Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Liu SS, Bellamkonda V, Phung TL. Angiosarcoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueangiosarcoma.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Angiosarcoma is a malignant neoplasm showing morphological or immunophenotypic evidence of endothelial differentiation
Essential features
- Irregularly shaped anastomosing vascular channels or sheet-like growth
- Highly infiltrative architecture and poor demarcation
- Multilayering of endothelial cells, nuclear atypia, increased mitoses, necrosis
- Positive for vascular markers, such as CD31, CD34, ERG, VEGF and factor VIII, by immunohistochemistry
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9120/3 - Angiosarcoma
- ICD-11: 2B56.Y & XH6264 - Angiosarcoma, other specified primary site and hemangiosarcoma
Epidemiology
- Angiosarcoma accounts for about 2 - 3% of all soft tissue sarcomas in adults (Am J Cancer Res 2019;9:2303)
Sites
- Most common sites of angiosarcoma are skin of the head and neck (about 60% of cases); can also present within the soft tissues, visceral organs, bone and retroperitoneum
- Skin:
- Cutaneous angiosarcoma is the most common form, typically primary and occurring in sun exposed areas of older adults, with secondary cases less common (Ann Diagn Pathol 2011;15:93, Curr Probl Cancer 2015;39:258)
- Head and neck are the most common locations for cutaneous angiosarcoma, with rare occurrence on the trunk and extremities
- Breast:
- Primary angiosarcoma developing de novo
- Secondary angiosarcoma developing as a consequence of previous breast cancer treatment (e.g. postoperative radiotherapy or chronic lymphedema after treatment for breast cancer, associated with Stewart-Treves syndrome)
- They display varying degrees of nuclear atypia, hyperchromatic nuclei, enlarged nucleoli and frequent mitoses (BMC Cancer 2018;18:463)
- Extremities:
- Tumor can arise 5 - 15 years after radical mastectomy and axillary lymph node dissection associated from chronic lymphedema (Stewart-Treves syndrome)
- Kidney:
- Primary renal angiosarcoma, also referred to as renal hemangiosarcoma, is an extremely rare neoplasm
- To date, about 60 primary renal angiosarcomas have been described in the literature
- Most cases occur in the sixth and seventh decades (Curr Urol Rep 2018;19:4)
- Liver:
- Hepatic angiosarcoma is a rare malignancy accounting for up to 2% of primary hepatic neoplasms (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:581)
- Associated with vinyl chloride, arsenic and thorium dioxide (Thorotrast)
- Lung:
- Primary pulmonary angiosarcoma is rare and can present with respiratory symptoms such as hemoptysis, cough and dyspnea
- Less than 30 cases have been reported in the literature
- Has a very poor prognosis (Thorac Cancer 2016;7:607)
- Spleen:
- Rare and aggressive neoplasm with a high metastatic rate and poor prognosis
- Presents with left upper quadrant pain and systemic symptoms such as GI bleeding, splenomegaly and hemoperitoneum due to splenic rupture (J Surg Oncol 2005;92:312)
- Small intestine:
- Primary angiosarcoma of the small intestine is extremely rare with a very poor prognosis
- Ovary:
- Patients with ovarian angiosarcomas most commonly present with abdominal pain; however, some patients present with distant metastases, often to the lungs
- Tumor can spread beyond the ovary at the time of initial diagnosis in most reported cases with disease progression within less than a year after diagnosis (J Med Case Rep 2014;8:47)
- Salivary glands:
- Angiosarcomas of the salivary glands and oral cavity are extremely rare and comprise only 2% of all angiosarcomas
- Prognosis of salivary gland angiosarcoma is not known due to the paucity of cases in the literature (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:837)
Pathophysiology
- Pathogenesis of angiosarcoma is characterized by a rapid and extensive infiltrating overgrowth of vascular endothelial cells
- Angiosarcoma is a locally aggressive tumor with a high rate of lymph node infiltration and metastases
- Angiosarcoma has been shown to have upregulation of vascular specific receptor tyrosine kinases, including TIE1, KDR, TEK and FLT
- Upregulation of these genes and overexpression of VEGFR can cause endothelial cell expansion, angiogenesis and also vascular leaks
- KDR mutations are seen in primary breast angiosarcoma regardless of exposure to radiation
- c-MYC amplification is seen in radiation induced and lymphedema associated angiosarcoma
- FLT4 amplification has been detected in 25% of secondary angiosarcomas
Etiology
- Etiology is unknown in most cases
- A minority arise after radiation exposure or longstanding lymphedema (Stewart-Treves syndrome)
- Angiosarcoma is associated with exposure to vinyl chloride, arsenic and thorium dioxide (Thorotrast)
- Small numbers occur in association with implanted foreign material, in pre-existing hemangioma / vascular malformation and in regions of prior trauma or surgery
- Angiosarcomas occur in patients with certain syndromes (neurofibromatosis and Maffucci sundrome) and rarely as heterologous components of other neoplasms (benign or malignant nerve sheath tumors) (Cancer 1988;62:2436, Histopathology 1999;35:114, Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1319, Am J Nephrol 2011;34:42)
Clinical features
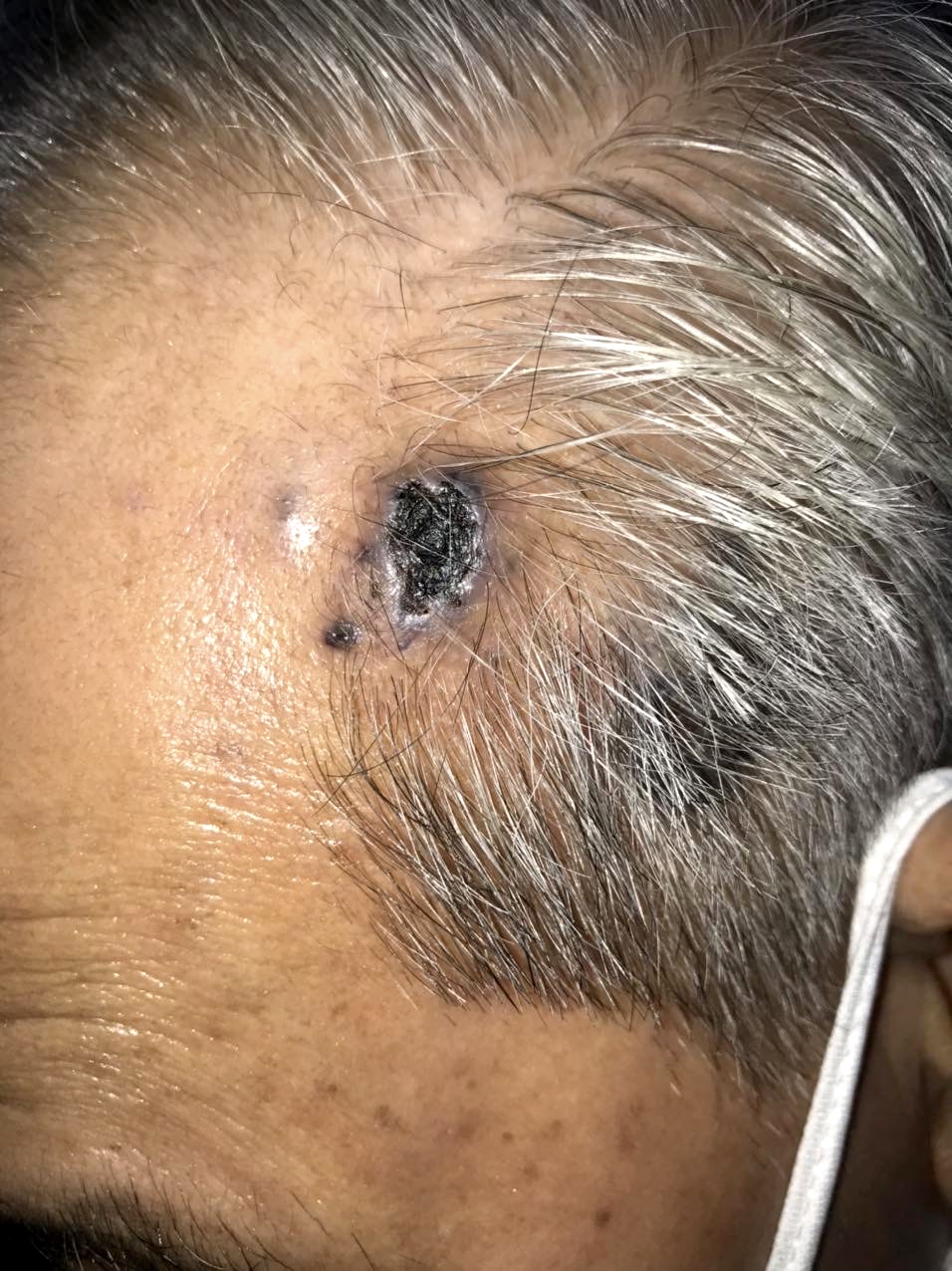
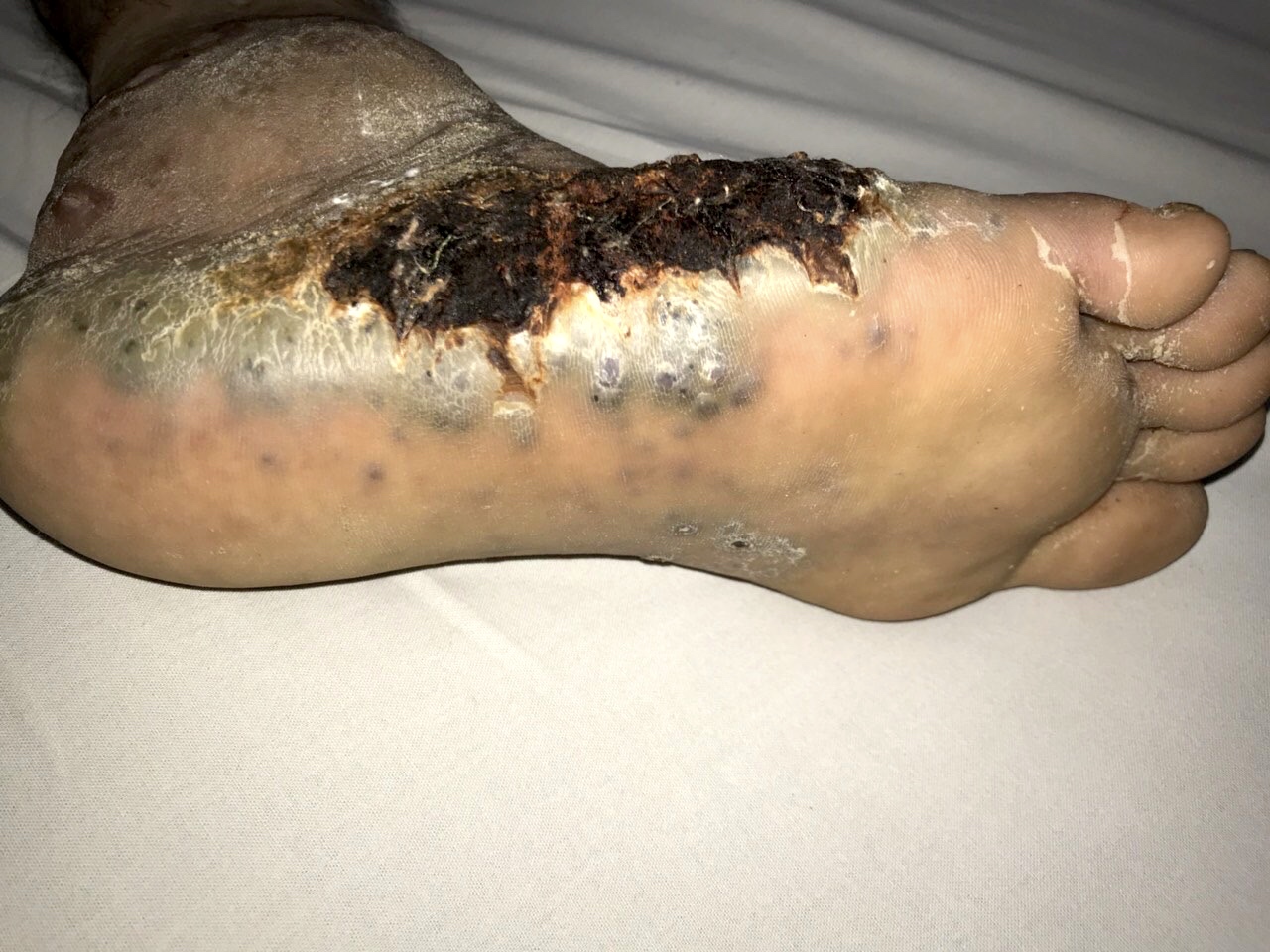
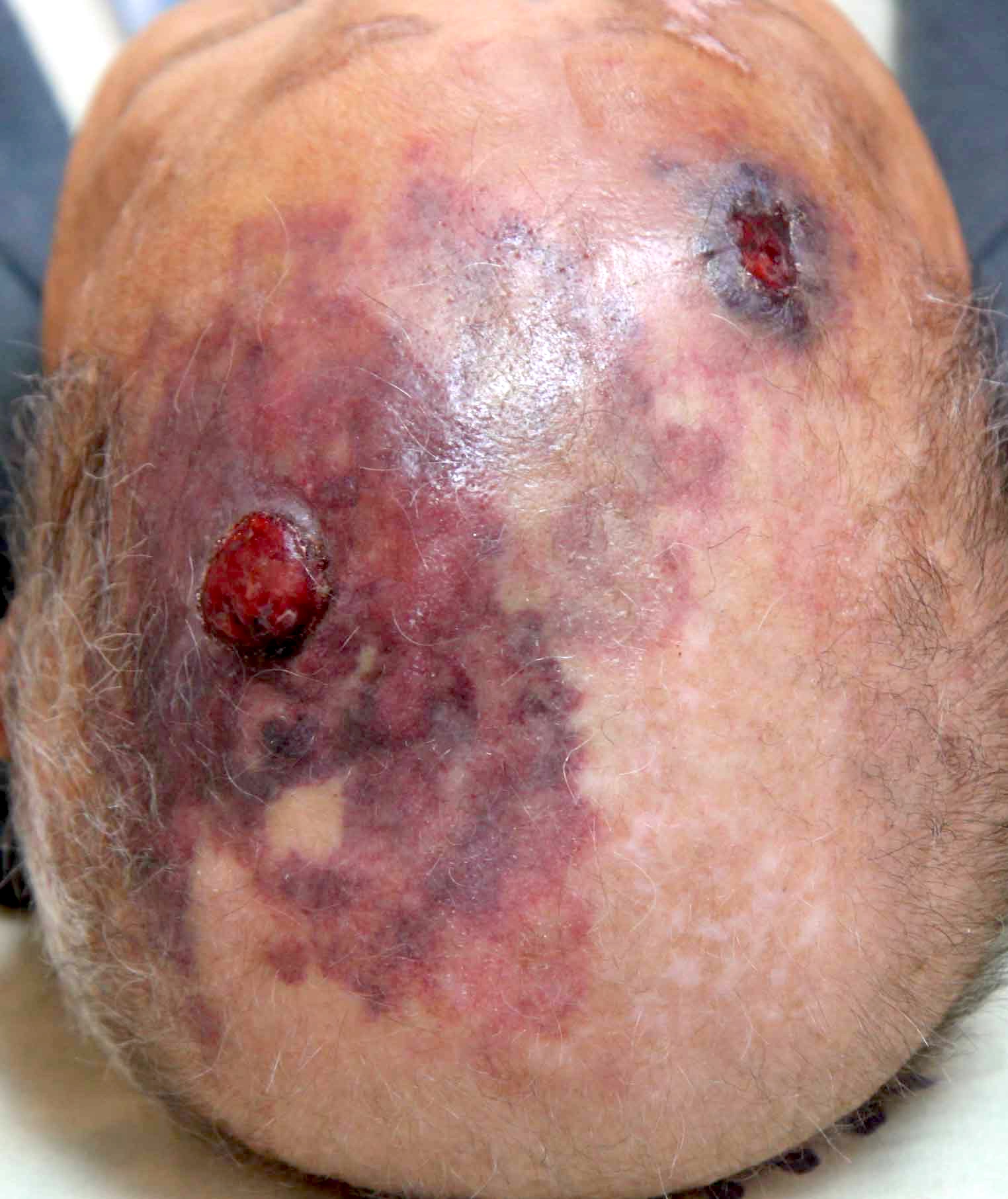
- Patients typically present with a blue or purple lesion on the scalp or face that has been present for several months and can be rapidly growing
- These lesions may appear macular, nodular or plaque-like
- Diffuse, clinically undetectable intradermal spread leads to indistinct borders and a high incidence of multicentricity
- Advanced lesions can show hemorrhage or ulceration
- Cervical lymphadenopathy is found in approximately 10% of patients at the time of presentation
Diagnosis
- Clinical presentation:
- Angiosarcomas often look like a bruised, purpuric area on the skin which can bleed easily when traumatized
- They grow larger over time and the skin around the bruised area can swell, accompanied by pain
- Imaging: MRI, CT or PET scan to assess tumor size and anatomic localization
- Biopsy of the lesion for microscopic examination
Laboratory
- Laboratory studies are usually unremarkable and not unique to angiosarcoma, unless mass effect causes compression of critical organs, leading to laboratory abnormalities (such as compression of the ureter, which can lead to renal failure) or the disease is fairly advanced to cause subtle lab abnormalities (such as anemia of chronic disease and elevated sedimentation rate)
- There are no specific lab abnormalities or biomarkers that could point towards a diagnosis of angiosarcoma
Radiology description
- Head and neck:
- MRI shows intermediate T1 signal intensity with possible areas of hyperintensity, indicating the presence of hemorrhage (Br J Radiol 2017;90:20170039)
- Soft tissue:
- Manifests as an irregular enhancing soft tissue mass on contrast enhanced CT (Radiographics 2011;31:1923)
- Breast:
- Nonspecific and may show a solitary ill defined uncalcified mass on mammography
- Heterogeneous mass of low signal intensity of T1 weighted and high signal on T2 weighted MRI (J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 2014;58:208, Br J Radiol 2017;90:20170039)
- Liver:
- Consistent with an aggressive vascular tumor
- Predominantly hypoattenuating mass with or without hyperattenuating foci on unenhanced CT with heterogenous enhancement, indicating necrosis and fibrosis on contrast enhanced CT (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;175:165)
- Bone:
- Destructive lytic pattern on radiographs without a sclerotic margin (Skeletal Radiol 1996;25:255)
Prognostic factors
- Although features such as tumor size, epithelioid component, high mitotic activity and margin status have been associated with adverse prognosis, these features have not been validated for routine clinical use (Ann Surg 2010;251:1098, J Surg Oncol 1996;61:170, Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:1267, Cancer 2005;104:2682)
- Association between histological grade and clinical outcomes has been debated and angiosarcoma is not routinely graded
Case reports
- 6 year old girl with a large upper neck mass extending into cheek (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:837)
- 32 year old woman with gradually increasing breast size with nodularity and nonspecific radiologic features (J Radiol Case Rep 2019;13:15)
- 56 year old man with an 11 cm poorly vascularized left renal mass on imaging (Open Med (Wars) 2019;14:443)
- 56 year old woman with massive splenomegaly (Case Rep Surg 2016;2016:4173060)
- 70 year old man with slowly widening induration, ulceration and oozing for 3 months on the scalp and face (Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 2017;38:363)
- 71 year old woman with heterogeneously enhancing mass involving adrenal gland (Case of the Month #509)
- 78 year old woman with a left upper lobe pulmonary mass (J Bras Pneumol 2016;42:68)
Treatment
- Surgical resection is the main treatment modality, in addition to chemotherapy and radiotherapy
- Targeted therapy and immunotherapy have been studied as a promising new treatment of angiosarcoma
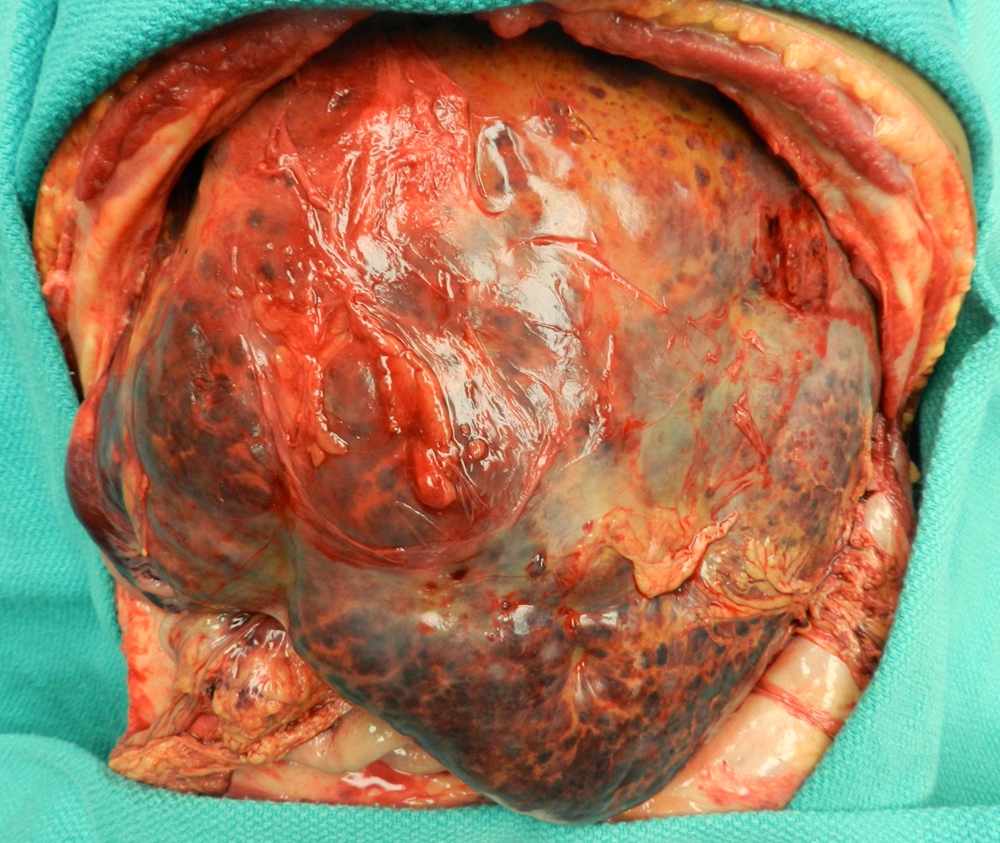
Clinical images
Gross description
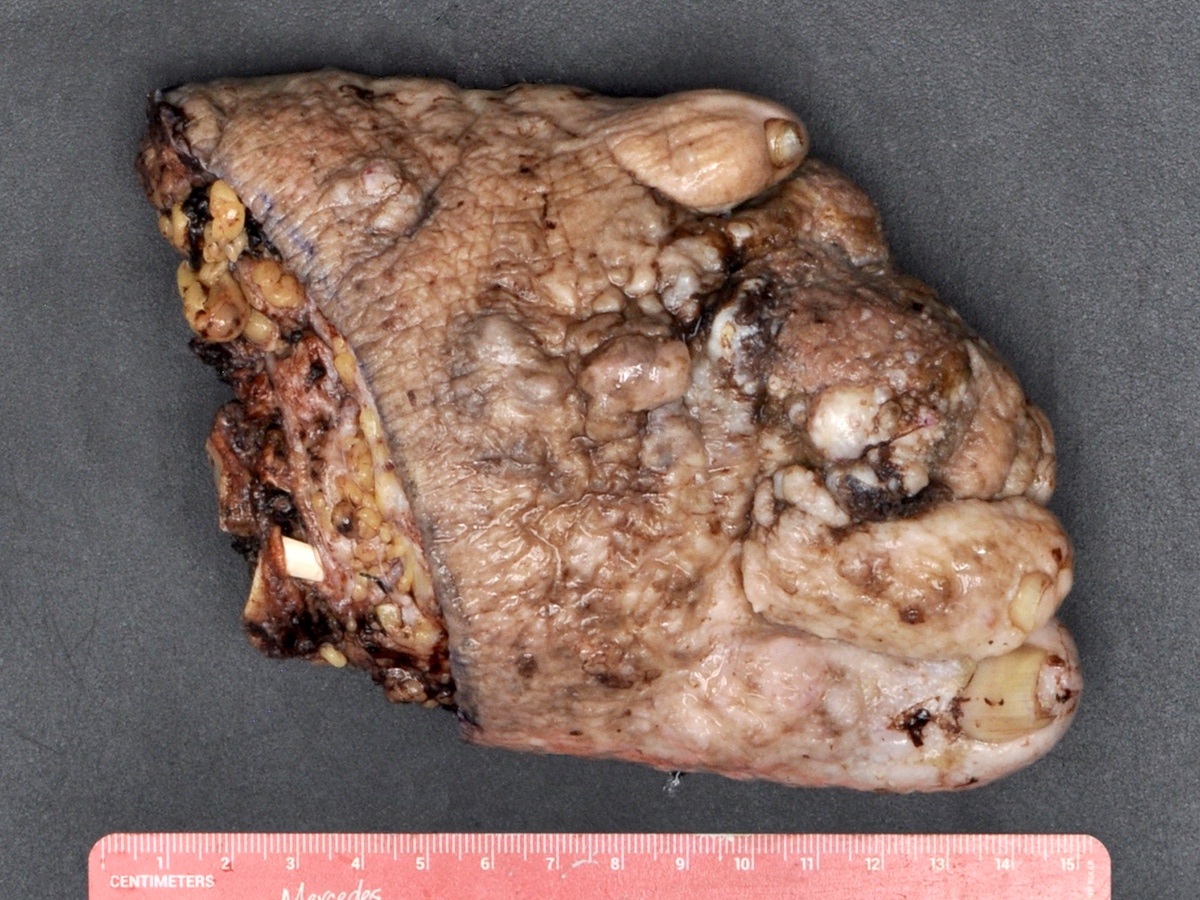
- Skin:
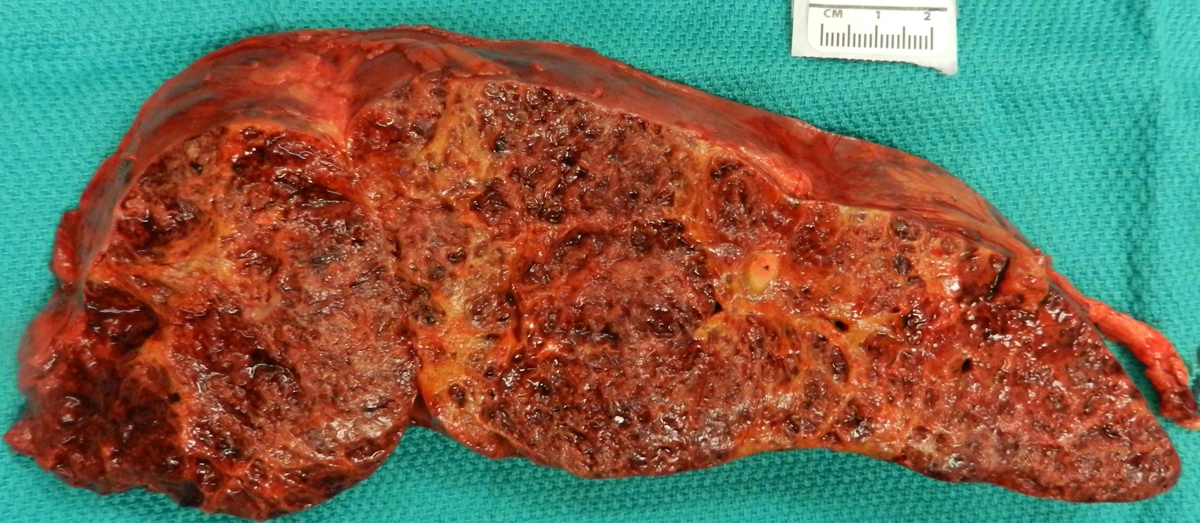
- Purple or maroon nodules or plaques with hemorrhagic or necrotic cut surface
- Breast:
- Lesions can be cutaneous or intraparenchymal
- Cutaneous lesion is grossly similar to other cutaneous forms in setting of postsurgical lymphedema associated with history of irradiation to breast or chest wall
- Intraparenchymal lesion is either solitary or multiple masses in breast
- Overlying skin may present with purple discoloration
- Deep soft tissue:
- Lesion most likely presents as a slow growing, painful and large mass associated with coagulopathy (in 33% of cases)
Gross images
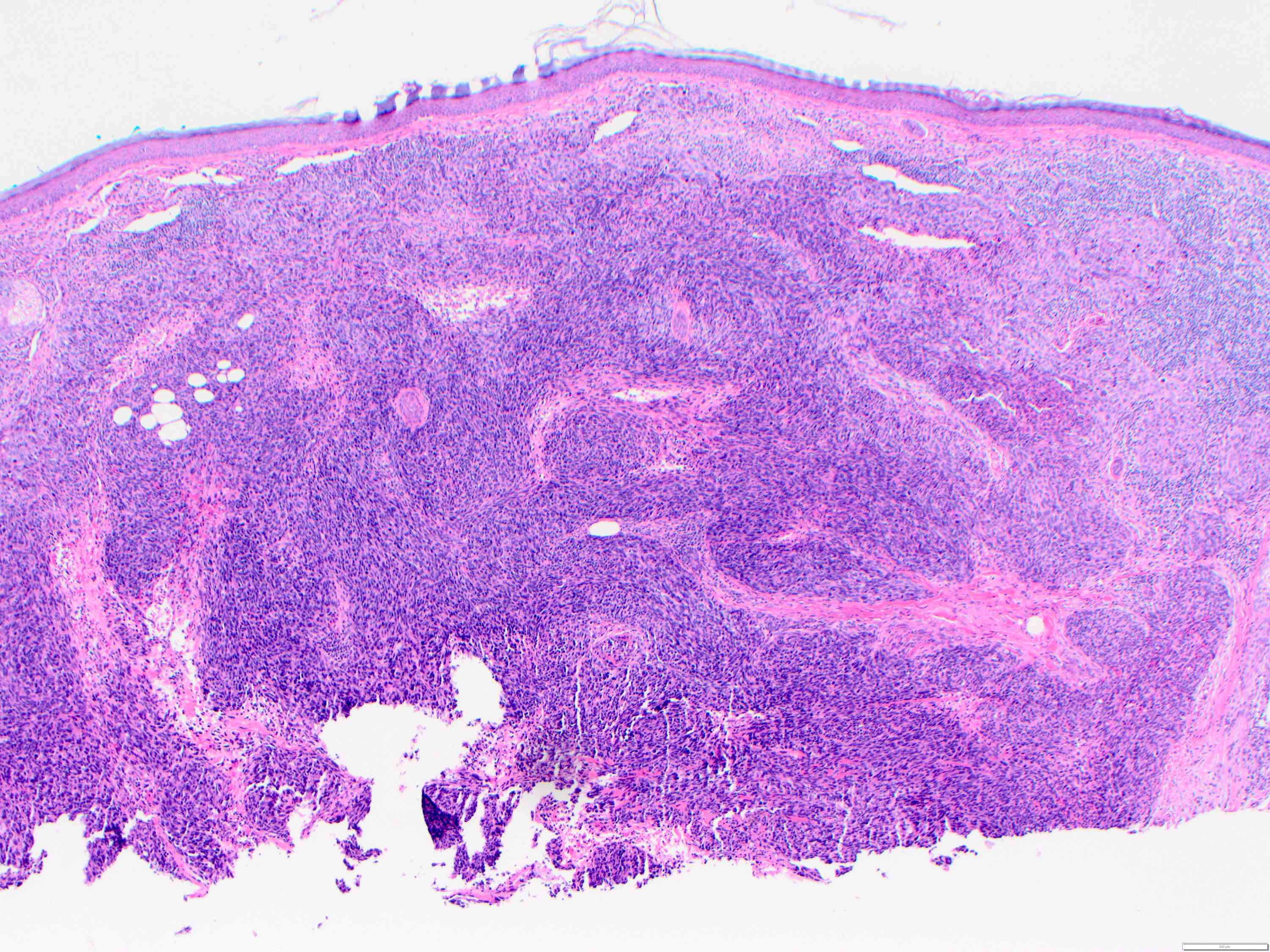
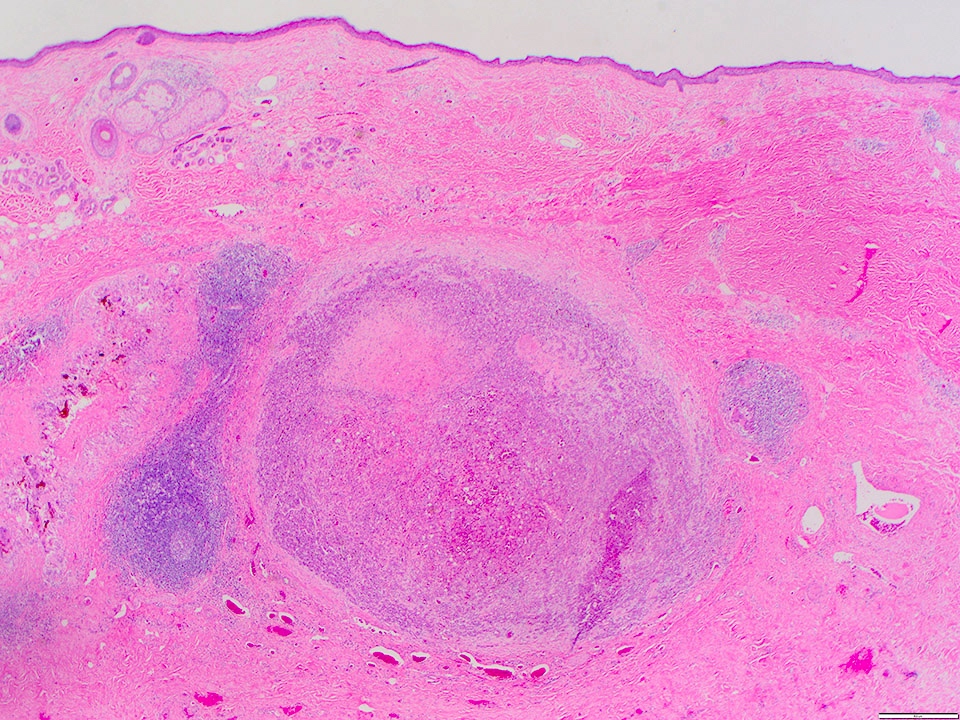
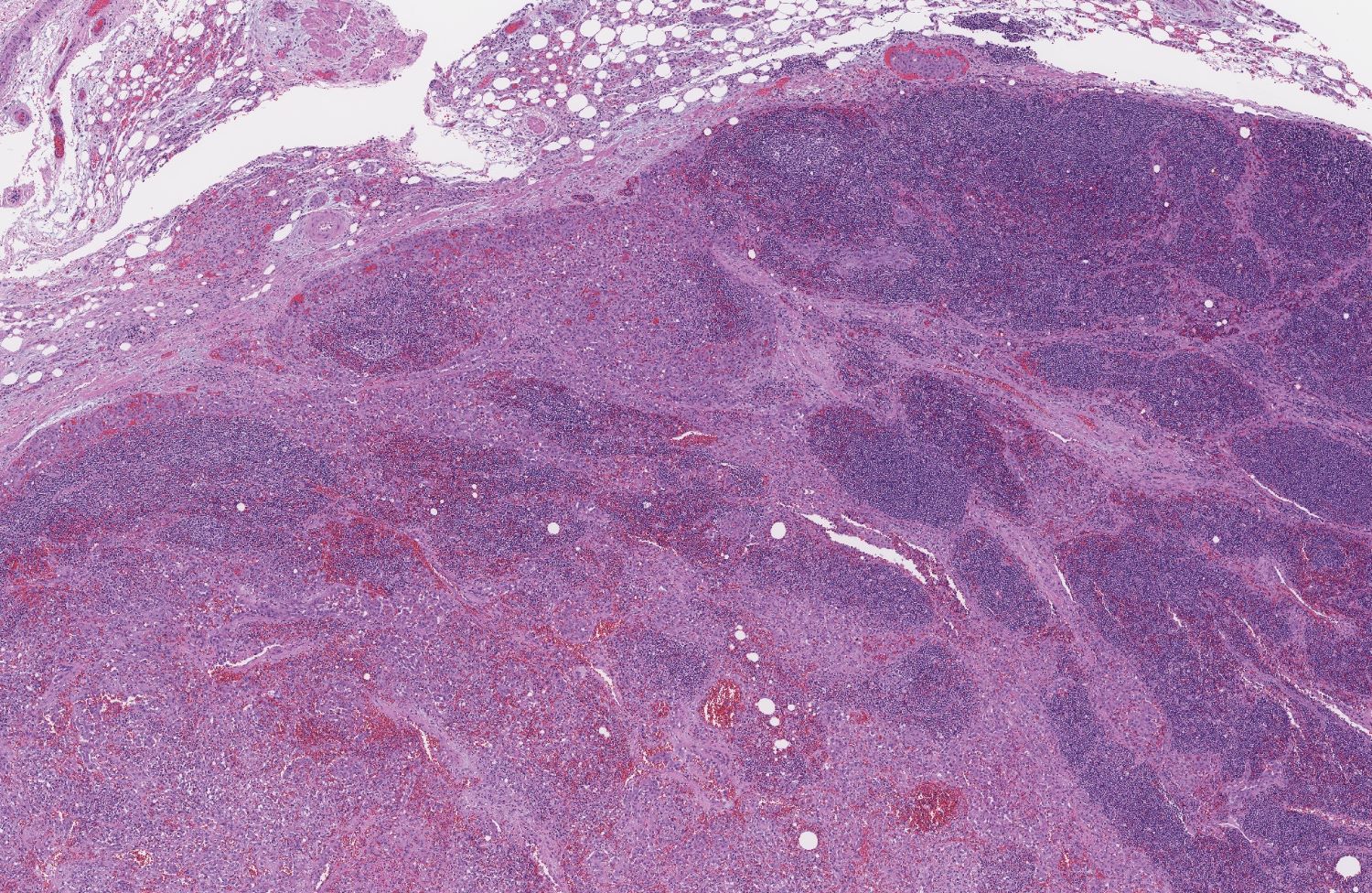
Microscopic (histologic) description
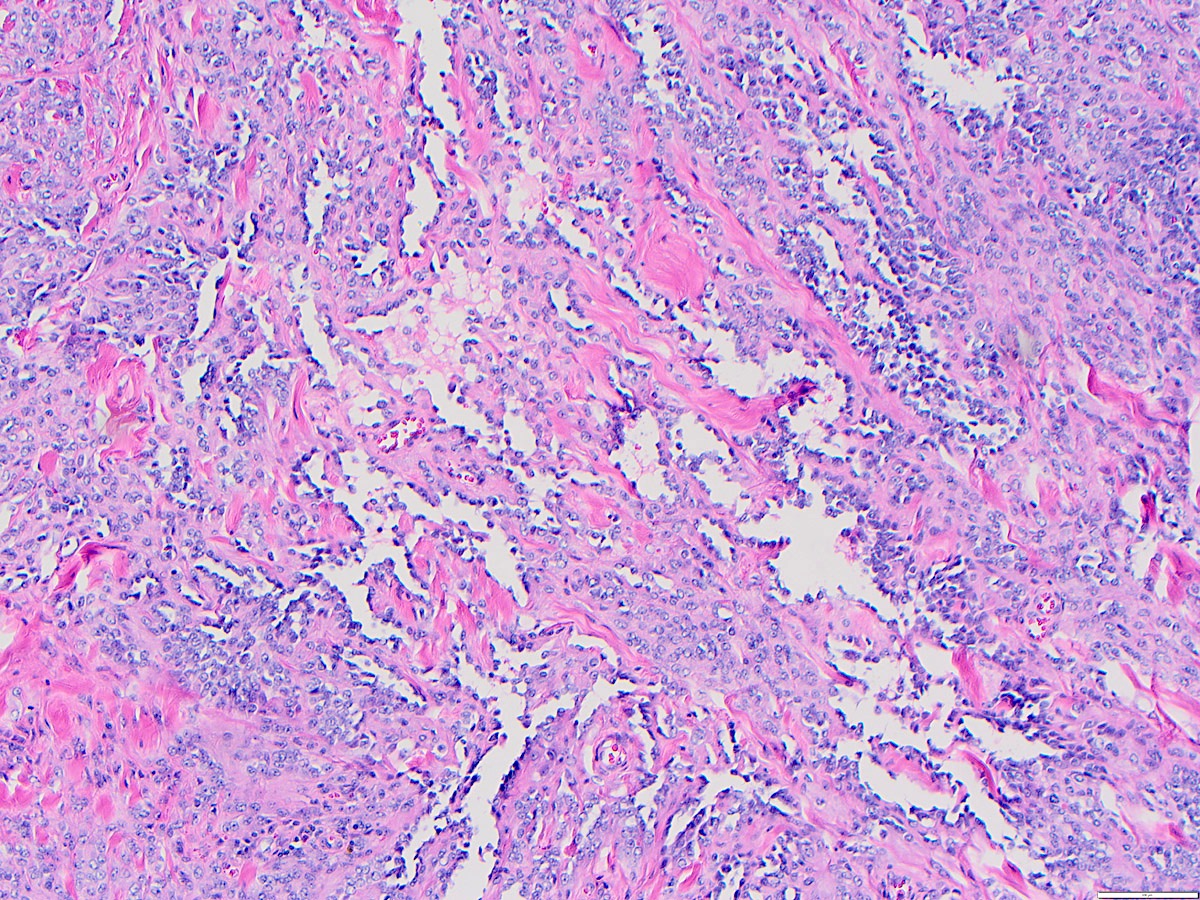
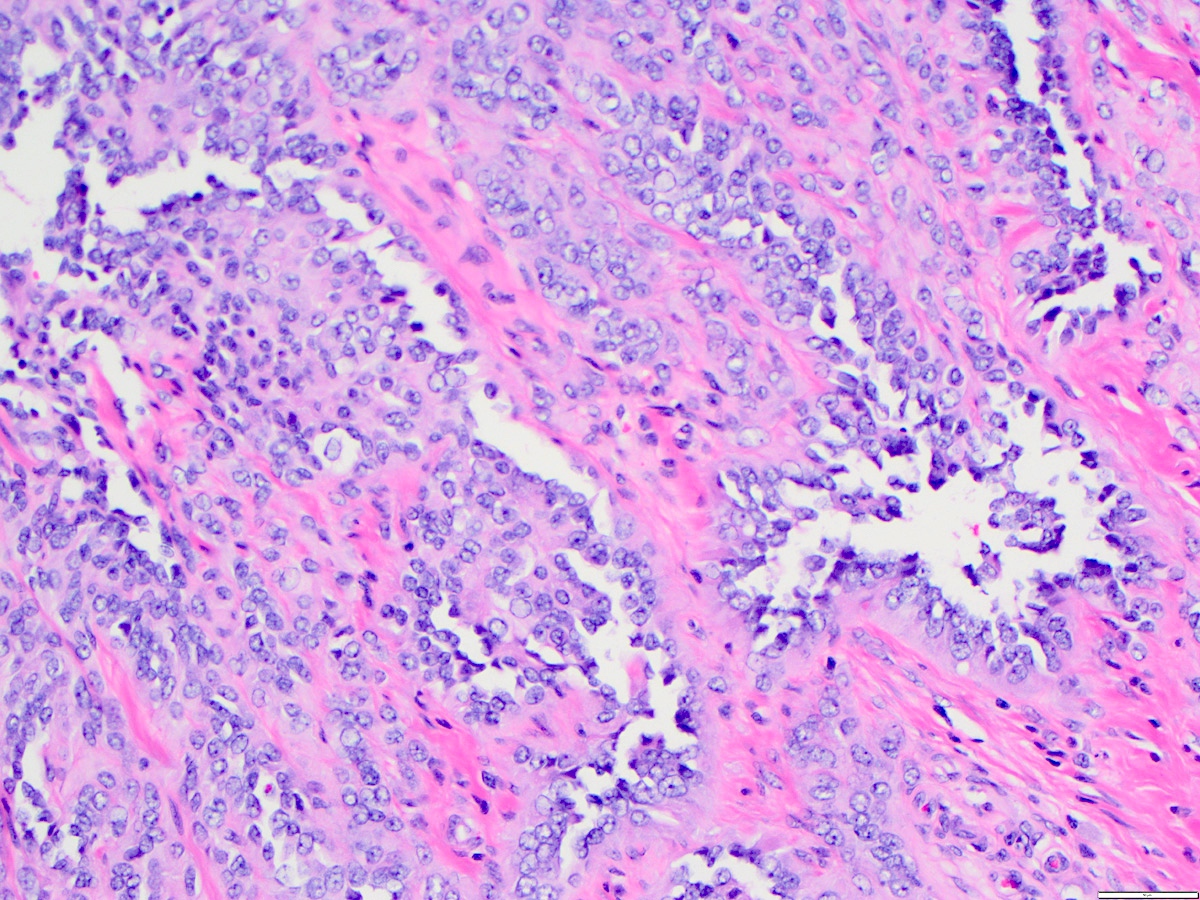
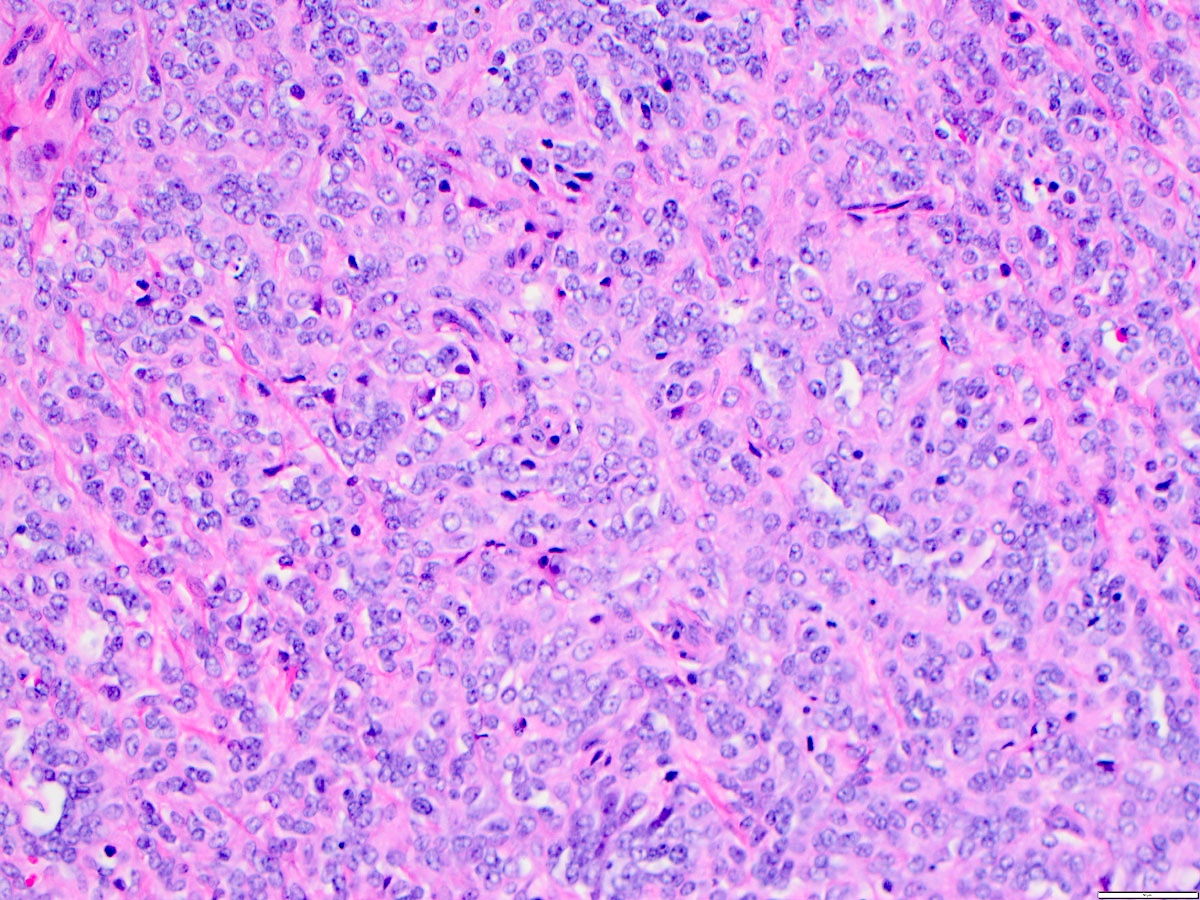
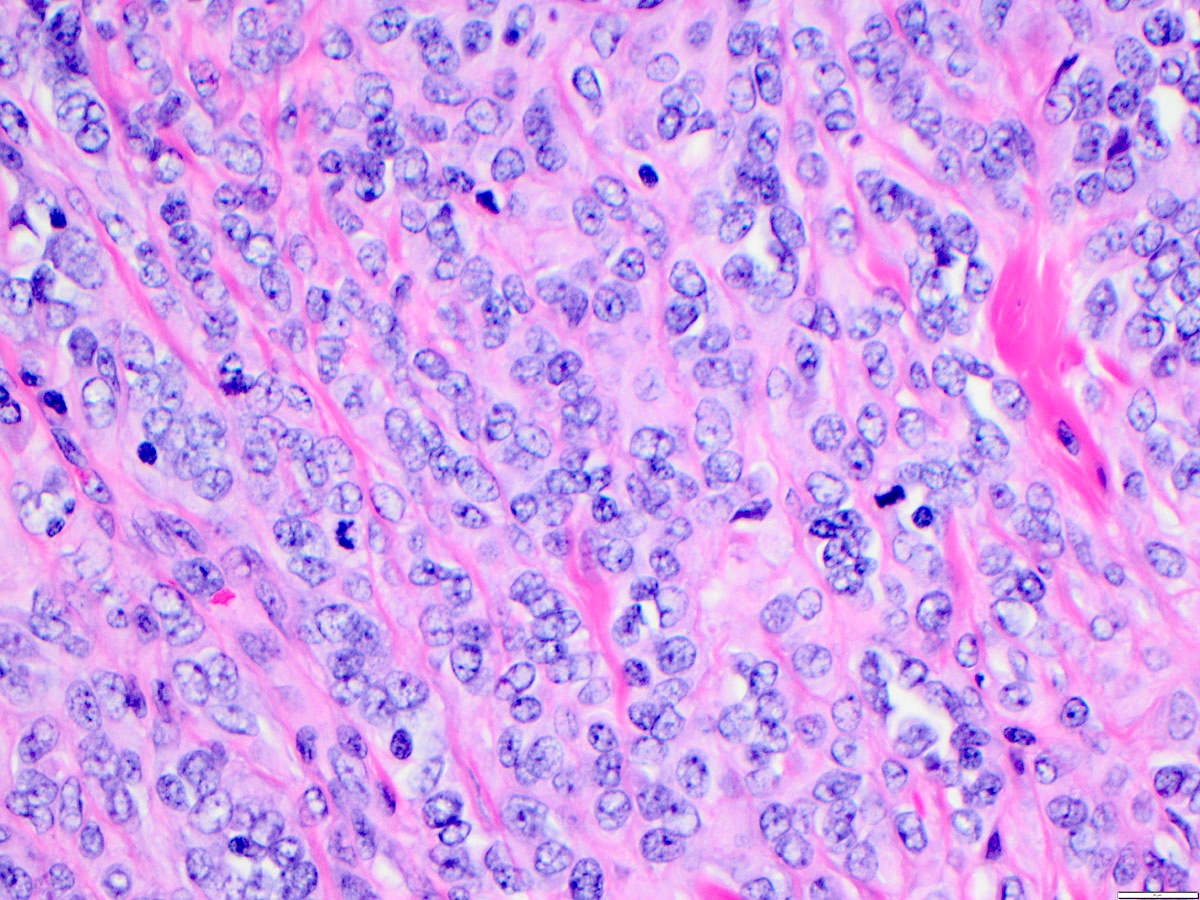
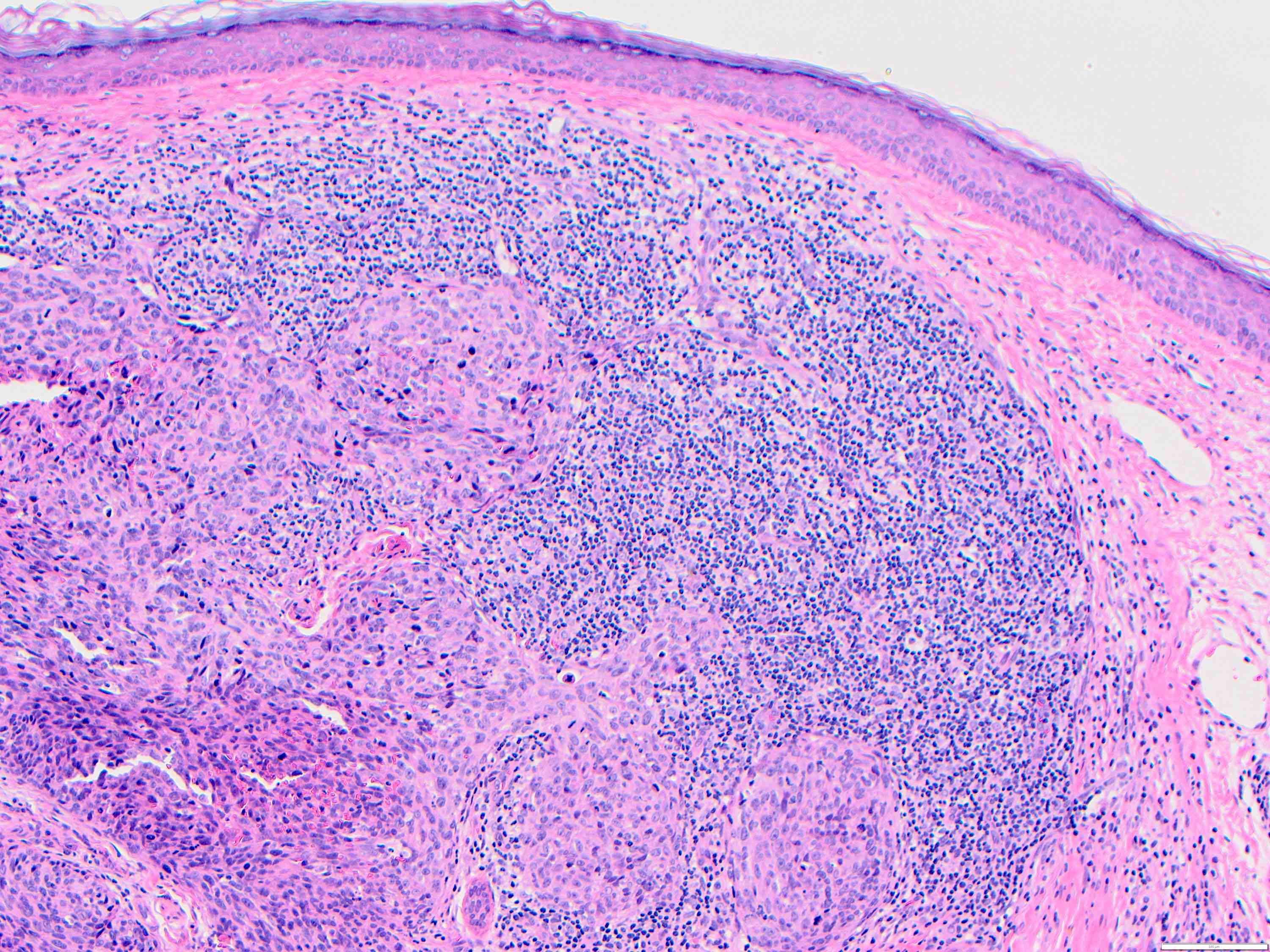
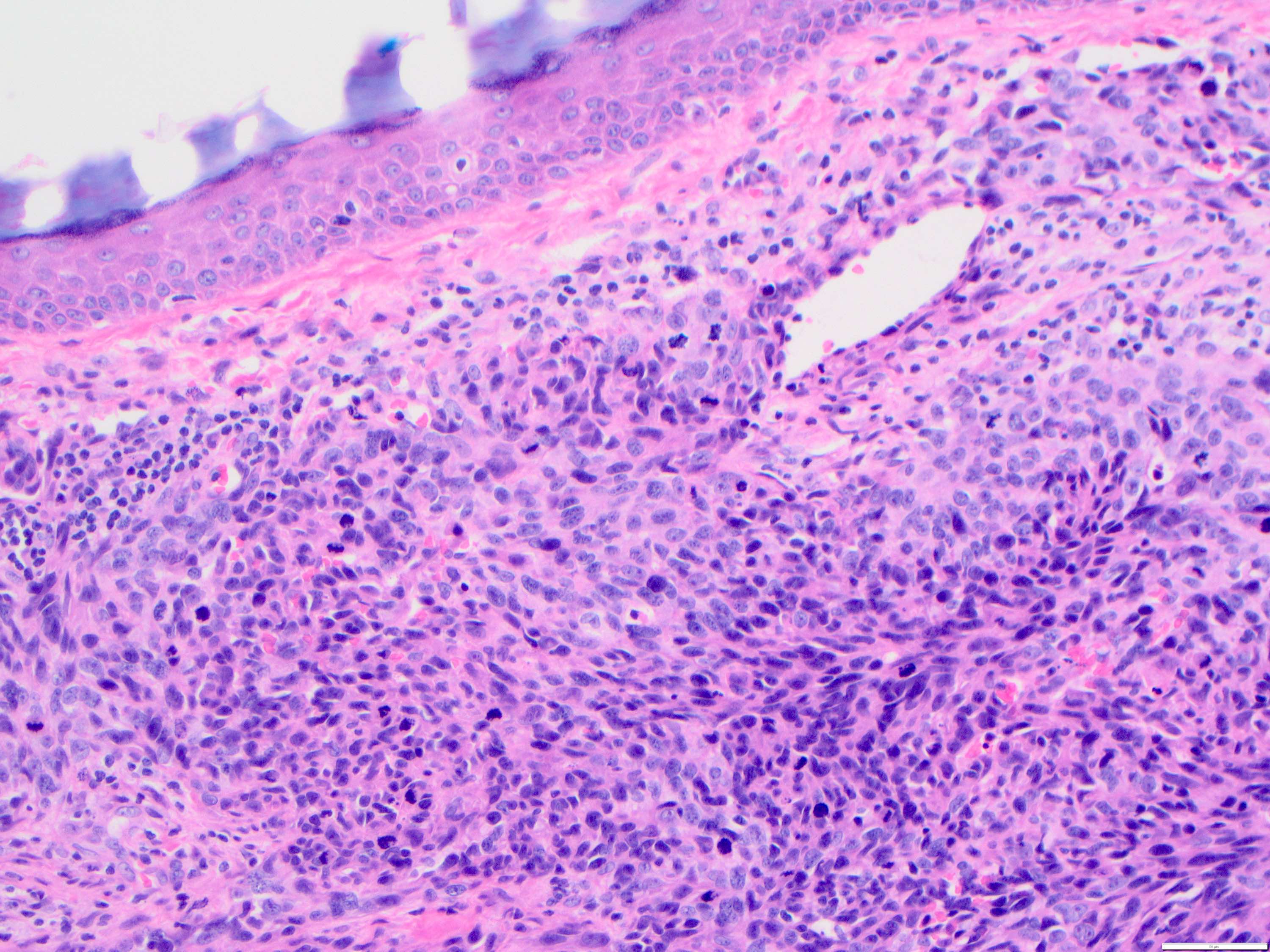
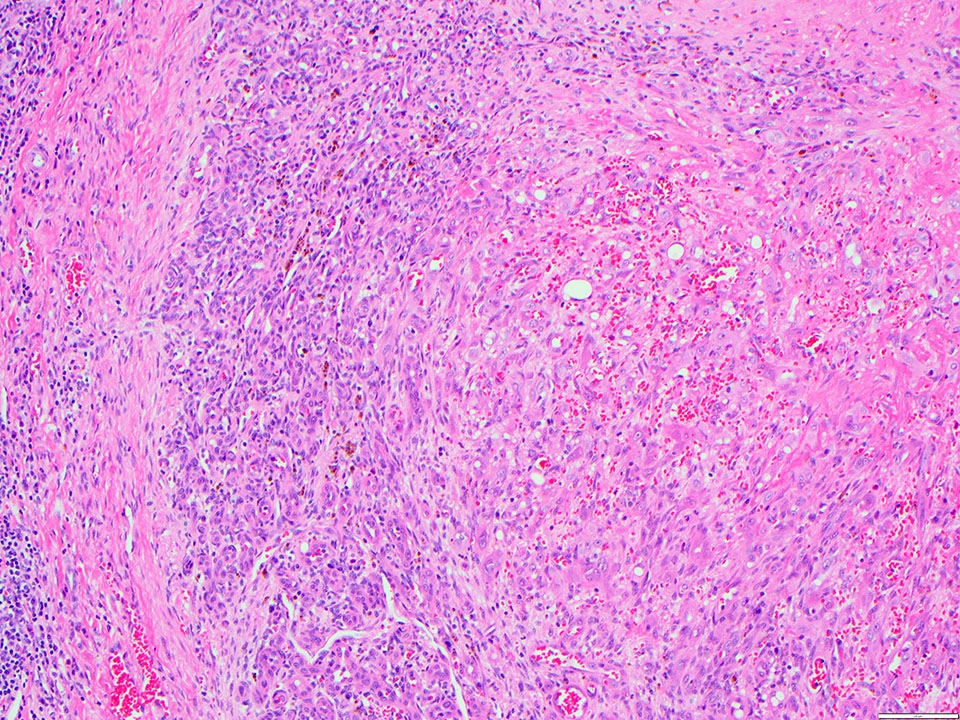
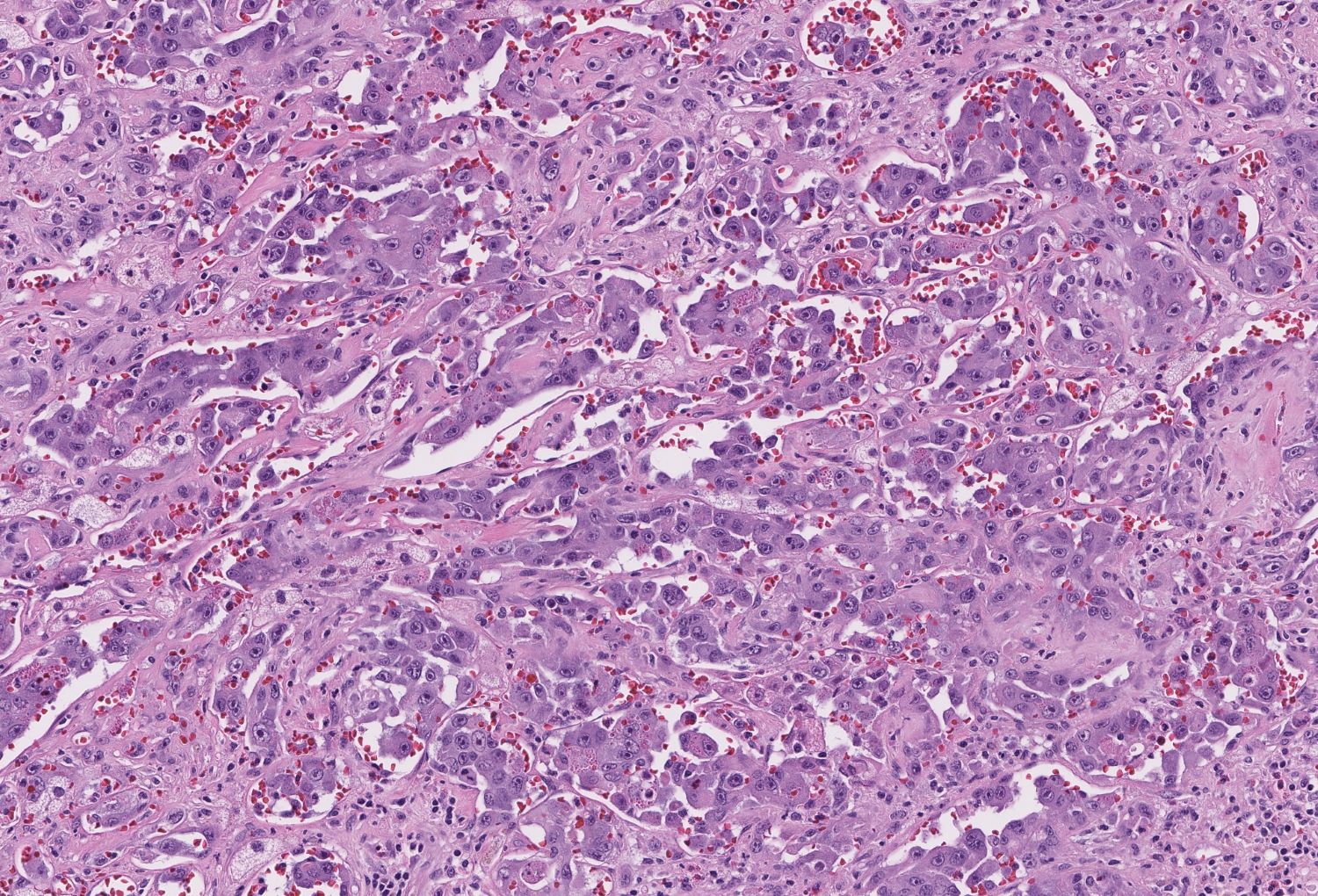
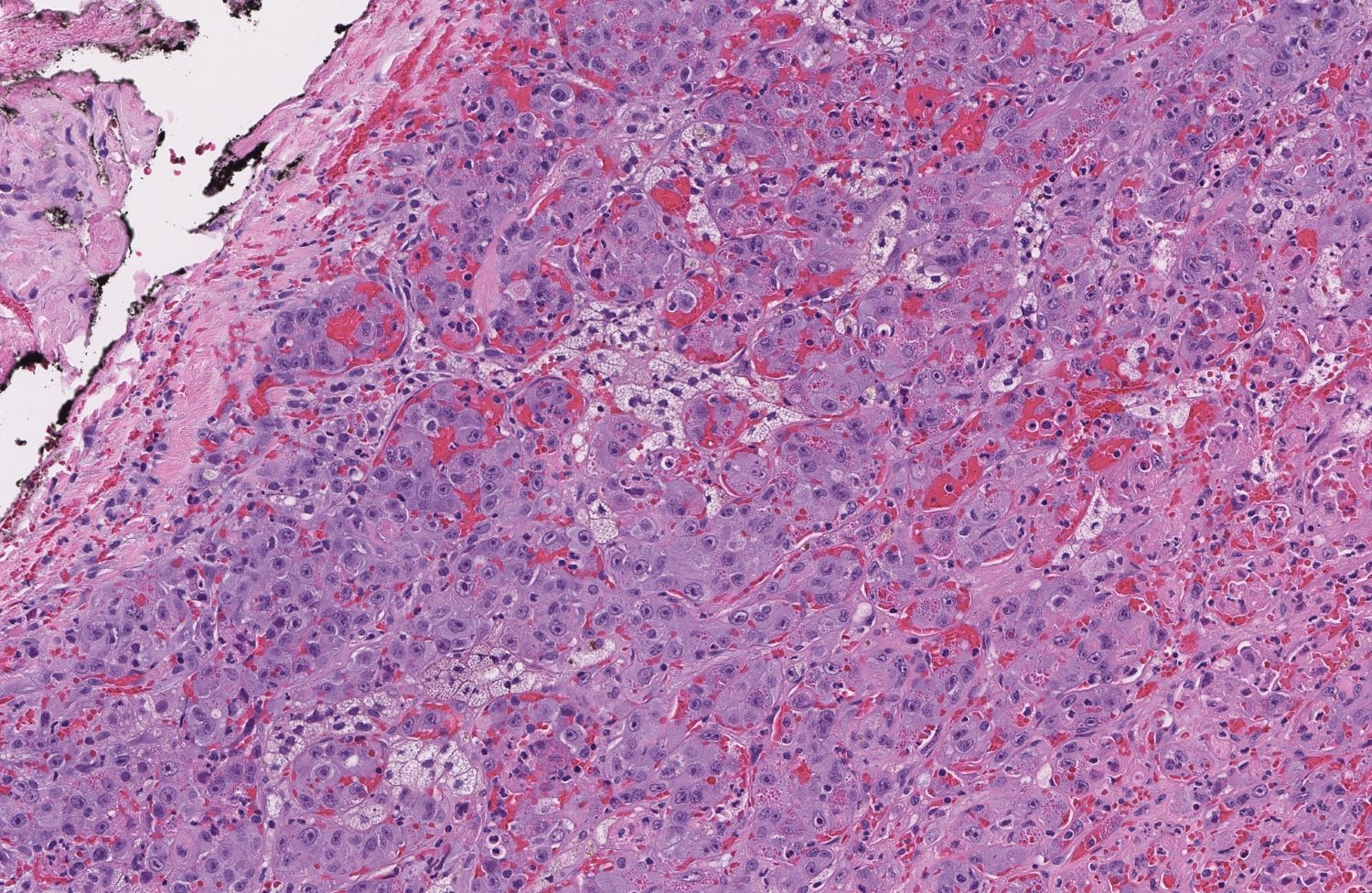
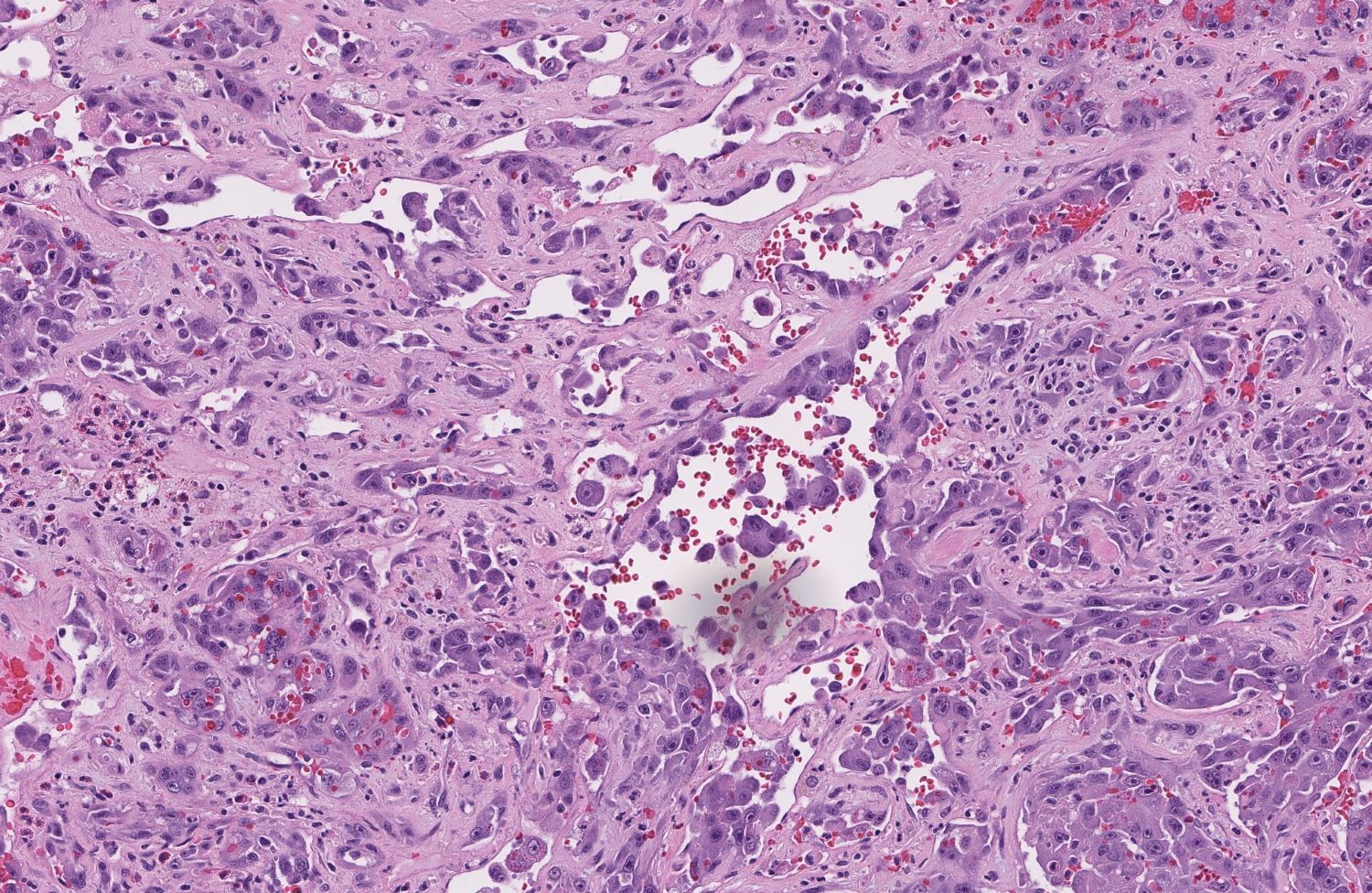
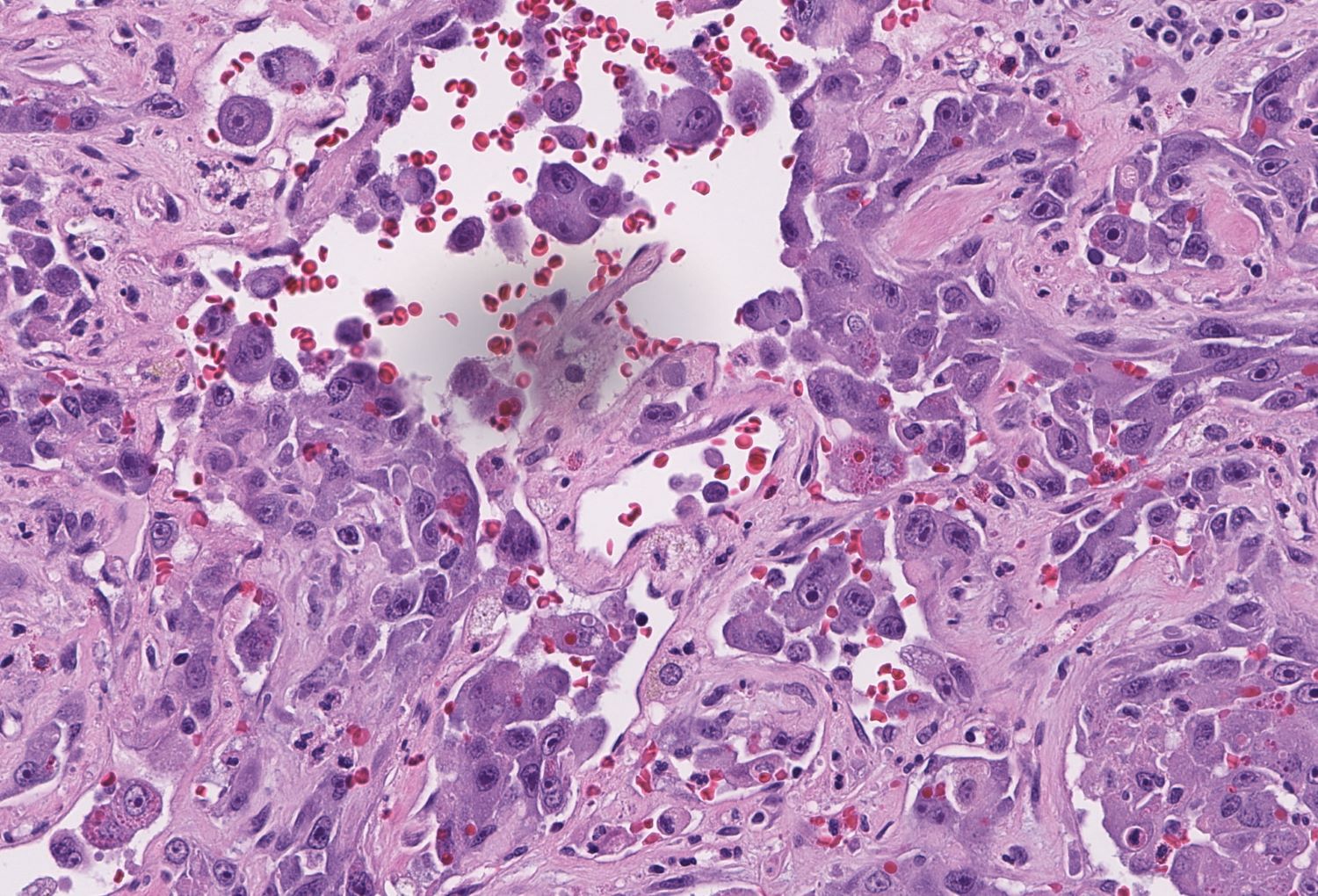
- Angiosarcoma has a wide morphologic appearance, ranging from lesions that are cytologically bland and vasoformative, to solid sheets of highly pleomorphic cells without definitive vasoformation
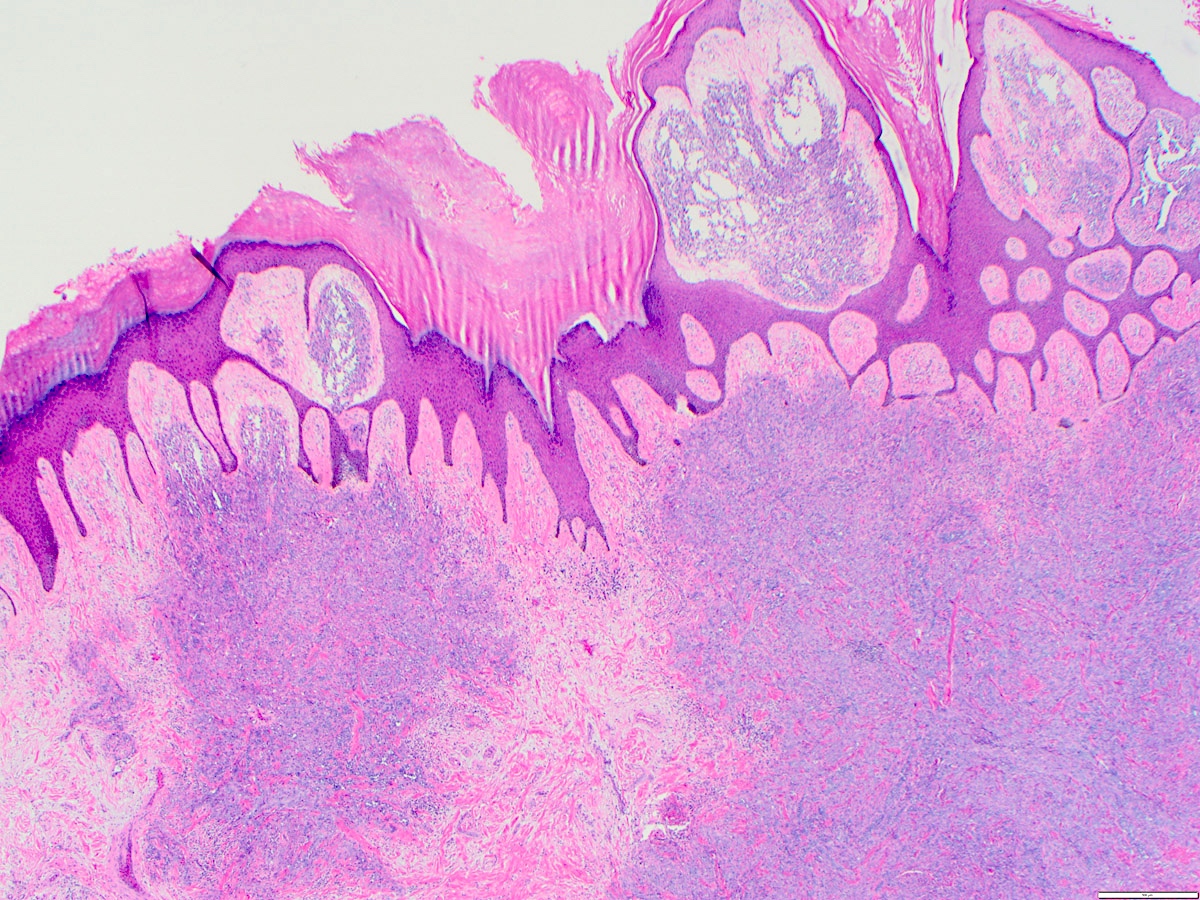
- Numerous irregularly shaped anastomosing vascular channels lined by atypical endothelial cells with a highly infiltrative architecture and poor demarcation
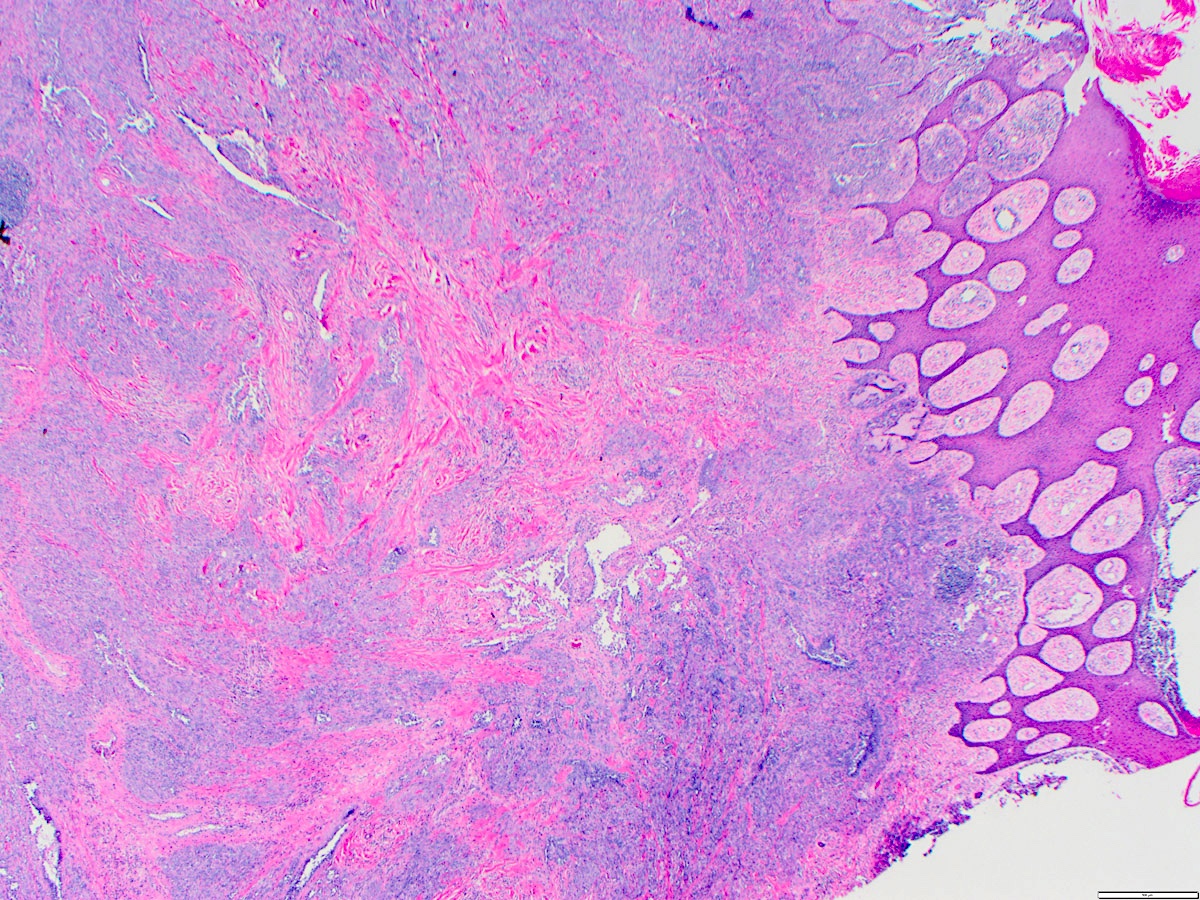
- Tumor cells are typically plump, pleomorphic and mitotically active
- They can be spindle shaped, polygonal, epithelioid and primitive round cells, forming papillae or solid nests within vascular lumina
- Tumor vessels ramify the dermis and intercalate through dermal collagen and subcutaneous soft tissues
- Because of the heterogeneous histologic features in poorly differentiated tumors, the histological identification of an angiosarcoma can be challenging
- Solid growth pattern often presents in poorly differentiated angiosarcoma
- Intratumoral hemorrhage is common
- Stromal lymphoid aggregates may also be present
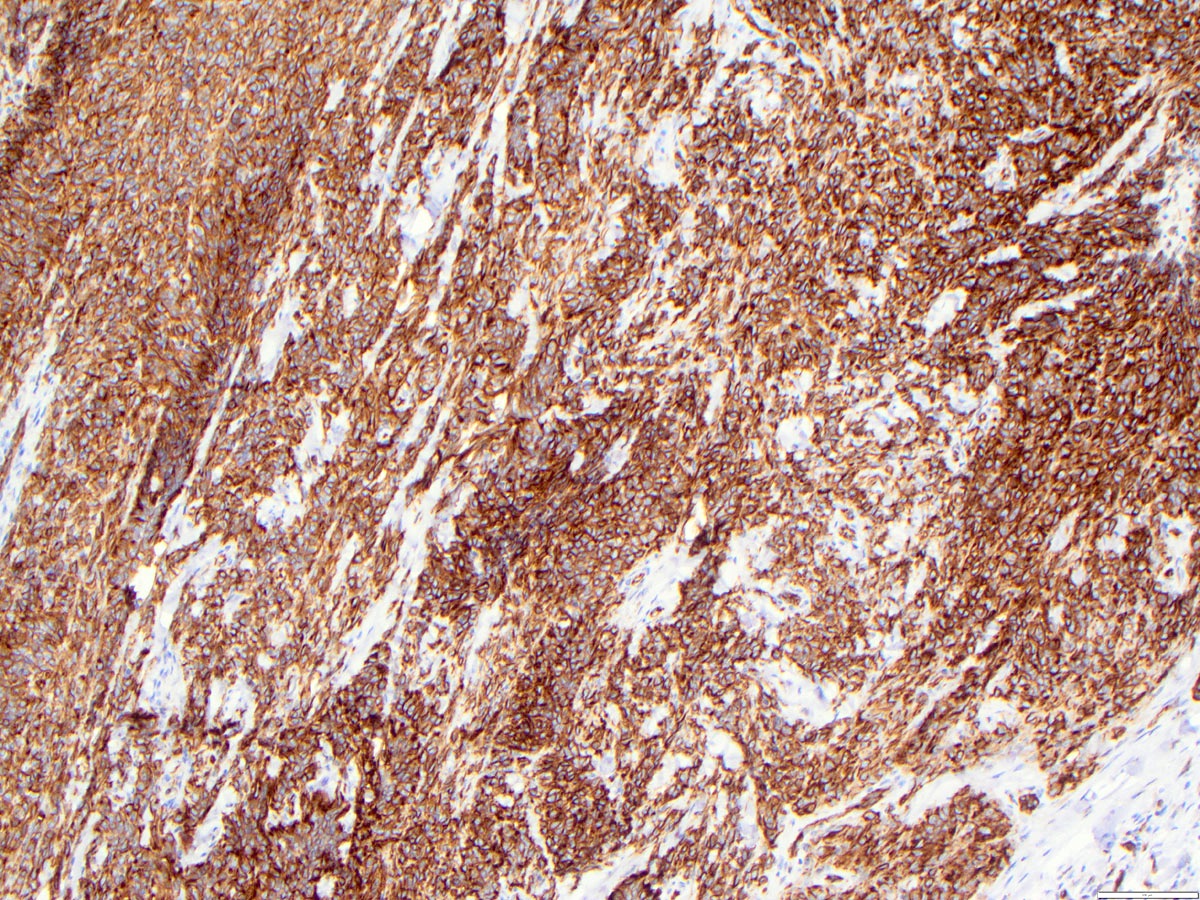
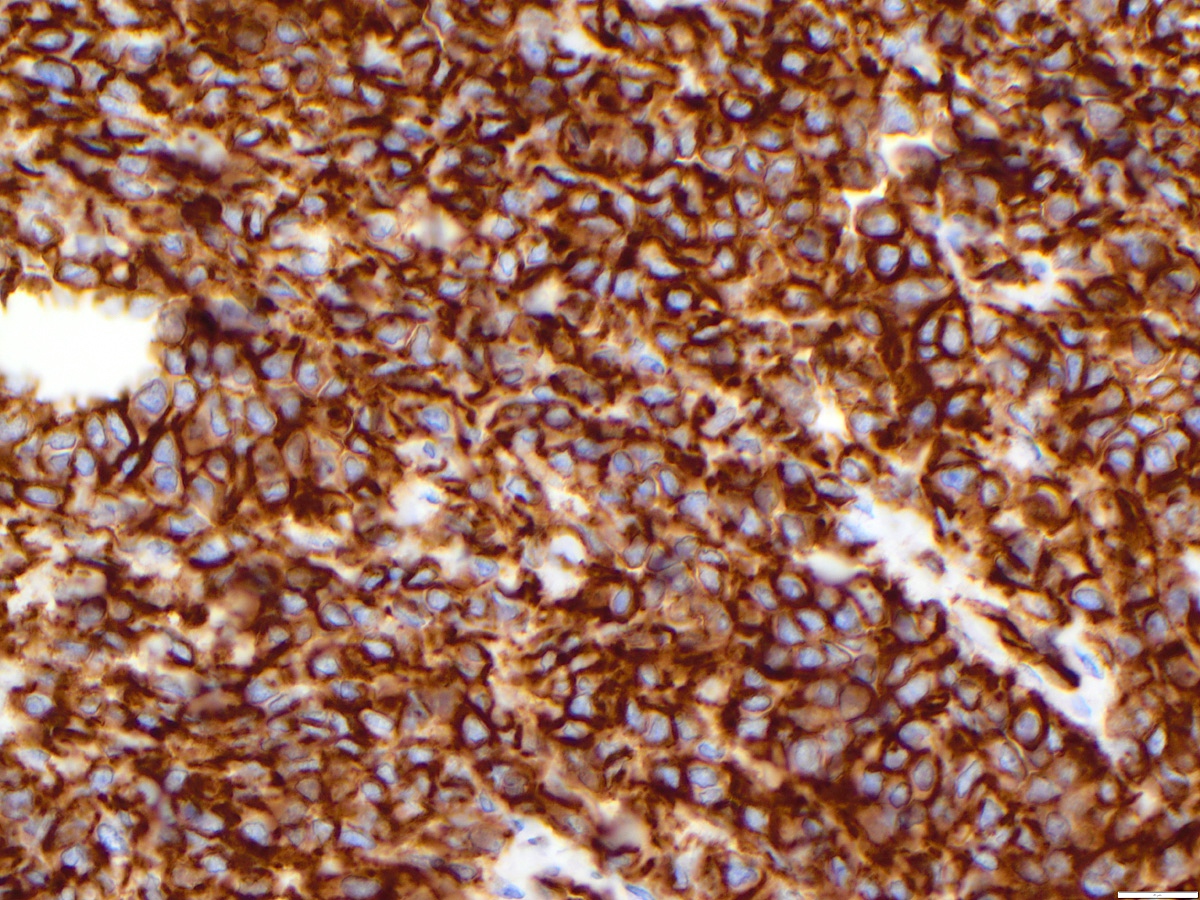
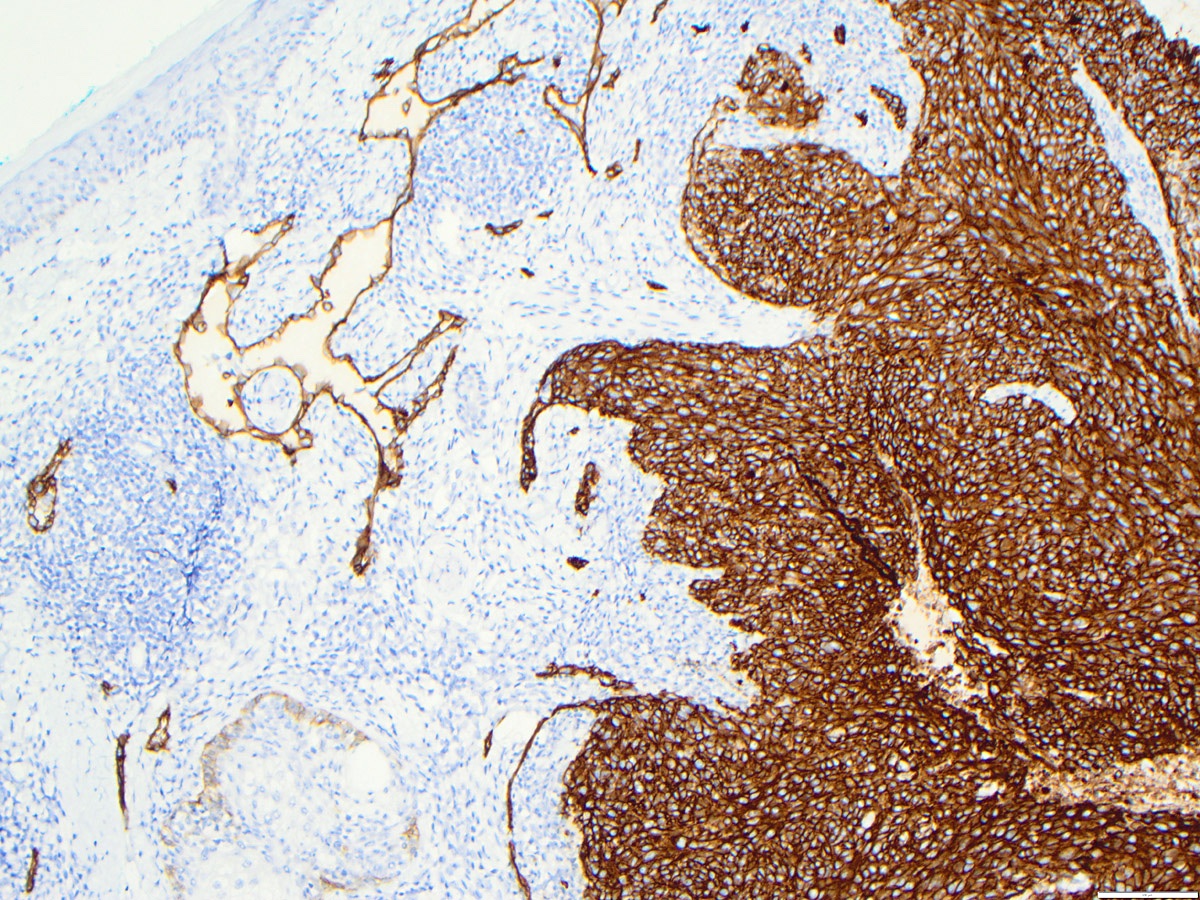
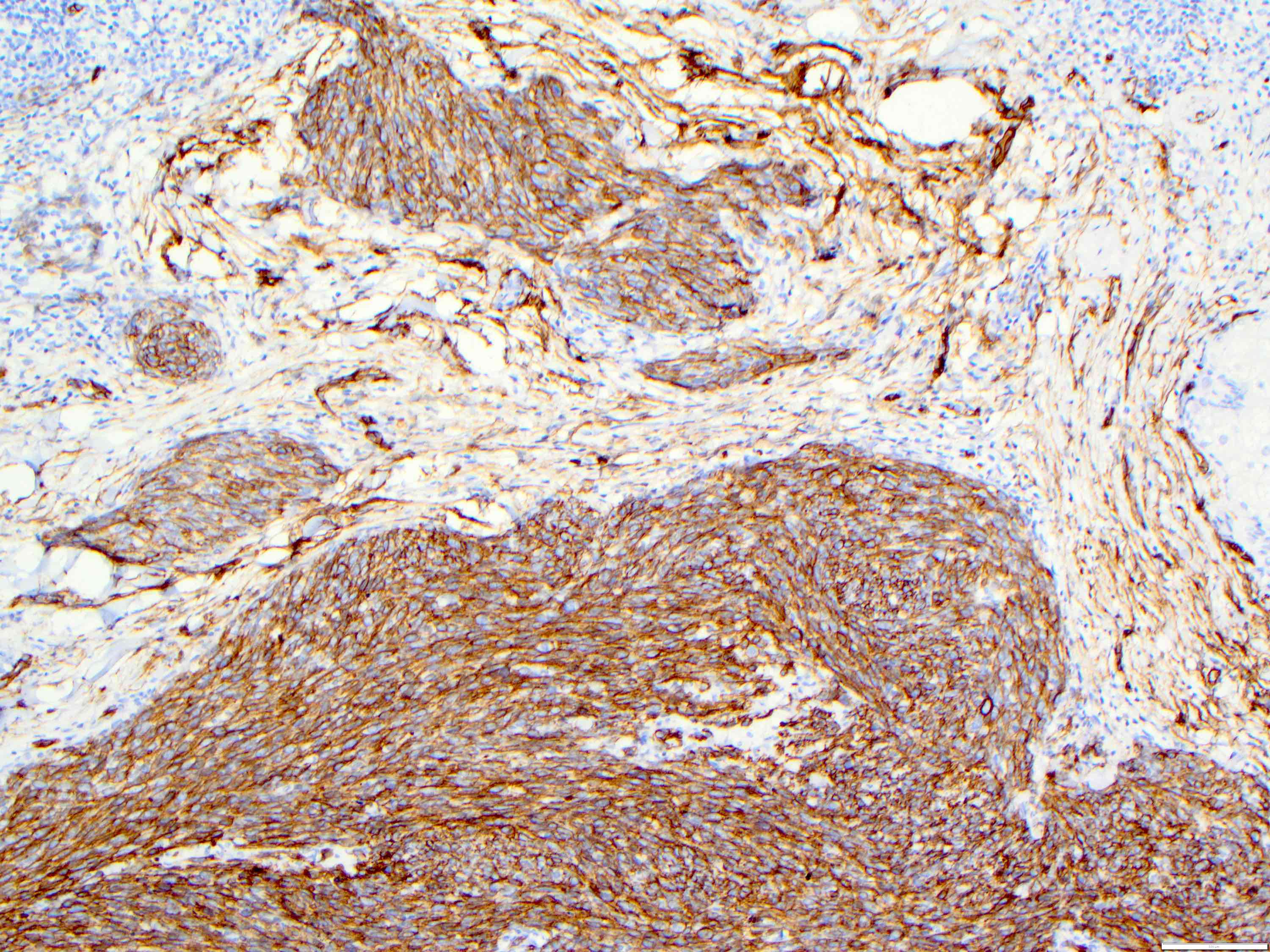
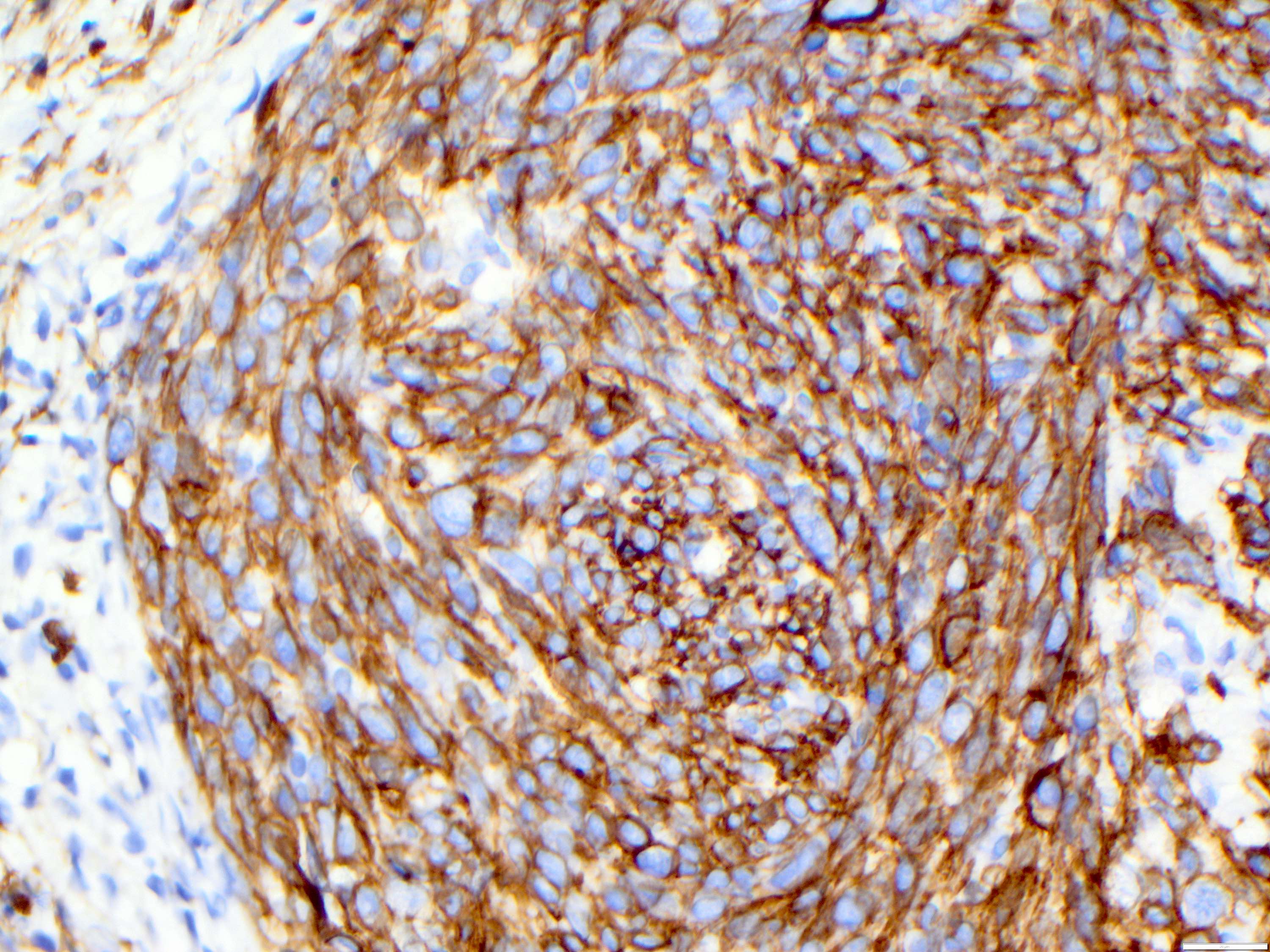
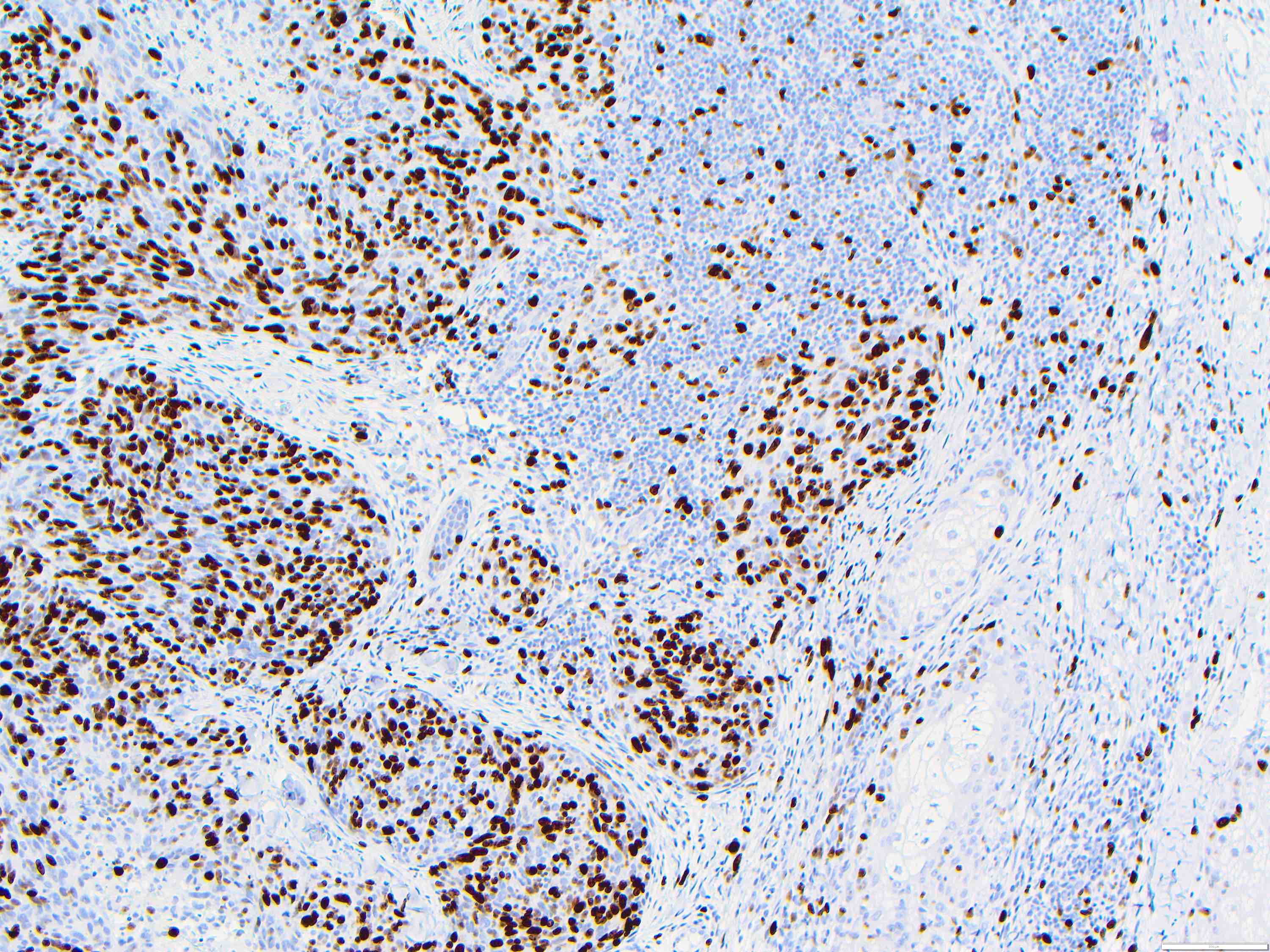
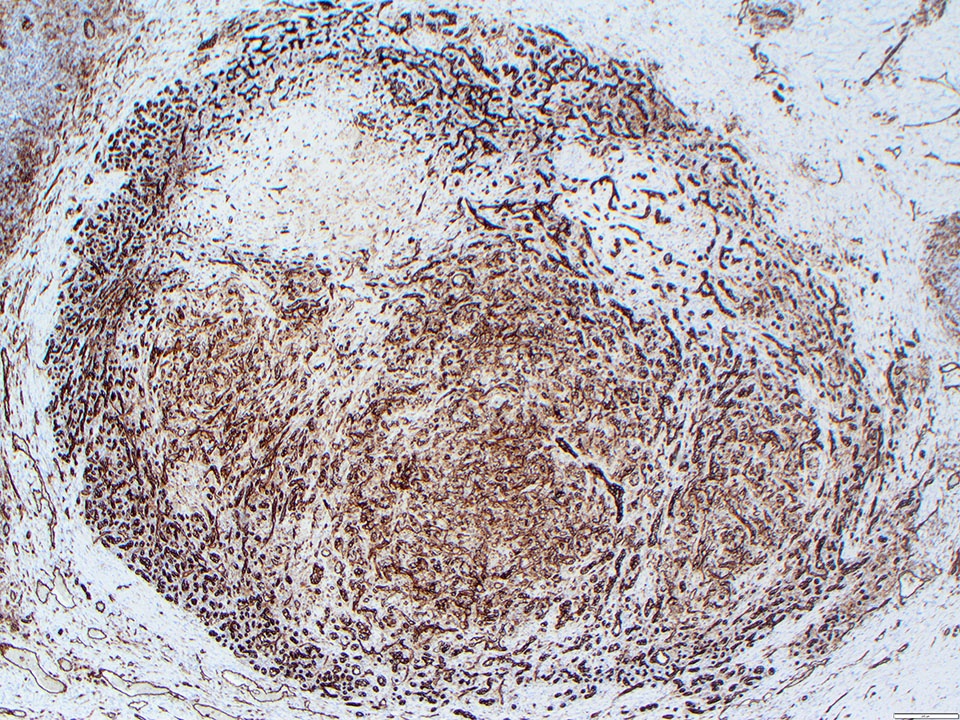
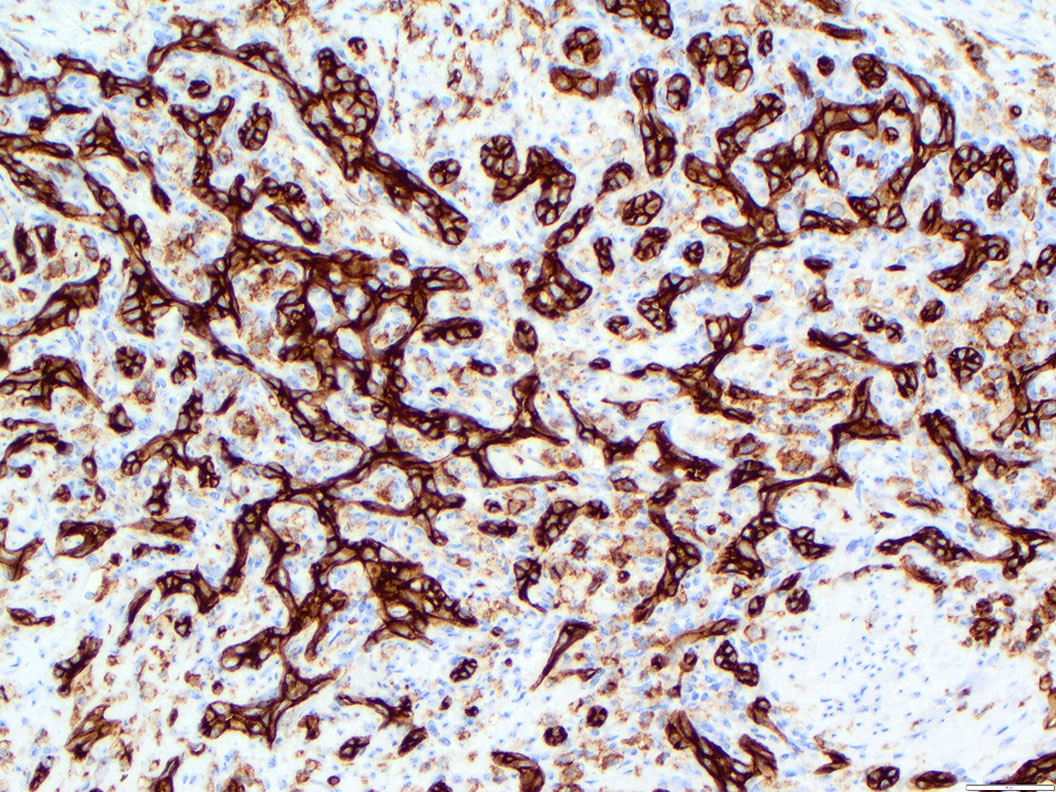
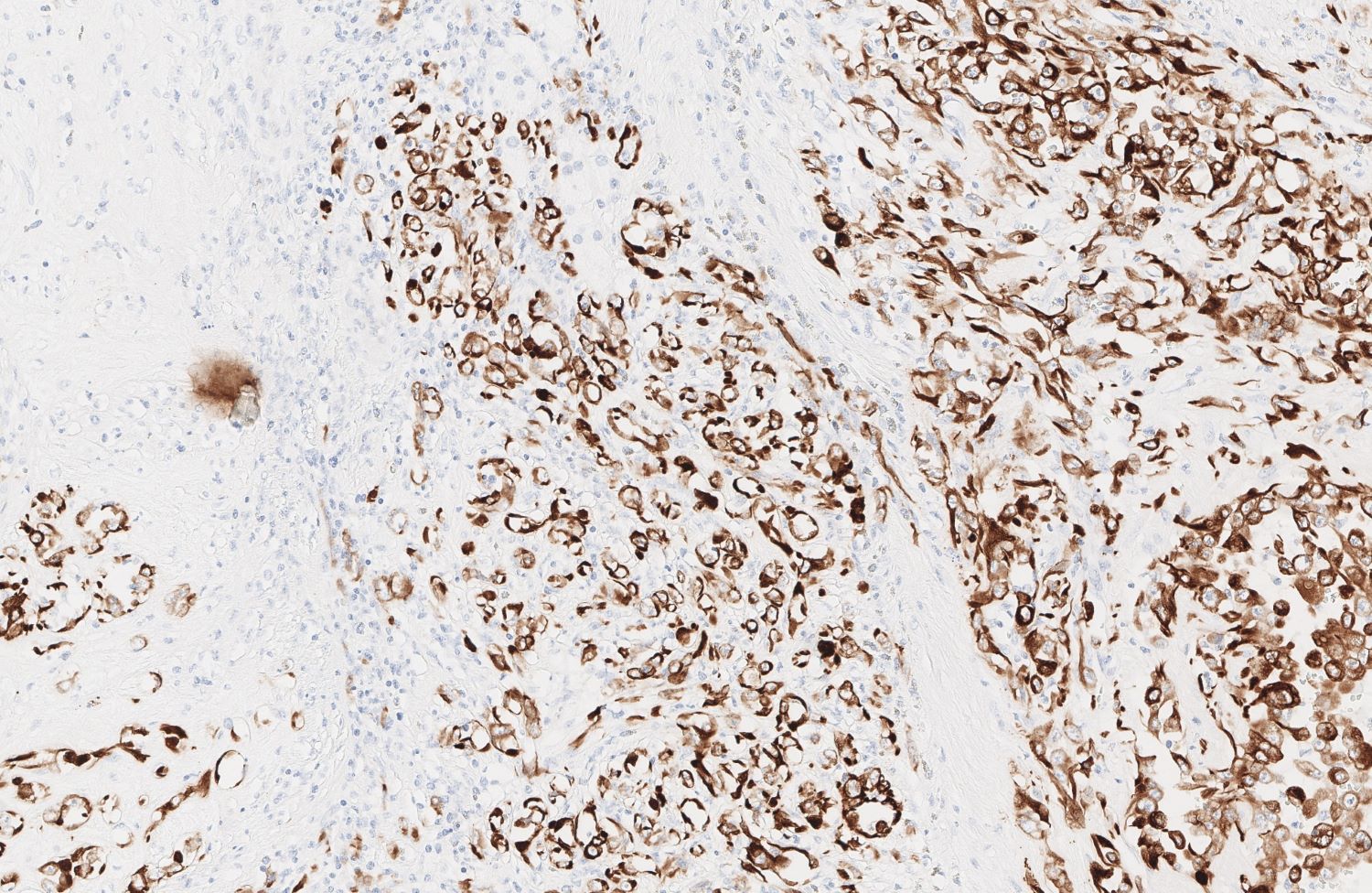
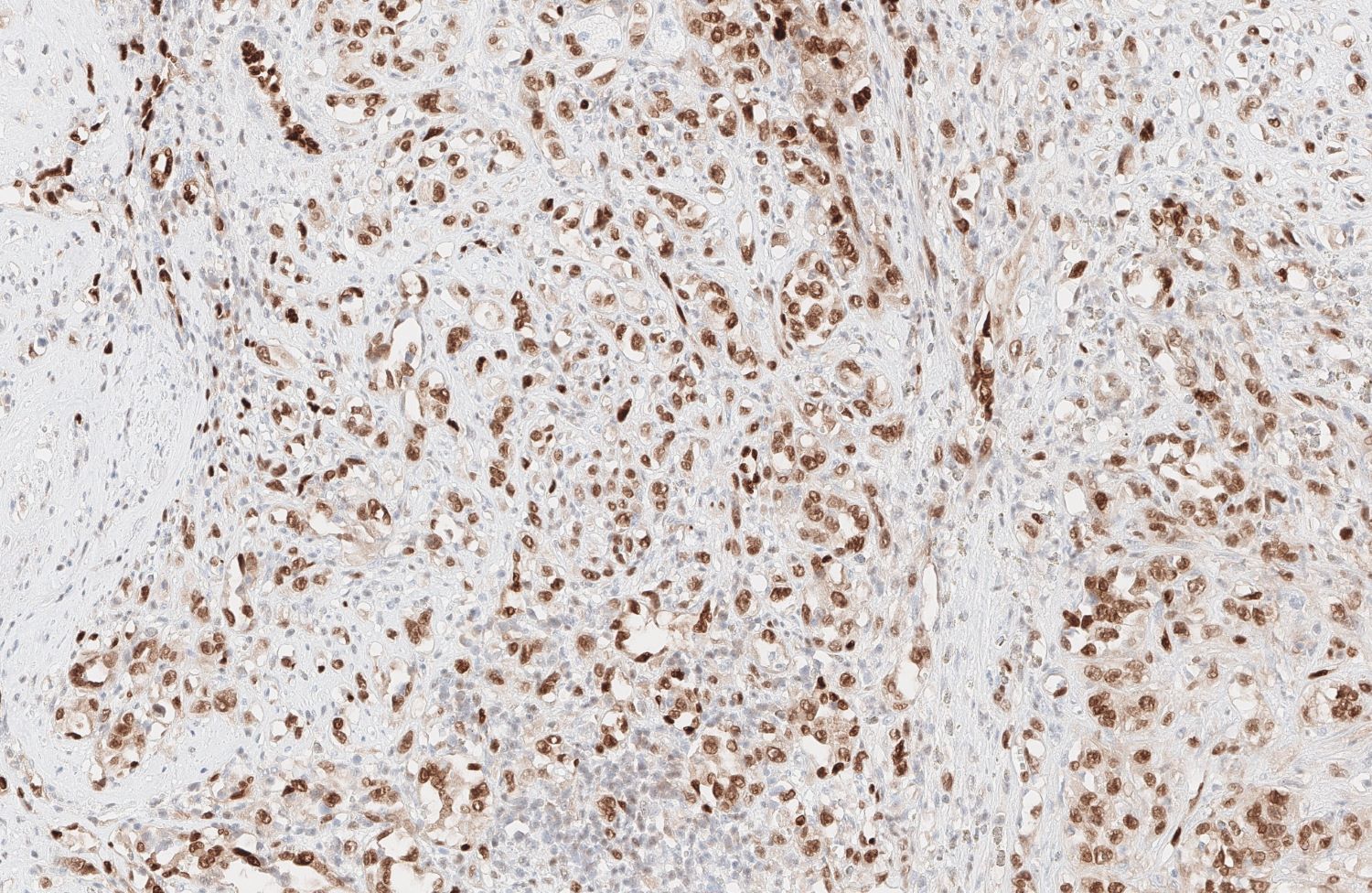
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Zan Ahmed, M.D., S. Shawn Liu, M.D., Ph.D. and Thuy L. Phung, M.D., Ph.D.
Contributed by Kyle Haggerty (M.D. candidate) and David Loeffler, D.O. (Case #509)
Positive stains
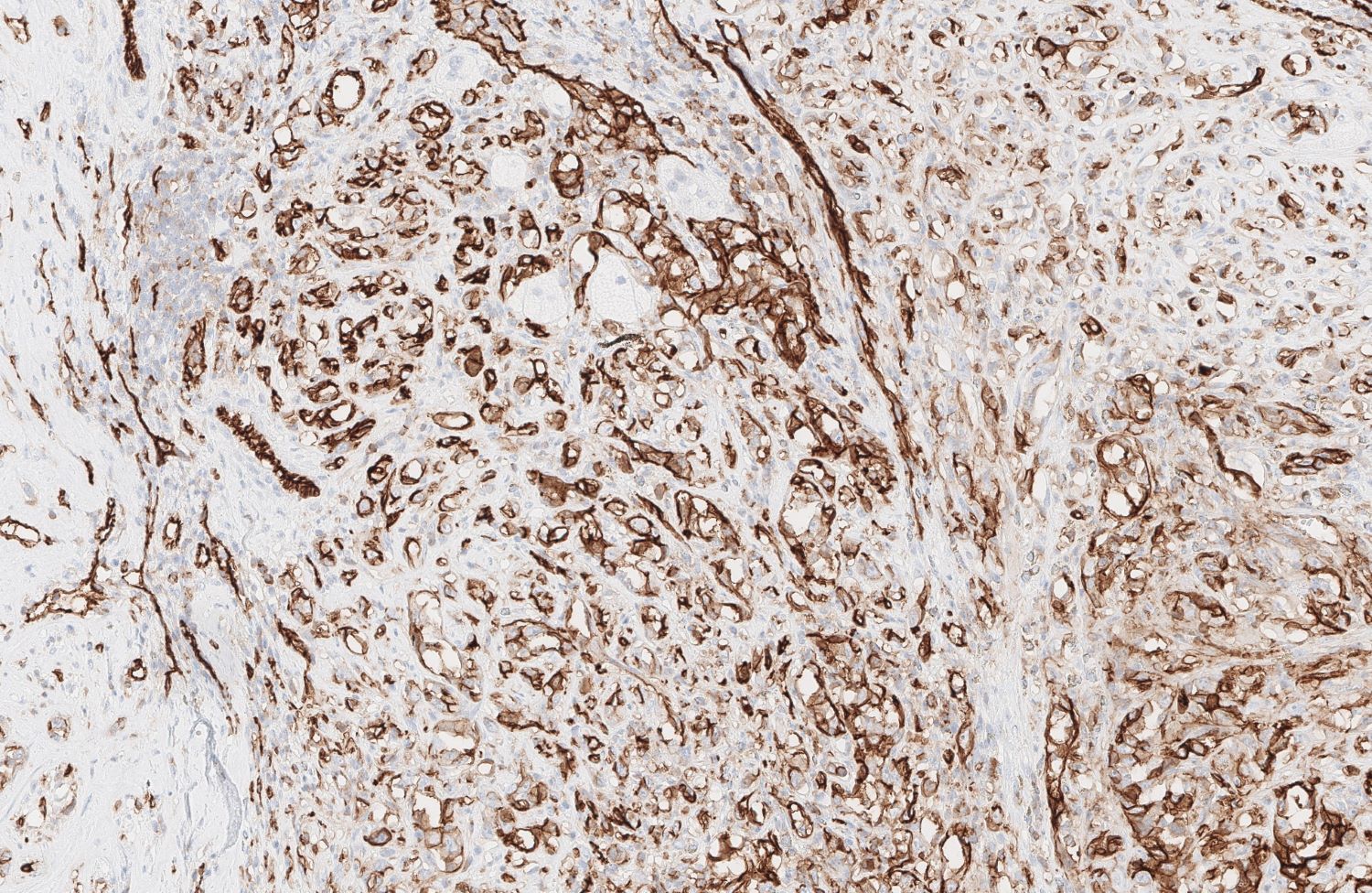
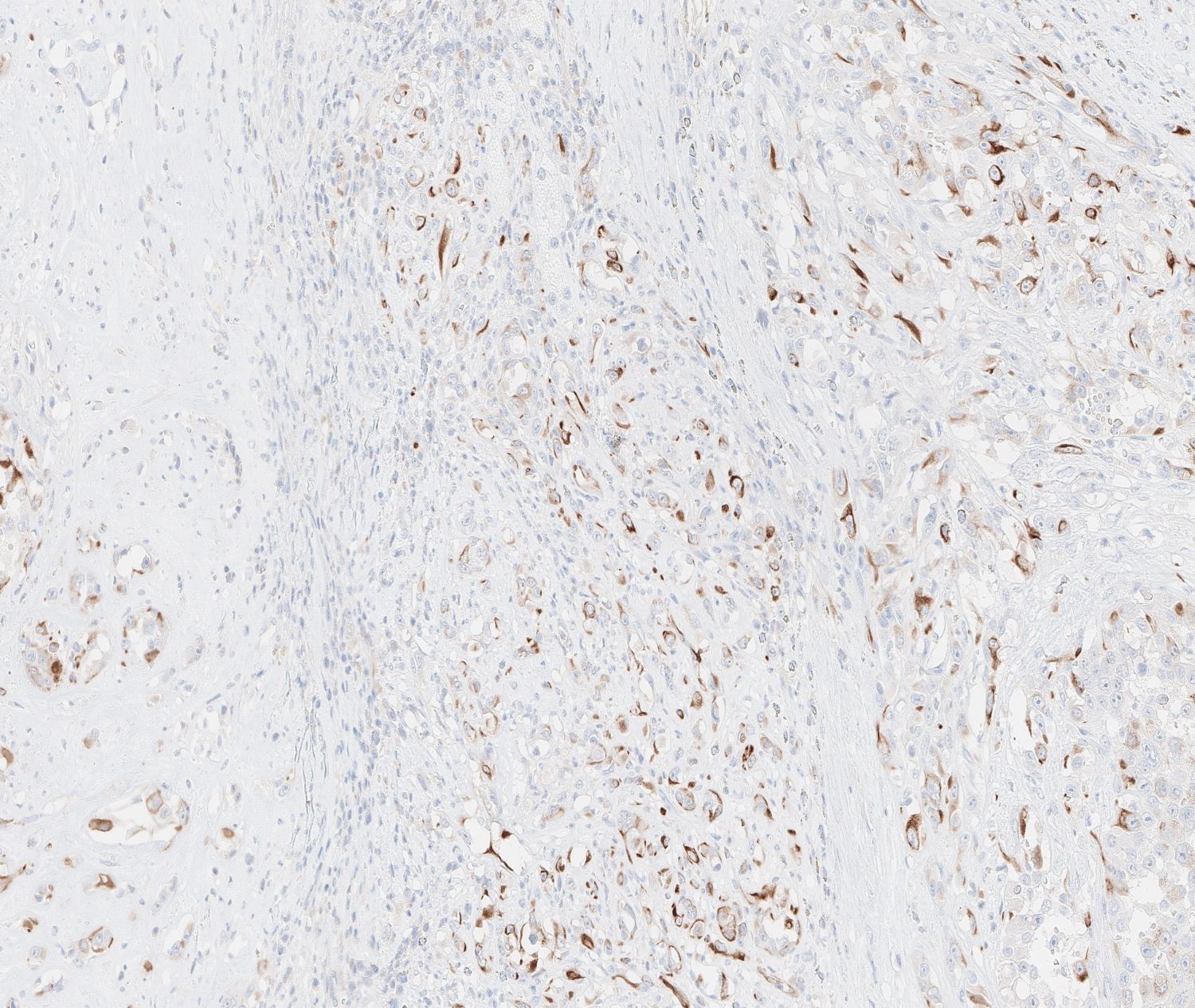
- Angiosarcoma expresses endothelial cell markers, including CD31, CD34, ERG, FLI1, VEGF and factor VIII
- Cytokeratin, EMA and CD30 may be expressed in a subset of epithelioid angiosarcoma
- Lymphatic marker podoplanin as determined by D2-40 immunostain is variably expressed and suggests focal lymphatic differentiation in the tumor
Negative stains
- Tumor is negative for HHV8 (human herpesvirus 8, a Kaposi sarcoma biomarker)
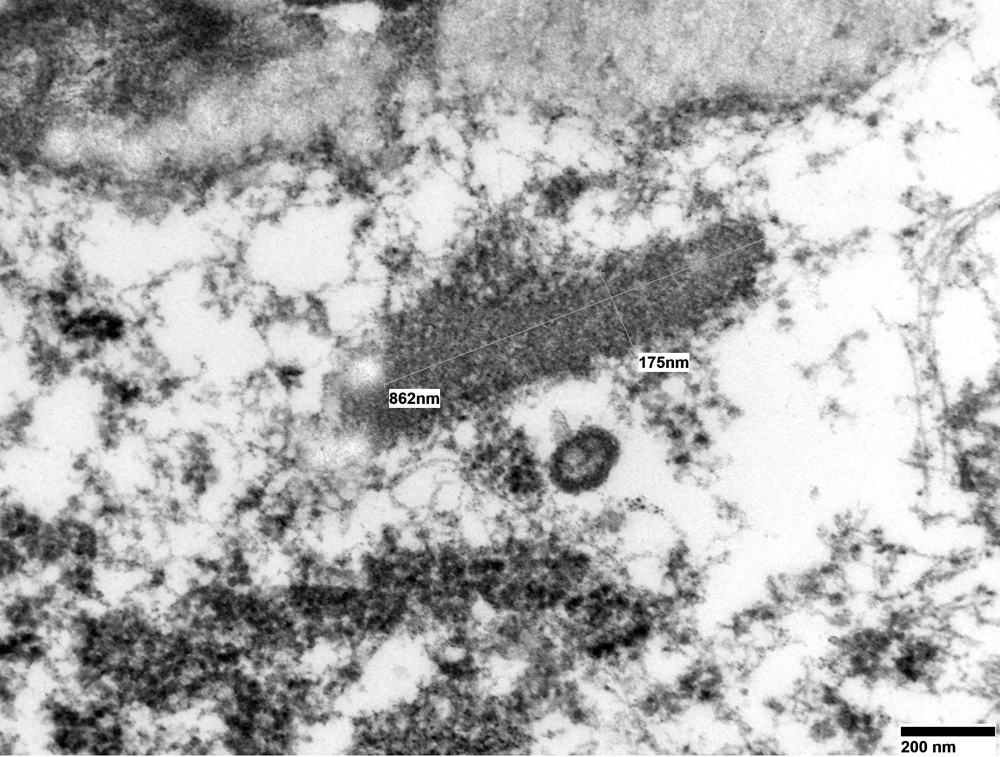
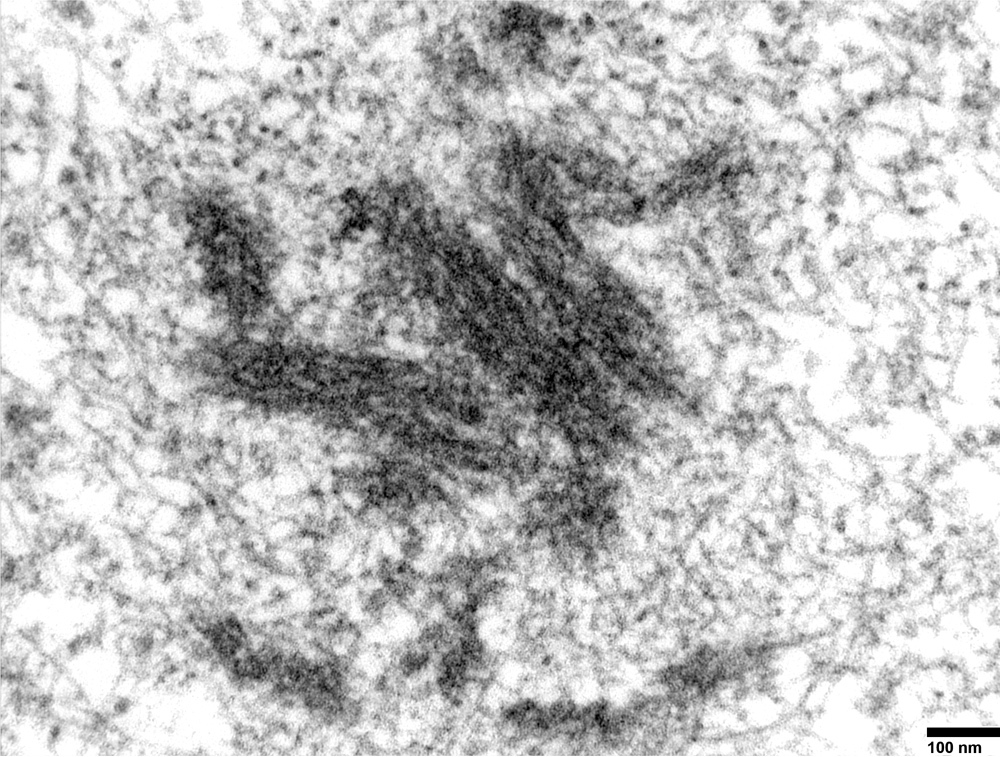
Electron microscopy description
- Weibel-Palade bodies, which are long, cylindrical, rod shaped bodies with a single membrane and containing microtubules in matrix, can be identified in the cytoplasm of endothelial cells
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Angiosarcoma is characterized by upregulation of vascular specific receptor tyrosine kinases, such as TIE1, KDR, TEK and FLT (Curr Urol Rep 2018;19:4)
- Has overexpression of HIF1 alpha and HIF2 beta, which are upstream regulators of VEGF (Curr Urol Rep 2018;19:4)
- High level of c-MYC gene amplification by FISH is seen in radiation induced and chronic lymphedema associated angiosarcoma (Curr Urol Rep 2018;19:4)
- Some tumors harbor recurrent PTPRB and PLCG1 mutations, which are involved in angiogenesis (Curr Urol Rep 2018;19:4)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, superior medial right forehead, biopsy:
- Superficial portion of an angiosarcoma, transected at the base (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show a dense and hypercellular dermal proliferation of spindle shaped and epithelioid malignant cells with enlarged pleomorphic and hyperchromatic nuclei with speckled chromatin pattern. The tumor is highly vascularized with numerous irregularly shaped blood vessels and hemorrhagic areas. Foci of tissue necrosis are present. The tumor stroma is desmoplastic and edematous with abundant lymphocytic infiltrates. There are numerous mitotic figures in the tumor. The tumor cells are strongly positive for the vascular markers CD31 and CD34 and for the lymphatic marker D2-40. Ki67 immunostain shows high cell proliferative activity throughout the tumor. The tumor cells are negative for S100, MART1, SMA (smooth muscle actin), pancytokeratin AE1 / AE3 and desmin. Immunostains and H&E findings support the diagnosis of an angiosarcoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Atypical fibroxanthoma:
- Hemangioma:
- Well demarcated lobular architecture with well established vascular channels and single luminal lining of benign endothelial cells
- Kaposi sarcoma:
- Patch stage shows a mild dermal vascular proliferation with minimal endothelial atypia
- Associated with lymphocytes or plasma cell infiltration and hemosiderin deposits
- At the plaque stage, dermal vascular proliferation varies in size and is associated with eosinophilic spindle cells, instead of lymphocytes or plasma cells
- Nodular stage presents predominantly as a well circumscribed dermal mass of eosinophilic spindle cells that often lack endothelial lining
- Nodular stage is associated with red blood cell extravasation
- Positive for HHV8 (human herpesvirus 8)
- Retiform hemangioendothelioma:
- Resembles well differentiated angiosarcoma
- Presents in the extremities of young patients with slit-like space lined by hobnail neoplastic endothelial cells
- No significant cytological atypia
- Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma:
- Consists of fascicles of spindle shaped endothelial cells, congested capillaries, slit-like vascular spaces in lobular and infiltrative patterns
- Areas of spindle shaped cells resemble Kaposi sarcoma
- Negative for HHV8
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma:
- Round, polygonal cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and vesicular nuclei arranged in short cords or nests
- Surrounded by hyaline and myxoid stroma
- Spindle cell hemangioma:
- Biphasic tumor
- Admixture of thin walled, congested cavernous vascular spaces and solid areas of spindled to epithelioid endothelial cells
- Large, calcified thrombi may be present
Board review style question #1
A 78 year old man presents with a rapidly growing purpuric and nodular cutaneous lesion on the left forehead. The H&E histological images of the biopsy of the lesion are shown above. What is the most likely diagnosis of this lesion?
- Angiosarcoma
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- Hemangioma
- Kaposi sarcoma
- Targetoid hemangioma
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following immunohistochemical stains is most likely negative for angiosarcoma?
- CD31
- CD34
- D2-40
- ERG
- HHV8
Board review style answer #2
Board review style question #3
Which stain will help differentiate epithelioid angiosarcoma from a poorly differentiated adrenal cortical carcinoma?
- ERG
- Pancytokeratin
- SF1
- VEGFR3
- Vimentin
Board review style answer #3
A. ERG. ERG is sensitive and specific for vascular differentiation. Although not on the list of potential answers, CD31 and Factor VIII are also sensitive and specific markers for vascular differentiation and can additionally be useful in this case. Steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1) is a transcription factor that has a role in steroidogenesis and is expressed in the adrenal cortex and other gonadotrophic cells in the pituitary and gonads. While usually a very specific marker, its expression may be lost in up to 12% of adrenal cortical carcinomas (Hum Pathol 2013;44:822). Both epithelioid angiosarcoma and carcinoma will stain positive for pancytokeratin. While VEGFR3 is specific for vascular differentiation, it is less sensitive and will have variable staining in angiosarcoma. While vimentin is quite sensitive for angiosarcoma, it may not be helpful because carcinomas may also stain positive for vimentin.
Comment Here
Reference: Angiosarcoma
Comment Here
Reference: Angiosarcoma