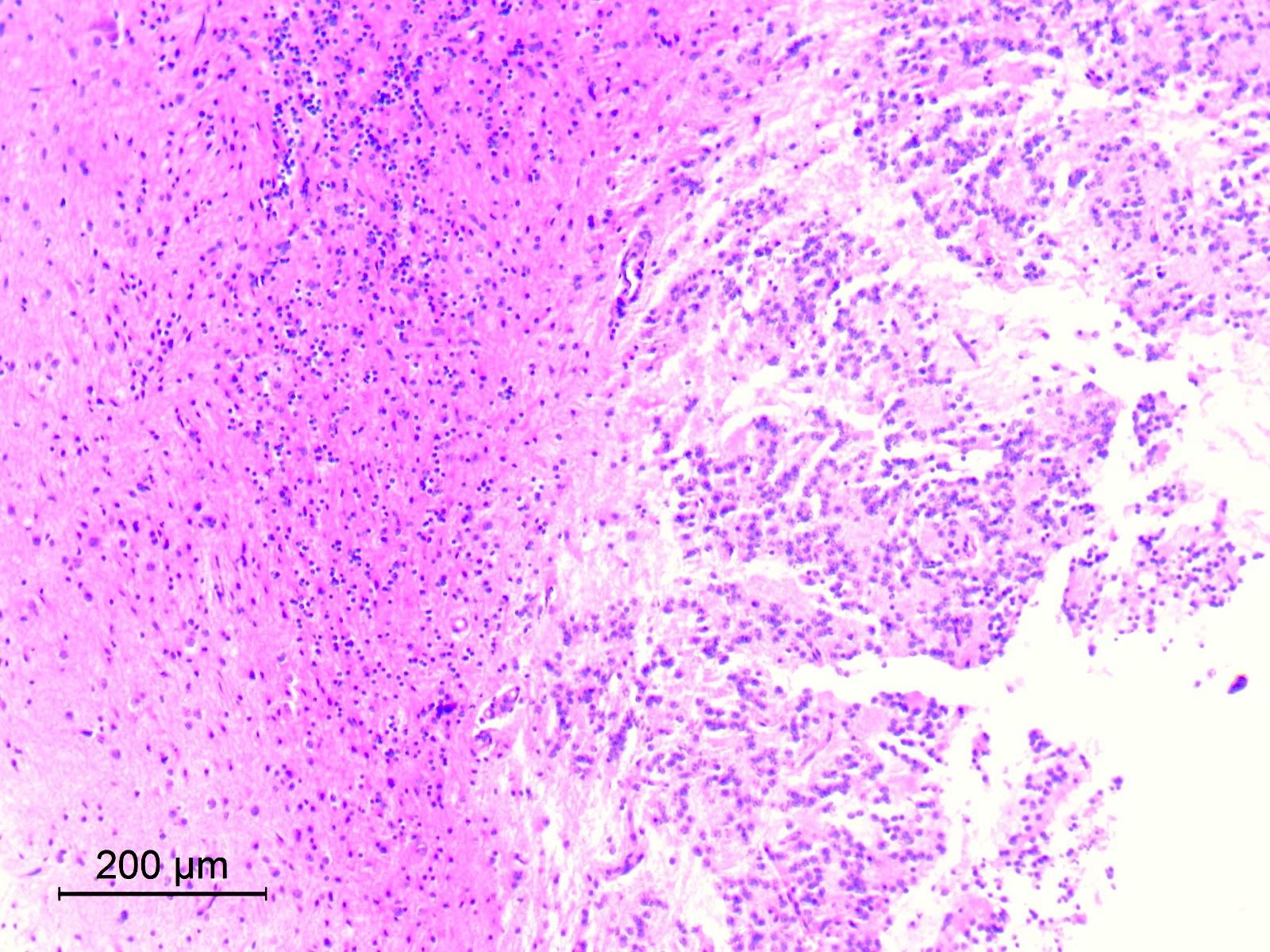
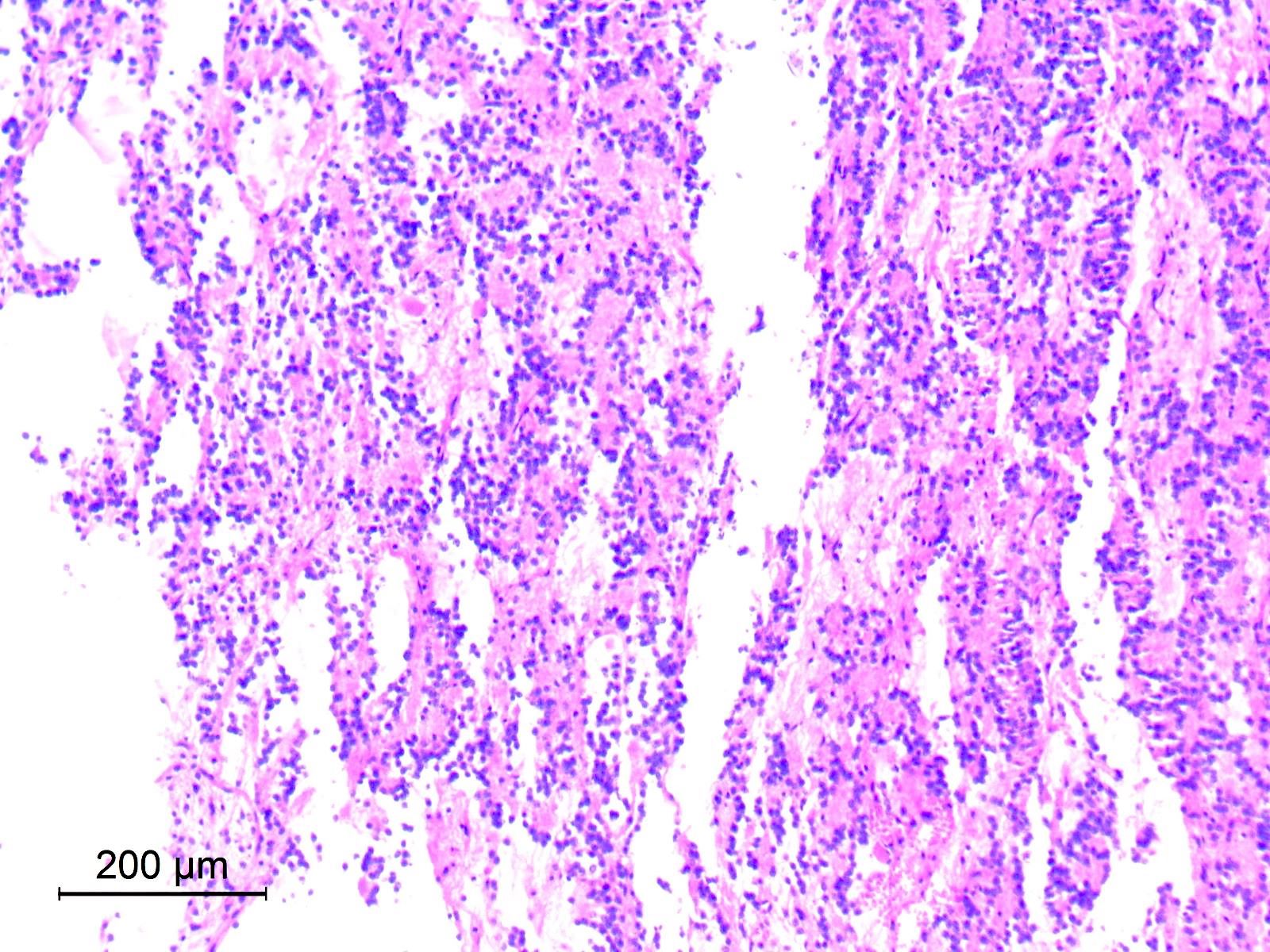
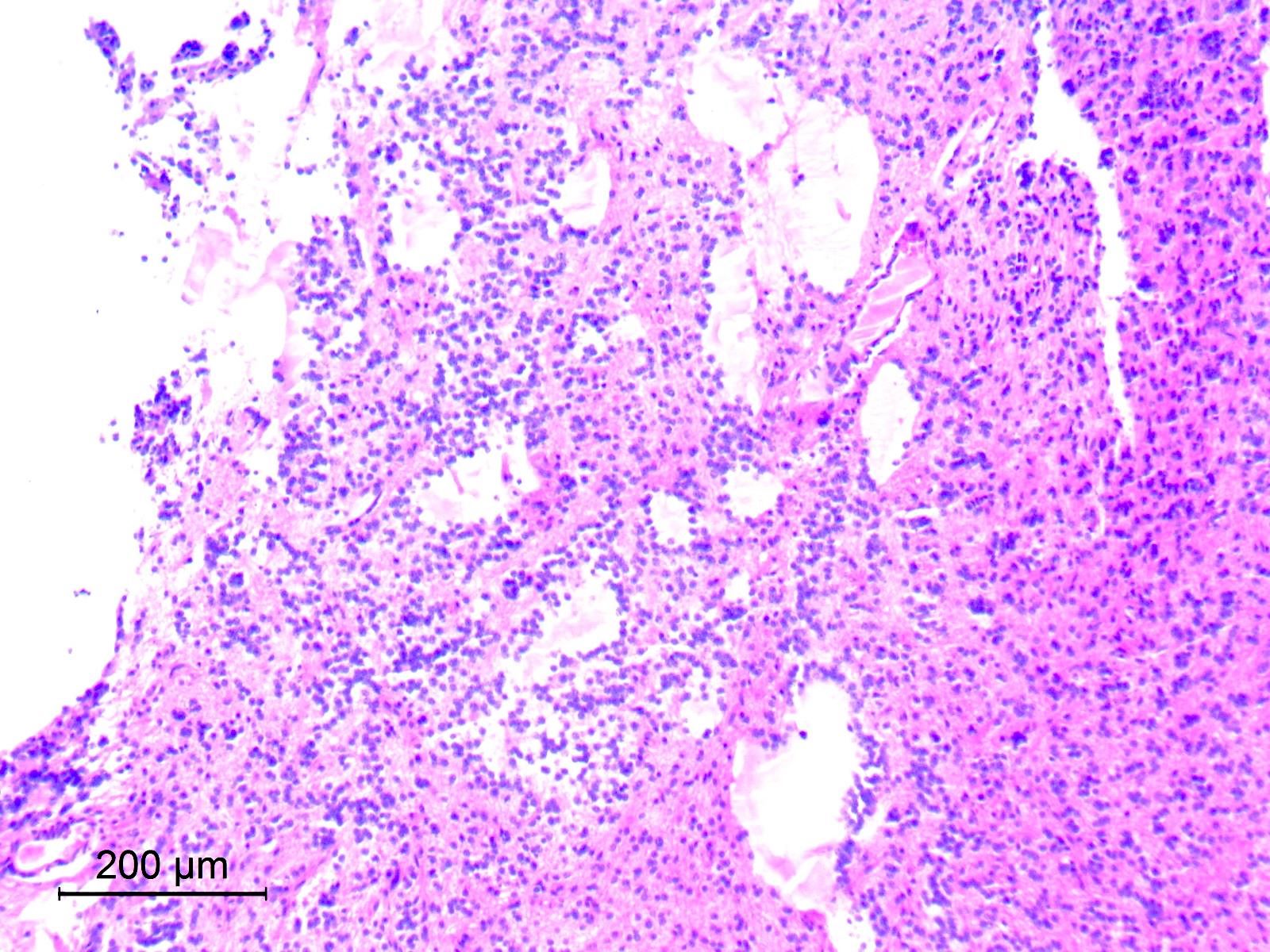
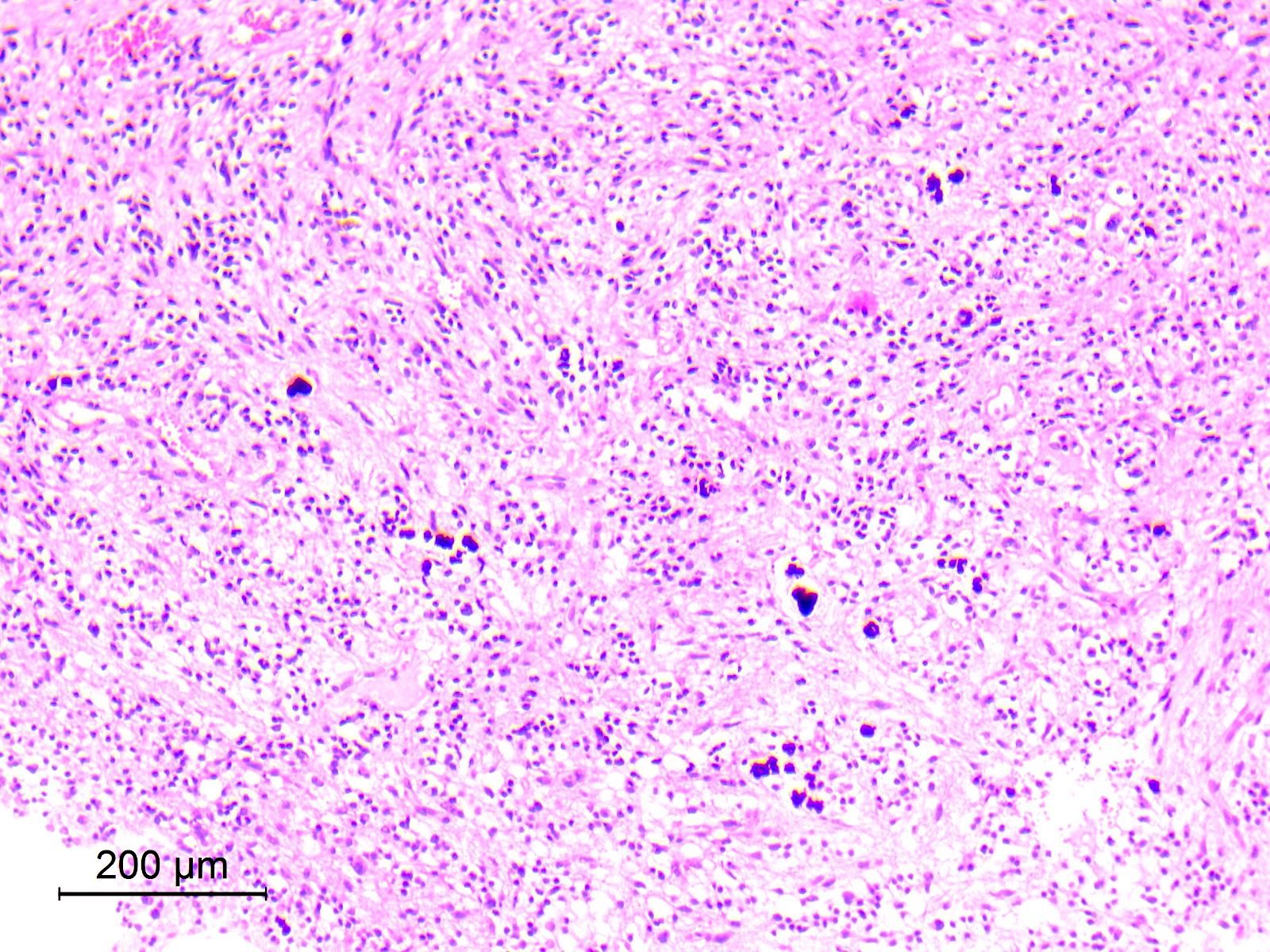
- Circumscribed, may show limited infiltration of surrounding parenchyma
- Biphasic with 2 distinct histological components: neurocytic and glial
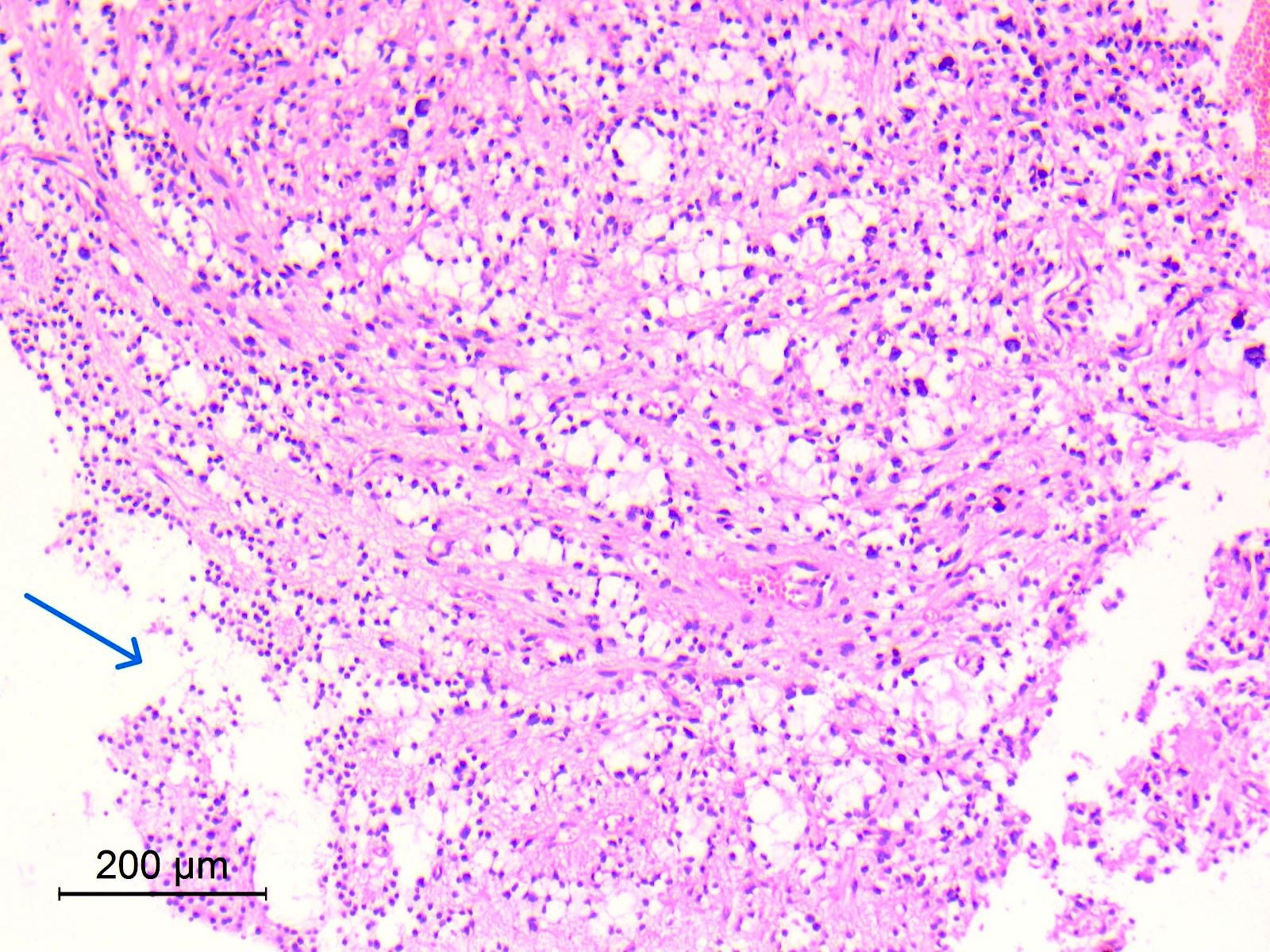
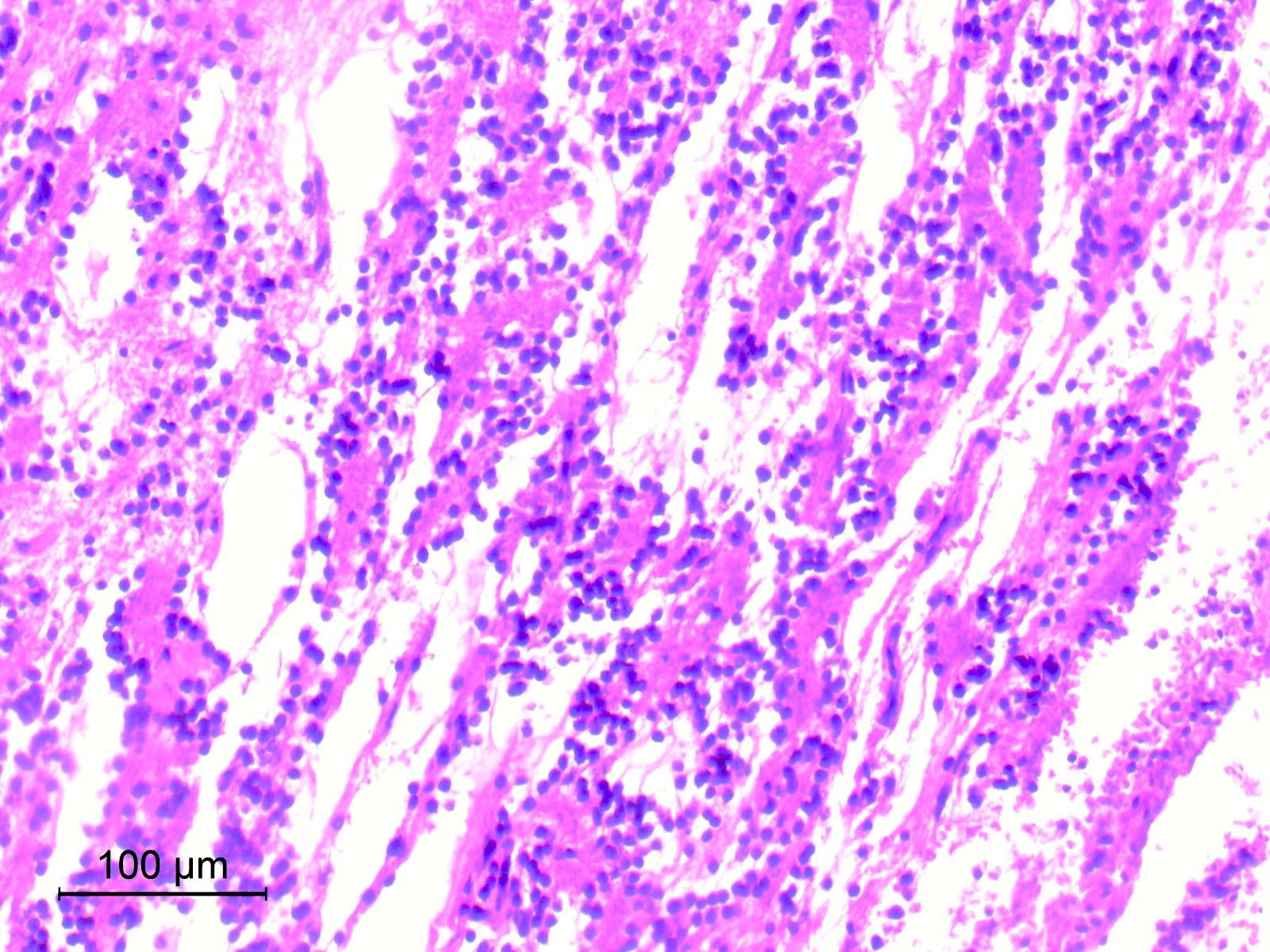
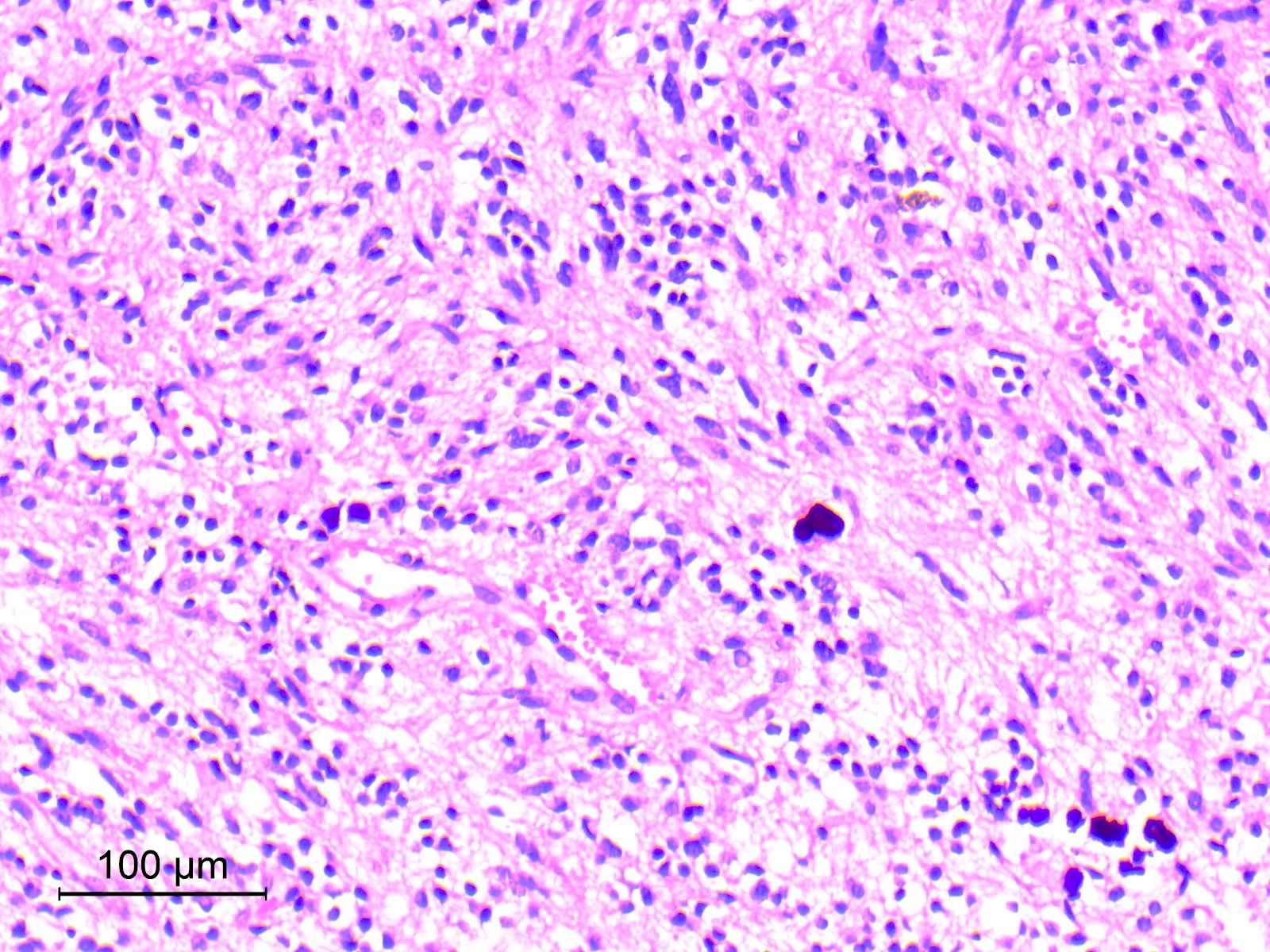
- Neurocytic component
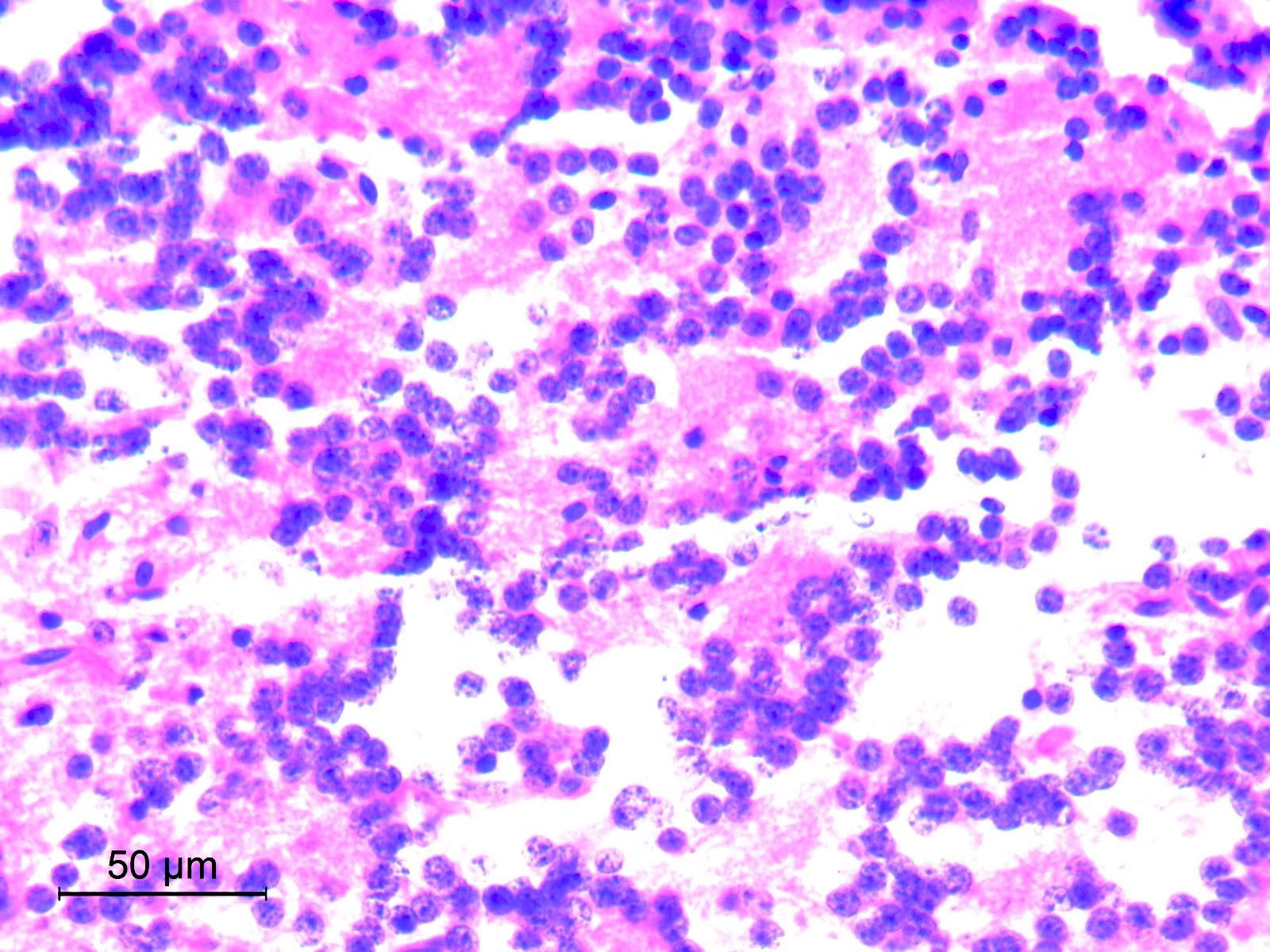
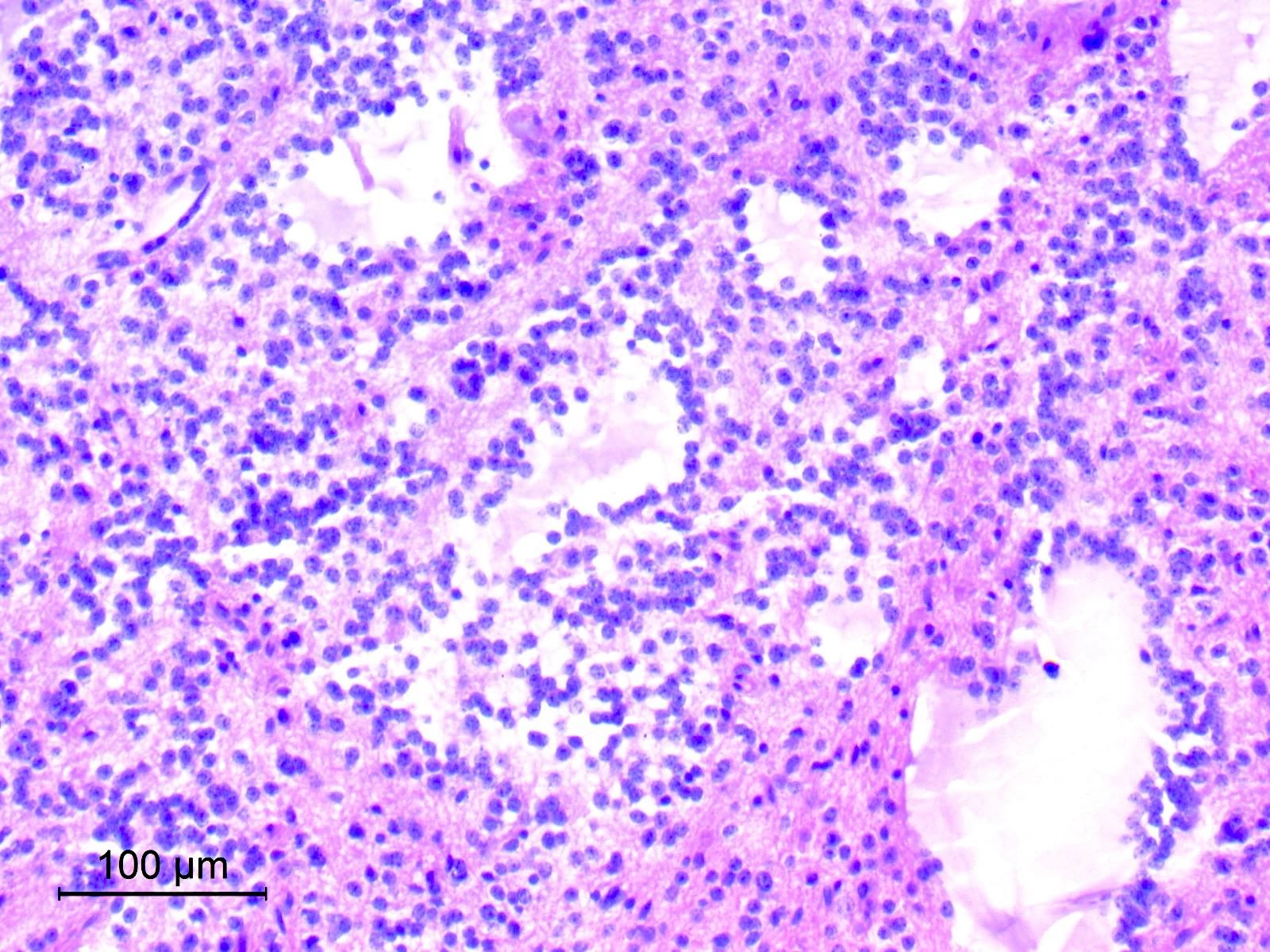
- Consists of uniform neurocytes forming neurocytic rosettes or perivascular pseudorosettes (Clin Case Rep 2021;9:e04355)
- Neurocytes have small round nuclei with fine stippled chromatin and scant cytoplasm
- Neurocytic rosettes are small with ring-like arrangement of neurocytes around delicate eosinophilic neuropil cores; may be arrayed in a cribriform pattern (Brain Pathol 2007;17:308)
- Perivascular pseudorosettes are narrow and formed of neurocytes with delicate cell processes radiating towards central vessels
- Neurocytic elements may lie unanchored in partly microcystic, mucinous matrix and, when sectioned longitudinally, may show a linear arrangement (Brain Pathol 2007;17:308)
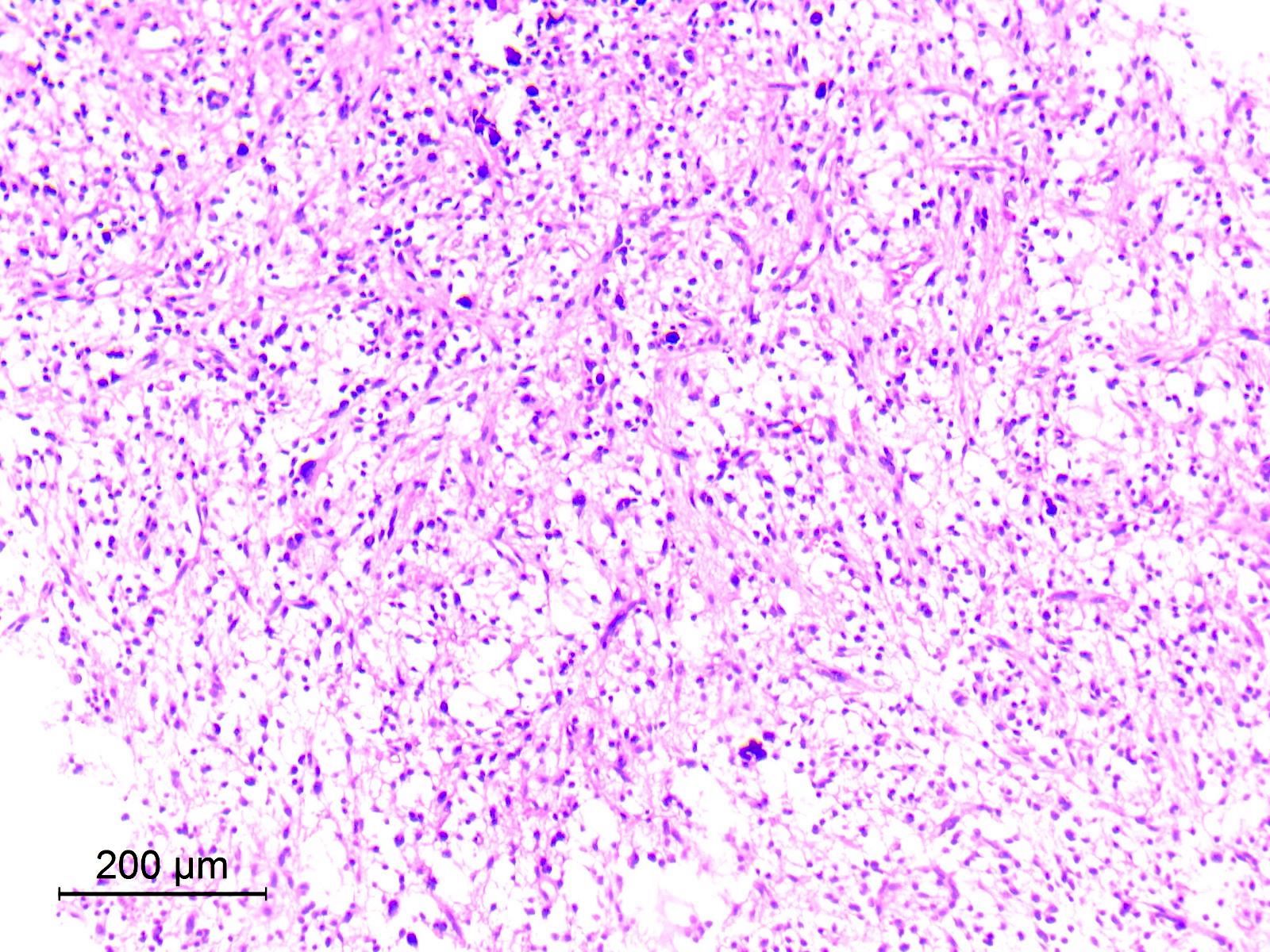
- Glial component
- Typically, dominant component and low grade
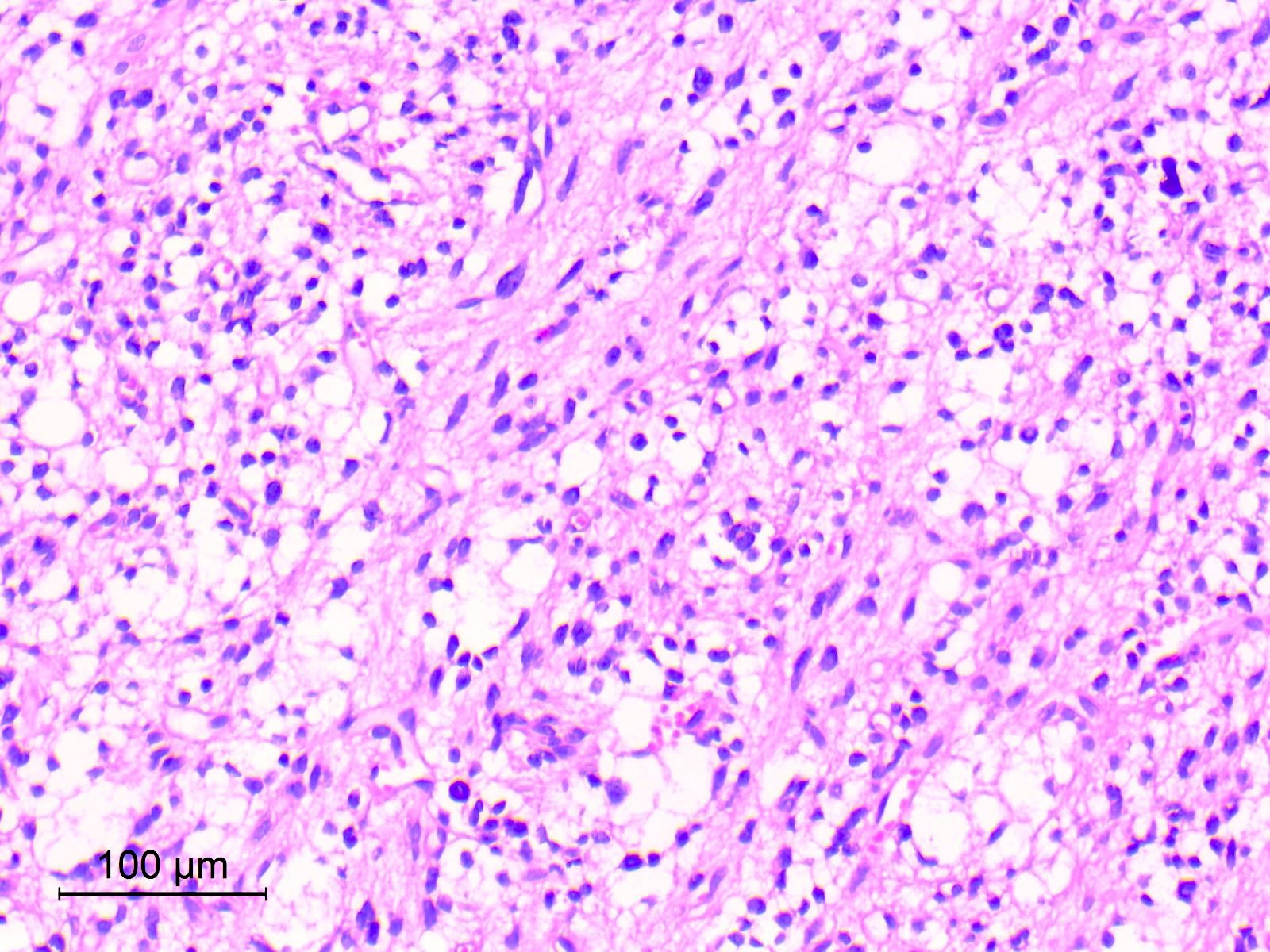
- Resembles pilocytic astrocytoma with piloid and oligodendroglia-like cells
- Astrocytic tumor cells are spindle to stellate in shape, with elongated or oval nuclei and cytoplasmic processes forming a compact to loosely textured fibrillary background (Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:497)
- May show oligodendroglia-like cells with perinuclear haloes arranged in microcystic pattern or diffuse sheets (Brain Pathol 2007;17:308)
- Mitoses and necrosis absent or rare, atypia absent or minimal (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175, Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:497)
- Rosenthal fibers, eosinophilic granular bodies (EGBs), microcalcifications and hemosiderin deposits may be seen (Brain Pathol 2007;17:308, Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:497)
