Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Anderson D, Tretiakova M. Sarcomatoid. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumormalignantrccsarcoma.html. Accessed April 17th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Sarcoma-like histology is not a distinct entity but a pathway of transformation (dedifferentiation) in subtypes of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) (Cancer 2005;104:1195)
- An estimated 4% to 5% of RCCs have a sarcomatoid component but it varies depending on subtype (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1188, Ann Diagn Pathol 2003;7:296, Nat Rev Urol 2020;17:659)
- Presence of sarcomatoid component is associated with a worse prognosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:275, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:435)
Essential features
- Represents RCC loss of epithelial phenotype and gain of mesenchymal characteristics, epithelial mesenchymal transition, a more aggressive phenotype with increased risk for local spread and high metastatic potential (Cancer 2005;104:1195)
- May be diffuse or focal; even focal sarcomatoid component is important and associated with a poorer prognosis
- Sarcomatoid morphology is categorized as WHO / ISUP grade 4 (CAP: Protocol for the Examination of Specimens from Patients with Invasive Carcinoma of Renal Tubular Origin [Accessed 13 January 2023])
Terminology
- Previously called carcinosarcoma of the kidney, sarcomatoid RCC and spindle cell carcinoma (J Pathol Bacteriol 1963;85:139, Cancer 1968;22:556, Jpn J Clin Oncol 1997;27:58)
- Currently not considered its own variant
- When the background carcinoma subtype is recognized, the primary histologic diagnosis should be the RCC subtype with sarcomatoid dedifferentiation mentioned in the report (e.g., papillary RCC with sarcomatoid features)
- Sarcomatoid elements, sarcomatoid dedifferentiation, sarcomatoid differentiation, sarcomatoid features and sarcomatoid component are terms that are used interchangeably
- If pure sarcomatoid with no recognizable epithelial component upon extensive sampling, it should be considered as an unclassified RCC once primary or metastatic sarcoma is excluded
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C64.9 - malignant neoplasm of kidney, unspecified laterality
Epidemiology
- Mean age: 60 years
- M:F = 1.3:1 - 2:1
- Usually presents with locally advanced or metastatic disease at presentation (stage III or IV)
- Aggressive with median survival of 4 to 19 months (J Urol 2002;167:65, Oncologist 2012;17:46, Urol Oncol 2015;33:427.e17)
- Patients with clear cell RCC (ccRCC) with a sarcomatoid component have a worse prognosis than those without at every stage of disease (World J Urol 2016;34:1429)
- 5 year disease specific survival for stage I, II, III and IV: 77.7%, 67.8%, 35.4% and 3.5%, respectively (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2019;17:e447)
- For patients with no evidence of disease following nephrectomy, 77% of patients experienced a recurrence; median time to recurrence is 26.2 months (Urol Oncol 2015;33:166.e21)
- Metastases in decreasing order of prevalence: lung, bones, lymph nodes, liver and brain
Sites
- Kidney or metastatic sites
Pathophysiology
- Not clearly understood
- May arise from common cell of origin epithelial cell, which undergoes epithelial mesenchymal transition
- Beta catenin translocates to nucleus and acts as transcription factor for Snail, a transcriptional repressor for E-cadherin, loses epithelial phenotype and gains mesenchymal characteristics (upregulation of Snail and cytoplasmic N-cadherin) (J Clin Pathol 2011;64:1088, Cancer Sci 2010;101:293)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- 90% symptomatic with pain, gross hematuria, weight loss, fatigue, fever, nights sweats
- Presentation with advanced / late stage disease and metastasis is common
- 60.9% had stage IV disease at presentation (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2019;17:e447)
Diagnosis
- Sarcomatoid growth represents a pathway of transformation (dedifferentiation) in subtypes of RCC
- It is associated with poor prognosis and is therefore important to identify and document its presence and percentage
- It constitutes ISUP / WHO grade 4 in applicable RCC
- Extensive sampling should be performed in order to identify the primary RCC subtype and rule out involvement by other carcinomas (urothelial, adrenocortical) and sarcomas
- Immunohistochemistry may be helpful to subtype the neoplasm based on the histologic findings present in one's case and is generally best done in more well differentiated areas
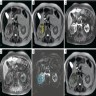
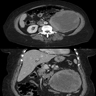
Radiology description
- No specific methods to identify sarcomatoid differentiation (J Urol 2009;182:2164, BJU Int 2012;110:1742)
- Sarcomatoid carcinoma component is more often associated with neovascularity, larger peritumoral vessels and a more heterogenous appearance on CT (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2015;204:1013)
