Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Marques-Piubelli ML, Miranda RN. MALT-marginal zone. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomamalt.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Extranodal, low grade B cell lymphoma that is composed of a heterogeneous population of centrocyte-like, monocytoid, scattered immunoblasts and centroblast-like cells
- May occur in any extranodal site with lymphoid follicles and is under the umbrella of marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), which also includes splenic marginal zone lymphoma and nodal marginal zone lymphoma (Blood 2016;127:2082, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361)
- First described by Drs. Peter Isaacson and Dennis Wright in 1983 and listed as a distinct entity in the 1994 Revised European-American Lymphoma (REAL) classification (Cancer 1983;52:1410, Blood 1994;84:1361)
Essential features
- Extranodal, low grade B cell lymphoma that is composed of a heterogeneous population of centrocyte-like, monocytoid, centroblast-like cells and scattered immunoblasts
- May occur in any extranodal bodily site with lymphoid follicle formation and is under the umbrella of MZL, which also includes splenic MZL and nodal MZL (Blood 2016;127:2082, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361)
- Represents up to 80% of all cases of MZL (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032)
- May occur at any extranodal site (Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:1891)
- Stomach is the most commonly involved site
- Indolent clinical course and symptoms are mainly related to the mass effect at the involved site (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Blood 2016;127:2082)
Terminology
- Low grade B cell lymphoma of MALT
- MALToma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Third most common non-Hodgkin lymphoma, corresponding to ~8% of all cases in Western countries (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57, World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022;14:153)
- Represents up to 80% of all cases of MZL (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032)
- Median age: ~60 years (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57)
- Slight female predominance (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032)
- Most common type of lymphoma in periorbital region and stomach (PLoS One 2014;9:e104004, Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:1069)
Sites
- May occur at any extranodal site (Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:1891)
- Stomach is the most commonly involved site
- Bone marrow involvement may occur in up to 20% of patients (Blood 2016;127:2082)
- Distant lymph node involvement is rare (Blood 2016;127:2082)
Pathophysiology
- Somatic hypermutation and rearrangements in immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) genes associated to cell surface and chemokine receptors of chronic inflammatory / infectious processes play an important role in the lymphomagenesis (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Blood 2016;127:2082, F1000Res 2018;7:406, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57, World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022;14:153, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2017;30:13, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2021;29:56)
- Most common mutated IGH VH families by site:
- Stomach: IGH VH3-30 and IGH VH3-23
- Ocular adnexa: IGH VH4-34
- Skin: IGH VH1-69 and IGH VH4-59
- Lung: IGH VH3 and IGH VH4
- Salivary gland: IGH VH1-69
- In all types of MZL, both canonical and noncanonical NFκB activation can mediate the activation, neoplastic transformation and maintenance of the neoplastic lymphocytes
- Antigen stimulation of BCR and TCR, followed by phosphorylation of CARD11, BCL10 and MALT1
- Interaction with TRAF6 and NFκB essential modulator
- TNFAIP3 (A20) performs a negative regulation of the whole pathway and due to mutations and deletions in this gene, the pathway may hyperactivate
- Antigen stimulation of BCR and TCR, followed by phosphorylation of CARD11, BCL10 and MALT1
- Cases of gastric MALT lymphoma related to Helicobacter pylori infection may have upregulation of cyclin A2 and loss of PTEN
- Same mechanism is described in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
- Most common mutated IGH VH families by site:
- Recurrent CCR6 mutations impair its internalization and consequently the neoplastic cells are more resistant to apoptosis and more likely to have malignant transformation (Haematologica 2022 Feb 10 [Epub ahead of print])
- HBD2, CCL20 and HD5 are ligands that could be expressed in epithelial cells
Etiology
- Infection and chronic inflammation (Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:1891, Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:1069, Blood 2016;127:2082, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361, Cancers (Basel) 2019;11:547)
- Stomach: Helicobacter pylori and Helicobacter heilmannii
- Cytotoxin associated gene A (CagA) protein
- Intratumoral T cells, BCL2 and BCLxL activation
- Ocular adnexa: Chlamydia psittaci
- Small intestine: Campylobacter jejuni
- Skin: Borrelia burgdorferi
- Lung: Acromobacter xylosoxidans
- Hepatitis C may be associated in several sites
- More common in nongastric topographies
- Stomach: Helicobacter pylori and Helicobacter heilmannii
- Autoimmunity (Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:1891, Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022;14:153, Ann Hematol 2022;101:91)
- Salivary gland: Sjögren syndrome
- Important role of CD40 / CD40L (noncanonical pathway) and BCL2 protein
- Thyroid gland: Hashimoto thyroiditis
- Thymic: Sjögren syndrome, thymoma and autoimmune thrombocytopenia purpura
- Salivary gland: Sjögren syndrome
Clinical features
- Indolent clinical course and symptoms usually are related to the mass effect of the involved site (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Blood 2016;127:2082):
- Ocular adnexa (PLoS One 2014;9:e104004, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57):
- Nodular / mass lesion as initial presentation
- Conjunctiva, lacrimal gland and orbital region are the most frequent sites
- Bilateral involvement in up to 15% of cases
- Lung (J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361, Eur Respir J 2009;34:1408):
- Single or multiple nodules or consolidations
- No topographic predominance
- Lymph node and pleural involvement are rare
- Asymptomatic or presenting with cough and dyspnea
- Stomach (Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:1069):
- Incidental finding or presenting with abdominal pain, vomiting and weight loss
- Obstruction, perforation and bleeding may occur
- Duodenal (J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;36:406):
- Asymptomatic or dyspepsia at initial presentation
- Complications in up to ~40% of cases
- Hemorrhage or stricture
- Nodules, ulcer, flat depression or subepithelial tumor
- Usually confined to mucosa
- Colonic (J Clin Pathol 2020;73:378):
- Asymptomatic; found on screening colonoscopy
- Abdominal pain, weight loss, mucoid stool, diarrhea or constipation
- Single or multiple lesions
- Flat, elevated or polypoid lesion with smooth or granular surface
- Skin (Am J Clin Pathol 2020;154:428):
- Indolent and confined to the skin at diagnosis
- Solitary or multifocal nodules localized in arms and trunk
- Thyroid (Eur Thyroid J 2020;9:11):
- Hypothyroidism or asymptomatic
- Painless mass and shortness of breath
- Association with carcinoma in up to 17% of cases
- Breast (Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2019;19:244):
- Abnormal screening mammogram
- Palpable mass
- Salivary gland (Oncologist 2015;20:1149):
- Sjögren disease related symptoms
- Nodular or mass lesion
- Ocular adnexa (PLoS One 2014;9:e104004, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57):
- B symptoms are rare (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57)
- Lymphadenopathy and dissemination to other sites in ~25% of patients (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57)
Diagnosis
- Gastric MALT lymphoma (Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:1069)
- Endoscopic mapping of the stomach is recommended due to the nonspecific presentation
- Minimum of 10 biopsies of visible lesions and no specified number of normal mucosae
- No standard protocol for follow up
- Usually, biopsies are performed every 3 - 6 months for the first 2 years of follow up
- Endoscopic mapping of the stomach is recommended due to the nonspecific presentation
Laboratory
- Laboratory abnormalities are not common (Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57, Br J Haematol 2022;196:1353)
- Elevated serum β2 microglobulin (~30%)
- Monoclonal gammopathy (~30%)
- Association with advanced stage and bone marrow involvement
- Elevated serum immunoglobulin paraprotein (~20 - 30%)
- Most common types are IgM κ, IgM L and IgG L
- Associated with advanced age, bone marrow involvement, B symptoms, advanced stage of disease, elevated serum β2 microglobulin, multiple sites of involvement, nodal involvement, high MALT International Prognostic Index (IPI)
- Iron deficiency anemia (~10%)
- Elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (~10%)
Radiology description
- For the detection of lesions, the value of 18F fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography is controversial; it seems to show more concordant results for lesions located in tissues with low and homogeneous physiologic uptake (Blood 2016;127:2082, Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:750)
Prognostic factors
- Factors associated with worse outcomes: MALT IPI (Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:1891, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57, Blood 2017;130:1409, Front Oncol 2021;11:681689)
- Low (0), intermediate (1) and high (≥ 2) risk according to the presence of the following factors:
- Advanced age (≥ 70 years)
- Elevated LDH
- Ann Arbor Stage III / IV
- Other factors that may be associated with worse outcome: relapse at the original or distant sites, elevated serum immunoglobulin paraproteinemia and bone marrow involvement
- Low (0), intermediate (1) and high (≥ 2) risk according to the presence of the following factors:
- Localized forms of MALT lymphoma are usually early stage (IE / IIE) of disease and have similar outcomes compared with localized nodal MZL (Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:1891)
- Transformation to DLBCL may occur in up to ~20% of cases and is associated with a worse prognosis (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Blood 2016;127:2082, Br J Haematol 2021;193:369)
- In cases of gastric MALT lymphoma, it is associated with hepatic involvement, advanced stage disease and hepatitis C infection
- Genetic factors associated with transformation: mutation and allelic loss of p53, hypermethylation of p15 and p16, and p16 deletion
- Cases of typical MALT lymphoma with different methylation profiles, MALT lymphoma with increased large cells and transformation to DLBCL
