Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Parsons DW, Hagen CE. Diversion colitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colondiversion.html. Accessed October 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Inflammatory condition that affects colon distal to an ileostomy or colostomy
- It can also occur in sigmoid segments used in colovaginoplasty procedures
Essential features
- Clinicopathologic condition often arising in colonic segments distal to an ileostomy or colostomy site; it may also occur in colonic pouches, such as those following colovaginoplasty
- Creation of an ostomy site alters the normal flow of fecal material through the bowel and thereby alters the microbiome of the gut resulting in alteration of the nutrients available for colonic enterocytes
- Patients may present with nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort and bloody bowel movements
- Histologic features may include lymphoid aggregates with germinal centers, muscularis mucosa hypertrophy, acute inflammation, architectural changes and ulceration
- When it occurs in patients with underlying inflammatory bowel disease, histologic distinction can be challenging
Terminology
- Defunctionalized bowel
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Generally reported that no significant associations exist between diversion colitis and age of onset, gender, stoma type or mode of surgery (Int J Colorectal Dis 2017;32:1191)
- However, Tominaga et al. reported a slight predominance in men (World J Gastroenterol 2018;24:1734)
- Greatest association with diversion colitis is simply the surgical interruption of the normal flow of fecal material through the bowel
Sites
- Colonic segments distal to colostomy or ileostomy, as well as segments of colon repurposed for use outside of the alimentary canal
Pathophysiology
- Pathophysiology of diversion colitis is thought to be multifactorial
- Disruption in the normal flow of fecal material may lead to changes in the microbiota
- In a normal healthy colon, luminal bacteria produce short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as acetate, propionate and butyrate, with butyrate likely being the most important of the 3 (Nutr Rev 1989;47:257)
- These SCFAs have been demonstrated to be important nutrients for colonic enterocytes
- SCFAs may also play a role in vascular smooth muscle relaxation
- Thus, deficiencies in SCFAs may lead to nutritional deficiencies for colonic enterocytes and increased arterial tone (World J Gastroenterol 2018;24:1734)
- It has also been hypothesized that patients with diversion colitis may have an increased population of nitrate reducing bacteria and thus higher levels of nitric oxide (NO); while lower levels of nitric oxide appear to play a protective role for the bowel, it has been hypothesized that an excess of nitric oxide may be toxic to colonic tissue (World J Gastroenterol 2018;24:1734)
Etiology
- Construction of ileostomy or colostomy are common causes for diversion colitis; for instance, this may occur following a Hartmann procedure (proctosigmoidectomy with creation of end colostomy) for management of colorectal cancer, severe diverticulitis or for treatment of refractory fecal incontinence (J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs 2008;35:231)
- Diversion colitis has also been reported in patients who underwent sigmoid neovaginal surgery for aplasia vaginae secondary to Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome (Müllerian agenesis), as well as those pursuing gender reassignment surgery (Frontline Gastroenterol 2016;7:227)
Clinical features
- Clinical features are highly variable but presentation may include
- Abdominal pain
- Tenesmus
- Anal and rectal pain
- Mucous discharge
- Rectal bleeding
- Some patients may present with endoscopic or histologic findings but may remain asymptomatic
- When evaluating clinical features, it is important to contextualize those signs and symptoms within the appropriate setting; for instance, the above features should raise suspicion for diversion colitis in patients with ileostomies, with some research to suggest that symptoms can arise from months to years after ileostomy construction (World J Gastroenterol 2018;24:1734)
Diagnosis
- Standardized diagnostic criteria have not been codified; thus, diagnosis must be suspected clinically and supported with imaging and histologic evaluation
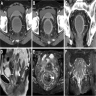
Radiology description
- Findings are largely nonspecific
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans will demonstrate findings consistent with intestinal discontinuity, such as an ileostomy, colostomy or a colonic pouch
