Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Genetics | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Reed RC. Dysplasia / hypoplasia / agenesis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumorcysticrenaldysplasia.html. Accessed September 17th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Dysplasia: abnormal renal development characterized by cysts and immature tubules with collarettes of immature mesenchyme
- Hypoplasia: reduced amounts of normal renal parenchyma; histologically normal kidney(s) with weight > 2 standard deviations below normal for age / body size
- Agenesis: unilateral or bilateral absence of renal tissue
Essential features
- Renal dysplasia often results from urinary tract obstruction
- Renal dysplasia is frequently associated with Müllerian tract abnormalities
- Cystic renal dysplasia can be distinguished from polycystic kidney disease by the presence of immature tubules, mesenchyme collarettes and cartilage
- Dysplasia, hypoplasia and agenesis are sporadic or associated with a broad range of genetic syndromes, many affecting additional organ systems
Terminology
- Dysplasia: multicystic renal dysplasia, multicystic dysplastic kidney
- Hypoplasia: simple hypoplasia
- Agenesis: aplasia
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Dysplasia
- Most common pediatric cystic renal disease
- Affects 1 in 1,000 - 4,300 live births; 90% of cases are unilateral
- 90% are associated with ureteropelvic obstruction, ureteral agenesis, atresia or reflux
- Many sporadic cases but also associated with numerous genetic disorders (see Genetics section)
- Hypoplasia
- When rigorously defined, hypoplasia is present in 1 in 400 live births (Adv Anat Pathol 2020;27:311)
- > 90% of cases are bilateral
- Associated with hypertension and extrarenal congenital abnormalities
- Agenesis
- Unilateral renal agenesis affects 1 in 1,000 live births; generally good prognosis if contralateral kidney is normal (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2021;225:B28)
- 33% of unilateral cases are associated with other congenital abnormalities of the kidney and urinary tract, most commonly vesicoureteral reflux
- 30% of unilateral renal agenesis cases in females are associated with unicornuate or bicornuate uterus or other Müllerian abnormality
- If contralateral kidney is involved by hypoplasia or dysplasia, high morbidity and mortality due to oligohydramnios sequence and pulmonary hypoplasia
- Bilateral renal agenesis affects 1 in 3,000 - 4,000 pregnancies; high morbidity and mortality due to oligohydramnios sequence and pulmonary hypoplasia
- For bilateral renal agenesis, M:F = 2:1
Sites
- Kidneys
Pathophysiology
- Dysplasia: abnormal differentiation of renal parenchyma results from genetic abnormality or urinary tract obstruction or reflux (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:547)
- WT1 expression stimulates ureteric bud development and early induction of renal mesenchyme
- PAX2 and BCL2 expression induces differentiation of mesenchyme to nephron epithelium
- In dysplastic kidneys, WT1 expression is decreased and there is persistent PAX2 and BCL2 expression, driving continued expression of immature epithelium
- Hypoplasia: inadequate branching of ureteric ducts results in a decreased number of reniculi (renal lobes) (Pediatr Res 2010;68:91)
- Agenesis: failure of the ureteric bud to develop or failure of the ureteric bud to induce metanephric mesenchyme differentiation (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2021;225:B28)
Etiology
- See Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Common genetic etiologies of renal dysplasia, hypoplasia and agenesis are covered in Genetics section; nonclinical associations include some maternal conditions, sporadic conditions and toxic exposures (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2020;15:723, Husain: Stocker and Dehner's Pediatric Pathology, 5th Edition, 2021)
- VACTERL association
- Prune belly sequence
- Maternal alcohol use (fetal alcohol spectrum disorder)
- Maternal diabetes (diabetic embryopathy)
Diagnosis
- Severe renal abnormalities are usually diagnosed prenatally via ultrasound (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2020;15:723)
- Oligohydramnios / anhydramnios is a common finding
- Less severe abnormalities may be found during workup for other congenital abnormalities, urinary tract infection or renal insufficiency
- Less severe abnormalities are sometimes discovered incidentally
Laboratory
- Evidence of renal failure: elevated BUN and creatinine
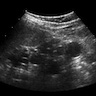
Radiology description
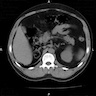
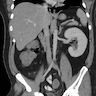
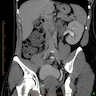
- Dysplasia (Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2008;13:142)
- Ultrasound: large bright kidneys
- Cystic spaces in cortex or uniformly echogenic parenchyma
- Hypoplasia
- Ultrasound shows reduced renal volume but cannot distinguish between true hypoplasia and dysplasia, scarring, atrophy or other etiologies
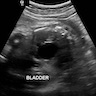
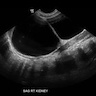
- Agenesis (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2021;225:B28)
- Ultrasound: empty renal fossa
- Lying down adrenal sign
- Oligohydramnios / anhydramnios after 16 - 18 weeks gestation
- Absent renal artery by Doppler
- Absent (nonvisualized) bladder
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Favorable: unilateral involvement with normal contralateral kidney
- Unfavorable: bilateral involvement or abnormalities of both kidneys
- Bilateral involvement results in oligohydramnios sequence and pulmonary hypoplasia in utero or renal insufficiency and end stage kidney disease following birth
- Recurrence risk in first degree relatives (including siblings): 4 - 20% (Int J Mol Sci 2017;18:796)
Case reports
- 19 week fetus with unilateral multicystic renal dysplasia (Cureus 2023;15:e37786)
- Term newborn boy with renal hypoplasia, biopsy demonstrated oligomeganephronia (Kobe J Med Sci 2021;67:E34)
- 31 year old woman with unilateral renal agenesis, uterus didelphys and obstructed hemivagina with hematohemicolpos (BJR Case Rep 2020;7:20200132)
Treatment
- Conservative management if renal function is adequate
- Nephrectomy of involved kidney to manage hypertension, abdominal mass or recurrent infection
- Renal replacement therapy (dialysis or transplant) for renal insufficiency / end stage kidney disease
- For fetuses with oligohydramnios / anhydramnios, clinical trial of amnioinfusion to promote lung development (Clin Perinatol 2022;49:849)
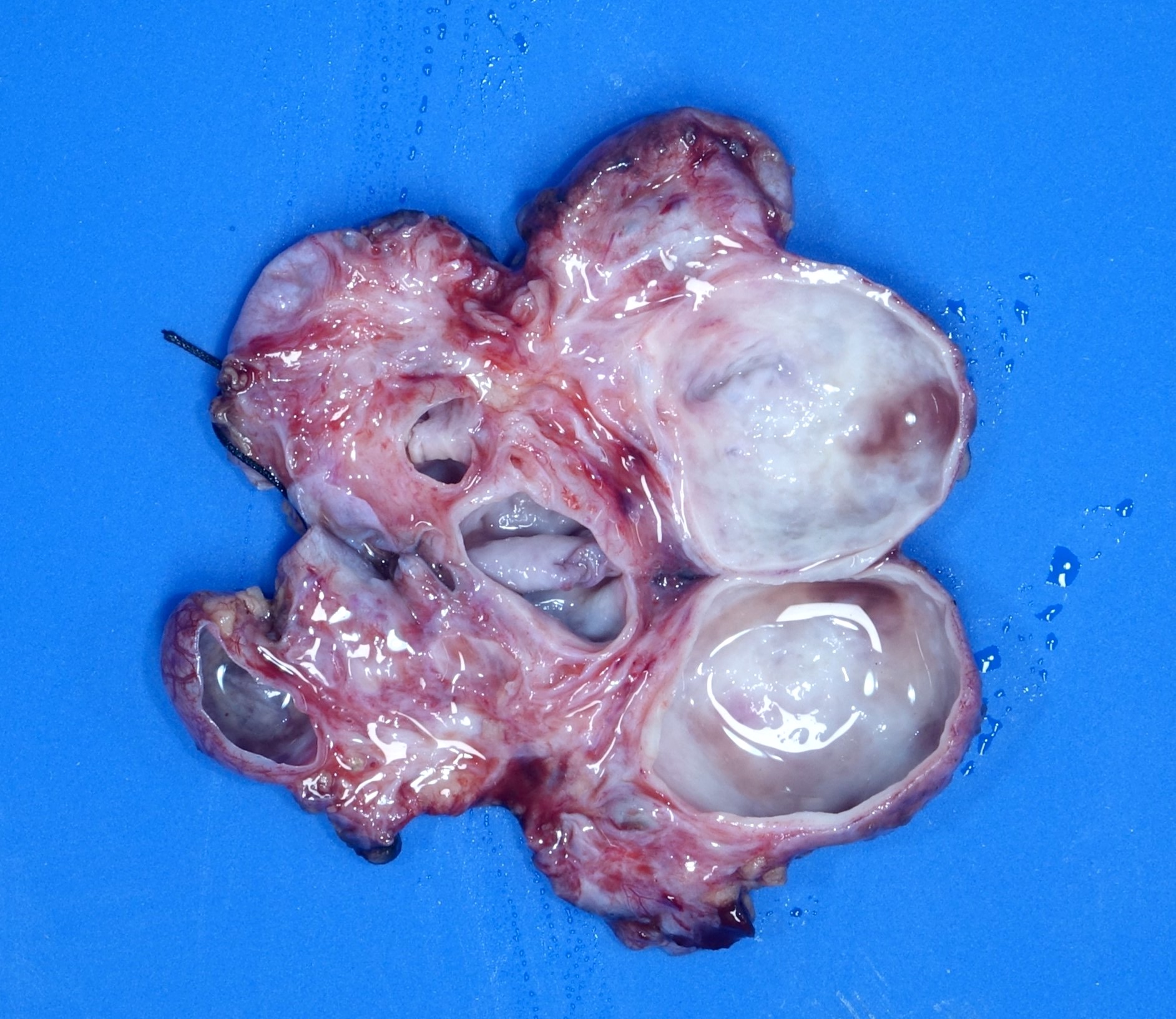
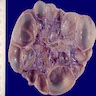
Gross description
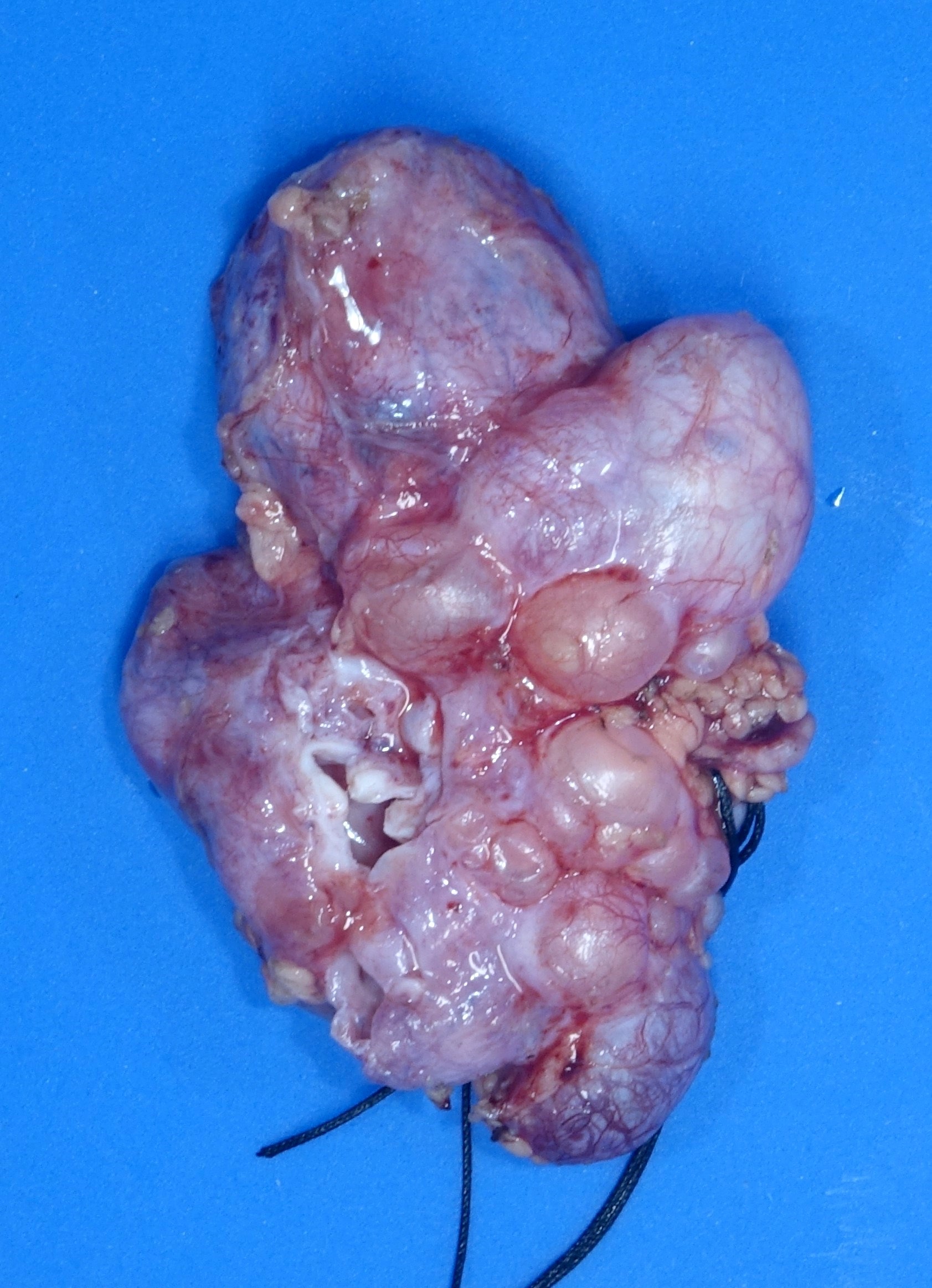
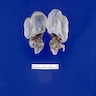
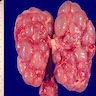
- Dysplasia
- Kidney may be small, normal in size or enlarged; shape is distorted by cysts and sometimes by pelvicalyceal dilation
- Ureter may be stenotic or dilated
- Small areas of remnant renal parenchyma are interspersed with cysts of varying sizes
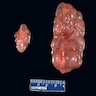
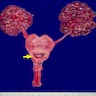
- Hypoplasia
- Weight > 2 standard deviations below median weight for patient age / size (Pediatr Res 2010;68:91)
- Reniform (kidney shaped) kidney with reduced numbers of renal lobes and calyces
- Normal number is ~10; in hypoplasia there are 5 or fewer
- Gross appearance is otherwise normal
- Ipsilateral adrenal gland may be disc shaped rather than triangular, because the kidney is not large enough to indent it
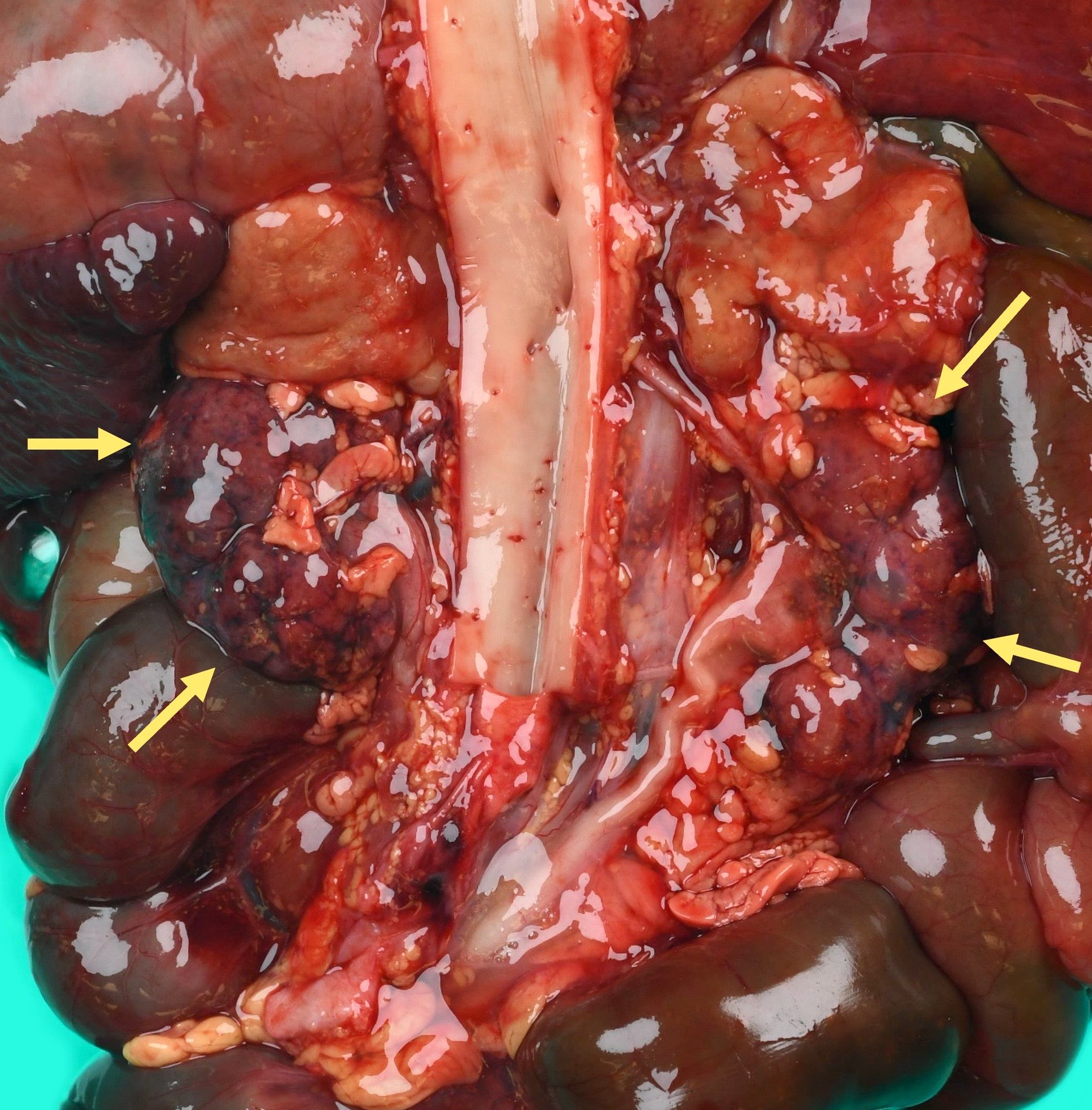
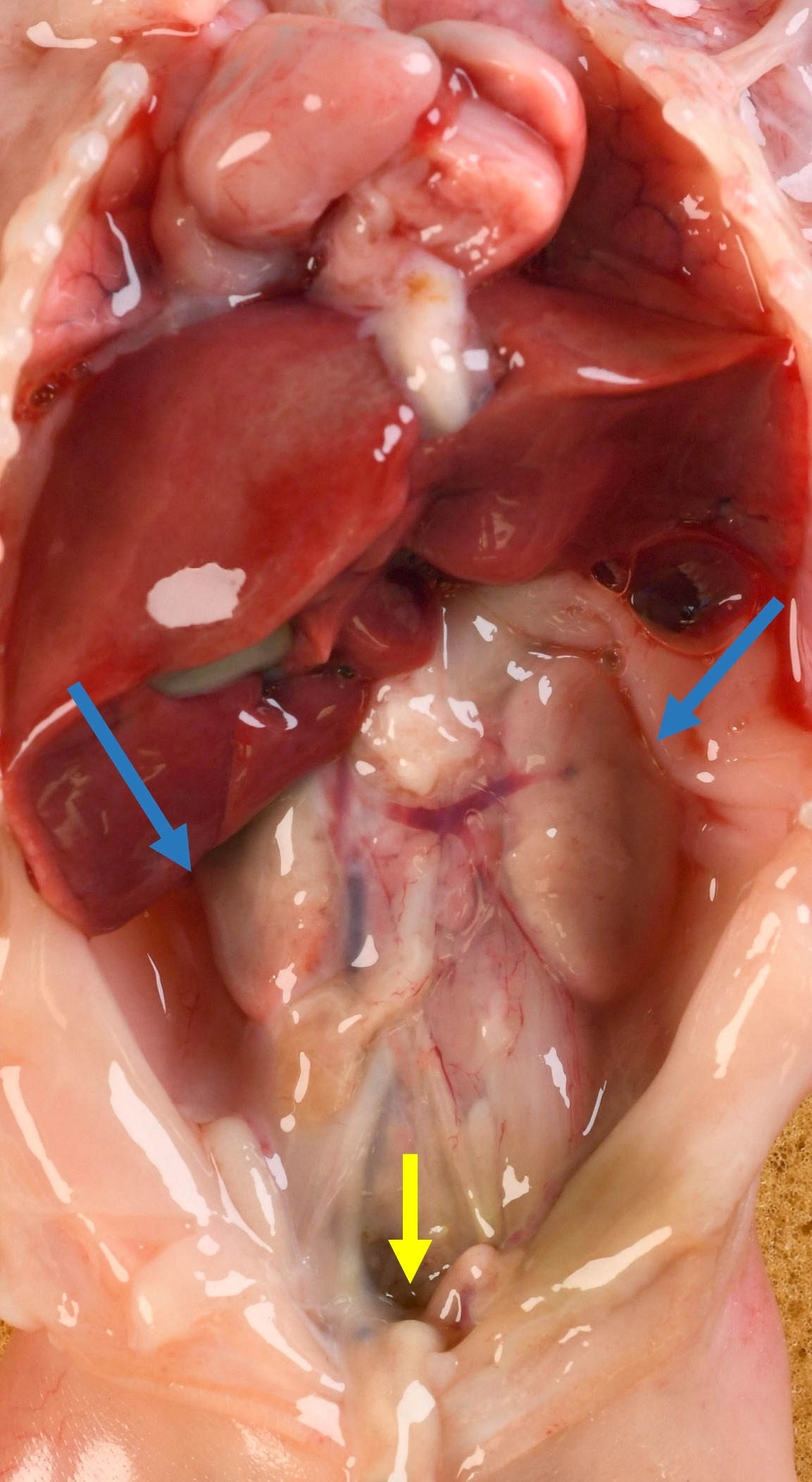
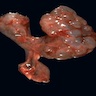
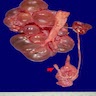
- Agenesis
- Absent kidney, ureter and renal artery and vein
- Ipsilateral adrenal gland is disc shaped rather than triangular, because the kidney is not there to indent it
Gross images
Contributed by Robyn C. Reed, M.D., Ph.D.
Images hosted on other servers:
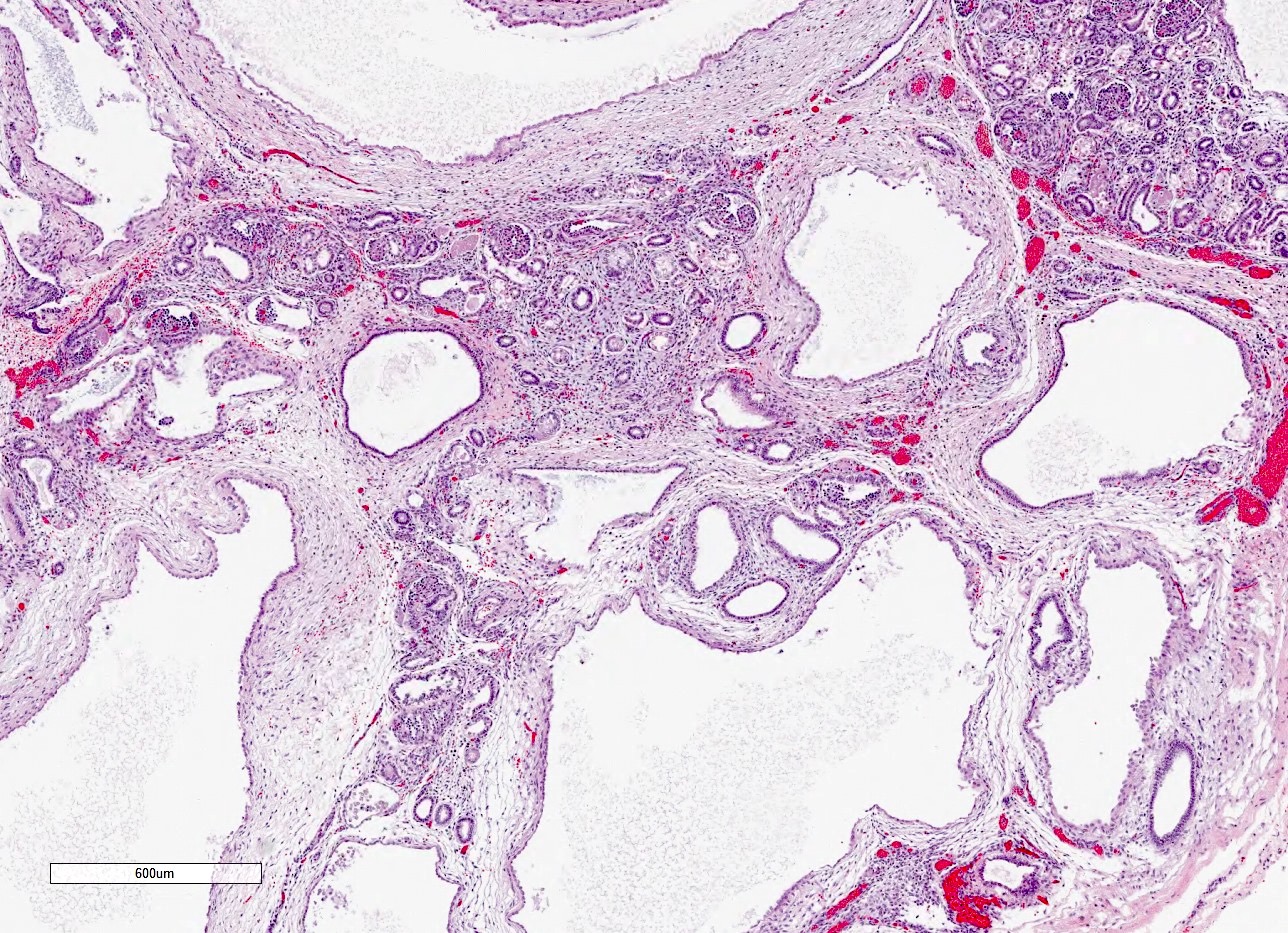
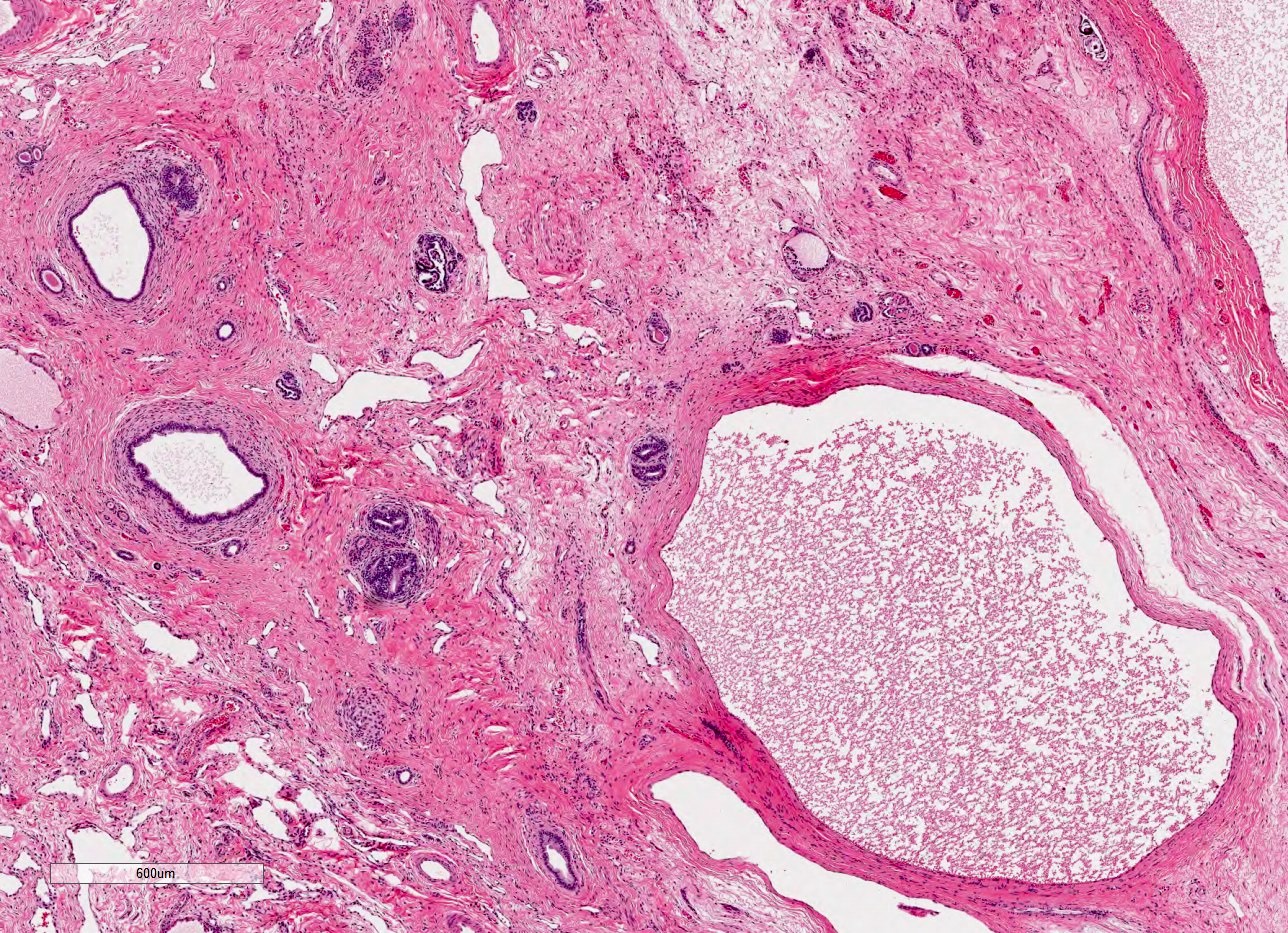
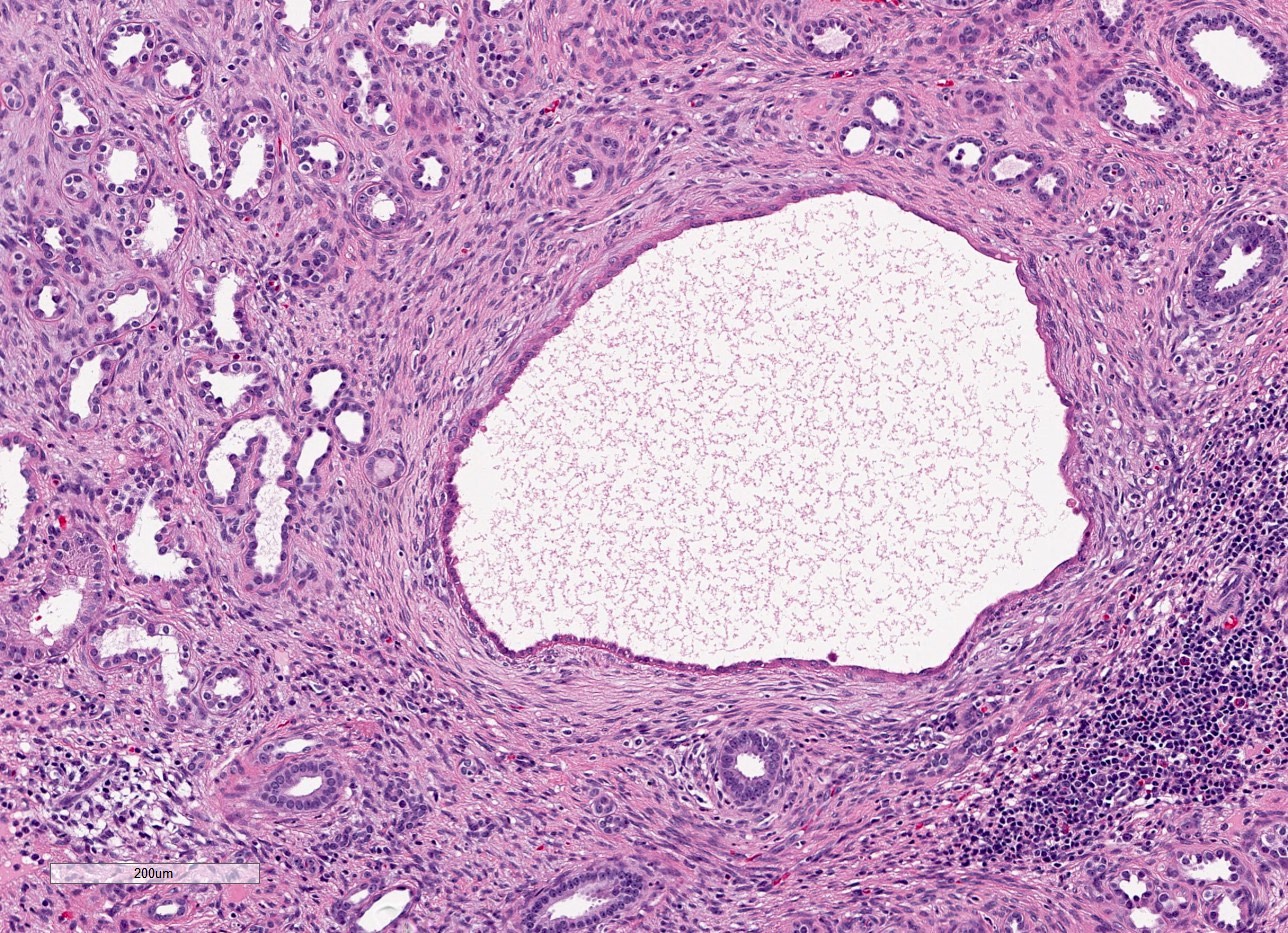
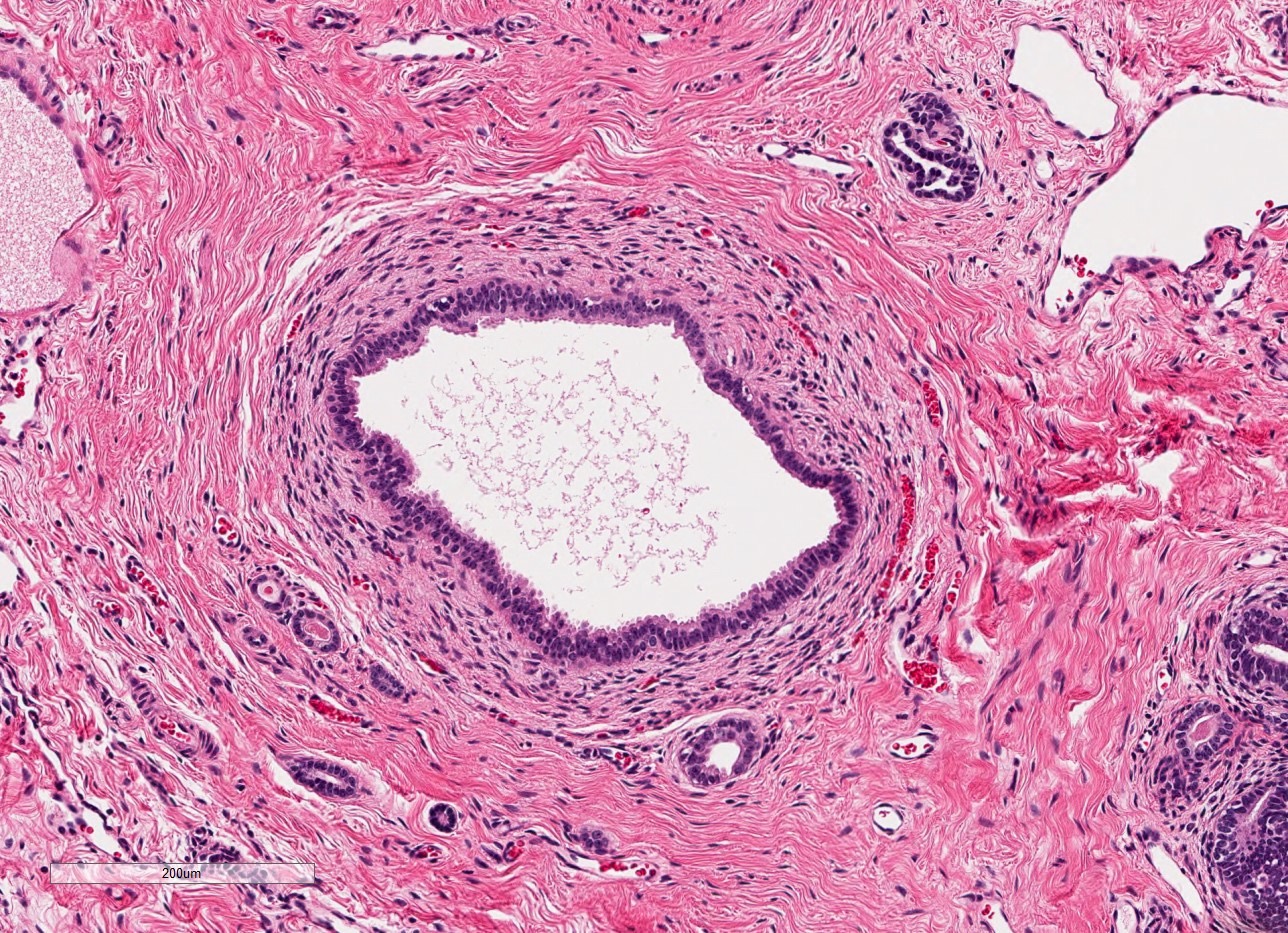
Microscopic (histologic) description
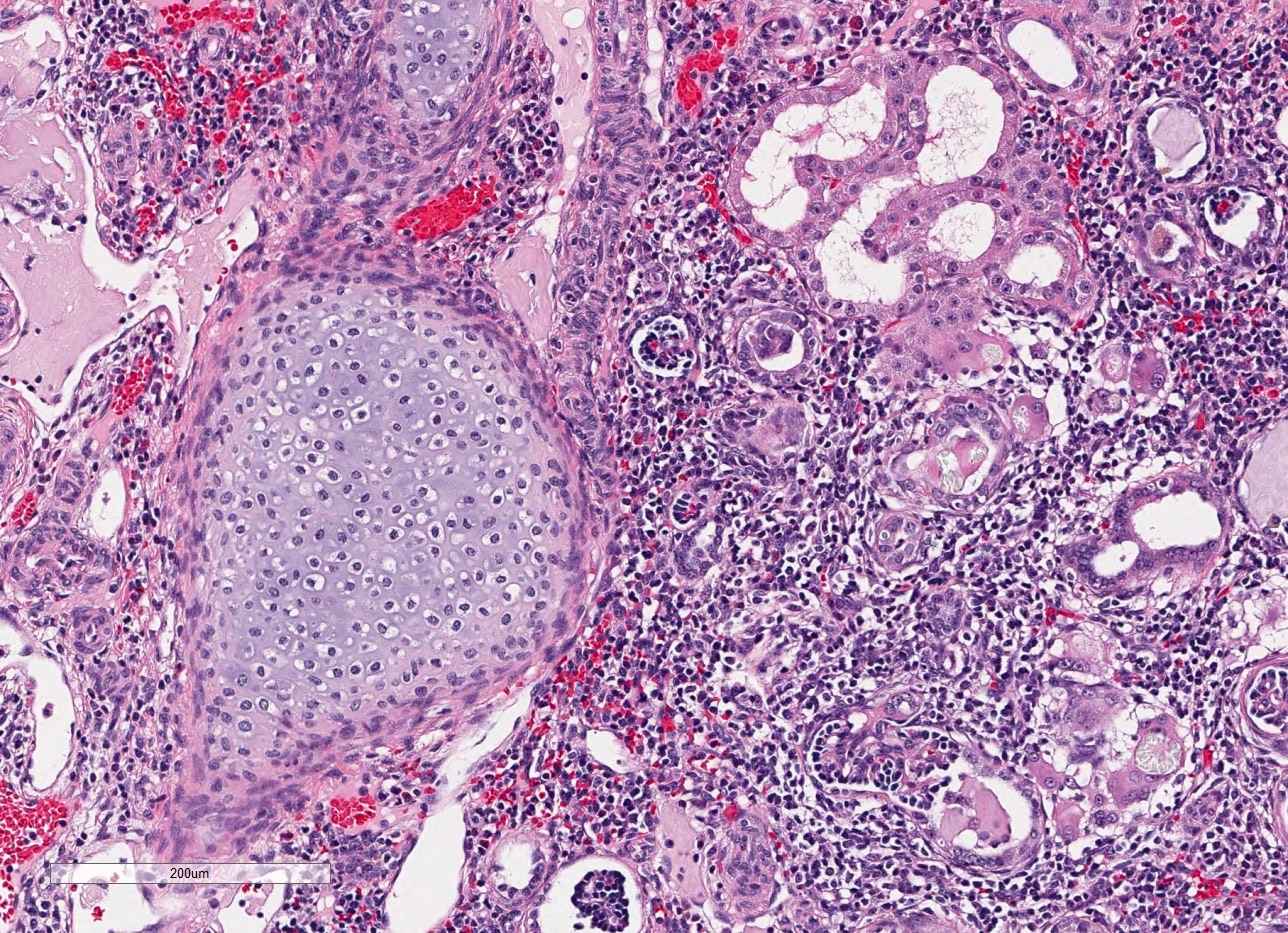
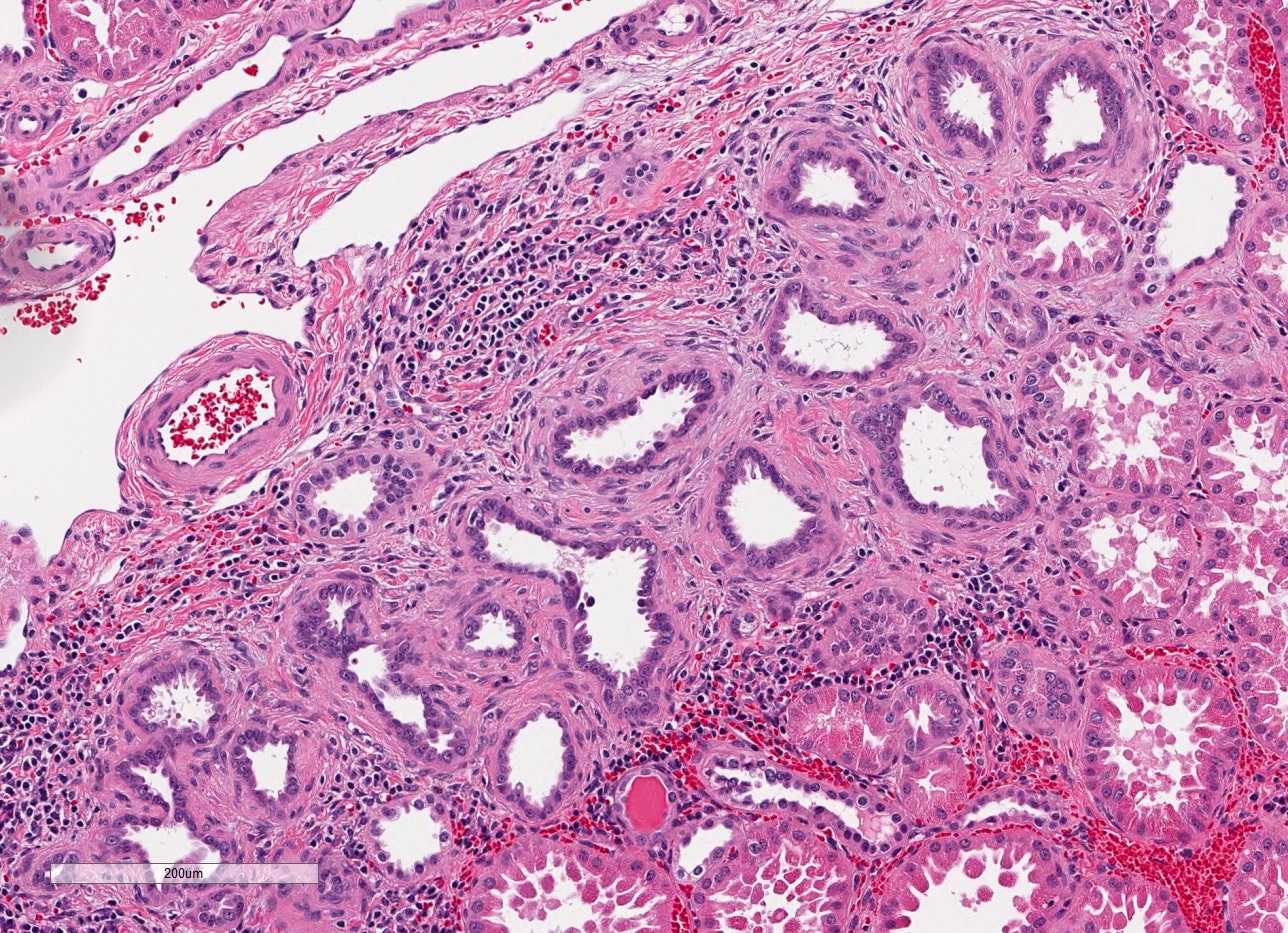
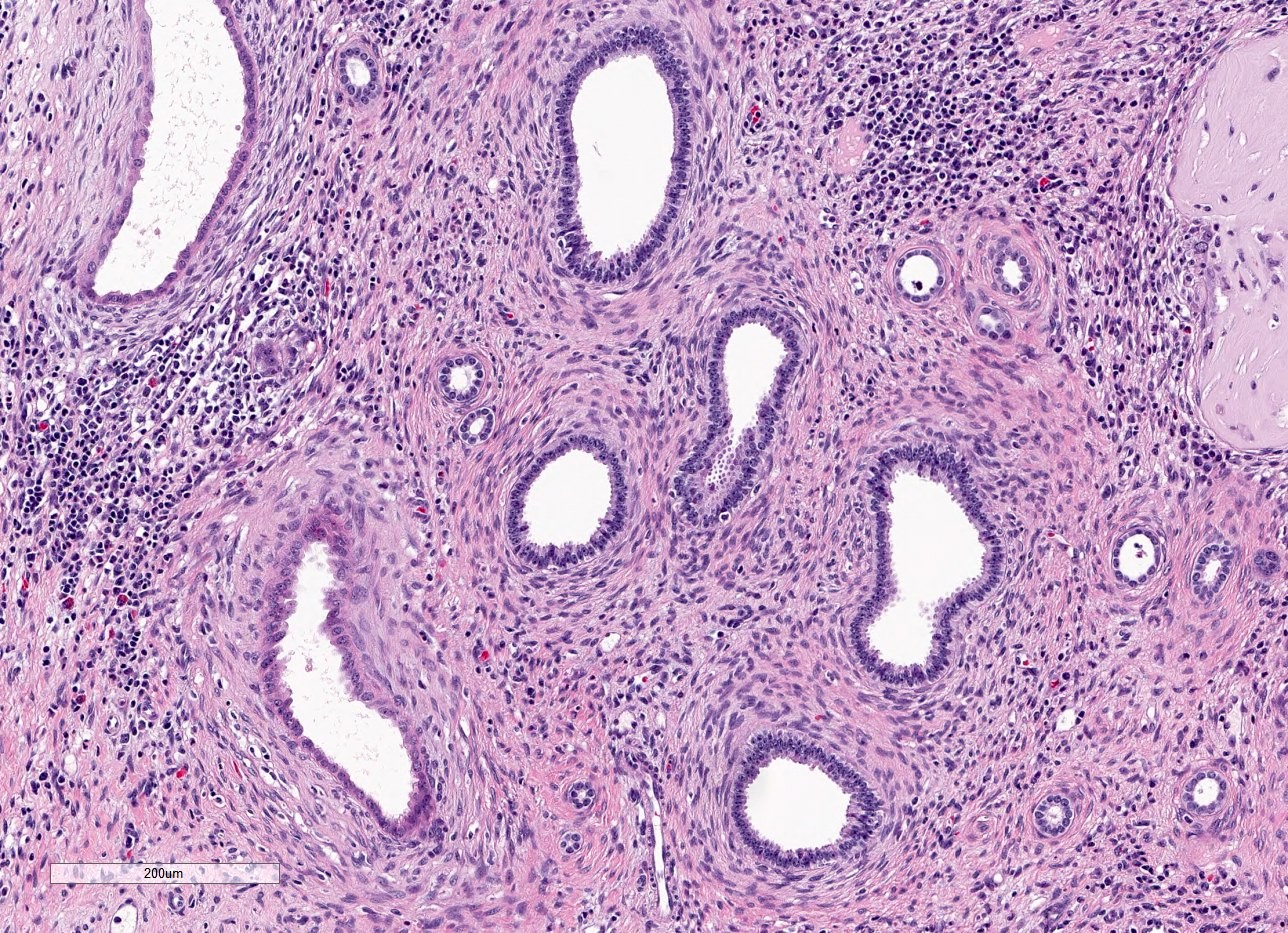
- Dysplasia
- Normal or scarred parenchyma alternating with cysts of varying sizes, lined by flat to cuboidal epithelium
- Collections of tubules lined by immature epithelium and surrounded by collarettes of immature mesenchyme
- Metaplastic cartilage
- Nodules of blastema (immature renal parenchyma) in 3 - 5% of cases
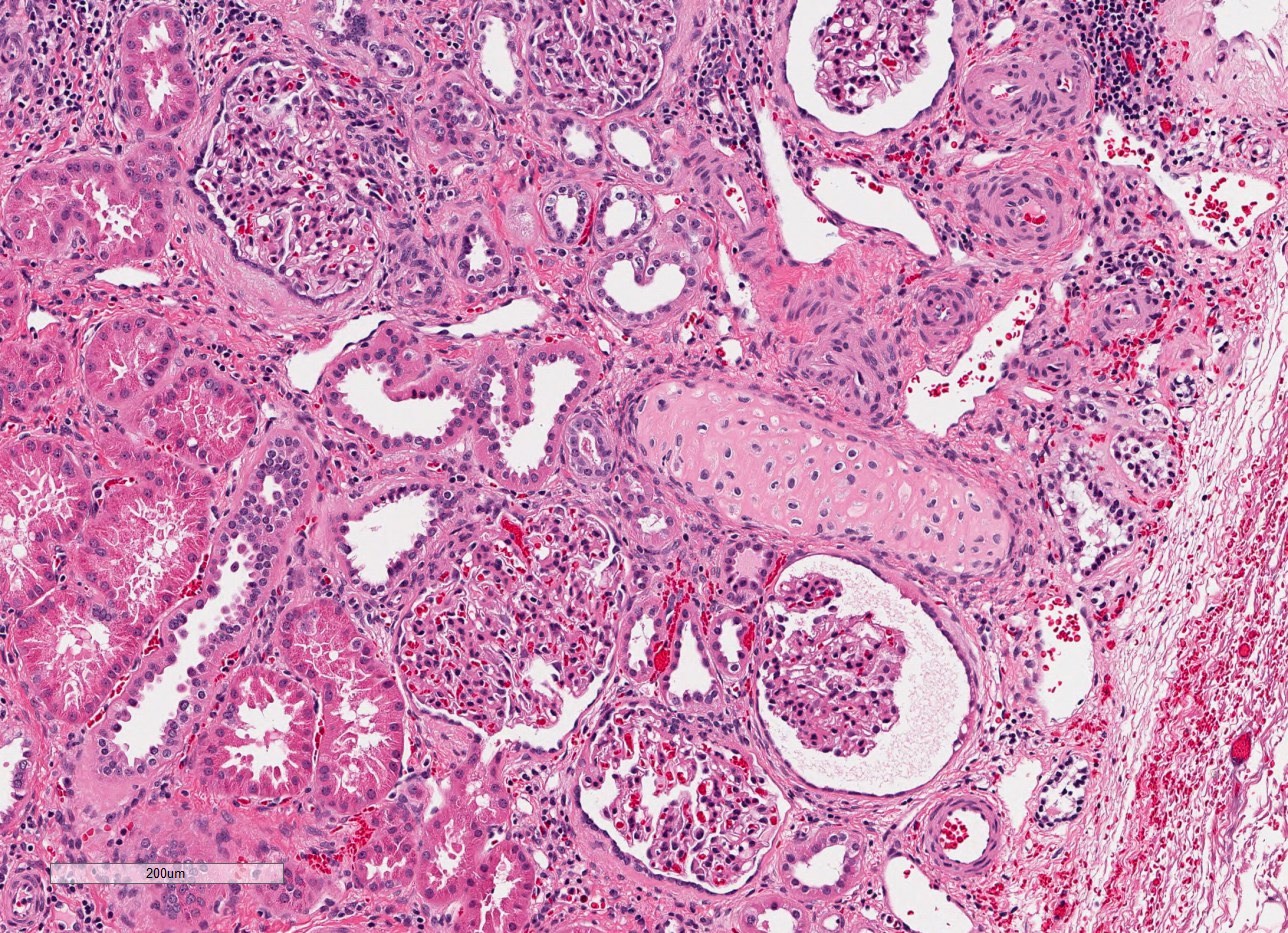
- Hypoplasia
- By definition, normal histology
- If dysplastic changes are present it is classified as dysplasia
- If glomeruli are markedly enlarged, consider oligomeganephronia (Adv Anat Pathol 2020;27:311)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Genetics
- At least 40 genes have been implicated in congenital abnormalities of the kidney and urinary tract, accounting for ~18% of cases (J Am Soc Nephrol 2018;29:36)
- Many genetic alterations have a phenotypic spectrum that encompasses dysplasia, hypoplasia, agenesis and other structural abnormalities
- Dysplasia is associated with numerous genetic disorders; this is a partial list (Fetal Pediatr Pathol 2014;33:293, Husain: Stocker and Dehner's Pediatric Pathology, 5th Edition, 2021)
- Meckel-Gruber syndrome (autosomal recessive, at least 16 genes) (GeneReviews: Nephronophthisis-Related Ciliopathies [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Joubert syndrome (autosomal recessive or X linked, at least 34 genes) (GeneReviews: Joubert Syndrome [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Zellweger syndrome (autosomal recessive, at least 13 genes) (GeneReviews: Zellweger Spectrum Disorder [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- HNF1B deficiency syndrome (autosomal dominant, HNF1B) (Cells 2023;12:307)
- Renal - hepatic - pancreatic dysplasia (autosomal recessive, NPHP3 or NEK8) (OMIM: Renal-Hepatic-Pancreatic Dysplasia 1; RHPD1 [Accessed 26 July 2023], OMIM: Renal-Hepatic-Pancreatic Dysplasia 2; RHPD2 [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Short rib polydactyly syndromes, including Jeune syndrome (autosomal recessive, at least 23 genes) (Hum Mutat 2018;39:152)
- Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency (autosomal recessive, CPT2) (GeneReviews: Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase II Deficiency [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Hereditary renal adysplasia (autosomal dominant, ITGA8 or FGF20) (Fetal Pediatr Pathol 2014;33:293)
