Cite this page: Balakrishna J, Sharabi A. Other pigment / foreign material. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodesotherpigment.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Asbestos
Terminology
Epidemiology
Sites
Clinical features
Diagnosis
Radiology description
Prognostic factors
Case reports
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
Asbestos with mesothelioma:
Gross description
Microscopic (histologic) description
Differential diagnosis
Additional references
- Also called Ferruginous bodies
Epidemiology
- Usually due to industrial / occupational exposure
Sites
- Most common in thoracic / hilar lymph nodes
- Concentration of asbestos fibers in lymph nodes is 2 - 3x higher than in lung
Clinical features
- Inhaled asbestos fibers have iron protein mucopolysaccharide coating
- Enlarged lymph nodes are common
- Associated symptoms / signs of pulmonary asbestosis
Diagnosis
- Biopsy of affected lymph node
- Bleach digestion for confirmation
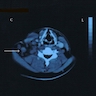
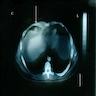
Radiology description
- Mediastinal / hilar lymphadenopathy
Prognostic factors
- Pulmonary asbestosis is a risk factor for lung carcinoma and mesothelioma
Case reports
- 26 year old man with mesothelioma due to asbestos exposure (Case Rep Med 2011;2011:951732)
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
Asbestos with mesothelioma:
Gross description
- Lymph nodes may be enlarged but show no significant abnormalities on cut surface
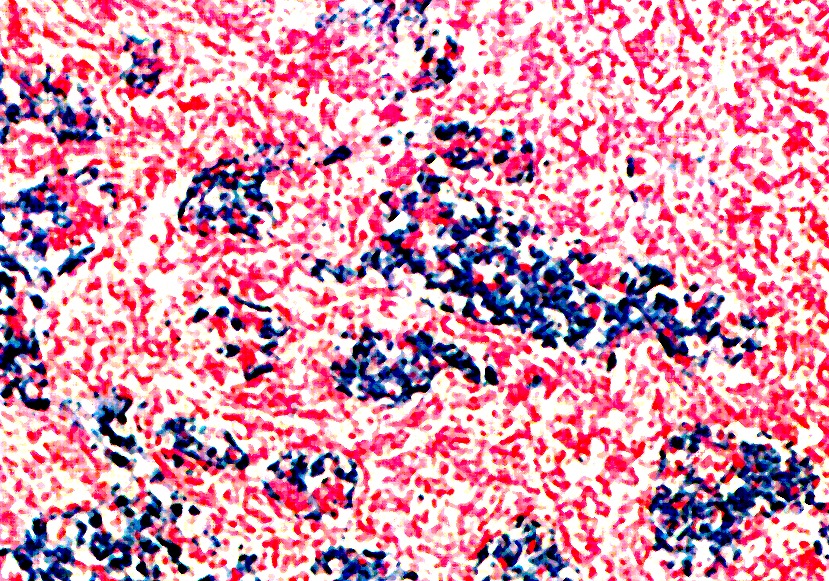
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Asbestos bodies are golden-brown, beaded or dumbbell shaped structures with a thin, translucent core
Differential diagnosis
- Pseudoasbestos bodies
- Other ferruginous bodies
Additional references
Gold
Definition / general
Sites
Clinical features
Diagnosis
Laboratory
Radiology description
Case reports
Gross description
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
Additional references
- Colloidal gold is used for anti-tumor therapy, to treat autoimmune diseases and for drug delivery (Wikipedia: Colloidal gold [Accessed 22 June 2018])
- Lymphadenopathy and lymph node infarction are uncommon complications of gold injections; occur via accumulation of gold particles in macrophages
Sites
- Cervical, axillary, mesenteric lymph nodes, depending on route of administration
Clinical features
- Tender enlarged lymph nodes
- Benign process with resolution of symptoms on withdrawal of gold treatment
Diagnosis
- Biopsy
- Darkfield microscopy and autometallography methods demonstrate gold nanoparticles 15 to 50 nm
Laboratory
- Polymorphonuclear neutrophilia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
- Hepatic toxicity
Radiology description
- Gold deposits can mimic intranodal axillary calcific deposits on mammography in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2013;26:28)
Case reports
- 34 year old woman with lymphadenopathy and lymph node infarction (J Clin Pathol 2001;54:562)
- Intramammary lymph node gold deposits simulating microcalcifications on mammogram (Hum Pathol 1988;19:992)
- Lymphadenopathy and lymph node infarction (Am J Med 1986;80:537)
Gross description
- Extensive necrosis of lymph node
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Subtotal or complete infarction with peripheral rim of organizing granulation tissue in region of subcapsular sinus
- Small focus of residual viable lymphoid tissue has features of follicular hyperplasia
- Center of node has ghost outlines of necrotic cells
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
- Immunohistochemical stains confirm the reactive nature of the process
Differential diagnosis
- Lymphoma
- Vascular thrombosis, infections and mechanical pressure can also cause infarction of lymph nodes
Additional references
Iron
Definition / general
Sites
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Diagnosis
Radiology description
Prognostic factors
Case reports
Treatment
Gross description
Gross images
Images hosted on other servers:
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Mark R. Wick, M.D.
