Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Frozen section description | Intraoperative frozen / smear cytology images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Barresi V. Chordoid meningioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorchordoidmeningioma.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Chordoid meningioma is a histological subtype of meningioma characterized by cords or trabeculae of epithelioid (or spindle) cells embedded in a mucin rich stroma and resembling chordoma
- It is classified as CNS WHO grade 2, regardless of the presence of worrisome histological features (mitoses, spontaneous necrosis, brain invasion)
Essential features
- Histological subtype of meningioma that is characterized by cords or trabeculae of epithelioid (or spindle) cells embedded in a mucin rich stroma and resembling chordoma
- CNS WHO grade 2
- Recurrence risk is associated with subtotal resection, high Ki67 labeling index and atypical histological features (mitoses, brain invasion, spontaneous necrosis, small cell with high N:C ratio, hypercellularity, macronucleoli, sheeting)
- Pure forms exist but it most commonly features intermingled areas of classical meningioma, with syncytial growth pattern, whorls and pseudoinclusions
- Immunohistochemistry: EMA+, podoplanin+, possible focal cytokeratin+, S100-, brachyury-, GFAP-
Terminology
- Chordoid meningioma
Epidemiology
- Rare meningioma subtype, accounting for 0.5 - 1% of intracranial meningiomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:899)
- M:F = 1:1
- Mainly affects adults (mean age: 47 years) (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:899)
- Mean age at presentation is nearly a decade younger than nonchordoid meningiomas (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:56)
- Mostly involves supratentorial meninges (88%) but may also occur at the (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:899)
- Skull base (World Neurosurg 2016;93:198)
- Cerebellar pontine angle (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:899)
- Spinal meninges (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:899)
- Cerebral ventricles (World Neurosurg 2016;93:198)
Pathophysiology
- Originates from arachnoid border cells or dura based cells (Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2021;163:57)
Etiology
- Risk factors may be similar to general meningioma: ionizing radiation (Eur J Epidemiol 2020;35:591)
Clinical features
- Unspecific symptoms, including headache, limbs weakness or numbness, cranial nerve disorders, epilepsy (World Neurosurg 2016;93:198)
- It has been associated with Castleman disease (Cancer 1988;62:391)
Diagnosis
- Based on imaging (CT, MRI) / biopsy / resection specimen
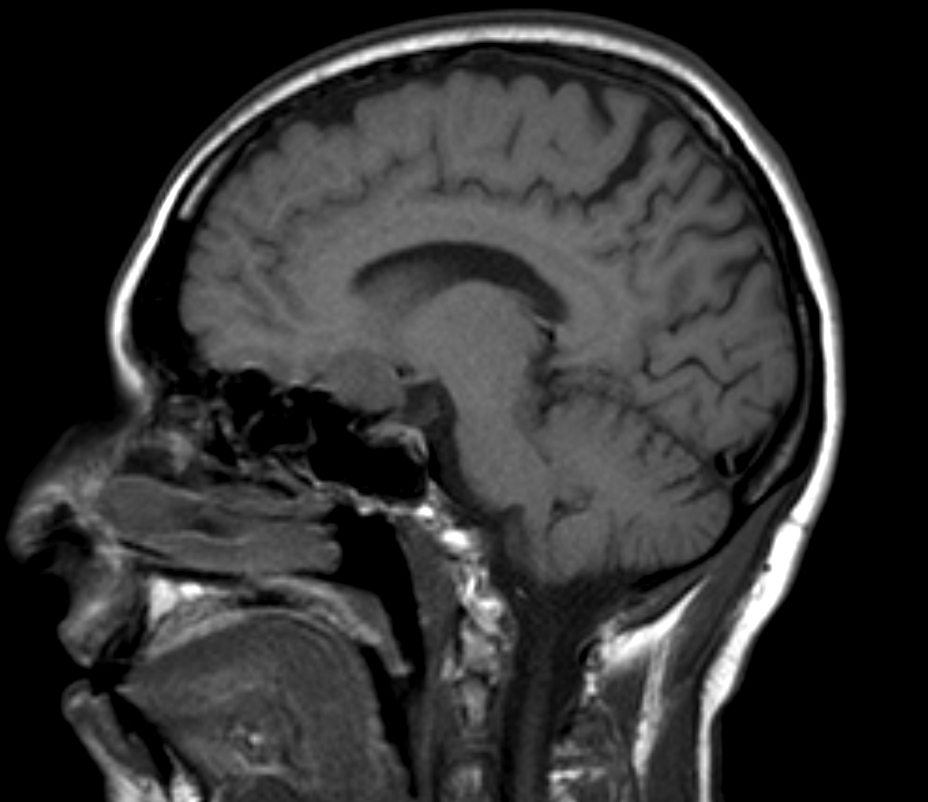
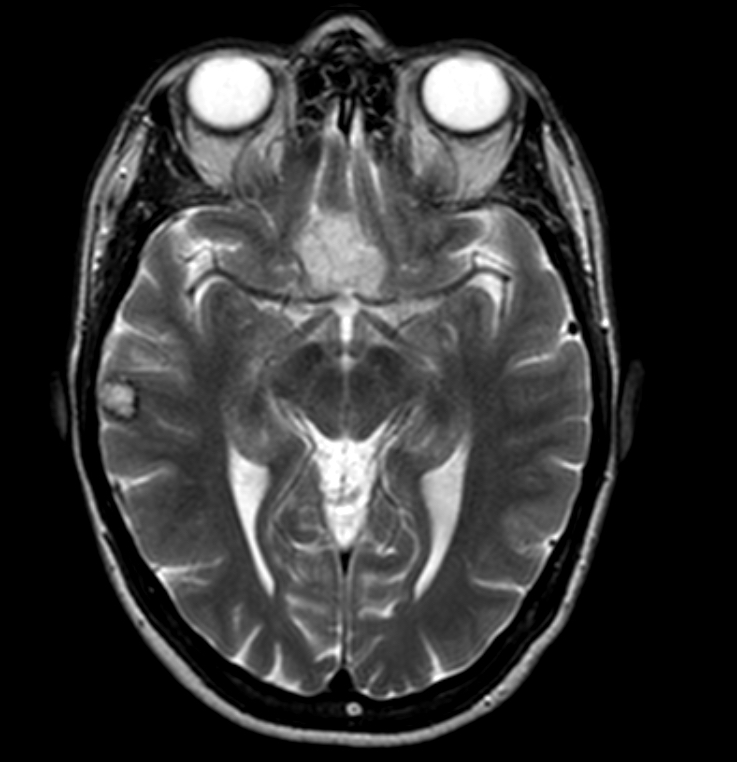
Radiology description
- At MRI, chordoid meningioma is hypoisointense on T1 weighted images and hyperintense on T2 and FLAIR, with contrast enhancement varying from homogeneous to heterogeneous (J Neurooncol 2018;137:575, Neuroradiology 2022;64:253)
- Contrast enhancement is more intense than in meningothelial, transitional or fibrous meningiomas (Neuroradiology 2022;64:253)
- Multicystic appearance is seen in some cases (Neuroradiology 2022;64:253)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- In a meta analysis of 220 patients with chordoid meningiomas, 23% had tumor progression after surgery, with a median time to recurrence of ~131 months (J Neurooncol 2016;126:107)
- 3, 5 and 10 year progression free survival (PFS): 76.0%, 67.5% and 54.4%, respectively (J Neurooncol 2016;126:107)
- Significant risk factors for recurrence include:
- Subtotal resection (World Neurosurg 2016;93:198, J Neurooncol 2016;126:107)
- Ki67 labeling index ≥ 5% (J Neurooncol 2016;126:107)
- Histological atypical features (high mitotic index, spontaneous necrosis, brain invasion, macronucleoli) (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:56)
- NF2 mutation, 1p, 8p, 10, 14, 22q loss and homozygous deletion of CDKN2A / CDKN2B (Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:225, Acta Neuropathol 2018;136:975)
- Methylation class intermediate or malignant (Acta Neuropathol 2018;136:975, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:56)
Case reports
- 22 year old woman presented with a foramen magnum lesion (Asian J Neurosurg 2018;13:834)