- MRI with T2 weighted low signal intensity (Clin Imaging 2013;37:908, Abdom Imaging 2015;40:112, Quant Imaging Med Surg 2018;8:373, Abdom Radiol (NY) 2022;47:2168)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Percentage of sarcomatoid component may be prognostic
- Higher percentage of sarcomatoid dedifferentiation may confer a worse prognosis; recommended to report percentage by ISUP consensus conference (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:435, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1490)
- 6% increase in risk of death for every 10% increase in the amount of sarcomatoid differentiation
- 52% more likely to die from RCC if ≥ 30% sarcomatoid differentiation (BJU Int 2015;115:405)
- > 40% less likely to be alive at 1 year (Urol Oncol 2015;33:427.e17)
- > 10% sarcomatoid component had higher risk of death (Urol Oncol 2015;33:427.e17)
- In ≥ T3, M0 disease, patients with ≥ 25% sarcomatoid features had ~30% increased overall risk of dying of any cause over those without sarcomatoid features
- Overall survival was not affected by % sarcomatoid in patients with cM1 disease (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2015;13:225)
- Older age, higher tumor stage and nephrectomy found to independently affect disease specific survival (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2019;17:e447)
Case reports
- 45 year old woman with sarcomatoid chromophobe RCC with squamous differentiation (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:1672)
- 53 year old man with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease on hemodialysis with pure sarcomatoid RCC (CEN Case Rep 2021;10:199)
- 56 year old Japanese man with acquired cystic disease associated RCC, sarcomatoid change and rhabdoid features (Ann Diagn Pathol 2011;15:462)
- 62 year old man with sarcomatoid RCC with wide metastasis (J Kidney Cancer VHL 2018;5:1)
- 71 year old woman with divergent growth pattern (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:1057)
Treatment
- No clear treatment guidelines
- Radical nephrectomy with or without extended lymph node dissection (Quant Imaging Med Surg 2018;8:373, J Urol 2004;172:465, Clin Genitourin Cancer 2019;17:e447, Curr Oncol 2022;29:5475, Cureus 2022;14:e25395, J Urol 2009;182:2164)
- For localized disease, surgical resection is standard of care (Urol Oncol 2015;33:166.e21)
- Combination chemotherapy with cytotoxic regimens (Eur Urol 1995;27:138, J Urol 2002;168:959, Cancer 2004;101:1545, Med Oncol 2012;29:761, Clin Genitourin Cancer 2017 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print], Cancer 2015;121:3435, J Clin Oncol 2016;34:833, J Clin Oncol 2016;34:4511)
- Targeted therapies are investigational but response remains poor
- VEGF inhibitors (J Clin Oncol 2009;27:235, Eur J Med Res 2010;15:287, Clin Genitourin Cancer 2015;13:e79, BJU Int 2011;107:741)
- mTOR inhibitors (Ann Oncol 2014;25:663, Clin Genitourin Cancer 2015;13:e79)
- Antiangiogenesis targeted therapies (Am J Clin Oncol 2011;34:454)
- Cytokine therapy (J Urol 2017;198:530, Am J Clin Oncol 2011;34:454, J Urol 2002;167:65, PLoS One 2017;12:e0190084)
- PDL1 expression is increased in sarcomatoid dedifferentiated renal tumors, suggesting potential benefit from PD-1, PDL1 immune checkpoint blockade or anti-CTLA4 therapy (Nat Rev Urol 2020;17:659, Clin Genitourin Cancer 2017;15:e1127, Eur Urol 2015;68:912, J Oncol Pract 2018;14:511, Mod Pathol 2019;32:1344, J Clin Oncol 2016;34:833, Clin Cancer Res 2021;27:78, J Clin Oncol 2019;37:4500, Annals of Oncol 2019;30:361, Eur Urol 2021;79:659, Lancet 2019;393:2404, Curr Oncol 2022;29:5475, J Med Case Rep 2022;16:193, Front Genet 2022;13:985641, J Kidney Cancer VHL 2021;8:38, Cancer Rep (Hoboken) 2021;4:e1356, Eur Urol 2021;79:663)
- Combination immunotherapy recommended by Society of Immunotherapy of Cancer as first line treatment option (J Immunother Cancer 2019;7:354)
- No survival benefit from postnephrectomy metastasectomy (J Urol 2009;182:2164)
- Radiotherapy does not seem to increase overall survival (Int Urol Nephrol 2015;47:1653)
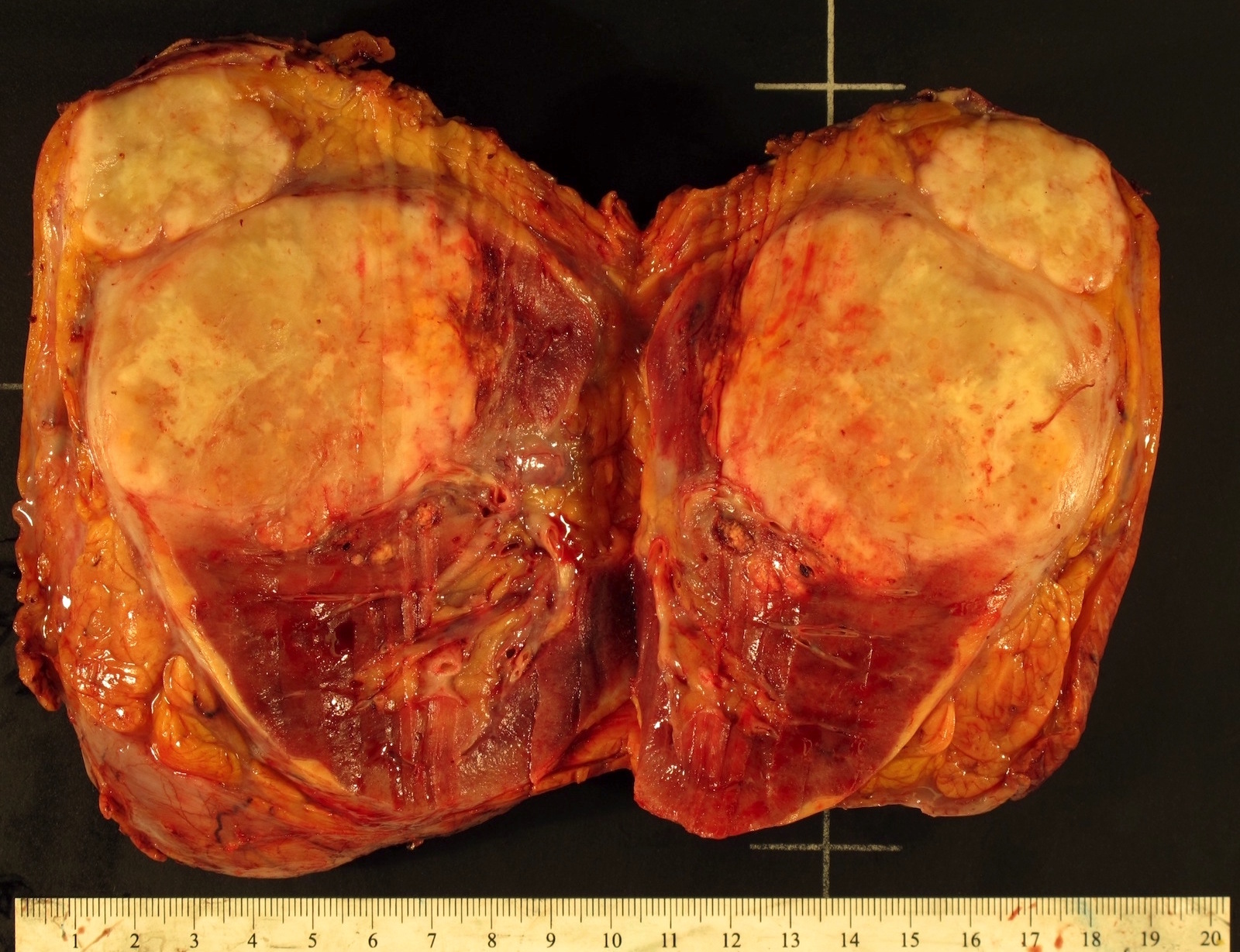
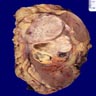
Gross description
- Grayish white bulging mass with infiltrative margins and fleshy to fibrous cut surface; must sample these areas
- Mean size: 9 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:275)
- May have heterogeneous patchy appearance: yellow, hemorrhagic, necrotic
Gross images
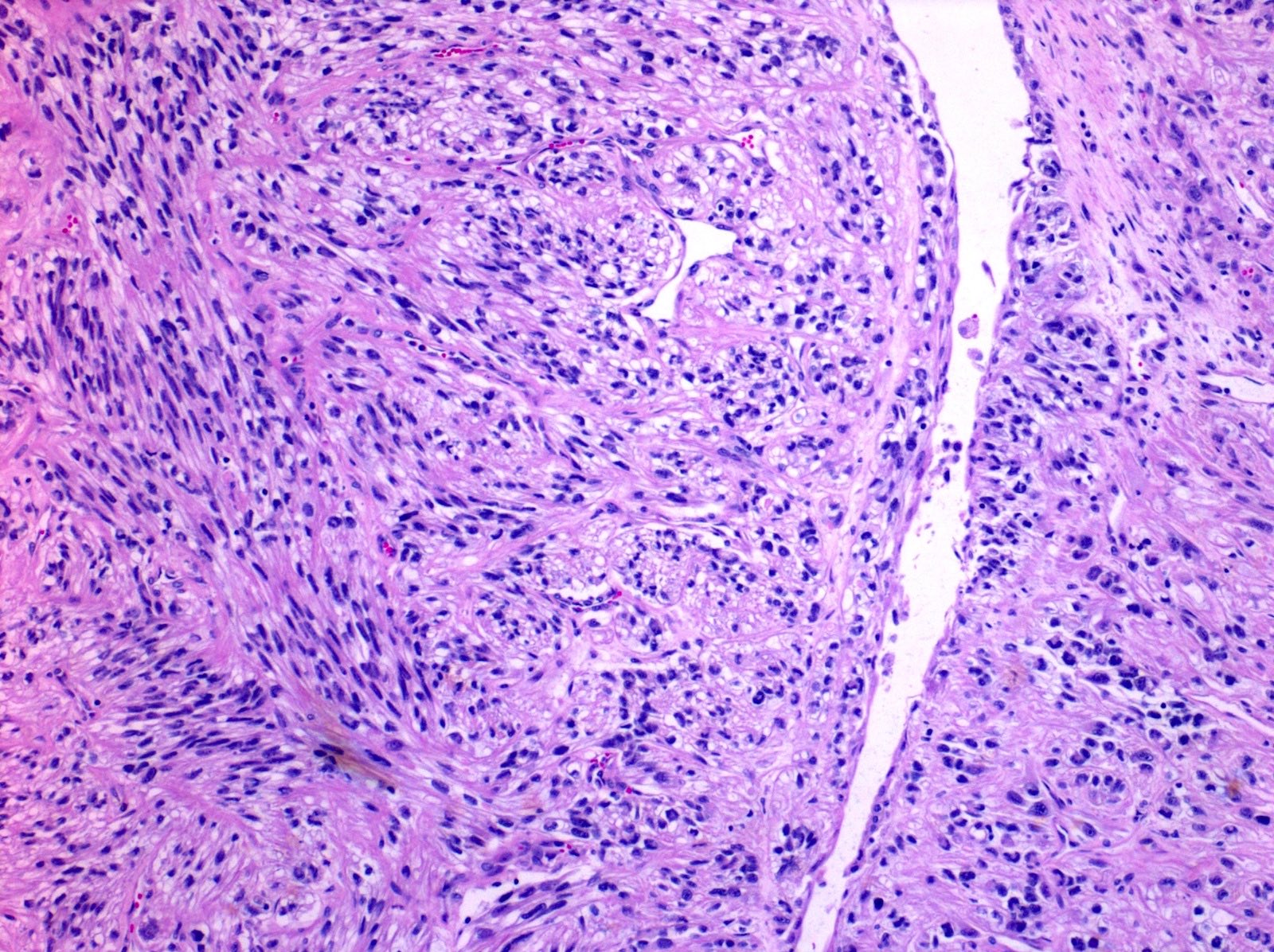
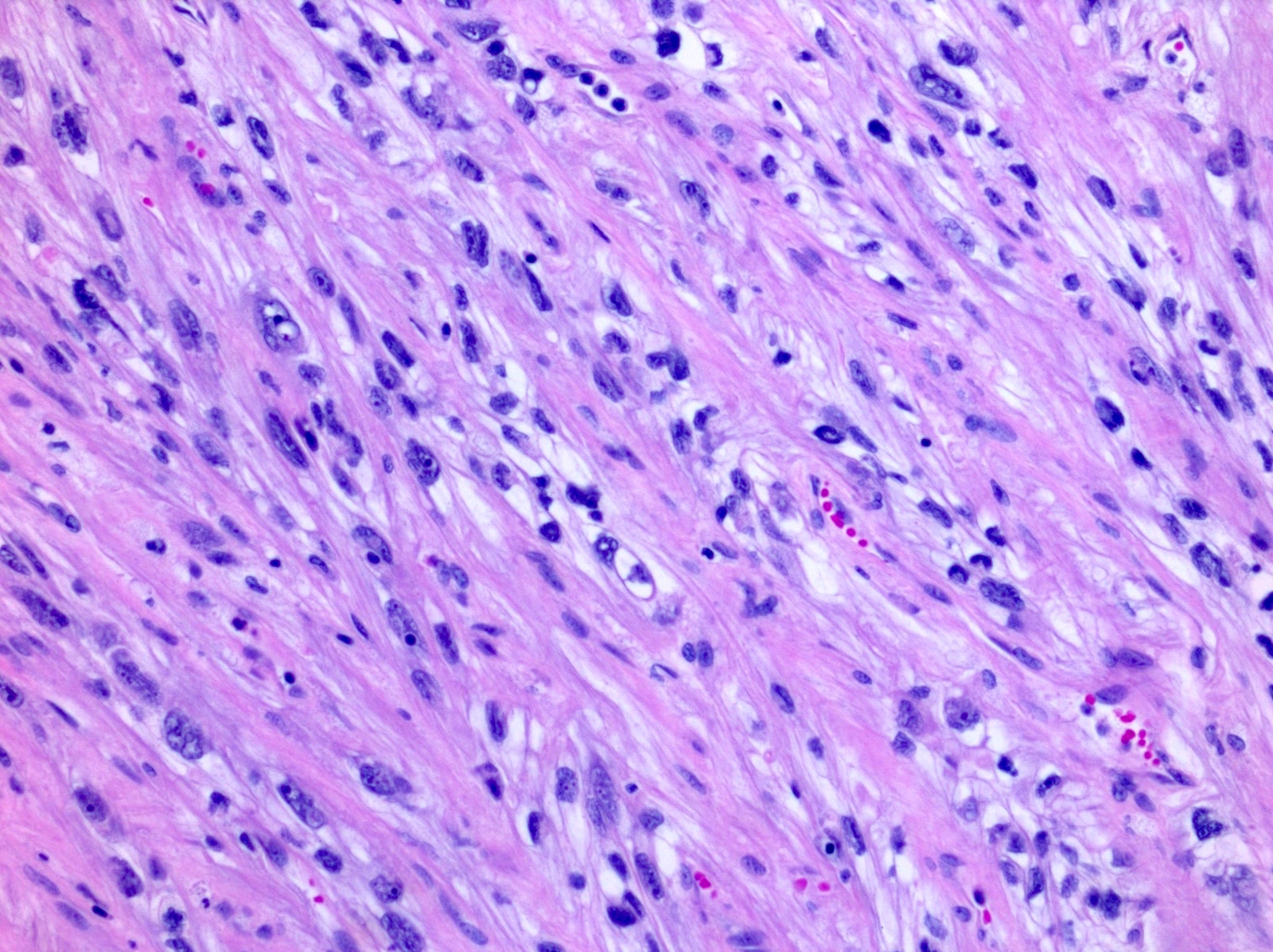
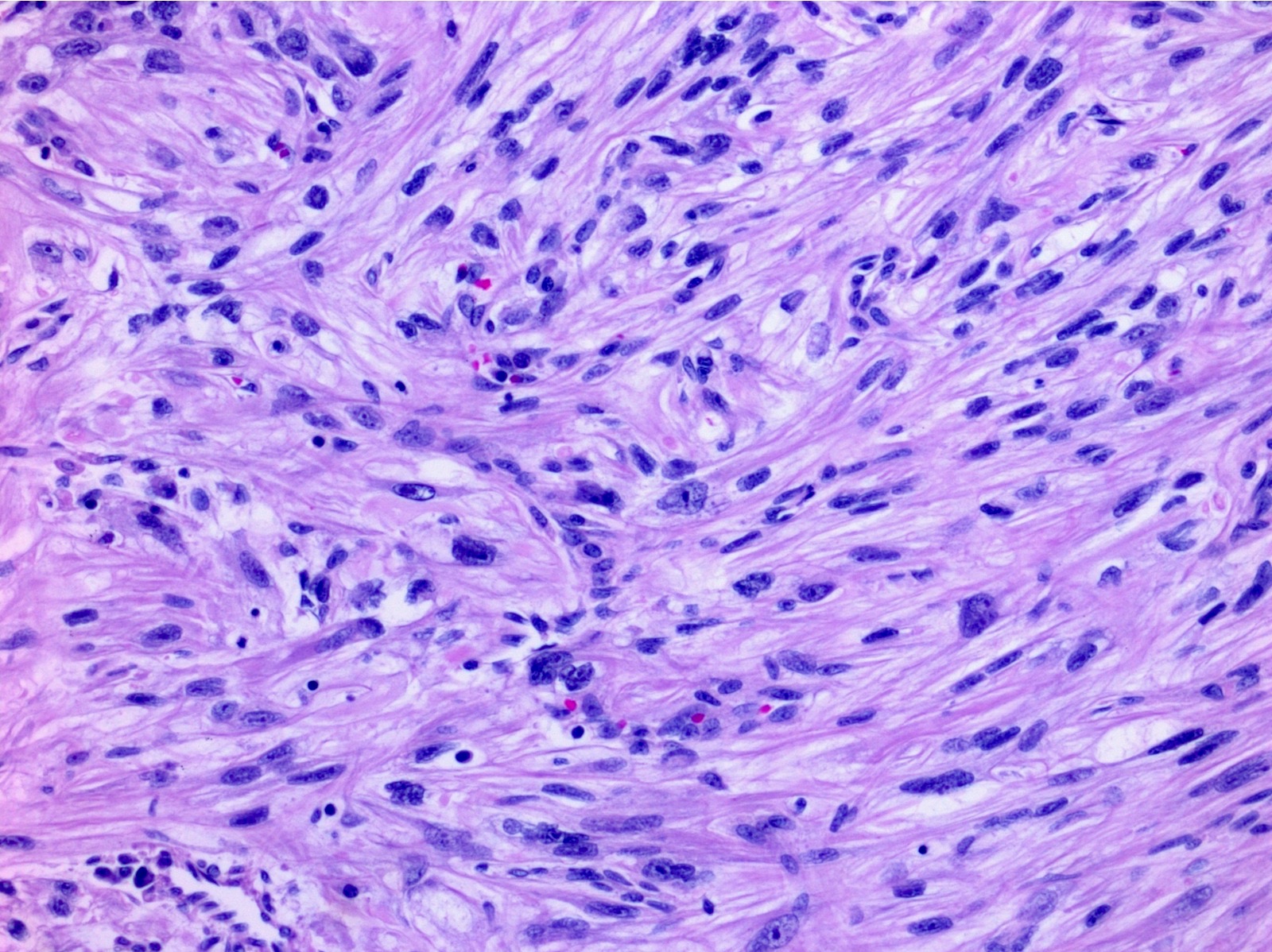
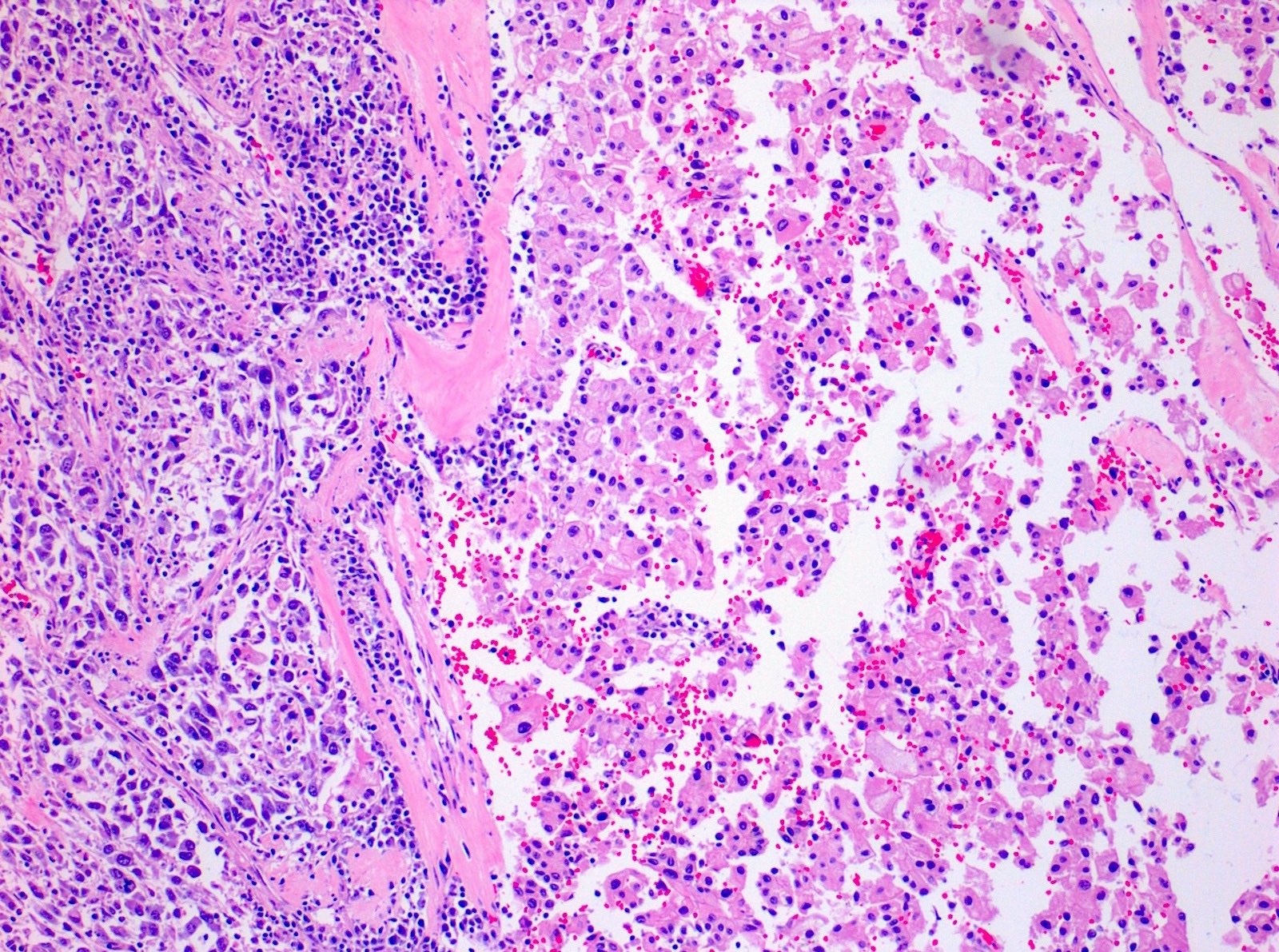
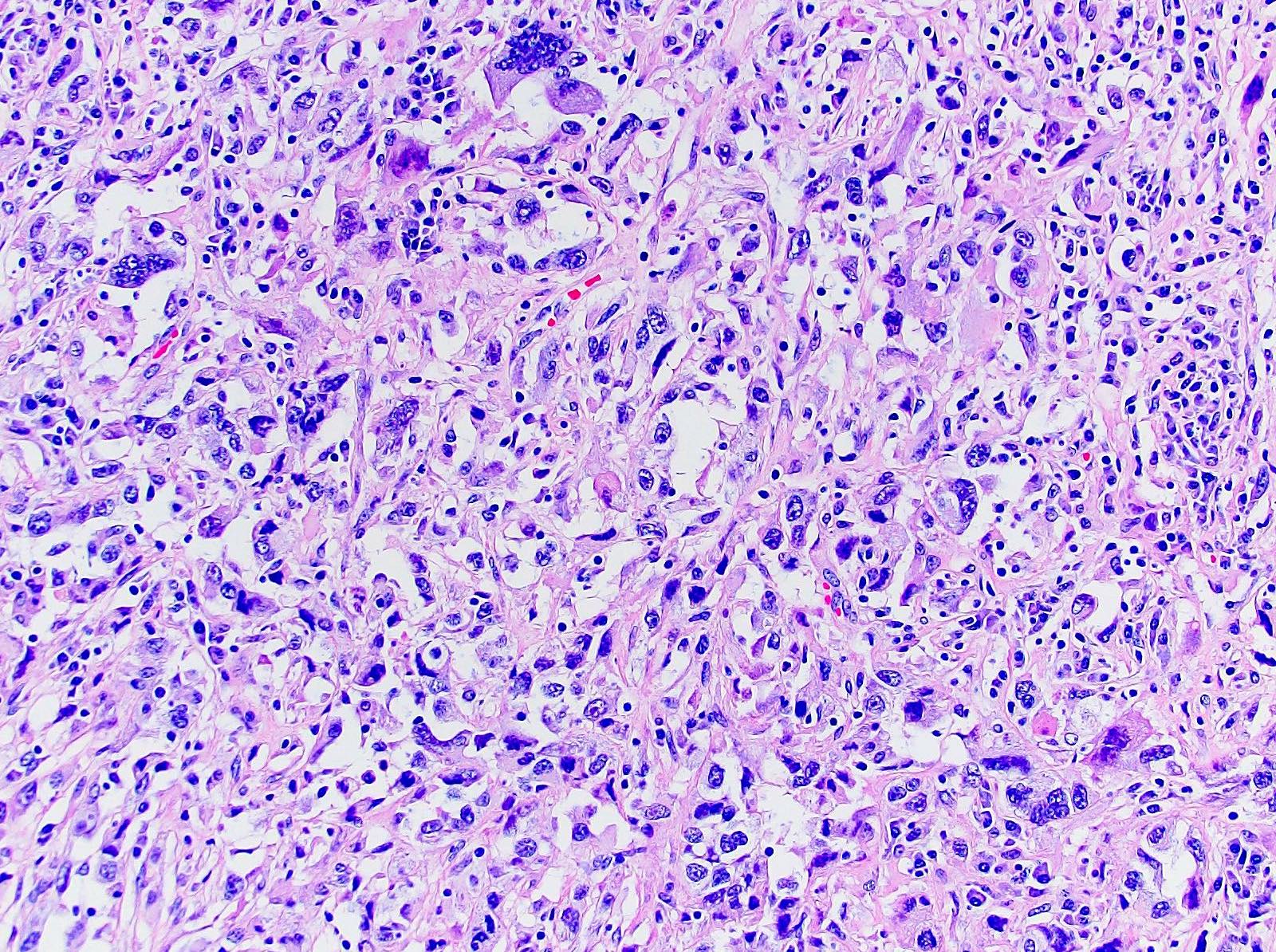
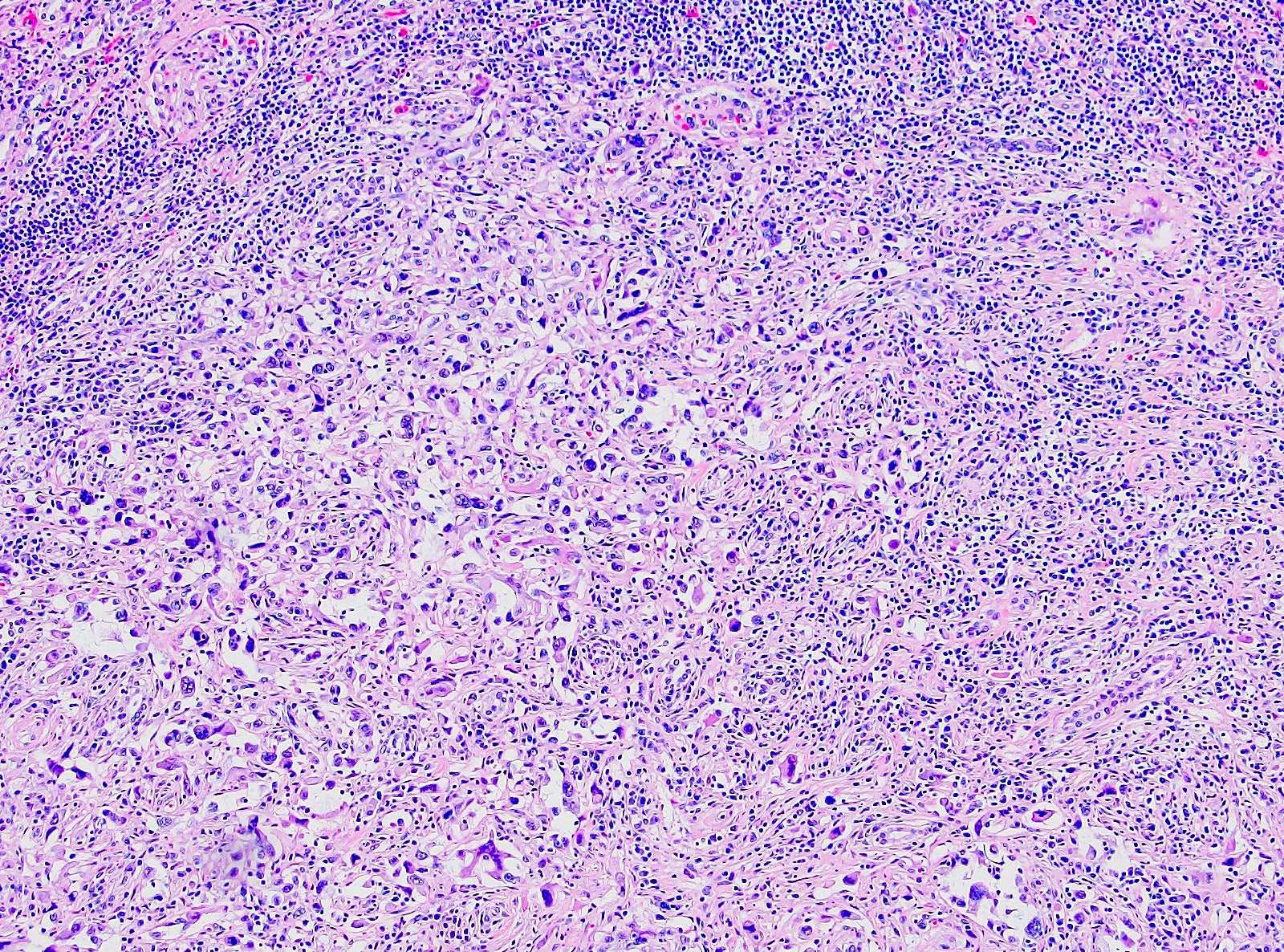
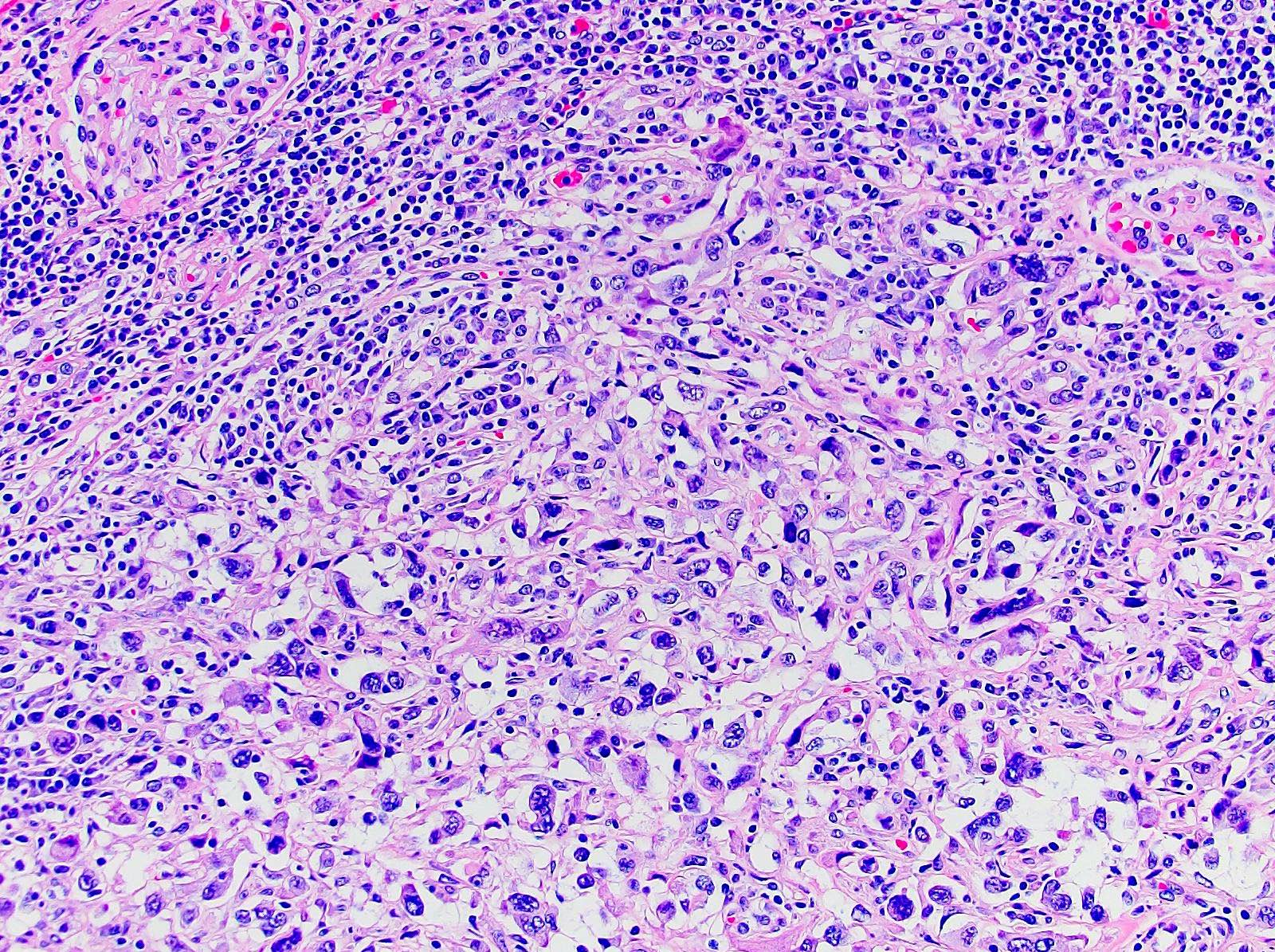
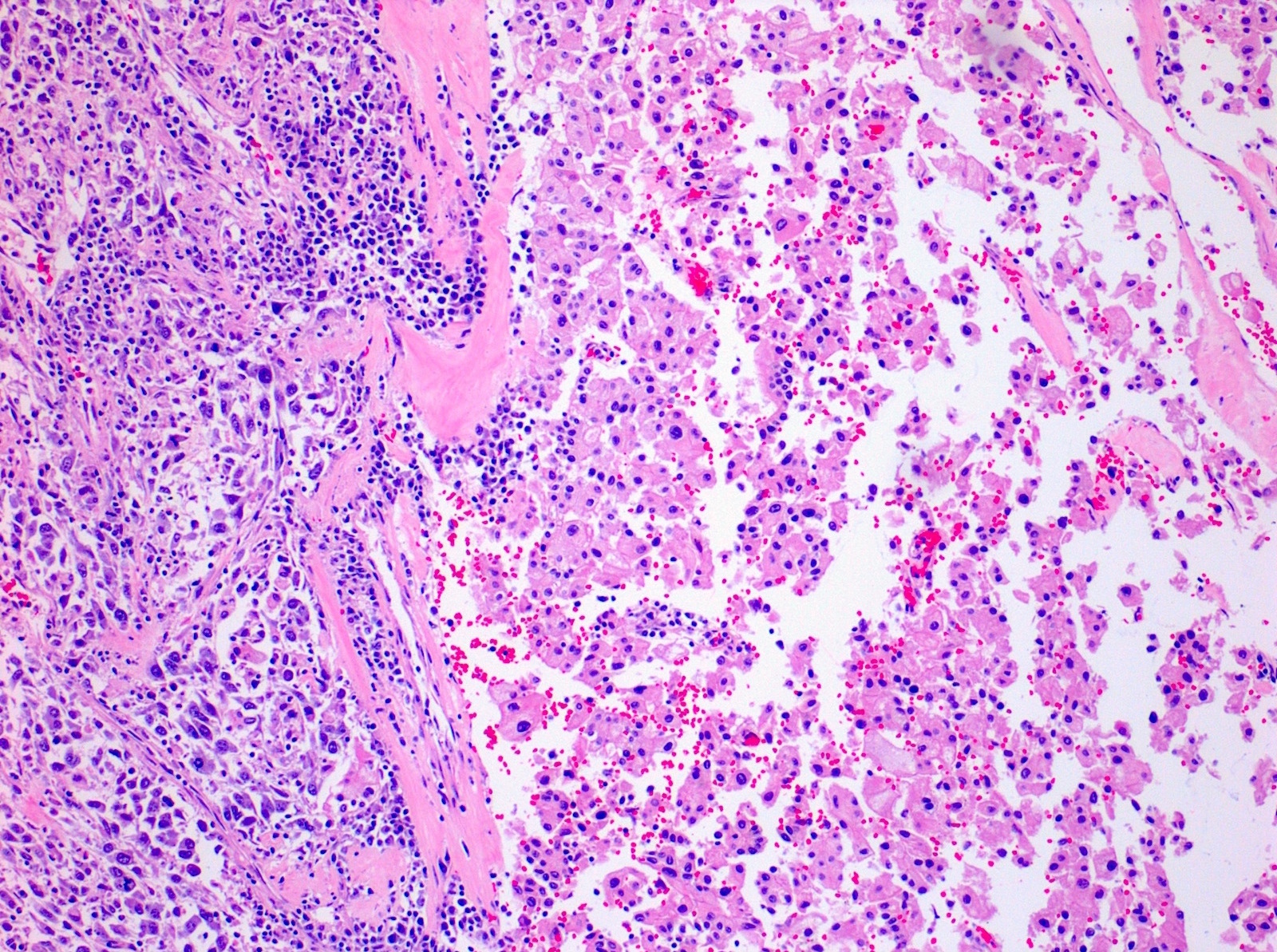
Microscopic (histologic) description
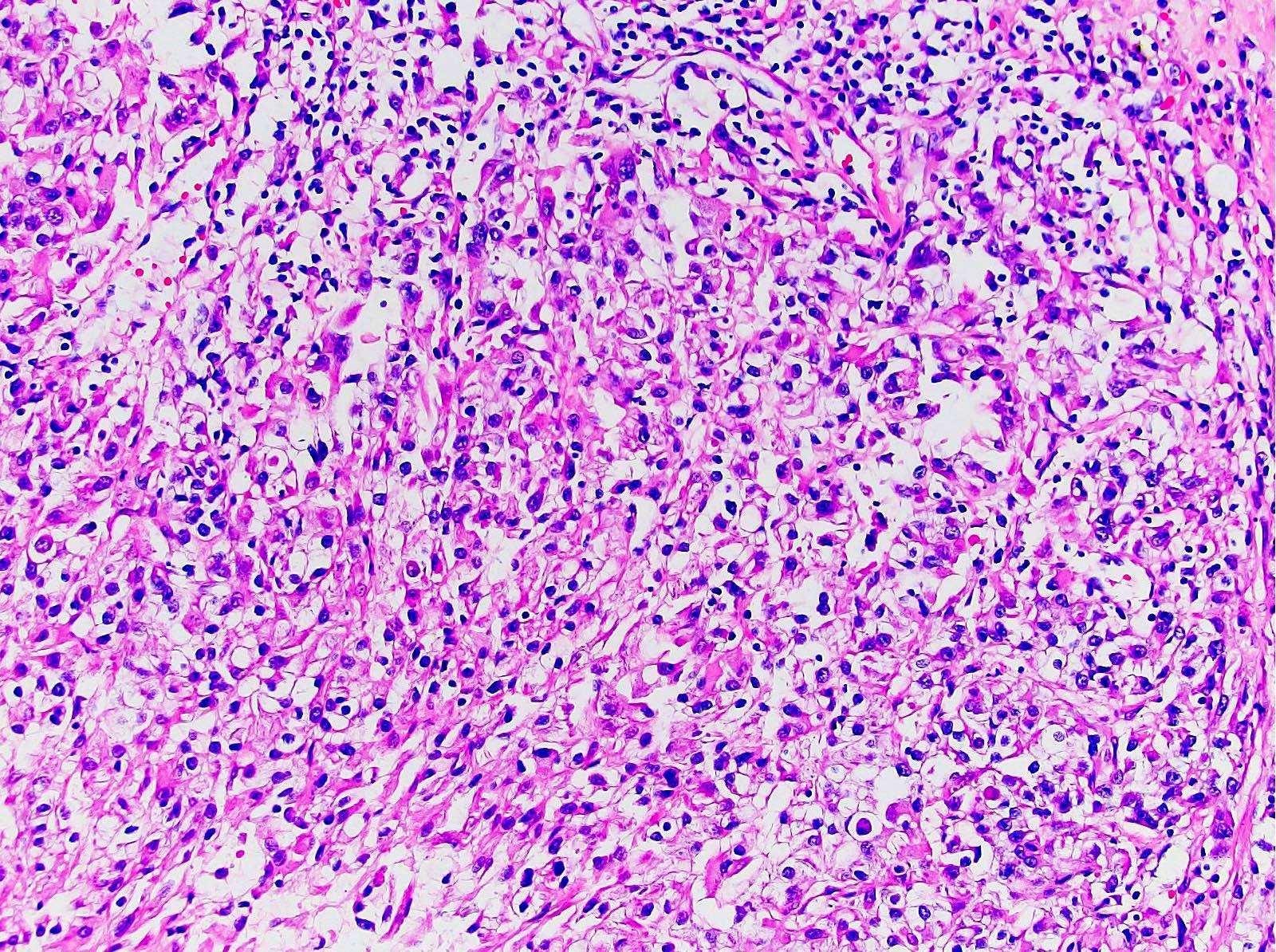
- Areas of sarcomatoid dedifferentiation may be heterogenous or uniform and may display fibrosarcoma-like, pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma (malignant fibrous histiocytoma-like) or unclassified morphology
- Heterologous differentiation such as chondrosarcoma, osteosarcoma or rhabdomyosarcoma is rare
- Usually fibrosarcoma-like with haphazard, infiltrative growth without well formed fascicles
- Atypical, spindle cells or tumor giant cells with marked nuclear pleomorphism
- Frequent mitosis, abnormal mitotic figures
- Necrosis common
- Sarcomatoid pattern is due to dedifferentiation from subtype of RCC
- Sarcomatoid and carcinomatous areas may be intermingled or may show sharp demarcation (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1490)
- Most will have an epithelial component with generous sampling; pure sarcomatoid is extremely rare (4%)
- Sarcomatoid change occurs in 5.2% to 8% ccRCC, 1.9% to 5.4% papillary RCC, 2% to 9% chromophobe RCC, 25% to 29% collecting duct RCC, 11% unclassified RCC (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:275, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1490)
- Carcinomatous subtype does not appear to impact prognosis
- Additionally reports of sarcomatoid dedifferentiation in hereditary leiomyomatosis RCC syndrome associated RCC / fumarate hydratase deficient RCC and acquired cystic disease associated RCC (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:567, Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:627, Ann Diagn Pathol 2011;15:462)
- Metastases of sarcomatoid RCC can exhibit only sarcomatoid (58%), only carcinoma pattern (38%) or both components; > 30% sarcomatoid pattern in primary tumor frequently associated with metastatic sarcomatoid histology (Cancer 2010;116:616)
- Sarcomatoid morphology by definition is WHO / ISUP grade 4
- Rhabdoid regions that maintain epithelial features should not be considered sarcomatoid but reported separately (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:435, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1490)
- Biopsy's ability to detect sarcomatoid differentiation low on primary biopsy is ~7.5% (J Urol 2017;198:530)
- Presence of any amount of sarcomatoid dedifferentiation sufficient for diagnosis of sarcomatoid differentiation (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1490)
- ISUP consensus conference addressed definition and issues surrounding sarcomatoid RCC (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1490)
- 41% of participants felt that a tumor is sarcomatoid if it consists of atypical spindle cells and resembles any form of sarcoma
- 34% voted that a spindle cell morphology need not be present as long as the tumor is very atypical and resembles any form of sarcoma
- 22% considered a tumor sarcomatoid if it had a spindle cell pattern
- 3% considered a tumor to be sarcomatoid if it showed early sarcomatoid change characterized by elongation of epithelial tumor cells
- Consensus among participants (71%) that a minimum proportion of sarcomatoid tumor was not required to make a diagnosis of sarcomatoid carcinoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
- AE1 / AE3, vimentin (56%), EMA (50%), CAM 5.2 (40%)
- N-cadherin (cytoplasmic) (Anticancer Res 2013;33:4875)
- CAIX in sarcomatoid ccRCC
- PAX8; however, lack of staining does not exclude renal origin
- p53 overexpression (Cancer Res 1995;55:658)
- PDL1 overexpression (Mod Pathol 2019;32:1344, Cancer 2017;123:4823, Cancer Immunol Res 2015;3:1303, CEN Case Rep 2021;10:199)
Negative stains
- Actin (33%) and LeuM1 (22%) may be expressed in spindled areas
- High molecular weight keratin 34 beta E12, S100 (usually) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1993;117:636)
- Focal desmin is uncommonly seen
Electron microscopy description
- Shows epithelial differentiation, including desmosomal cell junctions with sarcomatoid differentiation such as rhabdomyosarcomatous differentiation (Hum Pathol 2002;33:68)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Complex set of chromosomal gains and losses, -13q (75%) and -4q (50%)
- Similar X chromosome inactivation patterns in both sarcomatoid and parent tumor suggesting common cell origin (Cancer 2005;104:1195)
- Significant heterogeneity in the tumor components, suggesting genetic divergence (Mod Pathol 2007;20:303, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;113:2170, Clin Cancer Res 2017;23:6686, CEN Case Rep 2021;10:199)
- Sarcomatoid component in comparison to epithelioid component have
- Higher mutational burden / hypermutation status
- More frequent mutations of p53, RELN, SETD2, ARID1A, BAP1 and PTEN which were associated with decreased survival but fewer deletions of genes VHL (3p21-25) and PBRM1 (Clin Cancer Res 2017;23:6686)
- Reelin (RELN) inhibits TGFB1 induced cell migration
- Loss of heterozygosity on chromosomes 1p, 9, 10, 14, 17p, 18 and 22 (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;113:2170)
- Upregulation of TGFβ signaling
- In a single patient with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and sarcomatoid RCC, there were mutations in ATM (c.9156G>C), CTNNB1 (c.1187A>T) and NF2 (c.1021C>T); gene upregulation in Wnt, PI3K-mTOR, MAPK and interleukin 6 and downregulation of CDKN2A in the sRCC component (Mol Genet Genomic Med 2022;10:e1853)
- Some had increased expression of BAP1 (10.5%), ARIDA1A (15.7%) and novel somatic single nucleotide variants in FAT1, FAT2, FAT3, TSG101, LRIF1, RQCD1 and PTK7 (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;113:2170)
- Most frequently mutated genes were TP53 (42.3%), CDKN2A (26.9%) and NF2 (19.2%) (Eur Urol 2016;70:348)
- NF2 mutations may be associated with sarcomatoid papillary RCCs (CEN Case Rep 2021;10:199)
- Frequency of Hippo-YAP pathway mutations in sRCCs was significantly higher than in nonsarcomatoid RCCs (Sci Rep 2020;10:701)
- Increased prevalence of JAK2 amplification with coamplification of PDL1 and PDL2 on 9p24.1 locus; finding correlates with higher PDL1 IHC expression than grade 4 ccRCC (Mod Pathol 2019;32:1344, Cancer 2017;123:4823, Cancer Immunol Res 2015;3:1303, CEN Case Rep 2021;10:199)
- mRNA expression of POLR2A and RUNX2 increased and miR-378 suppressed in sRCC (Anticancer Res 2022;42:811)
- FOXO3A induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition of tumor cells by up regulating Snail
- Snail protein expression significantly associated with tumor stage, histological grade and presence of sarcomatoid differentiation
- Epithelial to mesenchymal transition orchestrates the sarcomatoid conversion of ccRCC, characterized by E-cadherin to N-cadherin switching, dissociation of beta catenin from the membrane and increased expression of Snail and Sparc (Mol Diagn Ther 2016;20:111)
- Study on sarcomatoid transformation in chromophobe RCC shows that TP53 variants followed by widespread loss of heterozygosity, likely whole genome duplication / imbalanced chromosomal duplication events, seem to underlie sarcomatoid transformation (Mod Pathol 2024;37:100396)
- Recurrent single nucleotide variants were found in RB1 (37.5% of cases) and PTEN (25% of cases)
- Copy number variant analysis showed the characteristic pattern of chromosomal losses associated with chRCC (1, 2, 6, 10, 13, 17, and 21) in the conventional histologic components only
Sample pathology report
- Right kidney, radical nephrectomy:
- RCC, unclassified (15 cm), WHO / ISUP grade 4 of 4, with sarcomatoid and rhabdoid features (see comment and synoptic report)
- Unifocal
- Tumor necrosis: present, 25%
- Sarcomatoid: present, 60%
- Tumor extension: tumor extends into the renal sinus and into major veins (renal vein or segmental branches), pelvicalyceal system and extends into the perinephric adipose tissue
- Margins: carcinoma is present in soft tissue at renal vein margin.
- Lymphovascular invasion: present, extensive
- Adrenal gland without significant diagnostic alteration; negative for neoplasm
- Comment: Immunohistochemistry is performed. The carcinoma cells are positive for AMACR, CD10, RCC, CAIX (focal) and TFE3 (patchy). CK7 and HMB45 are negative. Per report, TFE3 FISH is negative. On H&E stained slides, there are areas of tumor with clear cell features and areas of papillary growth with more oncocytic cytoplasm. CAIX displays staining that is not seen in ccRCC. Therefore, the tumor is best categorized as RCC, unclassified, due to the heterogeneity of morphological findings and unclear immunohistochemical pattern.
Differential diagnosis
- Adequate sampling is the most useful step in making the correct diagnosis
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma with early spindle cell change:
- Stroma is not malignant (Hum Pathol 2007;38:1372)
- Sarcomatoid urothelial carcinoma:
- Usually associated with prior history of lower tract urothelial carcinoma
- Filling defect on imaging, positive urine cytology
- If located in renal calyces or pelvis, urothelial carcinoma is favored
- Carcinoma in situ (CIS) or residual papillary component may be present in renal pelvis
- Careful sampling of renal pelvis is recommended
- Usually, lower stage disease at presentation
- Urothelial carcinoma typically p63+ / GATA3+ / uroplakin II+ and negative for PAX8 (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:965, Hum Pathol 2013;44:2651)
- Sarcomatoid adrenal cortical carcinoma:
- Clinical, radiologic and gross assessment to determine epicenter
- SF1, calretinin, inhibin, MelanA / MART1, synaptophysin+; PAX8-
- Mesenchymal neoplasms / sarcomas:
- Either primary or metastatic
- Primary renal mesenchymal tumor most often leiomyosarcoma (J Cancer Res Ther 2022;18:1186)
- Primary renal sarcomas have no epithelial component after careful sampling
- Leiomyosarcoma more often has well formed fascicles
- Nuclei may range from low grade tumors to prominent atypia
- Nuclei are often cigar shaped with perinuclear vacuoles
- Often relatively well circumscribed without infiltration around pre-existing glomeruli and renal tubules
- Desmin typically diffuse with negative PAX8, focal to negative cytokeratins
- DDx includes solitary fibrous tumor, synovial sarcoma, others
- Direct involvement by primary retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcoma
- Usually liposarcoma; will not have an epithelial component after careful sampling
- Angiomyolipoma:
- Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma:
- These neoplasms typically have characteristic areas of anastomosing tubules and bland spindle cells with myxoid / mucinous stroma without infiltrative growth, cellular atypia, necrosis and increased cellular density usually seen in sarcomatoid carcinoma
- However, high grade / sarcomatoid transformation has been rarely reported in this entity (Diagn Pathol 2015:10:168)
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
B. This finding has a worse prognosis. RCCs with higher percentages of sarcomatoid differentiation have a worse prognosis including distant metastases at time of nephrectomy and higher overall mortality than if no sarcomatoid component is present. In a recent study of chromophobe RCC, tumor necrosis and sarcomatoid differentiation was associated with increased risk of progression, poor prognosis and decreased overall survival and was proposed as a reproducible component of a 2 tiered chromophobe grading system (Annals of Oncol 2019;30:361).
Comment Here
Reference: Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma
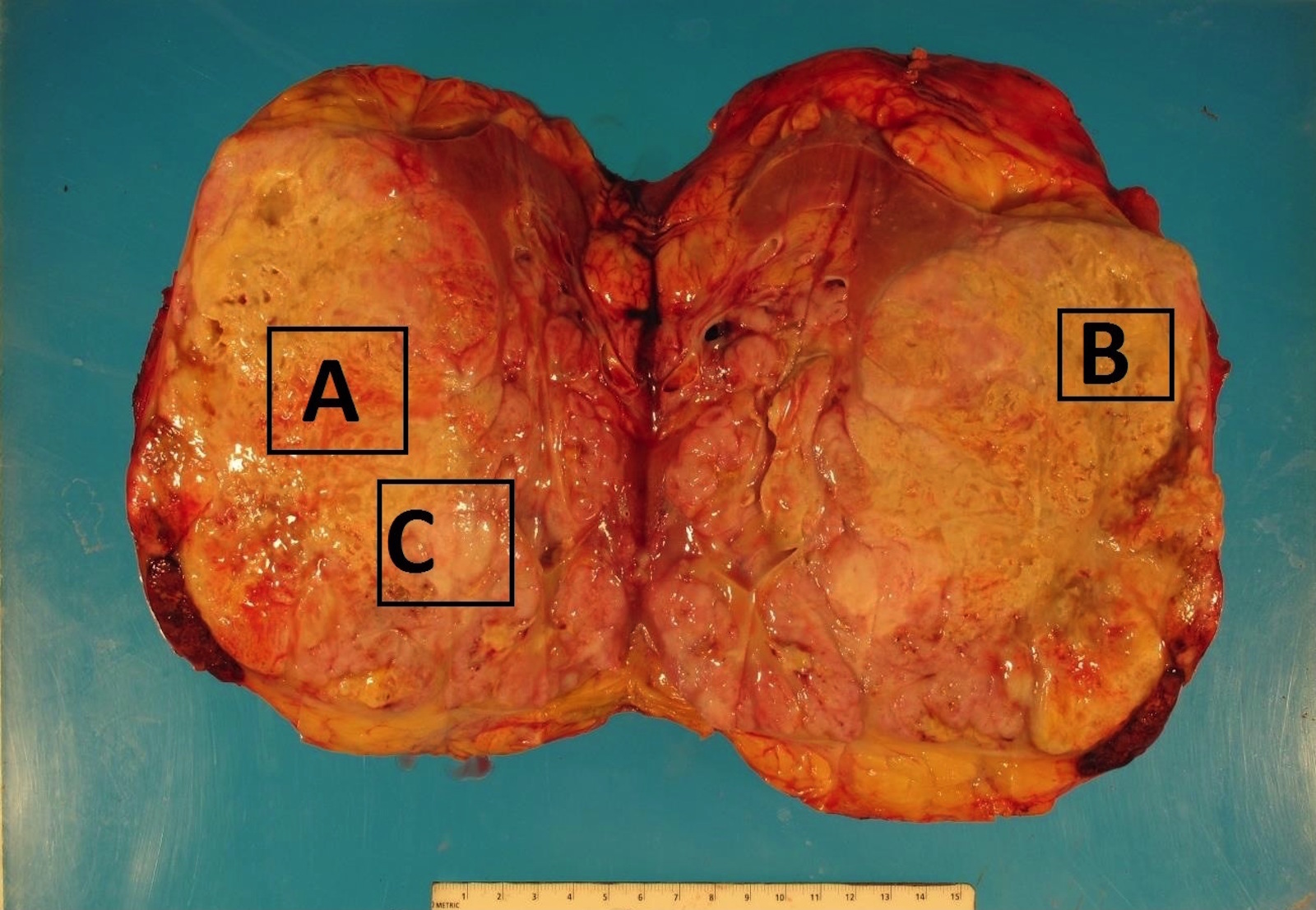
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
C. The area designated by letter C. Though there are multiple areas suspicious for sarcomatoid RCC, part C is most suspicious as this shows a more whitish, fleshy cut surface that appears to be different from the surrounding tumor, which was proven histologically. The yellow background of the tumor in A and B are grossly consistent with ccRCC.
Comment Here
Reference: Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma