Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Peripheral smear images | Additional referencesCite this page: Amita R. Folate deficiency anemia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/hematofolatedefanemia.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Folate deficiency is a low level of folic acid (Vitamin B9) in the body
Essential features
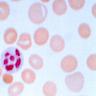
- Characterized by macrocytic anemia
Terminology
- Also called Vitamin B9 deficiency
Etiology
- Inadequate ingestion of folate containing foods due to: alcoholism (alcohol dehydrogenase binds folate), psychiatric morbidities, elderly
- Impaired absorption: celiac disease, tropical sprue, achlorhydria, anticonvulsant drugs (Dilantin), zinc deficiency, bacterial overgrowth in blind loops, strictures, jejunal diverticula
- Impaired metabolism, leading to inability to utilize absorbed folate: methotrexate and trimethoprim (folate antagonists)
- Hypothyroidism (decreases hepatic levels of dihydrofolate reductase)
- Congenital deficiency of enzymes of folate metabolism
- Increased requirement: infancy, pregnancy, lactation, malignancy, concurrent infection (immunoproliferative response), chronic hemolytic anemia (increased hematopoiesis)
- Increased excretion/loss: vitamin B12 deficiency (causes "folate trap"), chronic alcoholism (increased excretion of folate into bile), hemodialysis (may have excess folate loss)
- Increased destruction: superoxide can inactivate folate
Clinical features
- Symptoms due to anemia: weakness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, headache, palpitations, shortness of breath, cardiac failure
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea (especially after meals)
- Neurologic: cognitive impairment, dementia, depression
Complications:
- Coronary artery disease, stroke
- Pregnancy complications include spontaneous abortion, abruption placentae, congenital malformations (neural tube defects), severe language delay
Diagnosis
- Serum folate levels < 3 ng/mL and a red blood cell (RBC) folate level < 140 ng/mL indicate folate deficiency
- Normal serum folate level is 2.5-20 ng/mL
- Normal serum cobalamin is 200-900 pg/mL
Laboratory
- The RBC folate level generally indicates folate stored in the body
- Serum folate level tends to reflect acute changes in folate intake
- Mild hyperhomocystinemia is total plasma concentration of 15-25 mmol/L; moderate hyperhomocystinemia is 26-50 mmol/L
Case reports
- Pyrexia in a patient with megaloblastic anemia (Iran J Med Sci 2013; 38(2 Suppl): 198)
- Folic acid deficiency optic neuropathy (J Med Case Reports 2008;2:299)
- Severe folate deficiency in pregnancy with normal red cell folate level (Clin Lab Haematol 2006 Feb;28:66)
Treatment
- Important to rule out cobalamin (Vitamin B12) deficiency because folate treatment will not improve neurologic abnormalities due to cobalamin deficiency
Cytology description
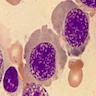
- Bone marrow biopsy and aspirate may show a hypercellular bone marrow with a megaloblastic maturation of cells, which morphologically resembles changes of vitamin B12 deficiency