- 50 year old woman presented with progressive headaches (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:e115)
- 68 year old man presented with a tuberculum sellae lesion (NMC Case Rep J 2020;7:53)
Treatment
- Surgery and adjuvant radiotherapy (World Neurosurg 2016;93:198)
Gross description
- Soft / gelatinous consistency, smooth contour and translucent areas (NMC Case Rep J 2020;7:53, Diagn Cytopathol 2016;44:811)
Frozen section description
- Differential diagnosis versus other tumor types: at least focal presence of psammoma bodies, meningothelial whorls or nuclear pseudoinclusions
- Differential diagnosis versus other meningioma subtypes: cords of cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm in a myxoid background (NMC Case Rep J 2020;7:53)
Intraoperative frozen / smear cytology images
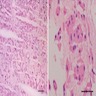
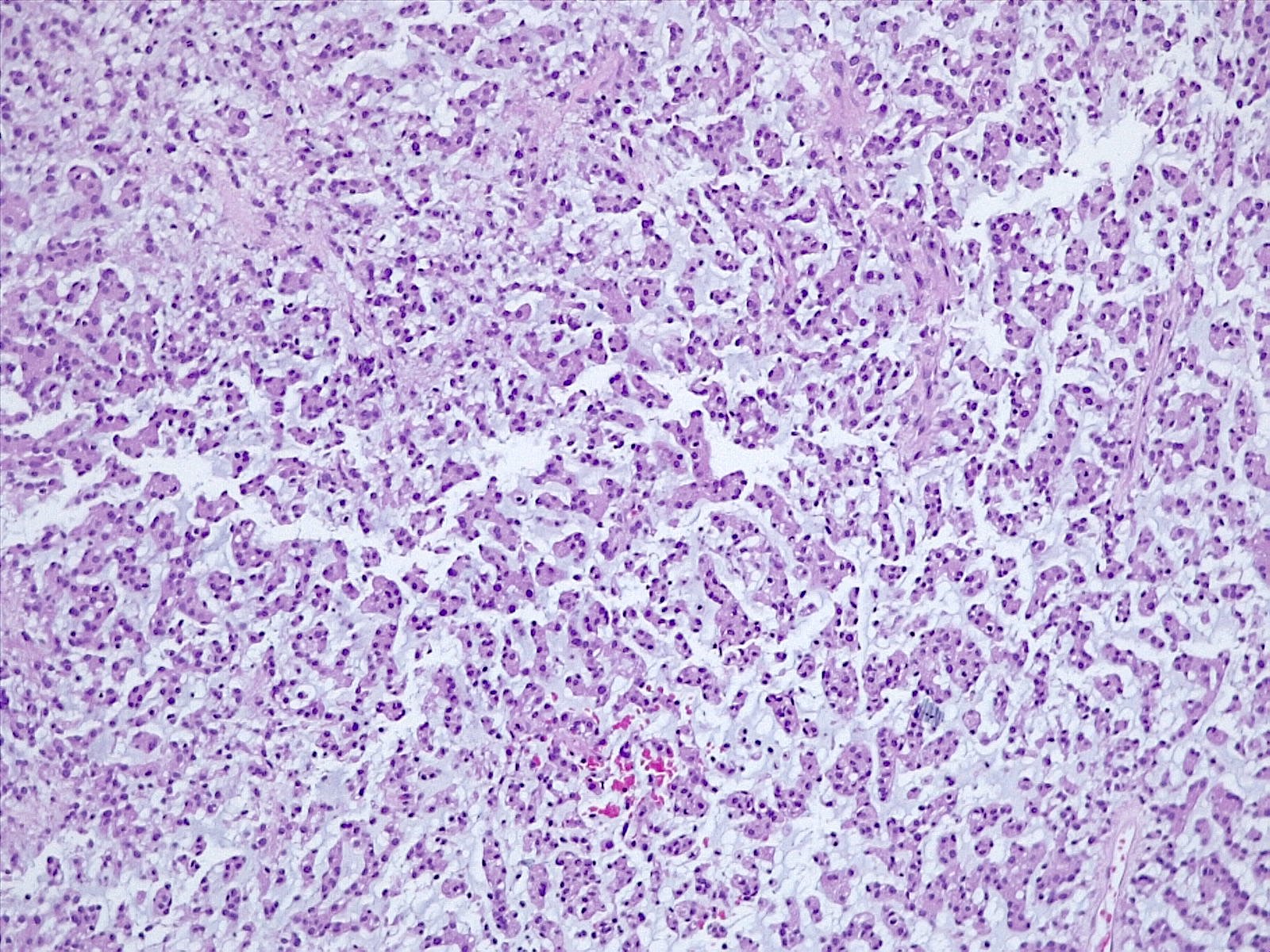
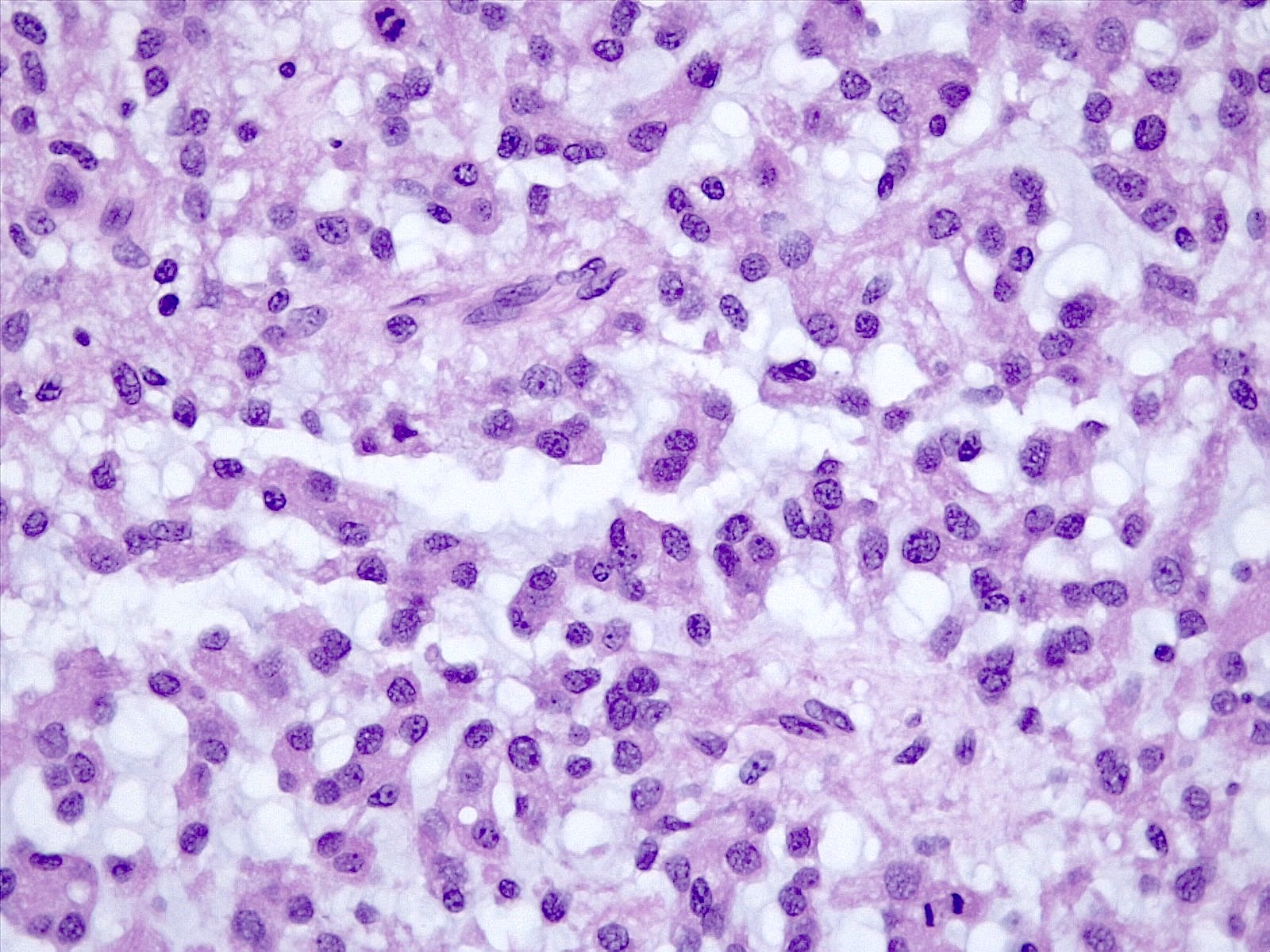
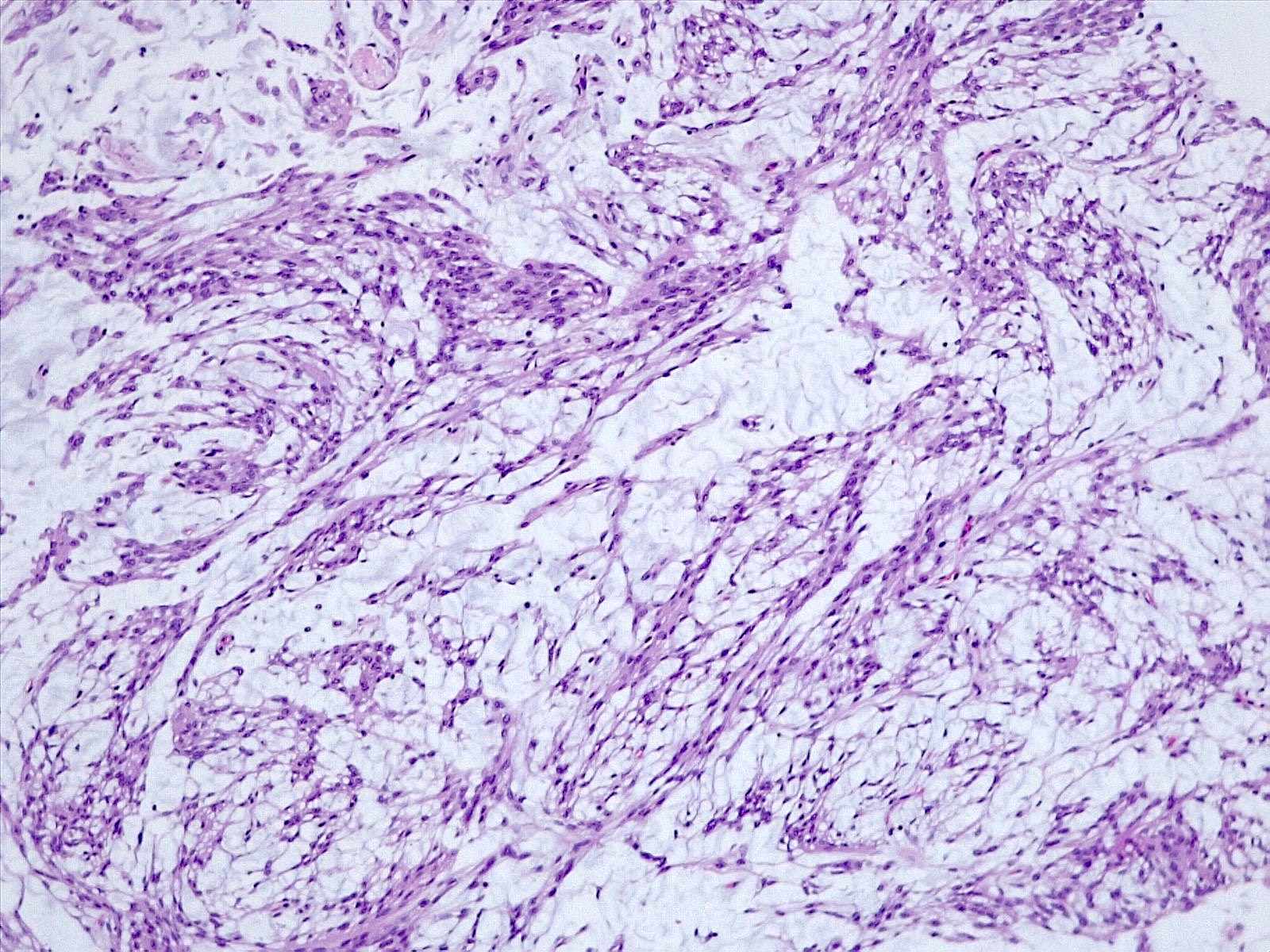
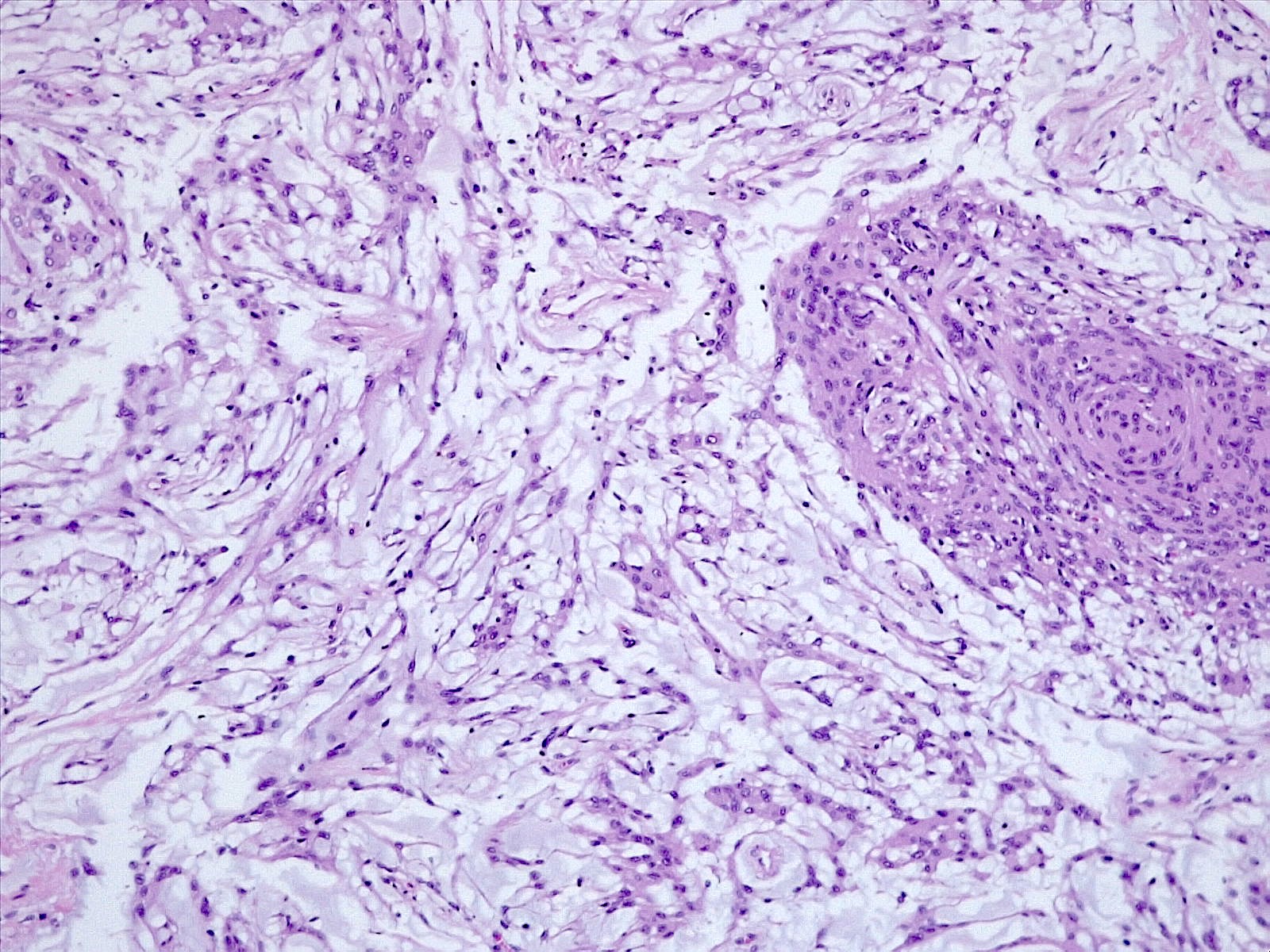
Microscopic (histologic) description
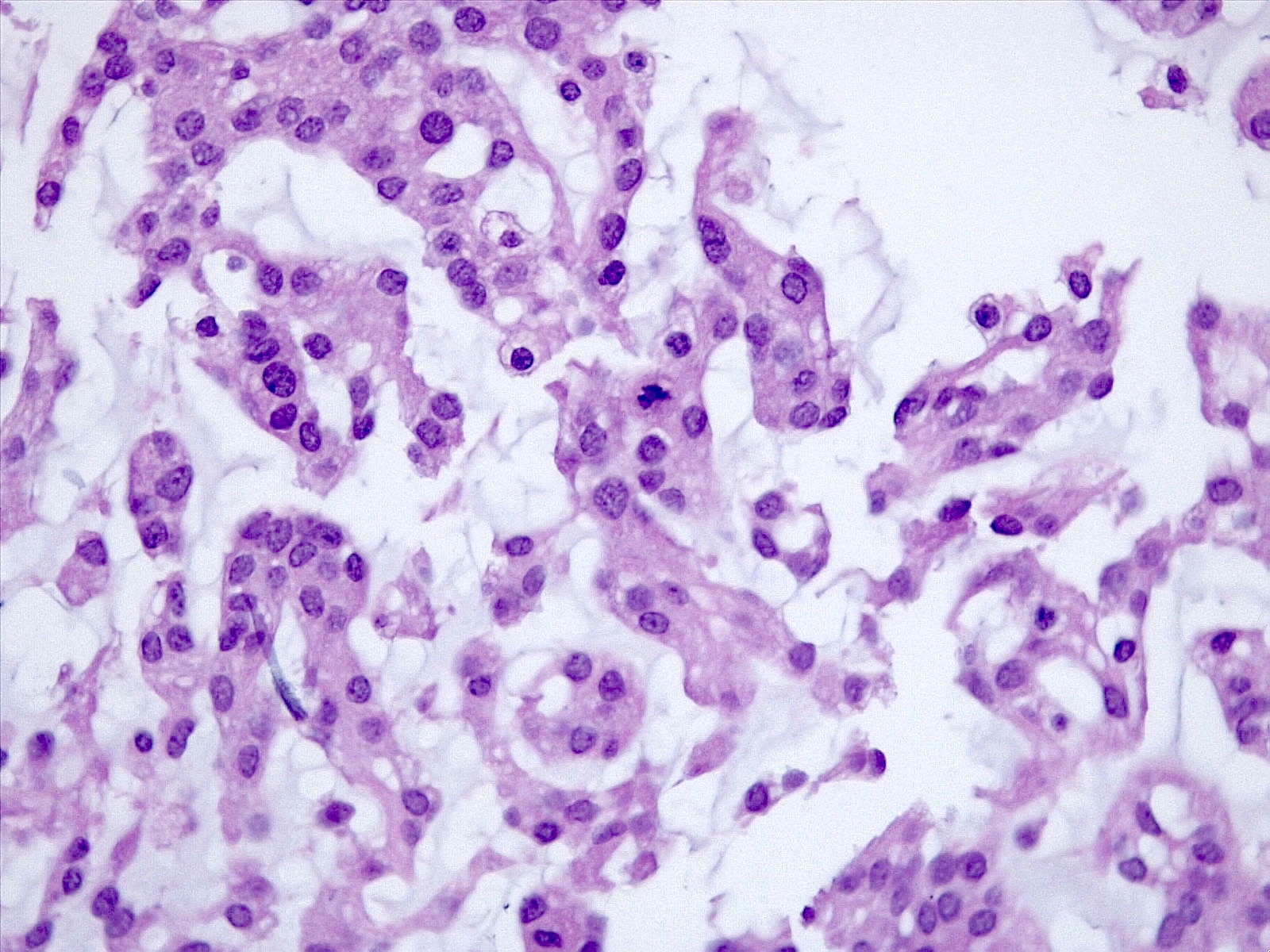
- Histologically reminiscent of chordoma, consisting of epithelioid cells or spindle cells (often partly vacuolated) that are arranged in cords within a pale basophilic myxoid matrix (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:899, J Neurooncol 2010;100:465, Histopathology 2013;62:1002)
