Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Sites | Clinical features | Radiology images | Case reports | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumorimt.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Low grade mesenchymal neoplasm that can arise in the colonic wall or mesentery, usually of children
- See also topic in Soft tissue chapter
Essential features
- Mesenchymal neoplasm, often pediatric, with spindled cells admixed with inflammation
- t(2;5) (TPM3-ALK) translocation
- Rare aggressive variant called epithelioid inflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma
Terminology
- Older terms include called inflammatory pseudotumor, inflammatory fibrosarcoma and plasma cell granuloma
- Epithelioid inflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma refers to a rare, aggressive variant with unique morphologic and molecular features (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:135)
Sites
- Can arise in the colonic wall or the mesentery
- Most common site in gastrointestinal tract is stomach
Clinical features
- Patients usually in the pediatric age range (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:509)
- Symptoms include anemia, abdominal pain, fever, weight loss and high sedimentation rate (J Pediatr Surg 2001;36:169)
- May recur but metastases rare; these outcomes may be more common in epithelioid inflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma
Case reports
- 11 year old boy with rectal tumor (Arch Iran Med 2006;9:277)
- 35 year old woman with clinical appendicitis, cecal tumor (Scott Med J 2004;49:157)
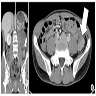
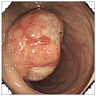
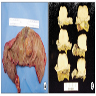
Gross description
- Circumscribed, often polypoid
Gross images
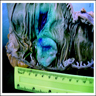
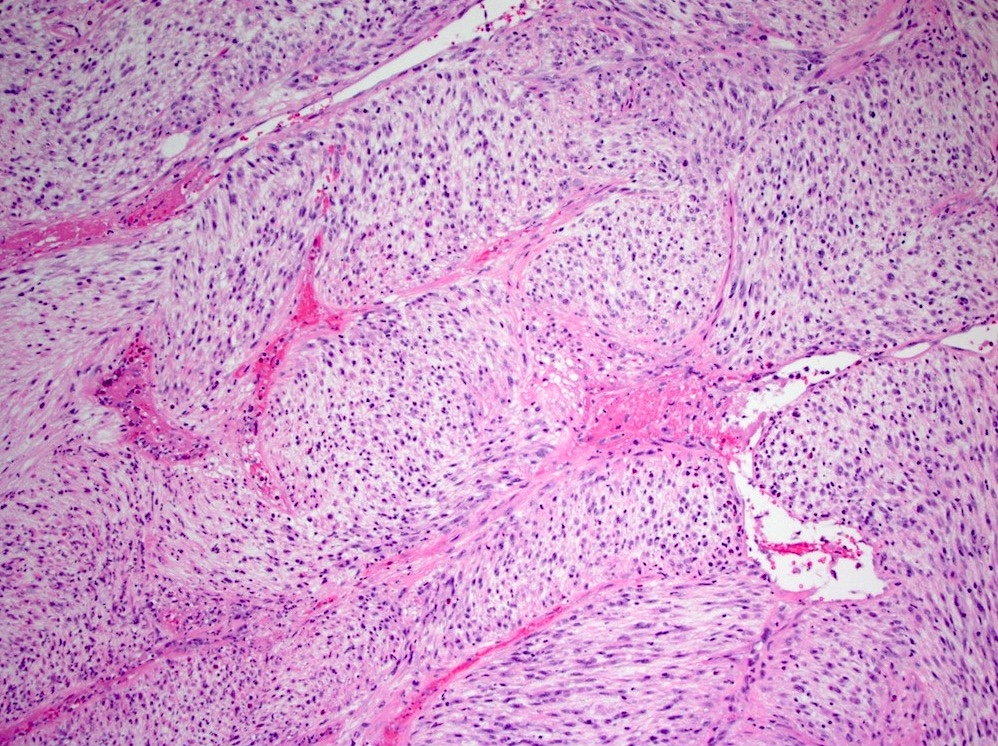
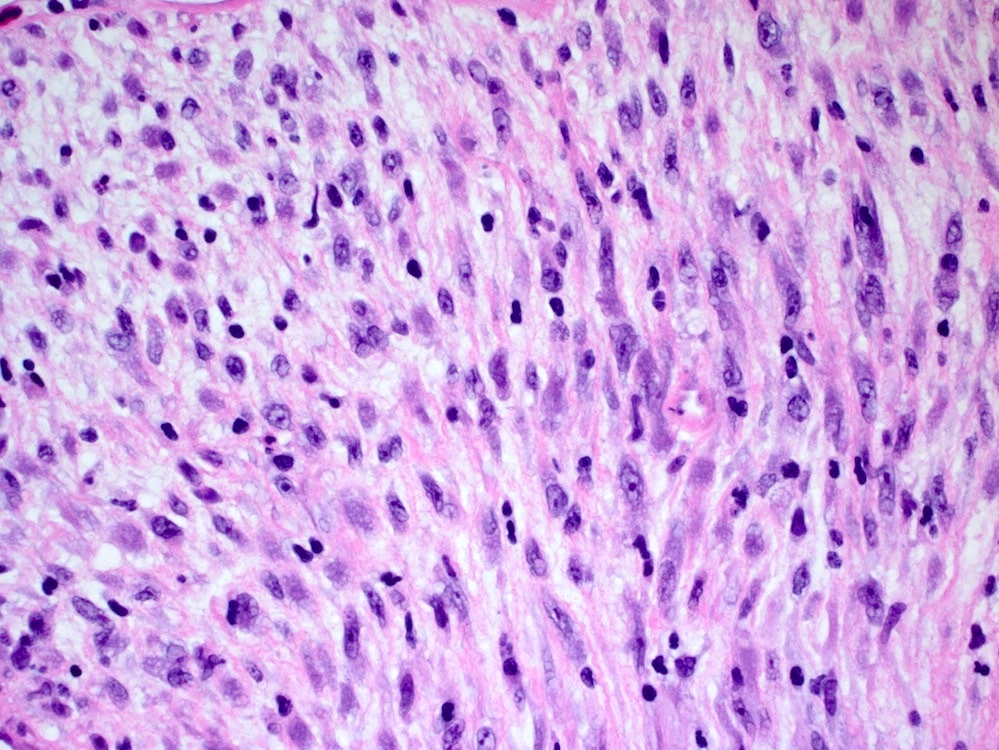
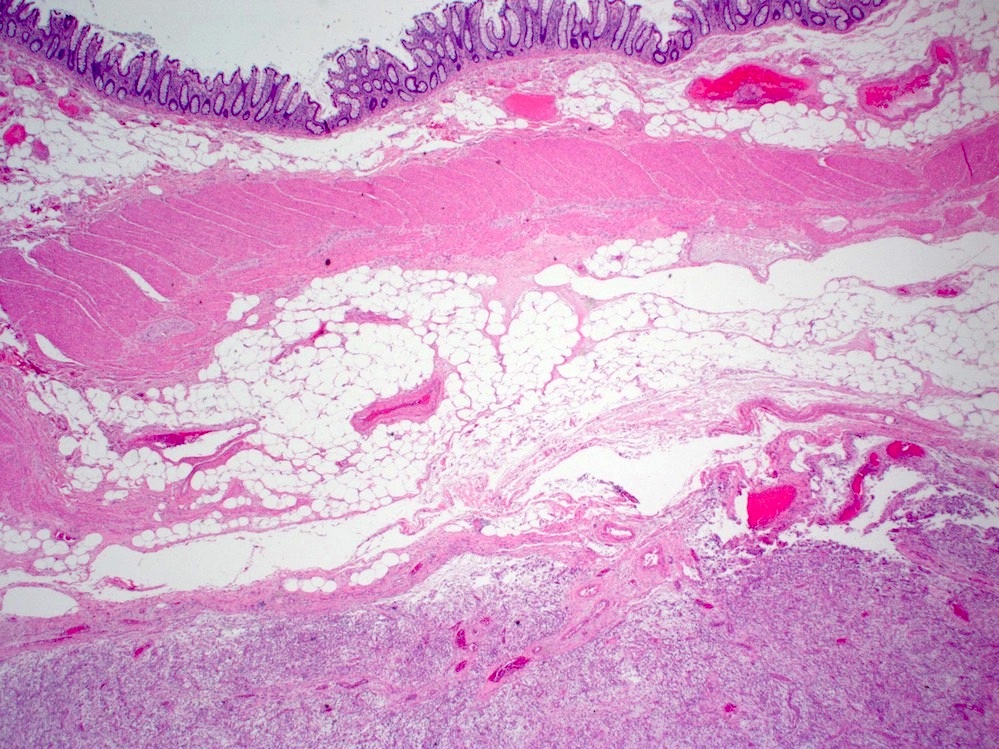
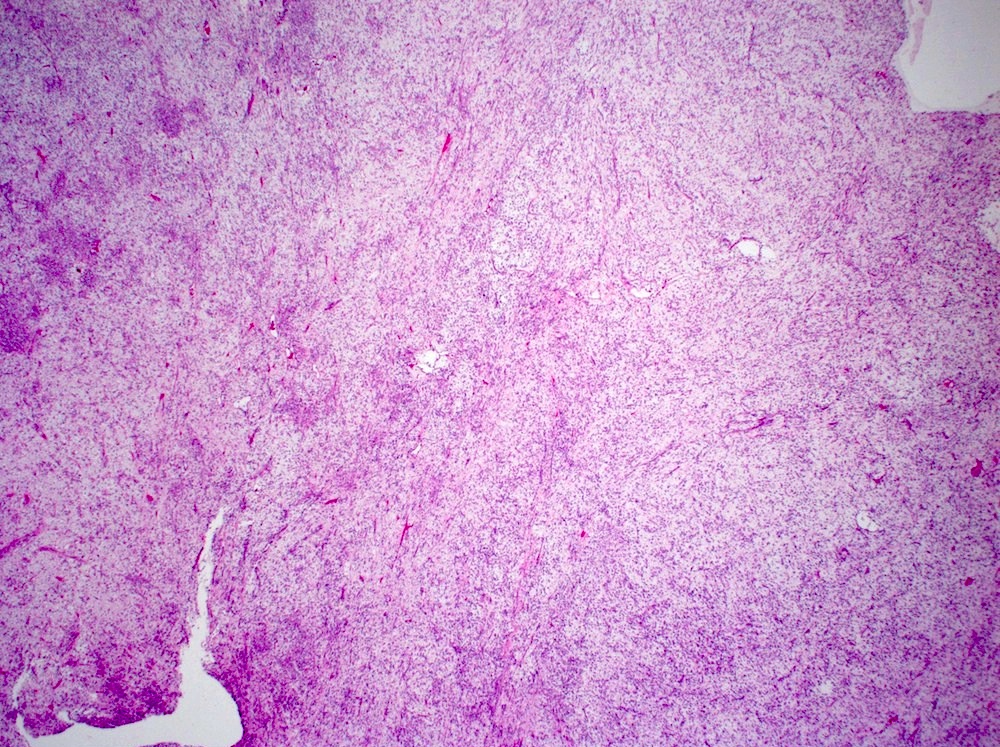
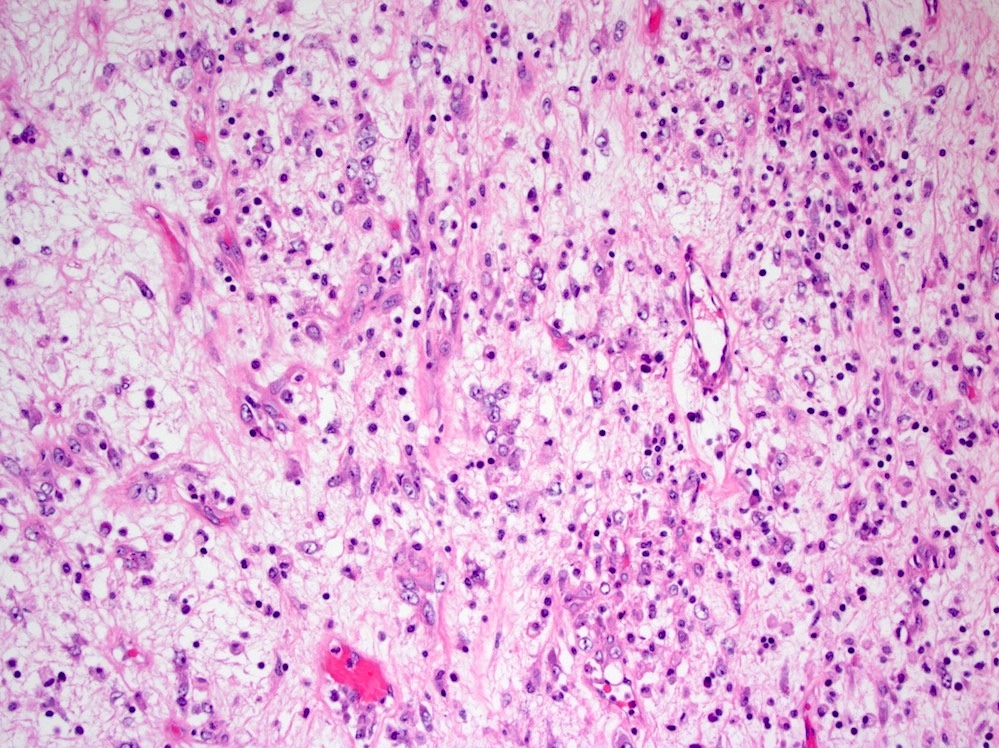
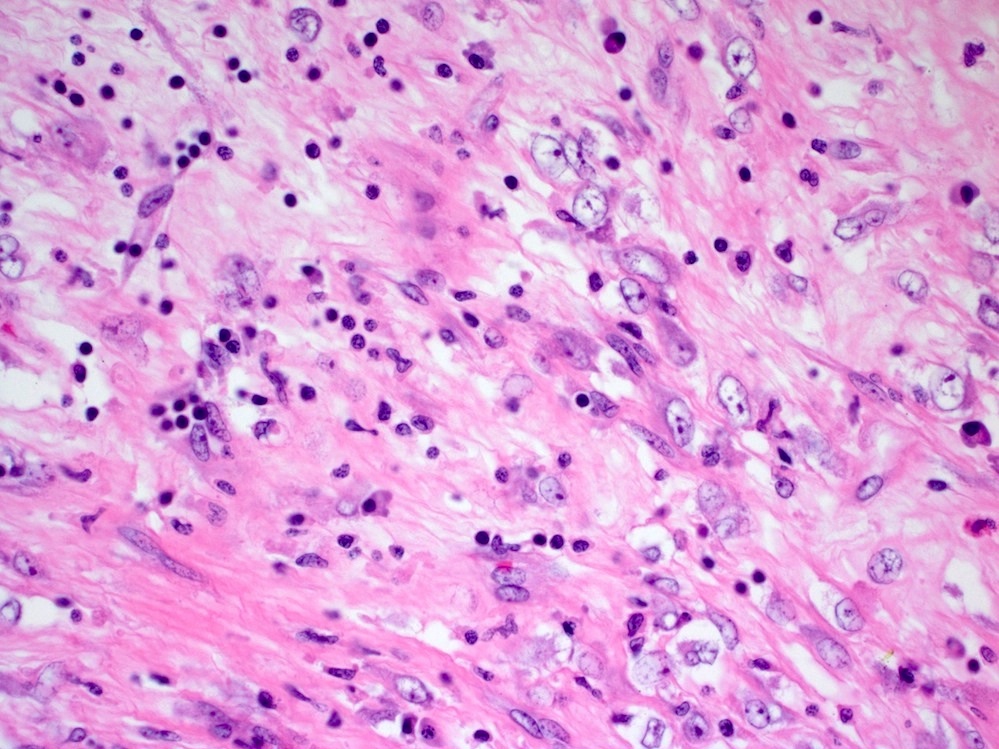
Microscopic (histologic) description
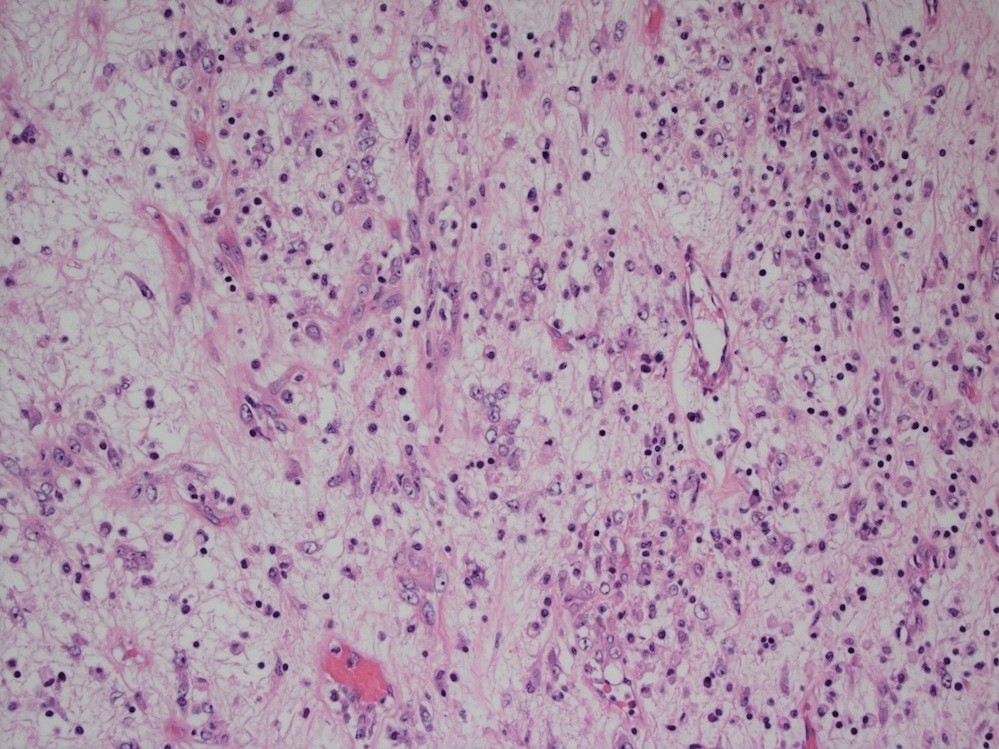
- Bland spindle cells with abundant amphophilic cytoplasm and variably prominent nucleoli
- Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with polyclonal plasma cells
- Background may show myxoid change or laminated / whorled fibrosis
- Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: similar, except cells are more epithelioid, with large nucleoli
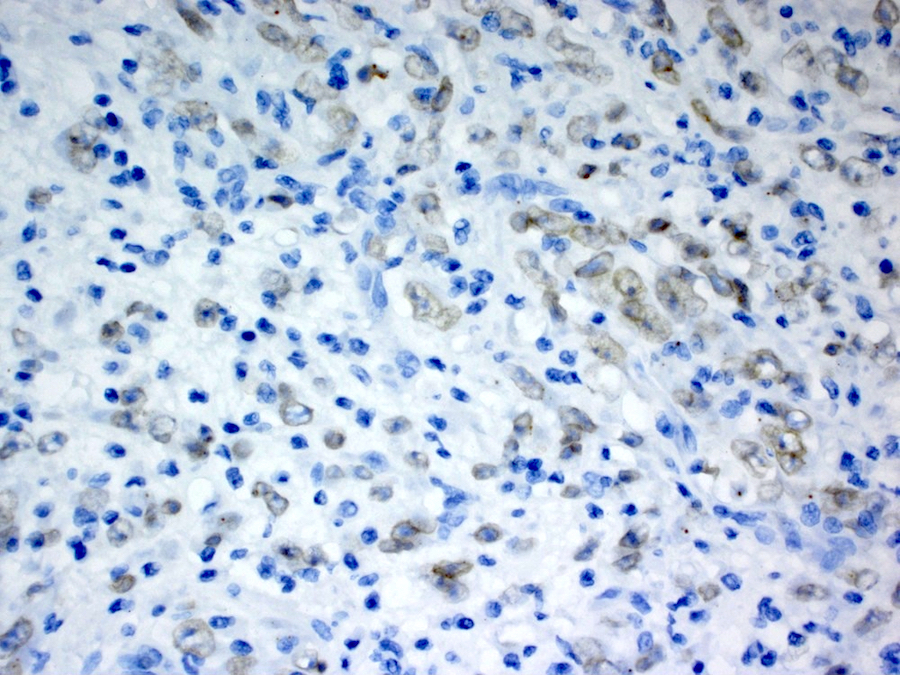
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Raul S. Gonzalez, M.D.
Contributed by Michael Feely, D.O.
Images hosted on other servers:
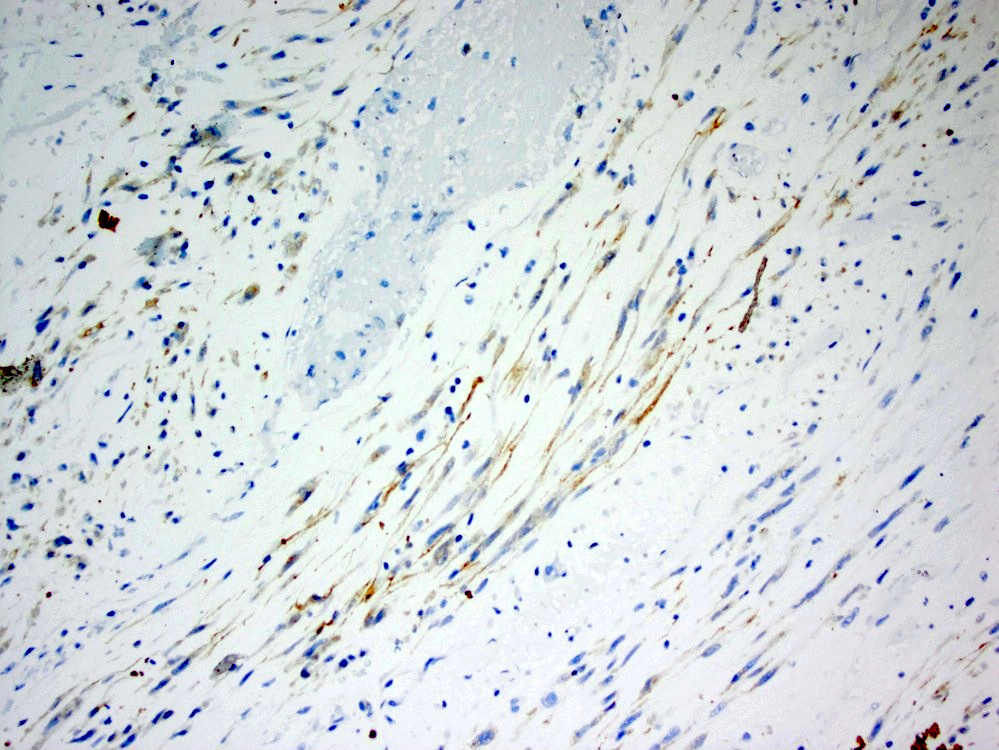
Positive stains
- Desmin, smooth muscle actin; variable cytoplasmic ALK1 (Mod Pathol 2002;15:931)
- Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: nuclear membrane ALK1
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Abnormalities of 2p23, usually t(2;5) (TPM3-ALK) translocation, in approximately half of cases; more common in children (Mod Pathol 2001;14:569)
- Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: t(2;2) RANBP2-ALK translocation
Sample pathology report
- Ascending colon, resection:
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (3.1 cm) (see comment)
- Margins of resection unremarkable.
- Two benign lymph nodes.
- Comment: An immunostain for ALK1 is positive in the tumor.
Differential diagnosis
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp:
- Patients older, tumors smaller with more eosinophils and CD34 positivity (Hum Pathol 2002;33:307)
- Fibromatosis:
- Nuclear positivity for beta catenin
- Schistosomiasis:
- May rarely form inflammatory pseuotumorous reaction (J Natl Med Assoc 2006;98:1365)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A young male patient presents with abdominal pain. Imaging reveals a large mesenteric mass, which is resected. An image of the tumor’s histology is seen above. Immunohistochemistry shows ALK1 staining of the nuclear membranes. What molecular abnormality is present in this tumor?
- ALK1 deletion
- ALK1 inversion
- t(2;2) RANBP2-ALK translocation
- t(2;5) TPM3-ALK translocation
Board review style answer #1
C. t(2;2) RANBP2-ALK translocation. This is an epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor