Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Balakrishna J. Amyloid. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodesamyloidosis.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Uncommon disease caused by the deposition of abnormal proteins within the soft tissues
Essential features
- Extracellular deposition of amorphous, eosinophilic, hyaline substance
- Amyloid is Congo red+
Terminology
- Amyloid, amyloidosis, amyloid lymphadenopathy
Epidemiology
- Rare
Sites
- Cervical, supraclavicular and mediastinal lymph nodes
- Any lymph node group can be affected
Pathophysiology
- Results from abnormal folding of proteins
- Proteins that form amyloid can be (a) normal proteins that have an inherent tendency to fold improperly, associate and form fibrils and do so when they are produced in increased amounts and (b) mutant proteins that are prone to misfolding and subsequent aggregation
Etiology
- As part of primary systemic amyloidosis
- As part of reactive systemic amyloidosis
- In uremic patients
- In non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- As isolated primary deposits in lymph nodes
Clinical features
- Lymph node enlargement
- In secondary cases, depending on the primary condition
Diagnosis
- Histologic demonstration of amyloid
Laboratory
- If associated with monoclonal proteins of B cell lymphoma, serum and urine protein electrophoresis will demonstrate monoclonal proteins
Radiology description
- None specific
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Prognostic factors
- Generalized amyloidosis tends to have poor prognosis
Case reports
- 46 year old man with localized lymph node light chain amyloidosis (Case Rep Hematol 2015;2015:816565)
- 77 year old woman with primary amyloidosis involving mediastinal lymph nodes diagnosed by EBUS TBNA (Respiratory Medicine CME 2009;2:51)
- 3 patients with AL amyloidosis manifesting as systemic lymphadenopathy (Amyloid 2008;15:117)
- Massive cervical and abdominal lymphadenopathy caused by localized amyloidosis (J Clin Oncol 2007;25:343)
Treatment
- Treatment of the associated condition
- Treatments inhibiting protein misfolding and fibrillogenesis are under study
Gross description
- Enlarged lymph node with firm waxy cut surfaces
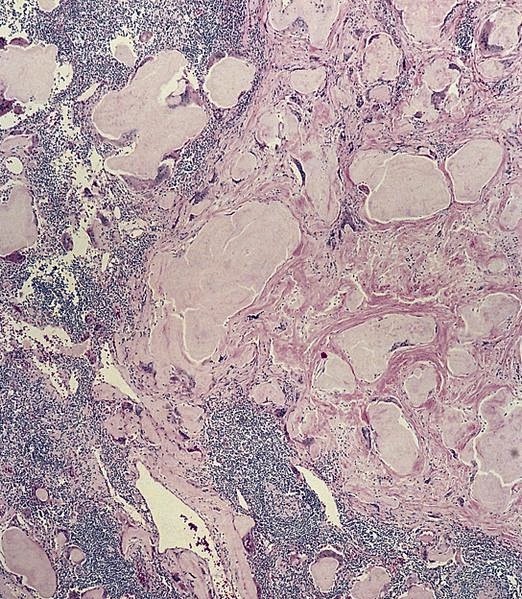
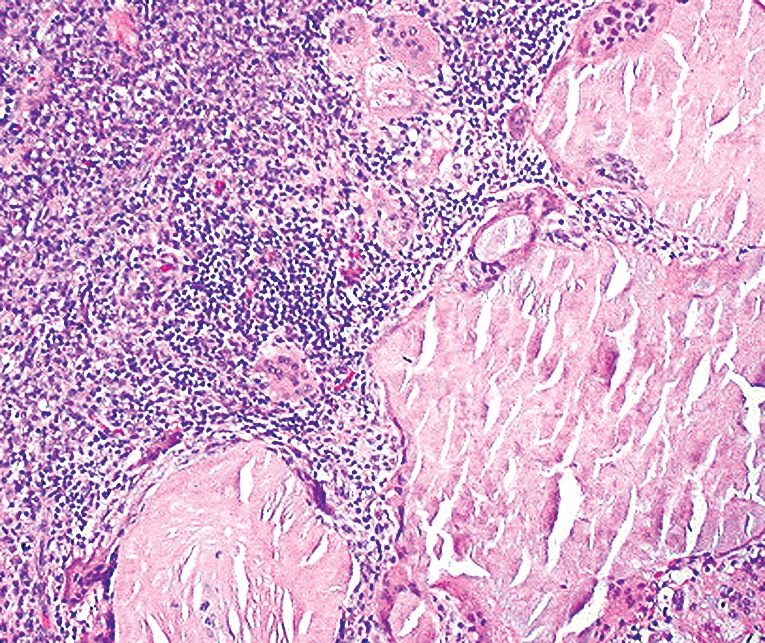
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Hyaline-like amorphous eosinophilic depositions positive for Congo red staining
- Polarizing microscope shows unique yellowish green birefringence
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Hyaline-like amorphous material on cytology smears
- Acellular and associated with connective tissue
- Eosinophilic to blue / green with Pap stain, deep blue with Diff-Quik
Positive stains
Electron microscopy description
- Clusters of round / oval nodules, often enclosed with cytoplasmic processes of macrophages or reticulum cells
- Fibrils are nonbranching, 7.5 nm in diameter, form parallel bundles close to cytoplasmic membranes
Differential diagnosis