- Blood vessels may be ectatic, hyalinized, thrombosed or show glomeruloid microvascular proliferation (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- Rarely, dysmorphic neurons may be seen in the glial regions (Brain Pathol 2007;17:308)
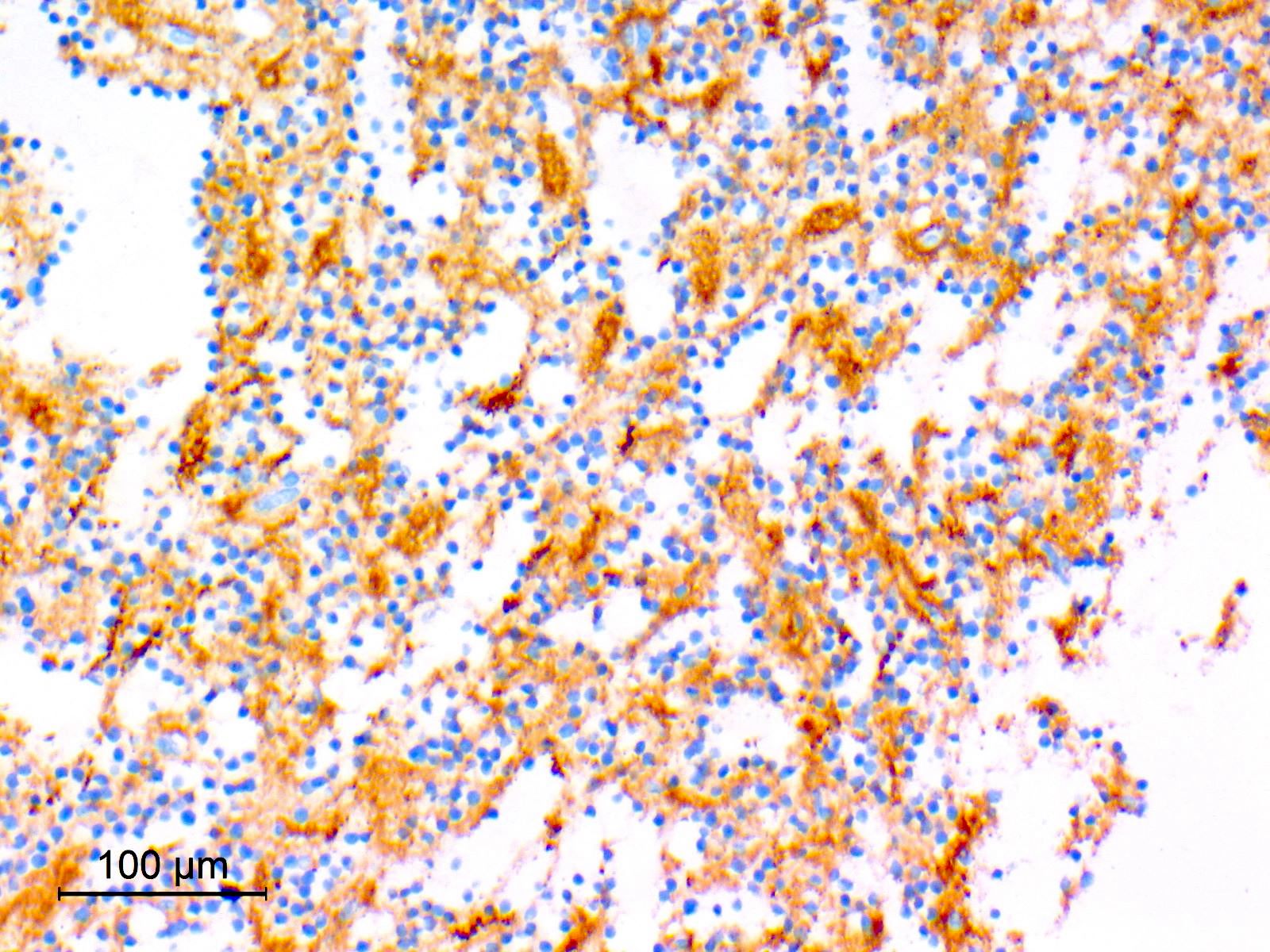
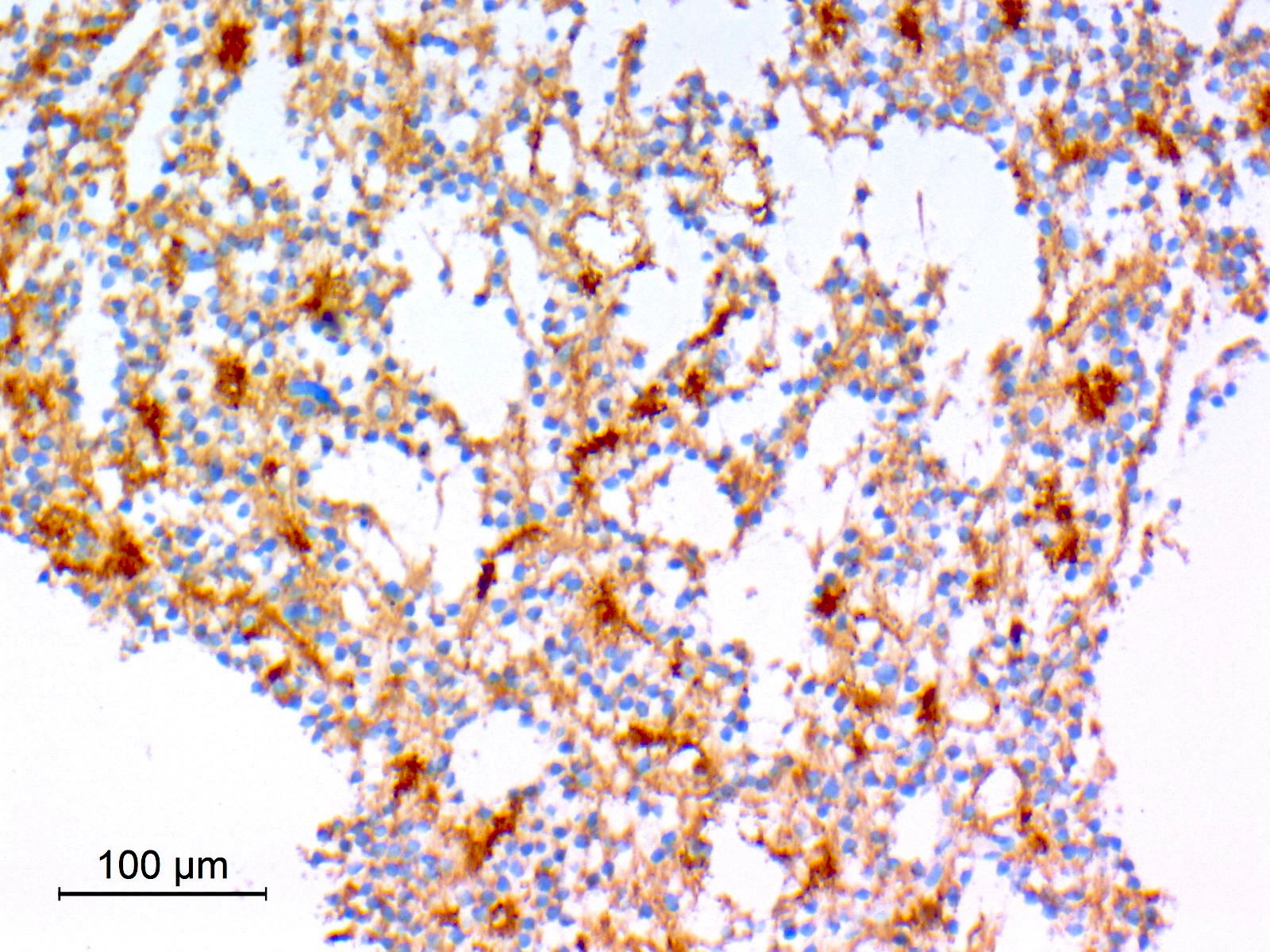
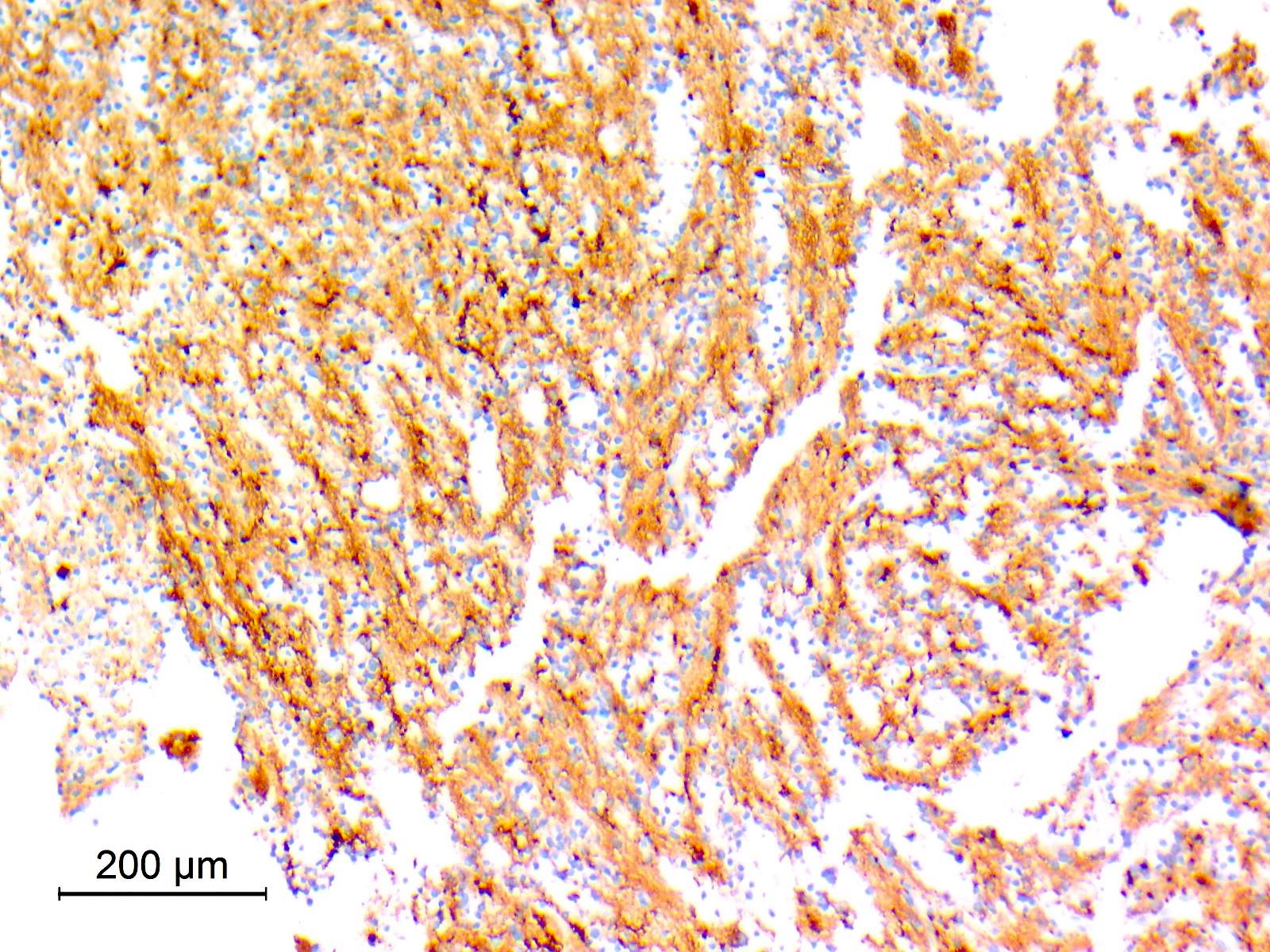
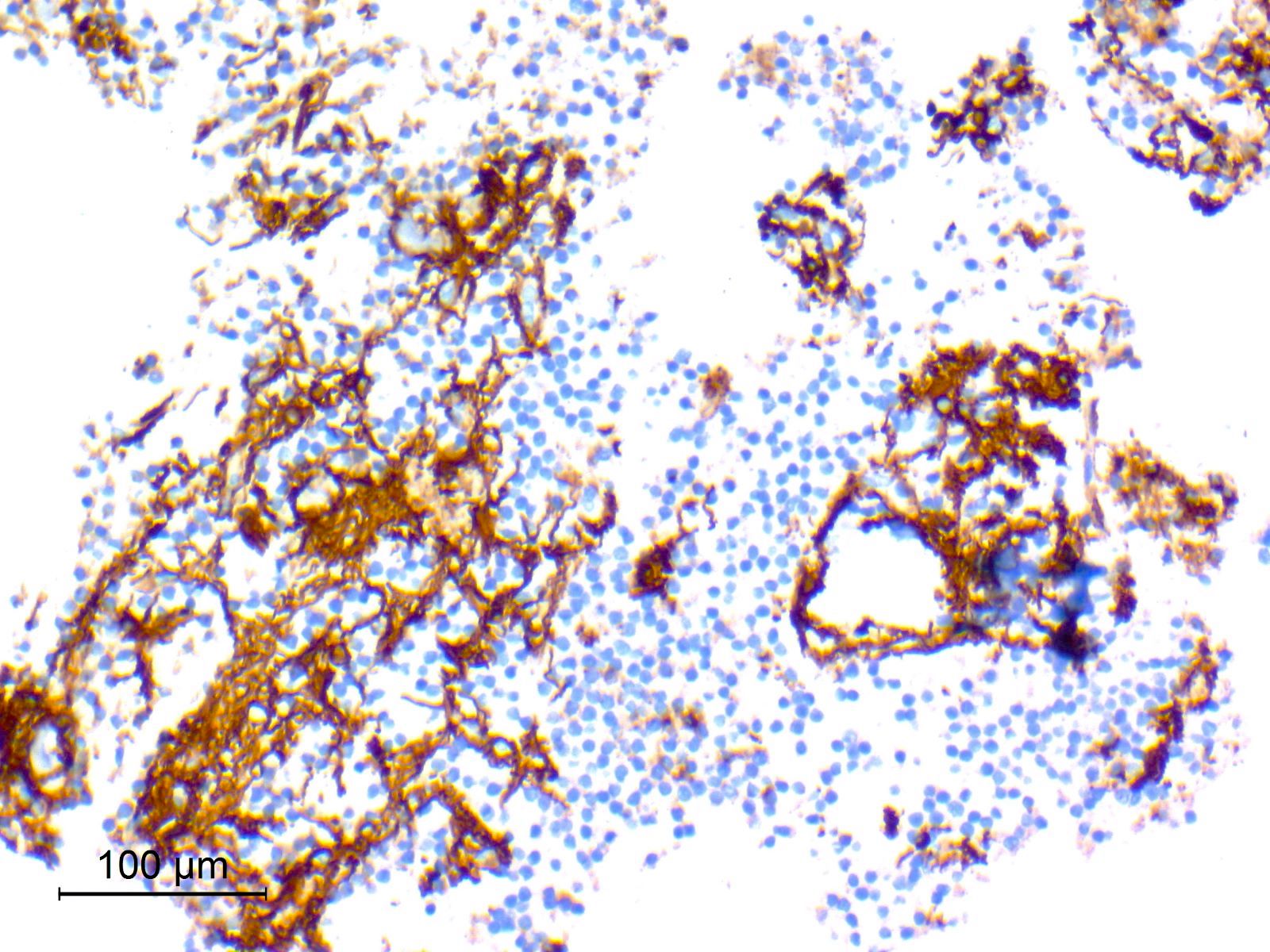
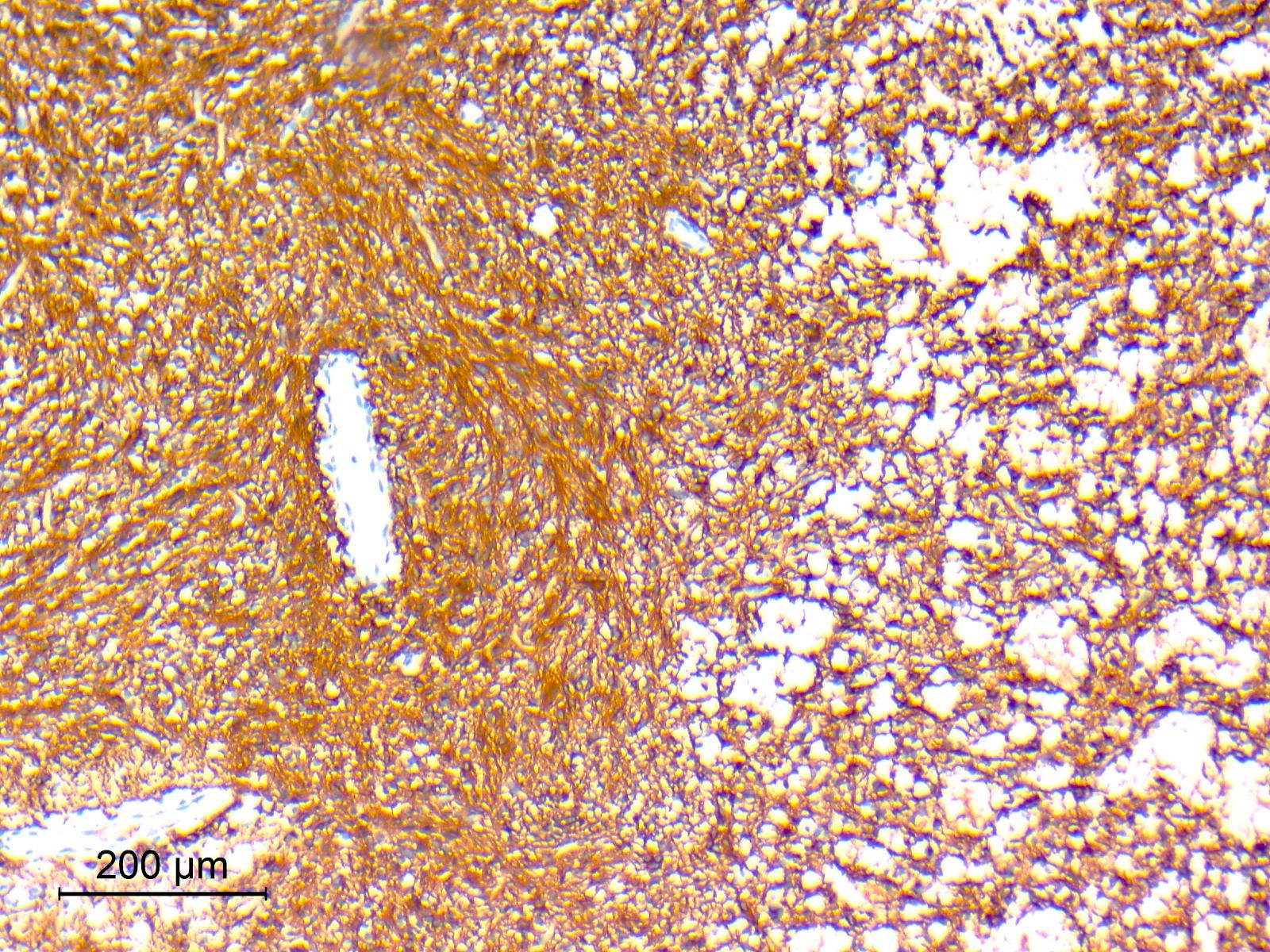
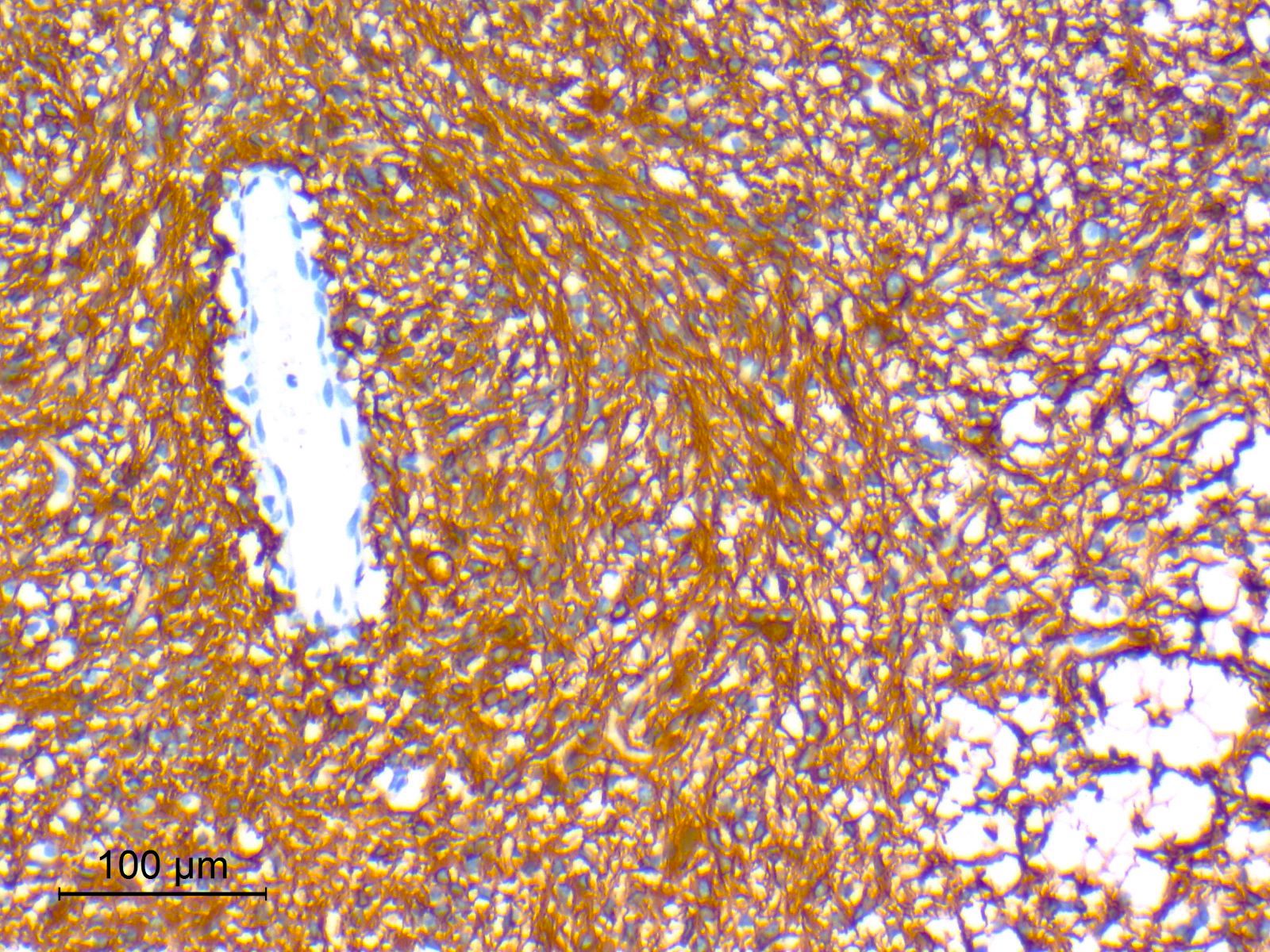
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Eman Abdelzaher, M.D., Ph.D.
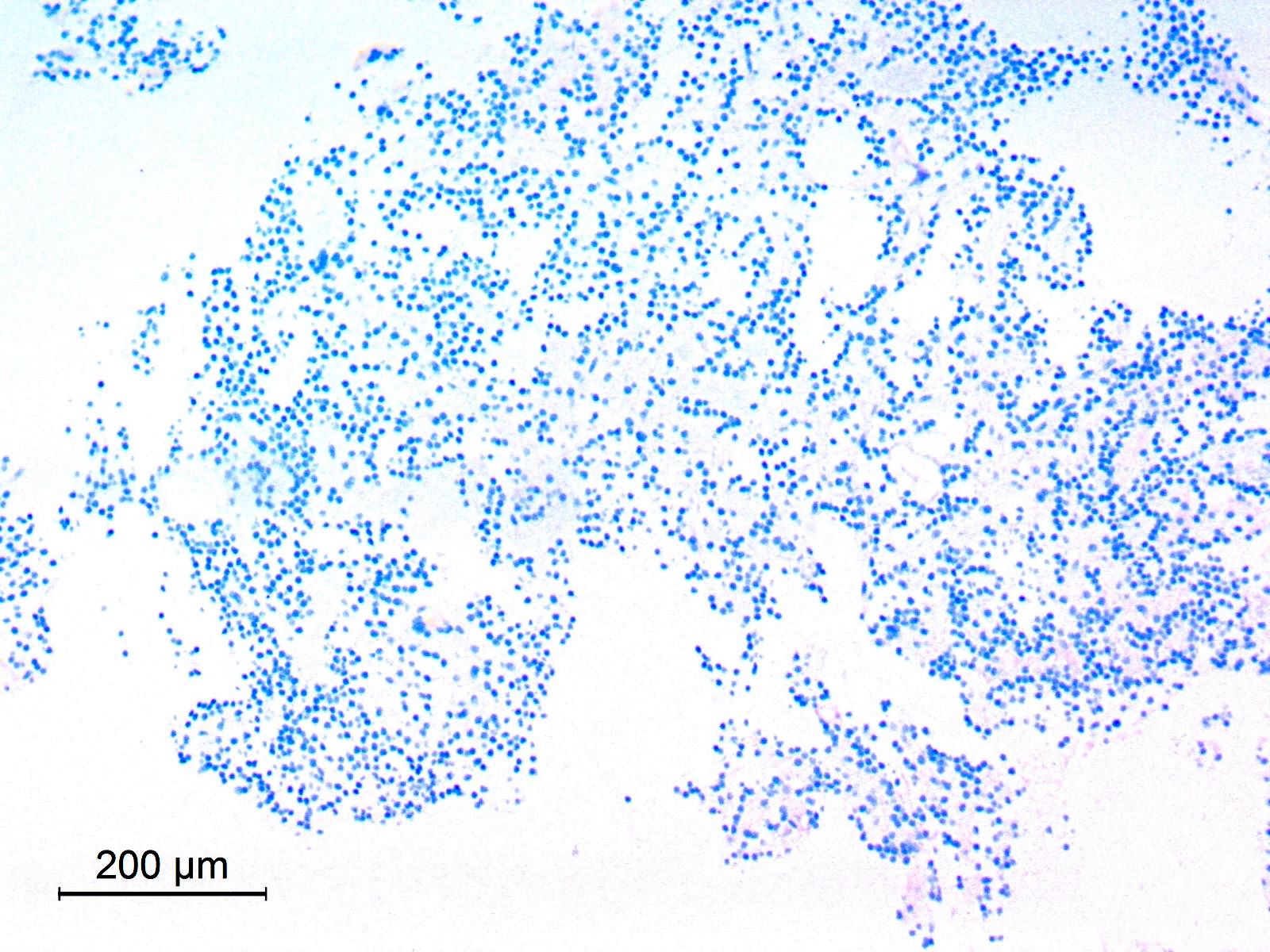
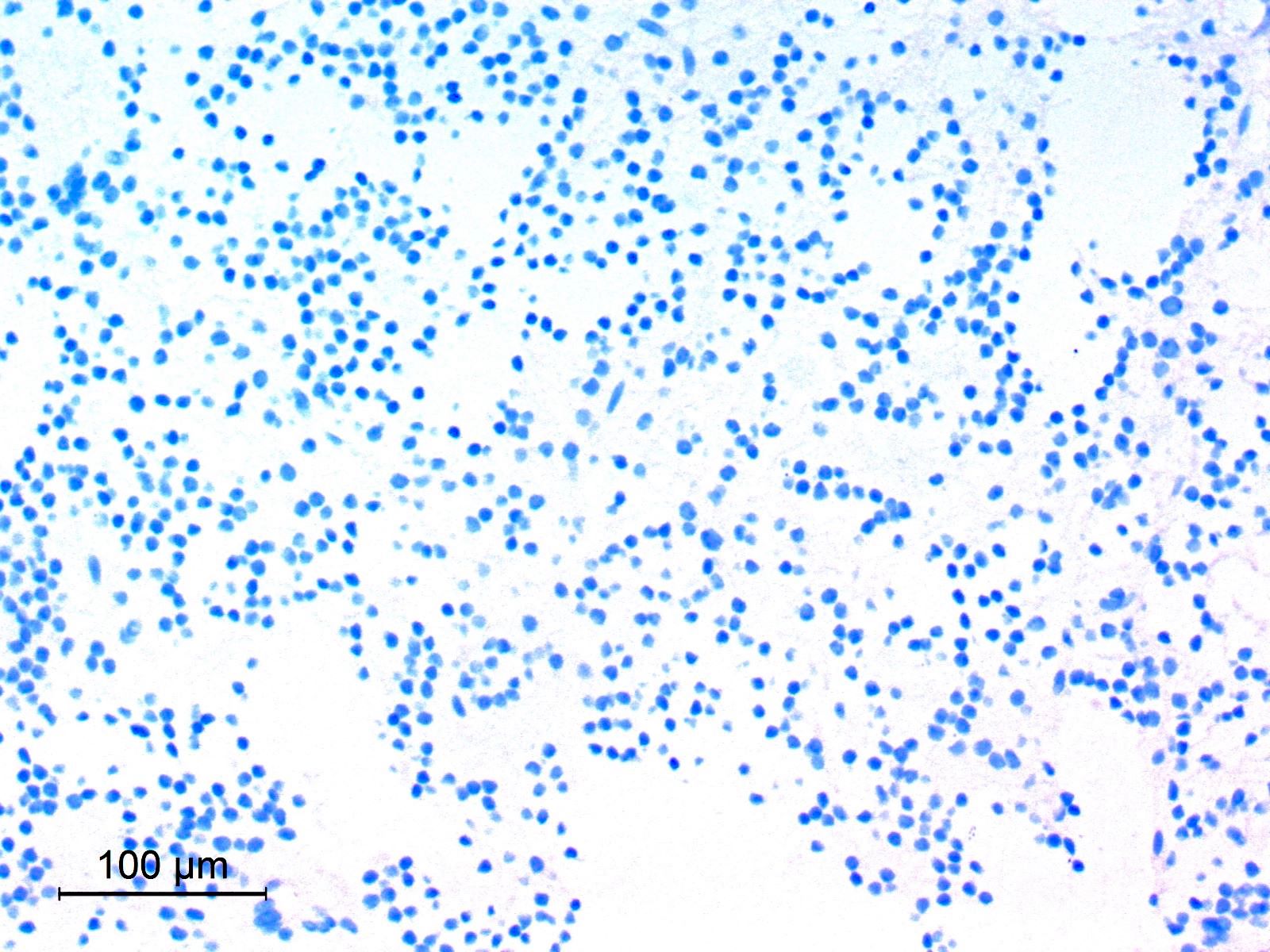
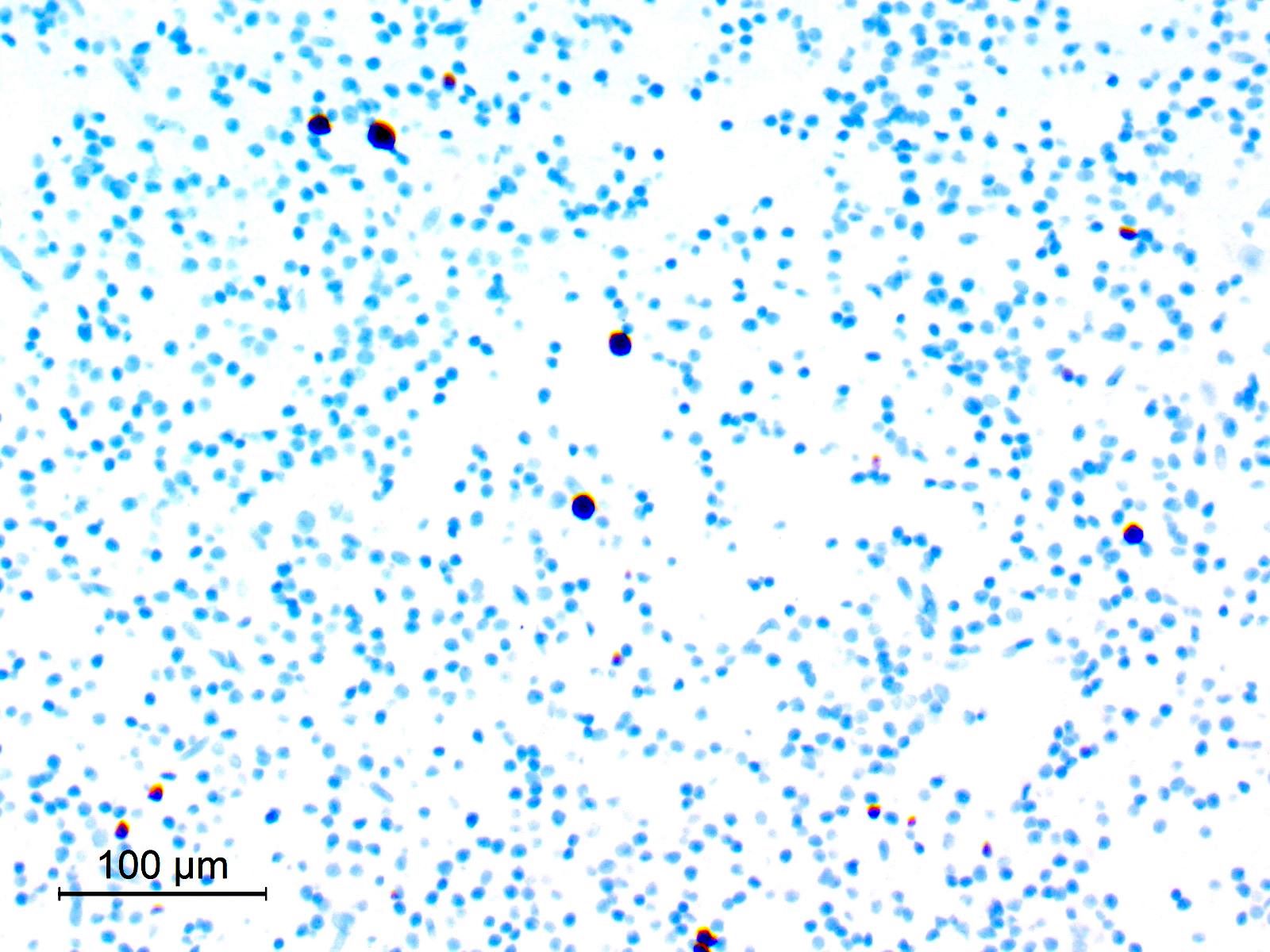
Cytology description
- Cellular smears
- Neurocytic cells have uniform round nuclei with delicate chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli and scant cytoplasm; neurocytic rosettes with fibrillar cores may be seen (Acta Cytol 2021;65:111)
- Glial, fibrillary fragments showing piloid astrocytes with elongated nuclei and coarse bipolar processes
- Dense extracellular mucoid substance
- No atypia
Positive stains
- Synaptophysin: highlights neuropil cores of neurocytic rosettes and neuropil of perivascular pseudorosettes (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175, Cancers (Basel) 2023;15:1120)
- MAP2: in neurocytic tumor cells
- Neuron specific enolase (NSE): in neurocytic tumor cells (92%) (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- Neurofilament protein (NFP): in neurocytic tumor cells (60.5%) (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP): in glial component (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- S100: in glial component (Cancers (Basel) 2023;15:1120)
- Olig2: in both neurocytic and pilocytic-like components (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175, Cancers (Basel) 2023;15:1120)
- Low Ki67 proliferation index: generally < 3% (ranging from 0 - 5%), rarely reaching up to 10% (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175, Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:497)
Negative stains
- Epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
- CD34 (Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:497)
- NeuN (34%) positive: in neurocytic tumor cells (Oncotarget 2017;8:109175)
Electron microscopy description
- Neurocytic component: neurocytic cells exhibit processes containing aligned microtubules, occasional dense core granules and rare mature synapses (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:582)
- Glial component: dense bundles of glial filaments (Neuropathology 2009;29:309)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Defined by a distinct DNA methylation profile (Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:497)
- FGFR1 hotspot mutations (FGFR1 p.N546 or p.K656) are typical, with co-occurrence of PIK3CA mutations in the majority of cases (Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:497, Acta Neuropathol 2012;123:285)
- Loss of function mutation in NF1 in a subset of cases
- Lack of BRAF alterations
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Videos
WHO classification of CNS tumors: glioneuronal tumors
Sample pathology report
- Brain mass lesion, fourth ventricle, gross total resection:
- Rosette forming glioneuronal tumor, CNS WHO grade 1
- Molecular genetics: methylation profile of rosette forming glioneuronal tumor
Differential diagnosis
- Pilocytic astrocytoma:
- No neurocytic component (Pathol Res Pract 2007;203:613)
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor:
- Almost always supratentorial (Pathol Res Pract 2007;203:613)
- Floating neurons
- Lacks well formed rosettes
- Features overlap in some cases with RGNT
- Oligodendroglioma:
- Rare in posterior fossa
- Diffusely infiltrative growth pattern
- No rosettes
- 1p / 19q codeletion in adults (Pathol Res Pract 2007;203:613)
- Ependymoma:
- Perivascular pseudorosettes are GFAP+ and often Olig2- and synaptophysin- (Pathol Res Pract 2007;203:613)
- Cerebellar liponeurocytoma:
- Diffusely synaptophysin+
- Lipidized tumor cells (Can J Surg 2009;52:E117)
- No rosettes
- Papillary glioneuronal tumor:
- Supratentorial
- Perivascular GFAP+ glial cells (Pathol Res Pract 2007;203:613)
- Diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor:
- Commonly shows diffuse involvement of the leptomeninges (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2020;41:2155)
- Absent or only focal GFAP immunoreactivity
- Characteristic molecular profile of KIAA1549::BRAF fusion with isolated 1p deletion or 1p / 19q codeletion
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 15 year old girl presented with a headache. MRI showed a posterior fossa mass lesion epicentered on the cerebellar vermis. Resection of the tumor was done and the histopathological features of the tumor are shown above. Which of the following is a typical genetic finding in this tumor?
- 1p / 19q codeletion
- BRAF alterations
- FGFR1 mutations
- PRKCA gene fusion
Board review style answer #1
C. FGFR1 mutations. FGFR1 hotspot mutations are typical of rosette forming glioneuronal tumors (RGNTs). Answer B is incorrect because RGNTs lack BRAF alterations. Answer D is incorrect because PRKCA gene fusion (mainly SLC44A1::PRKCA) is the hallmark of papillary glioneuronal tumors (PGNTs). Answer A is incorrect because 1p / 19q codeletion is characteristic of oligodendroglioma.
Comment Here
Reference: Rosette forming glioneuronal tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Rosette forming glioneuronal tumor
Board review style question #2
Rosette forming glioneuronal tumor is characterized by which of the following features?
- Diffuse growth pattern
- Exclusive supratentorial location
- Neurocytic rosettes with synaptophysin positive neuropil cores
- Papillary architecture
Board review style answer #2
C. Neurocytic rosettes with synaptophysin positive neuropil cores. Neurocytic rosettes with synaptophysin positive neuropil cores are the histologic hallmark of rosette forming glioneuronal tumors (RGNTs). Answer A is incorrect because RGNTs are generally demarcated with occasional limited infiltration of the surrounding parenchyma. Answer B is incorrect because RGNTs occur throughout the CNS with predilection to posterior fossa. Answer D is incorrect because papillary architecture is not a feature of RGNTs.
Comment Here
Reference: Rosette forming glioneuronal tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Rosette forming glioneuronal tumor