- Gastrointestinal MALT lymphoma may have inferior outcome when compared with nongastrointestinal localization (Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:1891, Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:1069)
- t(11;18) associates with less response to antibiotic eradication therapy in early stage MALT lymphoma (World J Gastroenterol 2023;29:2202)
- Advanced stage (III / E / IVE) may occur in ~30% of patients and recurrence may happen in extranodal and nodal sites (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032)
- 5 year overall survival (OS) by affected site (Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:1891):
- Central nervous system: 100%
- Thyroid gland: 95%
- Skin: 91%
- Oral cavity: 88%
- Bone and soft tissue: 86%
- Ocular adnexa: 84%
- Breast: 79%
- Lung and respiratory tract: 77%
- Colon: 72%
- Stomach: 71%
- Urinary tract: 65%
- Median 10 year recurrence free survival: 57% (Blood 2016;127:2082)
Case reports
- 12 year old girl with gastric MALT lymphoma presenting with iron deficiency anemia and gastric perforation (BMC Pediatr 2019;19:63)
- 37 year old woman with primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma (PCMZL) presented as a rosacea-like lesion (JAAD Case Rep 2020;6:902)
- 56 year old woman with primary colonic MALT lymphoma presenting as a single mass on hepatic flexure of the colon (Am J Case Rep 2017;18:491)
- 73 year old woman with monoclonal gammopathy and primary oral cavity MALT lymphoma (BMC Oral Health 2021;21:597)
- 74 year old woman with a previous history of tuberculosis presenting with a pulmonary opacity diagnosed as a primary pulmonary MALT lymphoma (Biomed Hub 2019;4:1)
Treatment
- Watch and wait strategy may be considered, depending on the clinical setting (PLoS One 2014;9:e104004, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57)
- Usually not recommended for nongastric MALT lymphomas
- Antibiotic treatment
- Eradication of H. pylori (using antibiotics) is associated with long term remission in gastric MALT lymphoma in up to 75% of cases and can be used as initial strategy (Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:1891, Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:1069, Blood 2016;127:2082, Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:1005)
- Can be used even in cases with no evidence of H. pylori infection
- In cases of ocular adnexa MALT lymphoma, eradication of C. psittaci may be an upfront strategy (Blood 2016;127:2082, Blood 2016;127:2082, Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:1005)
- Doxycycline
- In cases localized to the skin and small intestine, use of antimicrobial therapy is controversial (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Blood 2016;127:2082, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57)
- Ceftriaxone in cases of primary involvement of the skin
- Intralesional interferon alpha and rituximab may be used in primary cutaneous PCMZL
- Tetracycline or metronidazole and ampicillin in cases of primary involvement of intestine
- Ceftriaxone in cases of primary involvement of the skin
- Eradication of H. pylori (using antibiotics) is associated with long term remission in gastric MALT lymphoma in up to 75% of cases and can be used as initial strategy (Leuk Lymphoma 2013;54:1891, Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:1069, Blood 2016;127:2082, Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:1005)
- Radiation and local surgery may be used in cases with early stage disease (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57, Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2019;19:244, Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:873, Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:1005)
- Involved field radiation therapy may also be used in patients with local recurrence, who failed antibiotics
- Surgery may represent the initial treatment in cases of excisional biopsies with negative margins
- MALT lymphomas of the breast are usually treated with radiation therapy or single agent / chemotherapy
- Systemic chemotherapy (e.g., CHOP - cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone) or single agents (e.g., rituximab, lenalidomide, fludarabine and cyclophosphamide) can be considered in cases with no association with an infectious agent, failure of antibiotics, and advanced disease (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Blood 2016;127:2082, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2018;31:57)
- No standard consensus
Microscopic (histologic) description
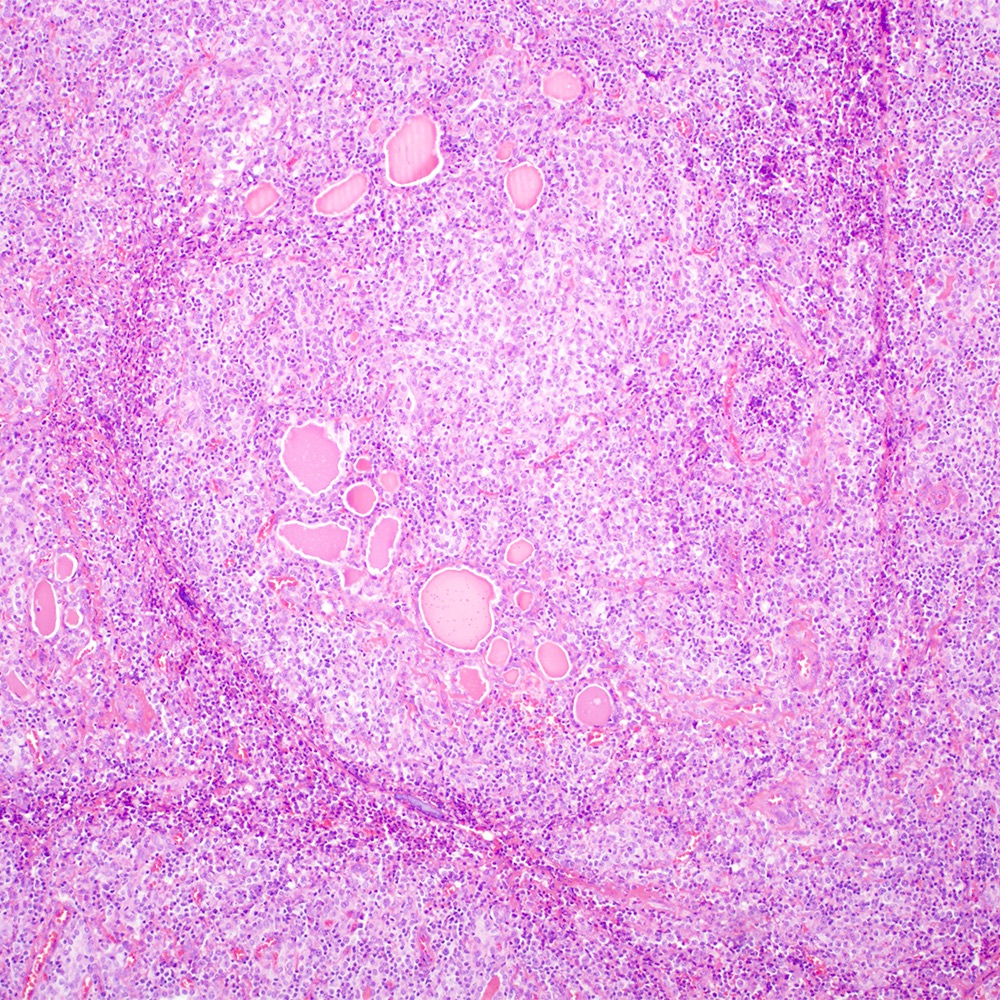
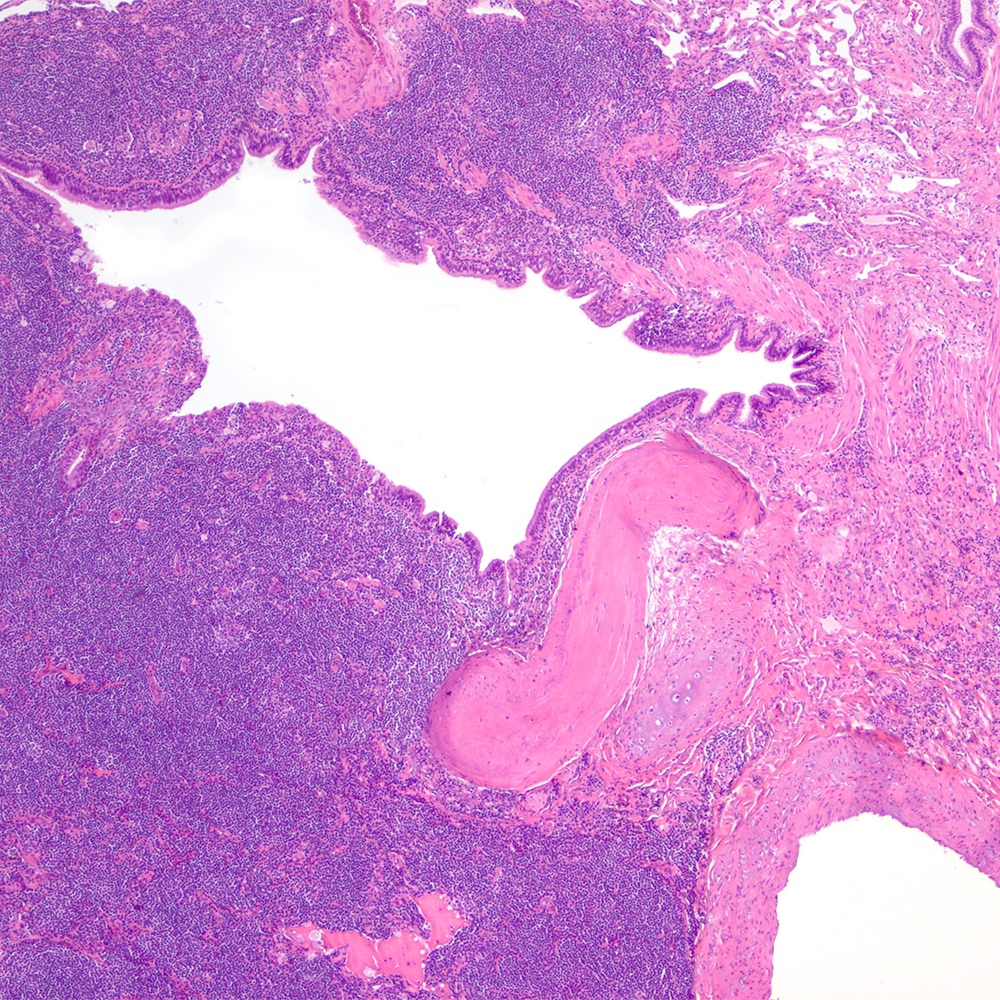
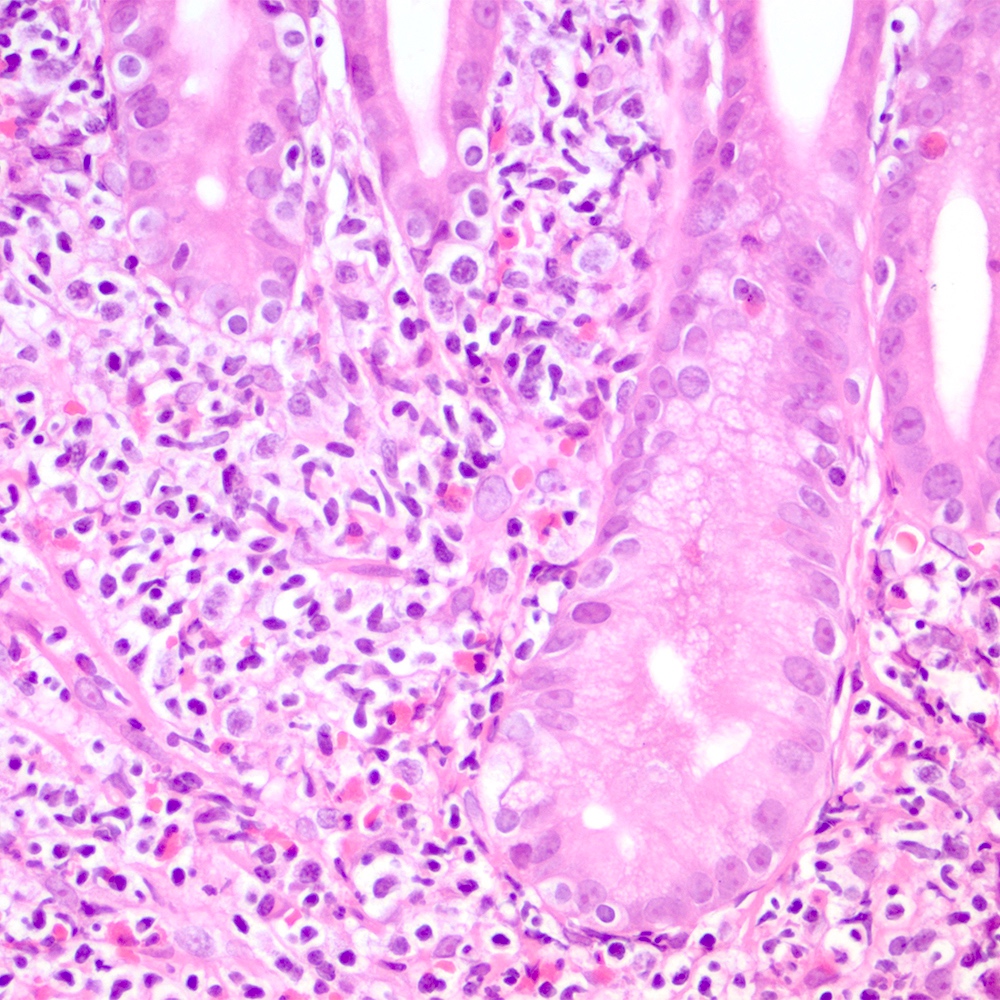
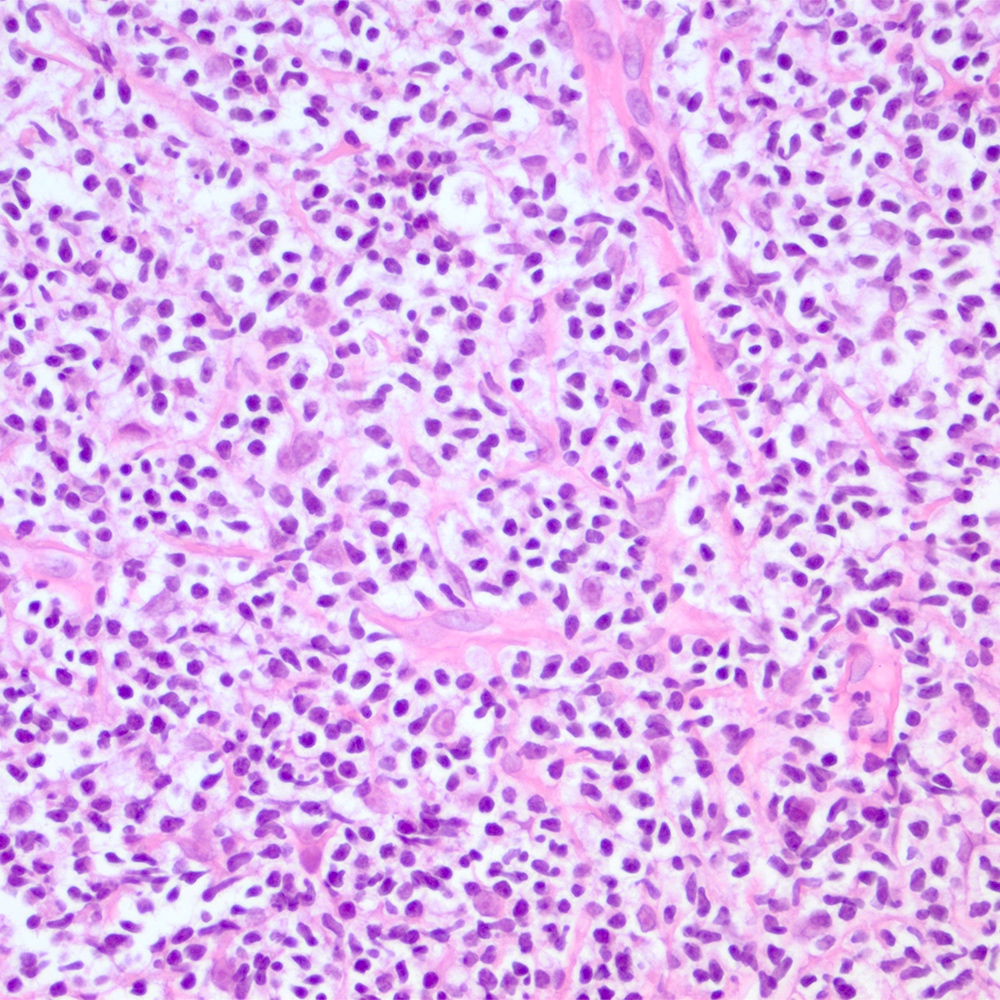
- Atypical lymphoid infiltrate is located in the marginal zone of reactive follicles and extends to interfollicular or intrafollicular (follicular colonization) regions (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361)
- Reactive follicles may be present and are helpful in the diagnosis (J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361)
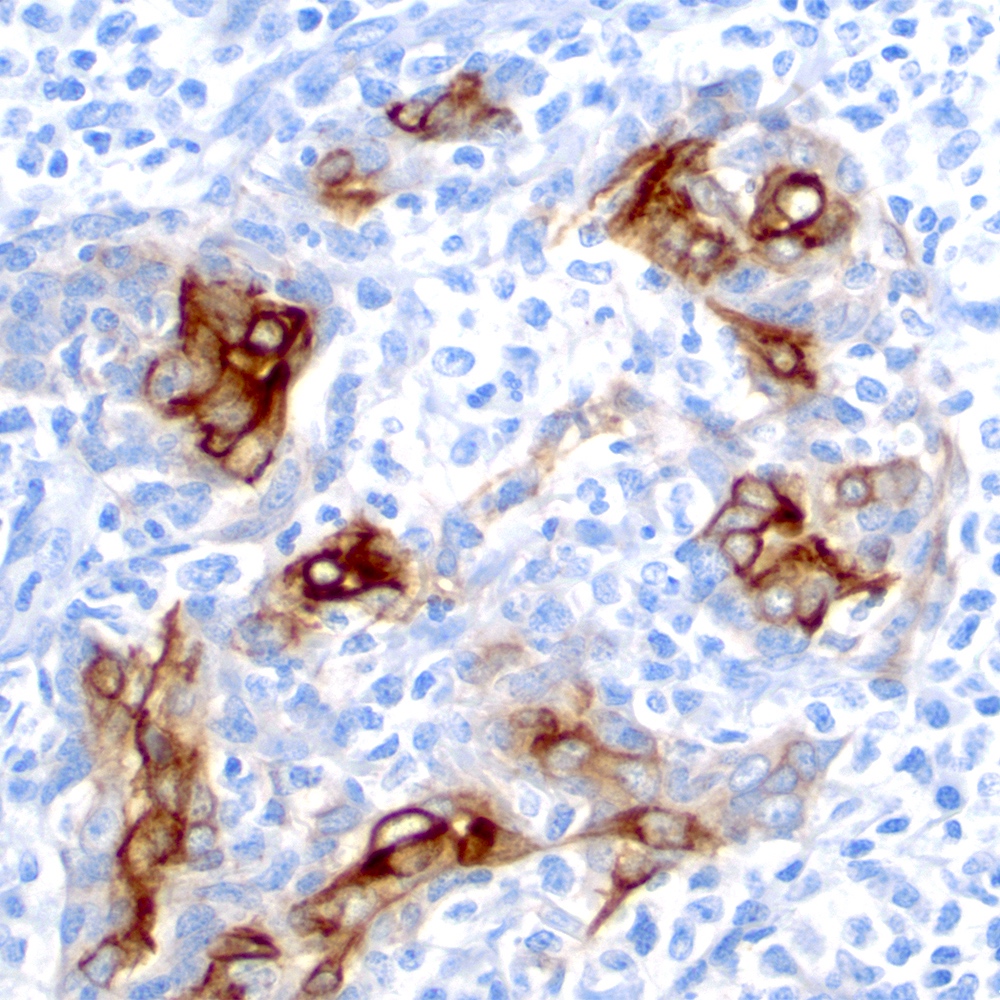
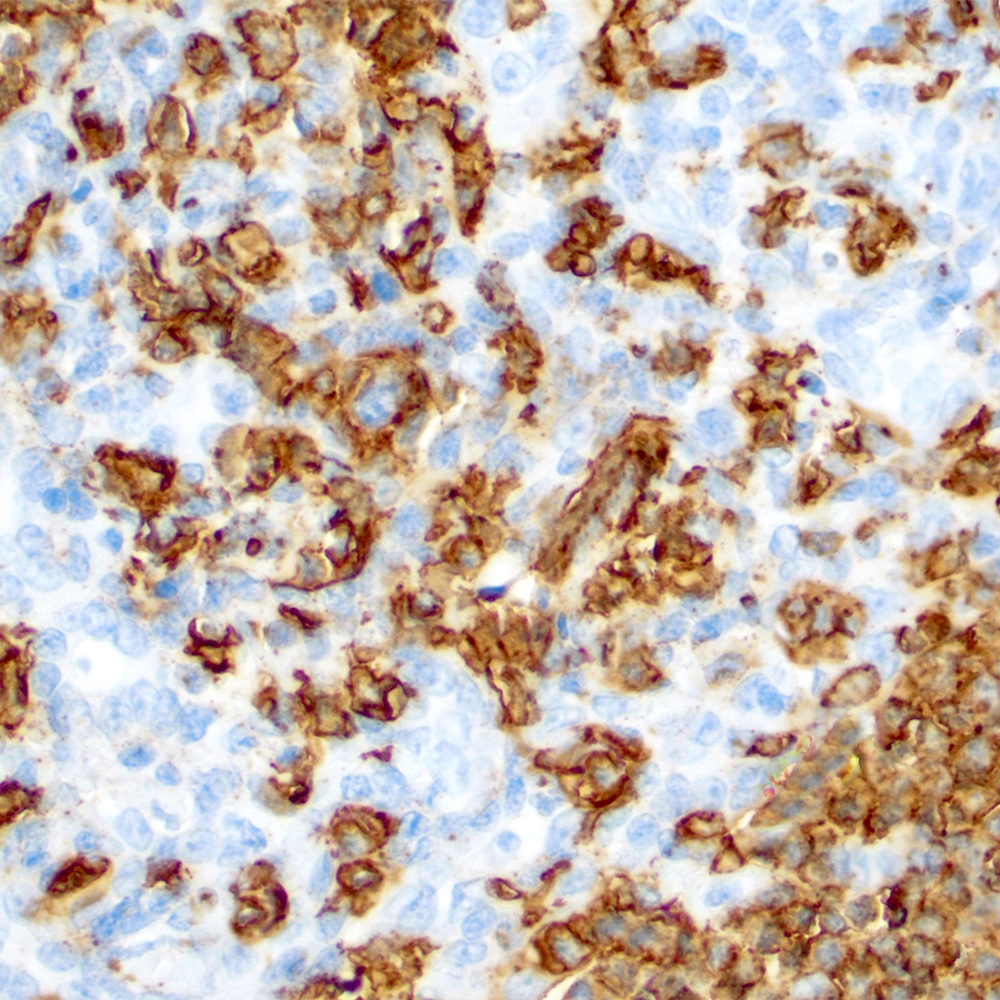
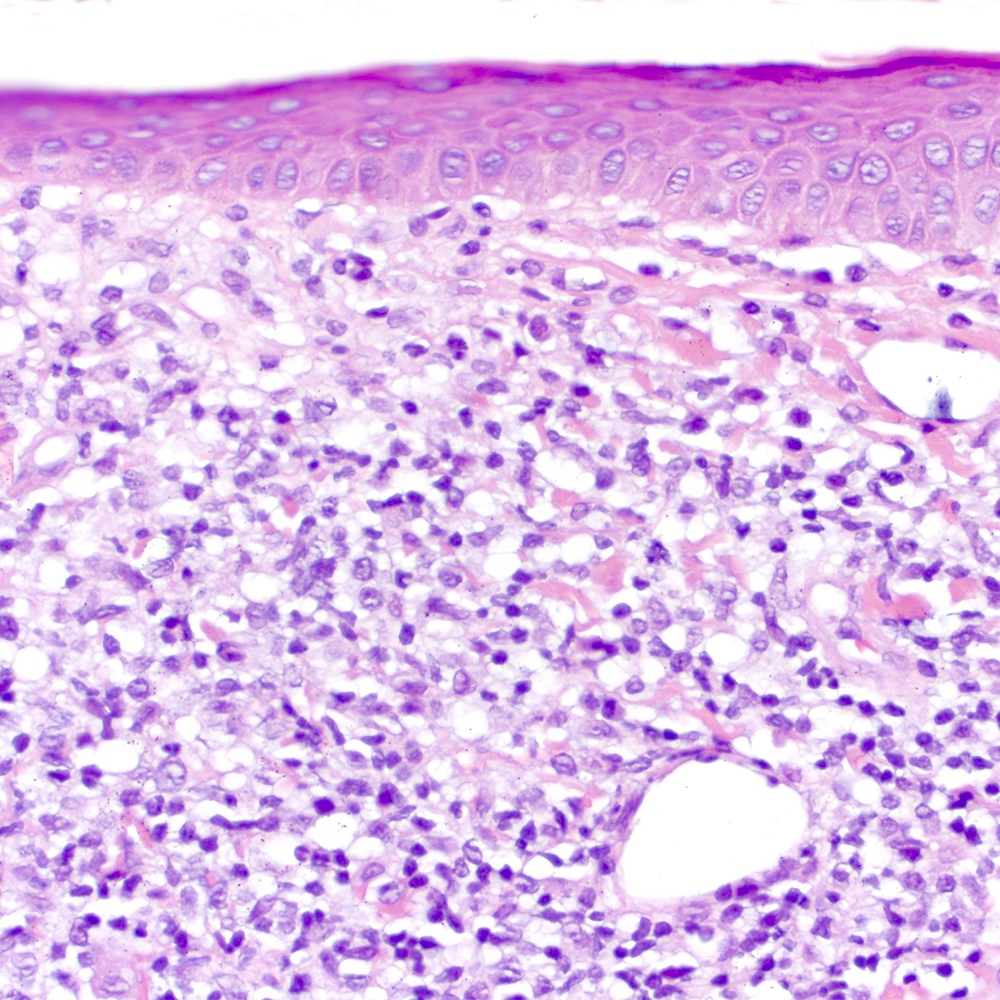
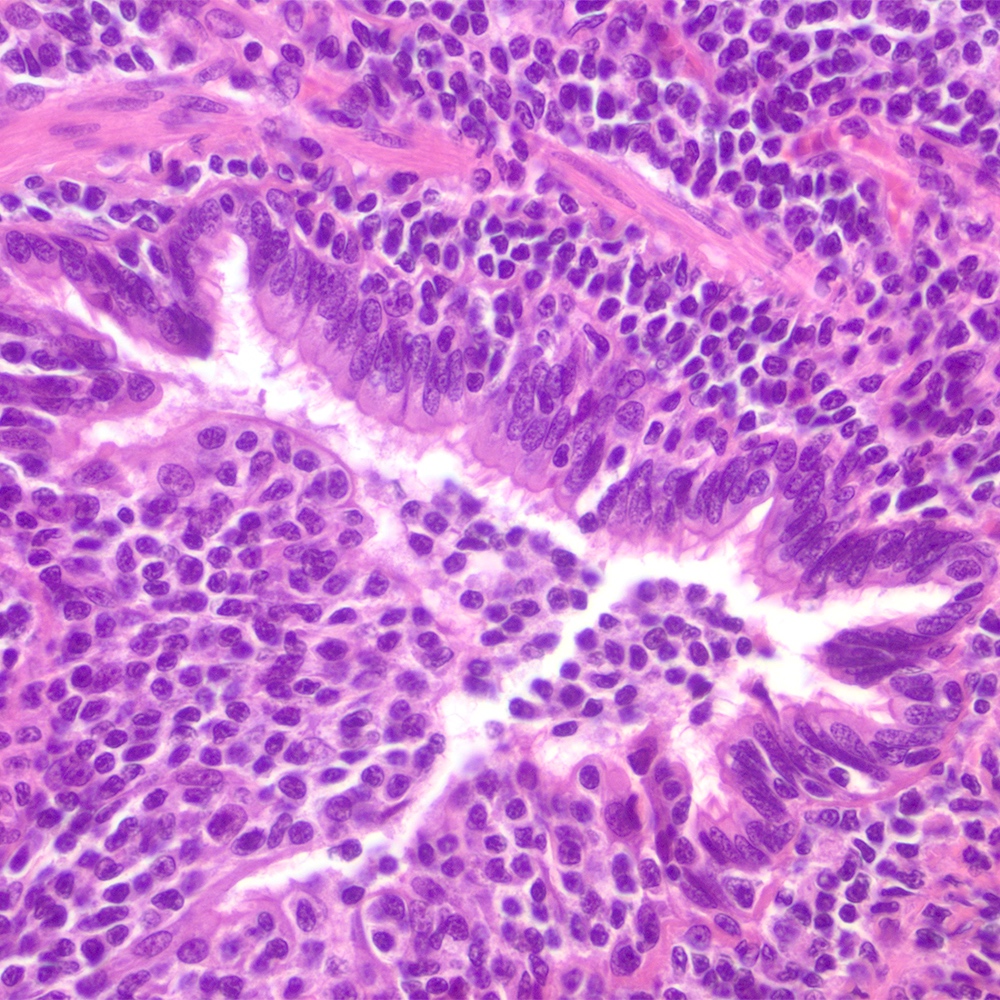
- Lymphoepithelial lesion (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:1069, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361)
- Aggregates of 3 or more marginal zone cells with distortion or destruction of the epithelium
- Presence of individual cells in the epithelium is not sufficient to define a lymphoepithelial lesion
- Eosinophilic degeneration is observed
- Presence is not pathognomonic for MALT lymphoma and can be found in reactive conditions
- Aggregates of 3 or more marginal zone cells with distortion or destruction of the epithelium
- Diagnostic clues for the diagnosis by site:
- Orbit (PLoS One 2014;9:e104004):
- Nodular or diffuse infiltrate composed by monocytoid, centrocyte-like and lymphoplasmacytic cells
- Stomach and intestine (Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:1069, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:23):
- Dense lymphoid infiltrate that replaces the lamina propria, associated or not with lymphoepithelial lesions
- Lymphoepithelial lesions are not common in colorectal cases
- Dense lymphoid infiltrate that replaces the lamina propria, associated or not with lymphoepithelial lesions
- Lung (J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361, Eur Respir J 2009;34:1408):
- Lymphangitic pattern of infiltration with spread through bronchovascular structures, interlobular septa and visceral pleura
- Lymphoepithelial lesion is seen on the bronchial or bronchiolar epithelium
- Angiotropism, fibrosis and necrosis may be found
- Salivary gland (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032):
- Background of chronic sialadenitis
- Atrophic acinar parenchyma
- Monocytoid cells around epithelial / myoepithelial islands
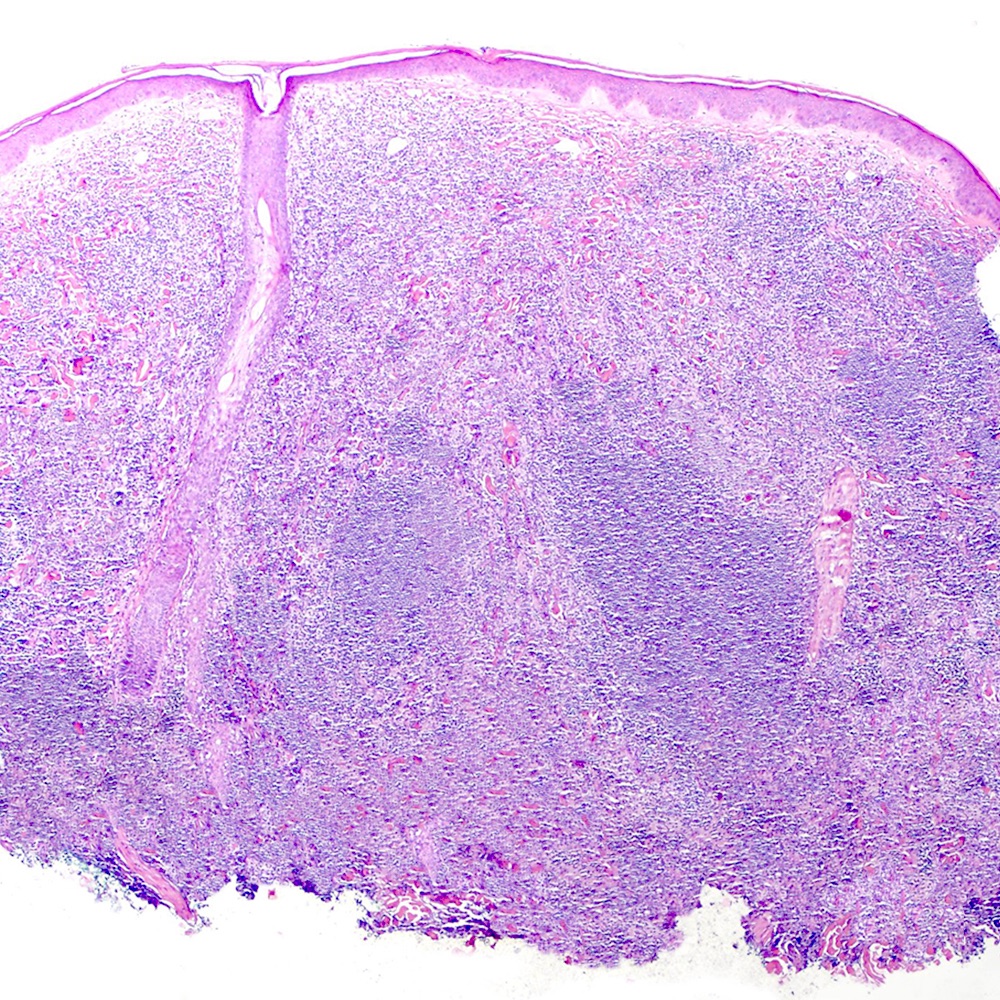
- Skin (Am J Clin Pathol 2020;154:428):
- Dense lymphoid infiltrate with nodular or diffuse pattern
- Admixture of small lymphocytes, lymphoplasmacytic and plasma cells
- Grenz zone
- Dense lymphoid infiltrate with nodular or diffuse pattern
- Breast (Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2019;19:244):
- Diffuse or nodular neoplastic infiltrate of monocytoid cells admixed with reactive follicles
- Lymphoepithelial lesions may be present
- Thyroid (Eur Thyroid J 2020;9:11):
- Lymphoepithelial lesions and epithelial ball
- Neoplastic cells inside a thyroid follicular epithelium
- Scattered hyperplastic germinal centers in the background
- Lymphoepithelial lesions and epithelial ball
- Orbit (PLoS One 2014;9:e104004):
- Transformation to DLBCL:
- Large cells with centroblastic appearance disposed in clusters of more than 20 cells, or sheet proliferation
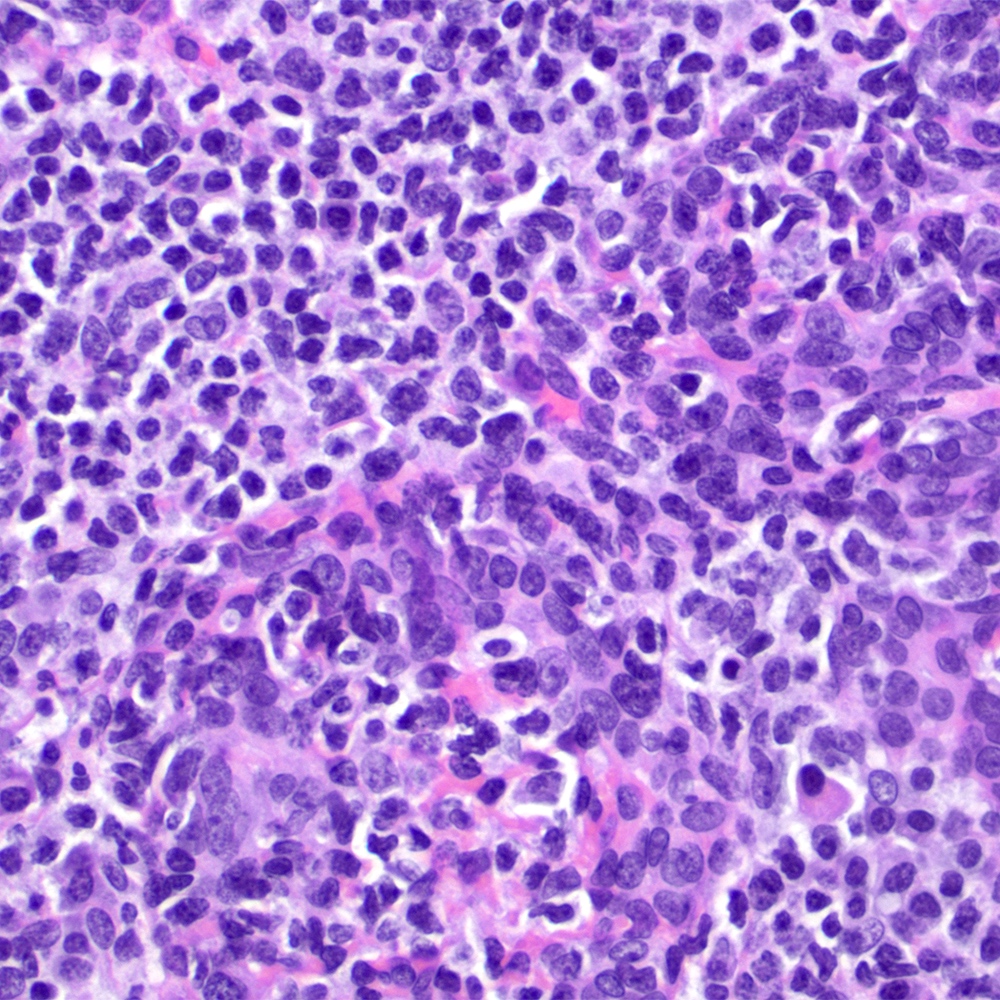
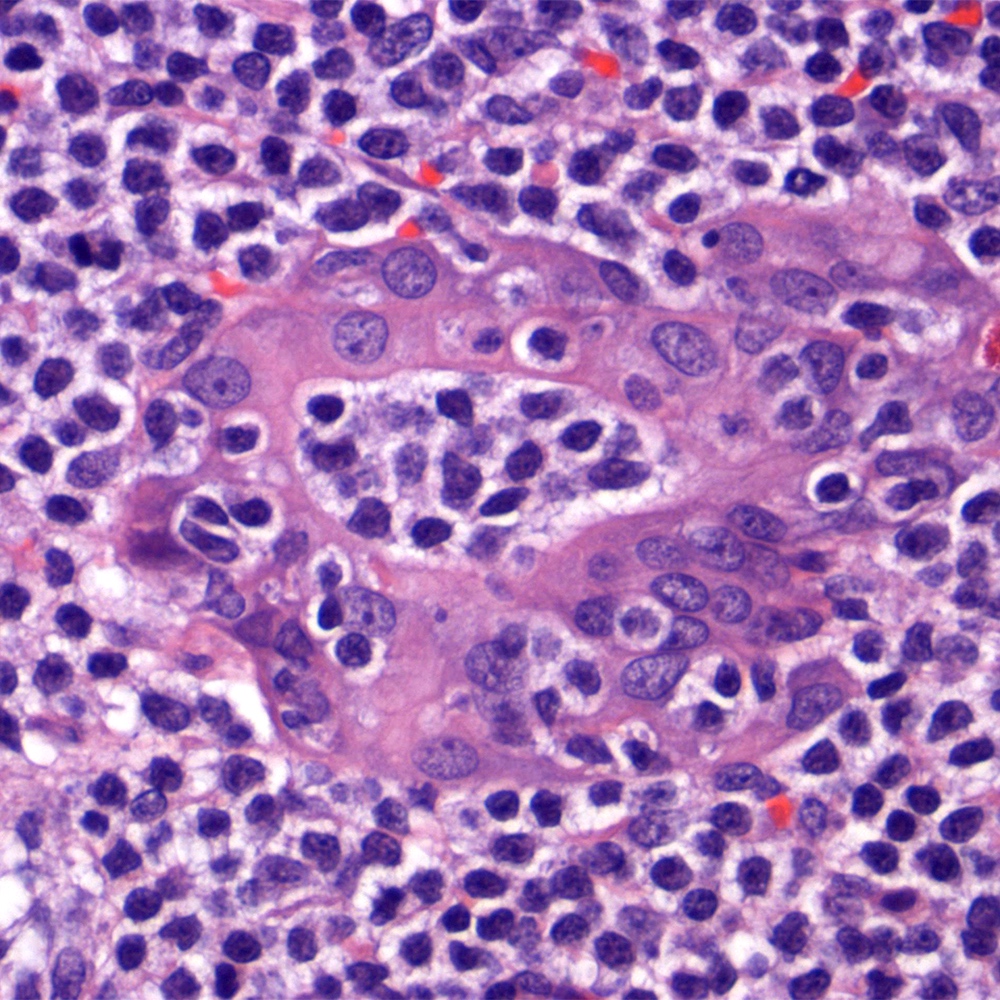
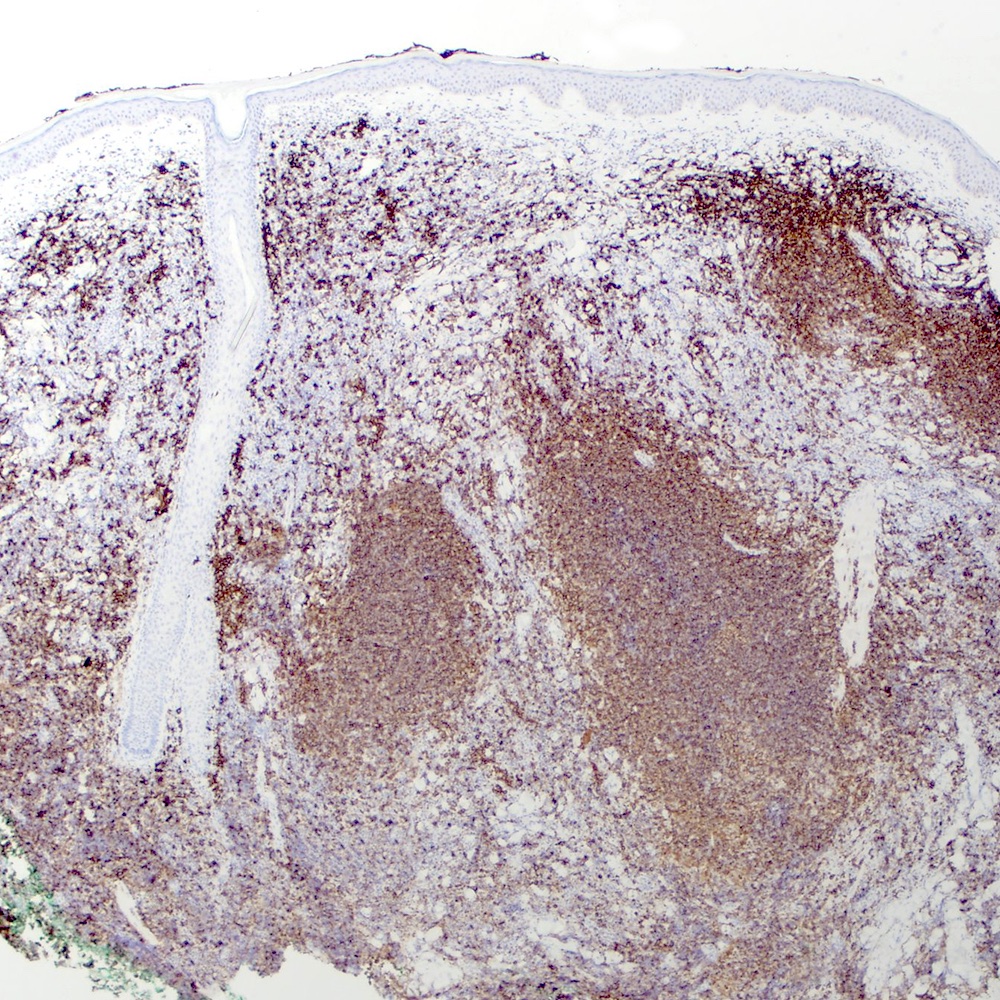
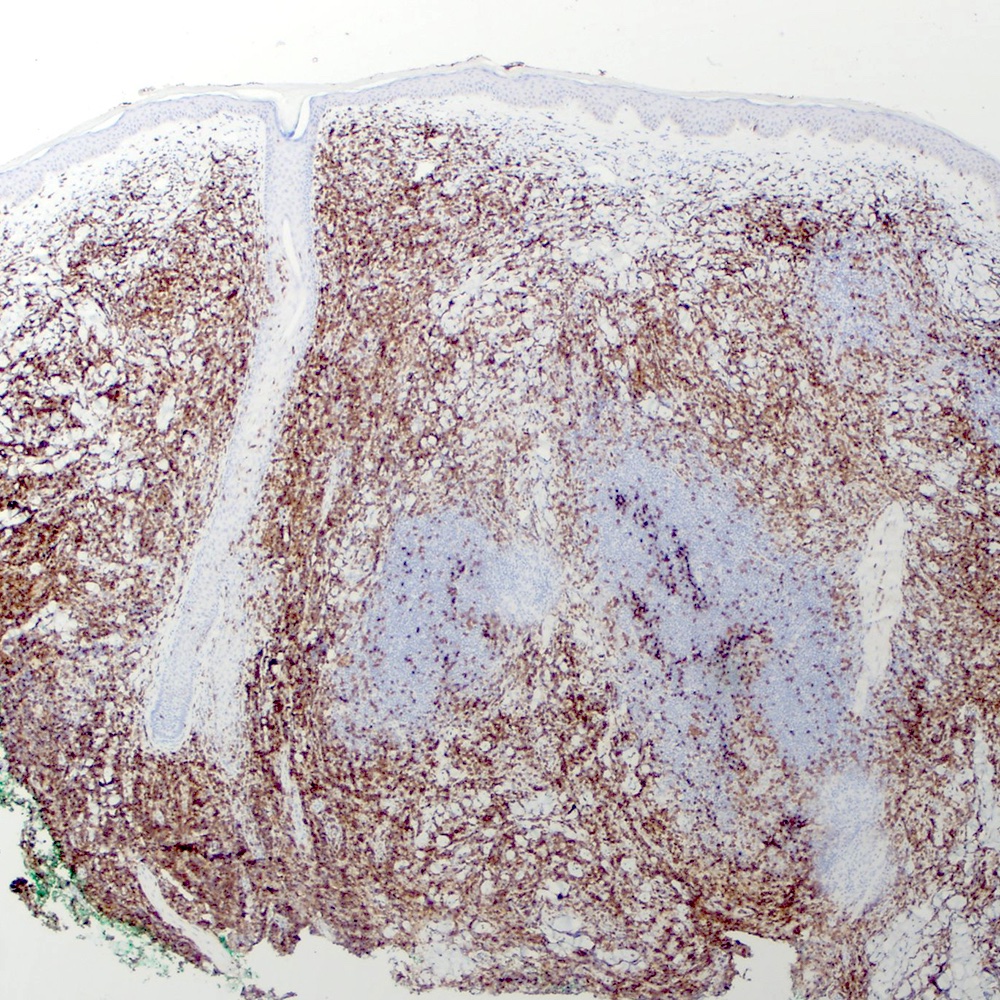
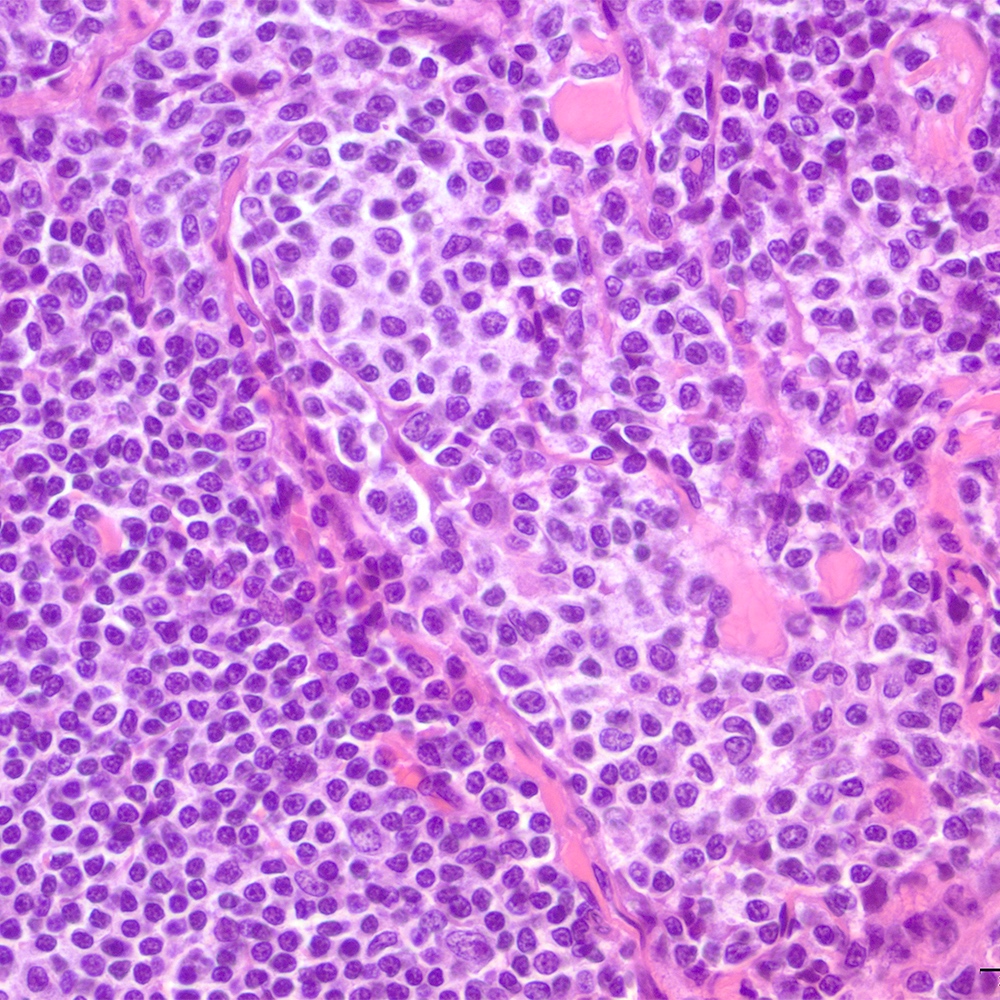
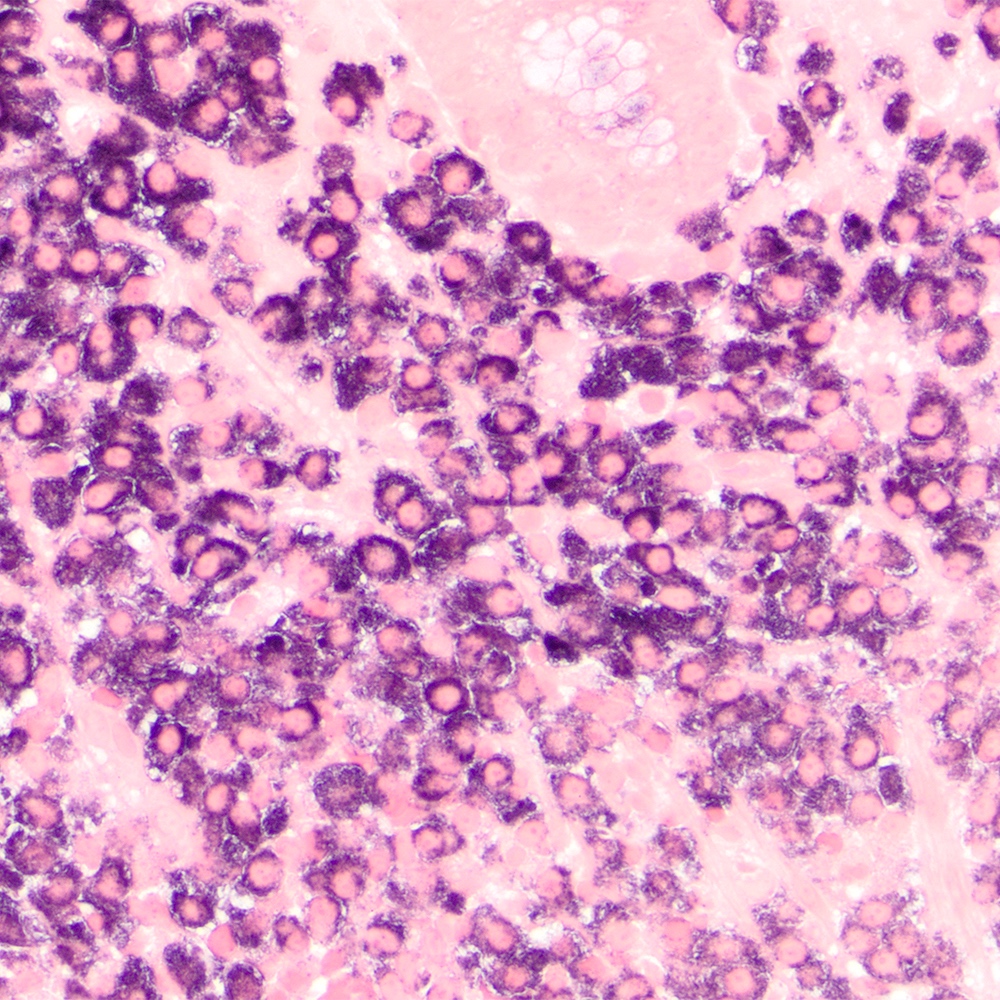
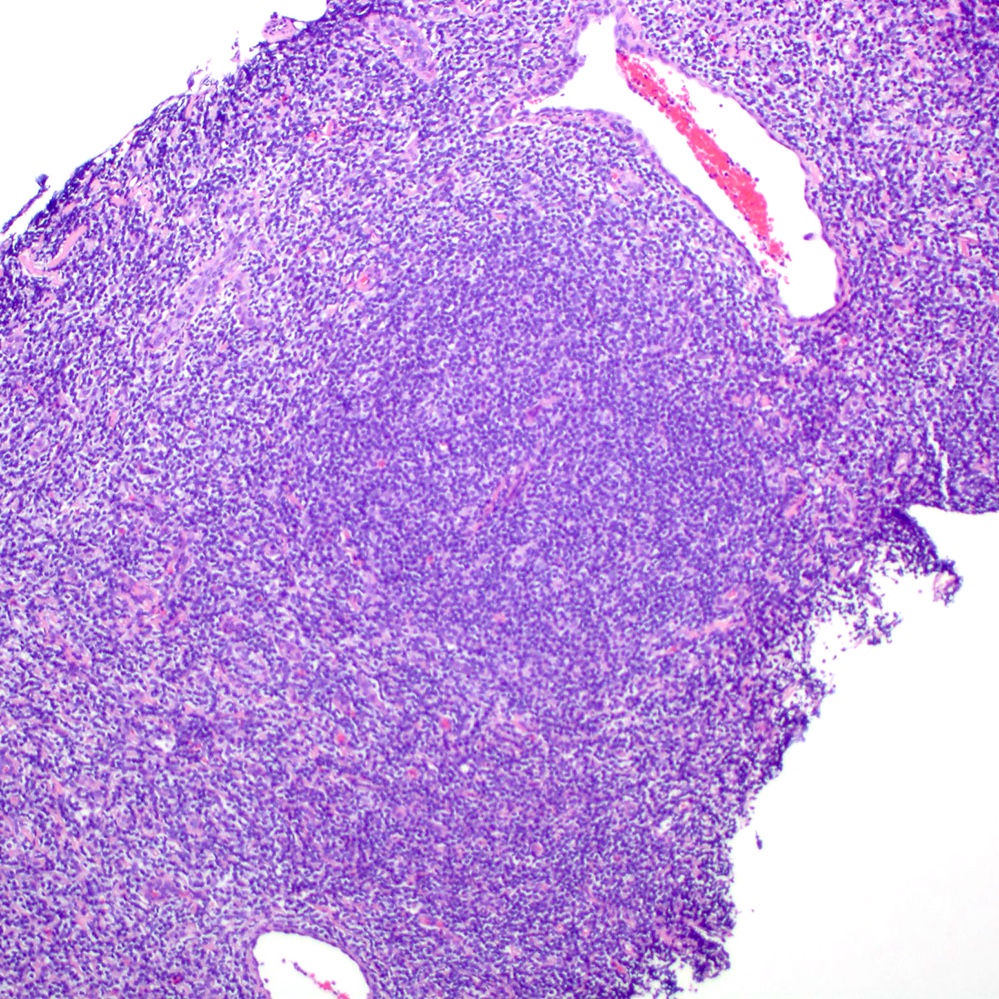
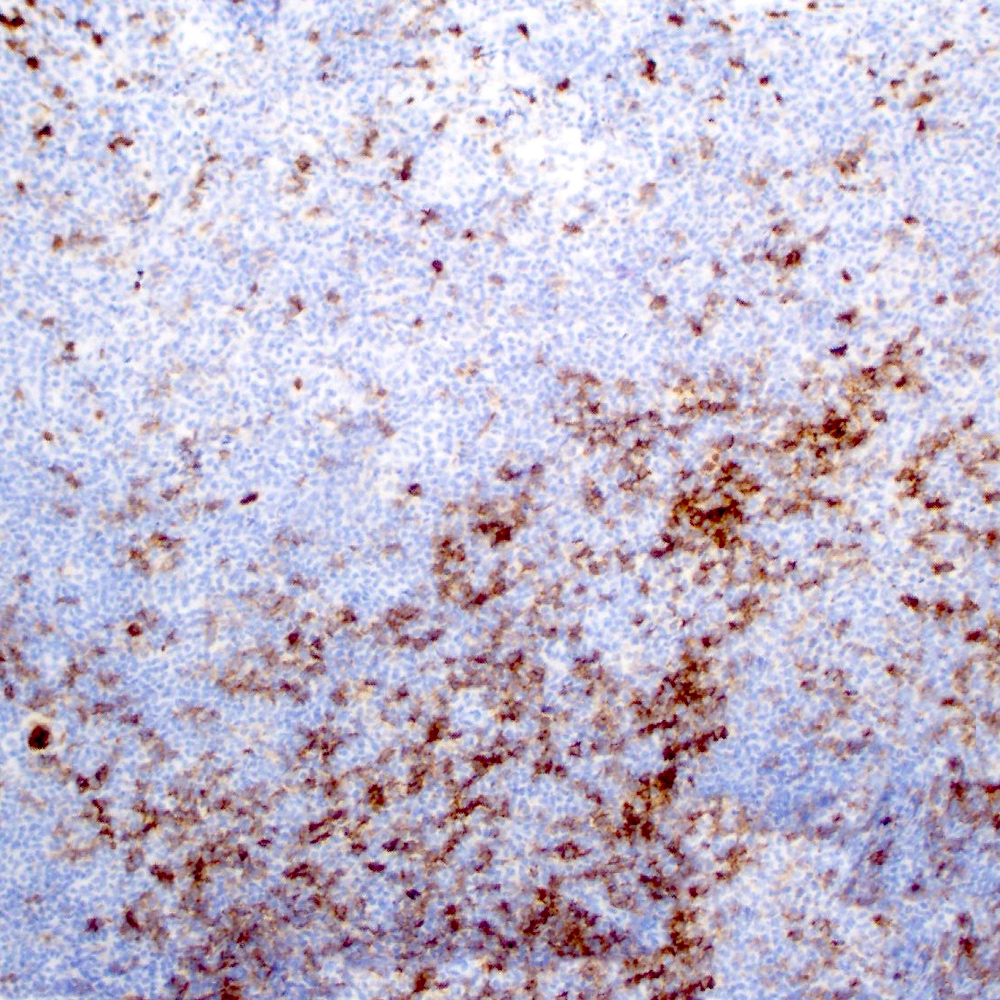
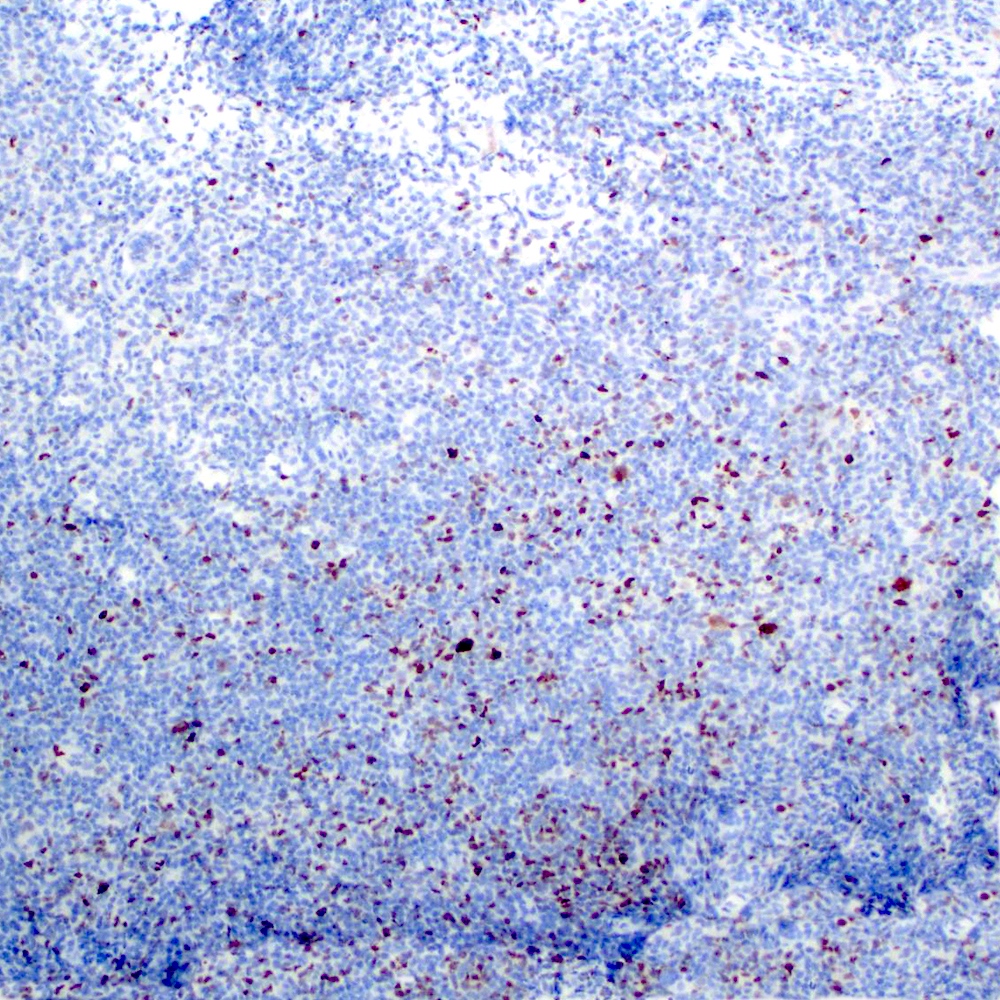
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D.
Cytology description
- Monomorphic pattern (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361):
- Monocytoid or centrocyte-like appearance: intermediate size, distinct cell borders, nuclei with regular contours and rim of clear cytoplasm
- Polymorphic pattern (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361):
- Lymphocytes with monocytoid, centrocyte-like (small to intermediate size, small irregular) nuclei are the most predominant component
- Scattered cells with centroblastic-like appearance: large cells with dispersed chromatin
- Plasma cells are frequent and close to the epithelium
Positive stains
- Pan B cell antigens (CD19, CD20, CD22, CD79a and PAX5) (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032)
- BCL2 (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032)
- CD35 highlights underlying follicular dendritic cell meshworks (World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022;14:153)
- CD43 (J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361)
- May be present in ~50% of cases
- IgM (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361, World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022;14:153, Am J Clin Pathol 2020;154:428, J Cutan Pathol 2022;49:55)
- Kappa or lambda light chain restriction (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032)
- Indicate plasma cell differentiation that occurs in subset of cases
- MNDA, partial expression (J Cutan Pathol 2022;49:55)
- Cereblon (Hematol Oncol 2018;36:62)
- CCR6 (Haematologica 2022 Feb 10 [Epub ahead of print])
- LEF1 and metadherin (Int J Ophthalmol 2017;10:705)
- Cases affecting ocular adnexa
- Low index proliferation rate (Ki67)
Negative stains
- Pan T cell markers (CD3, CD4, CD5, CD8) (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361, Am J Clin Pathol 2020;154:428)
- IgD (J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361, World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022;14:153)
- Cyclin D1 (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361)
- MALT1 (J Clin Pathol 2020;73:378)
- MUM1 (Hematol Oncol 2018;36:62)
- HBD2 and CCL20 (Haematologica 2022 Feb 10 [Epub ahead of print])
- CD10, CD21, CD23 and BCL6 (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361)
- Highlight disrupted germinal centers in cases of follicular pattern
- Basal normal aggregates may remain in cases with neoplastic regression
Flow cytometry description
- Most sensitive method to establish clonality of B lymphocytes; however, it is not routinely used (Intern Med 2018;57:1081, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:23)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Hypermutation of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable genes in up to 75% of patients (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361)
- B cell clonality may remain in cases with histological remission in up to 50% of patients (J Clin Pathol 2007;60:361)
- May be associated with delay in achieve complete remission and probability to relapse
- Recurrent chromosomal aberrations (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Blood 2016;127:2082, Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1546, Leuk Res 2020;95:106399):
- Stomach: t(11;18)(q21;q21), t(1;14)(p22;q32) and trisomies 3, 7, 12 and 18
- Ocular adnexa: t(11;18)(q21;q21), t(14;18)(q32;q21), t(3;14)(p14.1;q32), deletion 6p23 (TNFAIP3) and trisomies 3 and 18
- Intestine: t(11;18)(q21;q21), t(1;14)(p22;q32) and trisomies 3, 12 and 18
- Skin: t(14;18)(q32;q21), t(3;14)(p14.1;q32) and trisomies 3 and 18
- Lung: t(11;18)(q21;q21), t(14;18)(q32;q21), t(1;14)(p22;q32) and trisomies 3, 12 and 18
- Salivary gland: t(11;18)(q21;q21), t(14;18)(q32;q21) and trisomies 3, 7 and 18
- Thyroid gland: t(3;14)(p14.1;q32) and trisomies 3 and 12
- Breast: trisomies 3 and 18
- Aneuploidy is associated with t(14;18)(q32;q21) / IGH-MALT1 and t(1;14)(p22;q32) / IGH-BCL10 (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1546)
- Both MALT1 and BCL10 are associated with NFκB activation
- Somatic mutations in PIM1 and cMYC (World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022;14:153)
- Usually missense, 46% of gastric MALT lymphomas and 30% of nongastric
- Somatic mutations or deletions of PIK3CD, CREBBP, KMTDC, SPEN, TET2 and TNFRSF14 (F1000Res 2018;7:406, Haematologica 2019;104:e558)
- Somatic mutations or deletions of TNFAIP3 (6p23) (F1000Res 2018;7:406, Haematologica 2019;104:e558)
- Directly involved in NFκB activation
- Tumor suppressor genes can be silenced in cases of MALT progression (F1000Res 2018;7:406)
- CDKN2A, DAPK1 and CDH1
Sample pathology report
- Esophagus, endoscopic biopsy:
- Squamous epithelium with no significant pathologic changes
- Stomach (greater curvature), endoscopic biopsy of a mass:
- Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) involving gastric mucosa (see comment)
- Stomach (lesser curvature), endoscopic biopsy:
- Antral mucosae with moderate chronic inactive gastritis
- No intestinal metaplasia identified
- Helicobacter pylori present
- Duodenum, endoscopic biopsy:
- Duodenal mucosa with no pathologic changes
- Comment: According to clinical notes, patient is a 60 year old woman who presented with abdominal pain and anemia for the past 10 months. She underwent endoscopic examination that showed large ulcerated noncircumferential lesion on the greater curvature of the stomach, which was biopsied.
- Histologic sections from the mass in the greater curvature show gastric mucosa with dense infiltration of the lamina propria composed predominantly of small to intermediate monocytoid lymphocytes, small lymphocytes (centrocyte-like), plasma cells and eosinophils. The monocytoid lymphocytes show clear cytoplasm, irregular nuclear contour and hyperchromatic chromatin. Lymphoepithelial lesion is extensively present.
- Immunohistochemical studies were performed on the greater curvature lesion and the lymphoma cells were positive for CD20, PAX5, CD43, BCL2 and negative for CD3, CD5, CD10, BCL6 and SOX11. The lymphoma cells showed kappa light chain restriction. CD21 highlighted the follicular dendritic meshwork and Ki67 was ~20% on the neoplastic cells.
- No morphologic findings to support infiltration by lymphoma in esophageal, gastric lesser curvature and duodenum biopsies.
Differential diagnosis
- Reactive follicular hyperplasia (Mod Pathol 2013;26:S88):
- Duodenal type follicular lymphoma (Virchows Arch 2020;476:667):
- Usually incidental finding
- Second duodenal portion, colorectal and stomach
- Multifocal involvement
- Polypoid or nodular lesions
- Centrocytes infiltrate on mucosa and submucosa; spares the muscularis propria
- CD20+, CD10+, BCL2+ (strong), BCL6+
- BCL2 translocation
- Mutations of CREBBP, KMT2D, TNFRSF14 and EZH2
- Mantle cell lymphoma (Virchows Arch 2020;476:667):
- Extramedullary plasmacytoma (Gut Liver 2009;3:334):
- Chronic sialadenitis (Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2009;42:927):
- Related to several mechanisms: autoimmune disease, sialolithiasis and trauma
- Variable glandular destruction and fibrosis
- Lymphoepithelial lesions are common
- Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (Clin Chest Med 2016;37:463):
- Usually bilateral
- Associated with autoimmune disease, infection or immunodeficiency
- Indolent presentation
- Dyspnea, dry cough and systemic symptoms
- Diffuse interstitial infiltrate of polymorphic lymphocytes and plasma cells
- Normal germinal centers can be present
- Destruction of alveolar structure
- Polytypic lymphocytes: CD20+, CD3+, CD4+
- Cutaneous pseudolymphoma (J Cutan Pathol 2020;47:76):
- Related to several causative agents and variable clinical course
- According the clinicopathologic presentation may present in different forms
- Nodular pseudolymphoma:
- Pseudo mycosis fungoides or cutaneous T cell lymphomas:
- Epidermotropic component
- More prominent T cell component
- Intravascular pseudolymphomas:
- Disease confined to skin
- Variable CD30 expression
- Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma (Leuk Lymphoma 2012;53:1032, Am J Clin Pathol 2013;139:515):
Additional references
- Campo: WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th Edition, 2017, Medeiros: Diagnostic Pathology - Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas, 2nd Edition, 2017, Medeiros: Tumors of the Lymph Nodes and Spleen, 4th Series, 2017, Medeiros: Ioachim's Lymph Node Pathology, 5th Edition, 2021
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)?
- Association with infectious agents and autoimmune disorders is rarely described
- Bone marrow involvement is common and detected in up to 90% of patients
- NFκB pathway activation is a shared feature of several subtypes of MALT lymphoma
- Trisomies 3 and 18 are extremely rare in MALT lymphoma
Board review style answer #1
C. NFκB pathway activation is a shared feature of several subtypes of MALT lymphoma. There is an important overlap in the molecular signatures of different subtypes of MALT lymphoma, which involve activation of canonical and noncanonical NFκB pathway.
Comment Here
Reference: MALT - marginal zone
Comment Here
Reference: MALT - marginal zone
Board review style question #2
What is the characteristic immunophenotype of extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)?
- CD20+ / BCL2- / CD10- / BCL6+ / CD43- / EBER-
- CD20+ / BCL2+ / CD10- / BCL6- / CD43+ / EBER-
- CD20+ / BCL2+ / CD10- / BCL6- / CD43- / EBER+
- CD20- / BCL2+ / CD10+ / BCL6- / CD43- / EBER+
Board review style answer #2
B. CD20+ / BCL2+ / CD10- / BCL6- / CD43+ / EBER-. MALT lymphoma cells have a B cell phenotype (CD19+, CD20+, PAX5+) and are usually positive for BCL2 and CD43 and negative for CD10 and BCL6. EBV is not associated with MALT lymphoma.
Comment Here
Reference: MALT - marginal zone
Comment Here
Reference: MALT - marginal zone