Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Chan AWH. Granulomatous hepatitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/livergrannoninfect.html. Accessed August 26th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Liver disease characterized by the presence of granulomas in the liver
Essential features
- Liver disease characterized by the presence of granulomas in the liver
- There are different etiologies, which may be associated with different subtypes of granulomas
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K75.3 - granulomatous hepatitis, not elsewhere classified
Epidemiology
- Hepatic granulomas are present in 2 - 15% of all liver biopsy and excision specimens (Pathol Res Pract 2011;207:359)
Etiology
- Found in a wide range of infectious and noninfectious conditions (Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;8:455)
- Immune mediated: primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), autoimmune hepatitis
- Fatty liver disease with lipogranuloma (see alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [NAFLD])
- Drug induced liver injury
- Foreign material: periportal talc or other material from intravenous drug abusers, beryllium, mineral oil, thorotrast
- Neoplastic disorder: lymphoma (Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin), hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
- Systemic disease (e.g., chronic granulomatous disease, Crohn's disease, sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, IgG4 disease and other connective tissue disorders)
- Idiopathic: 10 - 15% of all hepatic granulomas
- Diagnosis of exclusion; excellent prognosis (J Clin Pathol 2003;56:850)
Clinical features
- Clinical manifestations depend on the underlying etiology
Diagnosis
- Identification of the presence of granulomas in the liver histologically
- Clinical, radiological and microbiological correlations are required to reveal the underlying etiology
Case reports
- 12 year old boy with IL2RA defect presented with granulomatous hepatitis (Ther Adv Chronic Dis 2022;13:20406223221116798)
- 37 year old man with primary hepatic sarcoidosis mimicking primary biliary cholangitis (J Yeungnam Med Sci 2022;39:256)
- 52 year old woman developed granulomatous hepatitis after immune checkpoint blockade for metastatic melanoma (J Immunother 2021;44:71)
- 58 year old woman with Augmentin induced granulomatous hepatitis (J Clin Transl Hepatol 2021;7:280)
- 68 year old woman developed granulomatous hepatitis in Richter transformation of chronic lymphocytic lymphoma to Hodgkin lymphoma (Am J Case Rep 2021;22:e932904)
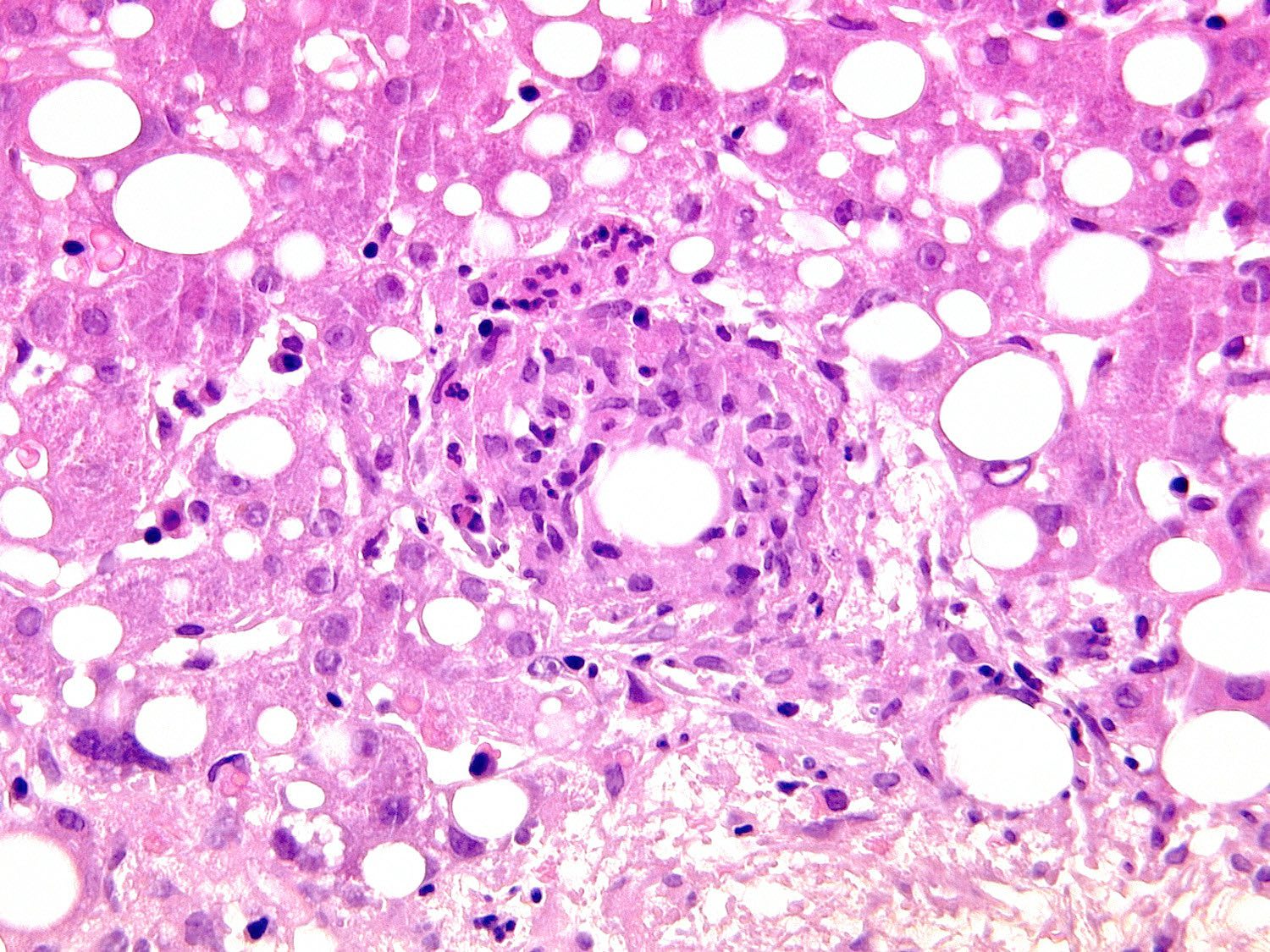
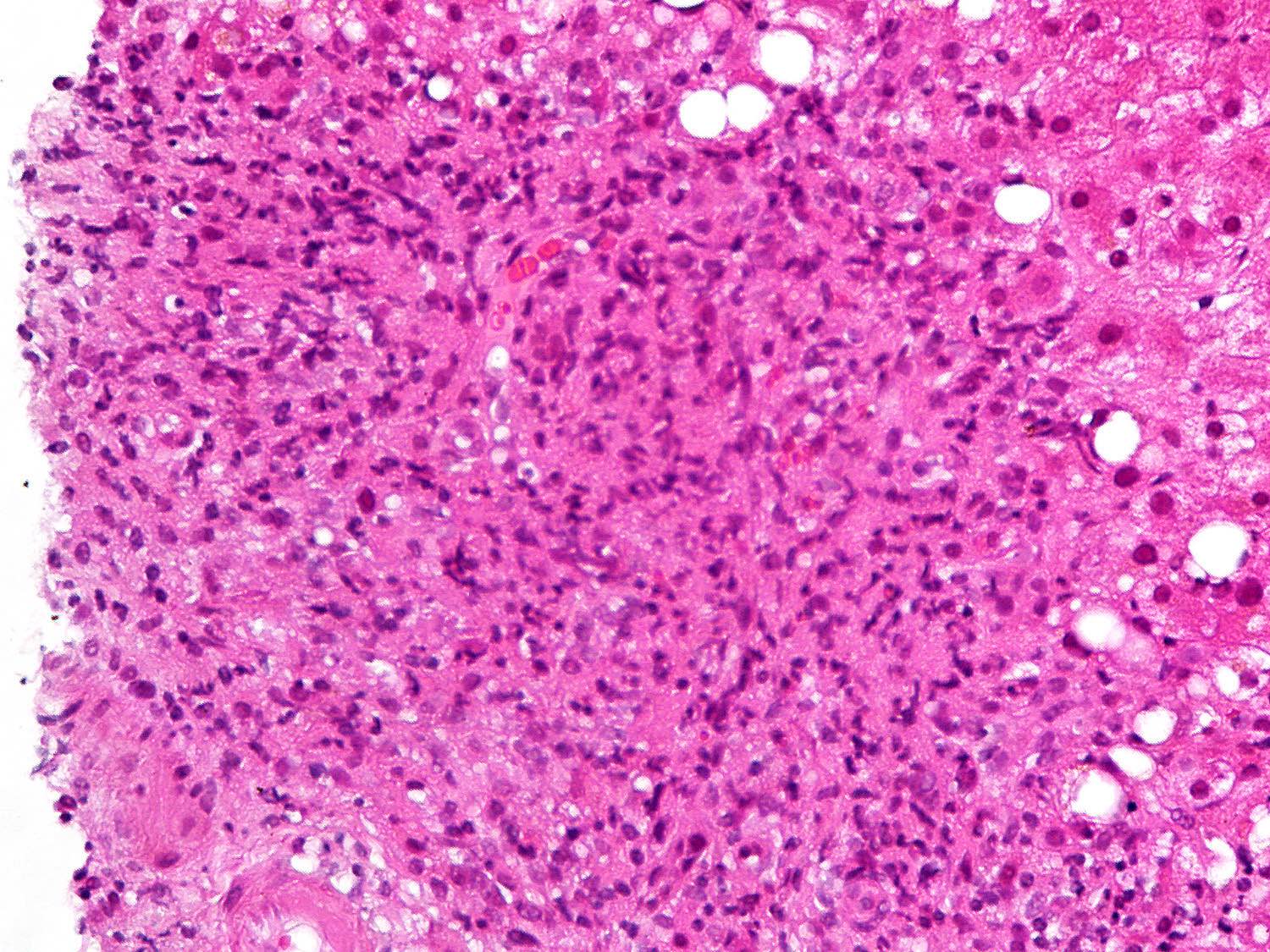
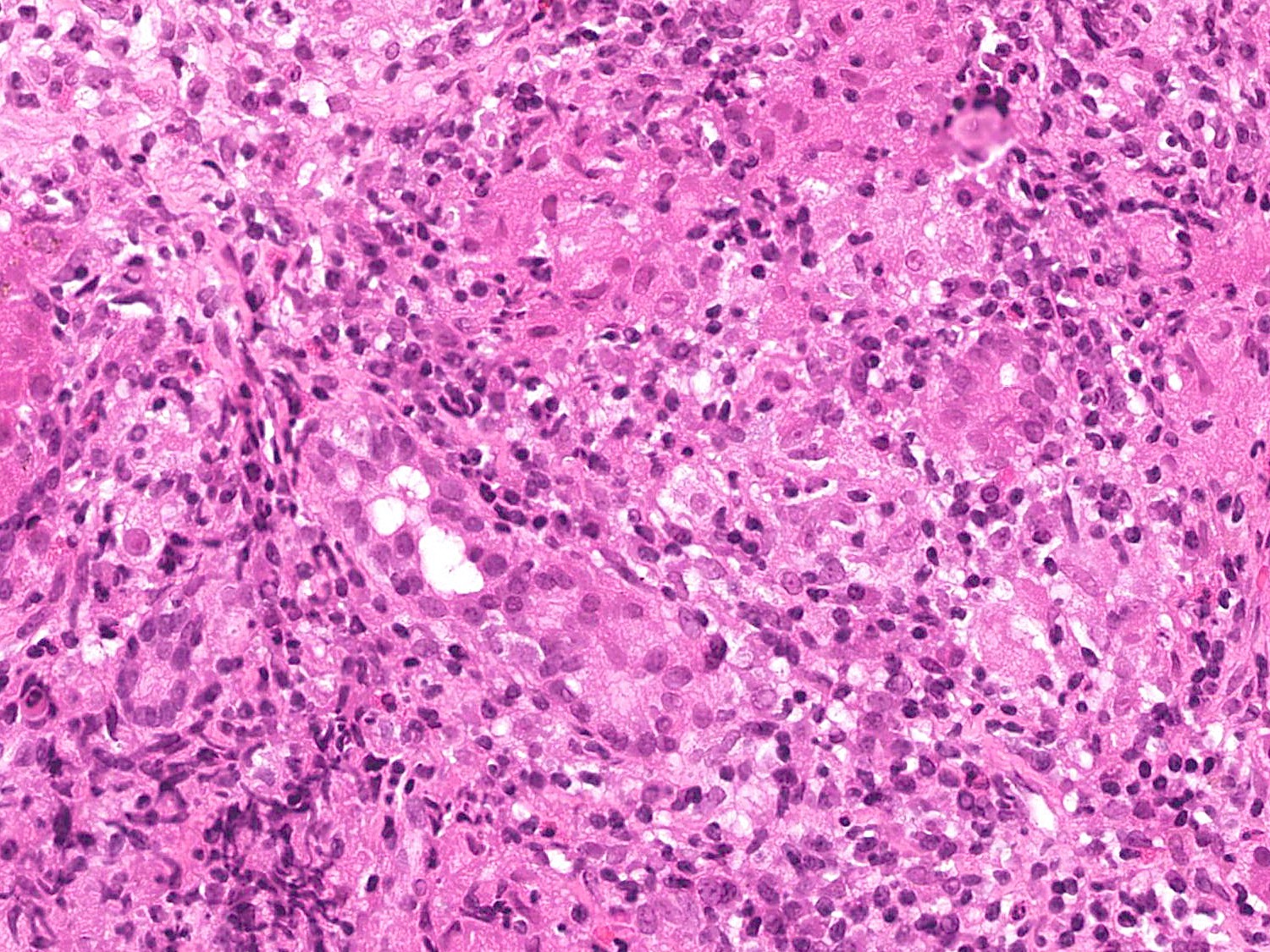
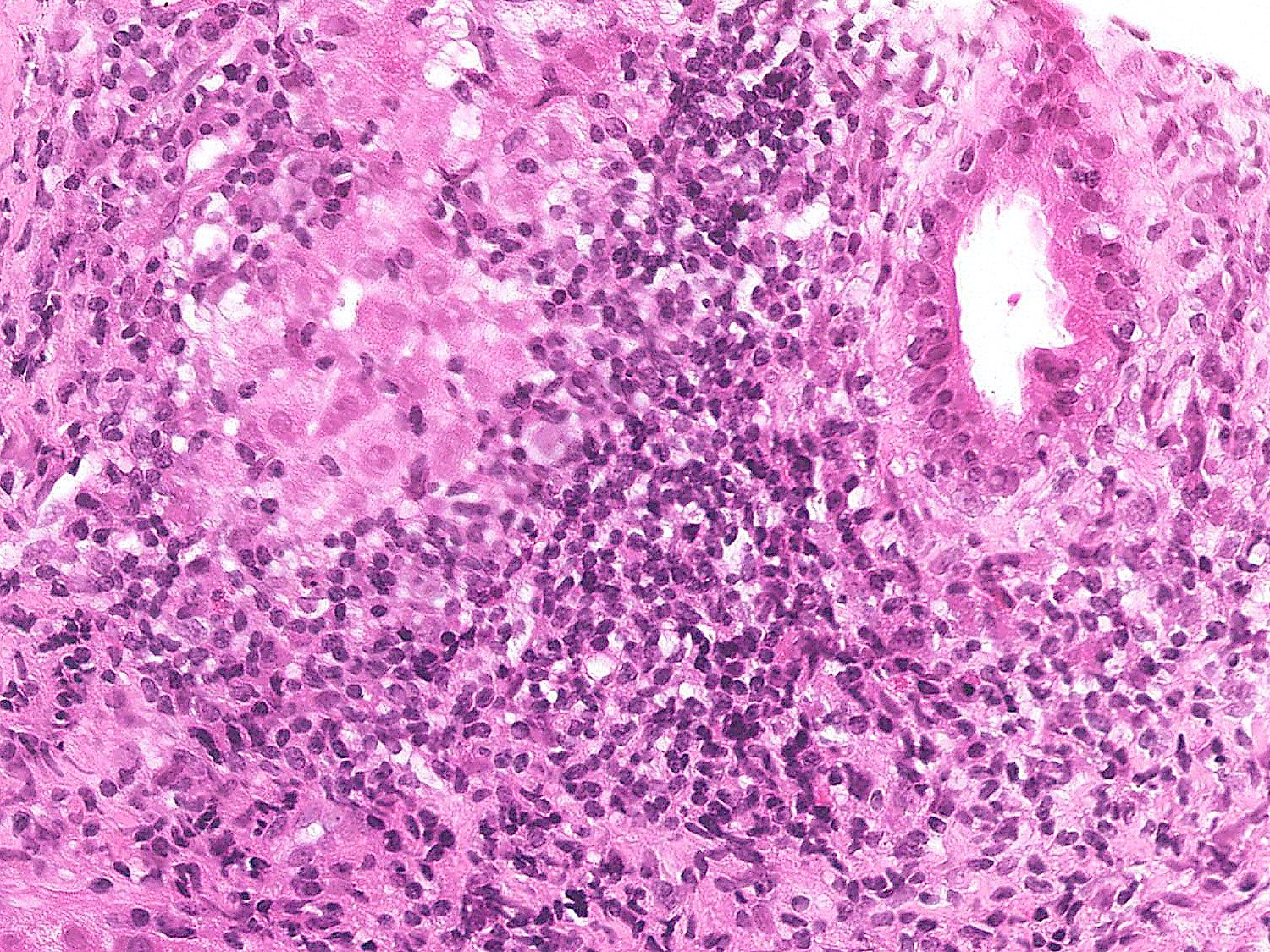
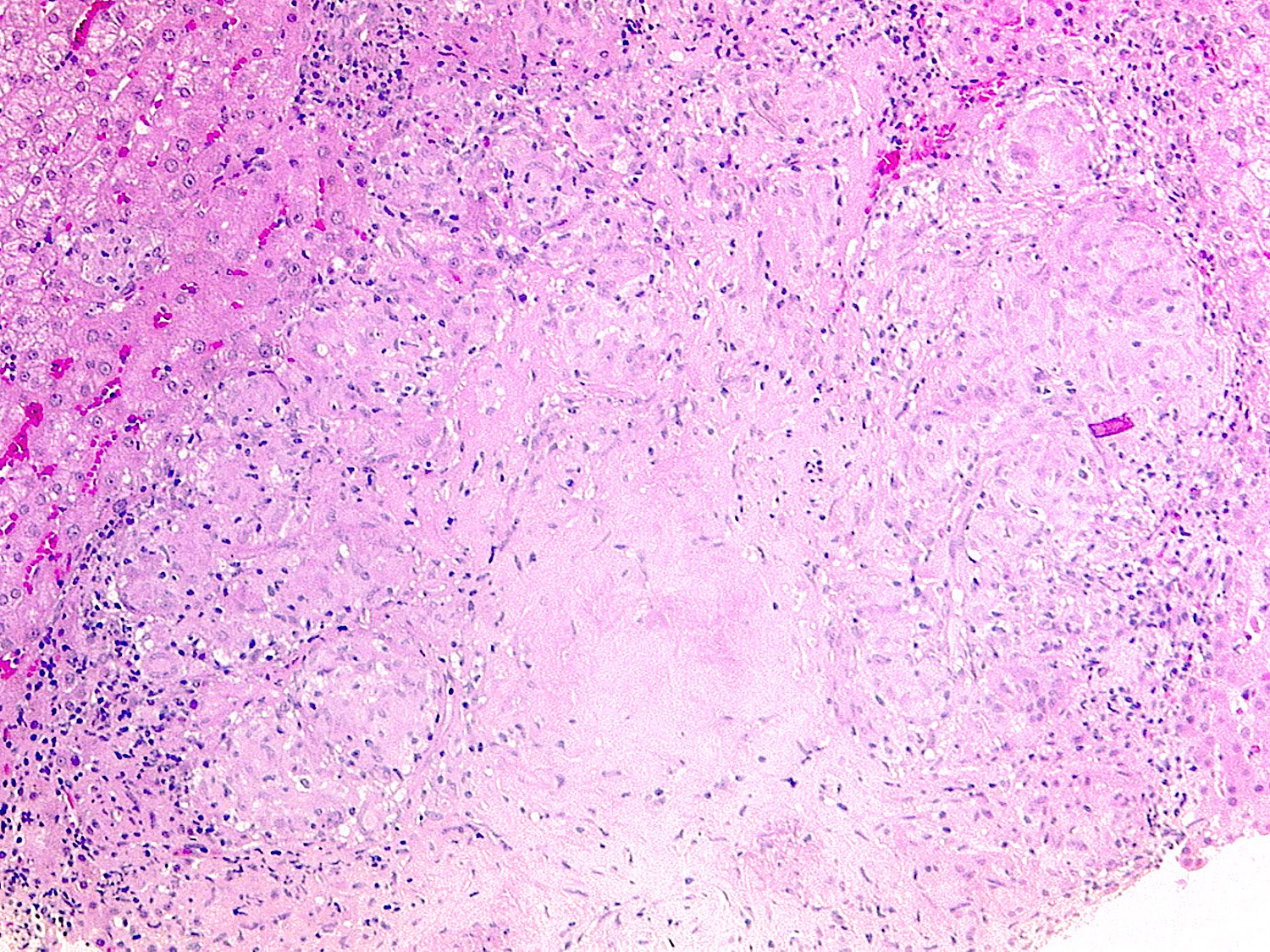
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Morphology (epithelioid, suppurative, fibrin ring or lipogranuloma) may suggest underlying etiology
- Epithelioid granuloma (aggregates of epithelioid histiocytes with or without multinucleated giant cells): infectious and noninfectious (e.g., primary biliary cholangitis, drug induced liver injury, foreign body reaction, sarcoidosis, Crohn's disease, chronic granulomatous disease, lymphoma)
- Caseating epithelioid granuloma (necrotic debris at the center surrounded by aggregates of epithelioid histiocytes with or without multinucleated giant cells): typically associated with infections, most notably tuberculosis
- Suppurative granuloma (granulomatous inflammation with stellate abscess formation or suppurative inflammation): bartonellosis, yersinosis, tularemia, listerosis, melioidosis, actinomycosis and fungal infection
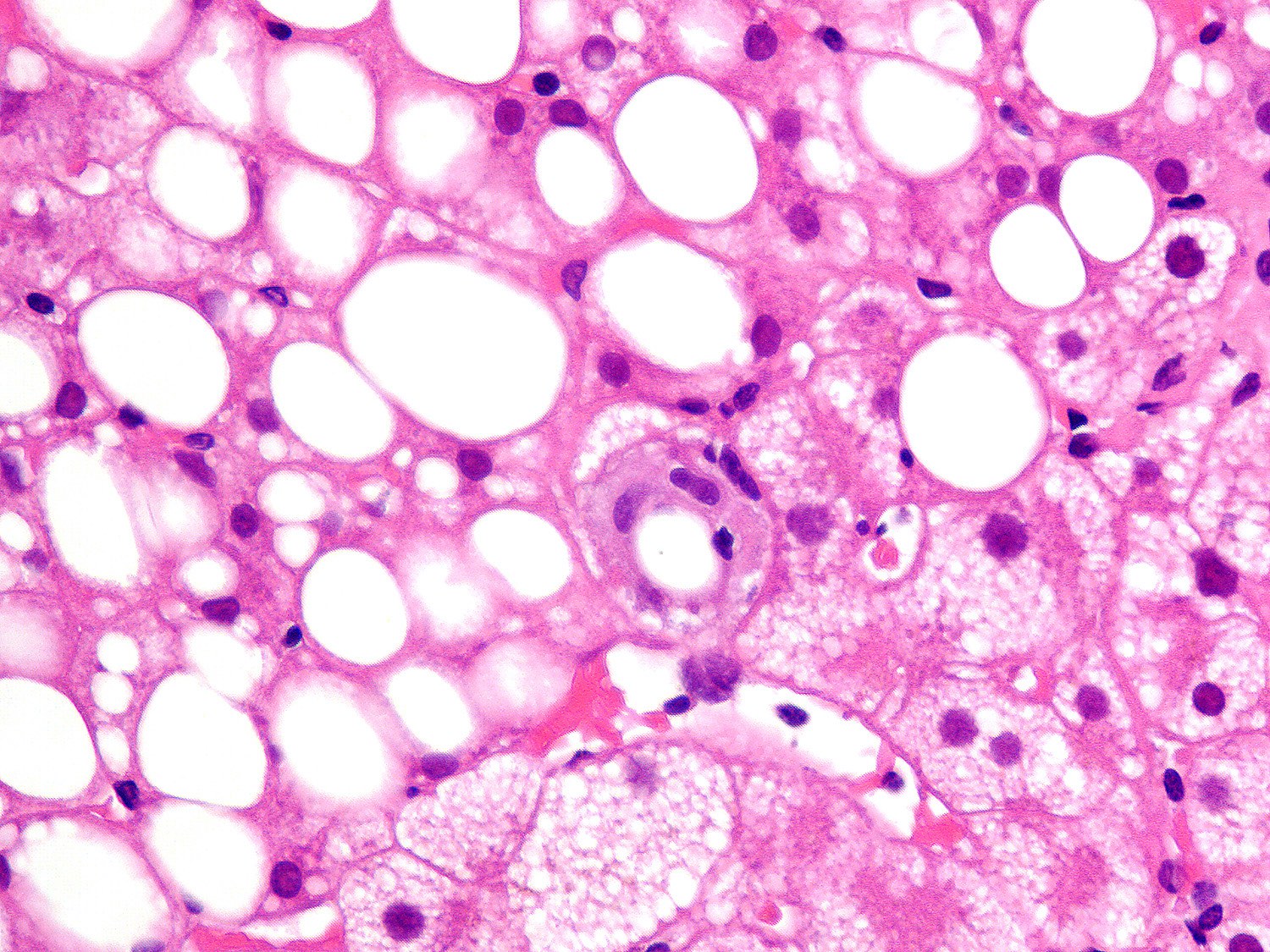
- Fibrin ring granuloma (also known as doughnut granuloma; central fat globule surrounded by a circumferential rim of fibrin and histiocytes): originally pathognomonic for Q fever (Coxiella burnetii); now considered as nonspecific and could be associated with mycobacterial infection, staphylococcal bacteremia, leishmaniasis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, acute hepatitis A, systemic lupus erythematosus, allopurinol toxicity and lymphoma
- Lipogranuloma (central fat globule surrounded by histiocytes without a fibrin ring): alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, mineral oil
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Liver, right lobe, biopsy:
- Granulomatous hepatitis without significant fibrosis (see comment)
- Comment: The biopsy shows lobular necroinflammatory activity and scattered noncaseating epithelioid granulomas. Infectious and noninfectious causes need to be considered. From the clinical history, the patient received a course of Augmentin for his upper respiratory tract infection before he was admitted for jaundice. Augmentin is one of several offensive agents associated with drug induced granulomatous hepatitis. Clinical follow up and monitoring of his liver function are recommended. Although histochemical stains for infectious agents (Gram, Grocott, PAS, PASD and Ziehl-Neelsen) do not reveal any specific organism, correlation with microbiological investigation is still recommended to exclude any infection.
Practice question #1
Which disease is classically associated with fibrin ring granulomas in the liver?
- Familial Mediterranean fever
- Q fever
- Scarlet fever
- Viral hemorrhagic fever
Practice answer #1
B. Q fever. Fibrin ring granuloma (also known as doughnut granuloma; central fat globule surrounded by a circumferential rim of fibrin and histiocytes) is originally pathognomonic for Q fever (Coxiella burnetii) but now considered as nonspecific features. Answers A, C and D are incorrect because familial Mediterranean fever, scarlet fever and viral hemorrhagic fever are not associated with granulomatous disease in the liver.
Comment Here
Reference: Granulomatous hepatitis
Comment Here
Reference: Granulomatous hepatitis
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2
C. Phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin (PTAH) is useful to highlight a thin rim of fibrin surrounding the central fat globule of the fibrin ring granuloma. Answers A, B and D are incorrect because mucicarcimine, PASD and ZN do not stain the fibrin in the fibrin ring granuloma although they are useful to identify microorganisms associated with granulomatous inflammation.
Comment Here
Reference: Granulomatous hepatitis
Comment Here
Reference: Granulomatous hepatitis