Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: van den Akker TA, Feldstein J. Toxoplasmosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodestoxoplasma.html. Accessed September 4th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Lymphadenitis caused by infection with the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii
Essential features
- Worldwide distribution:
- Toxoplasma infection is seroprevalent in approximately 33% of the world's population
- 10 - 20% of patients with acute infection may develop cervical lymphadenopathy (Centers for Disease Control DPDx: Toxoplasmosis [Accessed 6 January 2022])
- Most common parasite infection in the U.S.
- Cats are the only known definitive host (Centers for Disease Control DPDx: Toxoplasmosis [Accessed 6 January 2022])
- Humans infected through contaminated soil, pet litter boxes and ingesting undercooked meat
- Primary infection is subclinical
- Unilateral posterior cervical lymphadenopathy is classic presentation
- Infection during pregnancy can be detrimental to the fetus: congenital toxoplasmosis
- Histologic triad on microscopy (Ioachim: Ioachim’s Lymph Node Pathology, 4th Edition, 2008):
- Reactive germinal centers
- Perifollicular / interfollicular epithelioid histiocytes
- Patches of monocytoid B cells
Terminology
- Toxoplasma lymphadenitis
- Glandular toxoplasmosis
- Piringer-Kuchinka lymphadenopathy
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Common parasite worldwide (Centers for Disease Control DPDx: Toxoplasmosis [Accessed 6 January 2022])
- Prevalent in warm and humid climates
- Affects children and young adults most commonly
- No gender predilection
- 1.9% IgM and 32.9% IgG seroprevalence globally (Sci Rep 2020;10:12102)
- Most common parasitic infection in the U.S.
- 11% of U.S. population greater than 6 years have been infected with T. gondii (Centers for Disease Control DPDx: Toxoplasmosis [Accessed 6 January 2022])
- Humans can become infected by (Centers for Disease Control DPDx: Toxoplasmosis [Accessed 6 January 2022]):
- Eating undercooked meat of animals harboring tissue cysts
- Consuming food or water contaminated with cat feces
- Exposure to environmental samples
- Fecal contaminated soil
- Changing pet cat litter box
- Blood transfusion or organ transplantation
- Transplacental transmission from mother to fetus
- Greatest risk of infection in first trimester
- Risk of stillbirth in seropositive mothers
- Every year about 400 - 4,000 children are infected at birth in the U.S. (Am Fam Physician 2003;67:2131)
- Often an opportunistic infection of immunocompromised patients
- Infection may result from reactivation in patients with cancer or diabetes
- Asymptomatic infection of immunocompetent individuals
Sites
- Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan which can invade many cell types (Ioachim: Ioachim’s Lymph Node Pathology, 4th Edition, 2008)
- Lymph nodes are commonly affected: unilateral posterior cervical node is characteristic
- Other lymph nodes can often be involved
- Generalized lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly unusually occurs
- In the human host, the parasites form tissue cysts in skeletal muscle, myocardium, brain and eyes; these cysts may remain throughout the life of the host
Pathophysiology
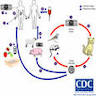
- Cats are the only known definitive host for sexual stage of reproduction (Centers for Disease Control DPDx: Toxoplasmosis [Accessed 6 January 2022])
- Cats become infected after consuming intermediate hosts harboring tissue cysts or by ingestion of sporulated oocysts
- Trophozoites multiply in intestine and produce oocytes
- Unsporulated oocysts are shed in the cat's feces
- Oocysts are usually shed for 1 - 3 weeks and in large numbers, up to several million (Lancet 2004;363:1965)
- Oocysts take 1 - 5 days to sporulate in the environment and become infective
- Intermediate hosts in nature (including humans, birds and rodents) become infected after ingesting soil, water or plant material contaminated with oocysts
- Through ingestion of contaminated soil or water
- Ingestion of infected, undercooked meat
- Oocysts are degraded by digestive enzymes and transform into trophozoites
- Tachyzoites are the crescentic / oval shaped, rapidly multiplying stage of the parasite (Lancet 2004;363:1965)
- Tachyzoites are released into the intestine
- Enter all nucleated cells, form cytoplasmic vacuoles, replicate, where finally host cells are disrupted, releasing tachyzoites (Lancet 2004;363:1965)
- Carried by macrophages and spread by lymphatics and blood vessels to infect tissues
- Tachyzoite form leads to the strong inflammatory response and tissue destruction, causing the clinical manifestations of the infection (Lancet 2004;363:1965)
- Tachyzoites are transformed into bradyzoites under the pressure of the immune response to form cysts (thousands of bradyzoites per cyst) and survive the lifetime of the host
Etiology
- Toxoplasmosis gondii infection
Clinical features
- Immunocompetent individuals:
- Asymptomatic infection with or without nontender, nonsuppurative lymphadenopathy (Lancet 2004;363:1965)
- Mild illness in the form of malaise, fever, myalgia (10 - 20%) (Medeiros: Diagnostic Pathology - Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas, 2nd Edition, 2017)
- Disease is usually benign and self limited with resolution in weeks or months
- Immunocompromised patients (Centers for Disease Control DPDx: Toxoplasmosis [Accessed 6 January 2022]):
- Caused by reactivation of chronic infection
- Often have central nervous system (CNS) disease
- Systemic disease occurs in severe immunodeficiency
- Myocarditis, pneumonitis, chorioretinitis, encephalitis
- In AIDS, toxoplasmic encephalitis is the most common cause of intracerebral mass lesions
- Congenital toxoplasmosis:
- In the U.S., the age adjusted seroprevalence among women of childbearing age (15 - 44 years) was 9% in 2009 to 2010 (Am J Trop Med Hyg 2014;90:1135)
- Third trimester has the highest risk of transmission
- First trimester poses greatest damage to fetus
- Neonatal clinical manifestations vary widely:
- Hydrocephalus, microcephaly, intracranial calcifications, chorioretinitis, strabismus, blindness, epilepsy, psychomotor or mental retardation, petechia due to thrombocytopenia and anemia (Lancet 2004;363:1965)
- In congenital infection, patients are often asymptomatic until the second or third decade of life, when lesions develop in the eye
- Rarely, ocular infection may lead to visual loss
- Ocular Toxoplasma infection, an important cause of retinochoroiditis in the U.S., can be the result of congenital infection or infection after birth
- T. gondii chorioretinitis develops in ~21,000 persons each year in the U.S. (Am J Trop Med Hyg 2014;90:794)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is usually achieved by serology, although tissue cysts may be observed in stained biopsy specimens
- Diagnosis of congenital infections can be achieved by detecting T. gondii DNA in amniotic fluid using molecular methods such as PCR (Centers for Disease Control DPDx: Toxoplasmosis [Accessed 6 January 2022])
Laboratory
- Sabin-Feldman dye test
- Highly sensitive and specific
- Requires live organisms so has been replaced with indirect immunofluorescence (IF)
- IF and enzyme immunoassays measure antibodies to T. gondii
- Can measure immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG antibodies to cell wall antigens
- IgM antibodies detected within a few days after infection
- IgG antibodies detected at 6 - 8 weeks
- Latex agglutination test and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- PCR can be used to amplify T. gondii DNA
- References: Ioachim: Ioachim’s Lymph Node Pathology, 4th Edition, 2008, Medeiros: Diagnostic Pathology - Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas, 2nd Edition, 2017
Prognostic factors
- Immunocompetent individuals (Lancet 2004;363:1965):
- Self limiting infection
- Immunodeficient patients:
- Risk of disseminating infection
- Almost always due to reactivation of chronic infection (Lancet 2004;363:1965)
- Encephalitis, chorioretinitis, pneumonia, multiple organ involvement or death
Case reports
- 11 month old HIV / AIDS girl with cerebellar toxoplasmosis (Neurol Sci 2012;33:1423)
- 29 year old man with disseminated toxoplasmosis associated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocystosis after kidney transplant (Transpl Infect Dis 2019;21:e13154)
- 33 year old pregnant woman with axillary lymphadenopathy (Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2020;102:e167)
- Squash preparation of a brain biopsy (Creepy Dreadful Wonderful Parasites: Case of the Week 519 [Accessed 6 January 2022])
Treatment
- Combination therapy of pyrimethamine and sulfadiazime with folinic acid (Centers for Disease Control DPDx: Toxoplasmosis [Accessed 6 January 2022], Lancet 2004;363:1965)
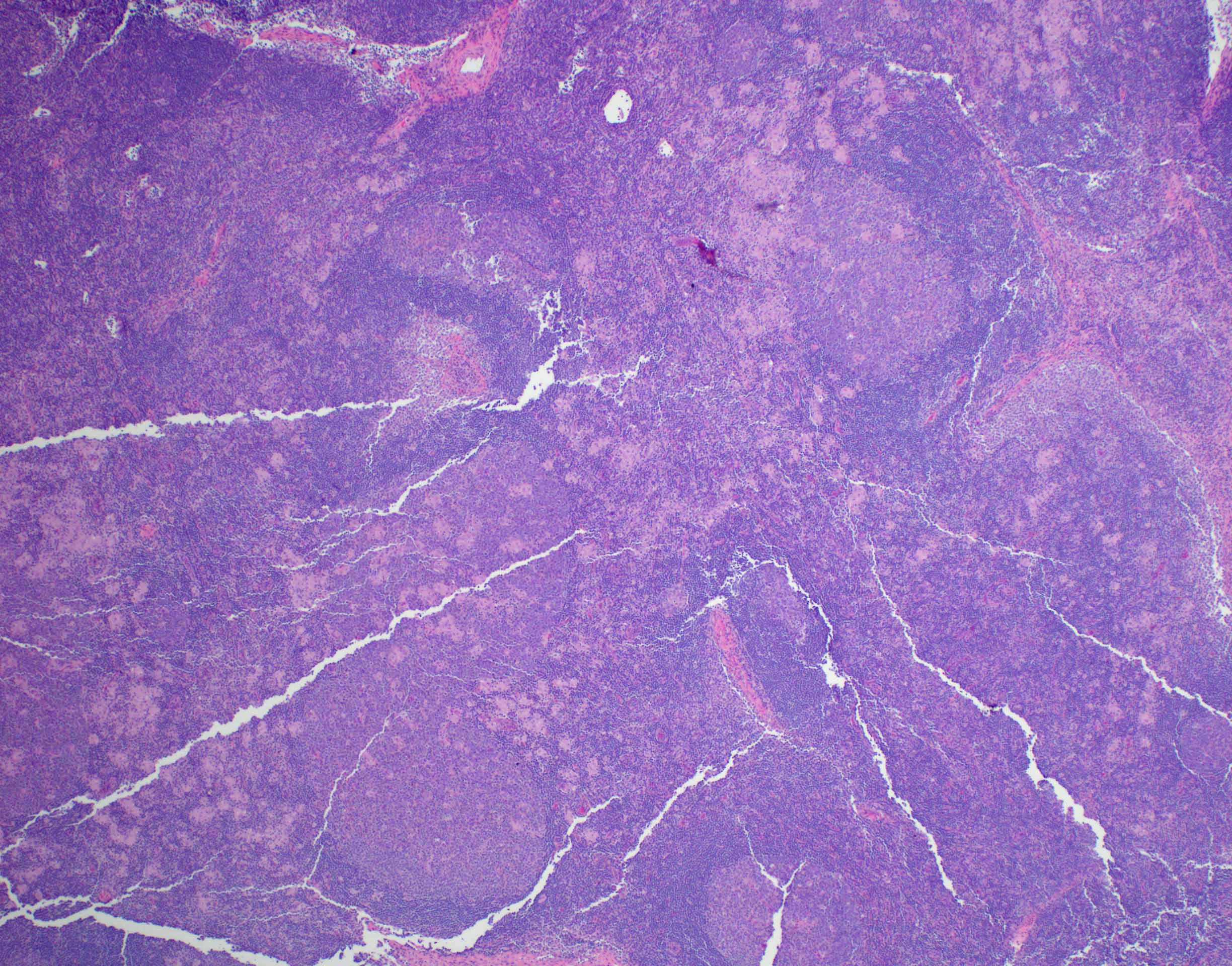
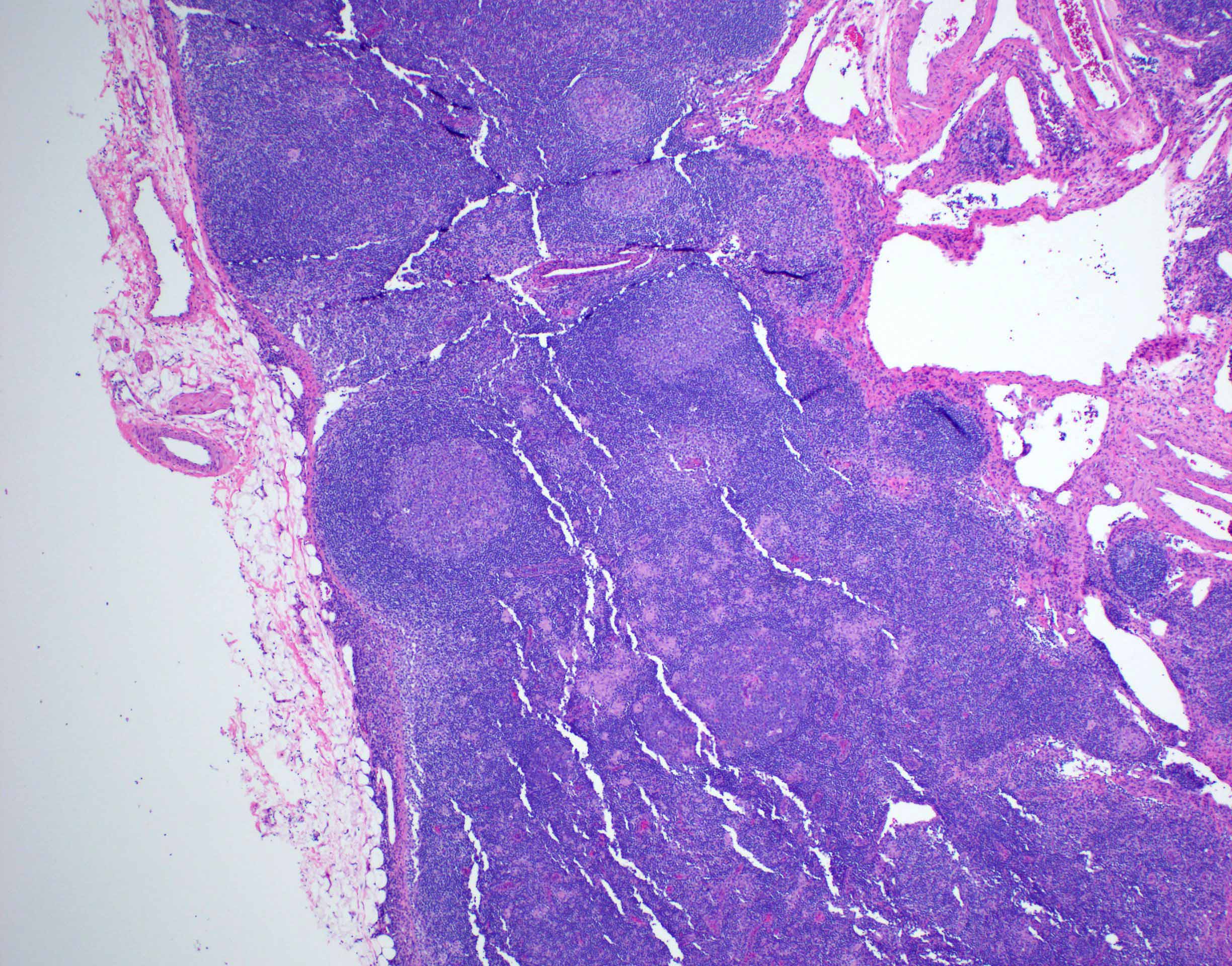
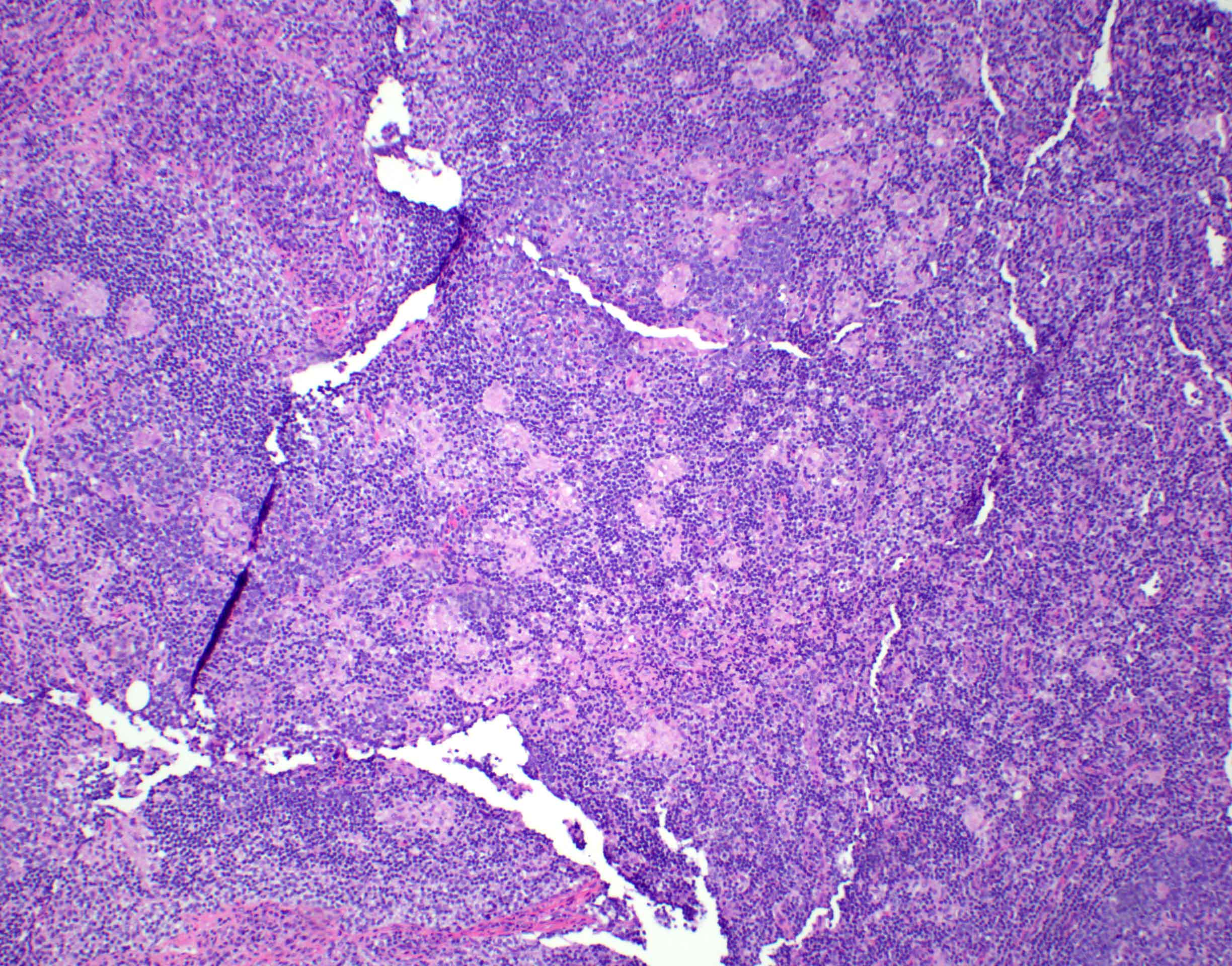
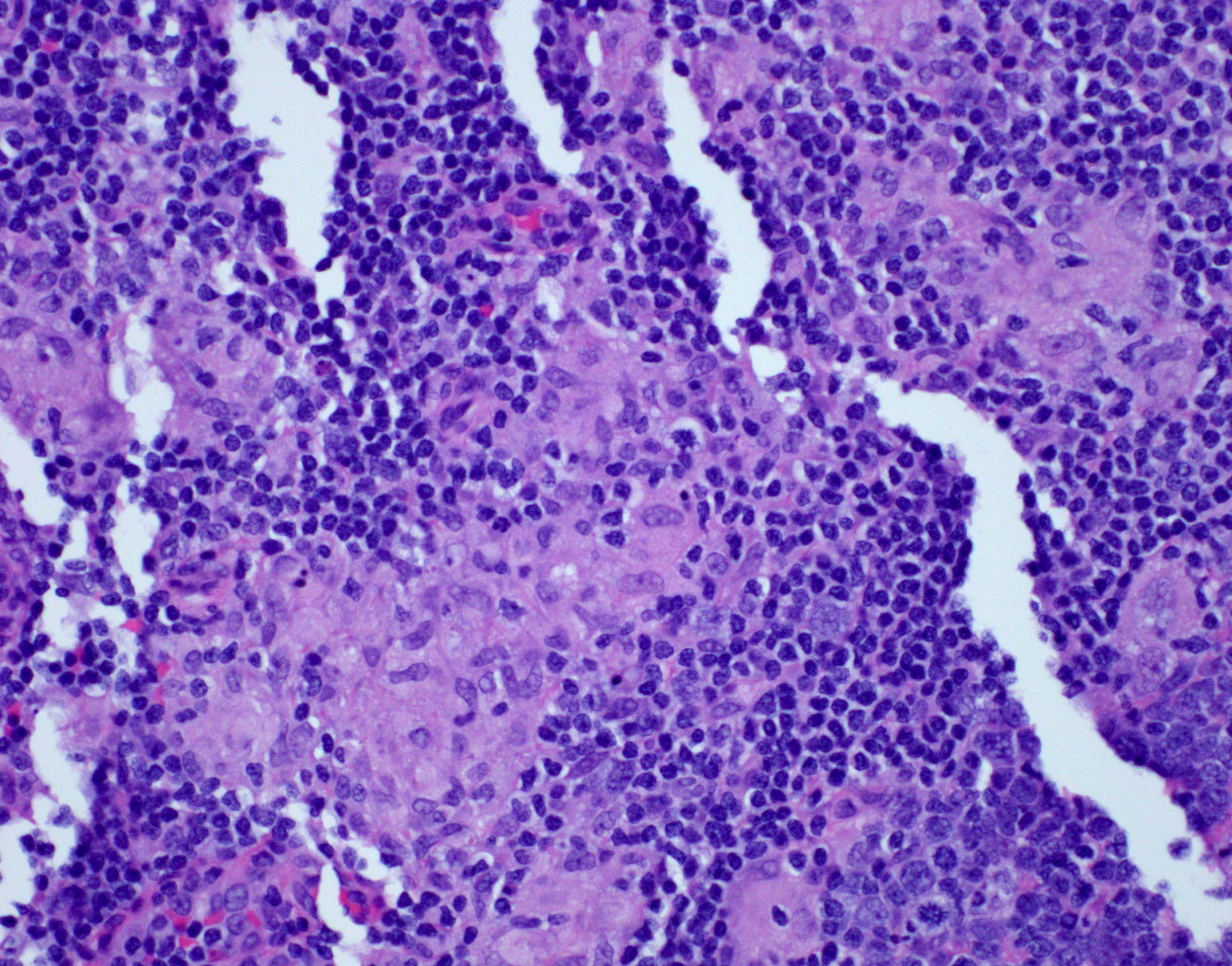
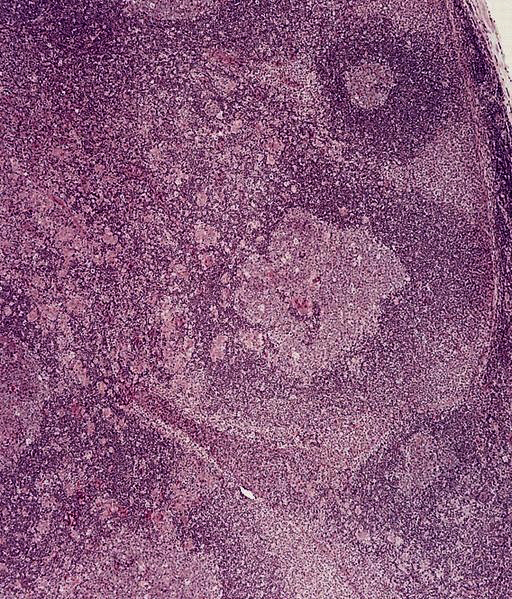
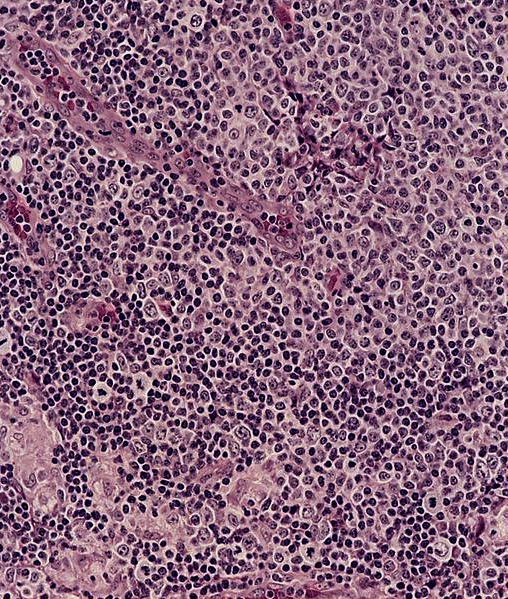
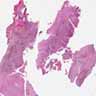
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Lymph node
- Preserved architecture
- Capsule / pericapsule: with minimal involvement
- Sinuses with distended monocytoid B cells
- Large cells with sharp cell boarders, clear cytoplasm and darkly stained nuclei
- Follicles with florid reactive follicular hyperplasia
- Numerous tingible body macrophages
- Germinal centers with ragged, indistinct margins
- Interfollicular and paracortical areas with epithelioid histiocytes
- Invade germinal centers
- Form collections of < 25 histiocytes (microgranuloma)
- Medullary cords with plasma cells and immunoblasts
- Toxoplasma cysts and bradyzoites are rare (1% of cases)
- References: Ioachim: Ioachim’s Lymph Node Pathology, 4th Edition, 2008, Medeiros: Diagnostic Pathology - Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas, 2nd Edition, 2017
Microscopic (histologic) images
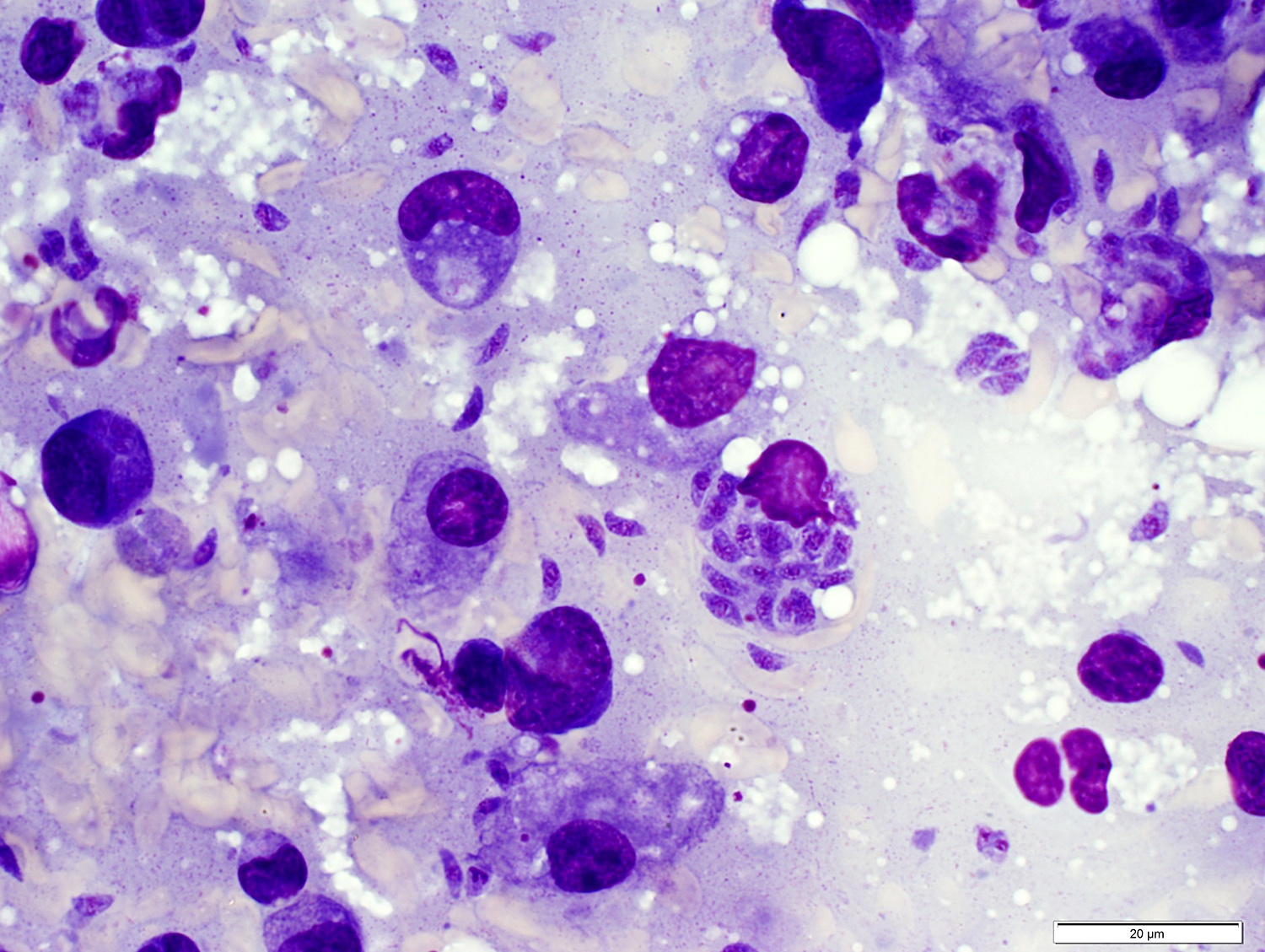
Cytology description
- Cytologic features based on fine needle aspiration biopsy:
- Polymorphous cell population
- Small and large lymphocytes
- Clusters of epithelioid histiocytes (microgranulomas)
- Parasitic cysts can be detected, rarely
- Polymorphous cell population
- References: Ioachim: Ioachim’s Lymph Node Pathology, 4th Edition, 2008, Medeiros: Diagnostic Pathology - Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas, 2nd Edition, 2017
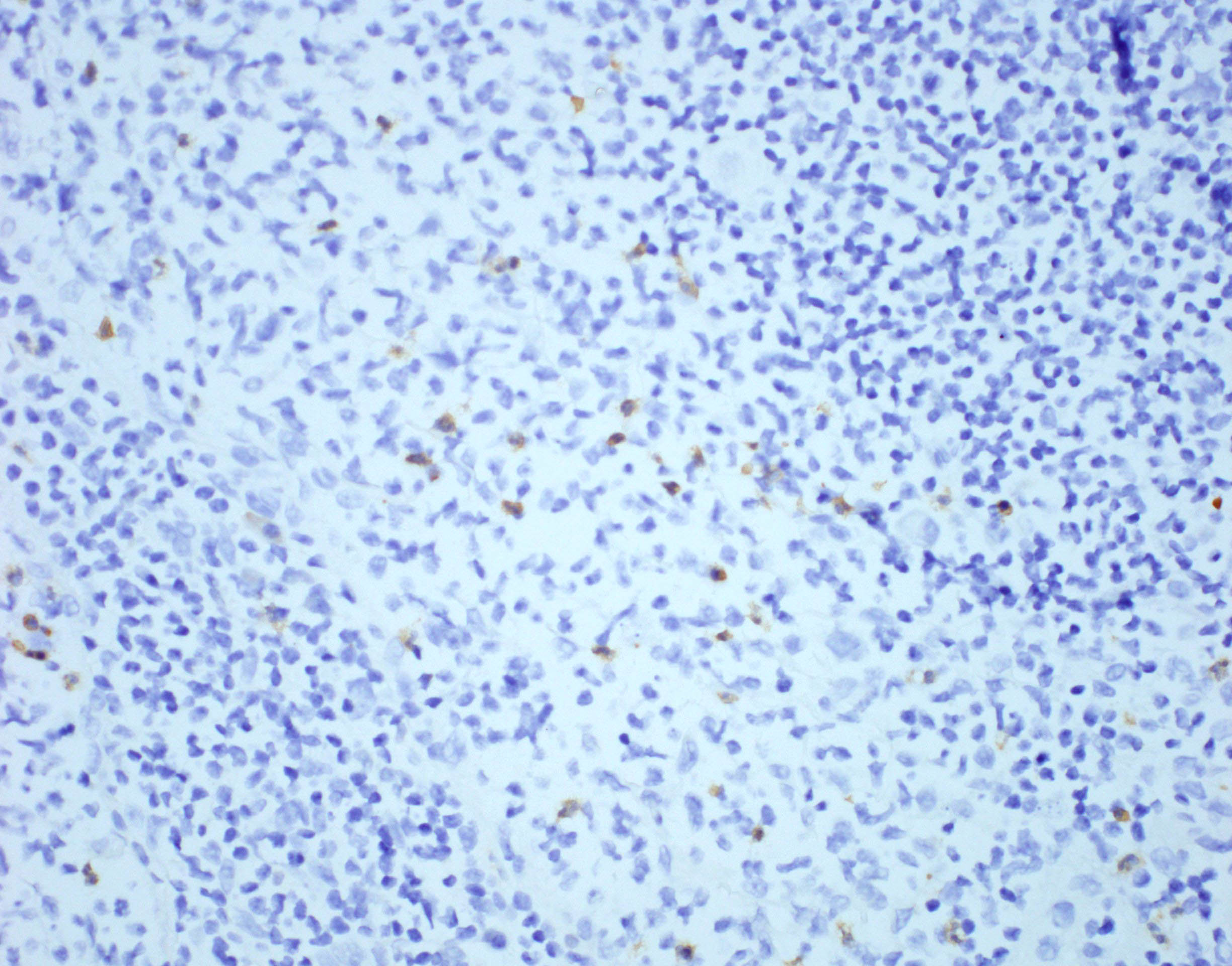
Positive stains
- Anti-T. gondii antibodies can detect parasites in tissue
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
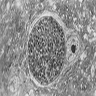
- Distinctive features on electron microscopy:
- Paired organelles, dense bodies
- Concoid nuclei at rounded posterior end
- Double layered pellicles
- References: Ioachim: Ioachim’s Lymph Node Pathology, 4th Edition, 2008, Medeiros: Diagnostic Pathology - Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas, 2nd Edition, 2017
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- Toxoplasma genomes are detected by conventional and nested PCR
Videos
Classic histomorphology of toxoplasma lymphadenitis
Great teaching case of cerebral toxoplasmosis
Sample pathology report
- Lymph node, right inguinal, excisional biopsy:
- Reactive lymphoid follicular hyperplasia, monocytoid B cell hyperplasia and aggregates of epithelioid histiocytes, suggestive of toxoplasma lymphadenitis (see comment)
- Comment: The classic triad present in this case (follicular hyperplasia, intrafollicular clusters of epithelioid cells and aggregates of monocytes) is reported to have a 91% specificity for toxoplasma lymphadenitis. There is no evidence of lymphoma. The morphologic findings are very suggestive of toxoplasmosis. Serologic studies are recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
- Microscopic description:
- Right cervical lymph node: The lymph node is enlarged and has a preserved architecture with a thin capsule and open sinuses. There is evidence of reactive lymphoid follicular hyperplasia. In addition, numerous small, well defined aggregates of epithelioid histiocytes are noted, including within the germinal centers. Focally, monocytoid B cell hyperplasia is present. There is no morphologic evidence of lymphoma.
- Special stains for AFB and GMS are negative for microorganisms.
- Immunohistochemical staining performed on block A1 shows that the CD20+ B cells are confined to the germinal centers, while the CD3+ T cells are interfollicular. Monocytoid B cells also express CD20. Immunohistochemical stain for toxoplasma is positive. There is no staining for cytomegalovirus. In situ hybridization for EBV encoded RNA (EBER) is negative.
- Note: Control slides show appropriate reactivity.
- Left inguinal lymph node for flow cytometry:
- The following analytes were tested: Kappa, Lambda, CD5, CD23, CD10, CD20, CD19, CD45, sCD3, CD57, CD4, CD7, CD8, CD2 (total of 14)
- Flow cytometry interpretation:
- Cytospin: Morphologic evaluation of Diff-Quik stained cytospin shows no increase in atypical lymphocytes.
- Flow cytometry: Analysis was performed with the above antigens. The T cells show no loss of pan T cell antigens. The B cells are polytypic. The findings provide no evidence of a non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Sarcoid lymphadenopathy:
- Well formed granulomas with multinucleated giant cells
- Usually lacks monocytoid B cells (Medeiros: Diagnostic Pathology - Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas, 2nd Edition, 2017)
- HIV lymphadenitis:
- Early stages of HIV lymphadenitis may mimic toxoplasmosis
- Pattern A: aggregates of monocytoid cells and florid follicular hyperplasia
- May lack clusters of epithelioid cells or may be present
- HIV p24 stains positive
- Leishmaniasis lymphadenitis:
- Histomorphologically very similar
- Multinucleated giant cells present
- Necrosis and fibrosis present with Leishmania infection
- Histiocytes contain Leishman-Donovan bodies within the cytoplasm (Medeiros: Diagnostic Pathology - Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas, 2nd Edition, 2017)
- Electron microscopy demonstrates presence of rod shaped kinetoplast and target shaped basal body
- Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy:
- Paracortical distribution of of histiocyte collections, pigment and lipids
- Histiocytes with twisted nuclei
- S100+, CD1a (+ in a subset) (Medeiros: Diagnostic Pathology - Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas, 2nd Edition, 2017)
Practice question #1
Which feature is included in the the classic histologic pattern of toxoplasmosis lymphadenitis?
- Fibrosis with necrosis
- Florid follicular hyperplasia, perifollicular epithelioid histiocytes and patches of monocytoid B cells
- Necrosis without neutrophils
- Reactive follicular hyperplasia, T cells and a lack of histiocytes
- Well formed granulomas with multinucleated giant cells
Practice answer #1
B. The histologic triad of Toxoplasma lymphadenitis includes reactive follicular hyperplasia, perifollicular / interfollicular epithelioid histiocytes and aggregates of monocytoid B cells.
Comment Here
Reference: Toxoplasmosis
Comment Here
Reference: Toxoplasmosis
Practice question #2
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii?
- Although prevalent worldwide, T. gondii is relatively uncommon in the U.S.
- Cysts containing tachyzoites localize in tissues (skeletal muscle, brain and eyes)
- Oocysts are shed, unsporulated, in the feces of cats and sporulate in the environment to become infective
- Rodents, cats and birds are definitive hosts, while humans are intermediate hosts
Practice answer #2
C. Oocysts are shed, unsporulated, in the feces of cats and sporulate in the environment to become infective. Cats are the only definitive host, while birds, rodents and humans are intermediate hosts. T. gondii is the most common parasite in the U.S. Oocysts transform into tachyzoites after ingestion. Tachyzoites localize in tissues and develop into tissue cysts containing bradyzoites.
Comment Here
Reference: Toxoplasmosis
Comment Here
Reference: Toxoplasmosis