Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Grading | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Bhaijee F, Akhtar I. Neuroendocrine carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/esophagusneuroendocrine.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Epithelial neoplasm with prominent neuroendocrine differentiation
- Pathologic spectrum from low grade neuroendocrine tumors (carcinoid, atypical carcinoid) to high grade neuroendocrine carcinoma (small cell or large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma)
Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma:
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma is analogous to pulmonary small cell carcinoma
- WHO definition
- Malignant epithelial tumor consisting or small cells with scant cytoplasm, ill defined cell borders, finely granular nuclear chromatin and absent or inconspicuous nucleoi
- Cells are round, oval and spindle shaped
- Nuclear molding is prominent
- Necrosis is typically extensive and the mitotic count is high
Terminology
- Synonyms
- Neuroendocrine tumor (low grade) = carcinoid tumor, atypical carcinoid tumor
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma (high grade) = small cell carcinoma, large cell carcinoma
Epidemiology
- Extremely rare in esophagus: about 100 reported cases (mostly high grade / small cell carcinomas)
- M:F ratio = 3:1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:467)
- Mean age: 62 years
Sites
- Middle or lower esophagus (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:467, Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:485)
Clinical features
- Usually incidental / unexpected finding on radiologic studies or upper GI endoscopy
- Dysphagia, weight loss, chest pain with high grade carcinoma (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:485)
- Typically diagnosed via biopsy or (less commonly) surgical resection
Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma:
- Very aggressive (Dis Esophagus 2014;27:152, Hepatogastroenterology 2005;52:1738)
- Median survival 18 months (BMC Cancer 2007;7:38)
- 5 year survival 8% or less (Chin Med J (Engl) 2007;120:355, Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:4239, Hum Pathol 1999;30:216)
Grading
- Grade 1: < 2 mitoses/10 HPF or < 2% Ki67 index
- Grade 2: 2 - 20 mitoses/10 HPF or 3 - 20% Ki67 index
- Grade 3: > 20 mitoses/10 HPF or > 20% Ki67 index (UpToDate: Classification of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms GI Tract [Accessed 27 February 2019], Pancreas 2010;39:707)
Prognostic factors
- Mitotic rate and Ki67 index determine grade
- Low grade lesions have favorable prognosis
- High grade carcinomas are very aggressive, as in other body sites
Case reports
- 51 year old man with collision tumor between papillary adenocarcinoma and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:411)
- 54 year old man with atypical carcinoid of the esophagus (Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2002;8:302)
Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma:
- 63 year old woman with coexisting paraneoplastic neurological syndrome (Jpn J Clin Oncol 2006;36:109)
- 66 year old man with rare collision tumor of squamous carcinoma and small cell carcinoma in esophagus in separate lymph nodes (J Thorac Dis 2013;5:E203)
- 79 year old man (BMJ Case Rep 2013 Sep 3;2013)
Treatment
- Surgical resection
- Chemoradiation for high grade carcinoma (Rare Tumors 2013;5:e6)
Gross description
- Polypoid or ulcerated mass on upper endoscopy
Gross images
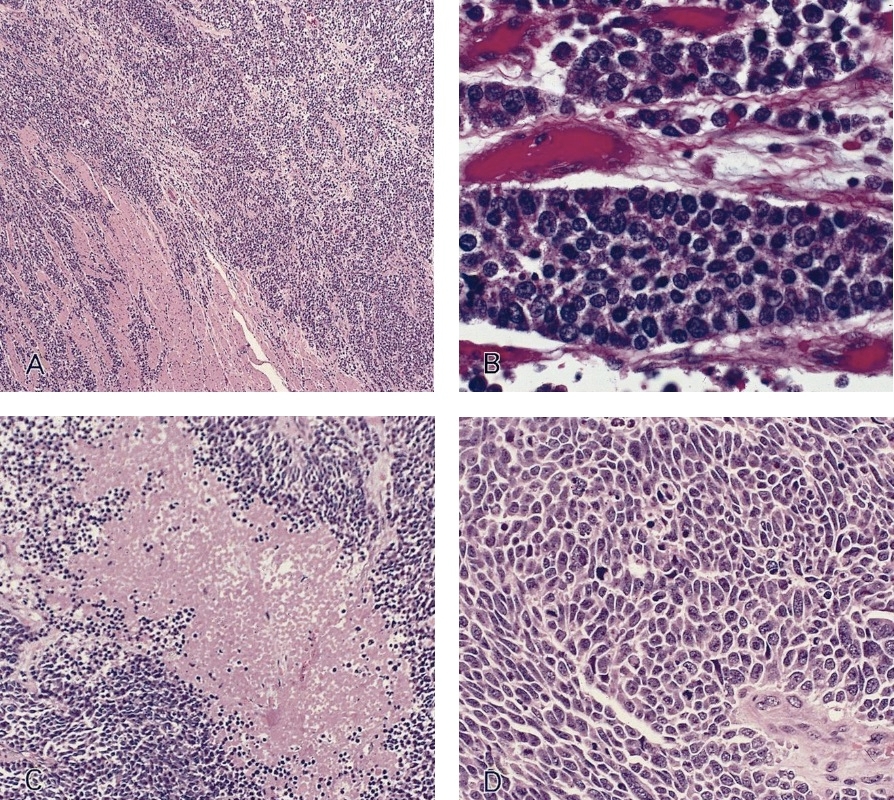
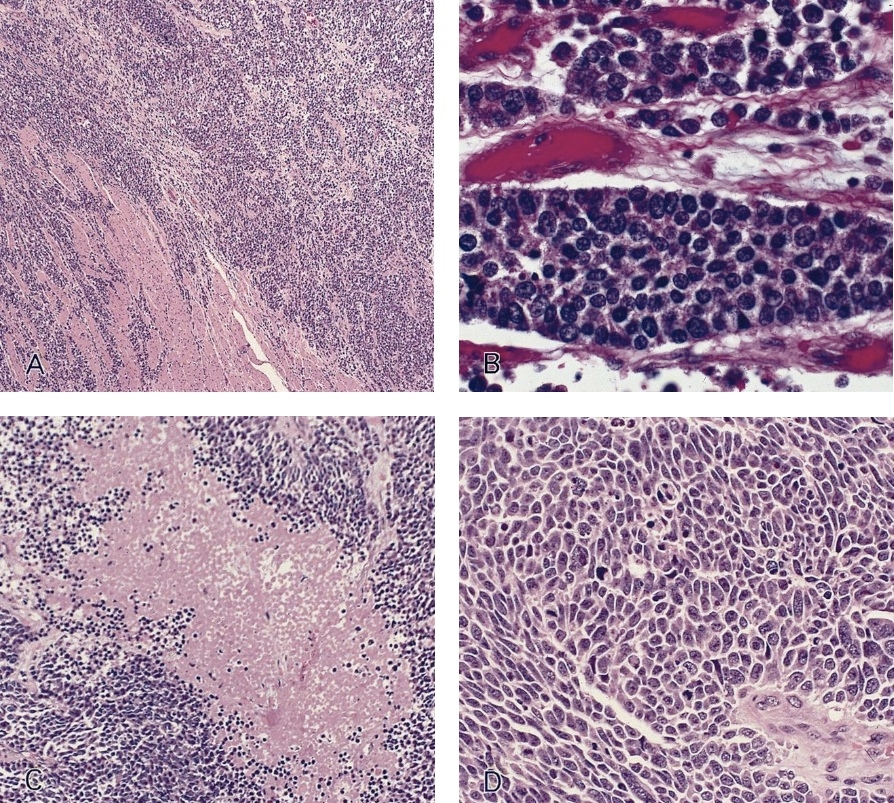
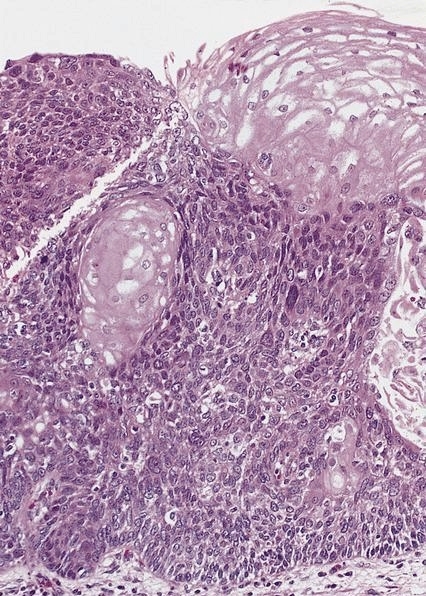
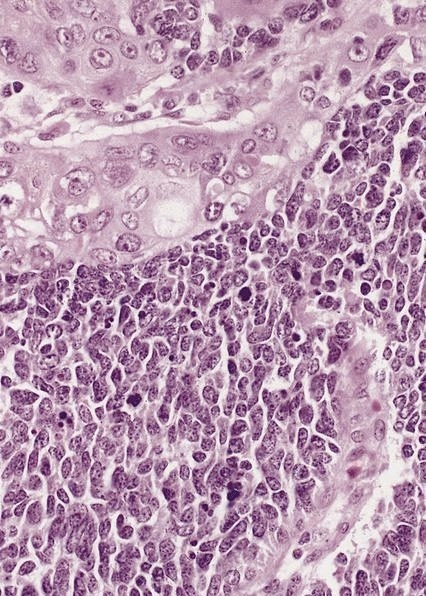
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Well differentiated (low grade) tumors
- Uniform, small, bland tumor cells in solid, trabecular, gyriform or glandular patterns
- May have Paneth cell differentiation
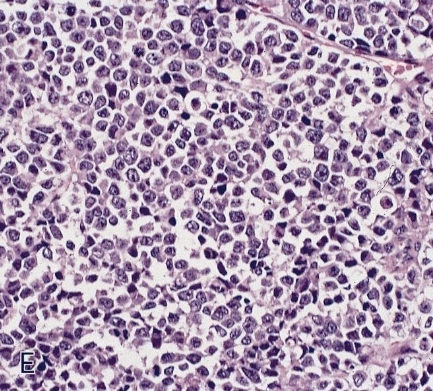
- Poorly differentiated (high grade) carcinomas
- Large cell type: nests of pleomorphic, large cells with prominent nucleoli and a moderate amount of cytoplasm
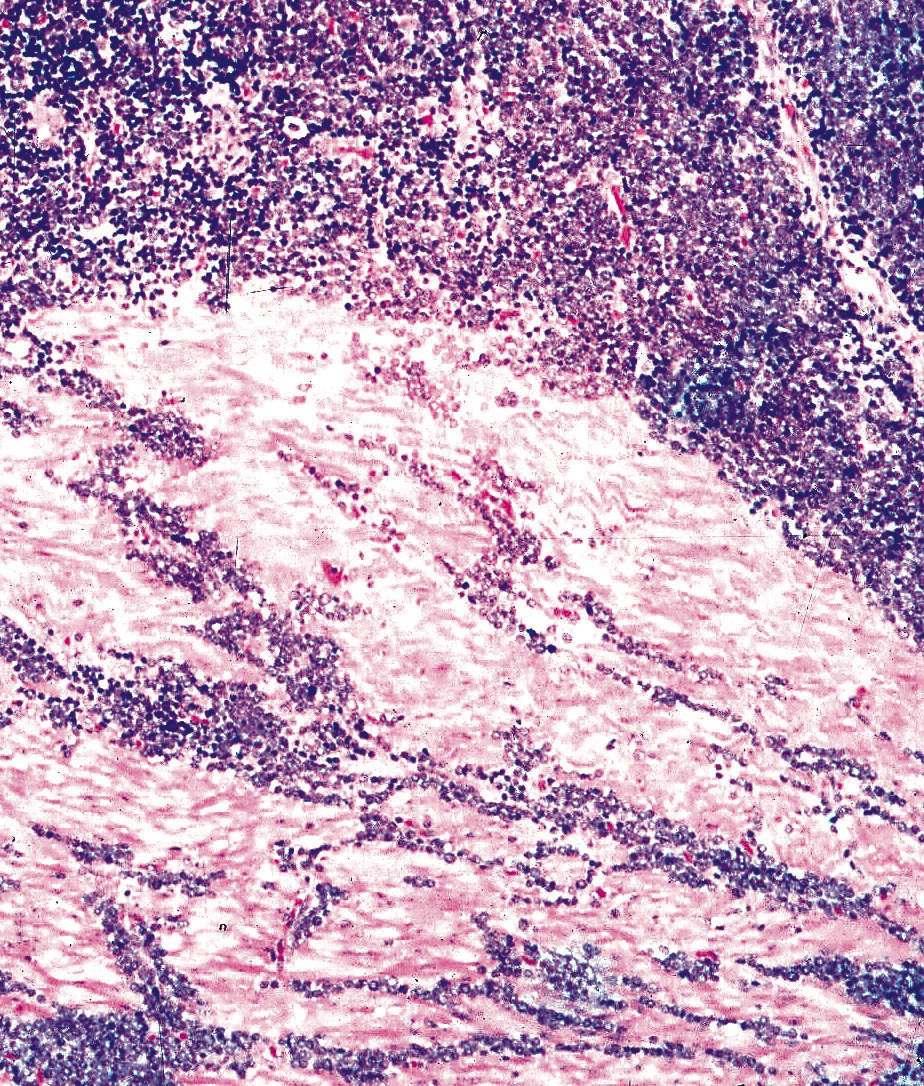
- Small cell type: sheets and nests of small cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and a minimal to moderate amount of cytoplasm; prominent crush artifact and Azzopardi phenomenon, as in small cell carcinomas at other sites
- Necrosis
- Increased mitotic activity
- Angiolymphatic invasion common
- Solid to cribriform growth
- Usually in lamina propria
- May be associated with heterotopic oxyntic mucosa or Barrett esophagus (large cell carcinoma)
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma may have small component(s) of adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma differentiation
Microscopic (histologic) images
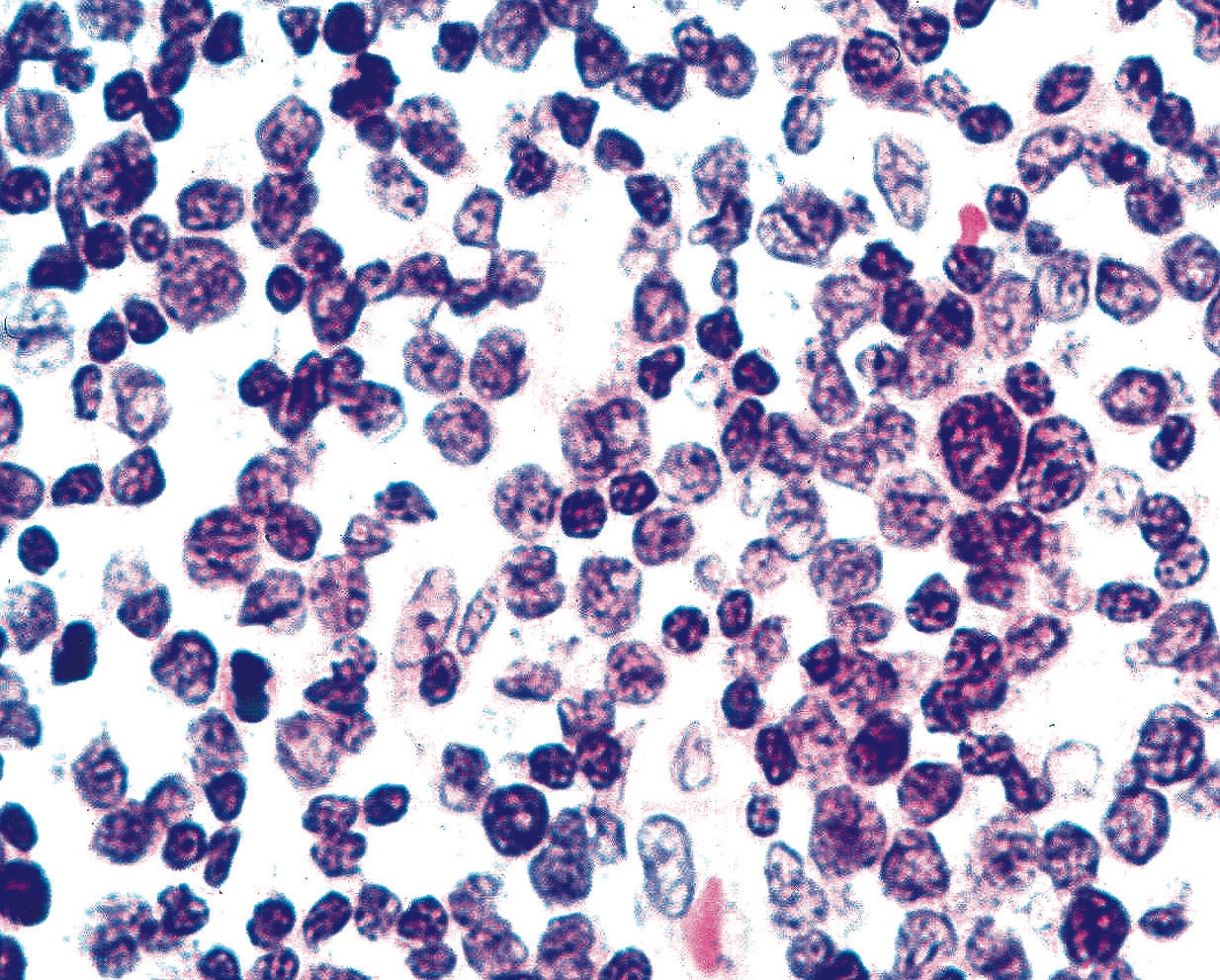
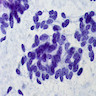
Cytology description
- Low grade tumors
- Flat sheets or loosely cohesive groups / cords of monotonously uniform plasmacytoid cells
- Eccentric nuclei, coarsely stippled (salt and pepper) chromatin, finely granular cytoplasm
- High grade carcinomas
- Obvious pleomorphism, marked nuclear molding, hyperchromatic nuclei, inconspicuous nucleoli
- Numerous mitoses, crush artifact, necrosis
- Apoptotic figures, blue bodies
Cytology images
Positive stains
- Keratins (e.g., CAM 5.2, AE1 / AE3)
- Neuroendocrine markers: synaptophysin, chromogranin, CD56, NSE
- Ki67 (essential for tumor grading see above)
- TTF1 positive in 71% of esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:467)
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Low grade tumors: glomus tumor, paraganglioma
- High grade carcinomas:
- Metastatic pulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma: exclude clinically, lymphoma, melanoma, basaloid squamous cell carcinoma