Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Oliveira RC. Transplantation - surgical / vascular complications. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/livertransplantcomplications.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Complications after liver transplantation
- Biliary and vascular complications are common
- Important cause of posttransplant morbidity
Essential features
- Biliary and vascular complications are common events after liver transplantation
- These events have implication on overall survival and quality of life of patients
- Retransplantation may be necessary
Terminology
- Post liver transplantation biliary complications include:
- Anastomotic strictures
- Nonanastomotic strictures
- Bile leaks
- Bile duct stones
- Bilomas
- Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
- Ischemic cholangiopathy
- Thrombosis
- Ischemia reperfusion injury
- Lipopeliosis
ICD coding
- ICD-10: T86.4 - complications of liver transplant
Epidemiology
- A major complication in patients submitted to liver transplantation (GE Port J Gastroenterol 2018;25:1)
- Biliary complications arise in 10 to 15% of patients (BMJ Open Gastroenterol 2022;9:e000778)
- Risk of biliary complications is higher in living donor transplantation, up to 30% (Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken) 2017;10:63)
- Biliary complications are associated with 13% of retransplantation and 19% of mortality (Clin Transplant 2004;18:647)
- Number of arterial anastomoses, low donor weight and previous history of abdominal surgeries are risk factors for hepatic artery thrombosis (Liver Transpl 2014;20:713)
Sites
- Liver
- Bile ducts
- Hepatic artery
- Portal vein
Pathophysiology
- Bile duct injury is the result of a multifactorial process
- Cold / warm ischemia, perfusion injury, bile salt toxicity and immune mediated lesions have been described as causative factors, especially for nonanastomotic strictures (Virchows Arch 2012;461:41)
- Lesions of the peribiliary vascular plexus and deep biliary glands are thought to be the main cause of nonanastomotic strictures (J Hepatol 2014;60:1172)
- Graft injury, especially with prolonged cold (> 12 hours) and warm (> 90 minutes) ischemia time, is prone to induce biliary injury (Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken) 2016;7:73)
- Donor graft quality: donors with older age with steatosis > 30% and hypotension are described as smaller for size allograft (Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken) 2016;7:73)
Etiology
- Ischemia
- Inflammation
- Infection
- Surgery complications
- Rejection
Clinical features
- If thrombosis
- Abdominal pain
- Fever (if infection)
- If biliary complications
- Jaundice
- Fecal acholia
- Brown urine
- Ischemia reperfusion injury
- Fatigue
- Jaundice
Diagnosis
- Usually by a combination of clinical, laboratory and radiologic findings
Laboratory
- If biliary complications
- Alkaline phosphatase, gamma glutamyl transferase, total bilirubin and conjugated bilirubin increase
- Nonspecific changes (Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2022;26:76)
- Liver enzyme increase, namely aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- International normalized ratio (INR) increase
- Acidosis
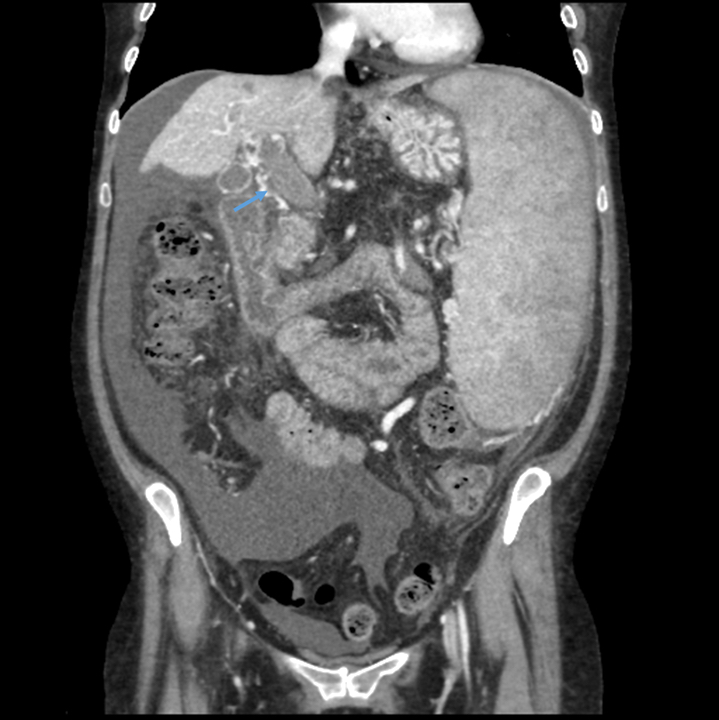
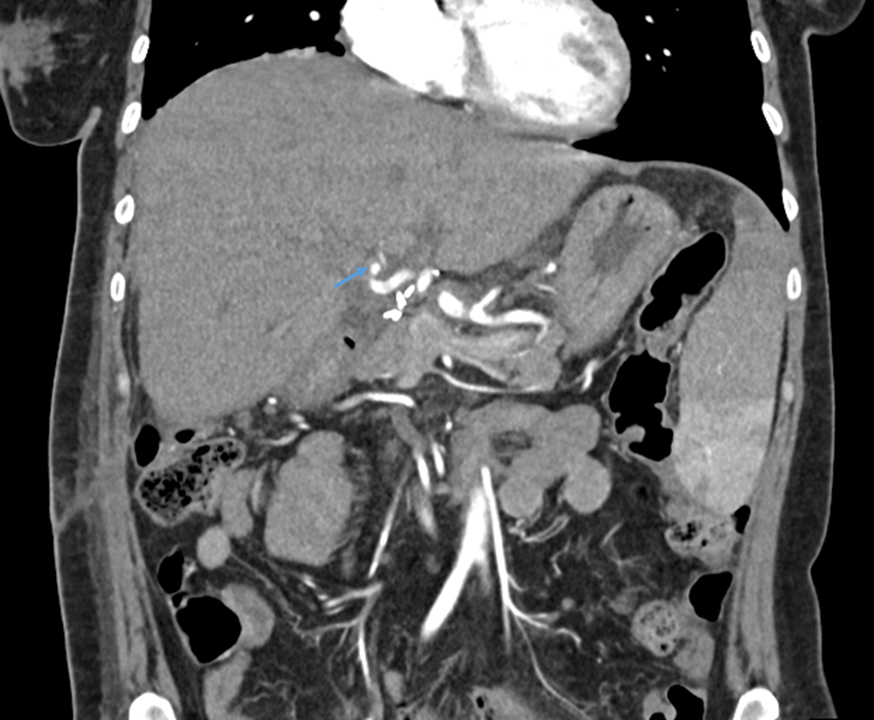
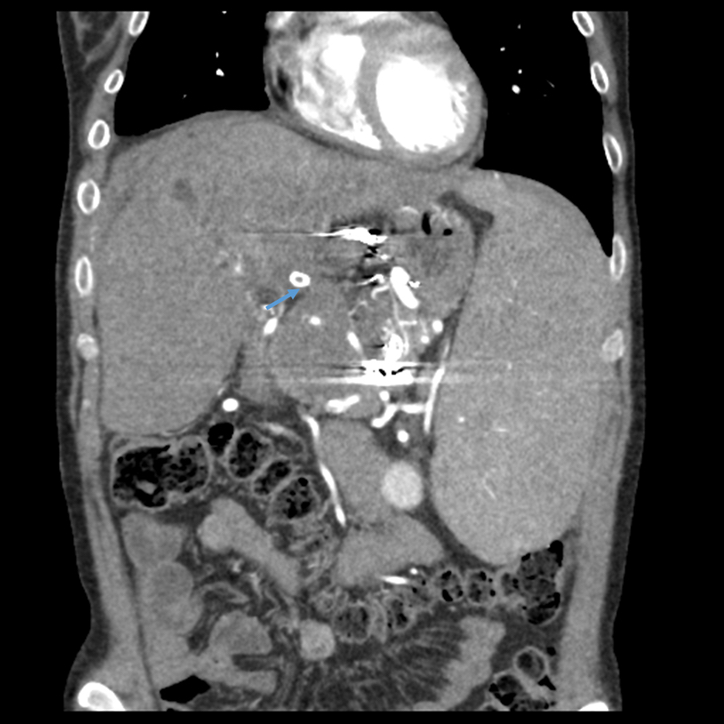
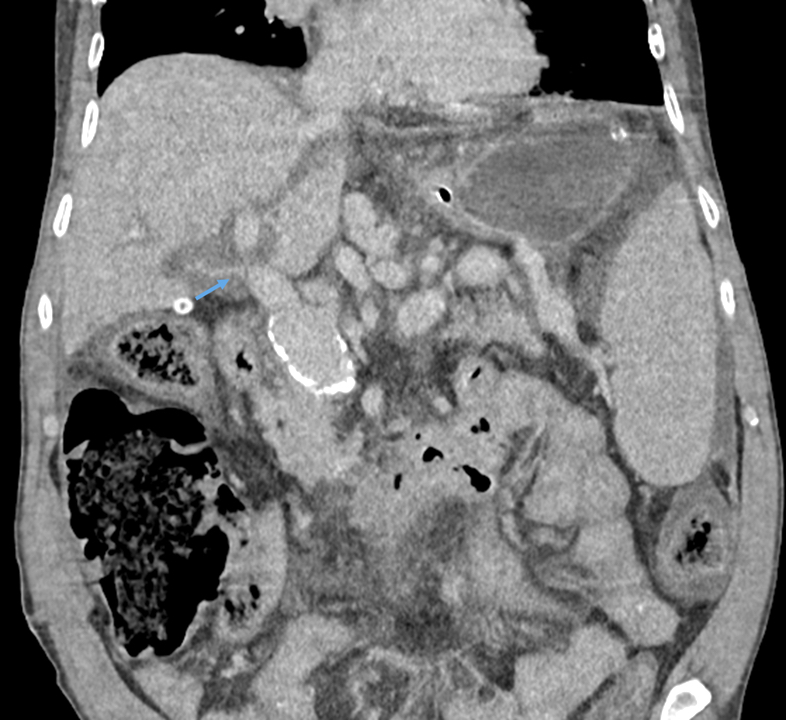
Radiology description
- If biliary complications
- Extravasation of contrast material in the region of the anastomosis on endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken) 2016;7:73)
- Cholangiography is able to detect strictures in the bile ducts (Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken) 2016;7:73)
- If thrombosis
- Contrast enhanced ultrasound shows an absence of Doppler flow in the hepatic artery proper and the intrahepatic branches; it has a sensitivity of nearly 100% (Clin Radiol 2020;75:845, Radiographics 2022;42:702)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Early elevation of laboratory values after liver transplantation is associated with biliary stenosis (Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2022;26:76)
- Severe liver injury is defined by AST > 3,000 and INR ≥ 2.5, or acidosis (arterial pH ≤ 7.3 or venous pH ≤ 7.25 or lactate ≥ 4 mmol/L) (Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken) 2016;7:73)
- Encephalopathy is a factor of worse prognosis
Case reports
- 30 year old woman with acute portal vein thrombosis after liver transplant (World J Hepatol 2019;11:234)
- 51 year old man with recurrent hepatic artery thrombosis following living donor liver transplant (SN Compr Clin Med 2021;3:2629)
- 60 year old man with an accidentally ligated and subsequently completely unflushed common bile duct (Int J Surg Case Rep 2017;41:200)
Treatment
- If biliary complications
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with balloon dilation or stenting
- ERCP with sphincterotomy
- Endoscopic ultrasound drainage
- If thrombosis
- Thrombolysis
- Ischemia reperfusion injury
- Shorter ischemia times (cold or warm)
- Use of machine reperfusion on liver graft
- In cases of disease progression / therapeutic failure
- Retransplant
- References: World J Hepatol 2016;8:36, World J Hepatol 2021;13:66, World J Hepatol 2015;7:2890, Visc Med 2022;38:243, Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 2019;8:490
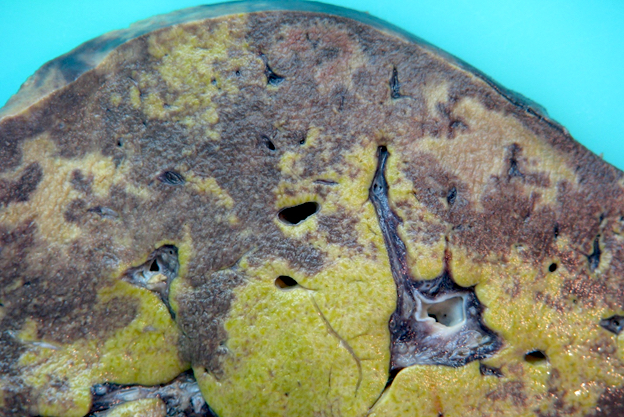
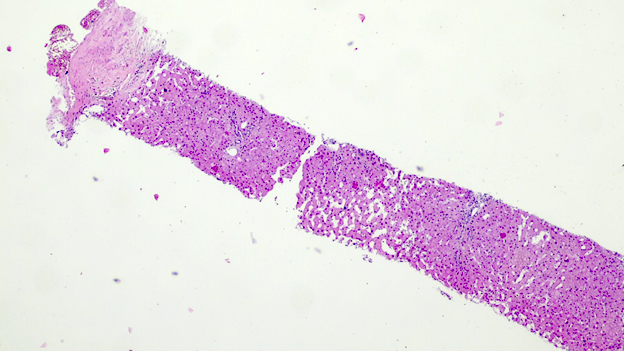
Gross description
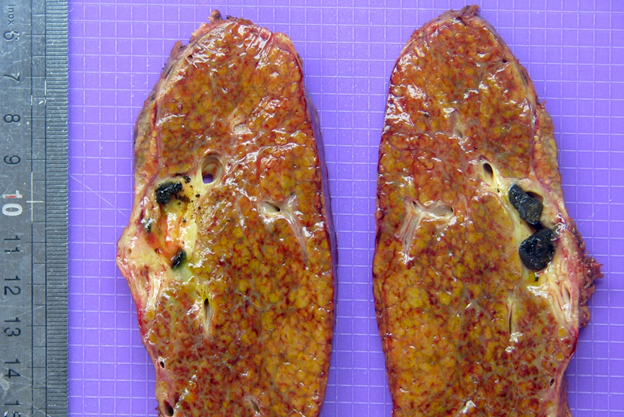
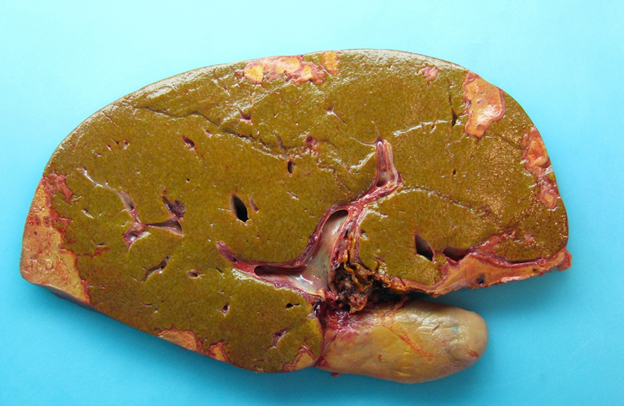
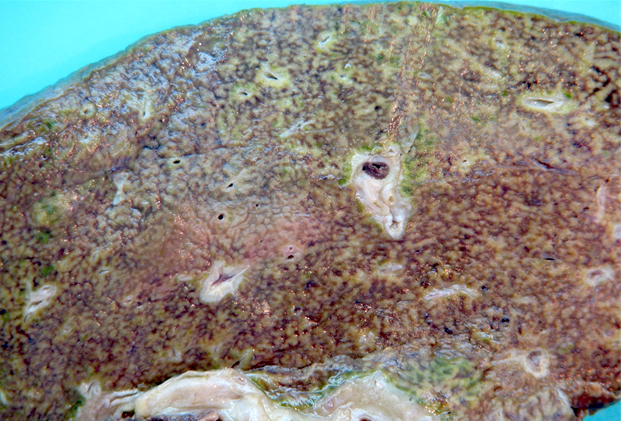
- Biliary complications
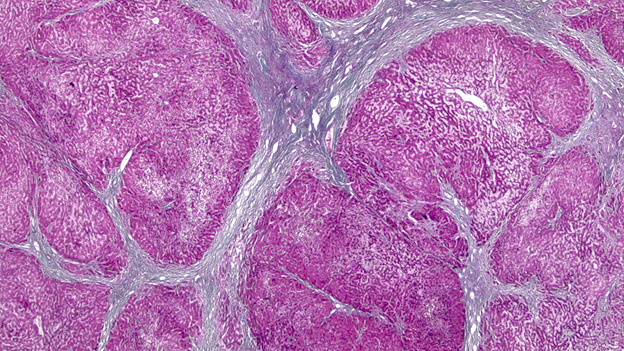
- Liver explant with biliary obstruction / fibrosis of the bile duct; on cut section, the liver shows mild to moderate fibrosis with bile casts and green tone
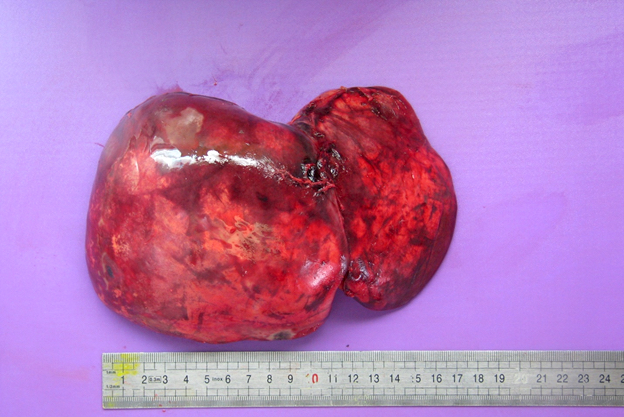
- Vascular complications
- Liver explant with hepatic artery / portal vein thrombosis, with complete / partial occlusion of vessel(s); on cut section, the liver is hemorrhagic and congestive
Gross images
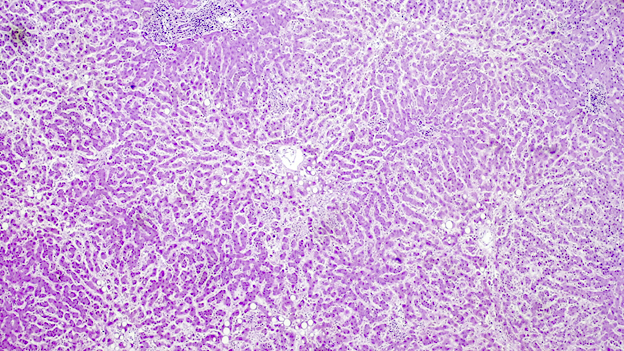
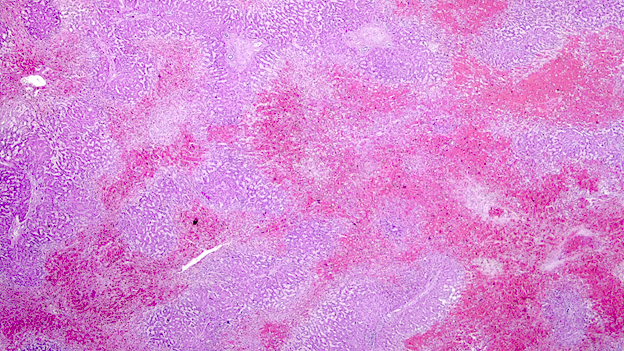
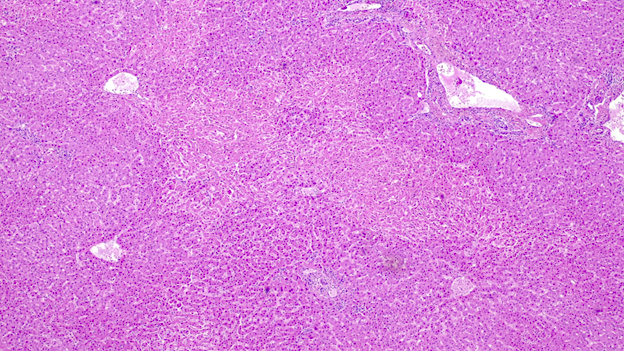
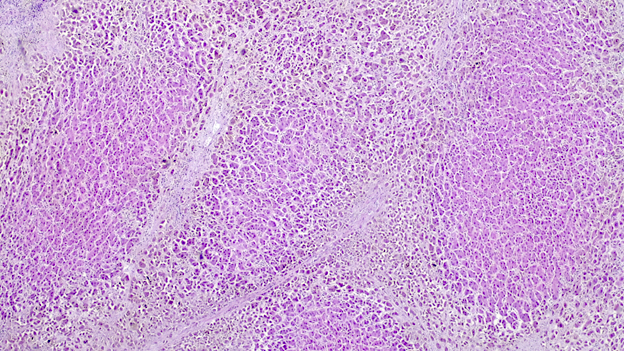
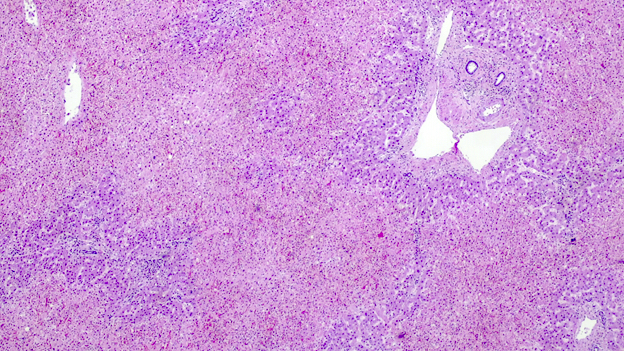
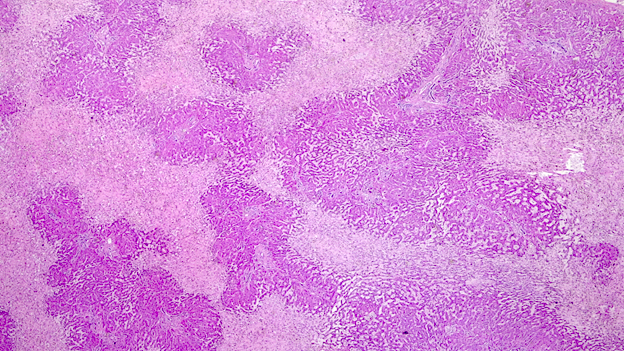
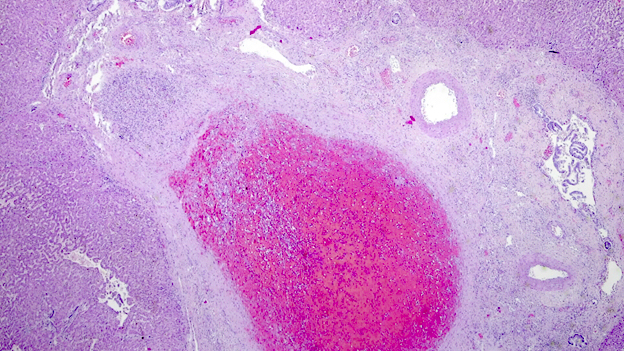
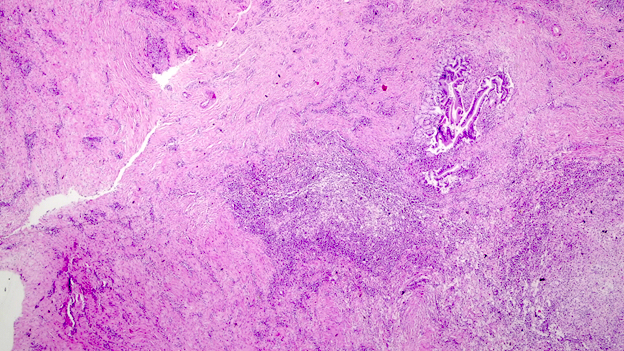
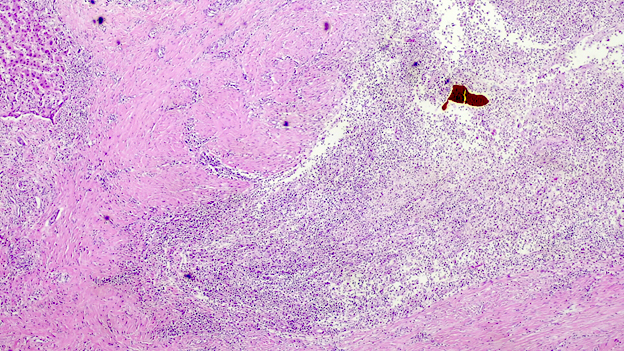
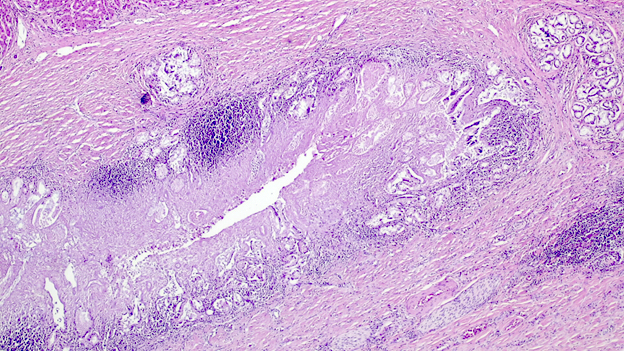
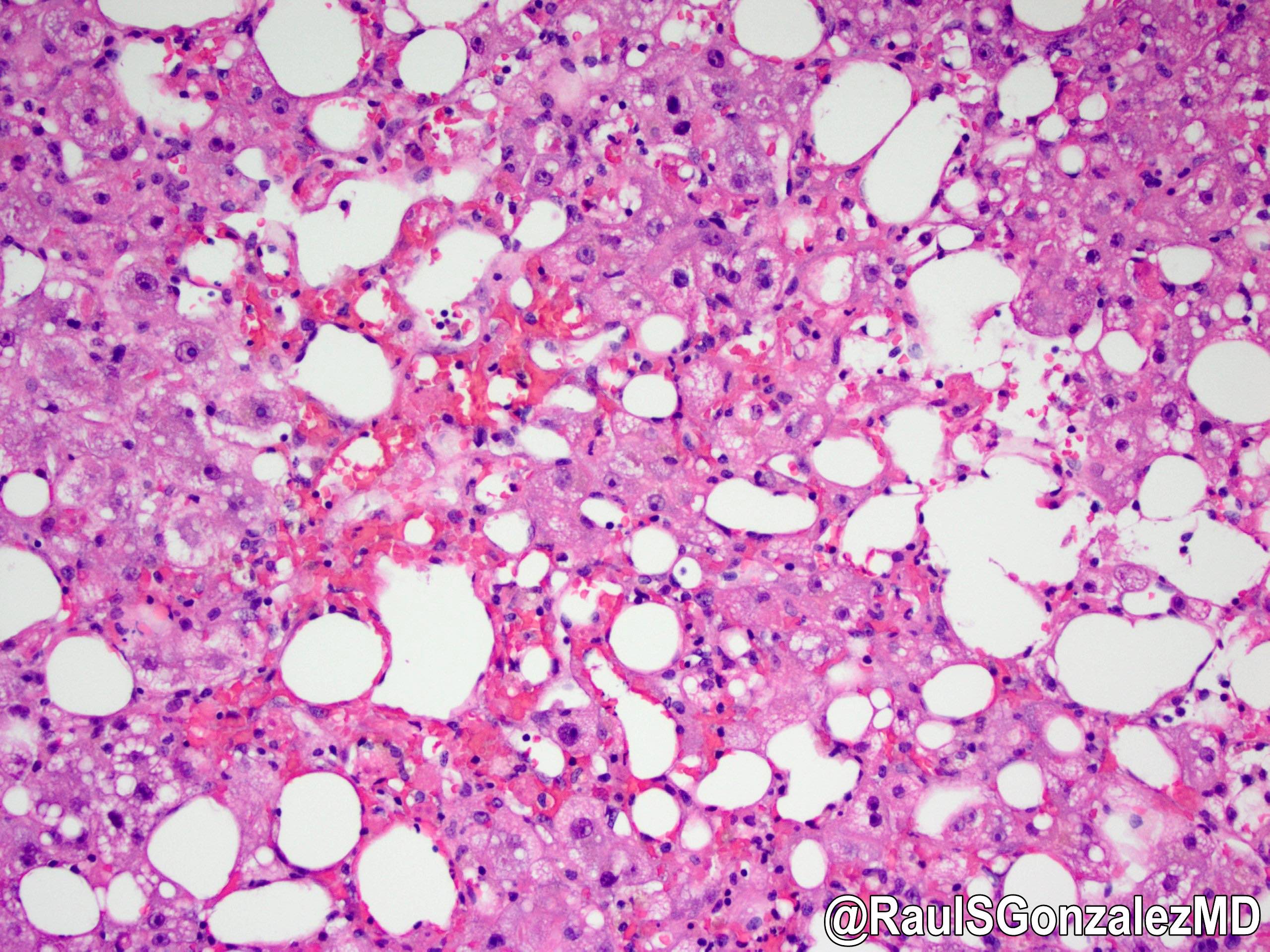
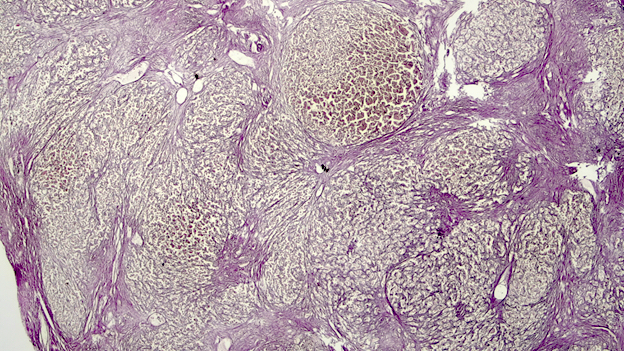
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Ischemia reperfusion injury appears as perivenular ballooning and cholestasis, neutrophilic infiltrate or hepatocyte necrosis in centrolobular regions (in the more severe lesions)
- Lipopeliosis corresponds to the release of fat from ischemia reperfusion hepatocytes in to the extracellular space, inducing sinusoidal compression, blood flow obstruction and ischemic necrosis
- Biliary pattern of fibrosis is common in ischemic cholangiopathy
- Ductular reaction and hepatocyte biliary metaplasia in cases of bile duct obstruction, associated with portal tract edema
- Sinusoidal dilation and congestion are common in venous drainage complications
- Ischemic necrosis is common in thrombosis
- Reference: Diagn Histopathol 2018;24:508
Microscopic (histologic) images
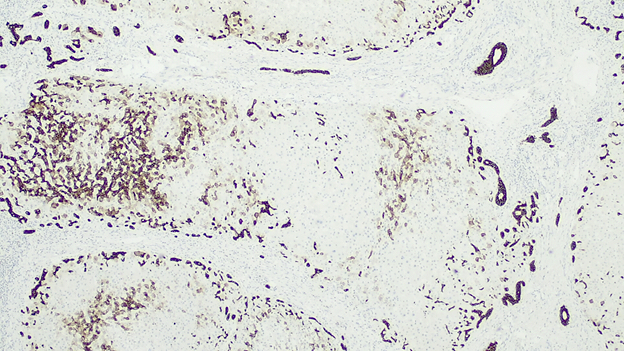
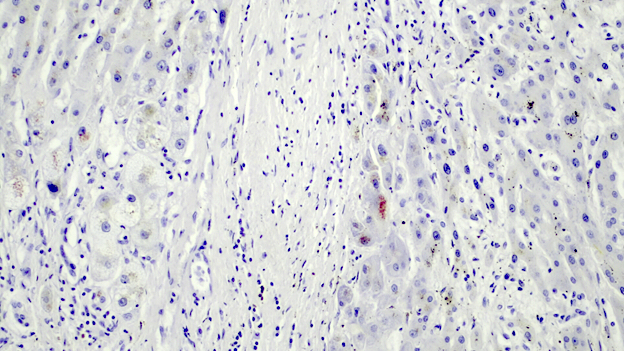
Positive stains
- CK7 may be useful in demonstrating ductular reaction and hepatocyte biliary metaplasia in cases of biliary obstruction
- Rhodanine stain usually demonstrates copper deposits in periportal hepatocyte in cases of chronic biliary obstruction
Sample pathology report
- Liver, retransplant:
- Biliary cirrhosis due to ischemic cholangiopathy (see comment)
- Comment: There is ulceration of the right biliary duct, with severe inflammation consisting of neutrophils and foamy histiocytes. Hepatic parenchyma exhibits architectural changes, with bridge forming cirrhosis in a jigsaw pattern. CK7 demonstrates a ductular reaction and there is copper accumulation in the periseptal hepatocytes.
Differential diagnosis
- Biliary complications:
- T cell mediated rejection (the major differential diagnosis) (Hepatology 2022;75:1014):
- Portal tract inflammation with eosinophils
- Endotheliitis
- Bile duct damage
- Chronic ductopenic rejection (Hepatology 2022;75:1014):
- Atrophic appearing duct with damaged and attenuated epithelium
- Bile duct absent in portal tract
- Recurrent primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC):
- Recurs in ~20 - 30% of patients by 5 years of transplantation
- Strictures are more common in patients transplanted for PSC than in those transplanted for other diseases
- Typical histological features include ductular reaction, mixed inflammation, lobular cholestasis, periductal fibrosis and bile infarcts
- Requires clinical history of liver transplantation due to PSC, since histological features are very similar to biliary obstruction (Transpl Int 2010;23:971)
- T cell mediated rejection (the major differential diagnosis) (Hepatology 2022;75:1014):
- Vascular complications:
- Paracetamol overload (Vet World 2019;12:1682):
- Clinical information of paracetamol intake
- Necrosis in acinar zone 3, or zone 2 or 3
- Sepsis (World J Gastroenterol 2008;14:1389):
- Inflammation with variable degrees of polymorphonuclear leukocyte infiltration, cholestasis and steatosis
- Liver architecture is preserved
- Intrahepatocytic or canalicular cholestasis may be found
- Hyperacute rejection:
- Occurs a few hours after liver transplantation
- Histological features include hemorrhagic necrosis, vascular thrombi and neutrophilic infiltrate
- Paracetamol overload (Vet World 2019;12:1682):
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
B. Biliary complications. The evidence of bile casts and biliary dilation in the context of liver transplantation is highly suggestive of ischemic cholangiopathy.
Comment Here
Reference: Transplantation - surgical / vascular complications
Comment Here
Reference: Transplantation - surgical / vascular complications
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is thought to be the main cause of nonanastomotic strictures following liver transplantation?
- Cytomegalovirus infection
- Lesions of the peribiliary vascular plexus and deep biliary glands
- Liver size
- Rejection
Board review style answer #2
B. Lesions of the peribiliary vascular plexus and deep biliary glands. Nonanastomotic strictures are usually associated with vascular injury of the peribiliary vascular plexus, inducing a hypoxia environment. The lesion of the deep biliary glands, a niche for stem cells, is also associated with the impairment of tissue repair.
Comment Here
Reference: Transplantation - surgical / vascular complications
Comment Here
Reference: Transplantation - surgical / vascular complications