Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Immunofluorescence description | Immunofluorescence images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Genetics | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Sağlam A. BK virus / polyomavirus. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneybkvirus.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Interstitial nephritis caused by invasion of the renal parenchyma by BK polyomavirus; most commonly seen in the posttransplant setting
- Resulting disease is referred to as polyomavirus nephropathy
Essential features
- Polyomavirus nephropathy is caused by a ubiquitous, opportunistic, nonenveloped double stranded DNA virus belonging to the Polyomaviridae, with a very high seroprevalence rate in adults
- It is characterized by interstitial nephritis and tubular injury and is most commonly encountered in the setting of immunodeficiency, especially in posttransplant patients, where the reactivated dormant virus in the uroepithelium escapes immunosurveillance
- Most common histomorphologic changes encompass patchy interstitial inflammation and cytopathic changes in the tubular epithelial cells
- Minimal and early stages of polyomavirus nephropathy may present with normal renal function and may not show intranuclear viral inclusion bodies, tubular injury or significant renal injury; this is why screening and routine staining of renal allograft biopsies (including surveillance biopsies) with SV40 immunohistochemistry is recommended: unchecked infection leads to renal scarring and allograft loss (BMC Nephrol 2021;22:226, Transplantation 2008;85:1008)
- Reduction of immunosuppression is mainstay therapy
Terminology
- BK polyomavirus nephropathy
- BK virus associated nephropathy
- Polyomavirus nephropathy
- Definitive BK polyomavirus nephropathy: patients with biopsy proven viral nephropathy
- Presumptive BK polyomavirus nephropathy: patients with high viremia titers but no histologic confirmation of renal disease
ICD coding
- ICD-10: B33.8 - other specified viral diseases
Epidemiology
- Encountered in the immunosuppressive settings, most commonly posttransplant and especially in those with overimmunosuppression
- Has become more prevalent with the introduction of new potent immunosuppressive medication
- More common in male patients, Afro-Caribbean ethnicity, pediatric patients and the elderly
- In kidney transplant recipients the incidence of BK polyomavirus viruria is ~30 - 40%, that of viremia is ~13% and that of BK virus nephropathy is ~8% (N Engl J Med 2002;347:488)
Sites
- Renal disease
Pathophysiology
- Virus is acquired by direct person to person contact, through contaminated surfaces, food and water
- Infection, which is most often subclinical, is usually encountered in childhood, where after the virus remains latent in the urothelial and renal tubular epithelial cells lifelong and is kept in check predominantly by T cells
- With immunosuppression (suppression especially of T cell immune surveillance) the virus, either the dormant one in the host or donor derived (in a portion of transplant cases), reactivates and causes viremia by crossing into the peritubular capillaries (J Med Virol 2019;91:1136)
- Lytic replication of the reactivated virus results in lysis of renal tubular epithelial cells, release of daughter virions into tubular lumens, infection of adjacent cells, basement membrane denudation, viruria, influx of inflammatory cells, and eventually leads to renal fibrosis and graft failure if left untreated
- Viremia seldom causes infection of glomerular endothelial and mesangial cells, podocytes and Bowman capsular epithelial cells, potentially resulting in glomerular damage (J Clin Med 2019;8:1477)
- BK virus genome, encodes 2 viral oncoproteins: the large T antigen (TAg) and the small t antigen (tAg), which have been shown to target p63 and pRb, and can potentially modify the normal cell cycle, leading to cell immortalization and neoplastic transformation (Am J Transplant 2016;16:398)
- References: Transplantation 2016;100:2276, Nephrol Dial Transplant 2021;36:587
Etiology
- BK virus infection is caused by a ubiquitous, opportunistic, nonenveloped double stranded DNA virus belonging to the Polyomaviridae family with a seroprevalence rate that can reach > 90% in adults (J Gen Virol 2003;84:1499, Transplantation 2014;97:451)
- It is nonpathogenic in the immunocompetent
- Infection is most common in renal transplant recipients followed by bone marrow transplant recipients; though it has also been reported following heart, liver and lung transplants (Transplant Rev (Orlando) 2015;29:175, Clin Kidney J 2016;9:310)
- Diminished cellular immune response seems to have a predominant contributory role (Transplantation 2008;85:185)
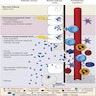
- Reported risk factors are (Transplantation 2014;97:451, see diagram below)
- Host immune status, pretransplant T cell senescence phenotype and genetic determinants (Transplantation 2017;101:1479, Transplantation 2014;97:451)
- Transplant procedure
- Intensity of immunosuppression
- Male gender
- Extremes of age
- Recipient and donor sero status
- Ureteral stents
- Initial viral load
- Afro-Caribbean ethnicity
- HLA mismatching
- Transplant rejection episodes
Clinical features
- Does not cause significant symptoms in the immunocompetent; causes subclinical infection
- Important cause of chronic kidney disease and early allograft failure following kidney transplantation
- It is also known to cause renal disease with a progressive decline in kidney function in nonrenal solid organ transplants
- In the immunocompromised it is associated with
- Fever
- Asymptomatic / symptomatic increase in serum creatinine levels
- Asymptomatic viruria
- BK virus associated nephropathy
- Hemorrhagic cystitis: gross hematuria
- Ureteric strictures
- Pneumonitis, retinitis, liver disease and meningoencephalitis in HIV patients and those with severe immunosuppression (Clin Infect Dis 2005;41:354, AIDS 2001;15:1196, J Infect 2014;68:S2, Lancet Infect Dis 2003;3:611)
- Possible association with bladder cancer and urogenital cancer (Clin Infect Dis 2005;41:354, Infect Agent Cancer 2018;13:12, Am J Transplant 2016;16:398)
- Reference: Clin Infect Dis 2005;41:354
Diagnosis
- DNA or RNA based PCR in blood or urine samples
- Detection of decoy cells in urine cytology
- Urinary polyomavirus Haufen test by electron microscopy
- Molecular sequencing techniques (Front Immunol 2020;11:1763)
- Renal biopsy: gold standard
- References: Semin Nephrol 2016;36:372, Intervirology 2020 Dec 17 [Epub ahead of print], Pathogens 2021;10:150
Laboratory
- Increased serum creatinine, mild proteinuria and hematuria
- Virus positivity in the serum
- Virus positivity in the urine
- References: Semin Nephrol 2016;36:372, Intervirology 2020 Dec 17 [Epub ahead of print], Pathogens 2021;10:150
Prognostic factors
- Without screening and treatment, the natural course of BK virus nephropathy leads to 50% graft loss (J Am Soc Nephrol 2018;29:680)
- With reduction in suppression, patient and graft outcomes are similar to uninfected patients (Nephrol Dial Transplant 2019;34:1240)
- Graft loss is more common in class 3 polyomavirus nephropathy (J Am Soc Nephrol 2018;29:680)
- Early diagnosis is associated with better outcome
- Risk of graft loss is also associated with (Am J Transplant 2004;4:2082, Am J Transplant 2017;17:2065)
- High level viremia or sustained viremia
- Deceased donor transplantation
- Late acute rejection
- SV40 large T antigen positivity on the follow up biopsy
Case reports
- 39 year old woman with heart transplant who developed BK virus nephropathy (J Bras Nefrol 2021;43:434)
- 41 year old woman with type I diabetes and pancreas / kidney transplant diagnosed with BK virus associated metastatic renal allograft carcinoma (Transplantation 2021;105:423)
- 58 year old woman with chronic lymphocytic leukemia who developed hematuria due to concurrent BK polyomavirus, adenovirus and cytomegalovirus (BMJ Case Rep 2021;14:e235981)
- 60 year old woman, a liver transplant patient with BK virus nephropathy of the native kidney (Kidney Int Rep 2021;6:1743)
Treatment
- Screening and reduction of immunosuppression is mainstay therapy but carries the risk of rejection and development of de novo donor specific antibodies
- mTOR inhibitor based regimen may be beneficial
- Novel therapies: on trial
- Immunotherapy: intravenous immunoglobulin, cellular therapy (virus specific T cells)
- Vaccine
- No effective antiviral medication present
- No effective prophylaxis treatment
- Regular screening between 1 - 24 months posttransplant is recommended
- Reference: Viruses 2021;13:487
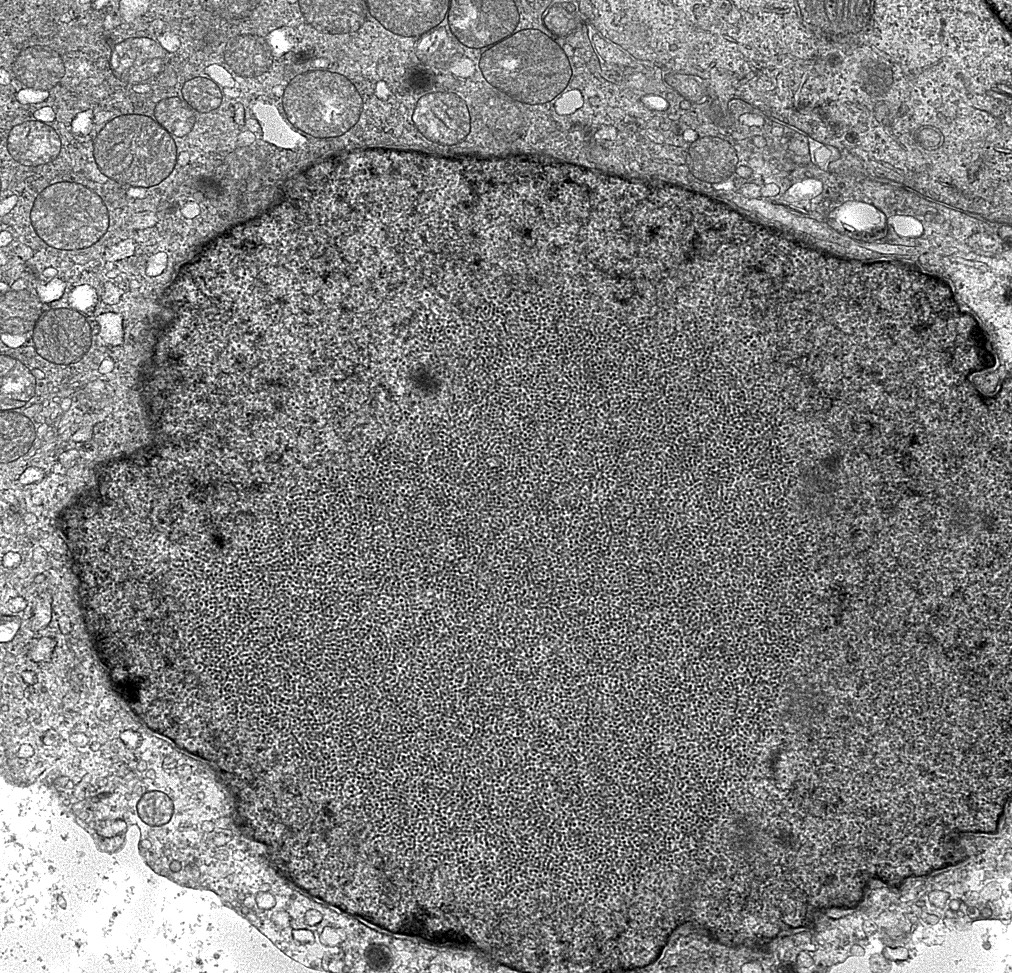
Microscopic (histologic) description
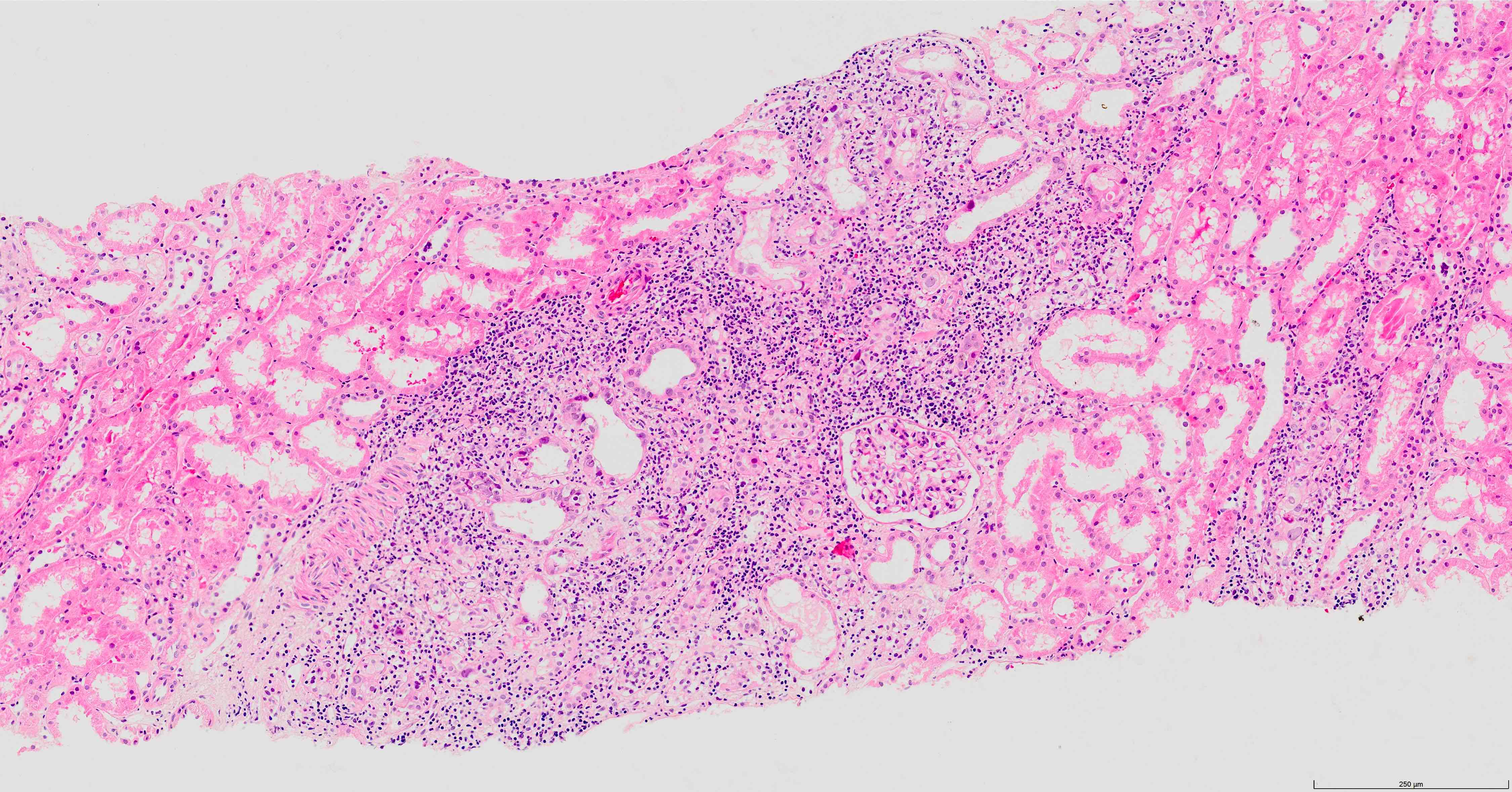
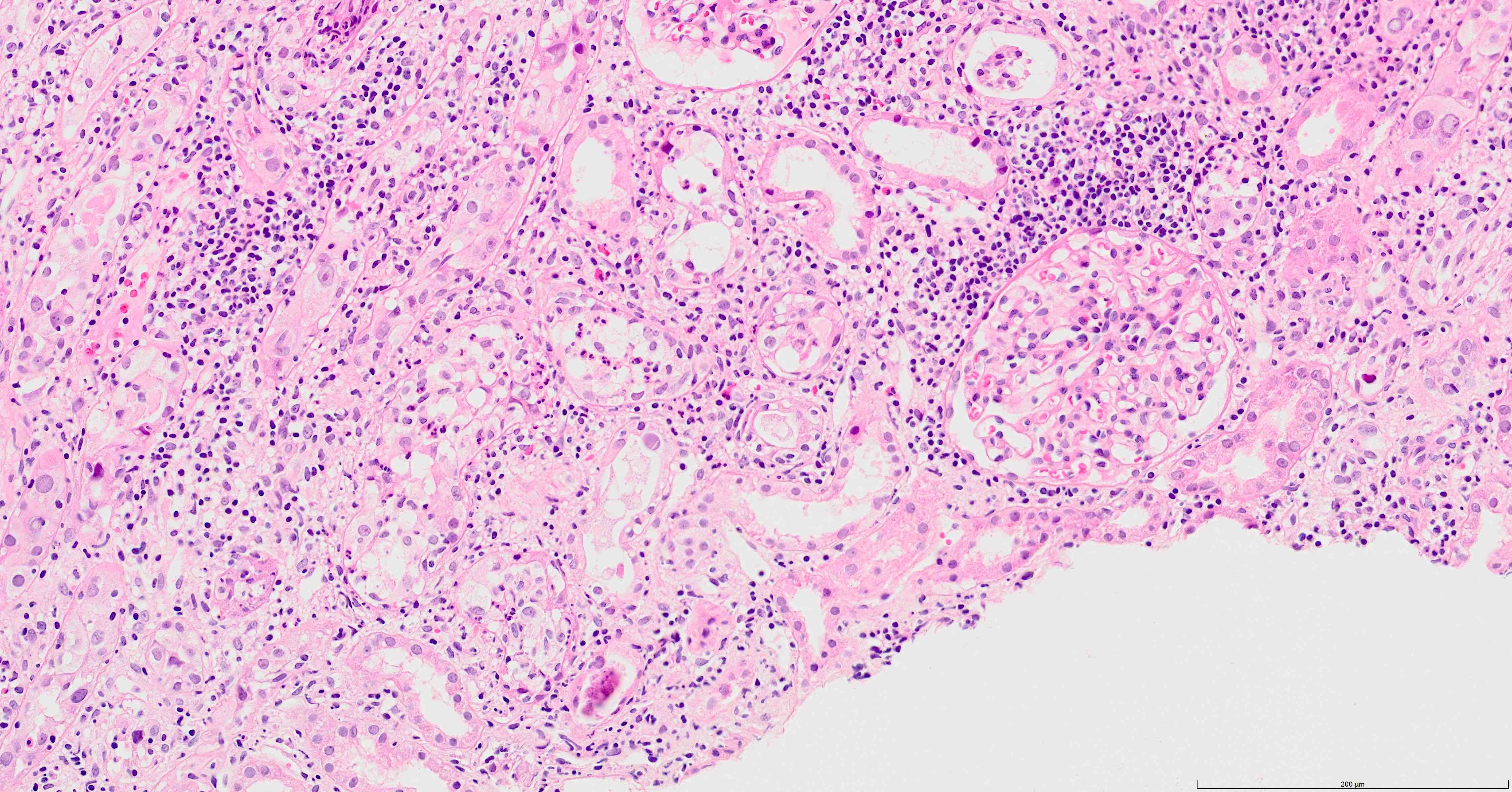
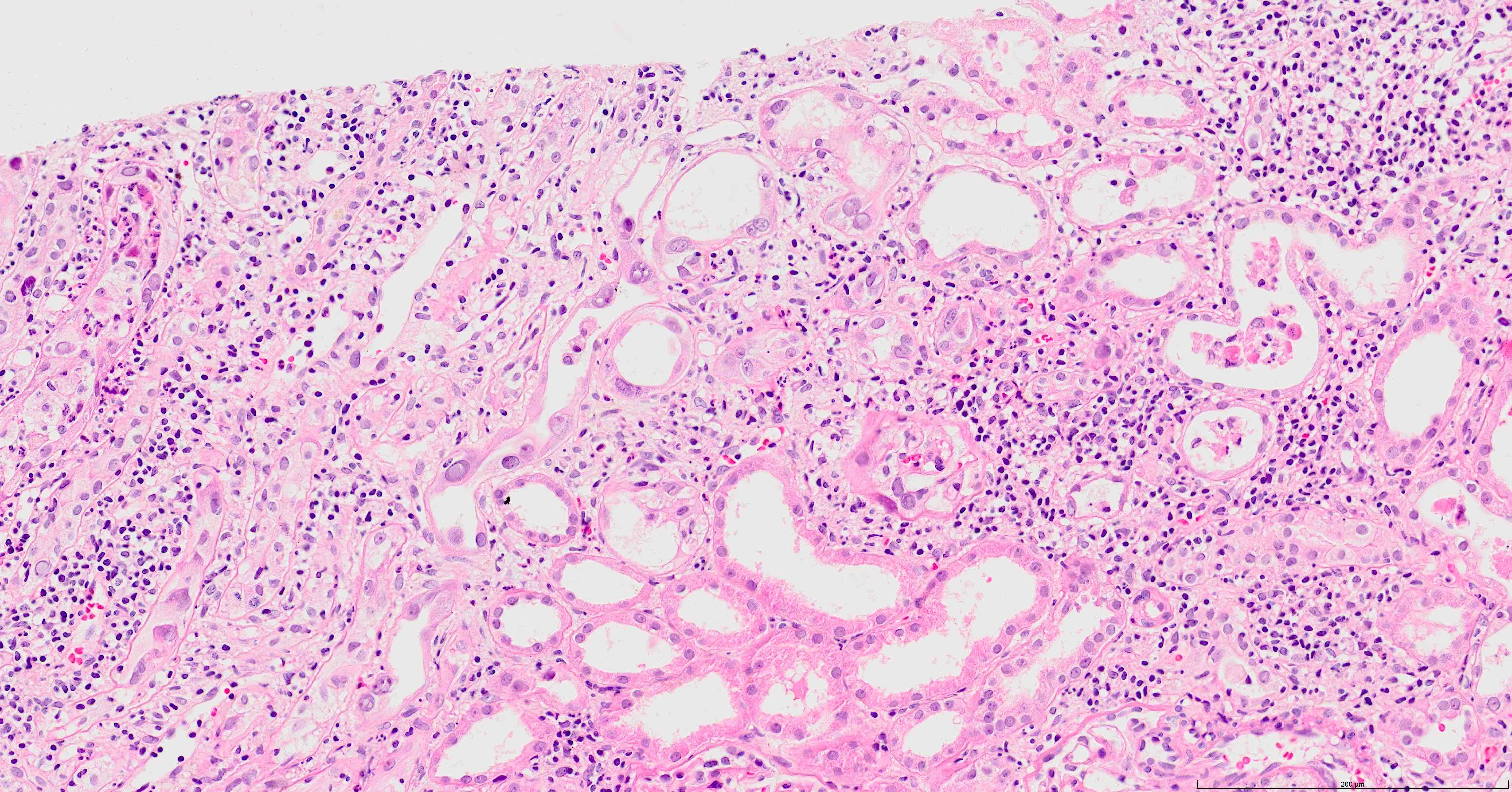
- Findings are composed of interstitial nephritis and tubular injury; these findings are focal
- Involvement is more prominent in the distal nephron, therefore evaluation of medulla is important, especially in early stage infection; it is recommended that 2 core biopsies be provided, at least 1 where the medulla is sampled (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2020;15:1015)
- Interstitial edema and inflammation, composed predominantly of mononuclear cells, accompanied by plasma cells and less frequently eosinophils and neutrophils; these changes may be absent in early stages of infection (Ren Fail 2019;41:855)
- Inflammation is patchy and associated with infected tubules, usually well demarcated from surrounding
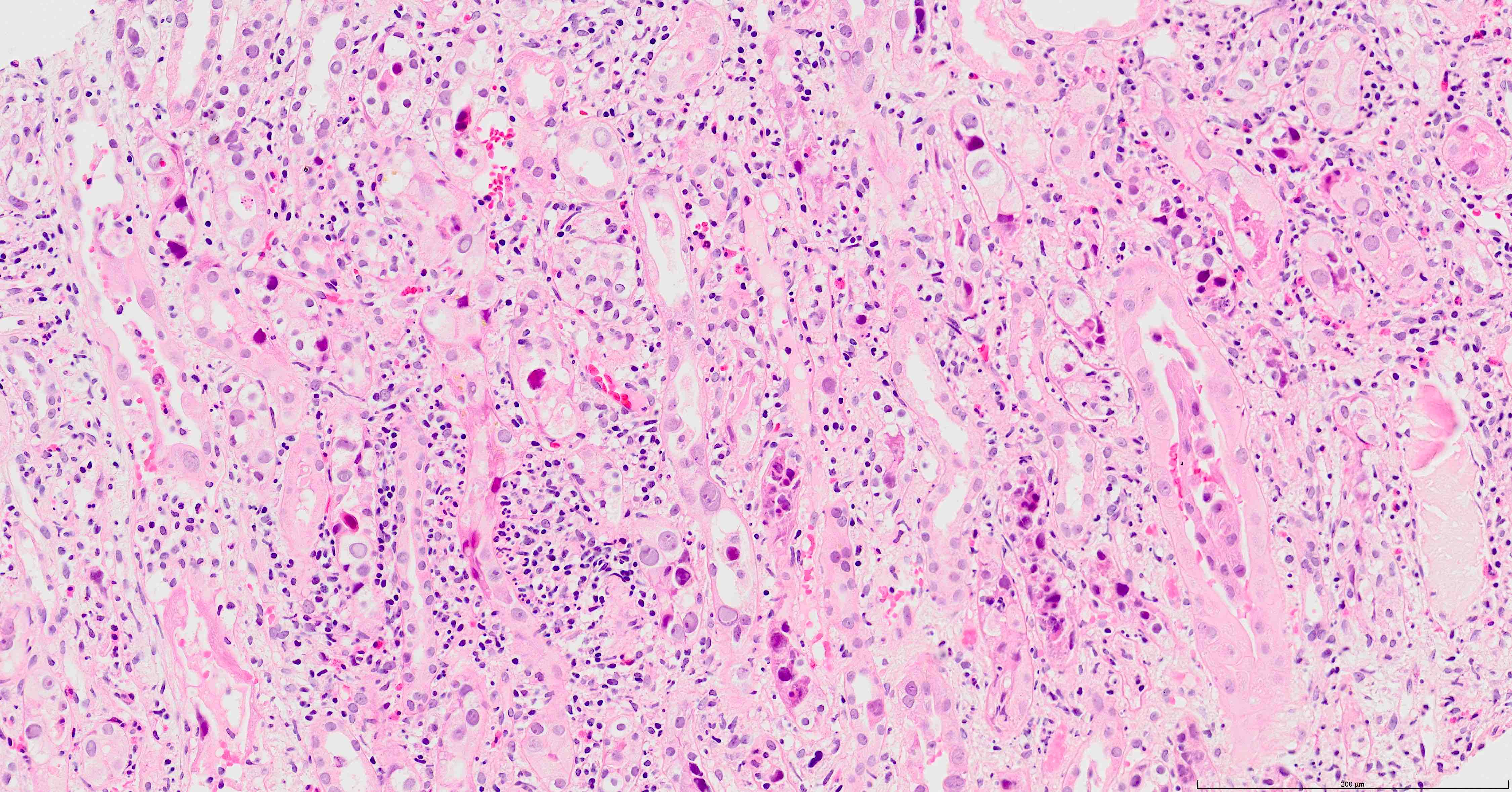
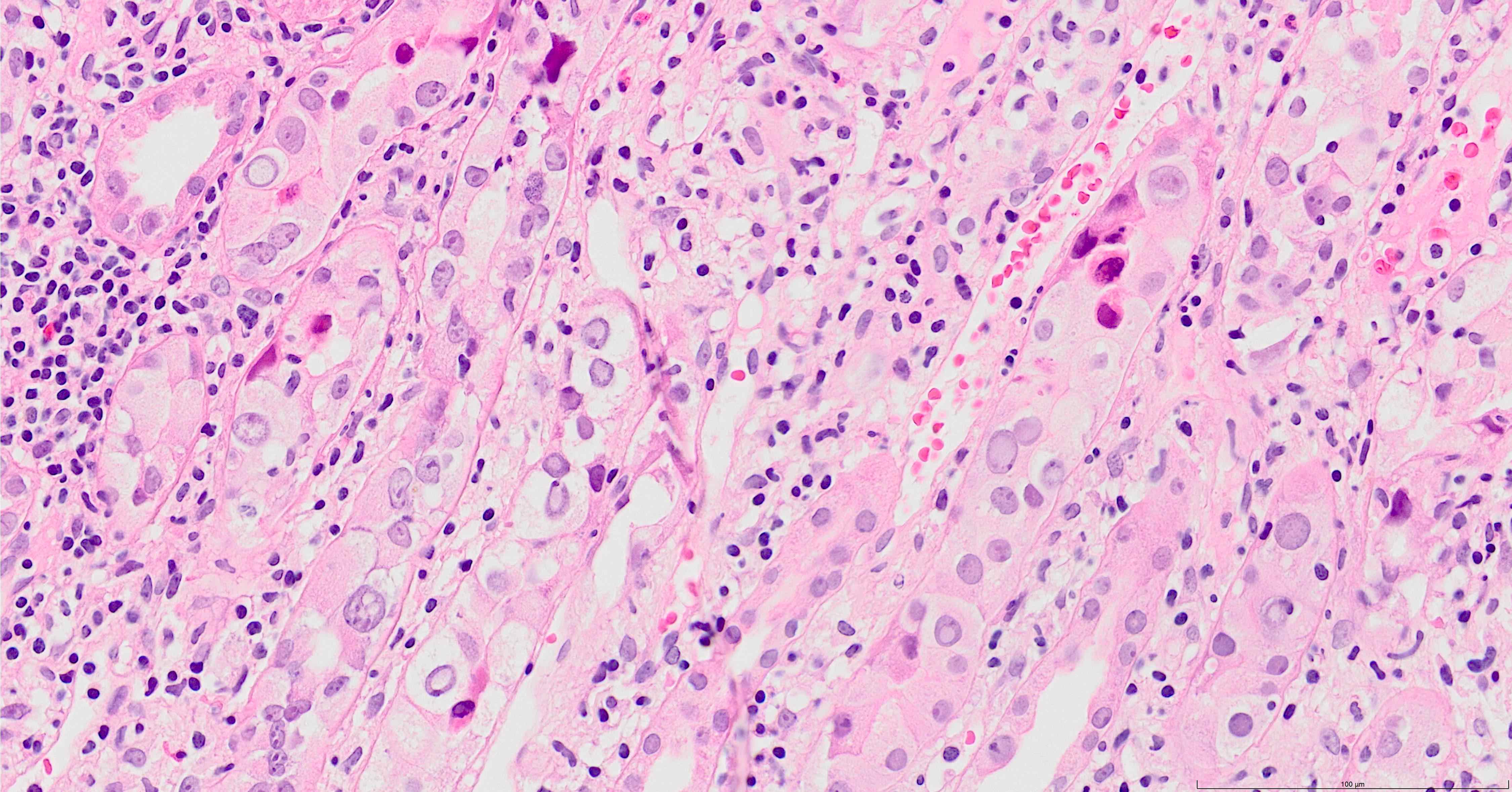
- Tubulitis and tubular cell injury; cell necrosis / dropout, desquamation / sloughing, flattening
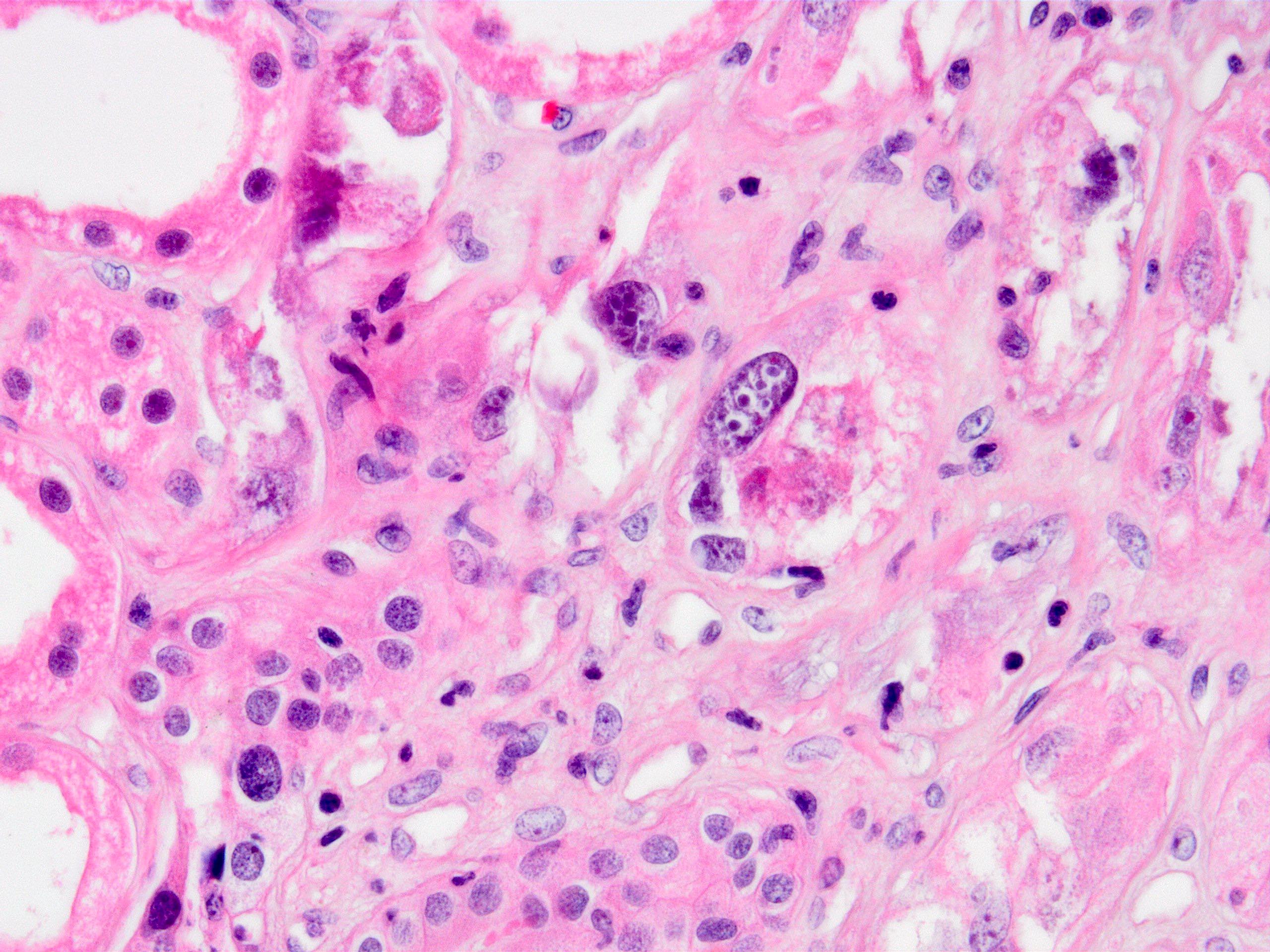
- Tubular epithelial cell cytopathy; maybe absent in early stages of infection
- Cell enlargement
- Nuclear hyperchromasia and anisonucleosis
- Intranuclear inclusions: basophilic granules, ground glass appearance or clearing, no halo; chromatin changes: smudging, clumping or peripheral margination
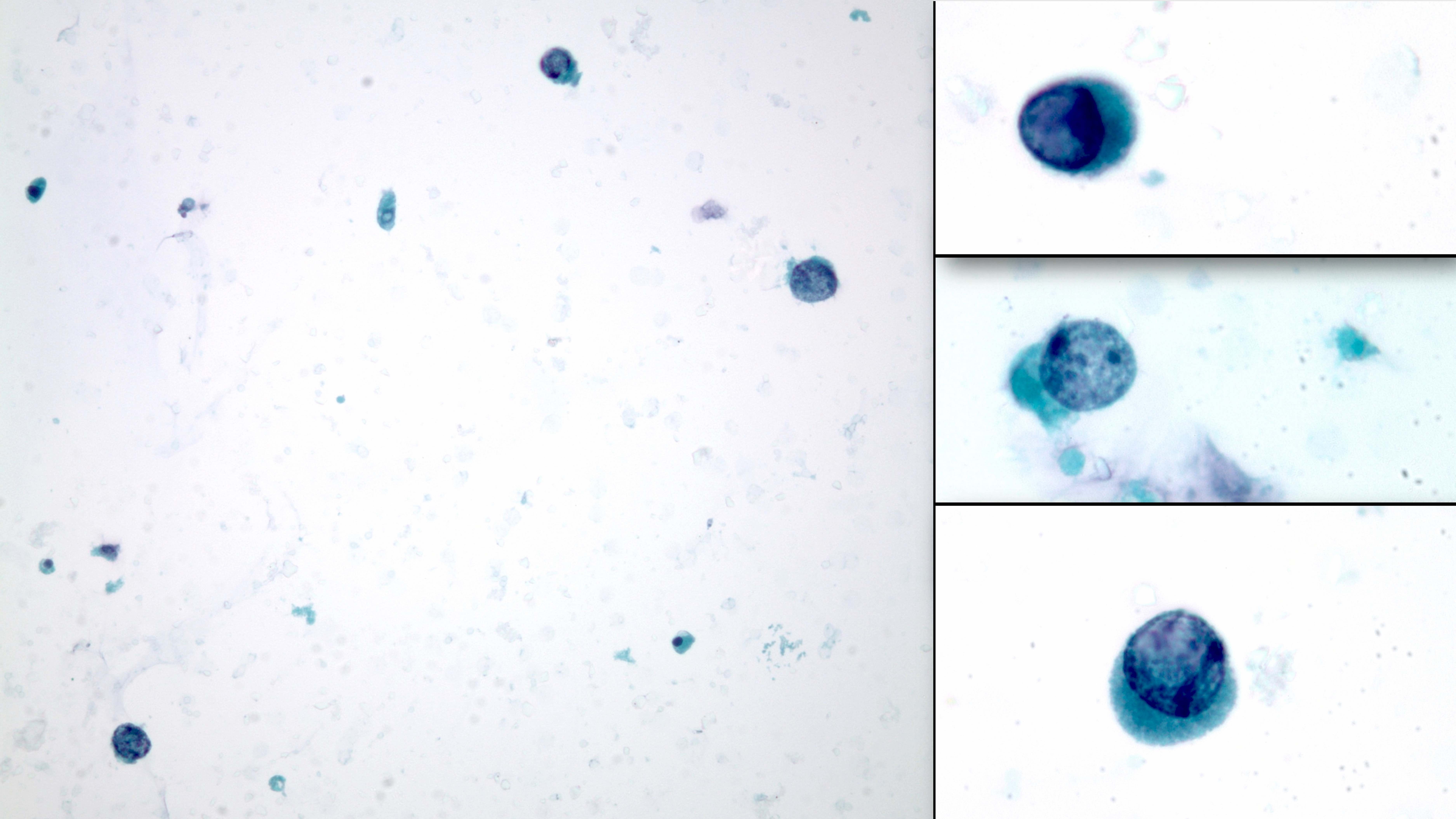
- Urine cytology: decoy cells (resemble cells in uroepithelial cancer); BK virus infected tubular epithelial cells that have been shed into the urine
- Rounded basophilic nuclei larger than the average transitional and tubular epithelial cells
- Nuclei have viral inclusions appearing as dense granular basophilia and no halo
- Dirty background: transitional, tubular and inflammatory cells and clumps of amorphous basophilic material (harder to appreciate in slides prepared with thin layer methods)
- Graded as rare, up to 4 per cytospin and > 10 per cytospin; when rare cells are present with lack of inflammation, chances of positive infection in biopsy sample is low
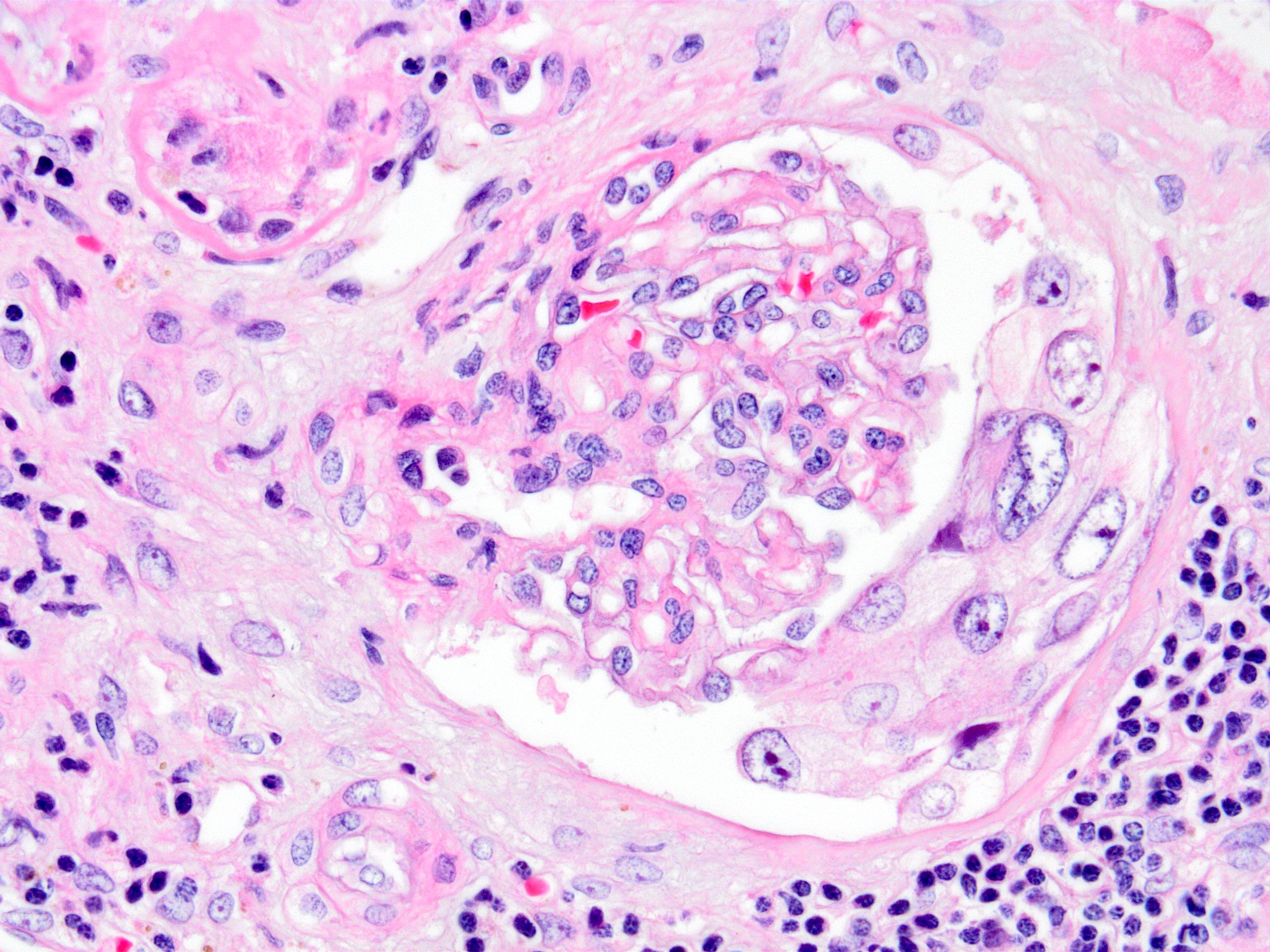
- Cytopathic changes of the glomeruli (Bowman capsular epithelial cells, podocytes, mesangial cells) and crescent formation may also be seen (J Clin Med 2019;8:1477)
- In early stage infection, morphological findings are only present in scattered cells, mostly in the medulla and may even be characterized by only a handful of SV40 positive cells without discernable cytopathy
- Interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy: late stage disease
- Histologic classification system: consisting of polyomavirus replication load / level (pvl) score and Banff score for interstitial fibrosis (ci) (J Am Soc Nephrol 2018;29:680)
- PVN class 1: pvl 1; ci ≤ 1
- PVN class 2:
- pvl 1; ci ≥ 2
- pvl 2; any ci score
- pvl 3; ci ≤ 1
- PVN class 3: pvl 3; ci ≥ 2
- Scoring of polyomavirus replication load / level (pvl): percentage of positive tubules / ducts by morphologic assessment of cytopathy or SV40 immunohistochemistry in the entire biopsy (cortex and medulla)
- pvl 1: 1%
- pvl 2: 1 - 10%
- pvl 3: > 10%
- References: Yonsei Med J 2004;45:1065, Nephrol Dial Transplant 2021;36:587
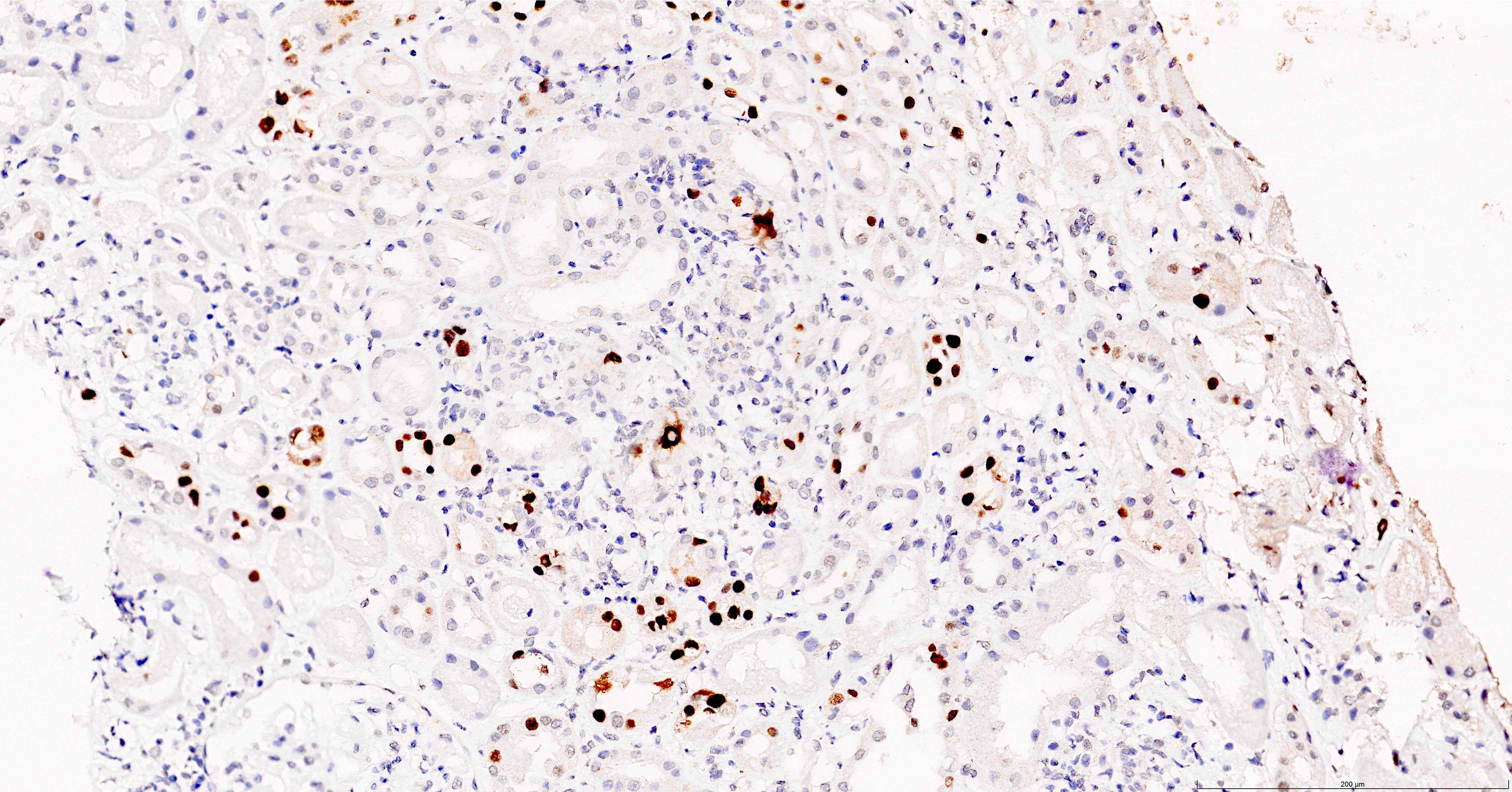
Microscopic (histologic) images
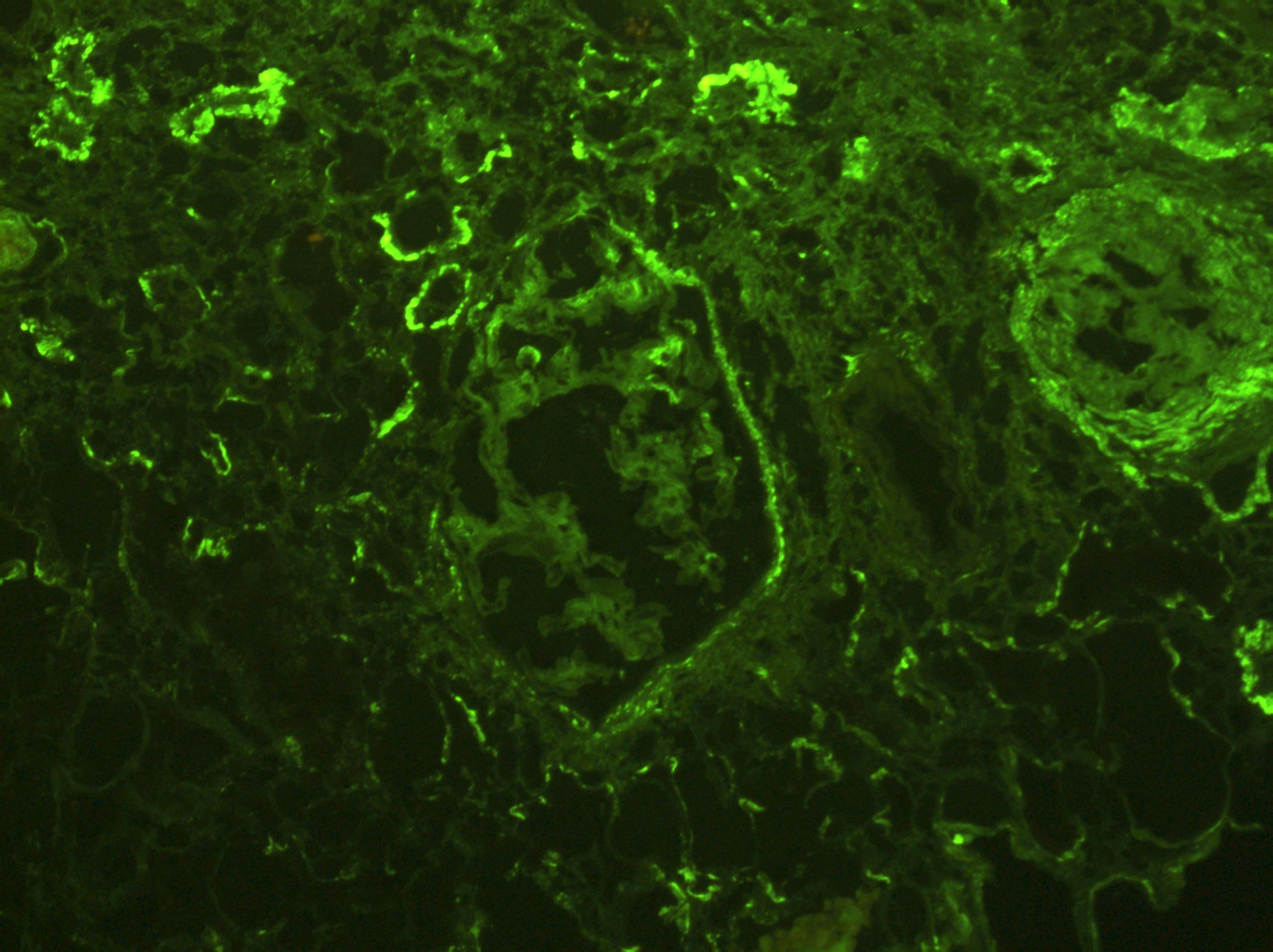
Immunofluorescence description
- No immunoglobulin or only nonspecific scarce staining
- Immune deposits (most commonly IgG and C3) may be present along tubular basement membranes (Am J Transplant 2007;7:1552)
- Peritubular C4d negative (positivity indicates accompanying antibody mediated rejection)
Positive stains
- Anti-SV40 antibody, immunohistochemistry, is positive (part of the routine panel used in transplant biopsy assessment)
- Large T antigen (LTAg), one of the proteins encoded by the BK polyomavirus genome shares sequence homology with the LTAg of the simian virus (SV40)
- Anti-SV40 antibody directed against the SV40 T antigen, hence crossreacts with the BK polyomavirus LTAg and is used to identify BK polyomavirus
- This antibody also crossreacts with the JC polyomavirus
- In situ hybridization for BK virus DNA
- Anti-BK polyomavirus VP1 recombinant antibody, immunohistochemistry: a novel monoclonal antibody directed against the viral VP1 capsid protein (Am J Transplant 2007;7:1552)
Negative stains
- C4d immunohistochemistry, routinely used to assess transplant biopsies: peritubular and glomerular capillary wall staining is negative unless accompanying antibody mediated rejection is present
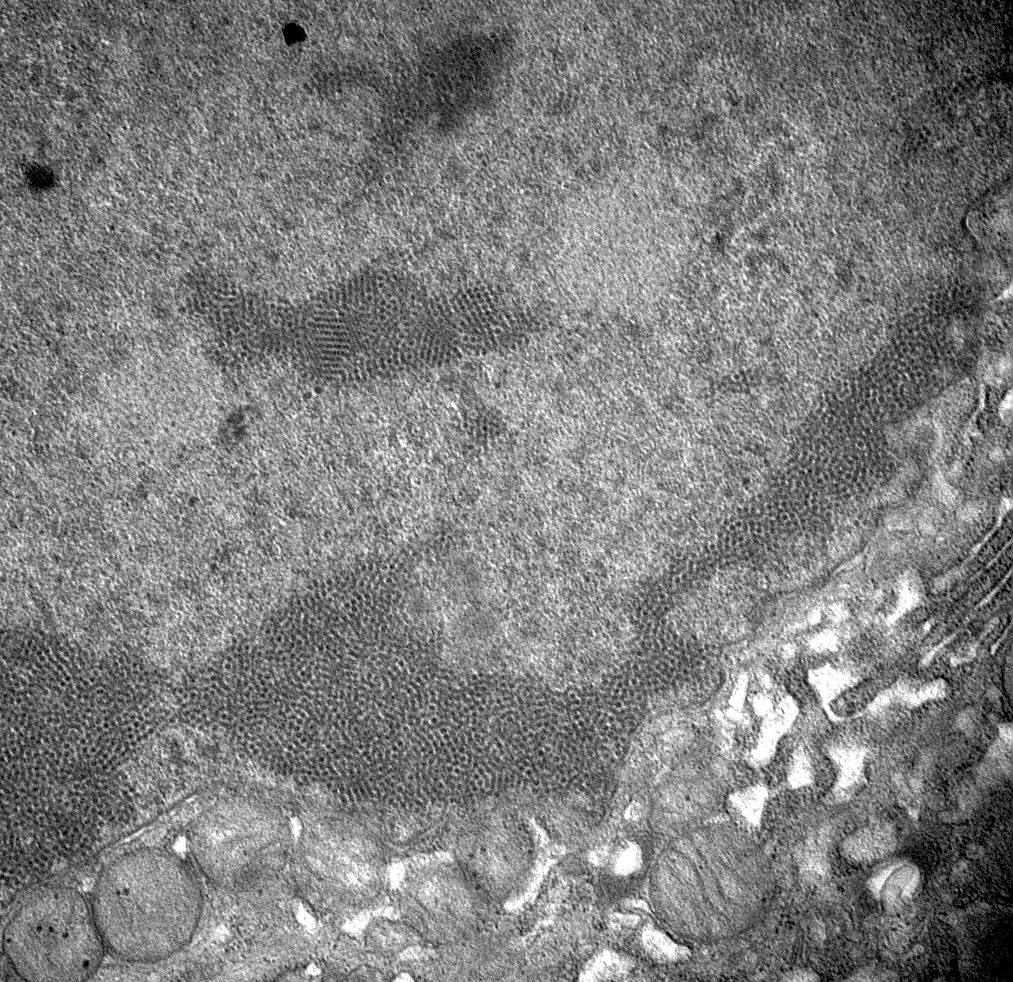
Electron microscopy description
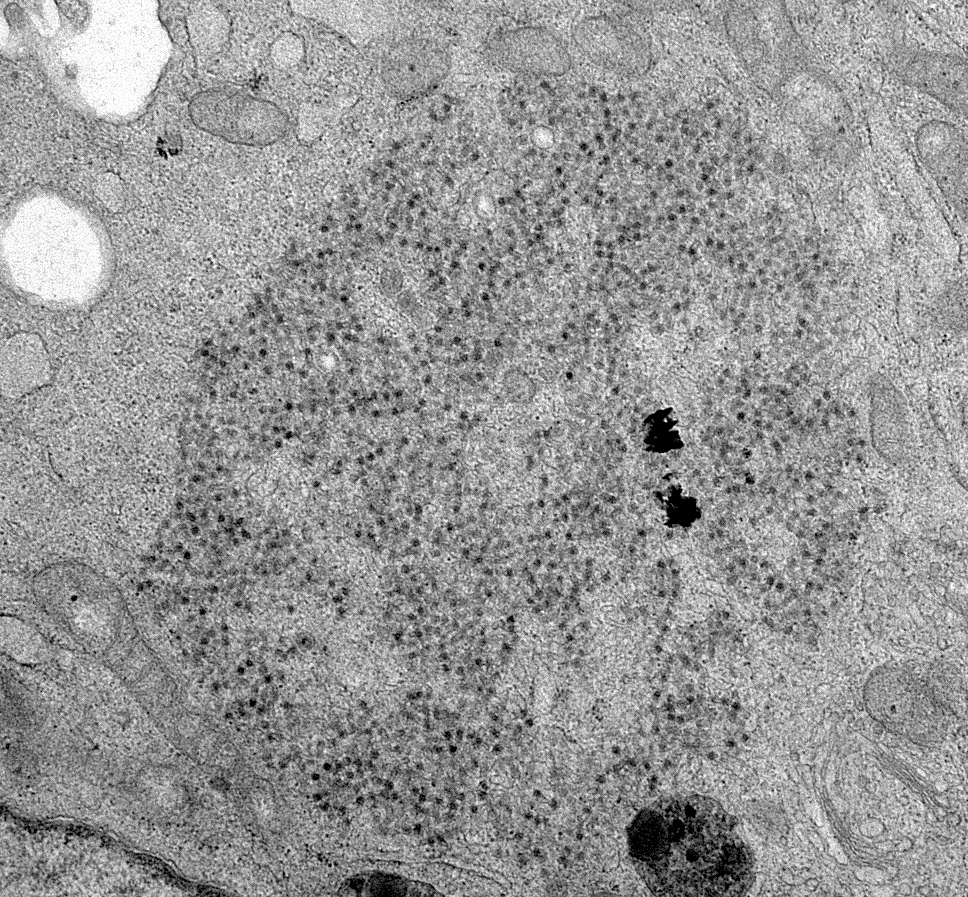
- Urine cytology: Haufen - icosahedral aggregates of polyomavirus particles and Tamm-Horsfall protein visualized using negative staining electron microscopy (Ultrastruct Pathol 2009;33:222)
- These are viral particles that form in virally injured tubular epithelial cells and excreted in the urine and hence represent evidence of active disease
- Presence of BK virions, 30 - 50 nm in diameter nonenveloped particles arranged in paracrystalline arrays, in tubular epithelial cells
- This finding is not diagnostic of BK polyoma nephropathy / interstitial nephritis since dormant virions can persist in the tubular epithelial cells (Ultrastruct Pathol 2005;29:469)
- Presence of necrotic tubular cells, prominent lysosomal inclusions and luminal protein and cellular cylinders should also be sought
- Tubular basement membrane immune deposits: finely granular electron dense deposit with no substructure along the tubular basement membrane (Am J Transplant 2007;7:1552)
Electron microscopy images
Genetics
- Presence of certain HLA alleles may predispose to (lack of HLA-C7) or protect against BK virus nephropathy
- Killer cell immunoglobulin receptor genes of NK cells are also correlated with risk of infection; genotyping of recipients in the pretransplant or early posttransplant period is being envisioned
- Genotype of the virus and single nucleotide polymorphisms in the genes coding for the major viral capsid protein VP1 and the noncoding control region affects pathogenicity of the virus
- References: Viruses 2020;12:1417, Kidney Int 2013;84:359, Viruses 2021;13:1502
Videos
Histomorphological characteristics of BK virus associated nephropathy in a transplant patient
by Dr. Arzu Sağlam
Sample pathology report
- Kidney, allograft biopsy:
- BK virus associated nephropathy (see comment)
- No significant deposition on immunofluorescence microscopy. No evidence of T cell or antibody mediated rejection. Interstitial fibrosis / tubular atrophy absent. Arterial intimal fibrosis (mild) arteriolar hyalinosis (ah2).
- Microscopic description: Serial sectioning shows 120 glomeruli, 5 of which are globally sclerotic. Glomeruli appear close to normal by light microscopy. Endocapillary or extracapillary proliferation, necrosis, intracapillary inflammatory cells (g0), intracapillary thrombi or double contouring of the capillary walls are absent (cg0). Interstitium shows patchy multifocal edema and inflammatory infiltrate with predominance of lymphomononuclear cells and plasma cells. Tubular epithelial cells in these areas display features of cytopathic changes characterized by nuclear enlargement, coarse granular chromatin and nuclear clearing with peripherally condensed chromatin. Some of the tubuli contain granular casts with sloughed epithelial cells, others show simplification with flattened epithelial cells and dilated lumina. Immunohistochemical staining for SV40 shows positivity affecting 5 - 10% of tubuli represented in the biopsy sample (pvl 2). Narrow foci of IFTA can be identified, comprising less than 10% of the cortical parenchyma with scattered mononuclear cells (i-IFTA0, ci0, ct0). Immunohistochemical staining for C4d is negative. Arteries display mild intimal fibrosis (cv1). Intimal arteritis is not identified (v0).
- Immunofluorescence microscopy: 3 glomeruli observed
- Anti-IgG Ab: no deposits
- Anti-IgA Ab: no deposits
- Anti-IgM Ab: no deposits
- Anti-C3 Ab: no deposits
- Anti-C1q Ab: no deposits
- Anti-kappa Ab: no glomerular deposits, 2+ staining of tubular casts
- Anti-lambda Ab: no glomerular deposits, 2+ staining of tubular casts
- Comment: Biopsy findings are consistent with BK virus associated nephropathy. Tubulitis is restricted to areas of viral cytopathy. There is no evidence of accompanying T cell or antibody mediated rejection or significant chronic tubulointerstitial damage.
Differential diagnosis
- JC virus nephropathy:
- Should be considered in patients with BK viremia loads inconsistent with strong SV40 staining in renal biopsy samples
- High grade urothelial carcinoma:
- Causes confusion especially in urine cytology, presence of Haufen in urine cytology and SV40 immunohistochemistry is diagnostic; other helpful morphologic findings are as follows:
BK virus: High grade urothelial carcinoma: - Hyperchromasia less pronounced
- Smudgy chromatin
- Homogeneous, opaque nucleus
- Absence of cell clusters
- Hyperchromasia more prominent
- Coarse chromatin
- Eccentrically located nucleus
- Presence of cell clusters
- Causes confusion especially in urine cytology, presence of Haufen in urine cytology and SV40 immunohistochemistry is diagnostic; other helpful morphologic findings are as follows:
- Acute T cell mediated rejection:
- SV40 immunohistochemistry is diagnostic (does not resolve diagnostic dilemma in cases with concurrent infection and rejection); other helpful morphologic findings are as follows:
BK virus: Acute T cell mediated rejection: - Cytopathic changes
- Tubulitis less prominent
- Inflammation patchy, well demarcated, more B cells
(Transplantation 2001;71:896) - No edema
- No vasculitis
- Neutrophils may be present
- Cytopathic changes absent but degenerative
regenerative changes may be confused with cytopathy - Tubulitis more prominent
- Inflammation less demarcated, more T cells
(Transplantation 2001;71:896) - Edema positive
- Vasculitis may be present
- Neutrophils rarer
- SV40 immunohistochemistry is diagnostic (does not resolve diagnostic dilemma in cases with concurrent infection and rejection); other helpful morphologic findings are as follows:
- Acute tubular injury:
- Nuclear degenerative / regenerative changes that accompany acute tubular injury may resemble viral cytopathy; the nuclear changes, however, are usually not as exaggerated, are composed of nucleolar enlargement and hyperchromasia and less often show chromatin changes that resemble intranuclear inclusions
- Moreover, inflammatory infiltration is not prominent, as that which accompanies viral infection
- SV40 immunohistochemistry also aids diagnosis
- Other viruses may have similar cytopathic changes, such as cytomegalovirus (presence of both intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions and perinuclear halo may aid histologic diagnosis), adenovirus and human herpes simplex virus (presence of both intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions may aid histologic diagnosis):
- Immunohistochemistry is diagnostic
- It should be kept in mind that concurrent infection with multiple viruses can be present in the immunosuppressed (BMJ Case Rep 2021;14:e235981)
- References: Yonsei Med J 2004;45:1065, Nephrol Dial Transplant 2021;36:587
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 36 year old kidney transplant patient presents with hematuria and laboratory tests show increased serum creatinine. Biopsy of the renal allograft reveals findings demonstrated in the photomicrograph above. Which of the entities below should be first on the differential diagnostic list?
- Acute tubular injury
- Antibody mediated rejection
- BK polyomavirus nephropathy
- High grade urothelial carcinoma
- T cell mediated rejection
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Below are the pathological examination findings of a bone marrow transplant patient:
What is your diagnosis?
- Intranuclear inclusions in tubular epithelial cells in renal biopsy
- Nuclear staining of tubular epithelial cells with SV40 immunohistochemistry in renal biopsy
- Inflammatory infiltrate composed predominantly of lymphomononuclear cells in renal biopsy
- Urinary Haufen in electron microscopic evaluation of urine cytology
What is your diagnosis?
- Acute hypersensitivity type tubulointerstitial nephritis
- Acute tubular injury
- BK virus associated nephropathy
- Graft versus host disease
- Pyelonephritis
Board review style answer #2