- Affected colonic segments may show fat stranding, wall thickening and fluid distension
- Target or water halo sign may be present, which is suggestive of inflamed colonic mucosa and edematous submucosa
- Reference: Insights Imaging 2019;10:41
Prognostic factors
- Protracted ostomy reliance generally portends a worse prognosis; additionally, inflammatory states, such as infection or underlying bowel disease, are thought to either precipitate, exacerbate or otherwise contribute to diversion colitis (BMJ Case Rep 2021;14:e243284)
Case reports
- 12 year old girl with myelomeningocoele with fecal incontinence managed with colostomy construction and subsequent resection of distal defunctionalized bowel (Histopathology 1994;24:395)
- 19 year old woman with Berdon syndome (megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome [MMIHS]) diagnosed with diversion colitis after ileostomy construction (Dig Dis Sci 2009;54:2338)
- 42 year old woman with androgen insensitivity syndrome with diversion colitis of sigmoid neovagina (Frontline Gastroenterol 2016;7:227)
- 51 year old woman with Crohn's disease and microcarcinoids in association with diversion colitis symptoms presenting more than 17 years after subtotal colectomy and ileostomy (J Crohns Colitis 2008;2:246)
Treatment
- Surgical management with reestablishment of intestinal continuity and stomal closure is generally regarded as the preferred and most successful treatment
- Medical management may be pursued in place of surgical intervention in patients who are not surgical candidates, at risk for anastomotic leakage or those with severe active bowel inflammation (BMJ Case Rep 2021;14:e243284, World J Gastroenterol 2018;24:1734)
- Medical management varies and may include
- Short chain fatty acid (SCFA) enemas
- 5-aminosalicylic acid
- Corticosteroids
- Irrigation with fibers
- Leukocytapheresis
- Autologous fecal transplant
- Dextrose spray
- TNFα inhibitors, such as infliximab
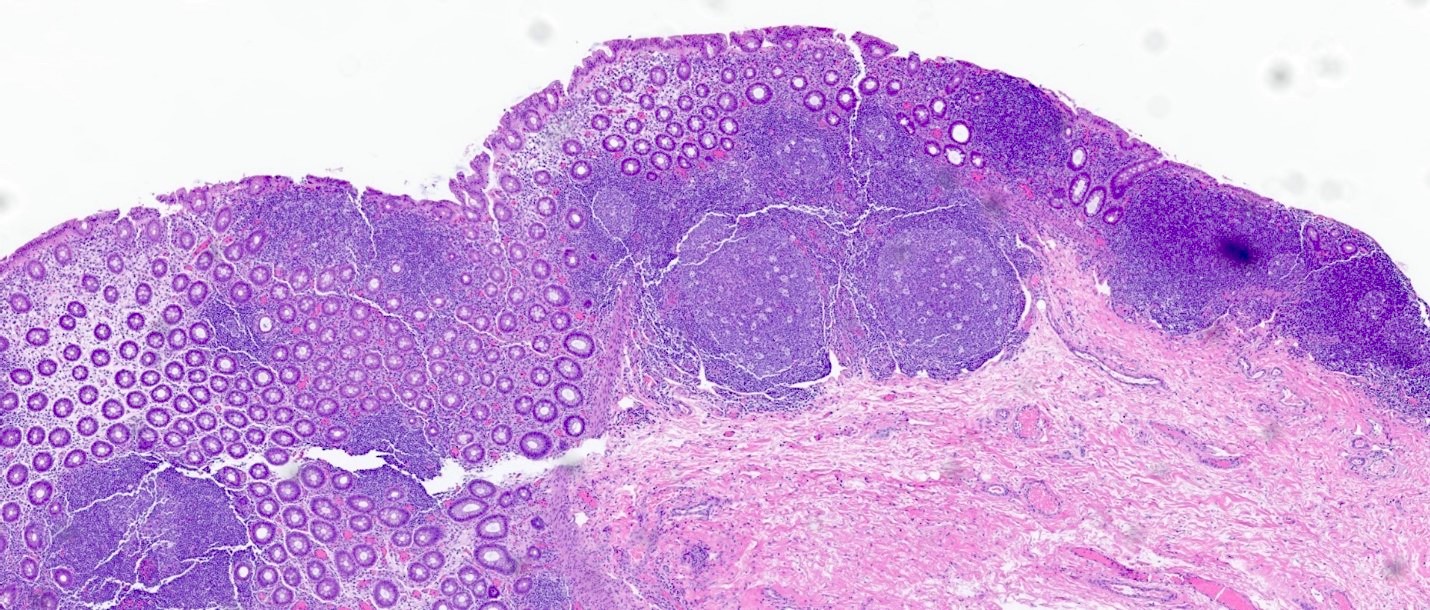
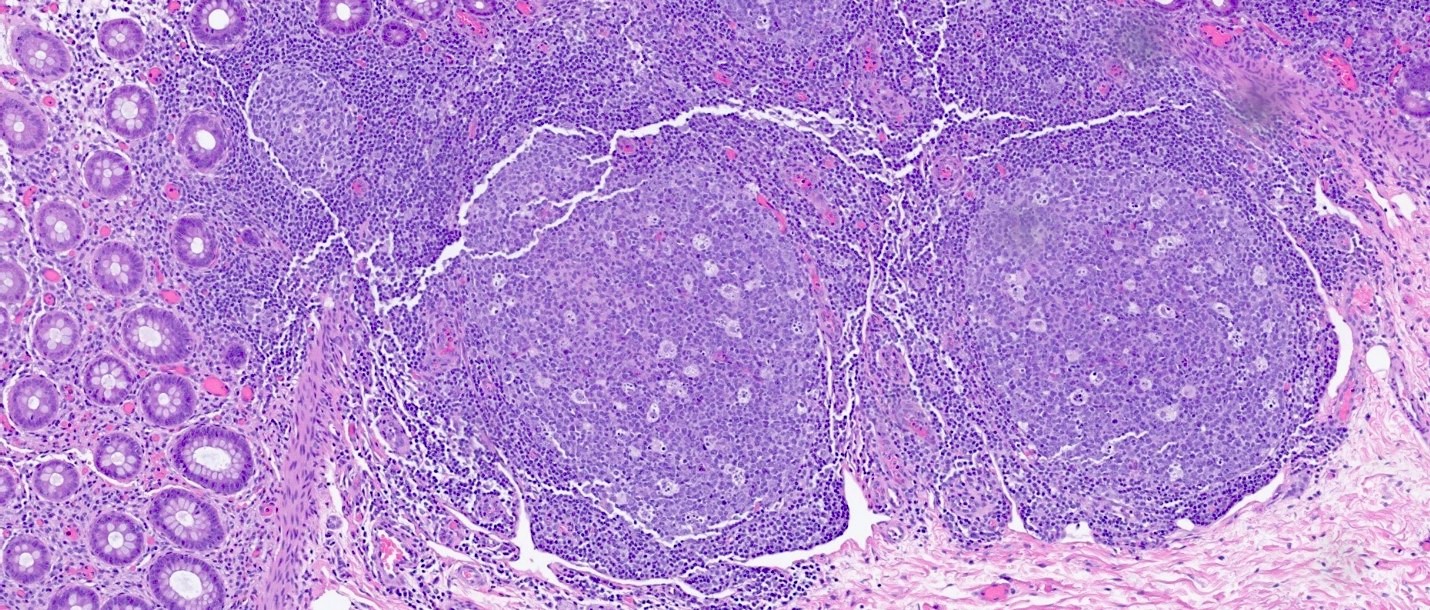
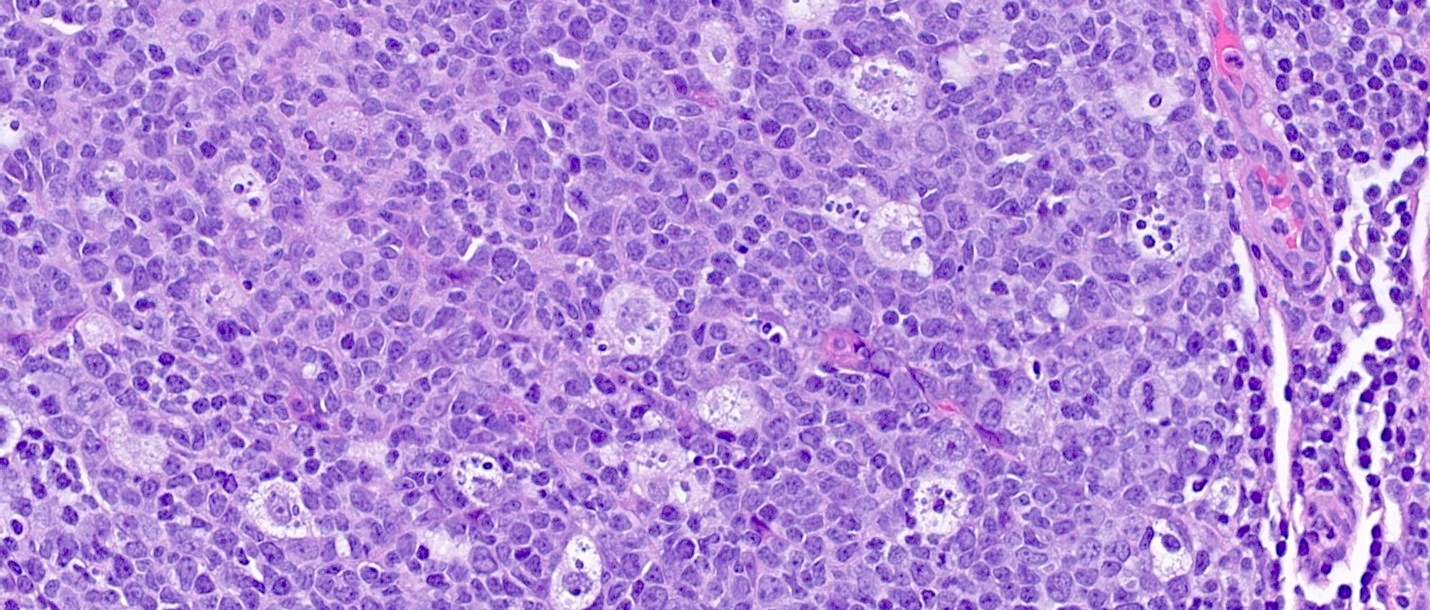
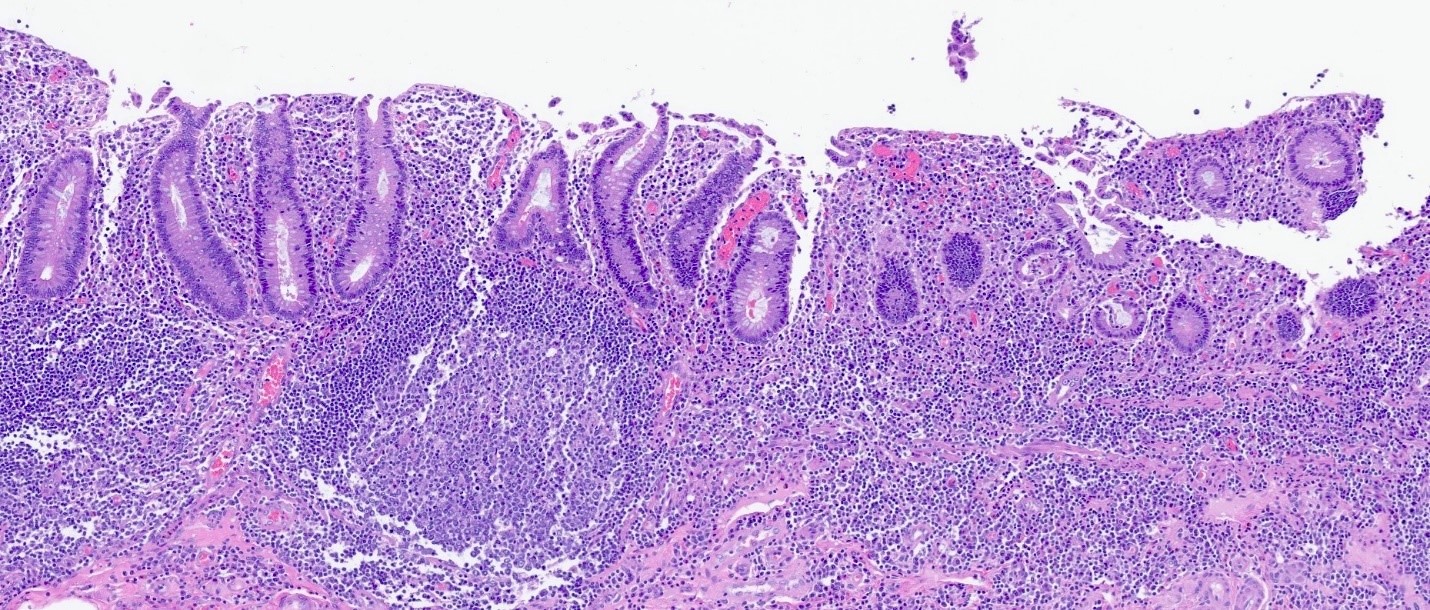
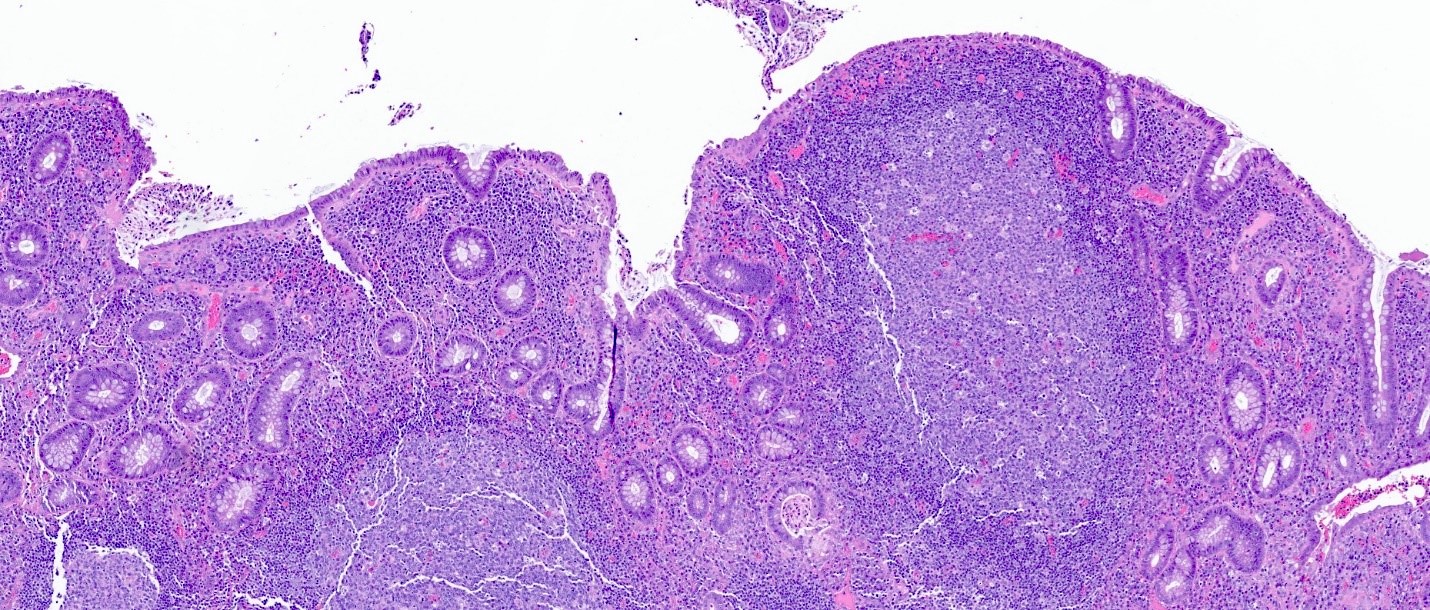
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Lymphoid follicular hyperplasia with germinal centers
- Muscularis mucosa hypertrophy, which is often patchy
- Architectural changes with distortion of crypts, crypt branching and loss of crypts
- Degenerative mucosal surface epithelium with cell exfoliation and pyknotic nuclei
- Loss of goblet cells and mucin
- Mucosal ulceration with granulation tissue
- Varying degrees of inflammation, with features of both activity (neutrophil predominant) and chronicity (lymphoplasmacytic)
- Focal edema
- Pseudopolyps
- Paneth cell metaplasia
- References: Hum Pathol 2022;123:31, World J Gastroenterol 2018;24:1734, Histopathology 1991;19:55
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Rectum, stump, biopsy:
- Diversion colitis (see comment)
- Comment: Colonic mucosa with prominent lymphoid aggregates and mild architectural changes compatible with diversion colitis.
Differential diagnosis
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease):
- Histologic distinction can be challenging and diversion colitis can co-occur with IBD
- More severe inflammatory changes may indicate superimposed IBD (Hum Pathol 2022;123:31)
- Segmental colitis associated with diverticulosis (SCAD):
- Occurs in segment of colon with diverticula and rectum is typically spared
- Radiation colitis:
- Occurs in patients with history of radiation therapy for malignancy (e.g., of prostate, colon, bladder)
- Acute radiation may demonstrate a number of histologic findings, including nuclear atypia, reduction in mitotic counts, eosinophilic inflammation (including eosinophilic cryptitis and crypt abscess formation), goblet cell derangements and fibroblastic proliferation
- Chronic exposure may result in Paneth cell metaplasia, architectural distortion, fibrosis of lamina propria, chronic inflammation, hyalinized vasculature, vascular ectasia and thrombosis
Practice question #1
A 5 month old infant is seen in the emergency department with bloody bowel movements. She appears uncomfortable and begins crying with abdominal palpation. She is afebrile and her white blood cell count is within normal limits. Medical history is significant for premature birth complicated by necrotizing enterocolitis with bowel resection and ileostomy construction. A biopsy of the colonic stump is likely to demonstrate which of the following findings?
- Crypt abscesses, Paneth cell metaplasia, marked architectural distortion, basal lymphoplasmacytosis
- Endothelial cells demonstrating owl eye intranuclear inclusions with associated clear halo
- Intraepithelial lymphocytosis
- Prominent lymphoid hyperplasia, muscularis mucosa hypertrophy and crypt abscesses
Practice answer #1
D. Prominent lymphoid hyperplasia, muscularis mucosa hypertrophy and crypt abscesses. These findings are characteristic of diversion colitis. The patient’s history of bowel resection with ileostomy should raise suspicion for diversion colitis. Answer A is incorrect because these findings are more demonstrative of ulcerative colitis. It can be difficult to separate out the 2 conditions and reports in the literature exist of concomitant ulcerative colitis and diversion colitis. With overlapping symptoms and the potential for finding crypt abscesses in both conditions, it can certainly pose a diagnostic challenge for pathologists trying to differentiate the 2 conditions on biopsy. The patient’s history of ileostomy construction should be a clue that diversion colitis may be favored here. Without a pre-existing diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), this is unlikely. Answer B is incorrect because the characteristic owl eye inclusions are consistent with cytomegalovirus (CMV) colitis. This consideration of this condition may be greater in patients with a history of immunosuppresion; for instance, in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or those receiving immunosuppressive therapy following solid organ transplant. Answer C is incorrect because intraepithelial lymphocytosis is characteristic of lymphocytic colitis, which typically presents with watery, nonbloody diarrhea. Microscopic colitis is uncommon in the pediatric population.
