Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Andeen NK, Tretiakova M. Metastases. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumormalignantmetastases.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Malignant neoplasm metastatic to kidney, not of primary renal or renal pelvis origin
- Most are carcinomas (80.8%)
- Primary site (BJU Int 2016;117:775)
- Usually lung (43.7%)
- Colorectal (10.6%)
- ENT (6%)
- Breast (5.3%)
- Soft tissue (5.3%)
- Thyroid (5.3%)
- Primary site (BJU Int 2016;117:775)
- Also melanoma, pancreas, ovary, testis
Essential features
- In surgical pathology based studies, metastasis to kidney is uncommon; usually recognized after the diagnosis of primary tumor and may not be seen until long after that diagnosis
Epidemiology
- Epidemiology differs depending on type of cohort data analyzed (radiographic, autopsy or surgical pathology)
- Radiology study showed that the kidney was the 8th most common site of metastases from nonrenal primary malignancies (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011;197:W680)
- Represents a small proportion of resected / biopsied renal masses (< 1% in one series) (Histopathology 2015;66:587)
- Mean age 56 - 61 years, M:F ratio = 1:1 (BJU Int 2016;117:775, Histopathology 2015;66:587)
Clinical features
- Presents with flank pain (30%), hematuria (16%) and weight loss (12%) (BJU Int 2016;117:775)
- Often solitary (77%), although most later develop more sites of metastasis (BJU Int 2016;117:775)
- 88% diagnosed after primary tumor, 9% concurrent with primary; in 2% the metastasis to kidney preceded diagnosis of primary tumor (Histopathology 2015;66:587)
- In 19%, there is a > 10 year interval between time of diagnosis of primary tumor and diagnosis of kidney metastasis (Histopathology 2015;66:587)
- 37% of patients have no other known metastasis at time of diagnosis (Histopathology 2015;66:587)
- Renal cell carcinoma is the most common recipient of tumor to tumor metastasis in malignant tumors (Urology 1987;30:35)
Radiology description
- Compared with renal primaries, more often solid and endophytic; no difference in tumor size, polar predominance or CT enhancement patterns (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011;197:W680)
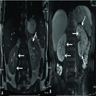
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- In a series of 151 patients with tumors metastatic to kidney, median overall survival from time of metastatic diagnosis was 1.1 years and median overall survival from primary tumor diagnosis was 3 years (BJU Int 2016;117:775)
Case reports
- 21 year old woman with osteosarcoma (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2008;6:124)
- 42 year old man with oral squamous cell carcinoma metastatic to kidney (J Clin Diagn Res 2015;9:TJ01)
- 53 year old woman with cervical metastasis resembling an abscess (Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 2007;16:526)
- 53 year old and 75 year old men with lung and pancreatic tumors metastatic to angiomyolipoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:1016)
- 65 year old woman with lung adenocarcinoma metastatic to clear cell renal cell carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:e49)
- Patient with breast adenoid cystic carcinoma metastatic to kidney (Hum Pathol 2007;38:1425)
- Parotid gland malignant mixed tumor with initial presentation as solitary kidney tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1159)
Treatment
- May be treated with ablation or resection
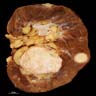
Gross description
- 30% multiple
- 23% bilateral
- 69% located in cortex (Histopathology 2015;66:587)
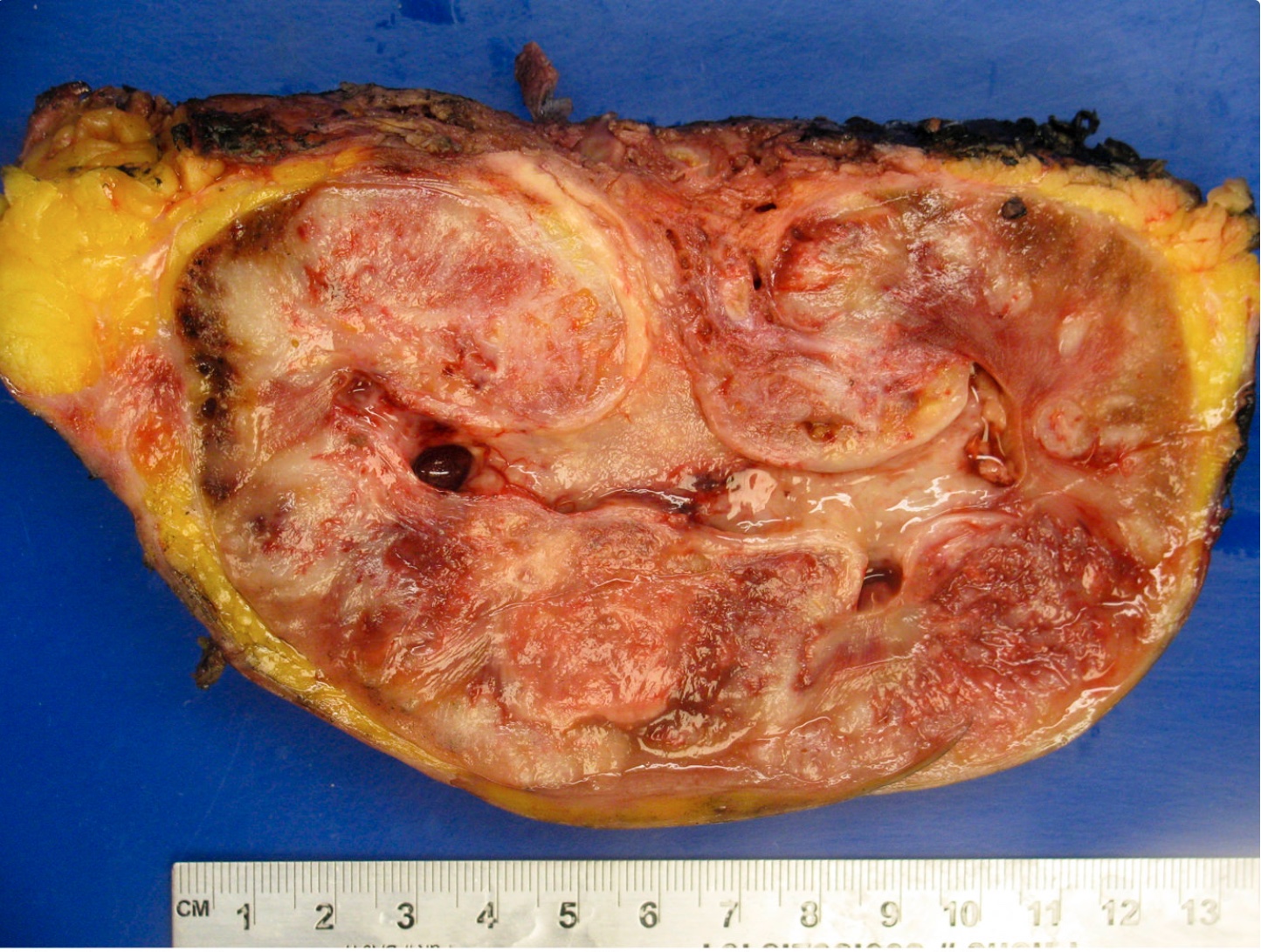
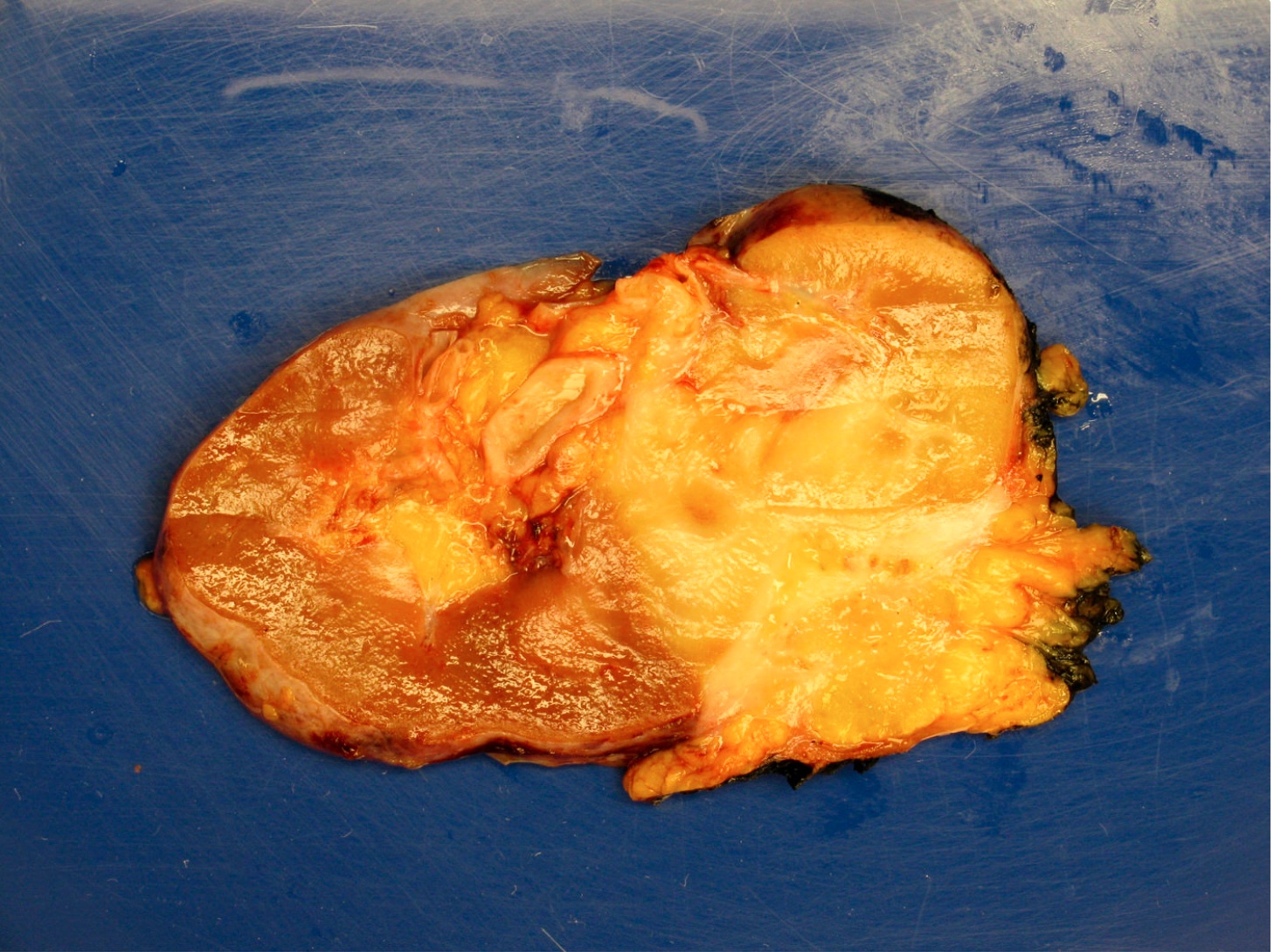
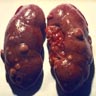
Gross images
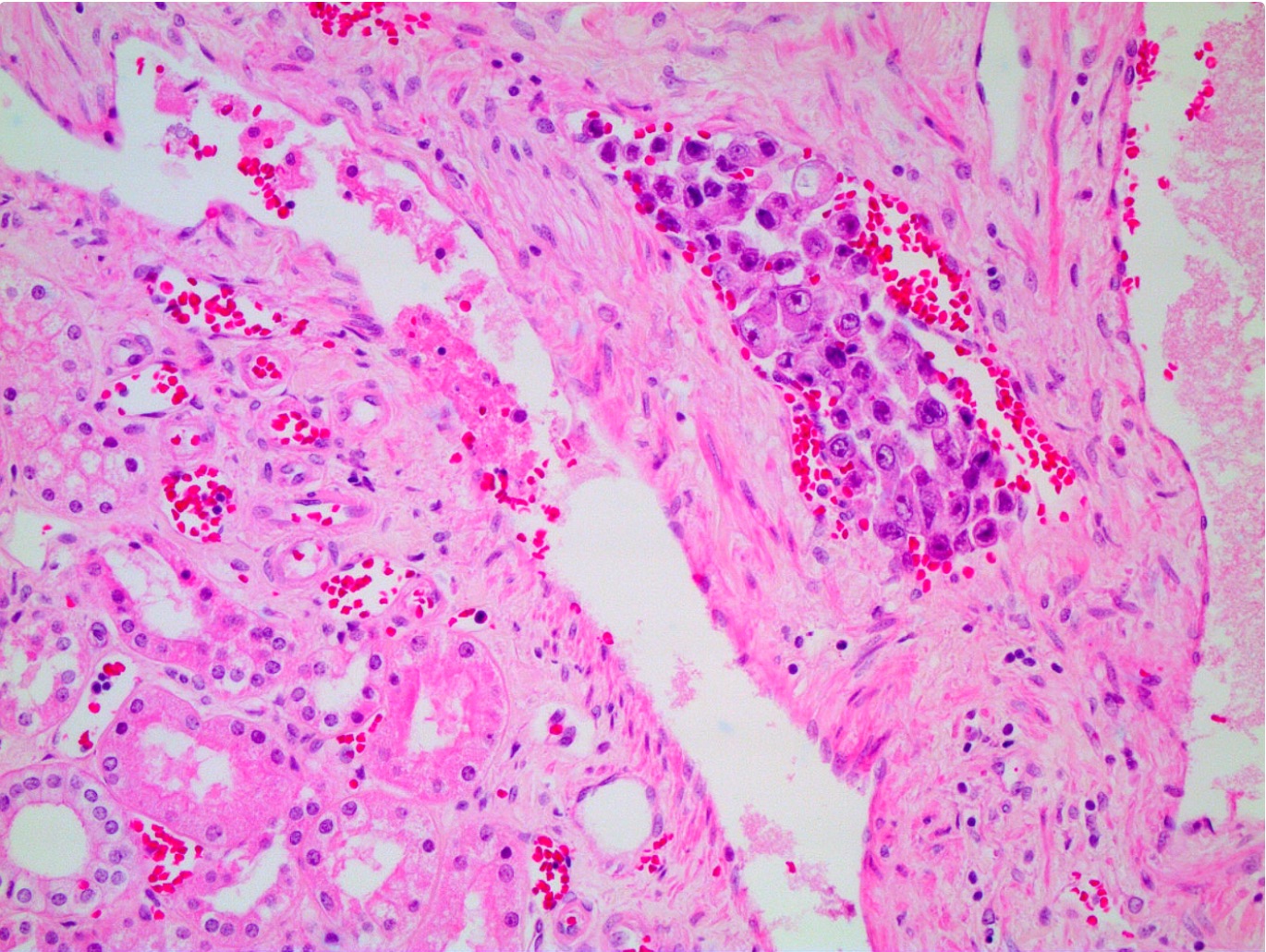
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Varies; may mimic urothelial carcinoma with divergent differentiation or unusual primary kidney tumors
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Uncommon to diagnose kidney metastases via cytology (Anal Quant Cytopathol Histpathol 2014;36:345, Nayar: Cytopathology in Oncology, 2013 )
Positive stains
- Other primaries: TTF1, CDX2, GATA3, ER, SF1, calretinin, inhibin, OCT 3 / 4, SALL4, synaptophysin, chromogranin (Adv Anat Pathol 2010;17:377)
Negative stains
- Renal cell carcinoma markers: PAX8 (83% of renal cell carcinomas are positive), EMA (78% of clear cell renal cell carcinomas are positive), CAIX (87% of clear cell renal cell carcinoma are positive), hKIM-1 (human kidney injury molecule-1) (83% of clear cell renal cell carcinoma are positive), PAX2, renal cell carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:678)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Molecular testing not currently used consistently; diagnosis is based on history, morphology and IHC
Differential diagnosis
- Depends on metastasis type; H&E and clinical history are best discriminators
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma: SF1 (86% adrenal vs. 0% clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) positive), calretinin (89% adrenal vs. 10% clear cell RCC positive), inhibin (86% adrenal vs. 9% clear cell RCC positive), MelanA (86% adrenal vs. 10% RCC positive) (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:678)
- Metastatic carcinoid: nested and insular growth pattern, positive for synaptophysin and chromogranin
- Type 1 papillary renal cell carcinoma: has true fibrovascular cores, foamy macrophages, negative for neuroendocrine markers
- Renal cell carcinoma: usually express PAX8 (83% RCC positive) and CAIX (87% clear cell RCC positive) (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:678)
- Urothelial carcinoma: based in renal pelvis, positive for p63, uroplakin, CK20 (variable expression in other metastatic diagnostic considerations)
Board review style question #1
Which is the most useful immunohistochemical panel to differentiate adrenal cortical carcinoma from clear cell renal cell carcinoma?
- Inhibin, calretinin, CD10, PAX2
- MelanA, CK7, RCC, PAX2
- SF1, calretinin, CAIX, PAX8
- SF1, CK7, RCC, CD10
Board review style answer #1