Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Jain D. Nevi-conjunctiva. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/eyenevi.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- See also Nevus of Ota in eyelid
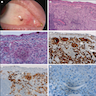
- Most common tumor of conjunctiva
- Rarely invades cornea, appears in fornix or over palpebral conjunctiva
- Rarely involves bulbar conjunctiva, caruncle, or plica semilunaris
- May be observed at birth or later
- May enlarge and become more pigmented at puberty or during pregnancy
- About half of excised pigmented lesions are nevi, remainder are melanomas or primary acquired melanosis
Case reports
- 11 year old girl with balloon cell nevus (Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2001;155:93)
Treatment
- Excision or watchful waiting, only rarely transforms (1 per 150K)
- Excise if newly acquired in adults, clinical growth, change in pigmentation, cosmetic reasons
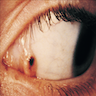
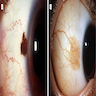
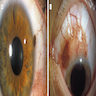
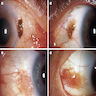
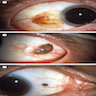
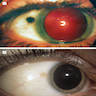
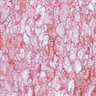
Clinical images
Gross description
- Discrete, flat or slightly elevated; circumscribed, pink, yellow-tan, brown or nonpigmented, in interpalpebral zone near limbus; 1/3 are amelanotic
Microscopic (histologic) description
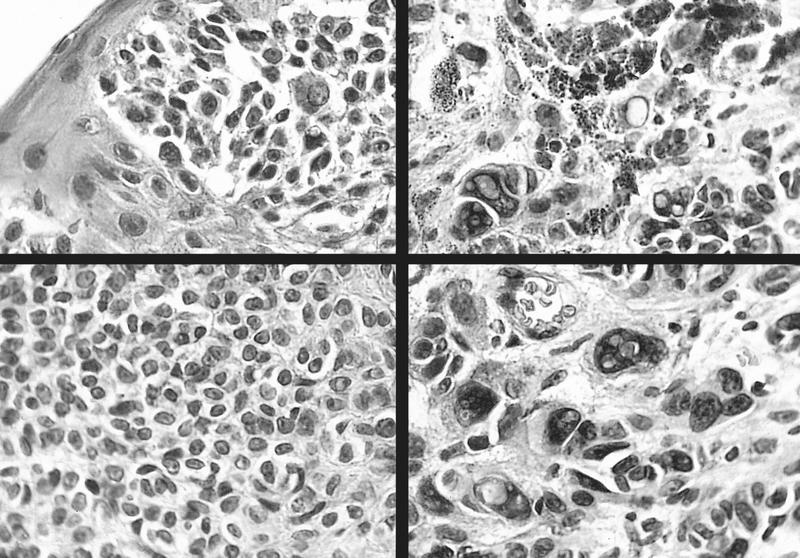
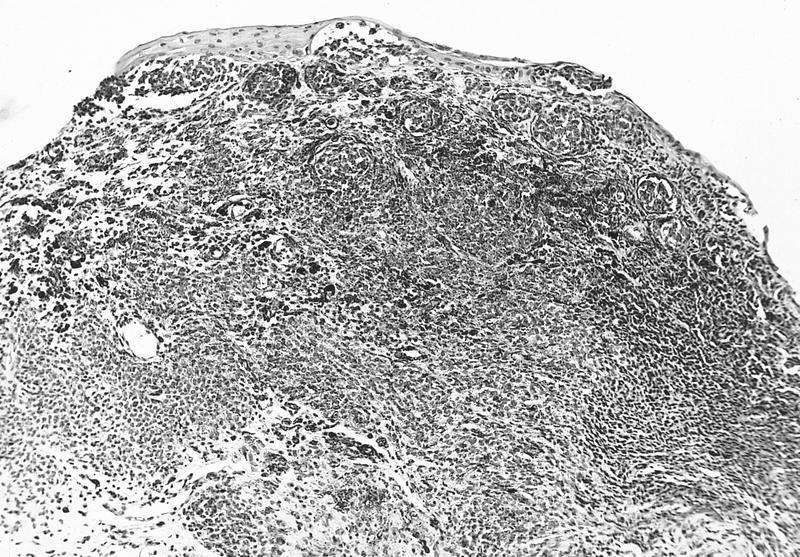
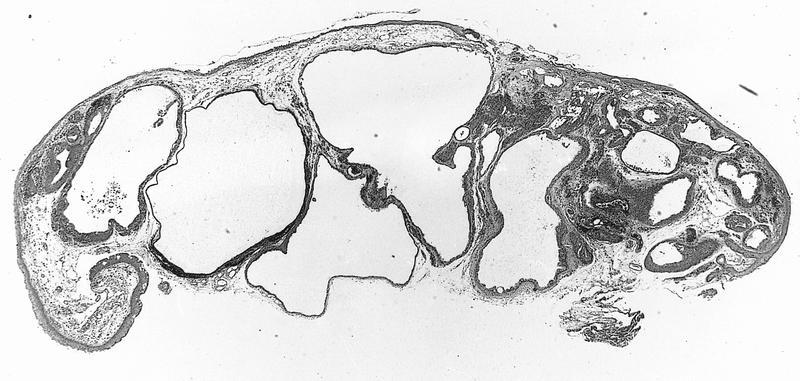
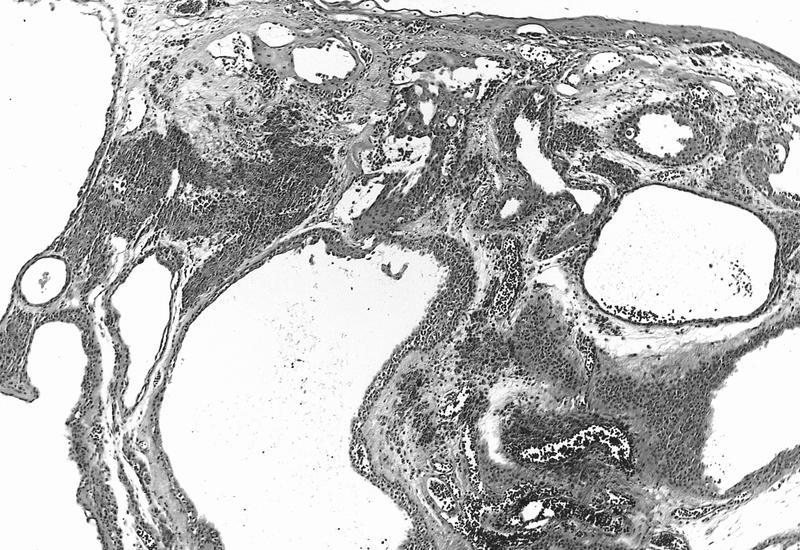
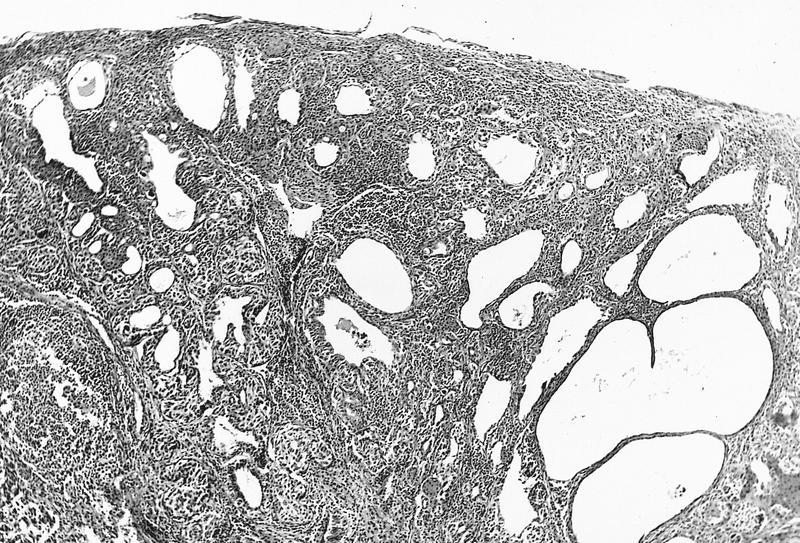
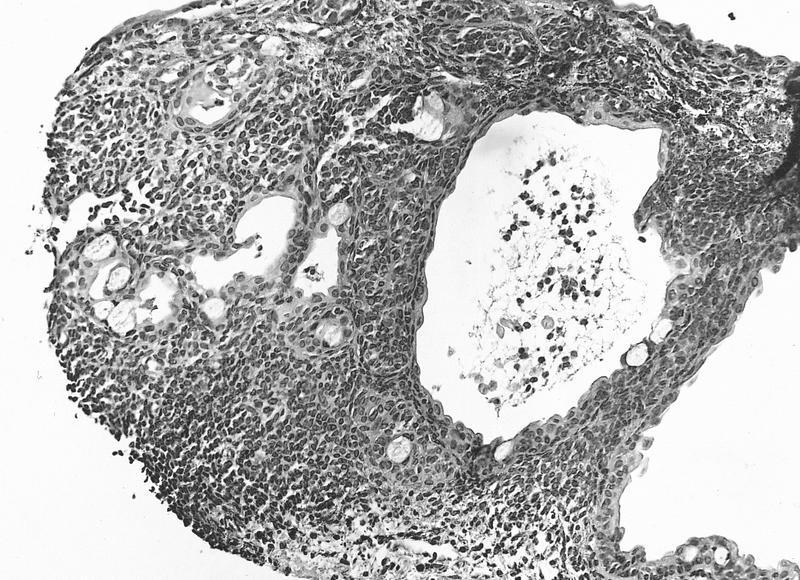
- Nevomelanocytes organized into intraepithelial nests of oval cells (type A), sheets of oval to cuboidal cells (type B), and spindled cells in subepithelium (type C)
- Often (50%) with solid and prominent cystic inclusions of conjunctival epithelium and chronic inflammatory infiltrate
- May have atypical features and mitotic figures during growth periods
- Compound (70 - 78%):
- Most common, nevi cells in epithelium and subepithelial connective tissue
- Cells have cysts lined by cuboidal and goblet cells and intranuclear inclusions
- May have large pigmented cells with prominent basophilic nucleoli
- Usually mixed inflammatory cells
- Junctional (5%):
- Contiguous nests of round / spindle melanocytes near basal cell region with oval nuclei, small nucleoli
- Nucleoli may be basophilic and prominent but no atypia
- Uncommon except in young children
- Resembles primary acquired melanosis with atypia
- Subepithelial (9%):
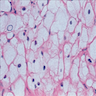
- Nevus cells only in subepithelial connective tissue, no pigment, bland nuclei
- May have clear cytoplasm due to lipid and central round nucleus (balloon cell nevus)
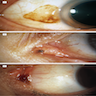
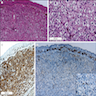
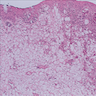
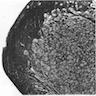
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Cystic compound nevus:
Images hosted on other servers:
Balloon cell:
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- Melanoma: cysts are rare, atypical intraepithelial component, atypical mitotic figures, necrosis, WT1+, HMB45+ (Arch Ophthalmol 2009;127:964), cytogenetic aberrations of 6p25, 6q23, 11q13, centromere 6 (J Cutan Pathol 2010;37:196, Br J Ophthalmol 2013;97:40)
Additional references