Table of Contents
Definition / general | Diagnosis | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Mihova, D. M5a. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/leukemiaacutemonocyticleukemiam5a.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Acute monoblastic leukemia (M5a)
- 5 - 8% of AML
- Children and young adults
Diagnosis
- 80%+ of monocyte lineage cells are monoblasts
Case reports
- 66 year old man with erythropoietin dependent transformation of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts into acute monoblastic leukemia (Blood 2001;98:3492)
- 73 year old woman with coexisting mantle cell lymphoma (Leuk Lymphoma 2005;46:1813)
- 82 year old man with acute monoblastic leukemia following granular lymphocyte proliferative disorder (Rinsho Ketsueki 2011;52:1870)
Microscopic (histologic) description
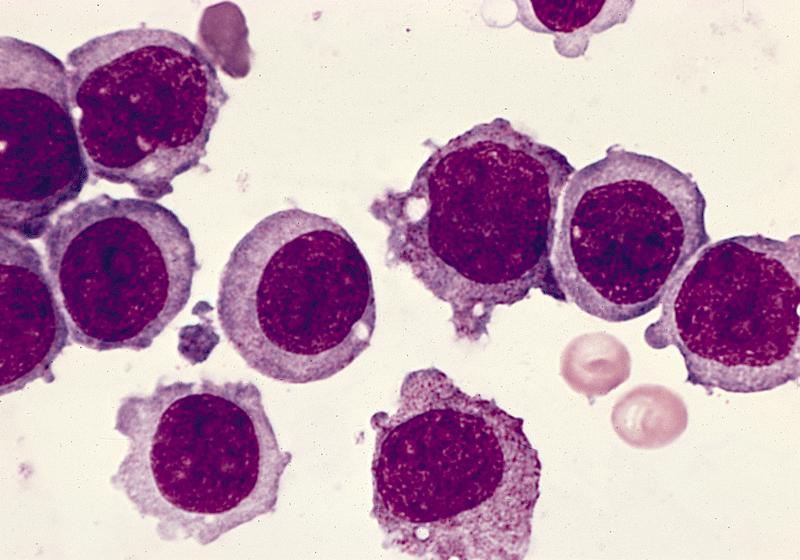
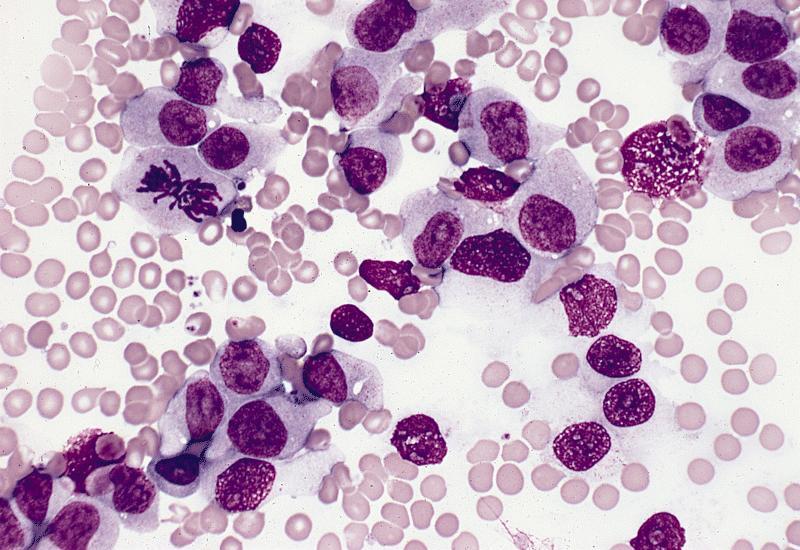
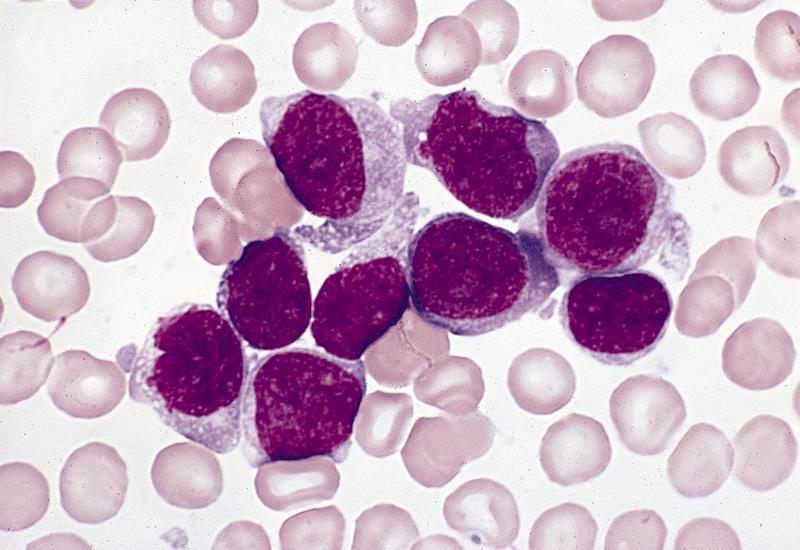
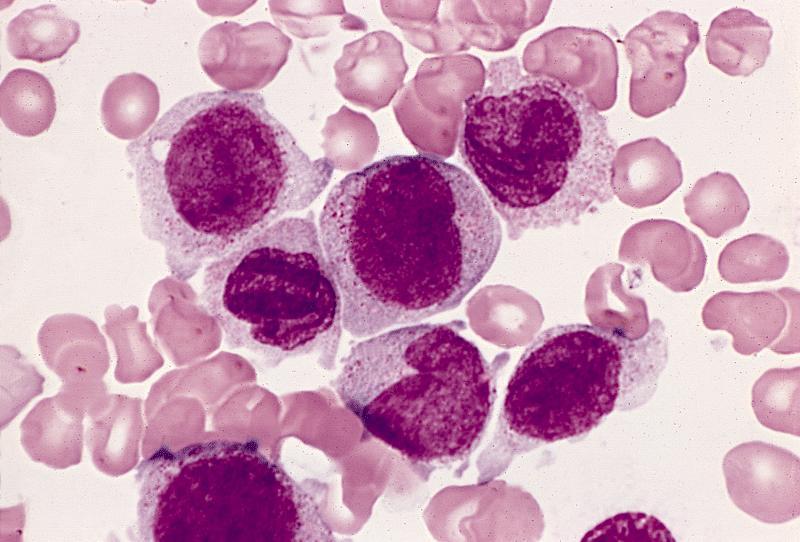
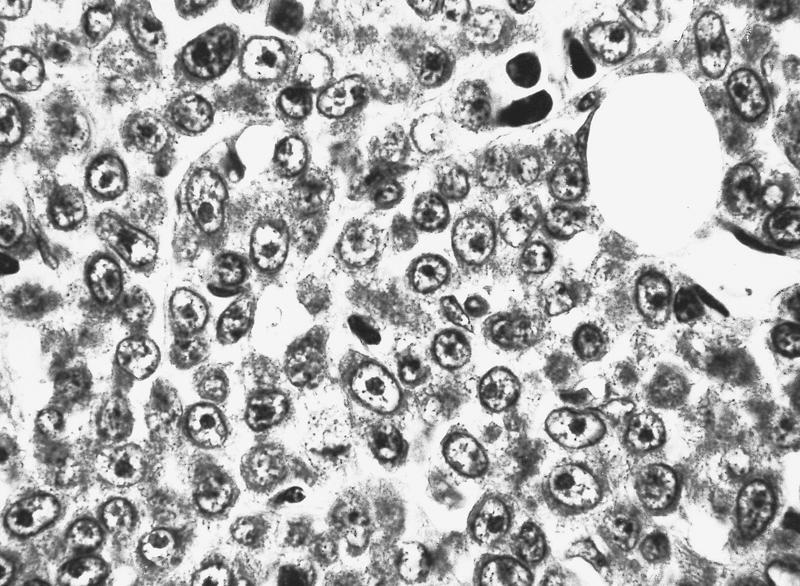
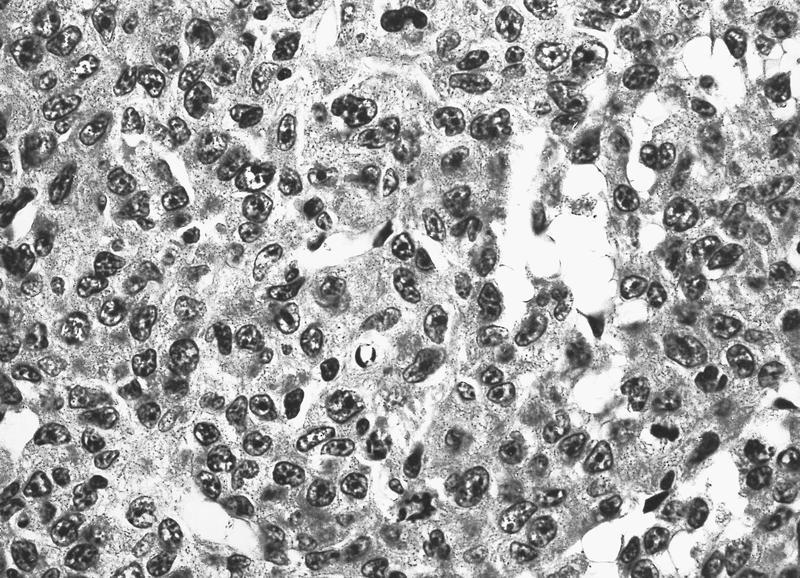
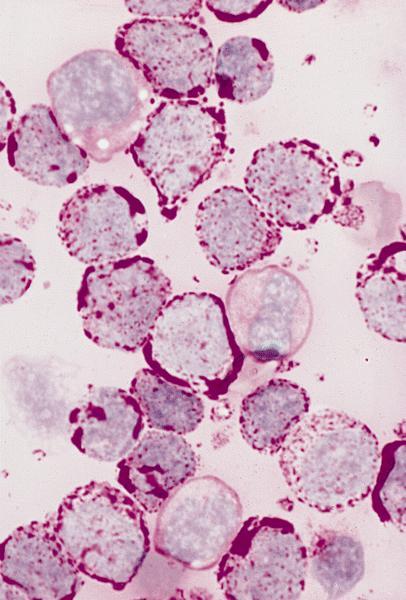
- Hypercellular marrow with large number of monoblasts
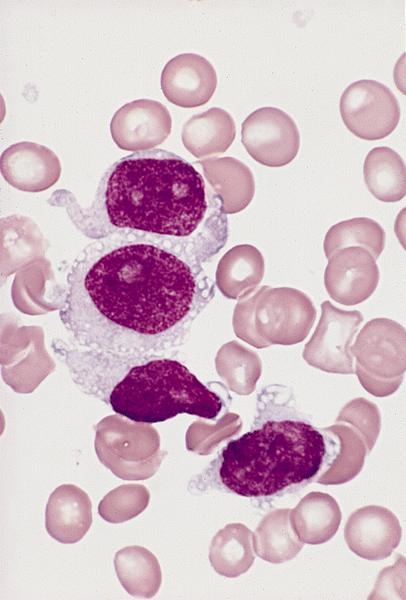
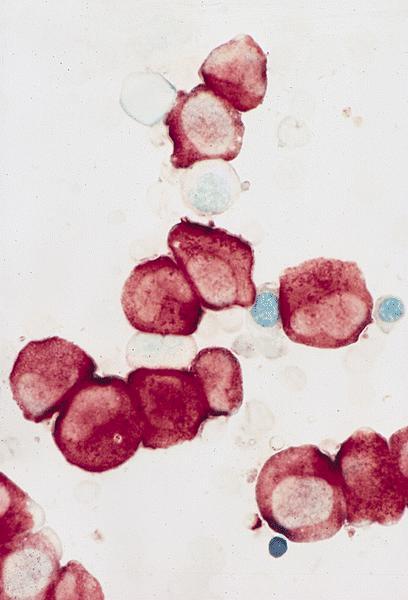
- Monoblasts are large with moderately abundant intensely basophilic cytoplasm, variably basophilic and delicate azurophilic granules but no / rare Auer rods
- May have pseudopods or vacuoles
- Have round nuclei and lacy chromatin with one or more prominent nucleoli but no folds
- Promonocytes have abundant less basophilic cytoplasm with obvious azurophilic granules and nuclei have delicate folds
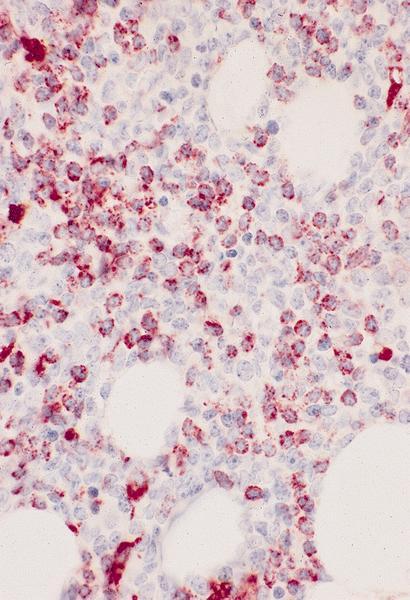
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Negative stains
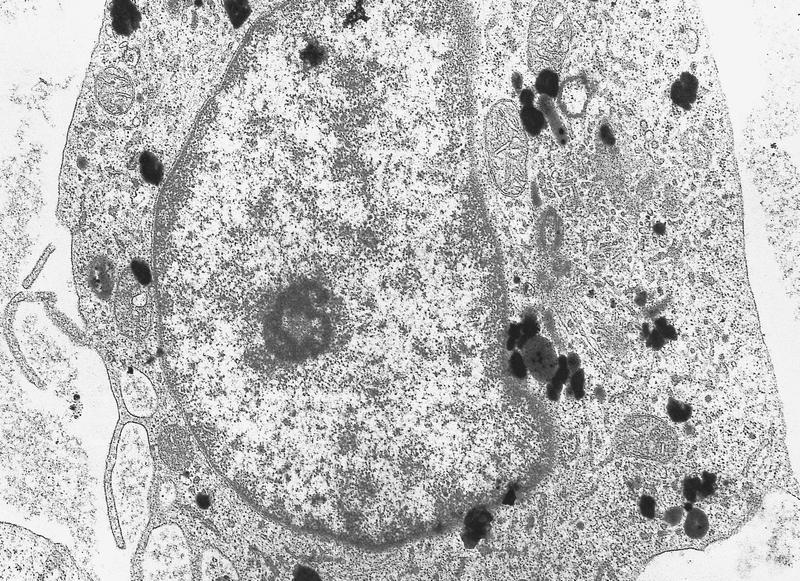
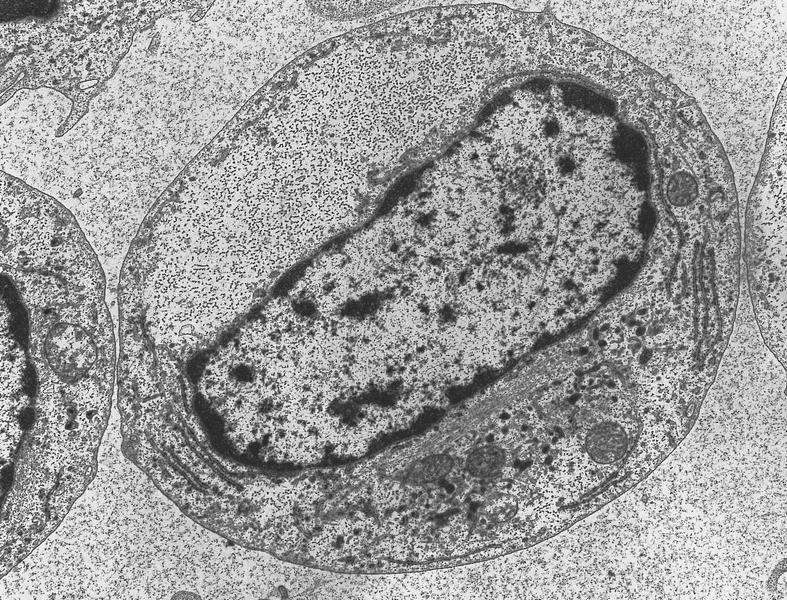
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- 75% have cytogenetics abnormalities, including 11q23 in 30% (these cases should be classified as a recurrent genetic abnormality)
- FLT3 mutations in 7%