- Nail patella syndrome (autosomal dominant, LMX1B) (GeneReviews: Nail-Patella Syndrome [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Genitopatellar syndrome (autosomal dominant, KAT6B) (GeneReviews: KAT6B Disorders [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Bardet-Biedl syndrome (autosomal recessive, at least 25 genes) (GeneReviews: Bardet-Biedl Syndrome Overview [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (usually sporadic, CDKN1C or 11p15.5 alterations) (GeneReviews: Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (autosomal dominant, 22q11.2 alterations) (GeneReviews: 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Trisomies 13, 18, 21 and numerous chromosomal deletions and duplications (sporadic) (Int J Pediatr Nephrol 1987;8:215)
- Dysplasia and other congenital abnormalities of the kidney and urinary tract have also been linked with alterations in numerous additional genes (Curr Opin Pediatr 2016;28:209, J Am Soc Nephrol 2018;29:36)
- Renal agenesis and hypoplasia are associated with numerous genetic disorders, including some of the disorders listed above for renal dysplasia as well as the following syndromes (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2021;225:B28)
- Acro renal ocular syndrome (autosomal dominant, SALL4) (GeneReviews: SALL4-Related Disorders [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Branchiootorenal syndrome (autosomal dominant, EYA1, SIX1 or SIX5) (GeneReviews: Branchiootorenal Spectrum Disorder [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Pallister-Hall syndrome (autosomal dominant, GLI3) (GeneReviews: GLI3-Related Pallister-Hall Syndrome [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Fraser syndrome (autosomal recessive, FRAS1, FREM2 and GRIP1) (OMIM: Fraser Syndrome 1; FRASRS1 [Accessed 26 July 2023])
- Renal agenesis has also been linked with alterations in GREB1L, GFRA1, ITA8 and FGF20 (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2021;225:B28)
Videos
Development of renal dysplasia
Development of renal agenesis; explanation of oligohydramnios sequence
Sample pathology report
- Kidney, left (32 g), nephrectomy:
- Multicystic renal dysplasia (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show frequently scarred renal parenchyma interspersed with multiple cysts, some lined by attenuated simple epithelium and some unlined. There are scattered collections of primitive tubules surrounded by collarettes of immature mesenchyme and a few foci of metaplastic cartilage. The features are typical of multicystic renal dysplasia.
Differential diagnosis
- Dysplasia:
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease:
- Familial, bilateral; presents at birth
- Uniform, radially arranged fusiform cysts arising in collecting ducts
- No immature mesenchyme or cartilage
- Alterations in PKHD1
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease:
- Familial, bilateral, usually presents in adulthood but does rarely present at birth
- No immature mesenchyme or cartilage
- Alterations in PKD1, PKD2 or PKD3
- Nephronophthisis:
- Familial, bilateral; presents in infancy or childhood
- Corticomedullary cysts with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy
- No immature mesenchyme or cartilage
- Alterations in NPHP1 or at least 24 other genes (Husain: Stocker and Dehner's Pediatric Pathology, 5th Edition, 2021)
- Medullary sponge kidney:
- Usually sporadic, usually bilateral, usually presents in adulthood but rarely in children and infants
- Ectatic and cystic collecting ducts in the renal medulla
- No immature mesenchyme or cartilage
- Cystic nephroma:
- Sharply demarcated from adjacent normal kidney by thick fibrous capsule, no renal tissue between cysts, no immature mesenchyme or cartilage
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease:
- Hypoplasia:
- Segmental hypoplasia (Ask-Upmark kidney):
- Exterior has one or more deep cortical grooves
- On cut section, normal parenchyma alternates with areas of marked cortical thinning and scar (Adv Anat Pathol 2020;27:311)
- Oligomeganephronia:
- Bilateral small kidneys with markedly enlarged glomeruli, juxtaglomerular apparatus and tubules (Adv Anat Pathol 2020;27:311)
- Acquired atrophy secondary to infarction of infection:
- Normal parenchyma alternates with areas of cortical scar or inflammation
- Segmental hypoplasia (Ask-Upmark kidney):
- Agenesis:
- Ectopic kidney (e.g., pelvic kidney, horseshoe kidney):
- Kidney is located elsewhere in body (usually pelvis or contralateral abdomen; rarely thorax)
- Severe acquired atrophy secondary to infarction or infection:
- Small scarred remnant kidney is present
- Ectopic kidney (e.g., pelvic kidney, horseshoe kidney):
Practice question #1
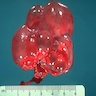
An infant died of respiratory insufficiency shortly after birth. At autopsy, both kidneys had the appearance shown in the image above. Which of the following is most suggestive of bilateral renal dysplasia as the correct diagnosis?
- Ectatic and cystic collecting ducts in the medulla
- Family history of congenital renal cysts in 2 of 5 siblings
- Foci of primitive tubules with collarettes of mesenchyme
- Known homozygous mutation in PKHD1
- Markedly small bilateral kidneys with normal histology
Practice answer #1
C. Foci of primitive tubules with collarettes of mesenchyme. The differential diagnosis in the case of a neonate with bilateral cystic kidneys includes bilateral cystic renal dysplasia, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and nephronophthisis. (Medullary sponge kidney and other causes of renal cysts are less likely, as onset is almost always postnatal.) The presence of primitive tubules with collarettes of mesenchyme is highly suggestive of renal dysplasia and is not seen in the other entities listed.
Answer A is incorrect because medullary collecting ducts are dilated in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease and nephronophthisis but are not specifically affected in renal dysplasia. Answer B is incorrect because this strong family history is more suggestive of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease or autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Although renal dysplasia can recur within families, inheritance is rarely Mendelian. Answer D is incorrect because mutations in PKHD1 are associated with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease, not renal dysplasia. Answer E is incorrect because small bilateral kidneys with normal histology is the definition of renal hypoplasia, not renal dysplasia.
Comment Here
Reference: Dysplasia / hypoplasia / agenesis
Answer A is incorrect because medullary collecting ducts are dilated in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease and nephronophthisis but are not specifically affected in renal dysplasia. Answer B is incorrect because this strong family history is more suggestive of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease or autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Although renal dysplasia can recur within families, inheritance is rarely Mendelian. Answer D is incorrect because mutations in PKHD1 are associated with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease, not renal dysplasia. Answer E is incorrect because small bilateral kidneys with normal histology is the definition of renal hypoplasia, not renal dysplasia.
Comment Here
Reference: Dysplasia / hypoplasia / agenesis
Practice question #2
Which of the following conditions, when identified prenatally, is most likely to result in severe renal insufficiency and oligohydramnios sequence?
- Agenesis of the left kidney, dysplastic right kidney
- Agenesis of the left kidney, normal appearing right kidney
- Horseshoe kidney with fused lower poles
- Normal appearing left kidney, hypoplastic right kidney
Practice answer #2
A. Agenesis of the left kidney, dysplastic right kidney. Clinical consequences of congenital abnormalities of the kidneys and urinary tract encompass the entire spectrum from asymptomatic to incompatible with life. Severity of renal abnormalities in utero depends on whether there is sufficient remaining renal parenchyma to support the ongoing production of fetal urine, contributing to amniotic fluid volume. If there is insufficient amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios), lung development and maturation is impaired, leading to respiratory insufficiency at birth. In the setting of contralateral renal agenesis, a dysplastic kidney is unlikely to contribute sufficiently to the amniotic fluid volume (and in fact it may be dysplastic due to an obstructive lesion within the urinary tract).
Answer B is incorrect because a single, normally functioning kidney is sufficient to support renal function and amniotic fluid production. Answer C is incorrect because, despite its aberrant shape and location, a horseshoe kidney maintains normal renal function in utero. Answer D is incorrect because a normal kidney and a hypoplastic kidney together are sufficient to support renal function and amniotic fluid production.
Comment Here
Reference: Dysplasia / hypoplasia / agenesis
Answer B is incorrect because a single, normally functioning kidney is sufficient to support renal function and amniotic fluid production. Answer C is incorrect because, despite its aberrant shape and location, a horseshoe kidney maintains normal renal function in utero. Answer D is incorrect because a normal kidney and a hypoplastic kidney together are sufficient to support renal function and amniotic fluid production.
Comment Here
Reference: Dysplasia / hypoplasia / agenesis