- Chordoid morphology must be the predominant pattern for diagnosis of chordoid meningioma and CNS WHO grade 2 designation
- Interspersed areas of more typical meningioma are frequent but pure chordoid cases may be seen (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:899, J Neurooncol 2010;100:465, Histopathology 2013;62:1002)
- Atypical features may be seen, including mitoses, brain invasion, spontaneous necrosis, macronucleoli, increased cellularity, sheeting or small cells with a high N:C ratio (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:899, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:56, Histopathology 2013;62:1002)
- Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate in 59.5% (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:899)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Spindle shaped or epithelioid cells, with frequent intracytoplasmic vacuolization, that are arranged as loosely cohesive groups or have evident cord-like disposition, in a background of extracellular myxoid material (NMC Case Rep J 2020;7:53, Diagn Cytopathol 2016;44:811)
- Presence of meningothelial whorls and intranuclear pseudoinclusions (Diagn Cytopathol 2016;44:811)
Positive stains
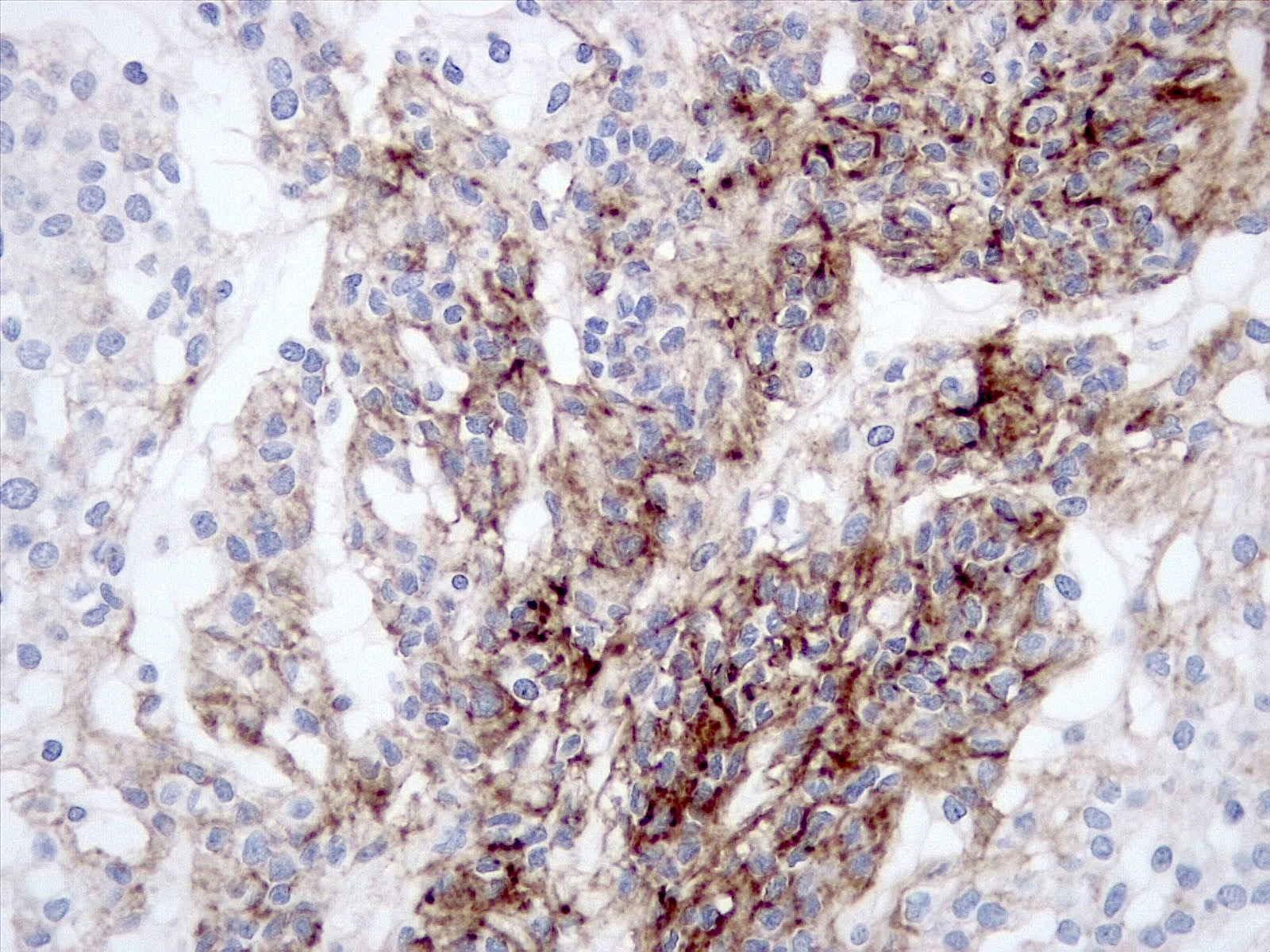
- EMA (92.6%) (World Neurosurg 2016;93:198)
- Progesterone receptor (92.3%) (World Neurosurg 2016;93:198)
- SSTR2A (Neurosurg Rev 2022;45:467)
- Podoplanin (80%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:669)
- Mucoid matrix is red on mucicarmine stain, pink in the PASD reaction and bright blue on Alcian blue stain at pH 2 (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:899)
Negative stains
- S100 (weak extent with average intensity; 40%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:669)
- Pankeratin (weak and patch; 20%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:669)
- Brachyury (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:669)
- CK18 (Pathol Res Pract 2012;208:567)
- CK19 (Pathol Res Pract 2012;208:567)
- CD34 (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:669)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Methylation profile is distinct from that of other meningioma subtypes, at whole genome DNA methylation analysis (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:56, Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:225)
- Frequent mutations in chromatin remodeling genes EP400 (73%), KMT2C (36%) and KMT2D (36%), at next generation sequencing (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:56, Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:225)
- Enrichment in chromosome 2p loss at copy number variation analysis (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:56, Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:225, Acta Neuropathol 2018;136:975)
- Lower frequency of AKT1, SMO, NF2, TRAF7, KLF4, SMO, AKT1 and SMARCB1 mutations compared with nonchordoid meningiomas (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:56)
- 1p, 8p, 10, 14, 22q loss and homozygous deletion of CDKN2A / CDKN2B detected in more aggressive cases (Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:225, Acta Neuropathol 2018;136:975, Neurol India 2018;66:156)
Sample pathology report
- Brain, extra-axial convexity mass:
- Meningioma, subtype chordoid, CNS WHO grade 2 (see comment)
- Comment: Meningothelial neoplasia showing epithelioid cells with vacuolated, eosinophilic cytoplasm or spindle cells, arranged in cords, within a myxoid matrix.
Differential diagnosis
- Chordoma:
- Most commonly arises in the sacrococcygeal region and is usually extradural and bone invasive
- Can be intracranial at the clivus, have secondary invasion of the dura or rarely may be extradural
- Podoplanin negative, brachyury positive and showing extensive staining for CK AE1 / AE3, S100 and EMA
- Chondrosarcoma:
- Chordoid glioma:
- Rare glioma that is typically localized at the third ventricle
- GFAP positive
- Metastatic carcinoma:
- Metastases of carcinomas may be meningeal
- They show extensive cytokeratin staining, while chordoid meningioma features only focal staining for keratins
Board review style question #1
An extra-axial mass is found at the clivus without bone invasion. Histological examination shows a tumor with eosinophilic epithelioid cells in a myxoid stroma and focal areas with a syncytial growth pattern, whorls and nuclear pseudoinclusions. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Chondrosarcoma
- Chordoid meningioma
- Chordoma
- Metastasis of carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
B. Chordoid meningioma. Chondrosarcoma may be meningeal and enter the differential diagnosis with chordoid meningioma. Chordoma is frequently localized at the clivus, though it is usually bone invasive. Even in the absence of immunohistochemistry, the presence of areas with meningothelial classical features (whorls, syncytial growth pattern, nuclear pseudoinclusions) is strongly suggestive of a meningioma.
Comment Here
Reference: Chordoid meningioma
Comment Here
Reference: Chordoid meningioma
Board review style question #2
An extra-axial mass is found in the spine. Histological examination shows a tumor composed of eosinophilic epithelioid cells in a myxoid matrix. At immunohistochemistry, it is EMA+, cytokeratin+ (focally), podoplanin+, S100- and brachyury -. Which is the most likely diagnosis?
- Chondrosarcoma
- Chordoid glioma
- Chordoid meningioma
- Chordoma
Board review style answer #2
C. Chordoid meningioma. Chordoma is EMA+ but also extensively positive for CK AE1 / AE3, S100 and brachyury, while it is negative for podoplanin. Chordoid glioma is localized at the third ventricle and is GFAP+. Chondrosarcoma is S100+ and EMA-.
Comment Here
Reference: Chordoid meningioma
Comment Here
Reference: Chordoid meningioma