Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Siddique S, Ali RH. Morton neuroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/jointsmortonsneuroma.html. Accessed September 18th, 2025.
Definition / general
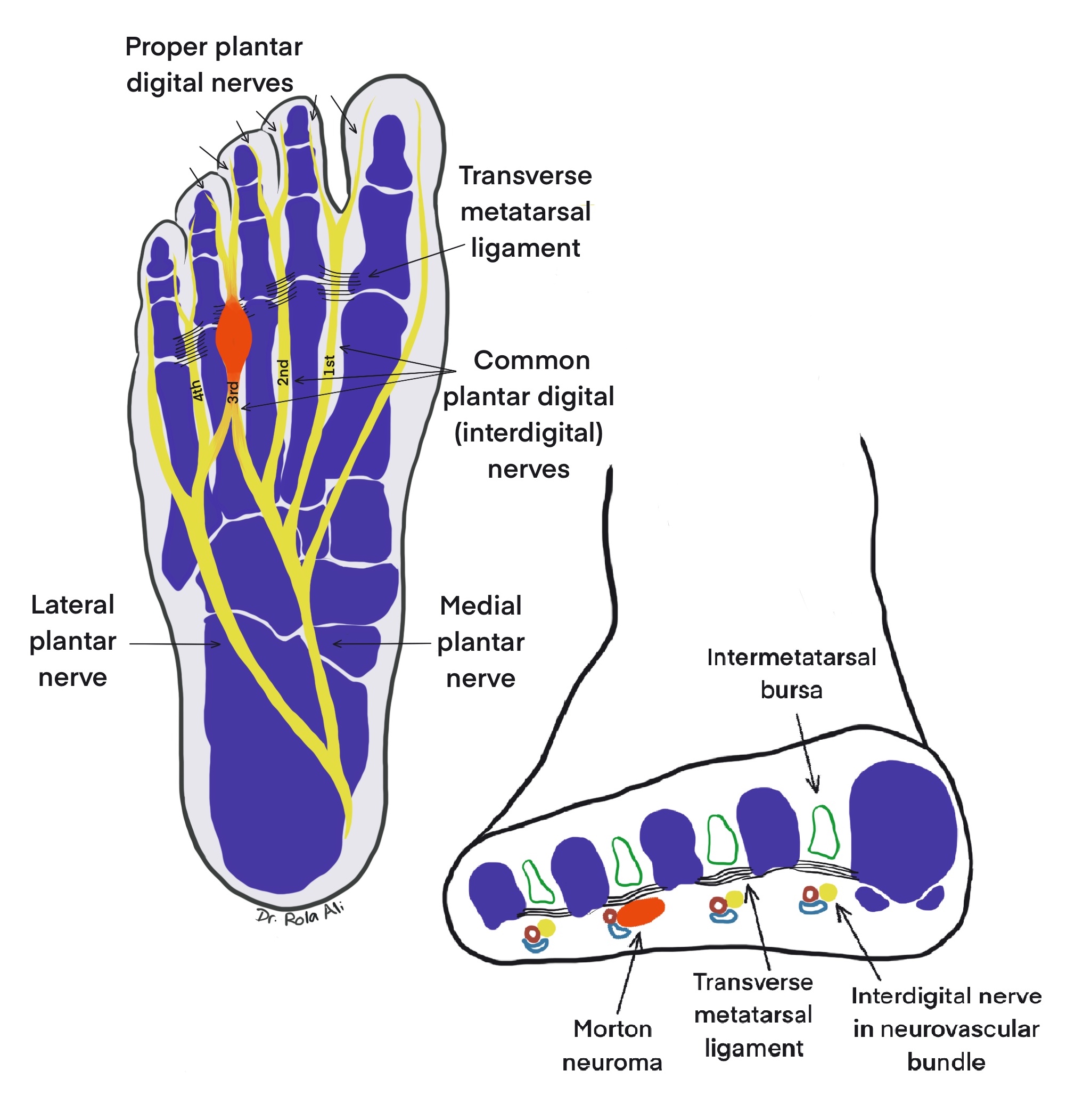
- Morton neuroma is a nonneoplastic, degenerative neuropathy with a strong predilection for the third interdigital nerve of the foot
- One of the most common disorders encountered in the foot (Clin Radiol 2021;76:235.e15)
Essential features
- Morton neuroma is a degenerative fibrotic neuropathy
- Typically affects the interdigital nerve that innervates the third webspace (Radiographics 1999;19:1253)
- Strong predilection for middle aged women (Foot Ankle 1983;3:238)
- Characterized microscopically by nerve fiber degeneration and excessive intraneural and perineural fibrosis
- Original series by Thomas Morton in 1876 (Am J Med Sci 1876;71:37)
Terminology
- The term neuroma is a misnomer
- Synonyms: interdigital neuroma, intermetatarsal neuroma, Morton metatarsalgia, plantar neuroma
ICD coding
- ICD-10: G57.6 - lesion of plantar nerve, applicable to Morton metatarsalgia
Epidemiology
- Strong predilection for middle aged women; F:M is as high as 18:1 (Radiographics 1999;19:1253, Foot Ankle 1983;3:238)
- Associated with wearing pointed and heeled shoes (J Foot Ankle Surg 1996;35:112)
Sites
- Classical: third interdigital nerve (also known as third common plantar digital nerve) that innervates the webspace between the third and fourth metatarsal heads
- Less common: second interdigital nerve
- Very rare in first and fourth interdigital nerves
- Could be multiple in the same foot, mostly third and second nerves (J Foot Ankle Surg 2015;54:320, J Foot Ankle Surg 2022;61:163)
- Neuromas that are morphologically similar to Morton may occasionally be encountered in the hand following chronic trauma (Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2022;10:e4035, J Hand Surg Am 2010;35:499)
- References: Clin Radiol 2021;76:235.e15, Radiographics 1999;19:1253, J Foot Ankle Surg 1996;35:112
Pathophysiology
- Not fully understood
- Hypotheses, probably multifactorial
- Repetitive microtraumas: mechanical stress of walking causes pinching of the interdigital nerve by the metatarsal heads and the metatarsophalangeal joints (Foot Ankle Int 2007;28:1007, Clin Radiol 2021;76:235.e15)
- Intermittent neural ischemia: degenerative changes in the common plantar digital artery precede the nerve fibrosis (J Bone Joint Surg Br 1948;30B:84)
- Intermetatarsal bursitis: causing compression of the nerve, secondary inflammation and subsequent neural fibrosis (J Bone Joint Surg Br 1951;33-B:94, J Bone Joint Surg Br 1980;62-B:184)
- Entrapment: nerve entrapped between the deep transverse metatarsal ligament and the plantar aspect of the foot (Clin Orthop Relat Res 1979;142:90)
- Unlike the other interdigital nerves, the third nerve has a double origin from the medial and lateral plantar nerves, producing a sling over the belly of the flexor digitorum brevis, thus tethering the nerve and rendering it vulnerable to traction upon dorsiflexion (Med J Aust 1940;1:514, Foot Ankle 1983;3:238)
Etiology
- Hyperextension of the toes by pointed, heeled shoes increases pressure on the forefoot and is implicated in nerve injury (J Foot Ankle Surg 1996;35:112)
Clinical features
- Sharp burning pain in the plantar aspect of the forefoot around the metatarsal heads and metatarsophalangeal joints that radiates to the toes (metatarsalgia) (Foot Ankle 1983;3:238)
- Pain that is aggravated by walking and wearing tight shoes or high heels and alleviated by rest and removing the shoe
- May be associated with numbness and the feeling of a pebble in the shoe (J Clin Orthop Trauma 2020;11:406)
- Symptoms associated with larger size (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;175:649)
- Smaller asymptomatic lesions may be relatively common with no gender predilection (Radiology 1997;203:516)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is based on clinical history, examination and imaging (StatPearls: Morton Neuroma [Accessed 5 July 2023])
- Mulder click: pain and a palpable click elicited upon squeezing the 2 metatarsal heads together while putting pressure on the webspace
- Sullivan sign: divergence of the digits on either side of the neuroma on plain Xray
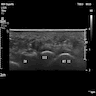
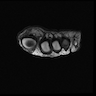
- Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are comparable modalities with high detection rates (Korean J Radiol 2007;8:148)
- Excellent concordance between clinical / intraoperative and histopathologic diagnosis (Foot Ankle Int 2016;37:70, Foot Ankle Spec 2017;10:520)
Radiology description
- Ultrasound: round to ovoid well defined hypoechoic lesion in the intermetatarsal space (Radiographics 1999;19:1253, Clin Radiol 2021;76:235.e15)
- MRI: low to iso signal on T1 weighted images and low to intermediate signal on T2 weighted images (Radiographics 1999;19:1253, Clin Radiol 2021;76:235.e15)
- Plain radiographs are usually normal but helpful to exclude other conditions (e.g., fractures, arthritis)
Prognostic factors
- Surgical interventions are associated with better pain relief compared to injection treatment: 68% after neurolysis and 74% after neurectomy (Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2021;163:531)
- Recurrence of symptoms postoperatively result from
- Formation of a traumatic neuroma in the stump (Foot Ankle 1992;13:153)
- Failure to resect the nerve as proximal as possible, leading to inadequate retraction of the nerve stump and subsequent tethering of remaining terminal branches (Foot Ankle 1992;13:153, Foot Ankle Clin 2014;19:437)
Case reports
- 30 year old man with history of traumatic little fingertip amputation and complicated surgeries developed fusiform enlargements of ulnar and radial proper digital nerves (Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2022;10:e4035)
- 46 year old woman with a 5 cm neuroma in the third webspace associated with macrodactyly and Raynaud phenomenon (Joints 2020;7:127)
- 55 year old woman with neuroma of the proper digital branch of the fourth toe presented with isolated extreme fourth toe pain (Cureus 2020;12:e8920)
Treatment
- Nonsurgical options: footwear modifications, orthoses, corticosteroid injections, alcohol injections, radiofrequency ablation (Acta Biomed 2020;91:60, J Clin Orthop Trauma 2020;11:406)
- Surgical options when nonoperative measures fail: neurolysis with or without nerve transposition, minimally invasive deep transverse intermetatarsal ligament release, metatarsal osteotomy, neurectomy (Foot Ankle Surg 2022;28:450)
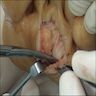
- Excision of the neuroma (neurectomy) by the dorsal or plantar approach is most successful (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2022;23:898)
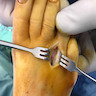
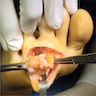
Clinical images
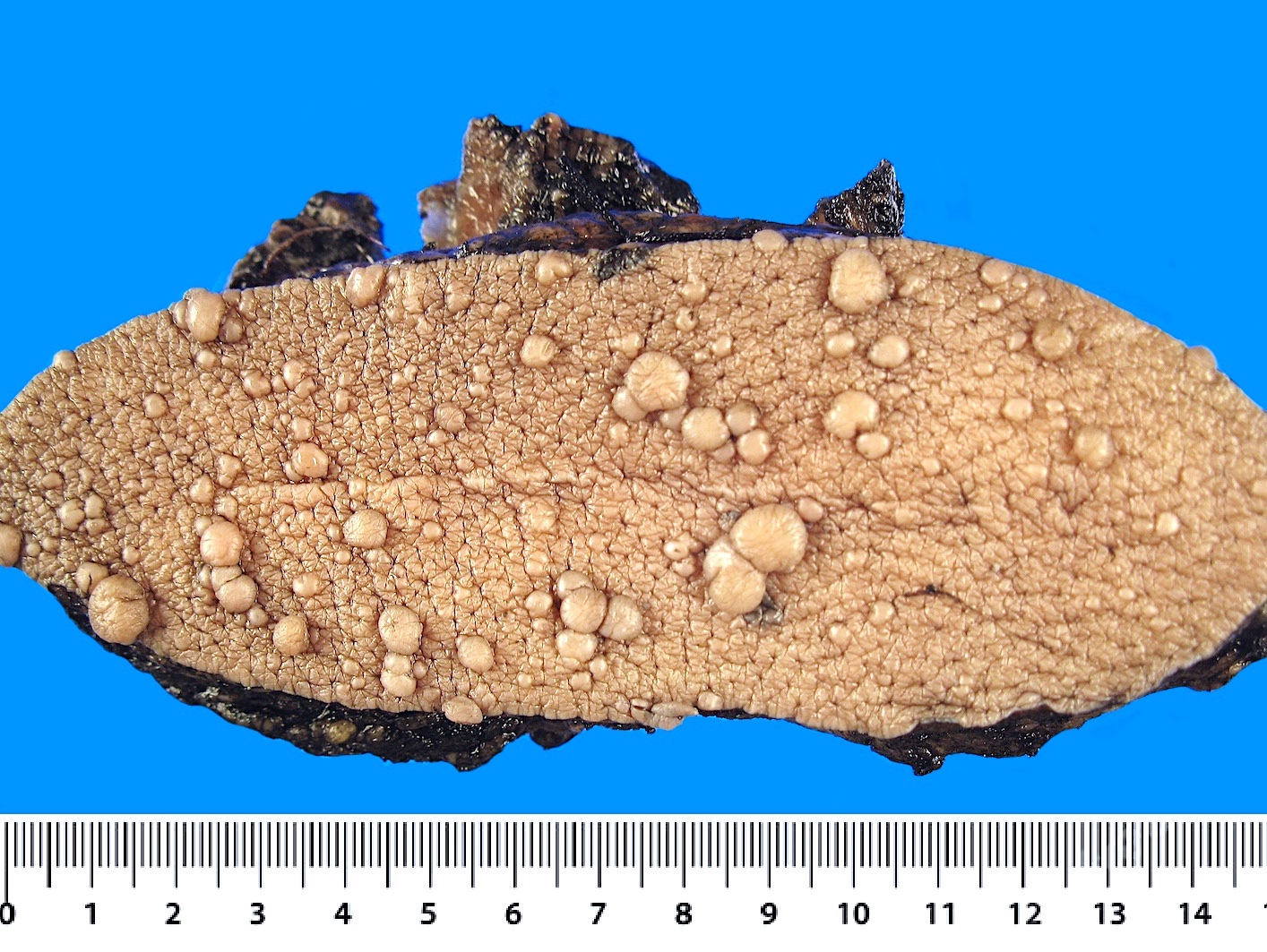
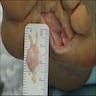
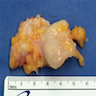
Gross description
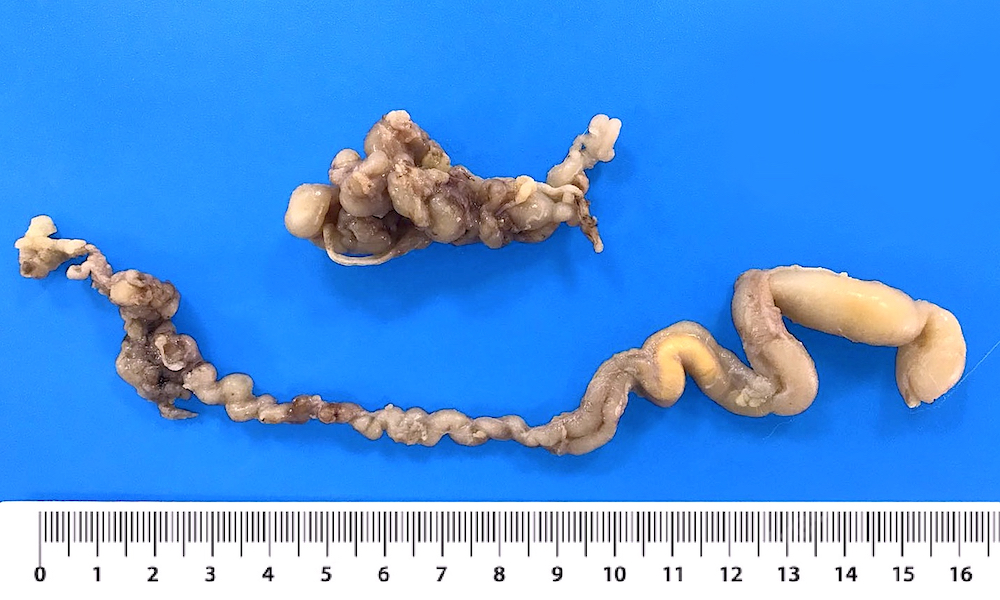
- Fusiform swelling of the nerve particularly at its bifurcation with adherence to fibrofatty tissue (Foot Ankle Int 2004;25:79)
Gross images
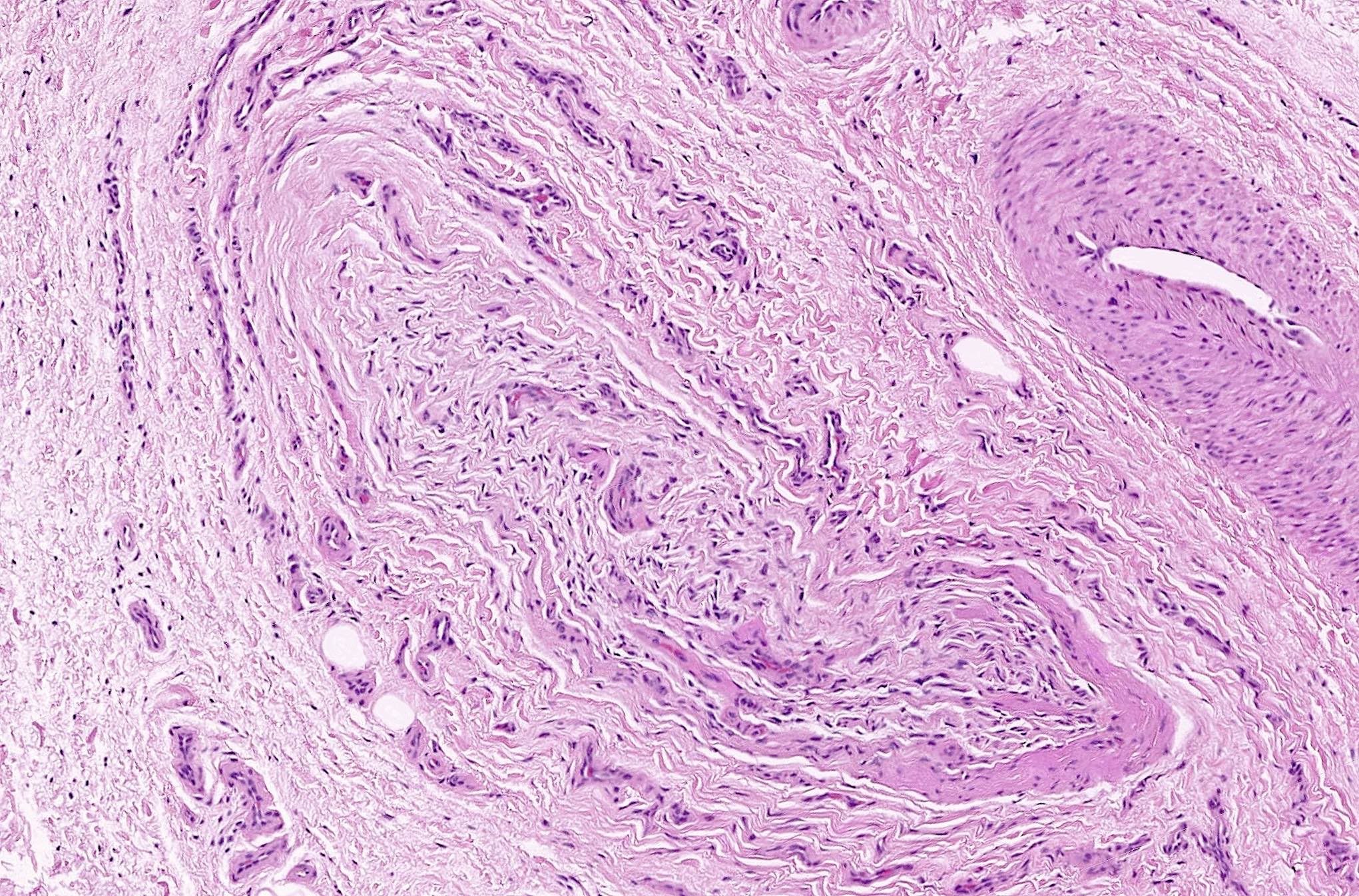
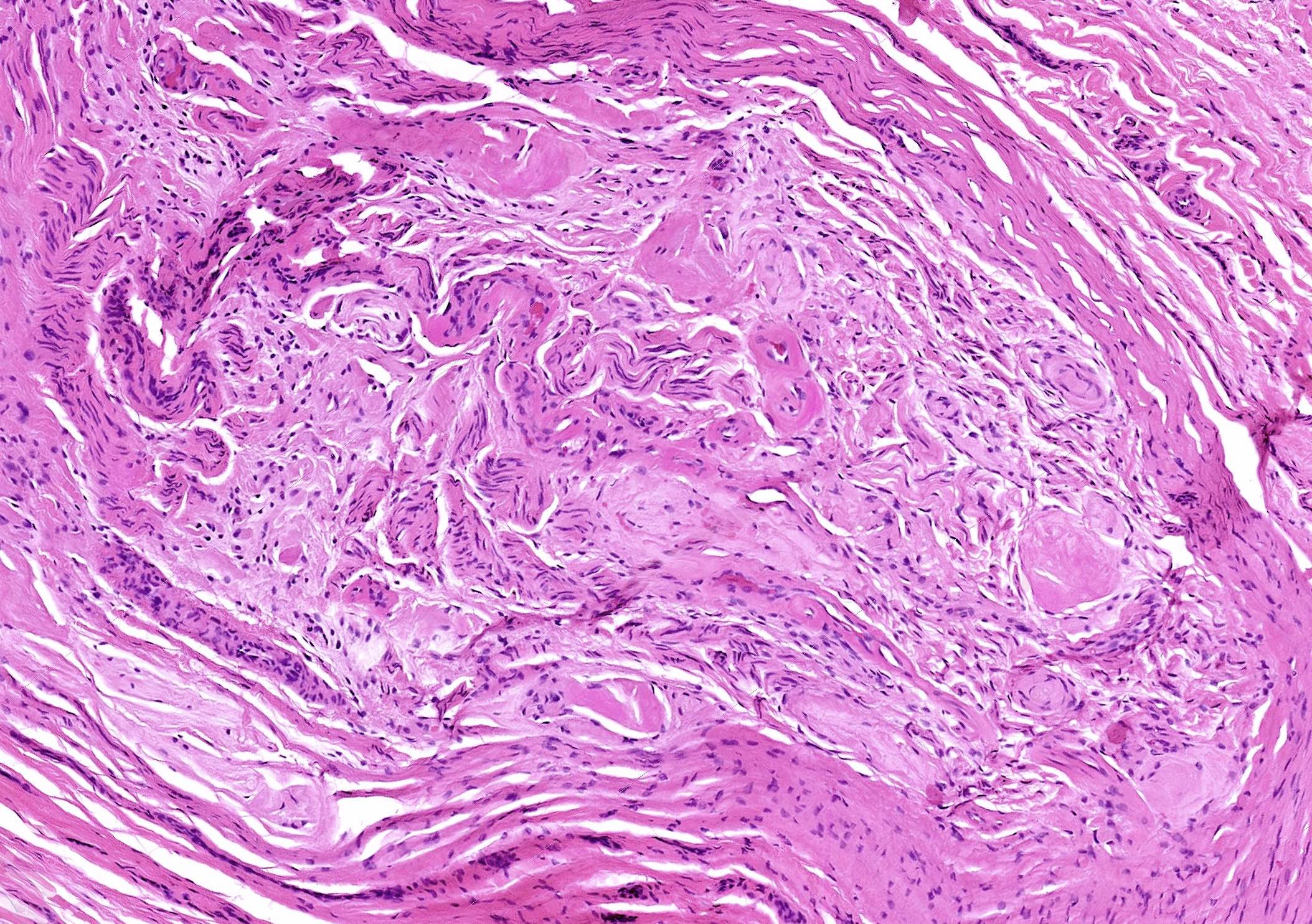
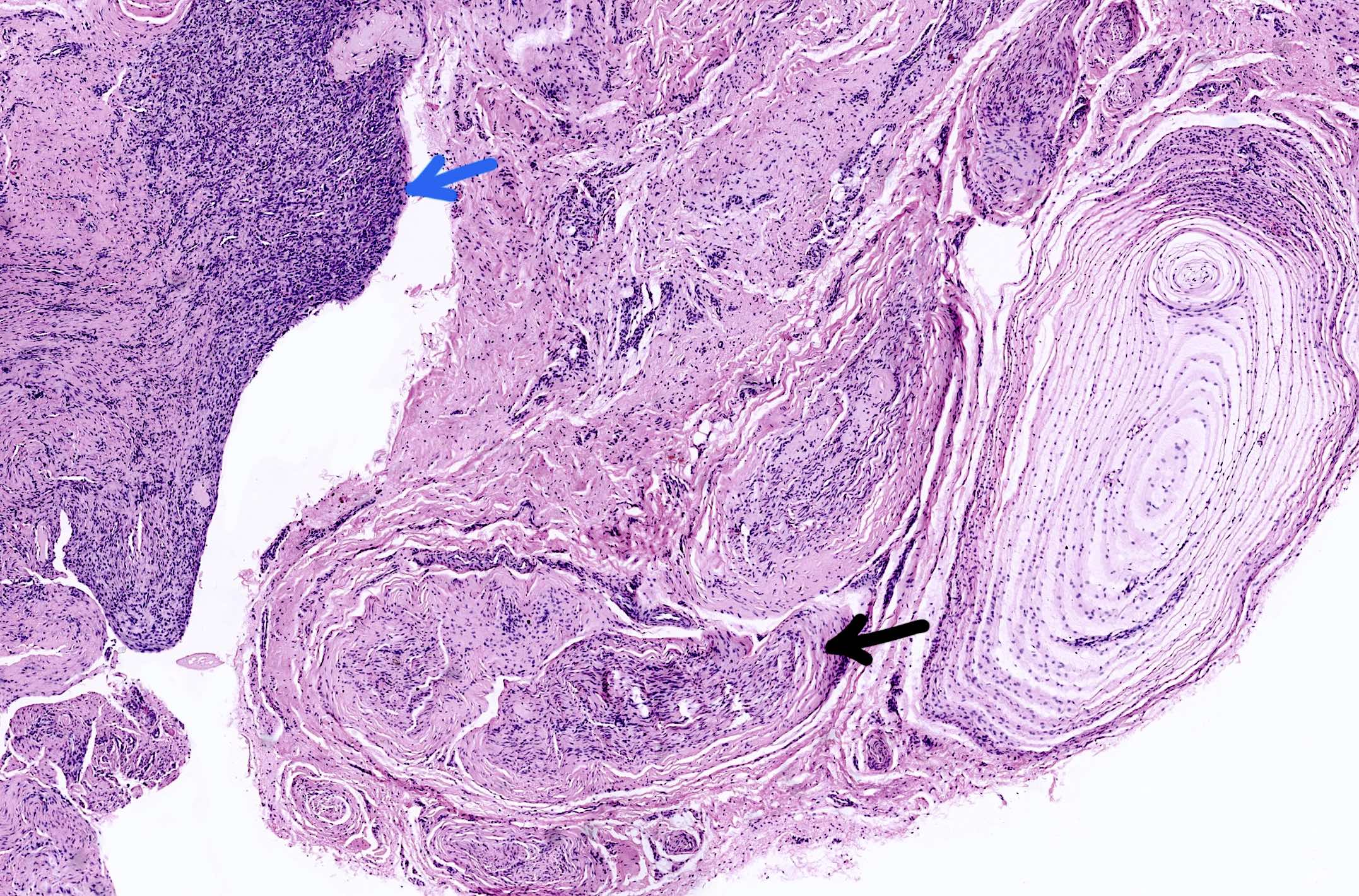
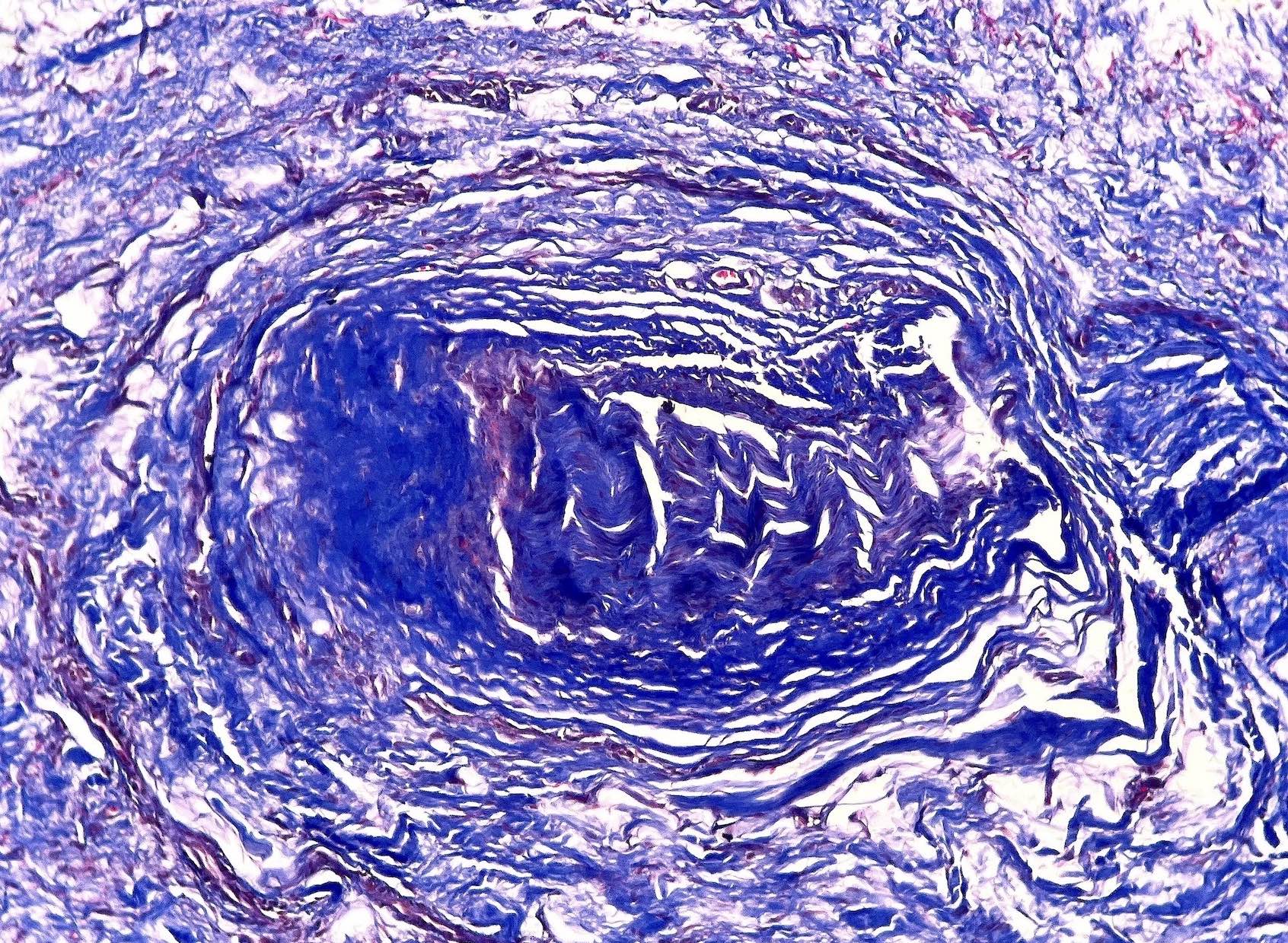
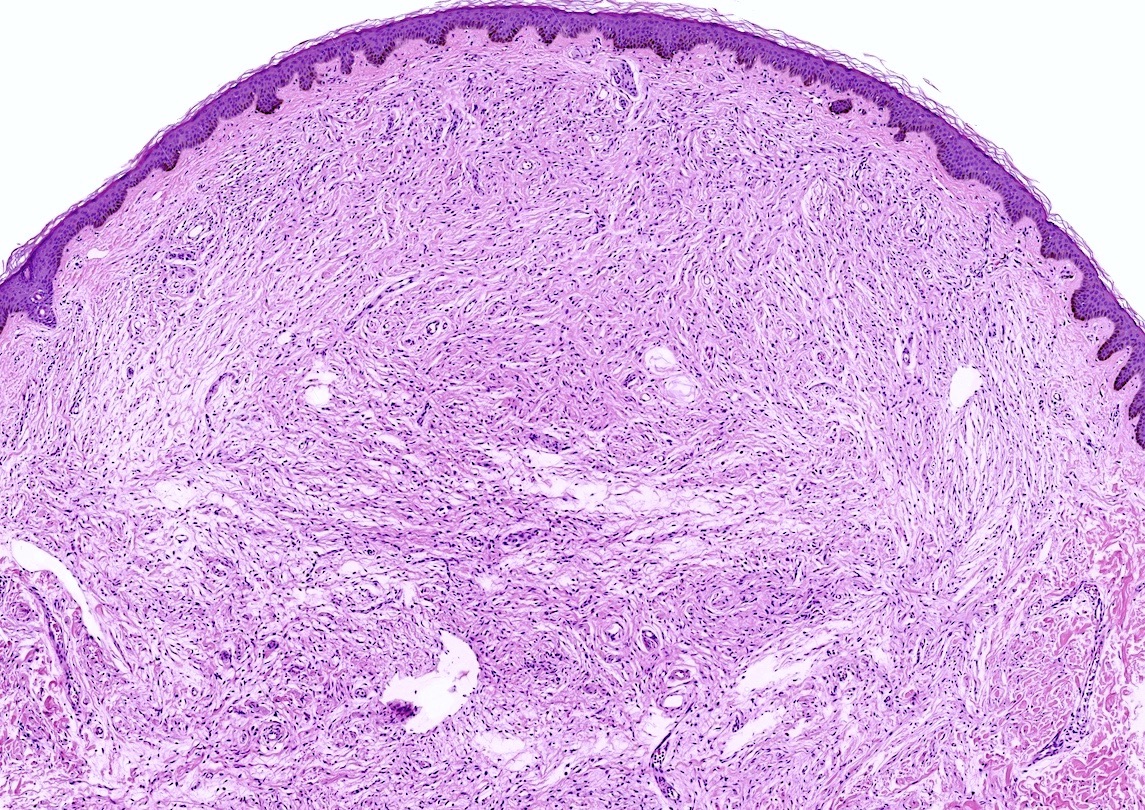
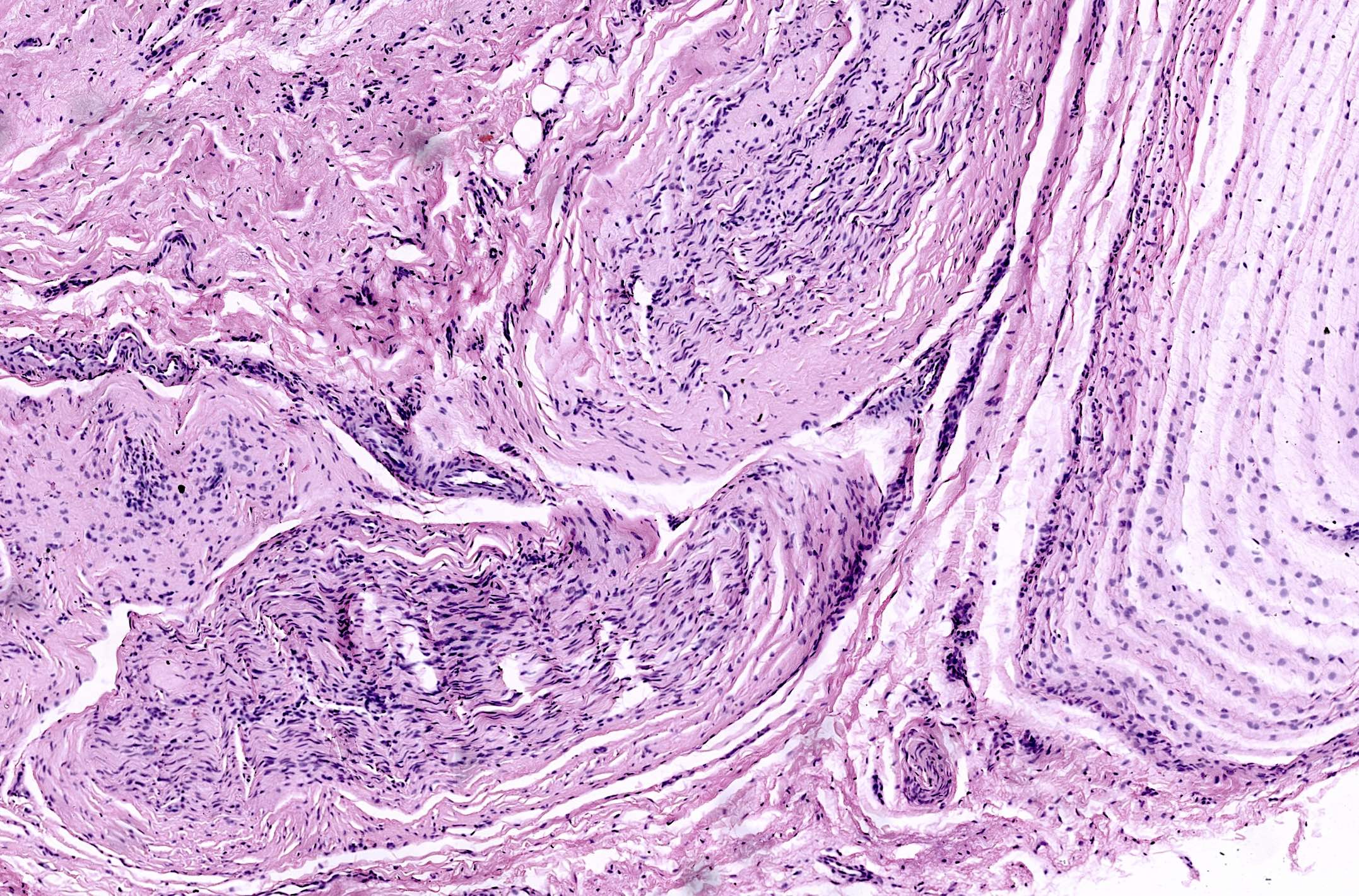
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Varying degrees of perineurial, epineurial and endoneurial fibrosis with axonal demyelination (Aust N Z J Surg 1994;64:421, J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2013;103:218, Foot Ankle Int 2004;25:79)
- Fibrosis may become extensive, enveloping the epineurium in a concentric fashion and extending into the surrounding soft tissue
- Epineurial and endoneurial vascular hyalinization may be seen (Aust N Z J Surg 1994;64:421, J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2013;103:218)
- Larger arteries may show fibroelastic thickening and intimal obliteration; however, these arterial changes are also detected in controls and probably related to older age (J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2013;103:218, Aust N Z J Surg 1994;64:421, Foot Ankle Int 2004;25:79, Foot Ankle Int 2006;27:801)
- Fibrosis of the interstitium with an increase in elastic fibers (Foot Ankle Int 2004;25:79)
- Neuroma may be accompanied by an adventitious bursa or synovial cyst arising from an adjacent metatarsophalangeal joint (Foot Ankle 1983;3:238)
- Re-excisions may reveal residual Morton neuroma (21%), traumatic stump neuroma (21%), both (46%) or fibrofatty tissue with or without foreign body reaction (12%), based on 39 specimens in one study (J Bone Joint Surg Am 1988;70:651)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- S100: highlights the Schwann cells
- EMA: highlights the perineurial layer (Am J Surg Pathol 1988;12:678)
Electron microscopy description
- Progressive fibrosis of the nerves and arteries, edema of endoneurium, axonal degeneration and necrosis (Clin Orthop Relat Res 1991;271:296, Clin Orthop Relat Res 1979;141:256)
Sample pathology report
- Foot, excision:
- Morton neuroma (see comment)
- Comment: The histology shows degenerative fibrosing neuropathy consistent with Morton neuroma.
Differential diagnosis
- Traumatic neuroma:
- M = F, history of trauma or surgery
- Location: may occur anywhere
- Histology: numerous small nerve twigs
- Localized neurofibroma:
- M = F
- Solitary lesions, mostly sporadic; multiple may be in NF1
- Location: may occur anywhere, deep and superficial
- Gross: when arising from a large nerve may look fusiform similar to Morton neuroma while cutaneous examples are not
- Histology: mixed population of Schwann cells, fibroblasts, perineurial cells and occasional mast cells along with scattered axons and shredded collagen usually in a myxoid stroma
- Plexiform neurofibroma:
- M = F; arises early in life
- Strongly associated with NF1
- Location: may occur anywhere
- Gross: tortuous nerve with a bag of worms appearance
- Histology: expanded nerve branches with cytological features of conventional neurofibroma
- Pacinian corpuscles and neuroma:
- Corpuscles often encountered in tissue sections of Morton neuroma
- Neuroma typically occurs on fingertips
- Histology: hyperplasia of Pacinian corpuscles usually following trauma
- Clinically, the differential may include intermetatarsal bursitis, rheumatoid arthritis, stress fracture and metatarsal / soft tissue tumors (Radiol Case Rep 2023;18:2416, Cureus 2022;14:e25305, Acta Biomed 2019;90:214)
Practice question #1
A patient has been experiencing bouts of burning pain and numbness localized to the plantar aspect of the left forefoot at the level of the metatarsal heads. The pain is exacerbated by walking and relieved by rest and removal of the shoe. Excision shows the histology above. What is the diagnosis?
- Morton neuroma
- Pacinian neuroma
- Perineurioma
- Plexiform neurofibroma
- Traumatic neuroma
Practice answer #1
A. Morton neuroma. The clinical presentation is typical. The histology image shows degenerative neuropathy with marked fibrosis and loss of nerve architecture. In contrast, all of the other answers are proliferative lesions. Answer B is incorrect because although a Pacinian corpuscle is seen on the right, there is no corpuscle proliferation. Answer C is incorrect because perineurioma of soft tissue is characterized by a proliferation of slender spindle cells with whorling. Answer D is incorrect because plexiform neurofibroma is composed of nerve bundles that are tortuous and expanded (as opposed to shrunken and fibrotic) by spindle cell proliferation. Answer E is incorrect because traumatic neuroma shows a haphazard proliferation of numerous nerve twigs.
Comment Here
Reference: Morton neuroma
Comment Here
Reference: Morton neuroma
Practice question #2
A 45 year old woman has been experiencing bouts of pain in her left foot and has undergone a surgical procedure to remove the lesion. The histology of the lesion is shown above. Where did the lesion most likely arise from?
- First common plantar digital nerve
- Lateral plantar nerve
- Medial plantar nerve
- Proper plantar digital nerve
- Third common plantar digital nerve
Practice answer #2
E. Third common plantar digital nerve. The picture shows a Morton neuroma, which classically affects the third common plantar digital nerve supplying the webspace between the third and fourth metatarsal heads. Answers A - D are incorrect because these nerves are not usually affected.
Comment Here
Reference: Morton neuroma
Comment Here
Reference: Morton neuroma