Table of Contents
Definition / general | Bronchogenic cysts | Duplication cysts | Inclusion cysts | Retention cystsCite this page: Weisenberg E. Esophageal cysts. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/esophaguscysts.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare; mostly developmental unless due to cystic degeneration of tumor
- Simple cysts are epithelial lined; duplication cysts have 2 muscle layers (eMedicine: Esophageal Cysts [Accessed 14 February 2019], Arch Pathol Lab Med 1977;101:136)
- Either intramural or attached to outer layers of esophagus
- Often asymptomatic, even if large; may cause obstructive symptoms
- See Retention cysts
Bronchogenic cysts
Definition / general
Case reports
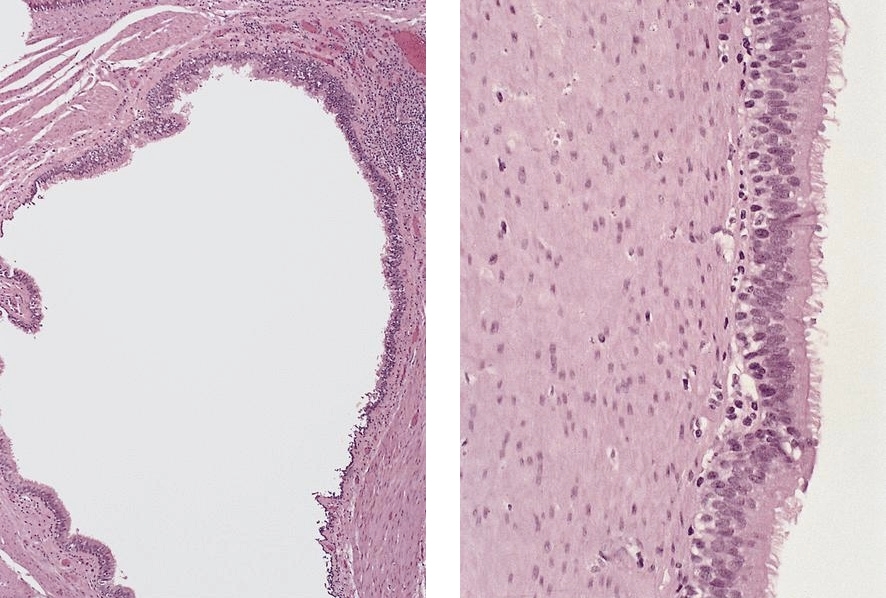
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images:
- Often young women with dysphagia or chest pain during exercise (Clin Imaging 2006;30:309)
- Developmental cysts arise from anomalous budding of foregut bronchial structures; contains cartilage and mucus glands, smooth muscle and ciliated columnar epithelium
Case reports
- 26 year old man with cystic lesion at lower esophagus (Dig Surg 2006;23:209)
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images:
Duplication cysts
Definition / general
Case reports
Treatment
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
- Also called gastroenteric cyst, foregut cyst
- Congenital anomaly, usually lower esophagus
- Most are intramural; usually isolated anomaly; however, duplications external to esophageal wall may be associated with vertebral anomalies
- 90% do not communicate with esophagus
- Usually symptomatic causing dysphagia or respiratory difficulty
Case reports
- 22 day old boy (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2006;49:396)
- 2 infants with respiratory distress (Pediatr Emerg Care 2005;21:854)
- 14 year old boy with fistula to lung (Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2000;18:117)
- 52 year old woman (Yonsei Med J 2005;46:859)
- 61 year old woman with squamous cell carcinoma (Br J Radiol 2003;76:343)
Treatment
- Surgery (if symptoms) or possibly observation (Endoscopy 2005;37:870)
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Mucosa, submucosa and muscular layers similar to GI tract; lined by either esophageal squamous, gastric, primitive, ciliated columnar or small intestinal epithelium
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Inclusion cysts
Definition / general
- Lined by squamocolumnar epithelium, may be ciliated
Retention cysts
Definition / general
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Also called mucocele
- Derive from obstructed submucosal gland ducts
- Small, usually in lower esophagus
- May cause intramural pseudodiverticulosis, with multiple flask-like invaginations into esophageal wall (Am J Clin Pathol 1976;65:314)
- Associated with chronic esophagitis and fibrosis; also surgically isolated segments of esophagus (Dis Esophagus 2002;15:96)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Saccular or flask shaped dilation of submucosal gland excretory ducts; rarely reaches muscularis propria
- In large lesions, muscularis does not accompany the lesion so are not true diverticula