Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Gama AP, Choy B. Juxtaglomerular cell tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumorjgtumor.html. Accessed September 23rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare renin secreting tumor arising from the specialized smooth muscle cells of the glomerular afferent arteriole in the renal juxtaglomerular apparatus
Essential features
- Occurs mostly in young adults; female predominance
- Frequently associated with severe and poorly controlled hypertension, hypokalemia and hyperaldosteronism secondary to tumor renin secretion
- Almost always benign with single case of metastatic disease
- Sheets of polygonal to spindle cells with well defined cell border and prominent vasculature
- Tumor cells are positive for renin, vimentin, CD34 and CD117
Terminology
- Reninoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8361/0 - juxtaglomerular tumor
Epidemiology
- ~100 cases reported
- Young adults (20 - 35 years) but has been reported in children and older adults (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854)
- F > M (~2:1) (Pediatr Nephrol 1993;7:404, Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854)
Sites
- Kidney cortex
Clinical features
- 3 clinical categories (Urol Oncol 2010;28:34):
- Typical variant:
- Majority of cases
- Characteristic hypertension, hyperaldosteronism and hypokalemia secondary to hyperreninemia (Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl 1973;45:279s4, J Urol 1973;109:349)
- Hypertension does not respond to medical antihypertensive therapy
- Atypical variant:
- Hypertension with normal potassium levels (Pediatr Nephrol 1993;7:404)
- Nonfunctioning variant:
- Very rare reports of nonfunctioning tumors without hypertension or hypokalemia (Pathol Int 1997;47:393, Case Rep Pathol 2013;2013:973865, Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e22057)
- Typical variant:
