Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Peripheral smear description | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: van den Akker TA, Geyer JT. Transient abnormal myelopoiesis associated with Down syndrome. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/leukemiaTAM.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Transient disorder of newborns with Down syndrome or phenotypically normal neonates with trisomy 21 mosaicism
- Presents within 3 - 5 days of birth and resolves spontaneously within 3 months
- Proliferation of nonerythroid blasts (commonly megakaryoblasts) in the peripheral blood or organs
- Morphologically indistinguishable from acute myeloid leukemia (AML), specifically acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL)
- Unique distinguishing clinical, immunophenotypic and molecular genetic features from AML not associated with Down syndrome
Essential features
- 10% of newborns with Down syndrome or trisomy 21 mosaicism
- Proliferation of nonerythroid blasts in the peripheral blood, bone marrow or organs
- Morphologically indistinguishable from other forms of AML
- Presents within first week of life and resolves within 3 months
- 20 - 30% may progress to nontransient AML (i.e. AMKL) within 1 - 3 years
- Associated with acquired GATA1 mutation
Terminology
- Transient abnormal myelopoiesis associated with Down syndrome (TAM)
- Transient myeloproliferative disorder (TMD)
- Transient leukemia (TL)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9898/1 - Transient abnormal myelopoiesis
Epidemiology
- Manifests in approximately 10% of neonates with Down syndrome
- 7 - 16% of TAM is seen in phenotypically normal neonates with trisomy 21 mosaicism
Sites
- Peripheral blood
- Common site of blasts, as fetal hematopoiesis occurs predominantly in the liver
- Peripheral blood involvement > bone marrow
- Bone marrow
- Less common site of fetal hematopoiesis
- Other organs
- Liver, spleen, skin, pancreas, kidneys, pleural fluid, pericardial fluid
Pathophysiology
- 3 step process (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:333):
- Perturbation of fetal liver hematopoiesis by trisomy 21
- Acquired or somatic mutation of GATA1 (chromosome X), hematopoietic transcription factor
- 20 - 30% progress to AML with further acquisition of oncogenic mutations
Etiology
- Risk factors for Down syndrome
- Advanced maternal age
Clinical features
- Most diagnosed at 3 - 5 days of age
- Most patients are asymptomatic but may present with myeloblast organ infiltration:
- Hepatosplenomegaly (common)
- Ascites, pericardial or pleural effusions, hepatic fibrosis, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (less common)
- Severe organ dysfunction causing renal, hepatic or cardiopulmonary failure (rare)
- If in utero, may present as hydrops fetalis secondary to cardiopulmonary failure and anemia
- References: Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:333, Silberstein: Hematology - Basic Principles and Practice, 7th Edition, 2017
Diagnosis
- No universal diagnostic criteria
- Children's Oncology Group (COG) (Blood 2011;118:6752):
- Detection of nonerythroid blasts in peripheral blood or organs
- Newborns < 90 days old
- Trisomy 21 or mosaicism
- Confirmation with:
- Second blood sample
- > 5% nonerythroid blasts in bone marrow
- Hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy or pericardial / pleural effusions
Laboratory
- Presence of megakaryoblasts in peripheral blood
- Thrombocytopenia is most common
- Moderate leukocytosis with myeloid left shift
- Basophilia
- Coagulopathy, specifically disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) (10%)
- Elevated conjugated bilirubin (common)
- Secondary to liver involvement
- References: Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:333, Silberstein: Hematology - Basic Principles and Practice, 7th Edition, 2017
Prognostic factors
- Majority resolve spontaneously over several weeks to 3 months
- Approximately 15 - 23% of patients may die as a result of secondary organ failure:
- Hepatic fibrosis
- Cardiopulmonary failure
- Poor prognostic factors for early death include:
- High WBC count
- Increased bilirubin
- Elevated liver function tests (LFTs)
- Failure to normalize blood counts
- 20 - 30% may develop nontransient AML (usually AMKL) within 1 - 3 years
- Greatest risk factors for AML progression are karyotypic abnormalities in addition to +21 in blast cells
- References: Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:333, Mycopathologia 2016;181:909
Case reports
- 7 day old neonate with TAM and severe multiorgan dysfunction (J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2021;43:e292)
- 8 day old phenotypically normal newborn with TAM associated with Down syndrome mosaicism (Children (Basel) 2020;7:52)
- 14 day old newborn with TAM and pericardial effusion (Clin Case Rep 2019;7:1280)
- 2 neonates with TAM (J Pediatr Genet 2019;8:187)
Treatment
- Treatment is often supportive due to spontaneous remission
- In severe organ dysfunction, exchange transfusion, leukapheresis or chemotherapy may be necessary
- In TAM progression to AML, cytosine arabinoside is the most commonly used chemotherapeutic agent
- Favorable prognosis
- References: Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:333, Pediatr Int 2019;61:222
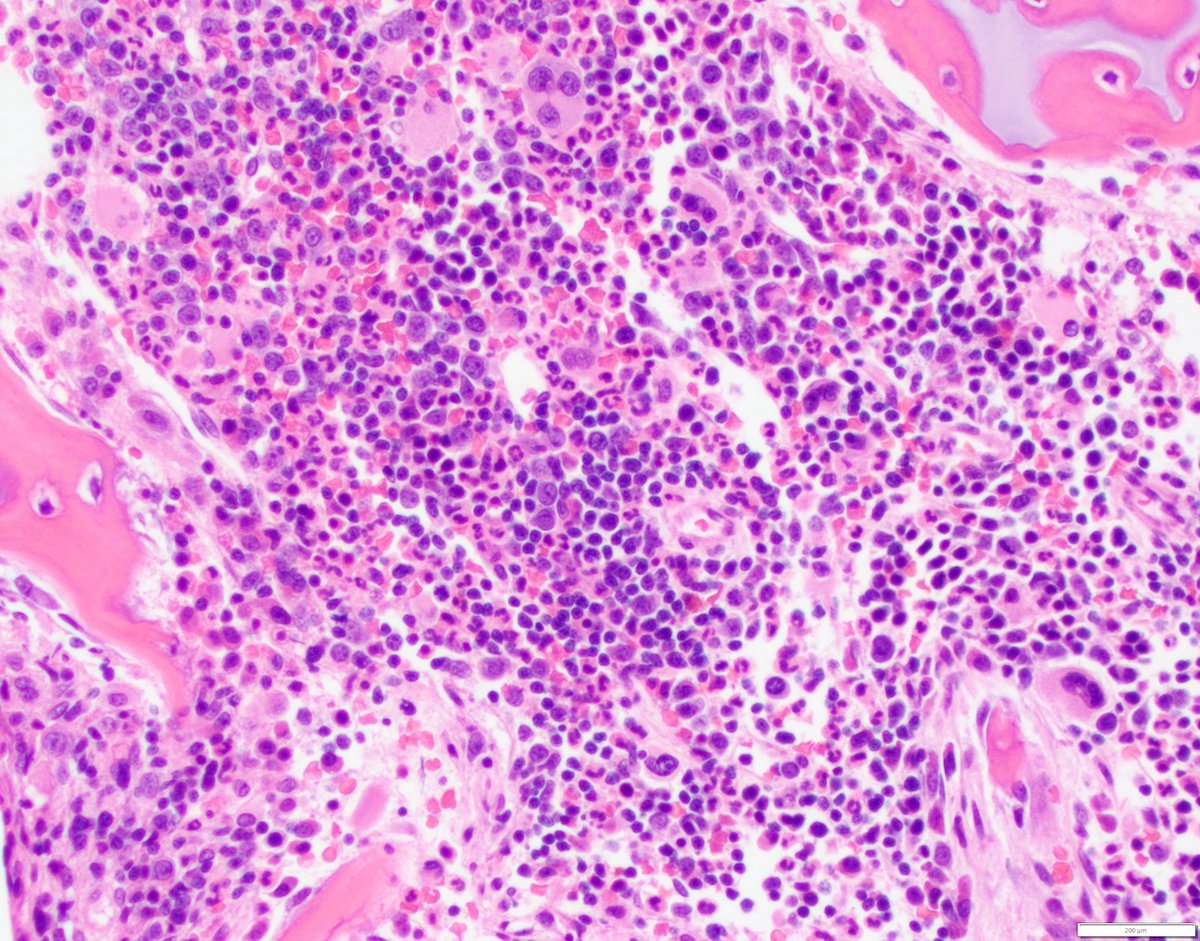
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Blasts are morphologically indistinguishable from those in AMKL associated with Down syndrome
- Features of megakaryoblasts
- Increased nuclear:cytoplasmic (N:C) ratio
- Dispersed nuclear chromatin
- Basophilic cytoplasm
- Coarse basophilic cytoplasmic granules
- Cytoplasmic blebbing
- Erythroid and megakaryocytic dysplasia are also seen
- Dyserythropoiesis with bi and trinucleated forms
- Dysmegakaryopoiesis with dysplastic small forms and micromegakaryocytes
Microscopic (histologic) images
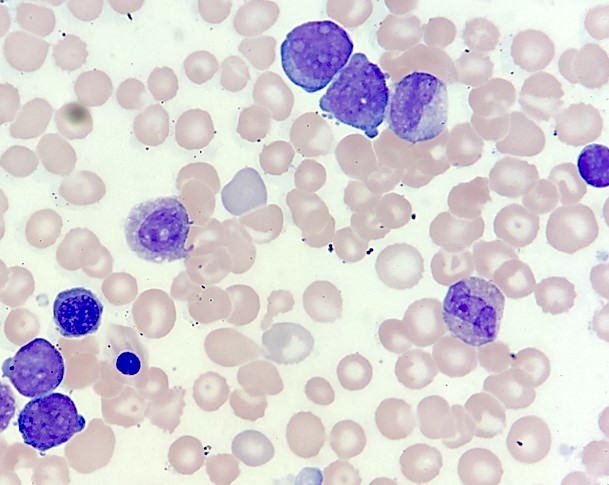
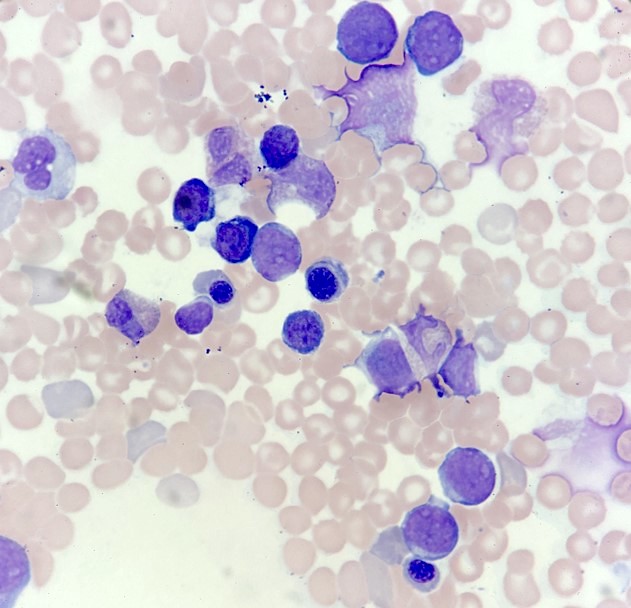
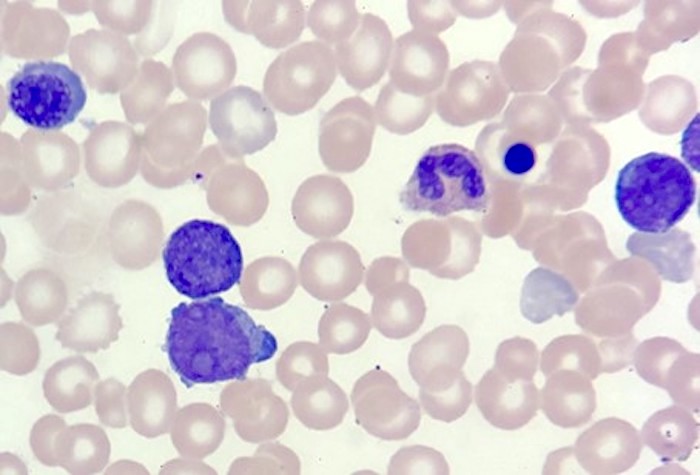
Peripheral smear description
- Features of megakaryoblasts in peripheral blood
- Increased N:C ratio
- Dispersed nuclear chromatin
- Basophilic cytoplasm
- Coarse basophilic cytoplasmic granules
- Cytoplasmic blebbing
- Basophilia
Positive stains
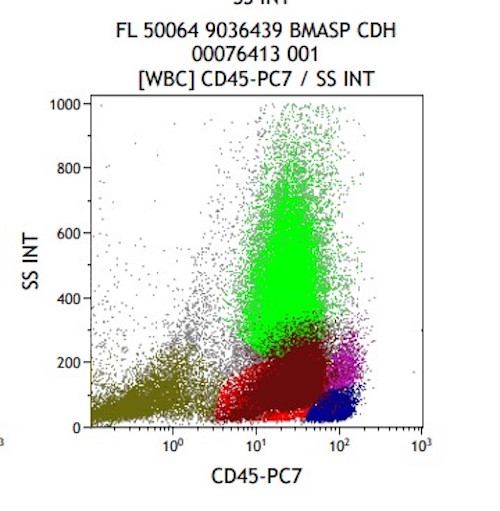
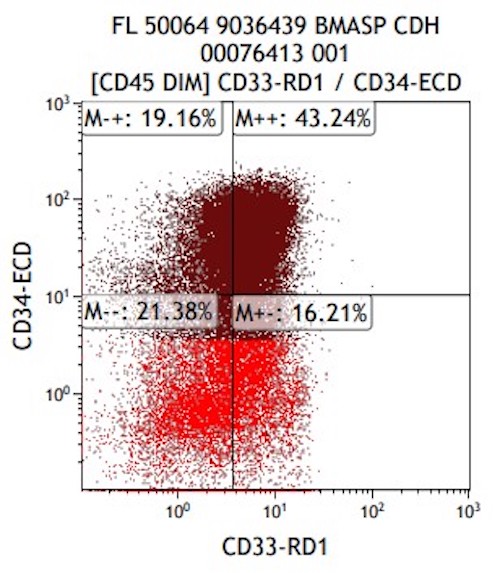
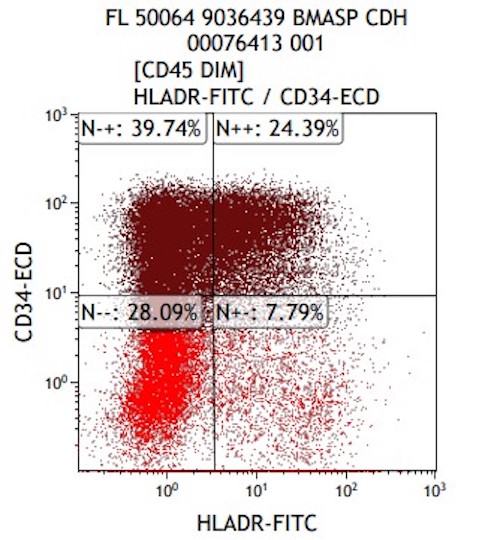
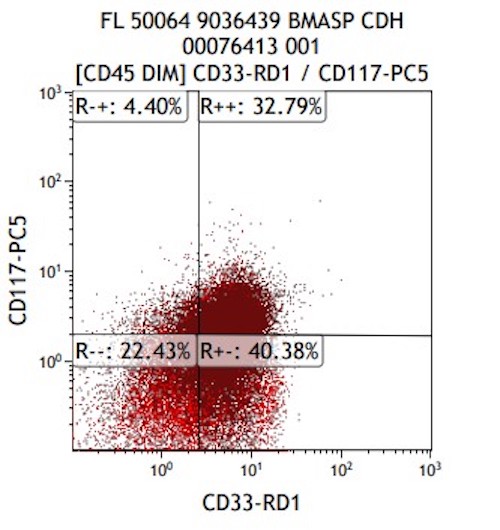
Flow cytometry description
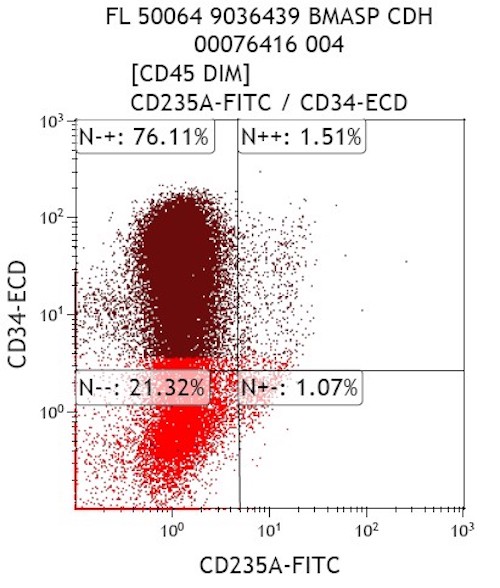
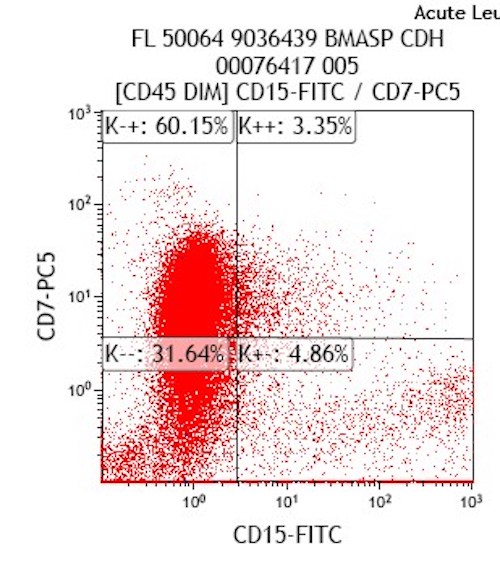
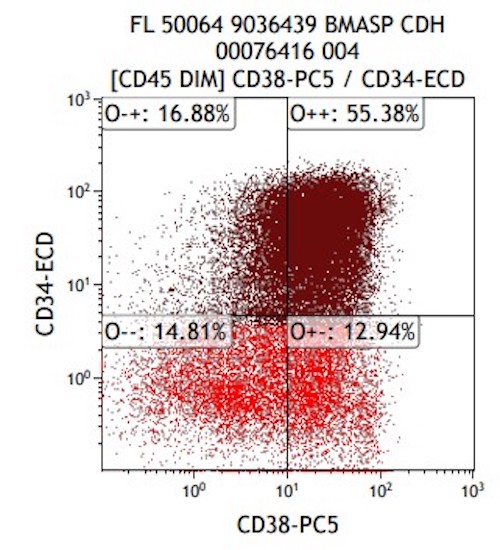
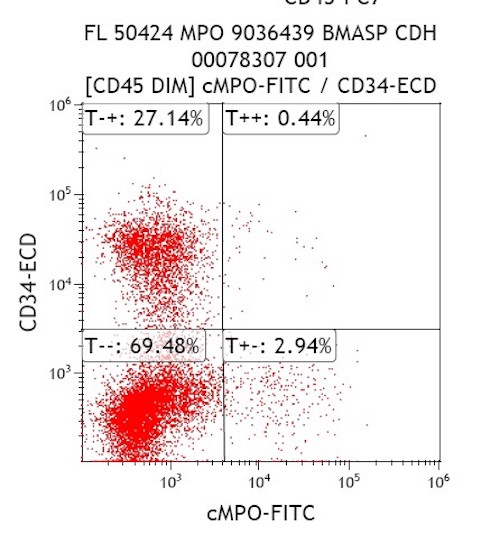
- Expanded population of CD45+ myeloid blasts (left shift in myeloid maturation)
- Increased CD34+ myeloid population, may exceed 20% in peripheral blood, expressing CD117, CD33, CD38
- Aberrant expression of CD7 and CD56
- Expression of CD41 and CD61
- Reference: Cherian: Flow Cytometry in Evaluation of Hematopoietic Neoplasms, 1st Edition, 2012
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Trisomy 21
- GATA1 mutation in blasts
- Expression of truncated protein, which promotes megakaryocytic and abnormal blast proliferation
- References: Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:333, Pediatr Int 2019;61:222
Sample pathology report
- Bone marrow, right posterior iliac crest and aspirate smears:
- Hypercellular marrow (100%), consisting predominantly of left shifted granulocytic precursors with focally interspersed small hypolobated megakaryocytes. Increased blasts (20%) with cytoplasmic blebs and prominent nucleoli. These findings are suspicious for transient abnormal myelopoiesis versus congenital AML (see comment).
- Comment: Flow cytometric analysis demonstrates an aberrant blast population (approximately 35% of total), exhibiting the following immunophenotype: CD45 moderate+, CD34+, CD33 dim+, HLA-DR partial+, CD117+, CD38+. CD7 heterogeneous+, CD4 dim+. These findings do not definitively distinguish between transient abnormal myelopoiesis and acute myeloid leukemia; clinical correlation is required.
- Bone marrow, left posterior iliac crest, trephine biopsy and clot: Quality: adequate. Cellularity: 100%. Normocellular marrow for age (~100%) consisting predominantly of left shifted granulocytic precursors. Megakaryocytes are increased, predominantly hypolobated forms and not seen in dense clusters. No granulomas. The bony trabeculae are unremarkable.
- Bone marrow aspirate smears: Quality: adequate. Blasts are increased, approximately 20% of total by manual differential count. Blasts with cytoplasmic blebs and prominent nucleoli.
Differential diagnosis
- AMKL in Down syndrome:
- Anemia, with preserved WBC count
- Occurs after the first year of life (versus first 3 - 5 days in TAM)
- May have a history of TAM
- Dyserythropoiesis and bone marrow fibrosis more common (versus TAM)
- Frequently negative for CD34, CD56, HLA-DR and positive for CD11b and CD13
- Complex karyotype and other cytogenetic abnormalities (i.e. JAK-STAT pathway) in addition to +21 and GATA1 mutation
- Acute myeloid leukemia not associated with Down syndrome:
- Commonly adults; median age: 65 - 68 years
- Poor prognosis compared with Down syndrome related AML (favorable prognosis)
- AMKL subtype is rare (< 5% AML)
- Absence of trisomy 21
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 4 day old boy with Down syndrome is diagnosed with a transient myeloproliferative condition associated with the cells seen in the above image. Which genetic abnormality would be expected in addition to the additional chromosome 21?
- GATA1 mutation
- NPM1 mutation
- PDGFRA mutation
- t(9;22) with p190 breakpoint
Board review style answer #1
A. GATA1 mutation
Comment Here
Reference: Transient abnormal myelopoiesis associated with Down syndrome
Comment Here
Reference: Transient abnormal myelopoiesis associated with Down syndrome
Board review style question #2
Which immunophenotype is observed in AMKL associated with Down Syndrome?
- CD2+, CD4+, CD8- CD7-, CD10+, CXCL13+, BCL6+
- CD7+, CD3+, MPO-, CD4+, CD8+, TdT+, CD34+
- CD19+, Cd20+dim, CD5+, CD10-, FMC7-
- CD117+, CD34-, CD41+, CD7+, CD56-, CD61+, MPO-
Board review style answer #2
D. CD117+, CD34-, CD41+, CD7+, CD56-, CD61+, MPO-. Answer A is seen in AITL, answer B is seen in T-ALL and answer C is seen in CLL.
Comment Here
Reference: Transient abnormal myelopoiesis associated with Down syndrome
Comment Here
Reference: Transient abnormal myelopoiesis associated with Down syndrome