Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Hossein-Zadeh Z, Feldstein J. Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/leukemiapanmyelosis.html. Accessed August 26th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), NOS (Blood 2016;127:2391)
- Accounts for 2% of all acute leukemias (Acta Med Port 2013;26:613)
- Does not fulfill criteria for AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities, myelodysplastic related changes or other AML entity
- Median survival is 2 - 9 months
Essential features
- Acute panmyeloid proliferation with increased blasts (≥ 20% of cells in the bone marrow or peripheral blood) and fibrosis of the bone marrow
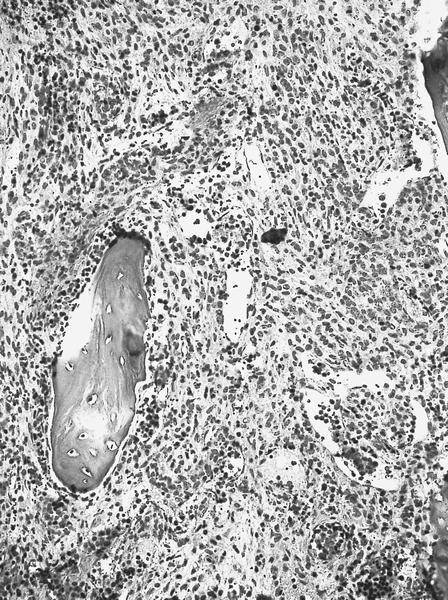
- Marrow is diffusely fibrotic, showing panmyelosis, with immature granulocytic, megakaryocytic and erythroid cells
- Weakness, fatigue, fever, bone pain, pancytopenia; usually no marked splenomegaly
Terminology
- Also called acute (malignant) myelofibrosis, acute (malignant) myelosclerosis, acute myelodysplasia with myelofibrosis
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C94.4 - acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis
Epidemiology
- Mostly adults; very rare in pediatric population
- Patients acutely sick at presentation with fever and bone pain
- Rare, rapid onset and aggressive course
- References: Acta Med Port 2013;26:613, Blood 2016;127:2391
Sites
- Bone marrow
Pathophysiology
- Involves granulocytic, megakaryocytic and erythroid cells, resulting in panmyelosis; marrow becomes fibrotic but with a high blast count of > 20%
Clinical features
- Acute onset of disease, pancytopenia and bone marrow fibrosis in the absence of splenomegaly
Diagnosis
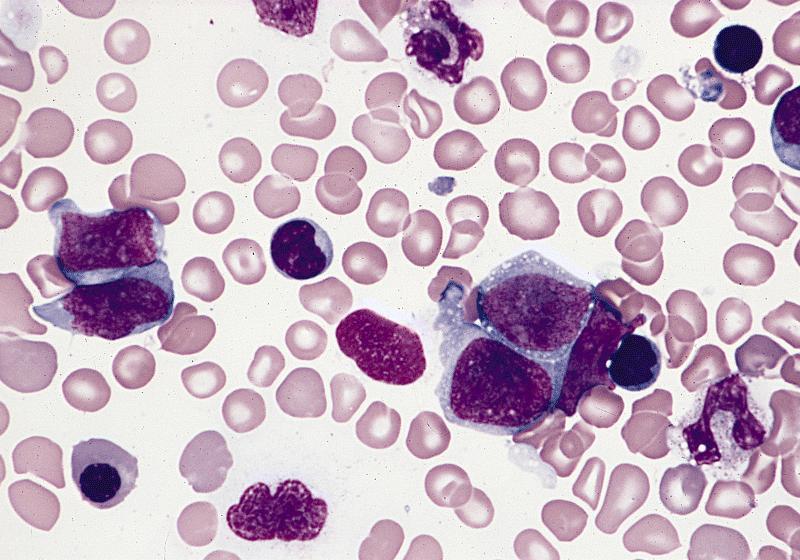
- Peripheral blood shows pancytopenia, which is usually marked
- Rare erythroblast can be seen, without presence of teardrop shaped cells
- Dysplastic changes in myeloid cells are frequent
- Abnormal platelets may be seen
- Bone marrow biopsy is often suboptimal or unsuccessful due to degree of fibrosis; on histology the bone marrow biopsy shows diffuse stromal fibrosis, with increased erythrocyte precursors, megakaryocyte precursors and granulocyte precursors (panmyelosis), which show dysplastic features
- Degree of presence of blasts in acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis (APMF) is uncertain but recent studies have reported 20 - 25%
- Degree of myelofibrosis is also variable but most patients have 3/3 reticulin fibrosis (Swerdlow: WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, Revised Edition, 2017)
Laboratory
- Complete blood count with differential (CBC w/ diff)
- Leukocytosis, lymphocytosis and atypical lymphocytes (if leukemic involvement)
- Comprehensive blood chemistry (CMP)
- Including liver and kidney analysis
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
- Elevated (indicator of tumor lysis)
- Serum beta 2 microglobulin
- Variable (indicator of tumor mass)
- Reference: Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2018;16:619
Prognostic factors
- Overall rapidly progressive clinical course, with a median survival of < 1 year
Case reports
- 16 year old boy admitted with severe pancytopenia and rapidly progressive bone marrow fibrosis (Acta Med Port 2013;26:613)
- 45 year old man with abrupt onset of rapidly progressing low backache, weakness, pancytopenia without organomegaly (Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis 2013;5:e2013042)
- 66 year old man with suspicion of acute myeloid leukemia was admitted and treated for acute myeloid leukemia, NOS and later found to have APMF with EVI1 amplification (Cancer Genet 2012;205:255)
Treatment
- Treated as acute myeloid leukemia: 3+7 induction regimen with idarubicin and cytarabine, followed by high dose intermittent ARA C (Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis 2013;5:e2013042)
- Hematopoietic cell transplantation (Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2019;25:2113)
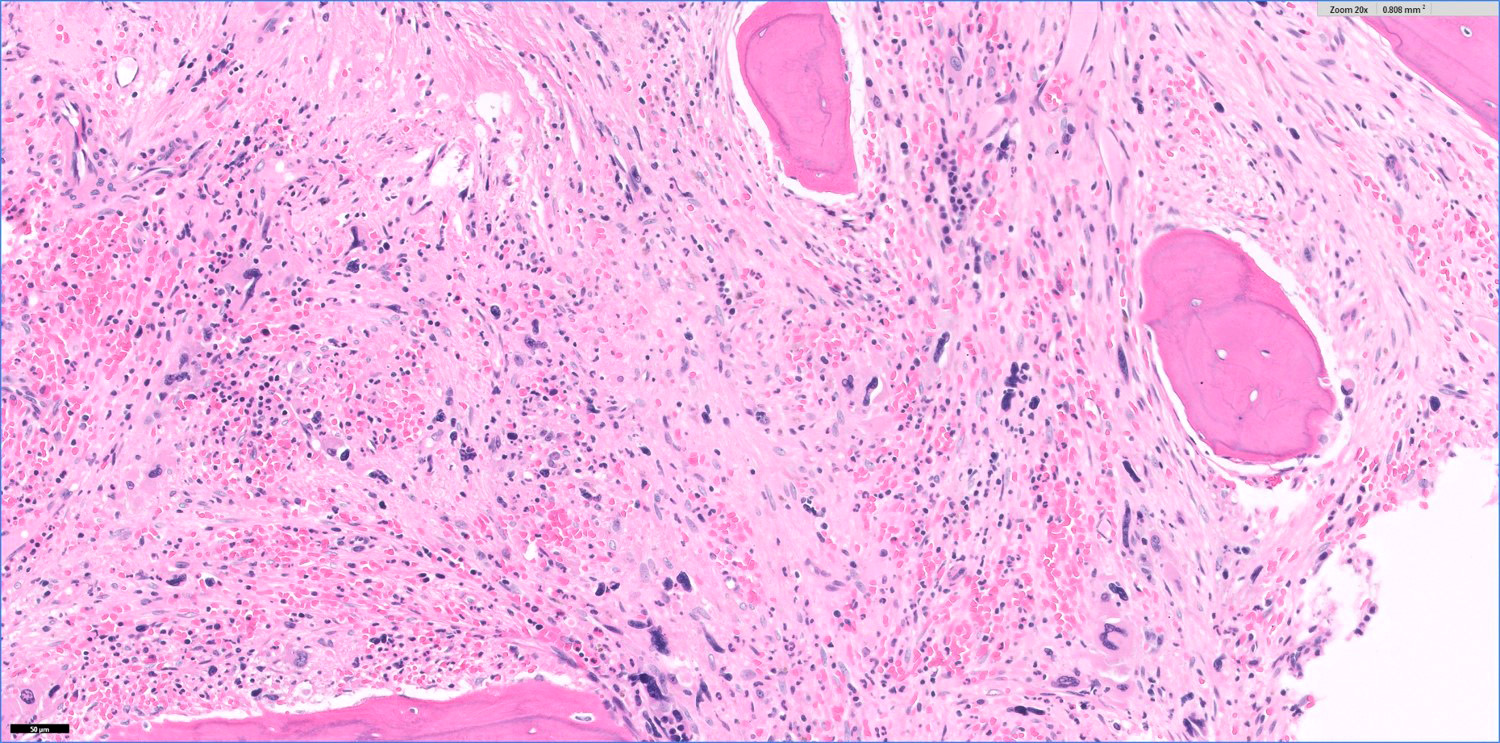
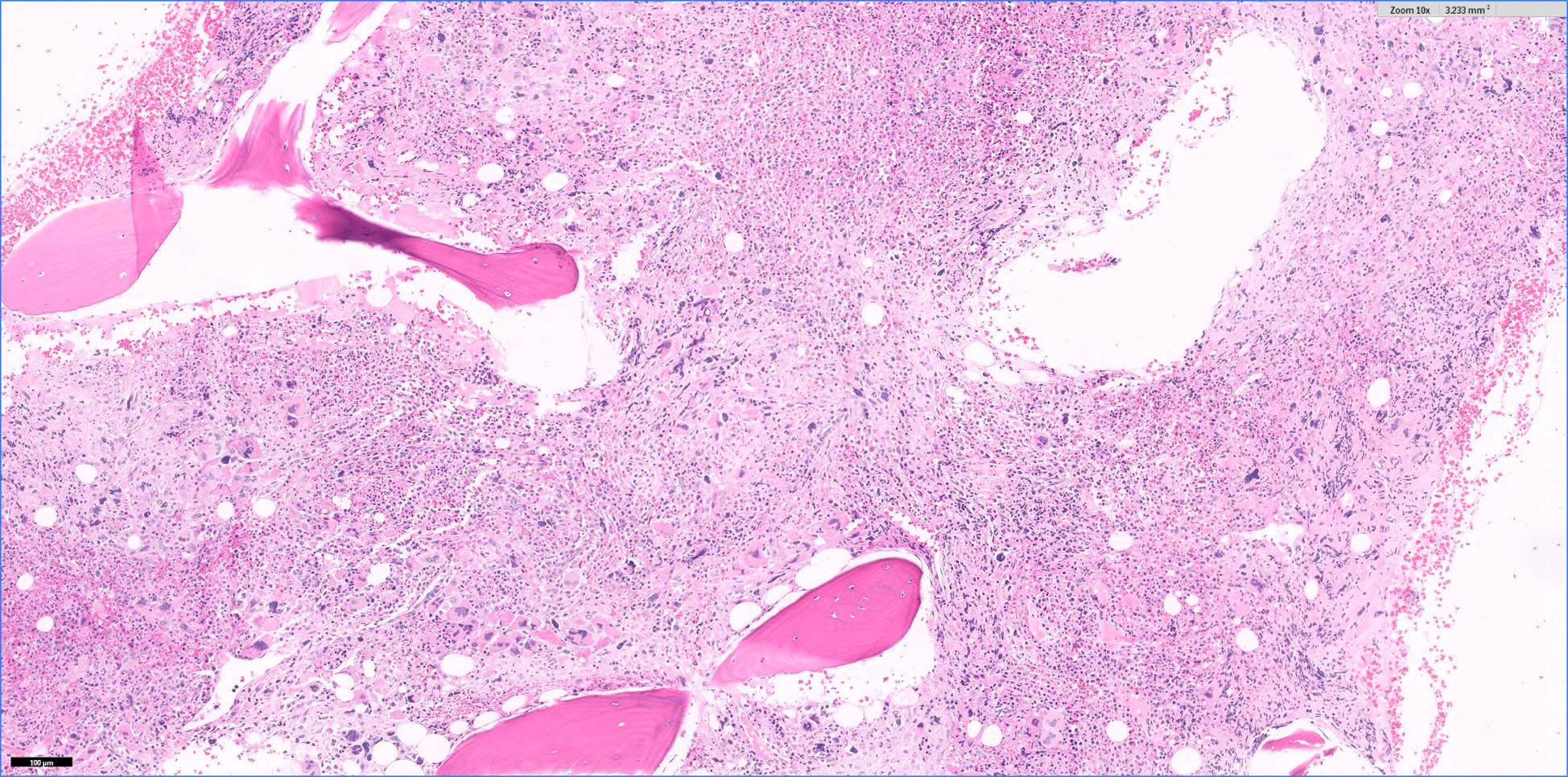
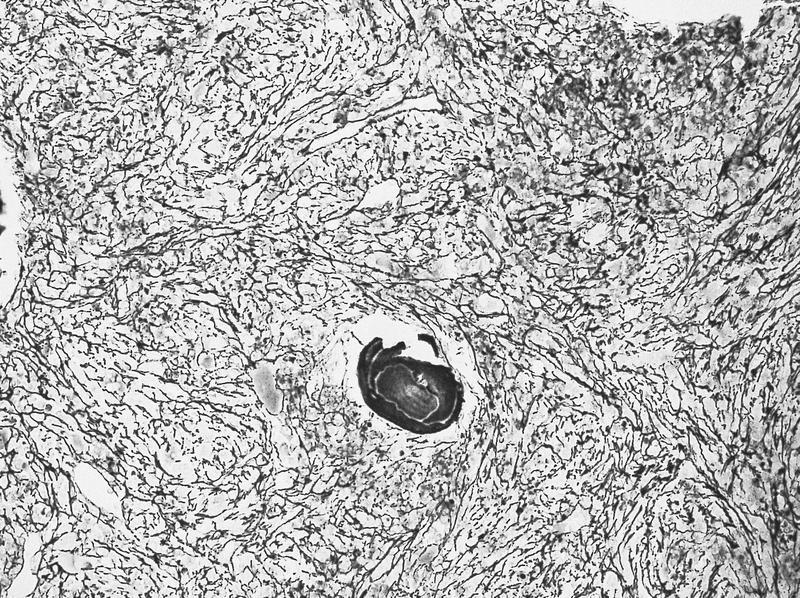
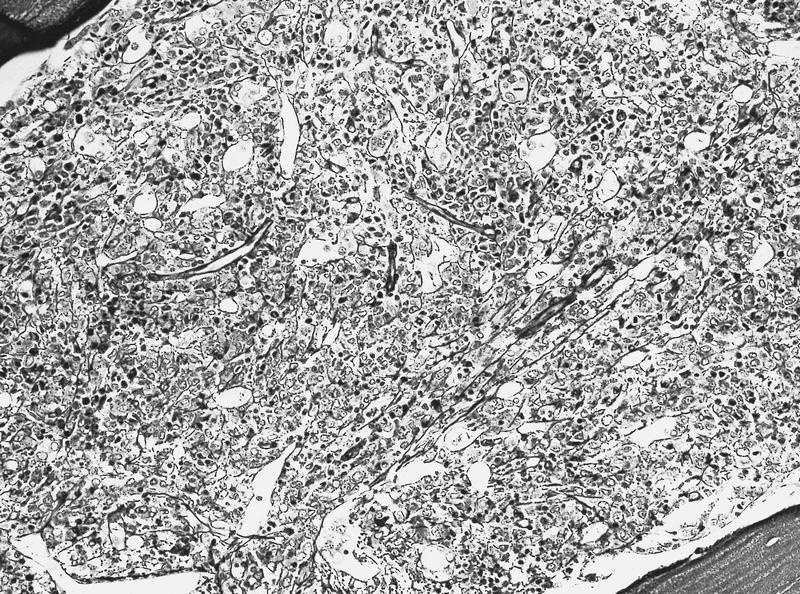
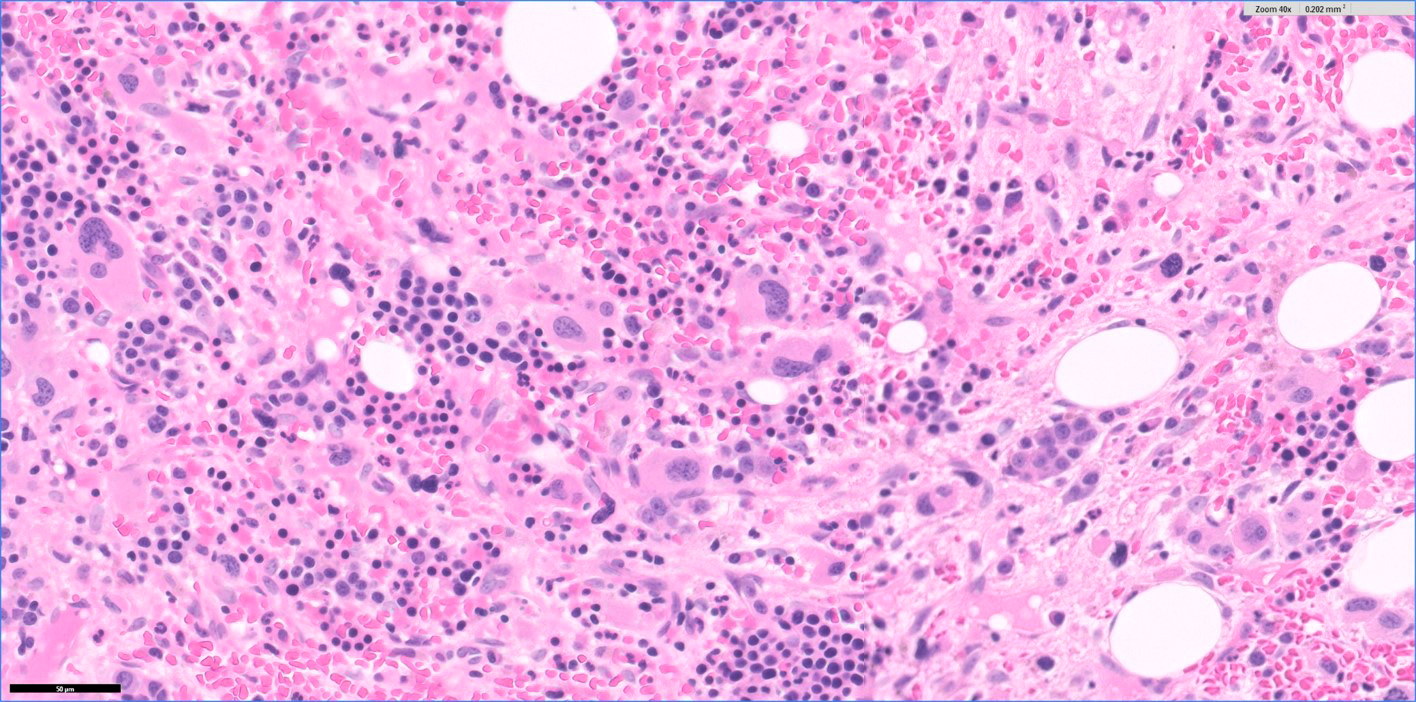
Microscopic (histologic) description
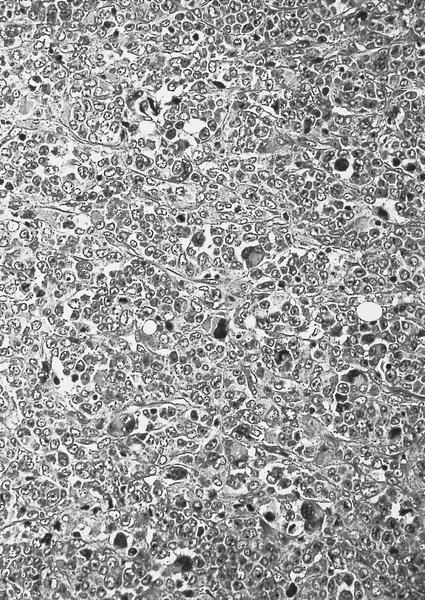
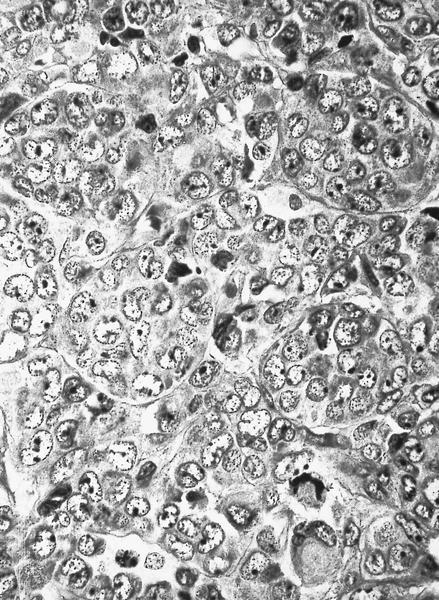
- Hypercellular marrow with erythroblasts, immature granulocytes, megakaryocytes (Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2018;16:619)
- Prominent megakaryocytic abnormalities with variation in size and dysplastic changes, immature granulocytes with dysplasia and immature erythrocytes (Leuk Lymphoma 2004;45:681)
- Megakaryocytes with nonlobulated or hypolobulated nuclei are often present (Leuk Lymphoma 2004;45:681)
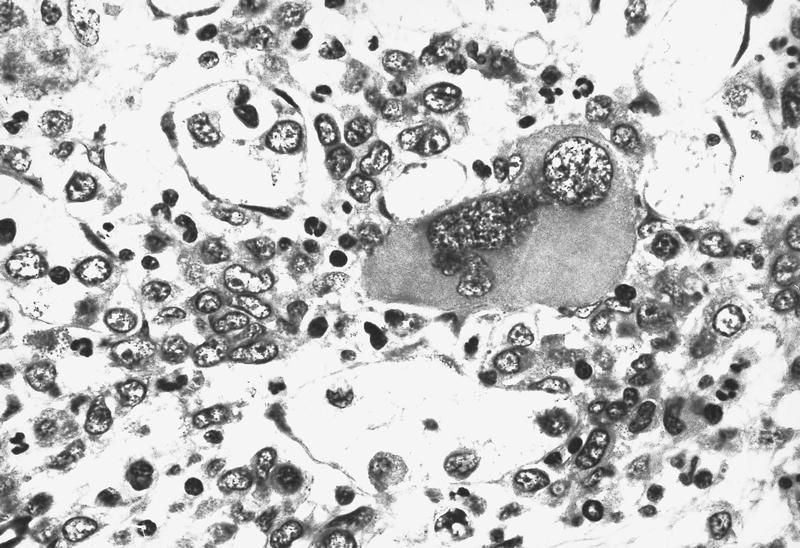
- Abnormal platelets may be seen
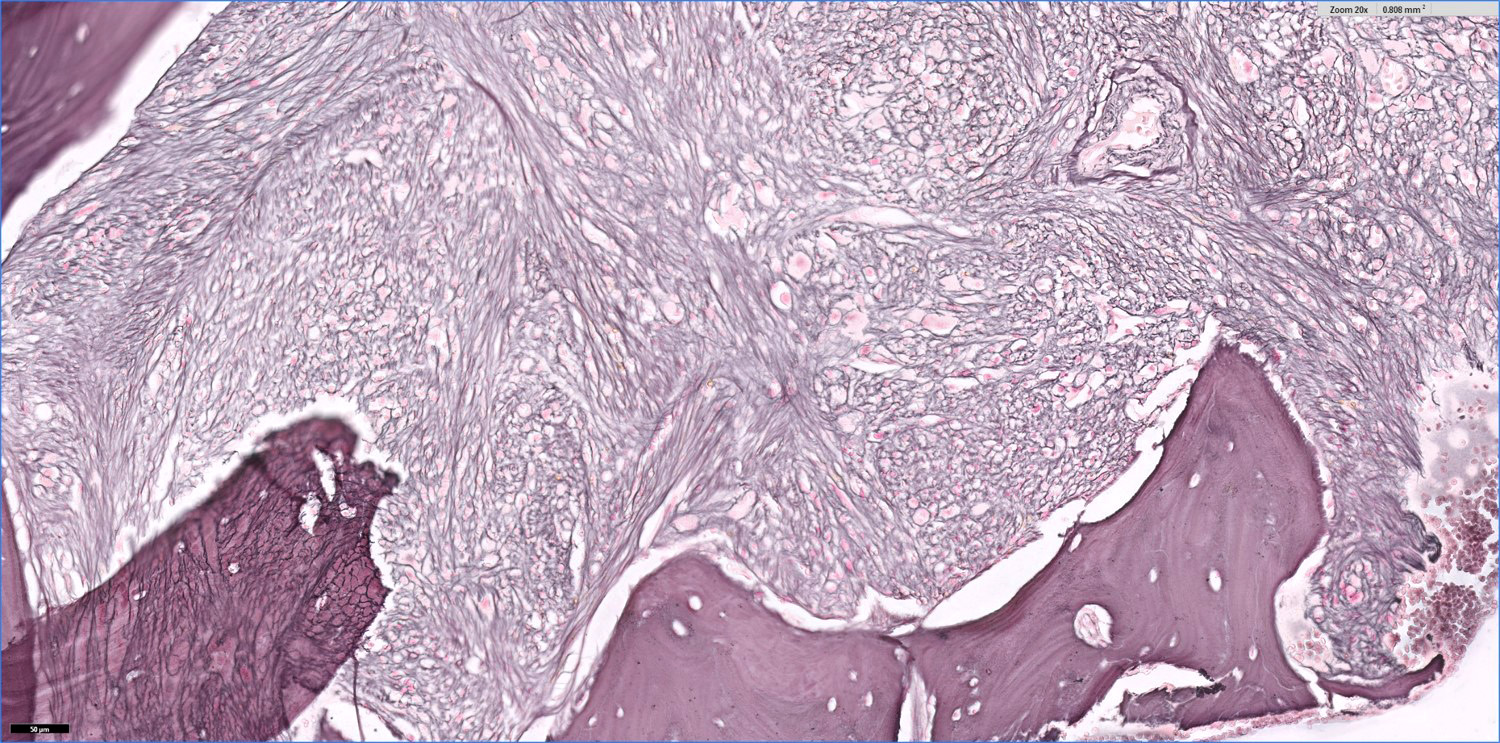
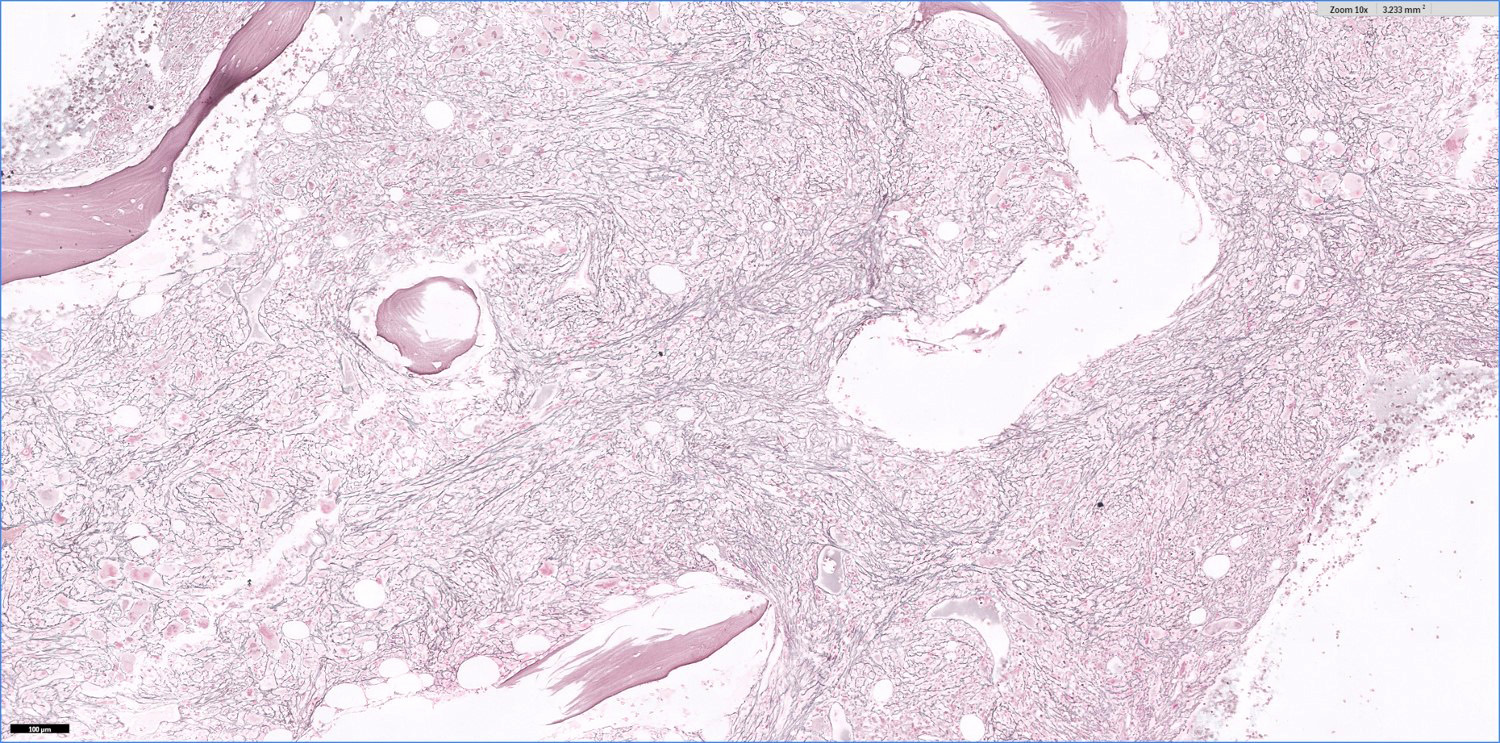
- Usually marked fibrosis (reticulin > collagen) (Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2018;16:619)
- Aspirate smear is often hypocellular due to marked fibrosis (Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2018;16:619)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Blasts: CD34, HLA-DR (Leuk Lymphoma 2004;45:1873)
- Erythroblasts: glycophorin A, hemoglobin A, CD71, E-cadherin
- Granulocytes: myeloperoxidase, CD13, CD33 and CD117
- Monocytes: lysozyme, CD68
- Megakaryocytes: CD31, CD41, CD61, PAS and factor VIII
Negative stains
- CD42b and MPO are usually negative in blasts (Mod Pathol 2005;18:603)
- Von Willebrand factor
Flow cytometry description
- Percentage of blasts varies between 3 and 30% (Mod Pathol 2005;18:603)
- Distinct population of myeloid blasts positive for CD34, CD33 and CD117
- Some cases have shown an aberrant coexpression of CD7 and CD13 antigens
- Myeloid blasts in acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis typically lack megakaryocytic associated antigens, such as CD41 and CD61 (Mod Pathol 2005;18:603)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Del(5q) and t(5q) (Ann Hematol 2004;83:513)
- Loss of chromosome 7 or del(7q) (Ann Hematol 2004;83:513)
- Nonspecific cytogenetic abnormalities reported in most cases with sufficient available material
- JAK2 mutations are typically absent (Ann Hematol 2004;83:513)
Sample pathology report
- A. Posterior iliac crest, bone marrow biopsy and aspirate:
- Acute panmyelosis (see comment)
- Reticulin fibrosis
- Comment: This is a hypercellular bone marrow for age featuring left shifted myeloid maturation with increased blasts. Numerous megakaryocytes with severe dysplastic features and focal clustering are seen. Flow cytometry shows left shifted myeloid maturation with increased blasts (~18%). The findings raise the differential diagnosis of acute panmyelosis with fibrosis versus MDS with excess blasts - 2. Clinical correlation regarding extramedullary hematopoiesis as well as molecular and cytogenetic results is recommended.
- Bone marrow biopsy:
- Iron: present (biopsy and smear)
- Reticulin: increased (2 - 3 of 3)
- Microscopic description:
- The biopsy is adequate and consists of trabecular bone and bone marrow elements. The cellularity ranges from 70 to 90% and consists of left shifted myeloids admixed with erythroid precursors. Numerous megakaryocytes are present and show marked dysplastic features, such as hyperchromatic and monolobated forms.
- CD34 immunostain is performed on formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) block A1, which highlights some of numerous dysplastic megakaryocytes as well as blasts, estimated around 15 - 20%.
- Bone marrow aspirate:
- Differential count:
- M:E = 4.6:1
- Blasts: 15%, promyelocytes: 6%, myelocytes / metamyelocytes: 15%, bands / segs: 34%, erythroids: 18%, lymphocytes: 14%, eosinophils: 1%, plasma cells: 1%, monocytes: 3%
- The aspirate smear is hypoparticulate and hypocellular. There is a moderate increase in blasts (13%). The blasts are small to intermediate in size, with scant cytoplasm and high N/C ratio. Mild dysplastic changes are noted in the myeloid precursors in the form of abnormal segmentation and few pseudo Pelger-Huët cells as well as occasional binucleated erythroids.
- Differential count:
Differential diagnosis
- Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia:
- No prominent changes in granulocytes or erythroid cells (Ann Hematol 2004;83:513)
- Chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis:
- Marked splenomegaly and prominent dysplasia
- Metastatic carcinoma with desmoplasia (Ann Hematol 2004;83:513)
- Myelodysplastic syndrome with myelofibrosis:
- Lacks high percentage of blasts
- Post polycythemia vera and post essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis
- Acute myeloid leukemia with fibrosis:
- Proliferative process is mostly of 1 cell type (such as myeloblasts) (Ann Hematol 2004;83:513)
- Primary myelofibrosis:
- Contains more numerous blasts and the megakaryocytes in primary myelofibrosis show distinctive cytologic atypia
- Primary myelofibrosis contains more numerous blasts and the megakaryocytes in primary myelofibrosis show distinctive cytologic atypia
- Secondary myelofibrosis after essential thrombocythemia (ET), polycythemia vera (PV):
- Usually with high hemoglobin and hematocrit (hemoglobin levels > 18.5 g/dL [hematocrit, 55.5%] in men or > 16.5 g/dL [hematocrit, 49.5%] in women)
- Associated with JAK2 mutations
- Autoimmune myelofibrosis:
- Associated with reactive deposition of fibrous connective tissue in the bone marrow and extramedullary hematopoiesis
- Hepatosplenomegaly often present (Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2018;16:619)
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 67 year old man previously in good state of health presented with fatigue, fever, bone pain and shortness of breath without splenomegaly. A complete blood count demonstrated anemia and thrombocytosis. A bone marrow biopsy shows a hypercellular marrow with panmyelosis, increased immature cells, dysplastic megakaryocytes and 2+ reticulin fibrosis. No other genetic abnormalities are found. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Acute myeloid leukemia
- Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Myelodysplastic syndrome
Practice answer #1
B. Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis. The symptoms and bone marrow biopsy support the diagnosis of acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis. The biopsy above shows hypercellular bone marrow with panmyelosis, increased immature cells, dysplastic megakaryocytes and 2+ reticulin fibrosis. Additionally, the patient's rapid progression of symptoms and lack of splenomegaly further support this diagnosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis
Comment Here
Reference: Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis
Practice question #2
What is the most common genetic mutation in acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis (APMF)?
- ABL
- CALR
- Del5;t5
- JAK2
Practice answer #2
C. Del5;t5. The most common but nonspecific chromosomal aberration seen in acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis (APMF) is chromosome 5 abnormalities, including del5;t5. Primary myelofibrosis cases harbor a phenotypic mutation in JAK2 (most commonly) and CALR mutations. ABL is seen in chronic myelogenous leukemia.
Comment Here
Reference: Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis
Comment Here
Reference: Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis