Cite this page: Pernick N. Iris. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/eyeuveairisgeneral.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
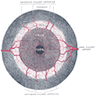
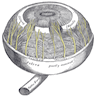
- Thin diaphragm of tissue with central opening (pupil)
- Forms boundary of anterior and posterior chamber
- Highly textured with folds and crypts
- Part of middle layer of eye (also ciliary body and choroid)
- Normally rests gently upon lens and bulges slightly forward
- Consists of stroma and posterior epithelial lining (two closely apposed epithelial layers, with numerous melanosomes); contains sphincter muscle within stroma that controls pupil
- Anterior iris lacks a cellular lining
- Color is due to number of stromal melanocytes; blue irises have few stromal melanocytes; brown irises have numerous melanocytes
- Blood vessels are usually surrounded by a thick collar of collagen fibers, resembling arteriolosclerosis
- Fewer melanosomes and melanocytes in patients with ocular and oculocutaneous albinism
- Regulates amount of light reaching pupil; muscles of iris dilate or constrict pupil in response to parasympathetic or sympathetic nerve impulses; normal diameter of pupil is 1 - 8 mm
- Iridectomy: excision of small segment of iris; place on filter paper to avoid folding
- Ectropion uveae: fibrovascular tissue on anterior surface of iris everts the papillary margin and pulls pigmented epithelia onto anterior surface of iris