- Other symptoms include headache, polyuria, nocturia, dizziness, vomiting (Pediatr Nephrol 1993;7:404, Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is suspected in young patients presenting with severe hypertension and hypokalemia and radiologic findings consistent with renal tumor
- Clinical workup to rule out other causes of hypertension
Laboratory
- Elevated serum renin and aldosterone levels
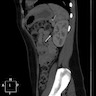
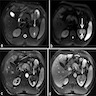
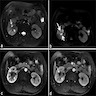
Radiology description
- Ultrasound: hypoechoic mass (Urology 2003;61:1259, Urol Int 2010;85:121)
- CT (Radiographics 2010;30:1525):
- Hypodense or isodense solid mass
- Dynamic CT shows hypovascular mass in arterial phase despite profuse vascularity
- Moderate enhancement during delayed phase
- MRI (Radiographics 2010;30:1525, Am J Kidney Dis 2019;73:566):
- Variable findings
- Isointensity or hypointensity on T1 weighted images
- Hyperintensity on T2 weighted images
- Renal vein sampling may be useful, especially in small tumors
- Renal arteriography shows no evidence of renal artery stenosis
Prognostic factors
- 90% of patients will become normotensive following tumor resection
- 10% remain mildly hypertensive despite surgical resection (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854)
- Unlikely to recur after resection
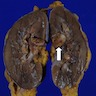
- Almost always benign, with single reported case of metastatic disease to the lung (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1098)
- Single case of death due to massive brain hemorrhage secondary to severe hypertension (Hum Pathol 1974;5:236)
- Single case of juxtaglomerular cell tumor causing fetal demise (Int Urol Nephrol 2011;43:365)
Case reports
- 16 year old boy with hereditary BRIP1 mutation and spindle cell hemangioma, presenting with juxtaglomerular cell tumor (Genes (Basel) 2021;12:220)
- 22 year old woman with juxtaglomerular cell tumor associated with membranous glomerulonephritis (Ann Diagn Pathol 2003;7:314)