Comment Here
Reference: Diversion colitis
Comment Here
Reference: Diversion colitis
Practice question #2
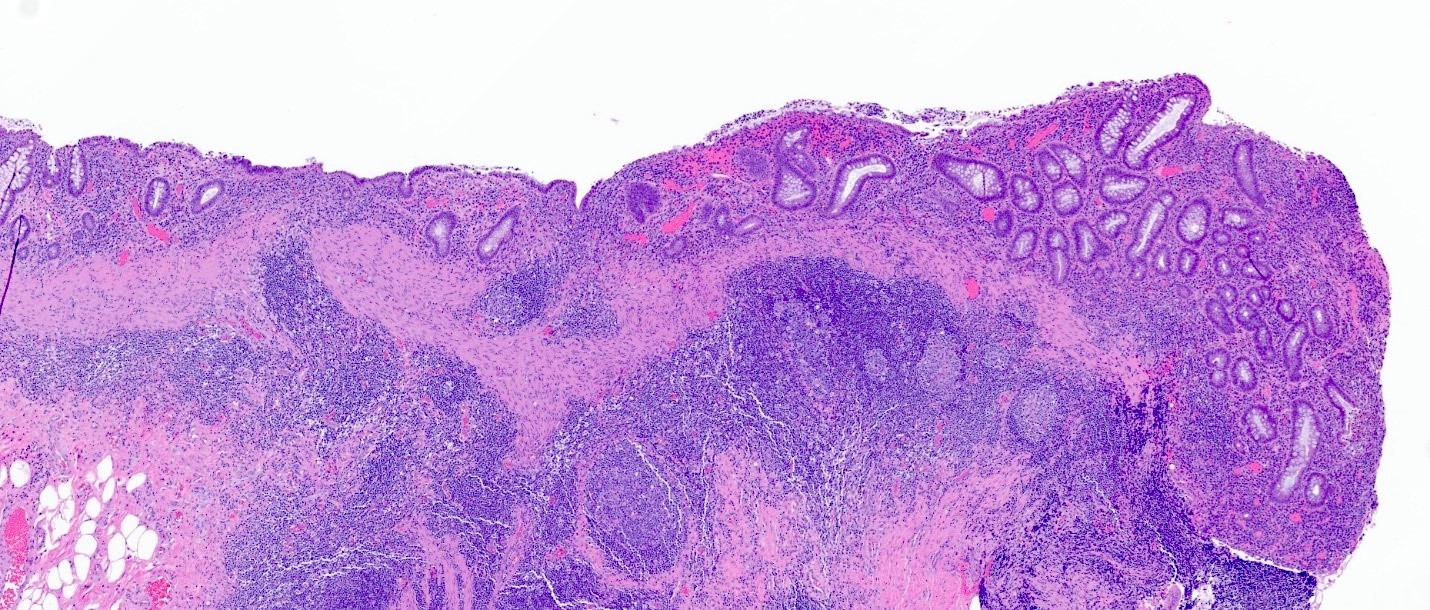
A 72 year old man with a history of colon cancer undergoes radiation therapy, followed by partial colon resection with construction of an ileostomy. He denies any history of inflammatory bowel disease. The image shown above demonstrates histologic findings of the resected portion of the colon. These findings are most consistent with which clinical presentation?
- Diversion colitis
- Infectious agent
- Radiation colitis
- Ulcerative colitis
Practice answer #2
A. Diversion colitis. The construction of an ileostomy should always raise suspicion for the possibility of diversion colitis. The prominent lymphoid aggregates are likely the most characteristic finding associated with diversion colitis. Other features appreciated here include patchy hypertrophy of muscularis mucosa, ulceration and loss of colonic crypts. Answer B is incorrect because the clinical vignette does not suggest any fevers or bowel symptoms consistent with an infectious etiology. Infectious colitis typically shows a histologic pattern of acute self limited colitis without architectural distortion. Answer C is incorrect because the presence of lymphoid aggregates should favor diversion colitis over radiation colitis. Radiation colitis is typically pauci-inflammatory with evidence of lamina propria fibrosis and hyalinized ectatic vessels. Answer D is incorrect because while diversion colitis can have overlapping histologic features with inflammatory bowel disease, given that the patient denies any history of underlying inflammatory bowel disease, this is unlikely to be a manifestation of ulcerative colitis.
Comment Here
Reference: Diversion colitis
Comment Here
Reference: Diversion colitis