Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: von Stillfried S, Boor P. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneyxantho.html. Accessed September 17th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare subtype of pyelonephritis, often occurring as a chronic consequence of nephrolithiasis or infections (Indian J Nephrol 2019;29:111)
- Pathognomonic features are lipid laden foamy CD68+ macrophages (xanthoma cells) that give the tissue a yellow-orange color on macroscopy (StatPearls: Pyelonephritis Xanthogranulomatous [Accessed 5 June 2023])
- Rarely associated with renal cell carcinoma or urothelial carcinoma (Indian J Nephrol 2019;29:111)
Essential features
- Lipid laden foamy CD68+ macrophages (xanthoma cells) give the tissue a yellow-orange color on macroscopy (hallmark)
- Extrarenal extension may be present and is suggestive of malignancy
- May mimic renal cell carcinoma clinically but also macroscopically and microscopically
Epidemiology
- Usually occurs unilaterally in all ages, more often in women and elderly patients
- Most often due to nephrolithiasis complicated with infections
Sites
- Kidney, almost always unilateral; left kidney more commonly affected (60%) (BJU Int 2023;131:395)
- May extend to perirenal / perinephric fat, perirenal and pararenal spaces or diffusely into the retroperitoneum
Pathophysiology
- Urinary obstruction occurs as a result of calculus, most commonly staghorn calculus (in almost 80% of patients), which serves as a nidus for infection, resulting in the destruction of the renal parenchyma (J Pediatr Genet 2020;9:114)
- In children, congenital ureteropelvic abnormalities may result in chronic urinary obstruction (J Pediatr Genet 2020;9:114)
Etiology
- Chronic pyelonephritis
- Nephrolithiasis
- Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, hypertension, immunocompromised individuals, abnormal lipid metabolism, renal transplantation (may be difficult to distinguish from rejection) and brachydactyly mental retardation syndrome in children (J Pediatr Genet 2020;9:114)
Clinical features
- Nonfunctional kidney
- Variable clinical presentation, including flank pain (92.5%), fever (62.5%), dysuria (47.5%), renal angle tenderness (40%) and a palpable lump on per abdomen examination (30%) (Indian J Nephrol 2019;29:111)
- Can raise suspicion for renal cell carcinoma clinically and macroscopically
- Can be associated with septic metastases, which may be clinically difficult to distinguish from neoplastic metastases (Aktuelle Radiol 1997;7:317)
- Intraabdominal or nephrobronchial fistulation is a rare complication of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (Br J Urol 1986;58:488, Int J Surg Case Rep 2022;98:107551)
- In prolonged disease course, secondary amyloidosis (amyloid AA) can occur, presenting as nephrotic syndrome (J Urol 1978;119:589)
Diagnosis
- Fever and raised inflammatory markers (C reactive protein [CRP] and erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR]) are most commonly associated with xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (J Pediatr Genet 2020;9:114)
- If present, the bear paw sign on CT imaging is a pathognomonic feature of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (J Pediatr Genet 2020;9:114)
Laboratory
- Complete blood count may show anemia and leukocytosis
- Elevated ESR and CRP
- Elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels
- Urinalysis may show pyuria, bacteriuria and hematuria
- Urine culture may be positive (Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis and others), urine culture sterile in 25% of cases (J Urol 1978;119:589)
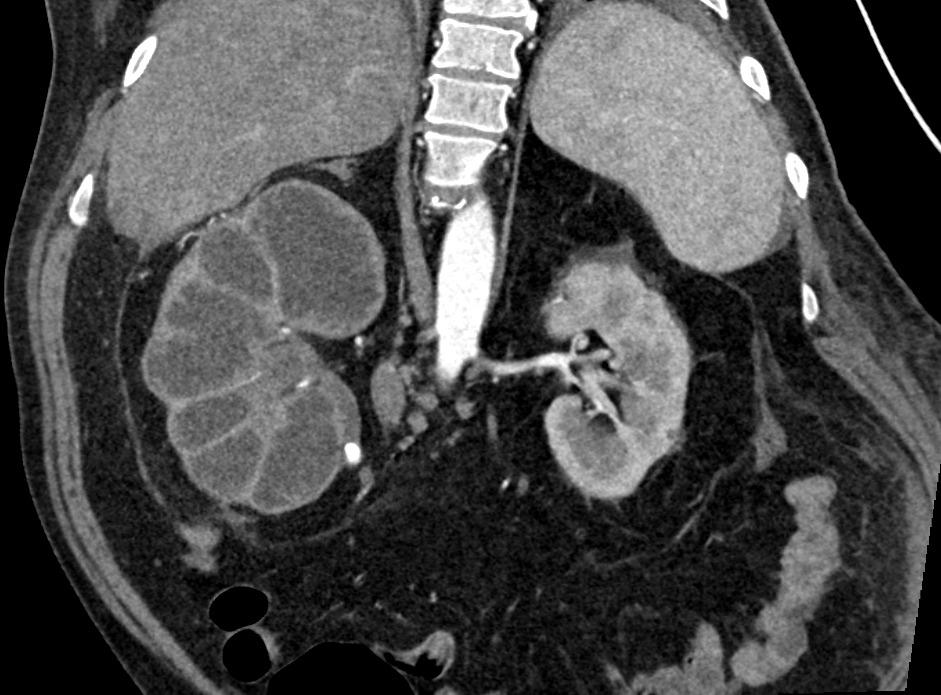
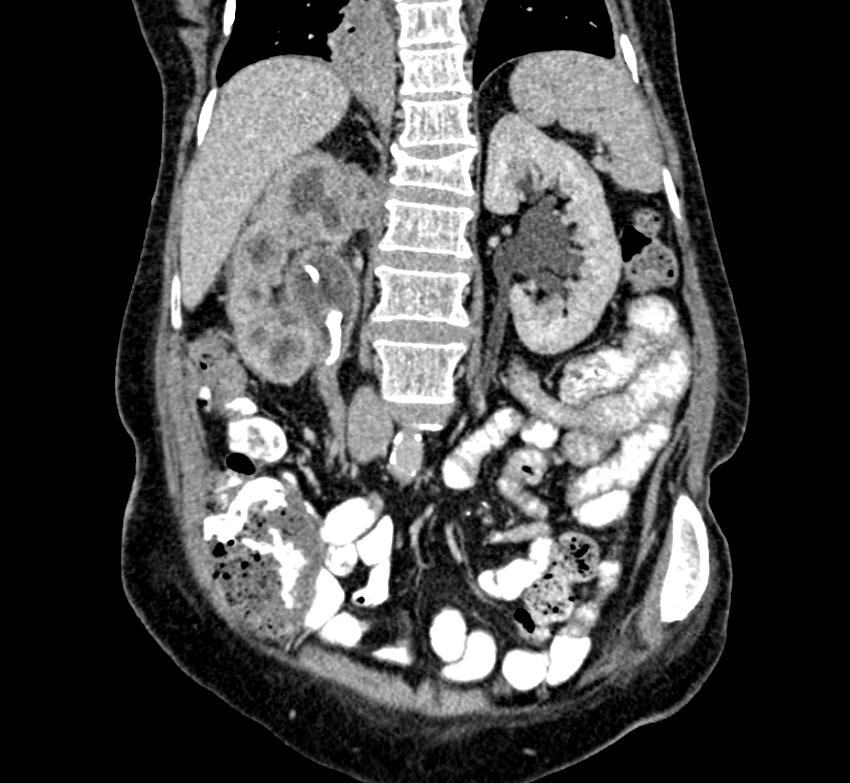
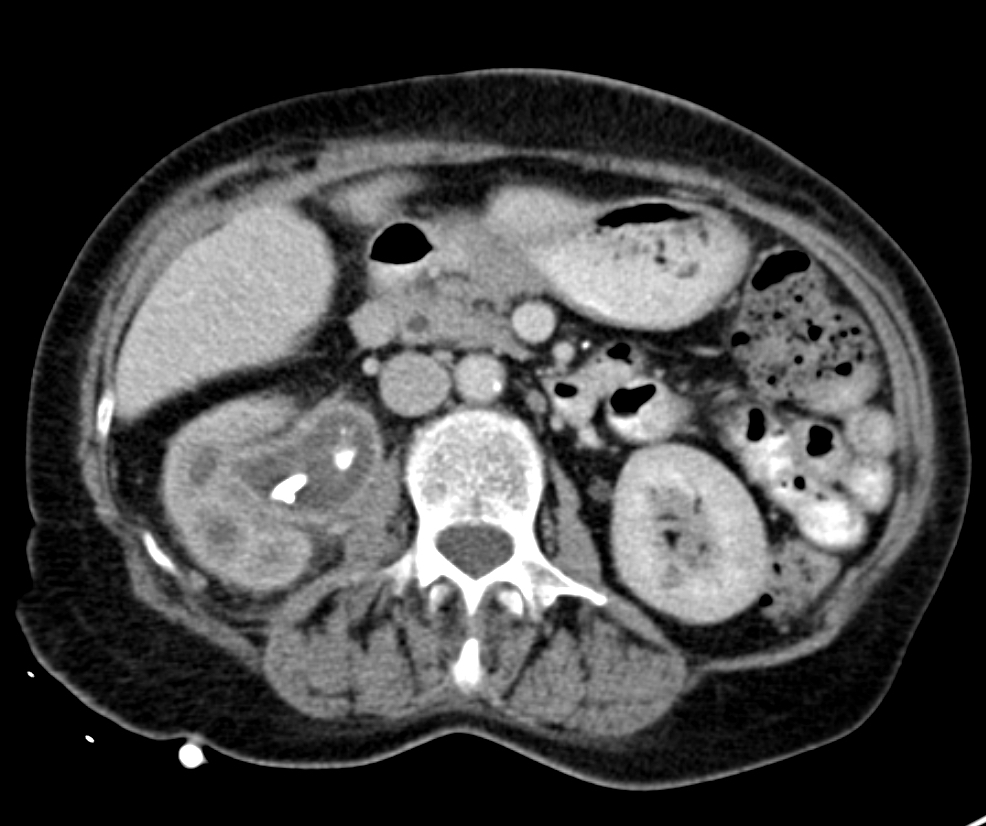
Radiology description
- Bear paw sign (i.e., dark dilated calyces surrounded by brighter renal parenchyma on CT imaging)
- Staghorn calculus on radiography in case of nephrolithiasis
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Excellent overall prognosis for xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
- Prognosis is better in unilateral cases, while bilateral cases are usually fatal
- Treatment of choice in diffuse cases is nephrectomy without any incidence of recurrence (StatPearls: Pyelonephritis Xanthogranulomatous [Accessed 5 June 2023])
Case reports
- 51 year old woman with a nodular tumor-like lesion on the upper left pole of the kidney (Patholog Res Int 2010;2010:602523)
- 55 year old man with palpable mass in his right lumbar region (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1986;63:246)
- 65 year old man with ureteral granulomatous inflammation involving the inferior vena cava (Cureus 2023;15:e34388)
- 66 year old man with renal calculi, squamous cell carcinoma and concomitant xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (Ochsner J 2023;23:72)
- 72 year old woman with xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis and concomitant renal cell carcinoma (BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e232097)
Treatment
- In focal or segmental cases, treatment with antibiotics and percutaneous drainage can be attempted, followed by partial (or total) nephrectomy if not successful
- In diffuse and advanced stages, nephrectomy is the treatment of choice (BJU Int 2023;131:395)
Gross description
- Zonal structure of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis may be visible upon macroscopy (Cureus 2021;13:e19133)
- Inner zone: dilated pelvicocalyceal system with necrotic debris
- Middle zone: granulation tissues surrounded by lipid laden macrophages (xanthoma cells) giving a yellow-orange appearance
- Outer zone: fibrosis may extend into renal fat capsule and beyond; decapsulation of kidney may not be feasible
Frozen section description
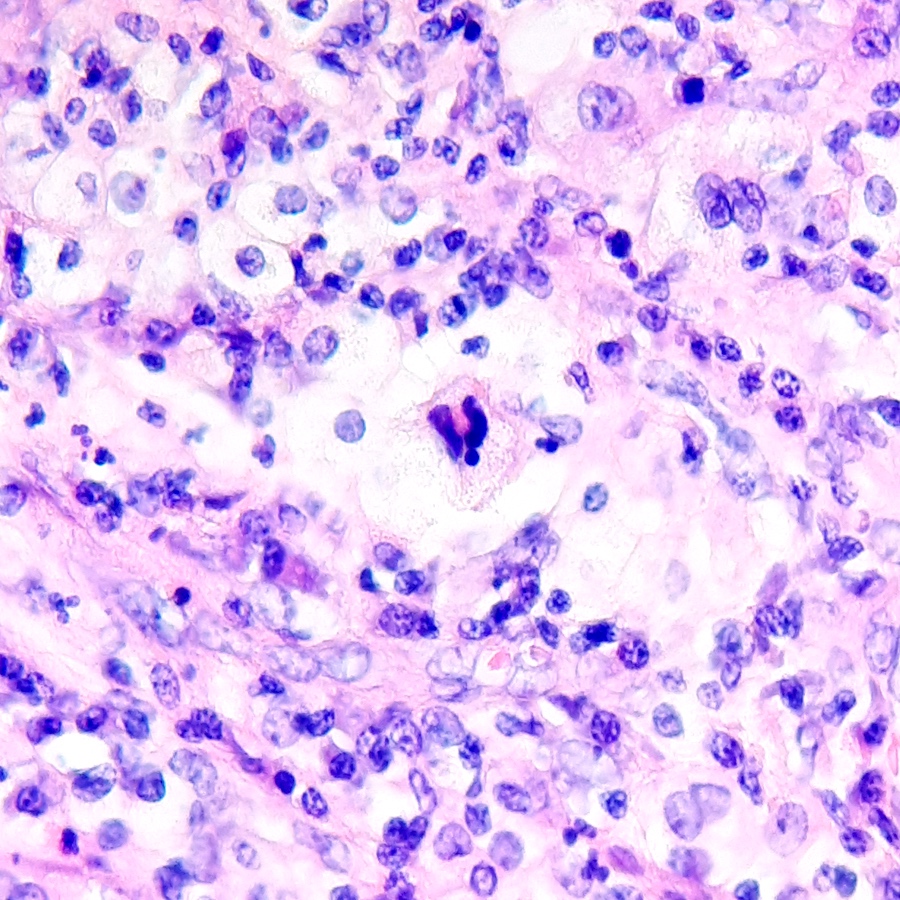
- Dense, sheet-like infiltrate of round cells with macro and microvesicular clear cytoplasm, inflammatory cells and multinucleated giant cells but no cytologic atypia or nucleoli
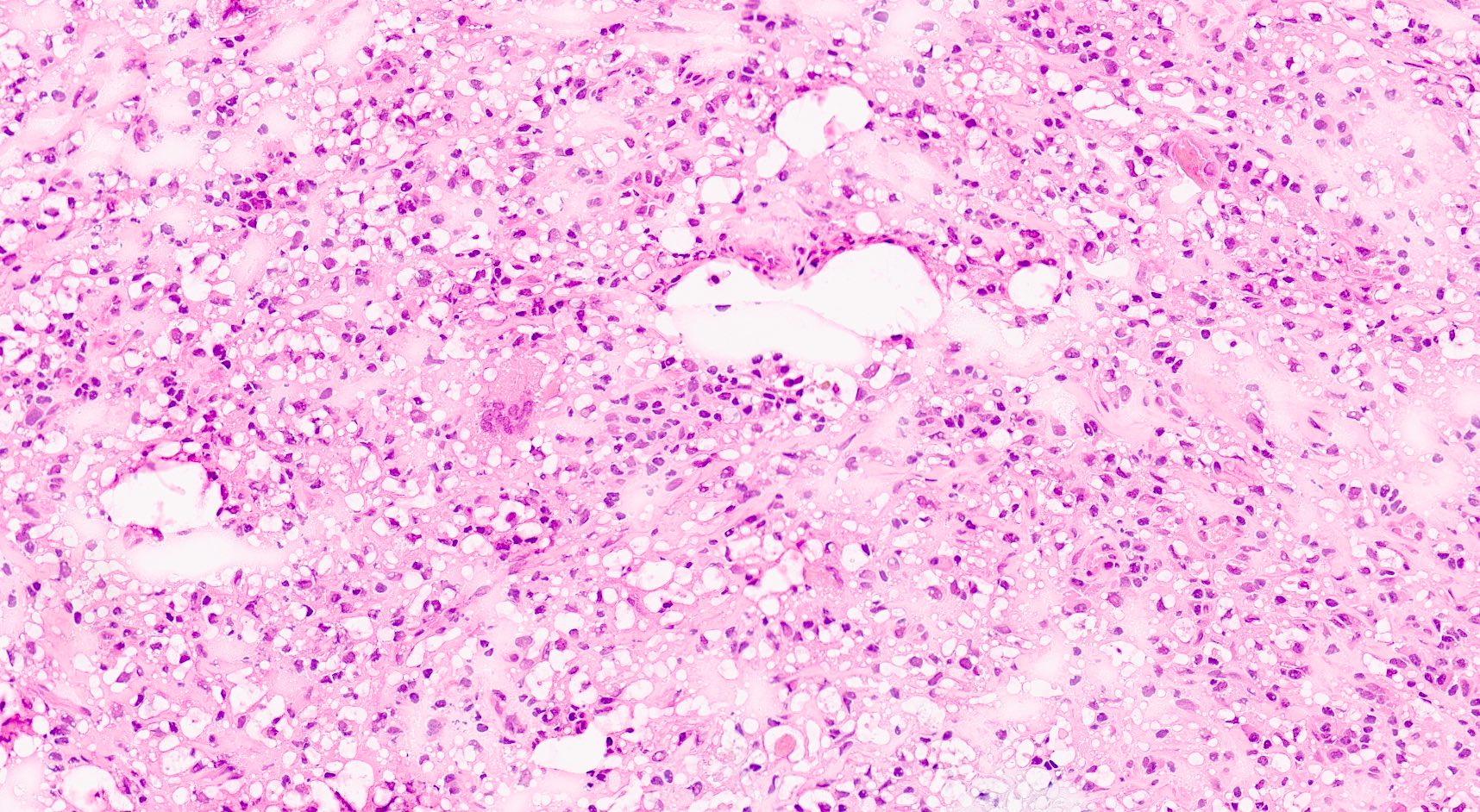
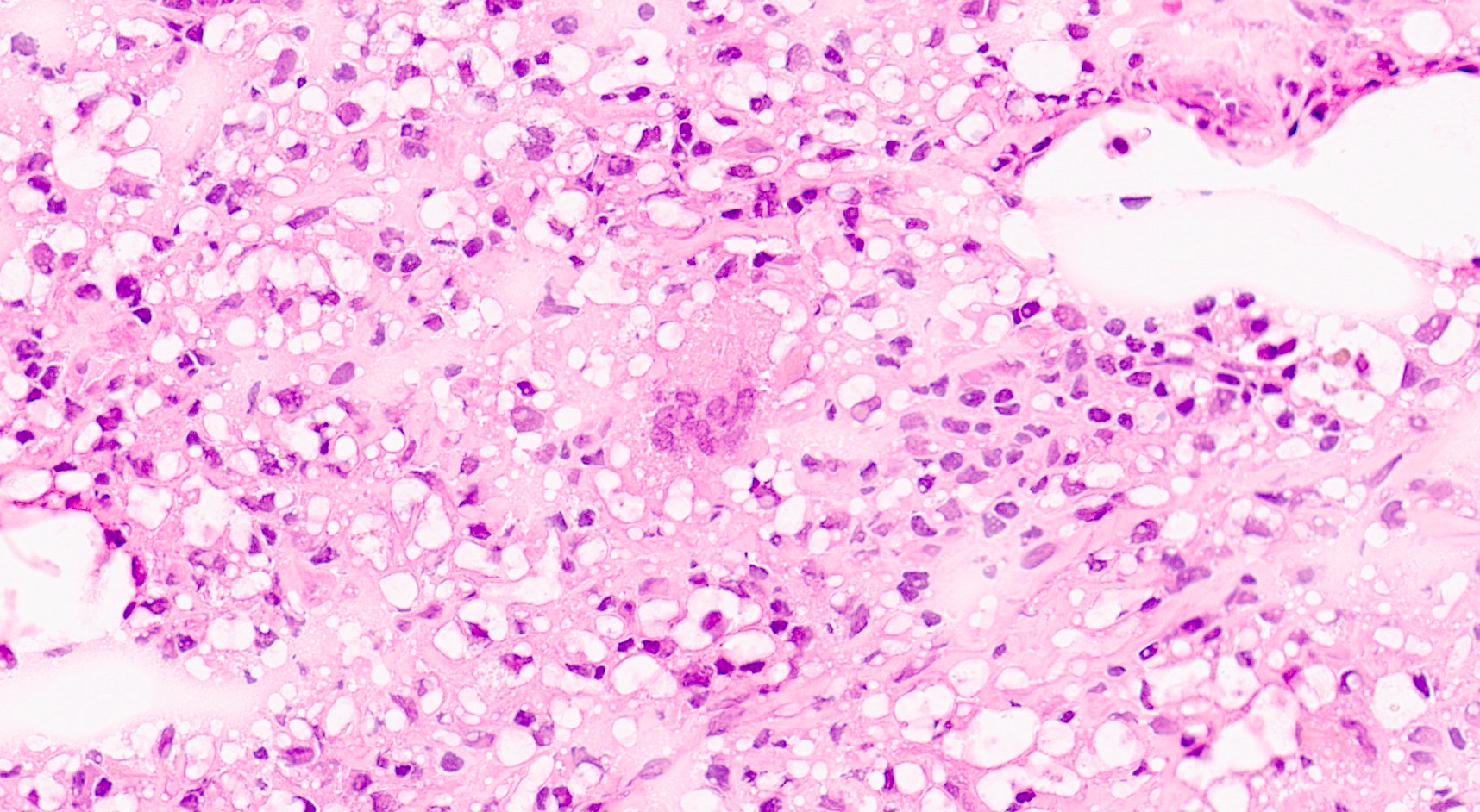
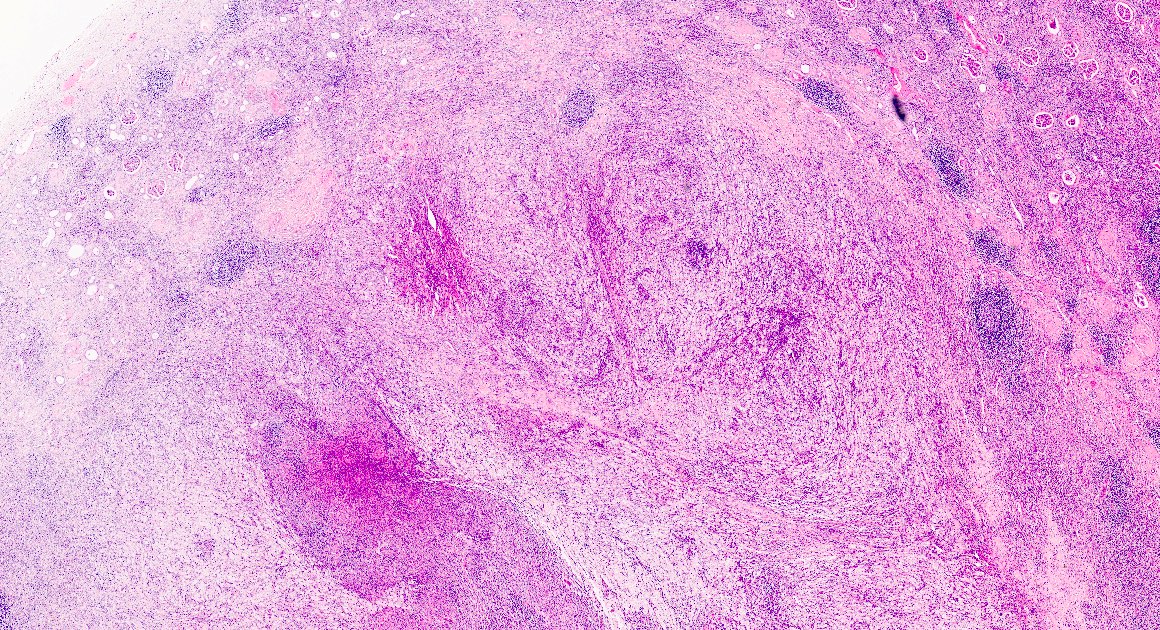
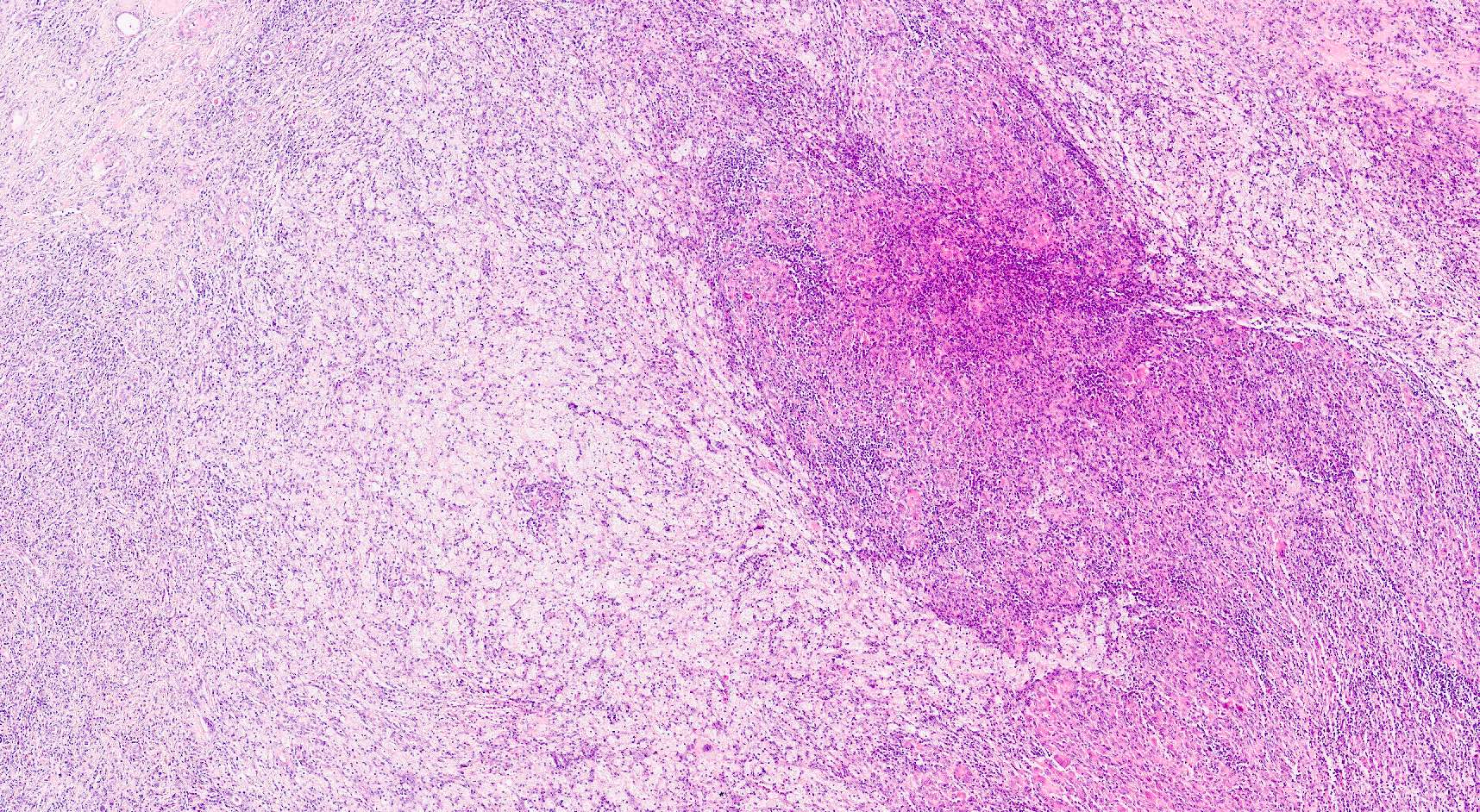
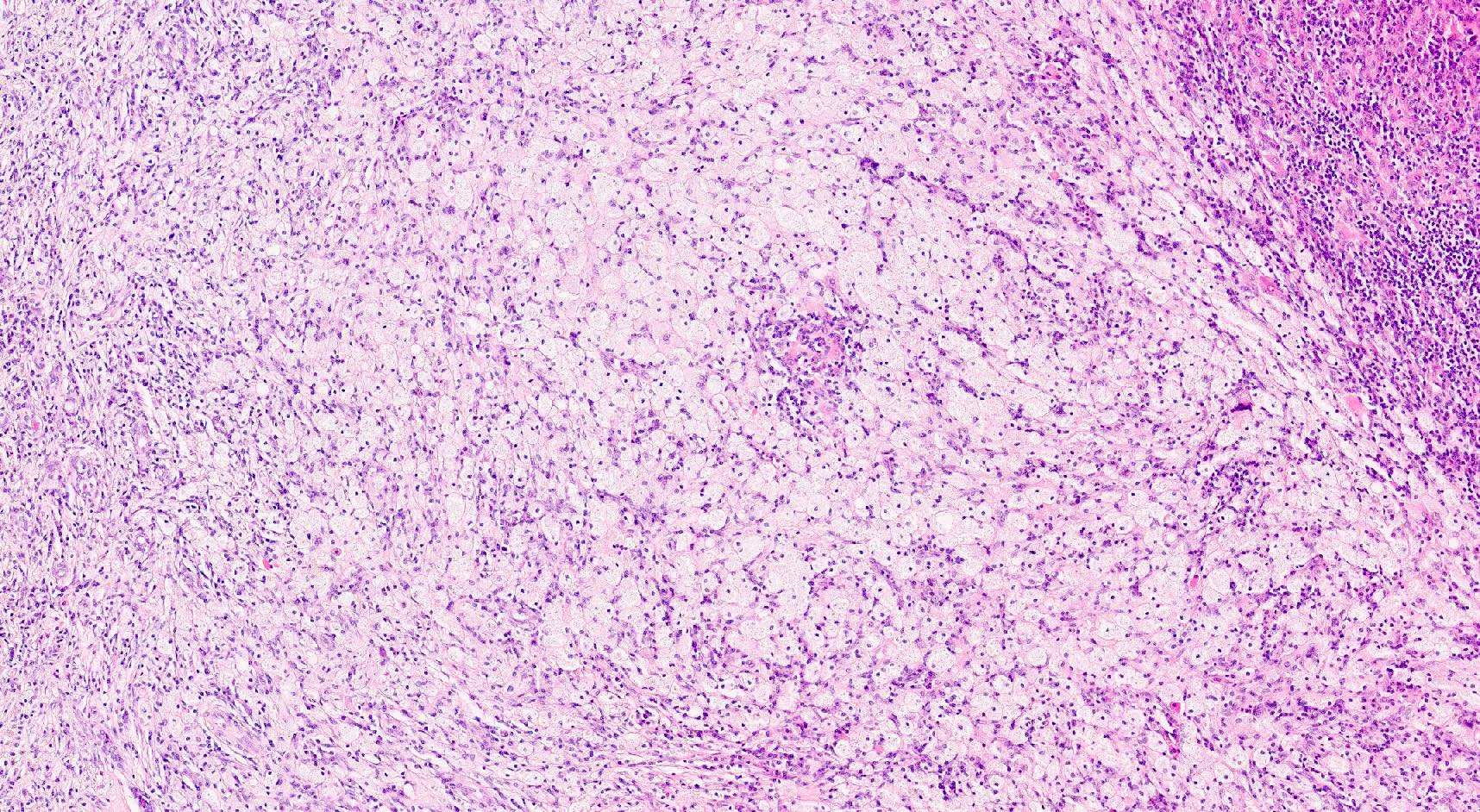
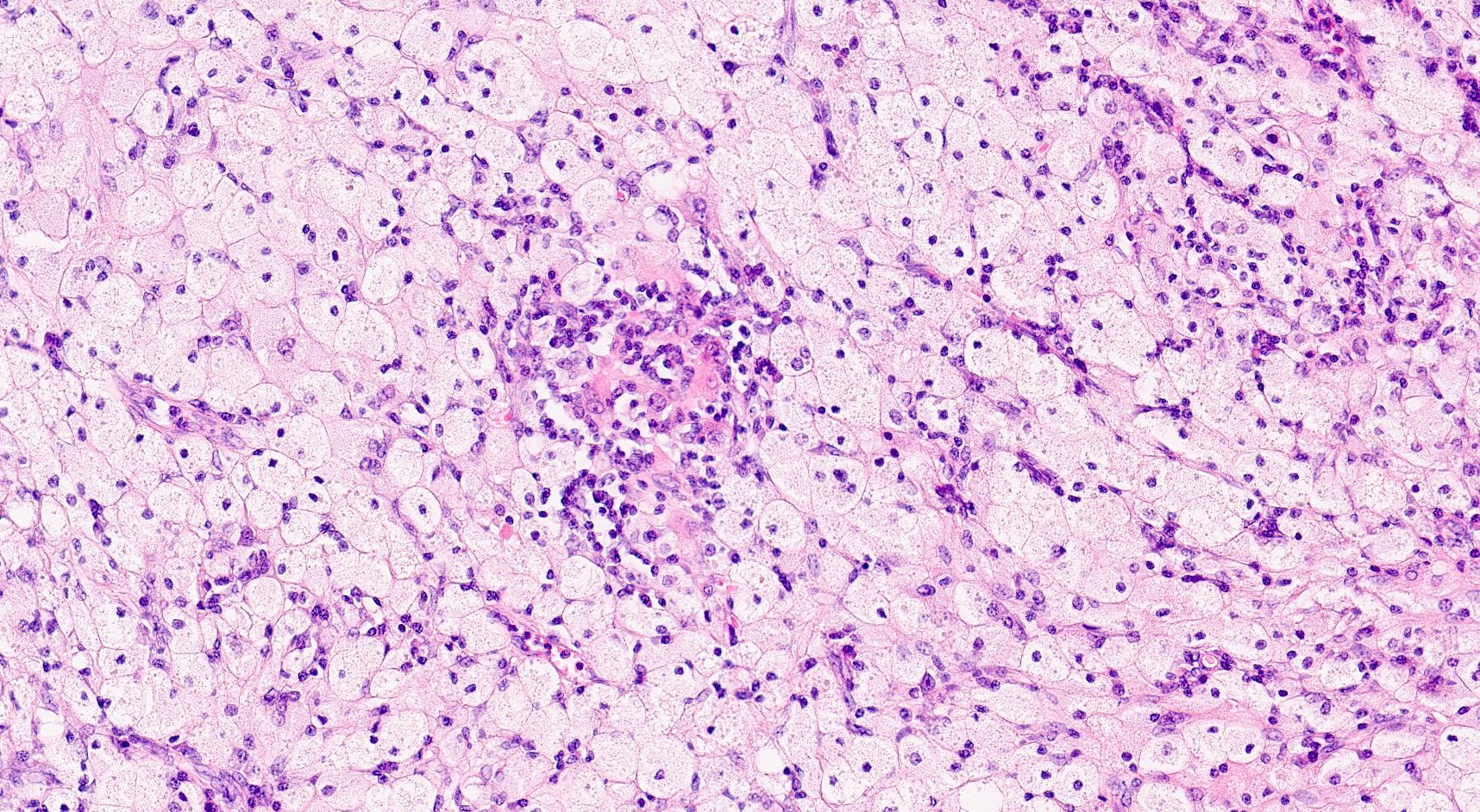
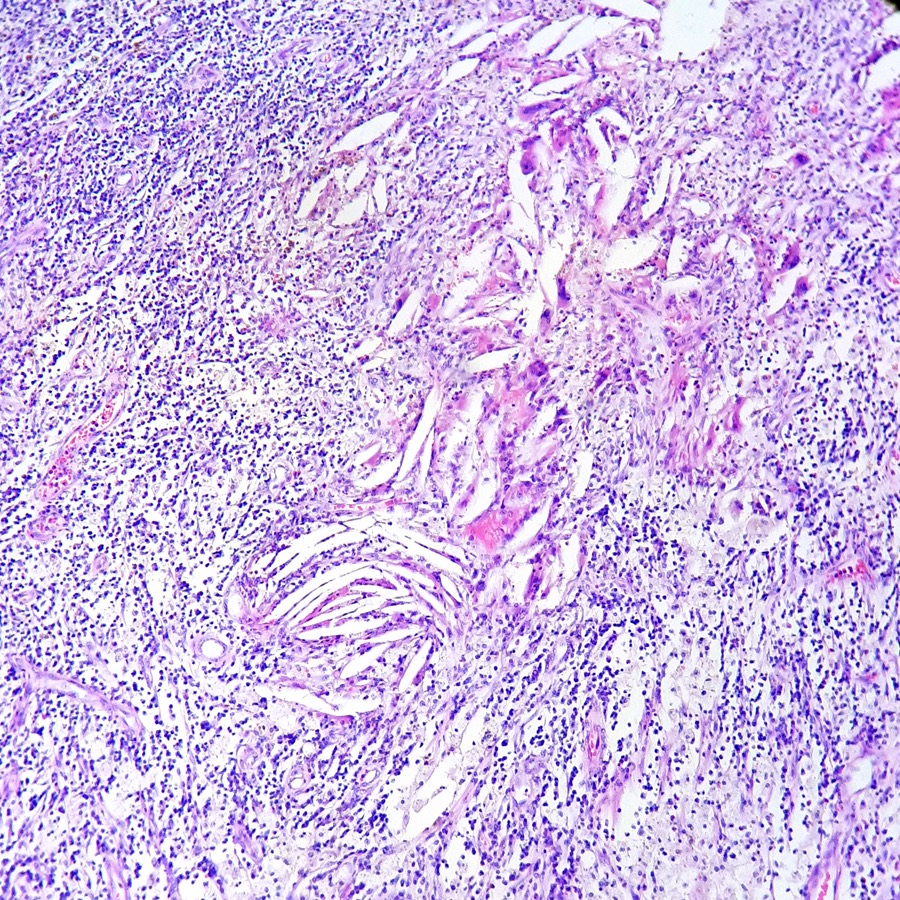
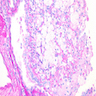
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Zonal distribution of inflammation may be seen
- Inner zone: bacteria, inflammatory cells (neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells), foreign body giant cells, foreign body granulomas, Liesegang rings, calcifications
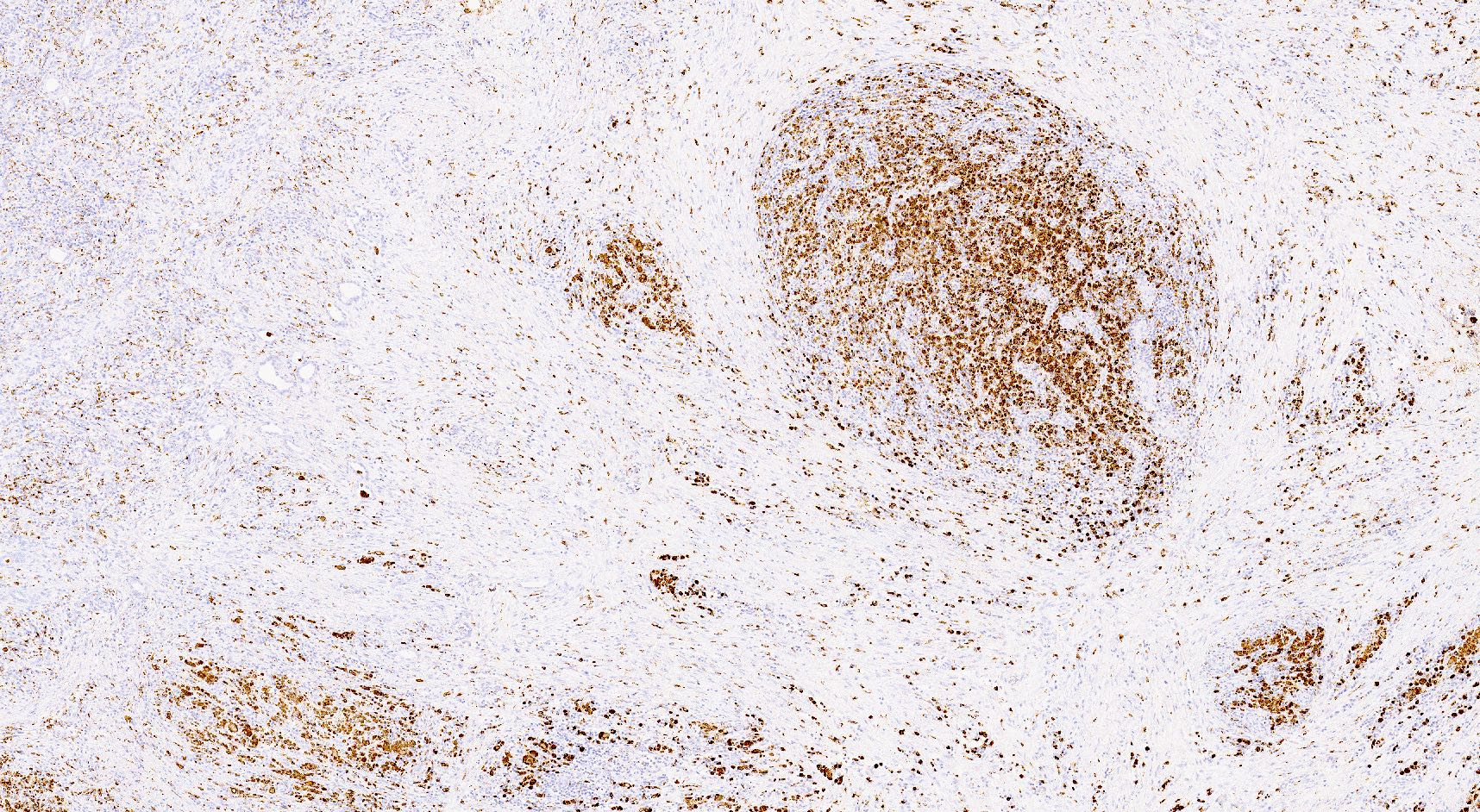
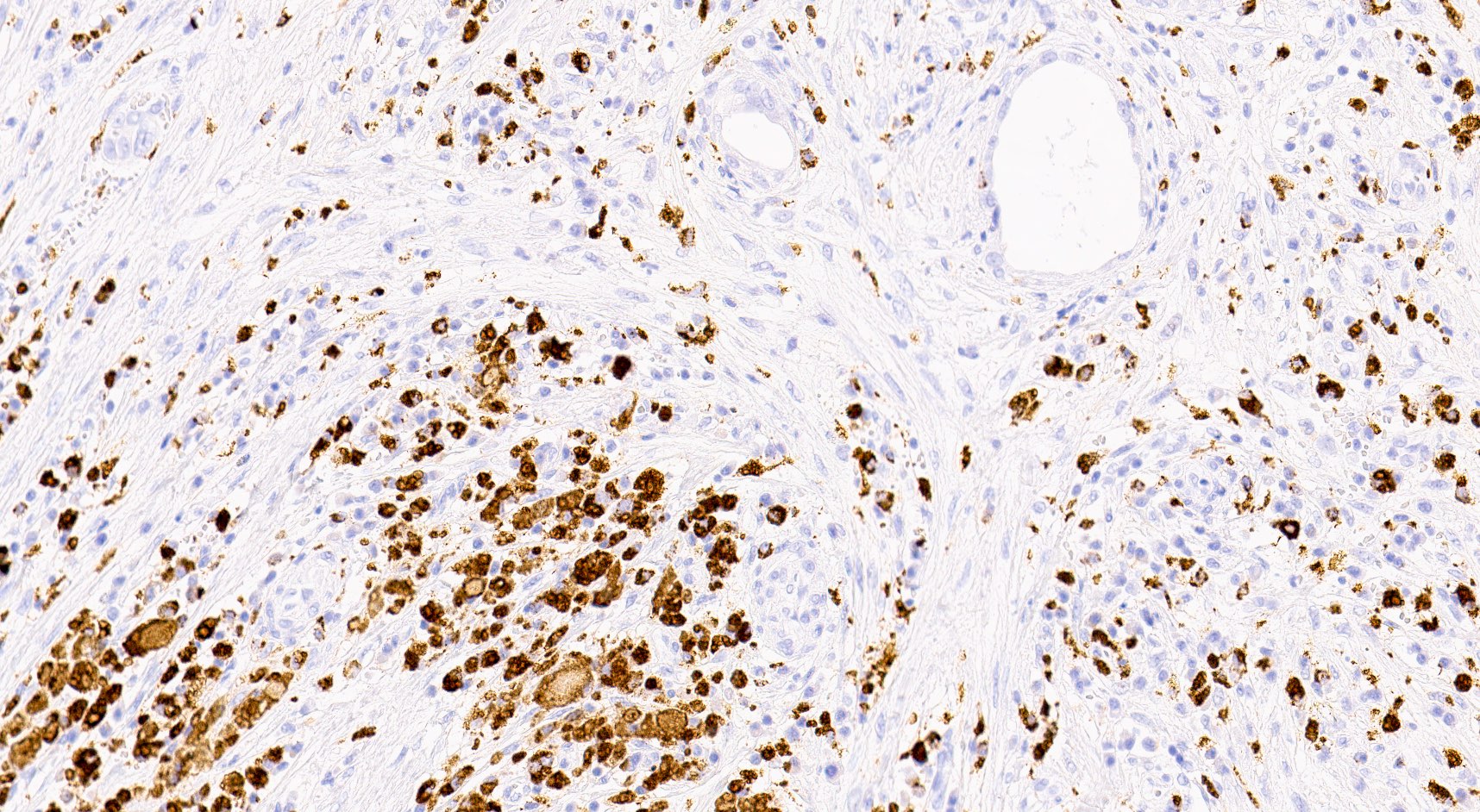
- Middle zone (hallmark for the diagnosis): granulation tissues surrounded by lipid laden foamy CD68+ macrophages (xanthoma cells), Touton giant cells, cholesterol crystal clefts
- Outer zone: consists of giant cells, cholesterol clefts and fibrous tissues with lymph follicles
- Zonal distribution may not be visible or zones may be admixed (e.g., xanthoma cells might be intermingled with inflammatory cells)
- Reference: StatPearls: Pyelonephritis Xanthogranulomatous [Accessed 21 June 2023]
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Pankeratin
- PAX8
- Melanocytic markers
- Acid fast bacteria
- Reference: Cancer Cytopathol 2018;126:711
Differential diagnosis
- Malakoplakia:
- Michaelis-Gutmann bodies
- Renal clear cell carcinoma:
- Cells with clear cytoplasm may resemble histiocytes but are keratin+, PAX8+, CD68-
- Arranged in compact, tubulocystic, alveolar or rarely papillary patterns
- Often glassy hyaline globules
- Usually nuclear grade 2 or higher
- Chicken wire / delicate vasculature is common (sinusoids near each packet of cells)
- Renal replacement lipomatosis:
- Atrophic renal parenchyma is replaced by adipose tissue, not xanthoma cells (Cureus 2021;13:e16596)
- Renal tuberculosis:
- Granulomas with caseating necrosis surrounded by histiocytes and Langhans type giant cells
- Acid fast bacteria stain (Ziehl-Neelsen) demonstrates red, rod shaped bacilli at periphery of necrosis
Practice question #1
What are the typical histologic findings in xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis?
- Caseating granulomas
- Chicken wire vasculature
- Foam cells
- Michaelis-Gutmann bodies
- Tubular casts
Practice answer #1
C. Foam cells. Foam cells (also known as xanthoma cells) are the pathognomonic feature of xanthogranulomatous inflammation. Answer A is incorrect because caseating granulomas are typical features of renal tuberculosis (see Renal tuberculosis). Answer B is incorrect because chicken wire vasculature is a typical feature of liposarcoma. Answer D is incorrect because Michaelis-Gutmann bodies are found in malakoplakia, a differential diagnosis of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (see Malakoplakia). Answer E is incorrect because tubular casts are found in cast nephropathy and other conditions.
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
A. CD68 positive. The pathognomonic cells in xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis are CD68 positive foam cells (xanthoma cells). Answer B is incorrect because xanthoma cells are not epithelial cells. Answer C is incorrect because inflammatory cells, such as MUM1 positive plasma cells, are found in various inflammatory conditions. Answers D and E are incorrect because PAX8 and WT1 are typical markers for epithelial renal cells, such as in renal cell carcinoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis