Cite this page: Parsons JC. Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/coagulationheparininducedthrombocytopenia.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Common complication of heparin therapy, may cause life threatening venous or arterial thrombosis (Postgrad Med J 2007;83:575)
- Prevent by monitoring platelet count for at least 20 days after initiation of heparin therapy
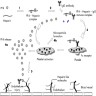
- Caused by formation of antibodies against heparin and platelet factor 4 complex
- Testing: ELISA assay screen followed by serotonin release assay for conformation
- Use 4T score (Online 4T Score Calculator) to evaluate pre-test probability of HIT
Clinical features
- Clinical note: platelet counts often fall slightly during the first 24 hours of heparin treatment, unrelated to heparin induced thrombocytopenia
Treatment
- Permanently discontinue heparin, avoid platelet transfusions
- Recommended to not use low molecular weight heparin (may cross react) or warfarin (may cause venous limb gangrene)
- Instead use danaparoid, hirudin or argatroban