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
Differential diagnosis
Additional references
- Iron deposition in lymph nodes is rare
- Also called hemosiderosis
- May be associated with hemochromatosis
Sites
- Portal, splenic, mesenteric or axillary, depending on the primary cause
Pathophysiology
- Parenteral iron administration
- Multiple transfusions: red blood cells are lysed and iron is deposited in macrophages in the liver and spleen followed by drainage to adjacent lymph nodes
- Hereditary hemosiderosis: abnormalities in iron transport - most common is HFE1 gene mutation; also mutations in TfR2, HJV, HAMP, ferroportin-V162del (Hepatology 2005;42:466)
- Anemia of inflammation: associated with rheumatoid arthritis, gout (Ann Rheum Dis 1970;29:81)
Clinical features
- Depends on the primary cause
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Diagnosis
- Biopsy with Perls Prussian blue stain
Radiology description
- CT: enlarged and hyperdense lymph nodes (AJR Am J Roentgenol 1981;136:1191)
Prognostic factors
- Depends on the primary cause, severity and extent of the disease
Case reports
- Women, 19 to 49 years, with lymphadenopathy after single infusion of iron dextran (J Clin Pathol 1968;21:492)
Treatment
- Reduce iron overload, treat the primary cause
Gross description
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Gross images
Images hosted on other servers:
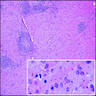
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Follicular hyperplasia, sinus histiocytosis, golden brown pigment deposition
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Mark R. Wick, M.D.
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Prominent phagocytic reticulum cells containing vacuoles, myelin figures, lipid droplets and very large lysosomal bodies with fine electron dense granules concentrated in these lysosomal bodies and in the cytoplasm, which show molecular structure of ferritin
Differential diagnosis
- Charcoal laden macrophages
- Hemazoin pigment: seen in malaria
- Melanin pigment deposition: melanoma, dermatopathic lymphadenitis
- Tattoo pigment
Additional references
Lipogranuloma
Definition / general
Case reports
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Also called lipophagic granuloma
- Secondary to various inflammatory and neoplastic conditions or primary lesion of lymph node
- In West, commonly due to mineral oil ingestion or total parenteral nutrition
Case reports
- 27 year old woman with prior giant cell tumor (Acta Cytol 2002;46:772)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Giant cells (mono or multinuclear) with foamy and vacuolated cytoplasm
Melanosis
Definition / general
Terminology
Epidemiology
Sites
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Case reports
Gross description
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
Additional references
- A rare manifestation of a completely regressed melanoma
Terminology
- Tumoral melanosis
- Nodular melanosis
- Nodal melanosis
Epidemiology
- Very rare in lymph nodes
Sites
- Sentinel lymph nodes of regressed melanoma
- Mesenteric lymph nodes
Pathophysiology
- Possibilities include:
- A regressed focus of metastatic melanoma
- Melanophages migrating to the lymph node from the primary lesion
Clinical features
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Yellow brown spindle bodies in mesenteric nodes may be due to melanosis coli (Histopathology 1978;2:47)
- The paucity of cases precludes adequate evaluation of long term implications and treatment outcomes
Case reports
- 36 year old man with lymph node melanosis and metastatic melanoma of unknown primary (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:1332)
- 83 year old man with melanosis coli involving pericolonic lymph nodes associated with the herbal laxative Swiss Kriss (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:565)
- Tumoral melanosis involving the sentinel lymph nodes (J Cutan Pathol 2007;34:284)
- Lymph node melanosis from a primary cutaneous lesion combining a nodular (tumoral) melanosis and a congenital dermal melanocytic nevus (Am J Dermatopathol 2012;34:653)
Gross description
- Enlarged lymph nodes with or without brown pigment deposition
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Subcapsular and sinusoidal accumulation of pigmented cells with vesicular chromatin and inconspicuous nucleoli
- Cells may be spindle shaped or epithelioid
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
Additional references