- 29 year old woman with nonfunctioning juxtaglomerular cell tumor mimicking renal cell carcinoma (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e22057)
- 52 year old man with metastatic juxtaglomerular cell tumor to the lung (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1098)
- 74 year old man with atypical juxtaglomerular cell tumor (Case Rep Pathol 2018;2018:6407360)
Treatment
- Surgical resection: partial or total nephrectomy
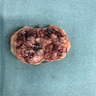
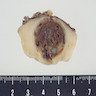
Gross description
- Unilateral and solitary (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854, Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80)
- Well circumscribed; fully or partially encapsulated
- Gray to yellow-tan, solid cut surface; may have hemorrhage and be partially cystic
- Average: 2 - 3 cm (range: 0.2 - 15 cm)
Gross images
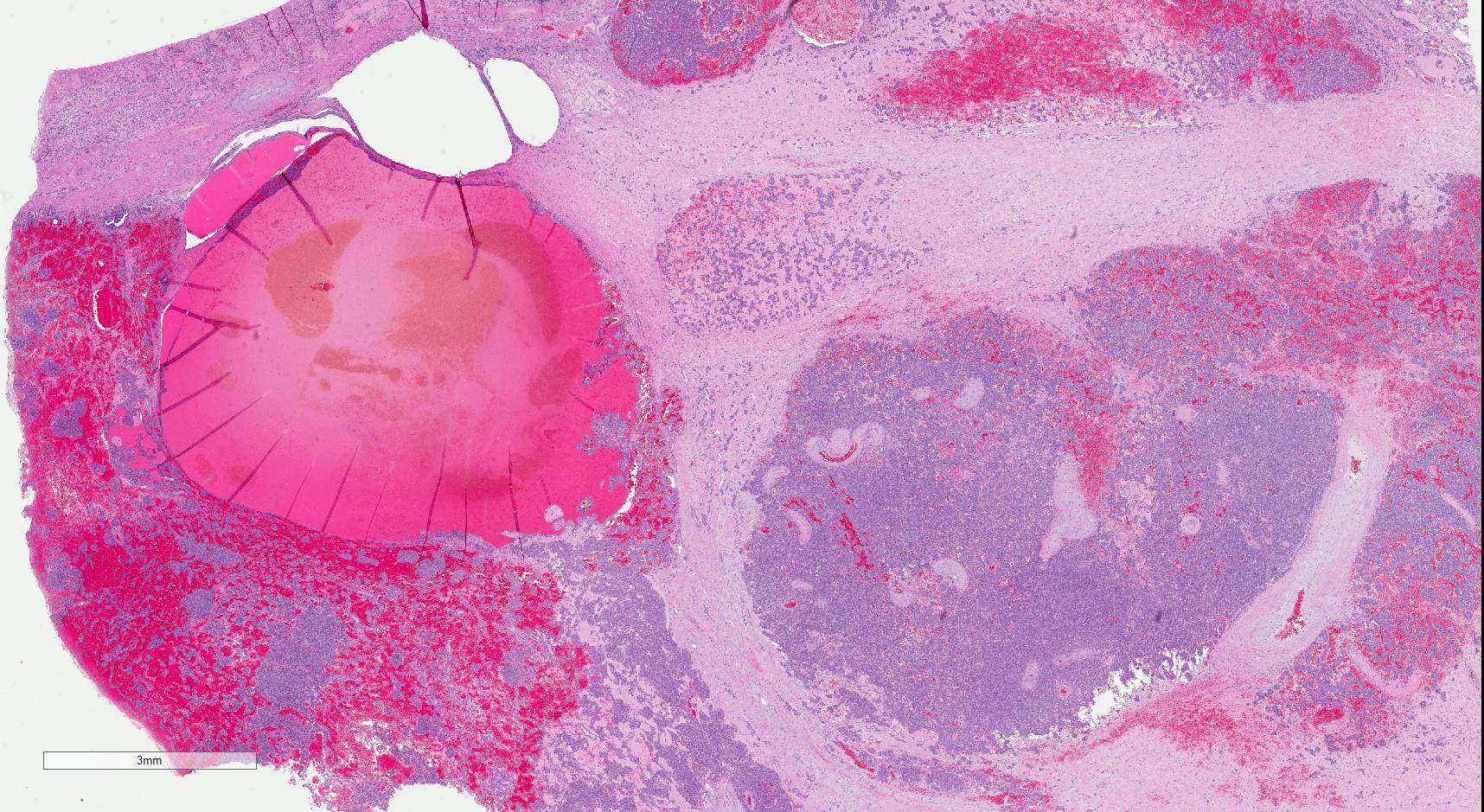
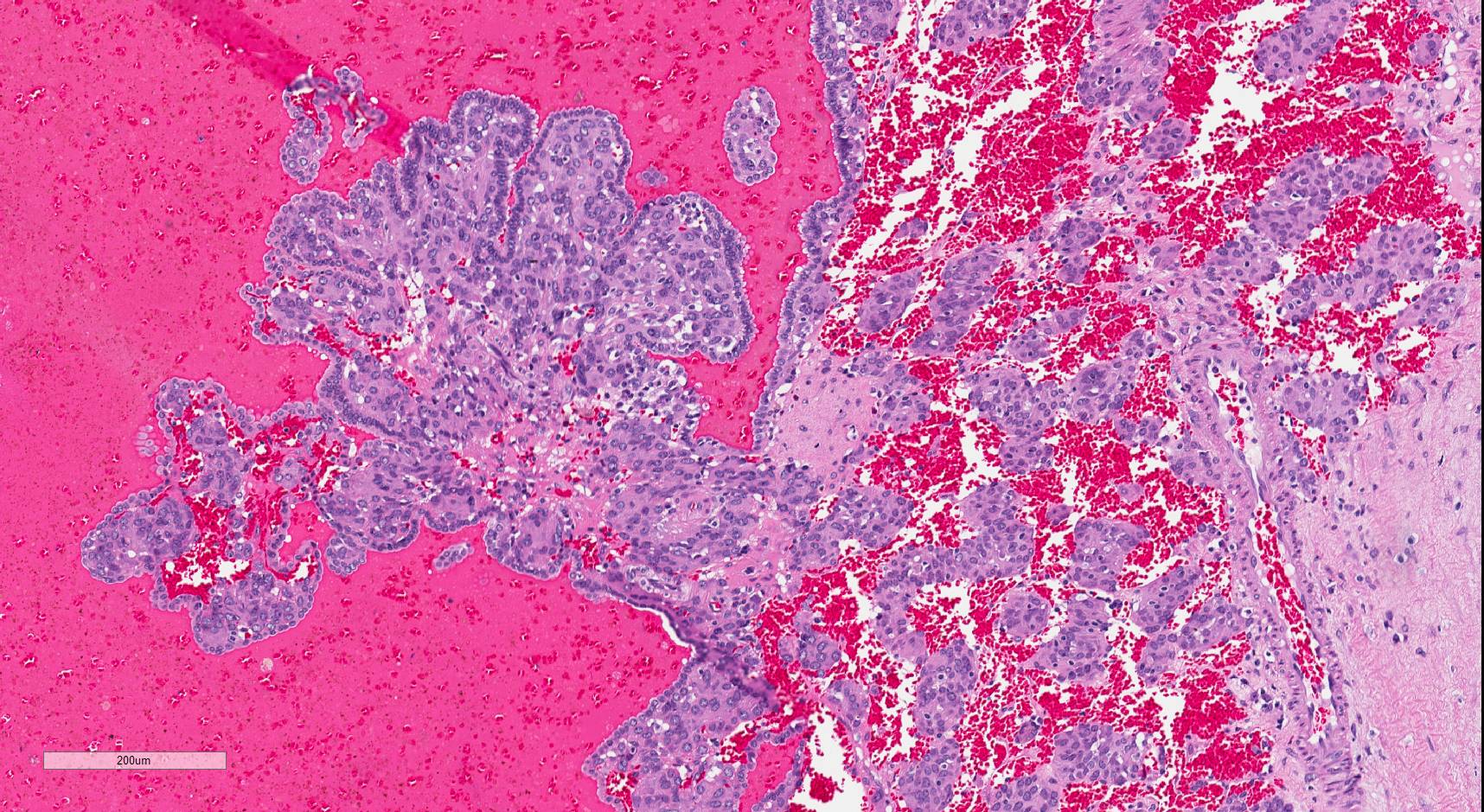
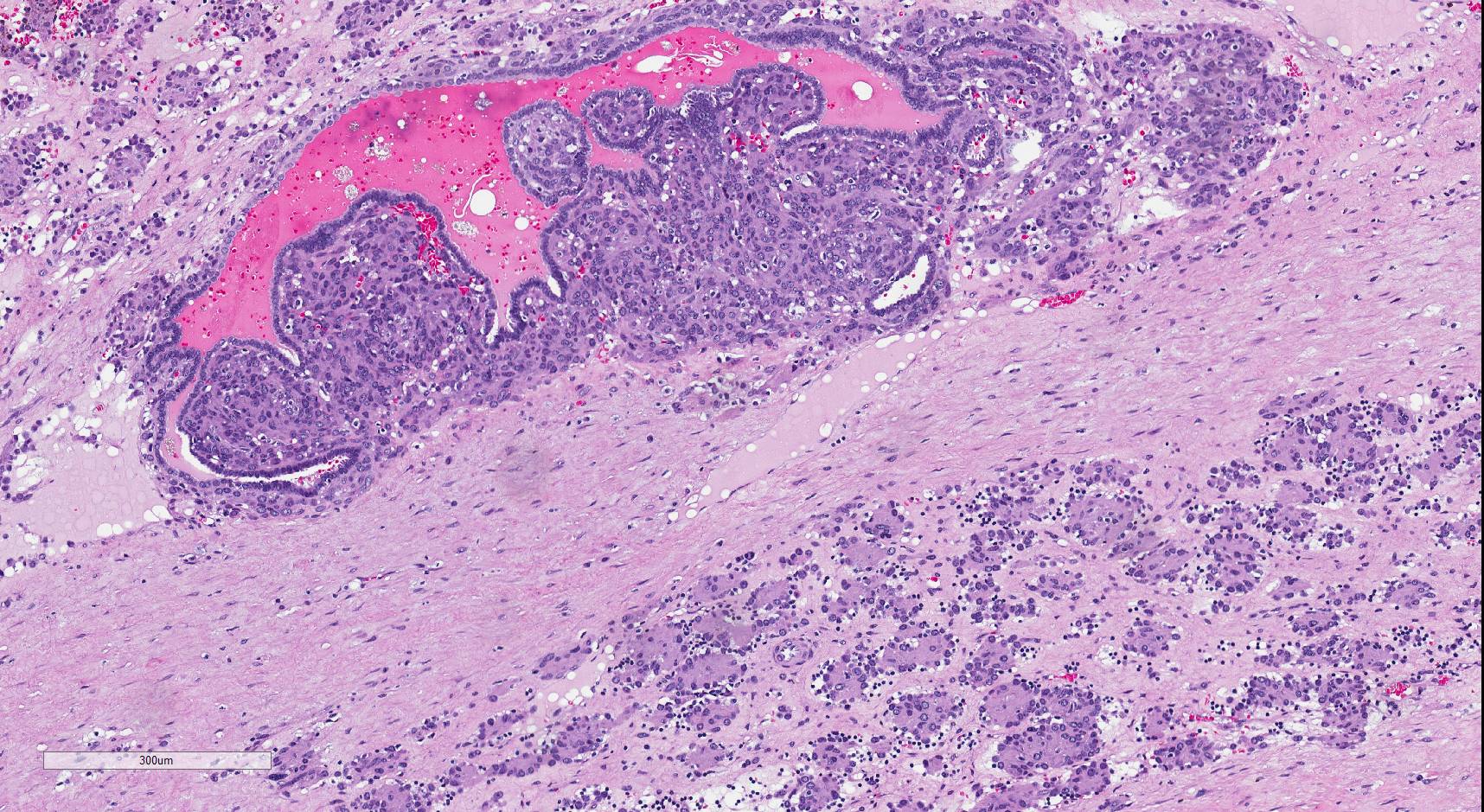
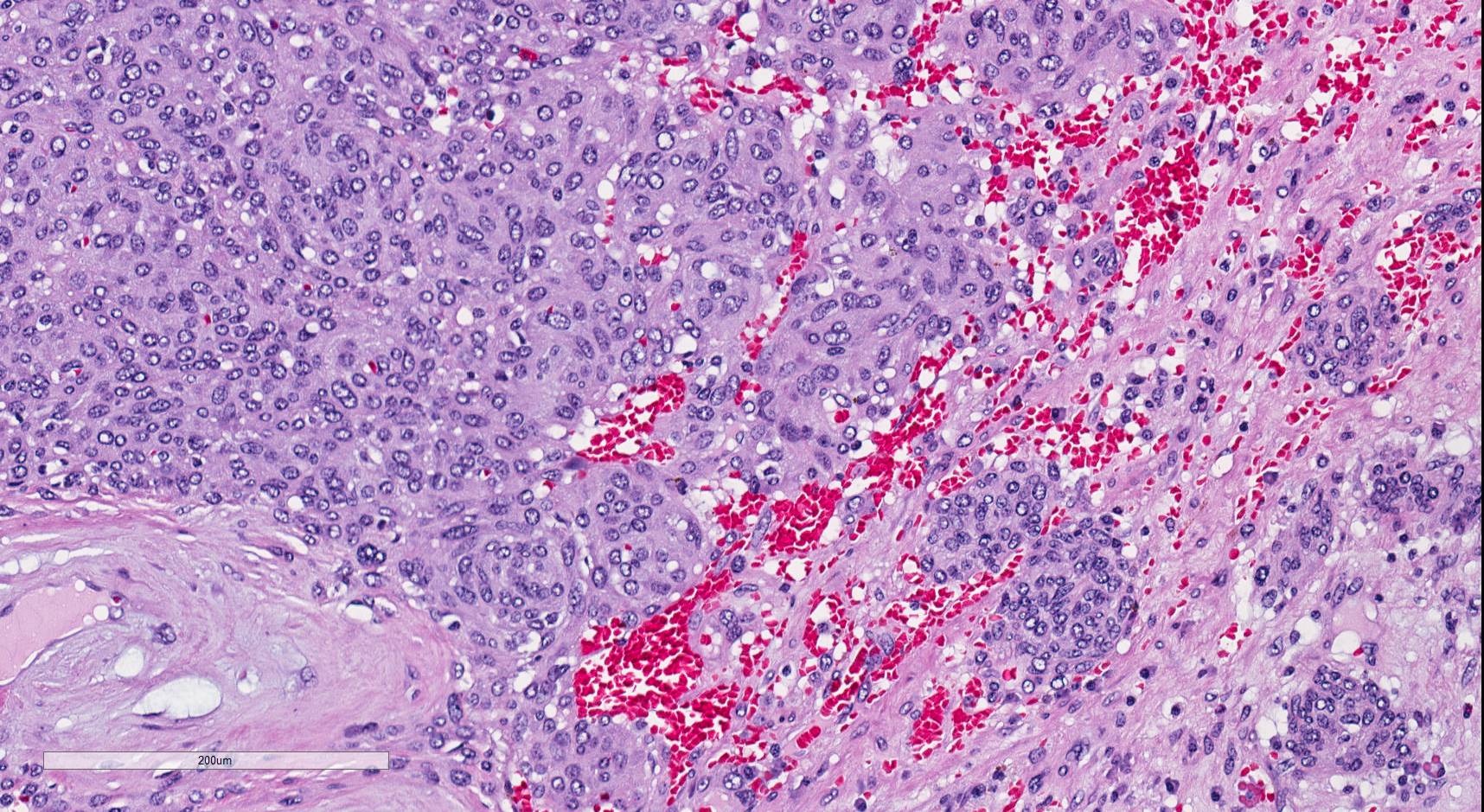
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Glomoid appearance with sheets of polygonal to spindle cells with well defined cell border (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854, Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80)
- Central, round, uniform nuclei
- Variable amount of clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm
- May demonstrate papillary architecture (Hum Pathol 1993;24:1168)
- Prominent vasculature component consisting of numerous small thin walled vessels and small clusters of thick walled, often hyalinized vessels
- Hemangiopericytoma-like capillaries with branching vessels may be seen
- Scanty, hyalinized or myxoid stroma
- Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate commonly present
- Entrapped renal tubules in periphery (~50% of cases), sometimes hyperplastic and with papillary pattern
- Mitotic activity, necrosis and pleomorphism are uncommon (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854)
- Rare capsular or vascular invasion (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1098, Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2008;4:458, Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:837)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Sheets of polygonal cells with indistinct cell borders, scant granular cytoplasm and hyperchromatic nuclei, showing mild or no pleomorphism (Int J Surg Pathol 2011;19:93)
- Nuclei with evenly distributed chromatin and occasional noticeable nucleoli
- Background of foamy histiocytes and red blood cells
Positive stains
- Renin: but may also be positive in some cases of Wilms tumor, renal cell carcinoma or renal oncocytoma (Am J Pathol 1987;126:73, Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:837)
- Vimentin: diffuse (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854, Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80)
- CD34: diffuse (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:707, Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854, Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80)
- CD117: variable (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:707, Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80)
- SMA, h-caldesmon: variable (Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80, Hum Pathol 2013;44:47)
- PDGFRA: focal to diffuse (Hum Pathol 2013;44:47)
- Beta catenin: nuclear (Hum Pathol 2013;44:47)
Negative stains
- Cytokeratins: AE1 / AE3, CAM 5.2 (highlights entrapped tubules) (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854)
- PAX8 (Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:87)
- Cathepsin K (Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:87)
- TFE3 (Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:87)
- CD31, factor VIII (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854, Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80)
- Neuroendocrine markers: chromogranin, synaptophysin (Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:837, Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854, Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80)
- S100 (Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:837, Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854, Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80)
- HMB45 (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854, Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80)
- Desmin: but can be focally positive (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:854, Diagn Pathol 2011;6:80, Hum Pathol 2013;44:47)
- Myogenin (Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:87)
- CD99, BCL2 (Hum Pathol 2013;44:47)
Electron microscopy description
- Abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Peripherally located rhomboid renin protogranules within the cytoplasm (secretory granules) (Invest Urol 1973;11:65, Pathology 1972;4:193, Ultrastruct Pathol 1997;21:201)
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Loss of chromosomes 9 and 11, as well as aneusomy (Cancer 2005;104:504, Hum Pathol 2008;39:459, Hum Pathol 2013;44:47)
- Whole genome expression analysis (in 2 cases): 415 upregulated genes, including renin and CD117 and 325 downregulated genes (Hum Pathol 2013;44:47)
Sample pathology report
- Right kidney, mass, partial nephrectomy:
- Juxtaglomerular cell tumor, measuring 2.5 cm in greatest dimension (see comment)
- Surgical margins, negative for tumor
- Comment: The sections show a well circumscribed tumor composed of sheets of uniform round to polygonal cells with clear to slightly eosinophilic cytoplasm and distinct cell borders. Immunohistochemistry was performed and shows diffuse positivity for renin, CD34 and CD117 in the tumor cells. The overall findings support the diagnosis of juxtaglomerular cell tumor.
Differential diagnosis
- Glomus tumor:
- Solitary fibrous tumor / hemangiopericytoma:
- Metanephric adenoma:
- Acinar growth pattern
- Psammoma bodies in the stroma
- PAX8 positive
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma:
- Atypia, pleomorphism
- PAX8 positive and renin negative
- Collecting duct carcinoma:
- Urothelial carcinoma:
- Nuclear hyperchromasia and pleomorphism
- GATA3 positive
- Epithelioid angiomyolipoma:
- Wilms tumor:
- Typically contains blastemal cells with nuclear overlapping
Practice question #1
A 25 year old woman presents with uncontrollable hypertension and subsequent workup found a 2 cm left kidney mass. She underwent a partial resection and sections showed the above histologic features. What is the likely diagnosis?
- Glomus tumor
- Juxtaglomerular cell tumor
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Solitary fibrous tumor
Practice answer #1
B. Juxtaglomerular cell tumor should be included in the differential diagnosis of renal tumors with concurrent hypertension, especially in young patients. Histologically, it is composed by sheets of polygonal to spindle cells with well defined cell border and prominent vasculature.
Comment Here
Reference: Juxtaglomerular cell tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Juxtaglomerular cell tumor
Practice question #2
A 20 year old man presents with severe hypertension, hyperreninemia and hypokalemia. Imaging during workup located a 3 cm mass in the right kidney. He underwent a partial nephrectomy and sections of the tumor show sheets of round to polygonal cells with clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm and well defined cell borders. The tumor cells will be positive for which of the following immunohistochemical stains?
- CD34
- CD99
- PAX8
- STAT6
Practice answer #2
A. CD34. Juxtaglomerular cell tumors are positive for renin, vimentin, CD34 and CD117.
Comment Here
Reference: Juxtaglomerular cell tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Juxtaglomerular cell tumor