Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Schmieg J, Auerbach A. T cell / histiocyte rich LBCL. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomadiffusetcell.html. Accessed September 17th, 2025.
Definition / general
- T cell / histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma (THRLBCL) is a large B cell lymphoma in which there are scattered neoplastic B cells that compose < 10% of the total cells and are seen in a background of numerous reactive small T cells and histiocytes with no significant small B cell component
- Subset of cases of THRLBCL are known to transform from nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL)
- There is no significant difference in the diagnostic criteria for THRLBCL in the WHO 5th edition versus the International Consensus Classification (ICC)
Essential features
- Typically, an aggressive lymphoma that may involve several anatomic sites and may be resistant to chemotherapy
- Often a diffuse growth pattern (Virchows Arch 2011;459:557)
- Neoplastic cells compose < 10% of total cells and are often scattered and not in aggregates (Virchows Arch 2011;459:557)
- Reactive cells compose > 90% of total cells with numerous small T cells and histiocytes but few reactive B cells
- Neoplastic B cells are positive for pan B cell markers and CD45 but typically negative for CD15 and CD30
Terminology
- T cell rich B cell lymphoma
- B cell lymphoma rich in T cells and simulating Hodgkin disease
- Histiocyte rich / T cell rich large B cell lymphoma
- T cell rich / histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma
- Histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma
- Secondary THRLBC has been used to designate cases of T cell / histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma that has progressed from NLPHL
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Usually middle aged adults or older, although rare pediatric cases are noted
- Mild preferential involvement in men compared to women
- In the United States, Black people are more often affected than White people
- References: Blood 2022;140:1229, Leukemia 2022;36:1720
Sites
- Typically involves lymph nodes but is also often detected in bone marrow, spleen and liver with a high stage at diagnosis (stage III - IV)
Pathophysiology
- Cells of origin are germinal center B cells that show somatic hypermutation
- Overlap between THRLBCL and NLPHL with some patients having both types of lymphoma either synchronously or metachronously (Pathology 2020;52:142)
- Both tumors have some similarities in their immunophenotype
- JUNB, DUSP2, SGK1, SOCS1 and CREBBP alterations have been detected in THRLBCL and in NLPHL variant (Haematologica 2019;104:330)
- Gene expression profiles for THRLBCL and NLPHL are similar
- This is thought to be from a proinflammatory host response with expression of interferons (such as IL4) and metal binding proteins (such as MT2A)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Patients often have B symptoms and are usually diagnosed at a high stage of disease (stage III - IV) unlike NLPHL, which is typically diagnosed at a lower stage (stage I - II)
- International prognostic index (IPI) score is usually intermediate risk or high risk
- Disease is often refractory to the chemotherapy regimens currently in use (Leuk Lymphoma 2019;60:3426)
Diagnosis
- Lymphadenopathy is often detected by clinical exam and by imaging studies with PET / CT scans looking for metabolically active lymph nodes
- Subsequent excision of a mass or lymph node with morphology exam and immunohistochemistry is necessary for an accurate diagnosis
- References: Blood 2022;140:1229, Leukemia 2022;36:1720
Laboratory
- Patients typically have elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Radiology description
- PET / CT scans show hypermetabolic lymphadenopathy with elevated maximum standard uptake value (SUV max)
- Total metabolic tumor volume is often more than that seen in diffuse large B cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (DLBCL, NOS) and NLPHL; splenomegaly and hepatomegaly are also frequently seen
- References: Blood 2022;140:1229, Leukemia 2022;36:1720
Prognostic factors
- Overall 5 year survival rate is 66% (Leuk Lymphoma 2019;60:3426)
- International Prognostic Index (IPI) score is used for risk stratification
- References: Blood 2022;140:1229, Leukemia 2022;36:1720
Case reports
- 29 year old woman with swelling of the right mandible (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:711)
- 47 year old man with CD5+ tumor (Mod Pathol 2002;15:1051)
- 52 year old woman with THRLBCL of the thymus (Case Rep Hematol 2016;2016:2942594)
- 53 year old man with hypersplenism (Oxf Med Case Reports 2022;2022:omac123)
- 60 year old woman with multiple erythematous umbilicated nodules on her left upper back (Medicine (Baltimore) 2023;102:e33407)
- 73 year old man with primary CNS tumor (Rare Tumors 2015;7:6084)
Treatment
- Chemotherapy is utilized to treat this lymphoma
- Rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone (R-CHOP) is most commonly used but may not be effective (Blood 2007;109:1857)
- References: Blood 2022;140:1229, Leukemia 2022;36:1720, Acta Haematol 2022;145:310
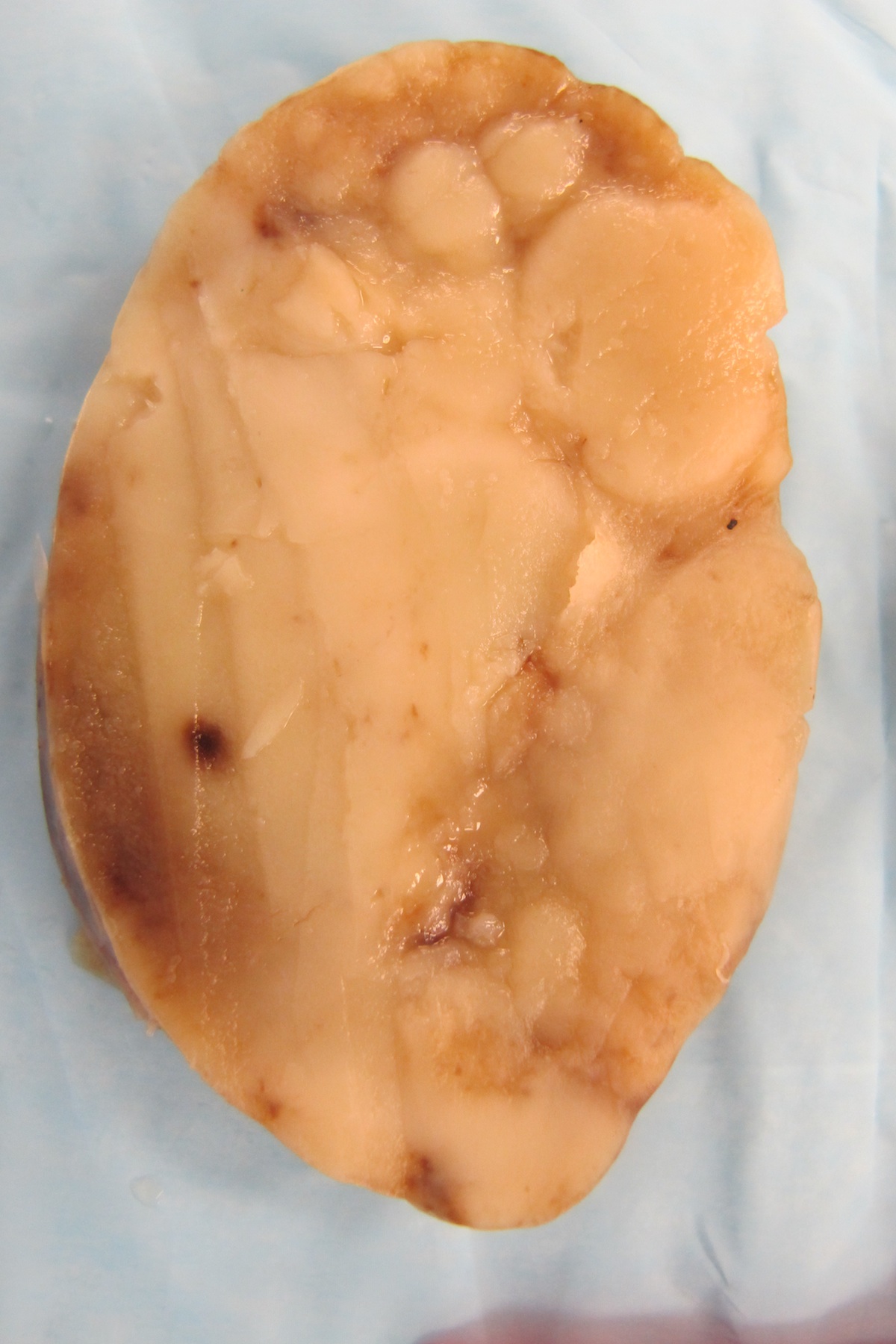
Gross description
- Lymph nodes are typically enlarged with a homogenous gray appearance on cut surface and no nodularity
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
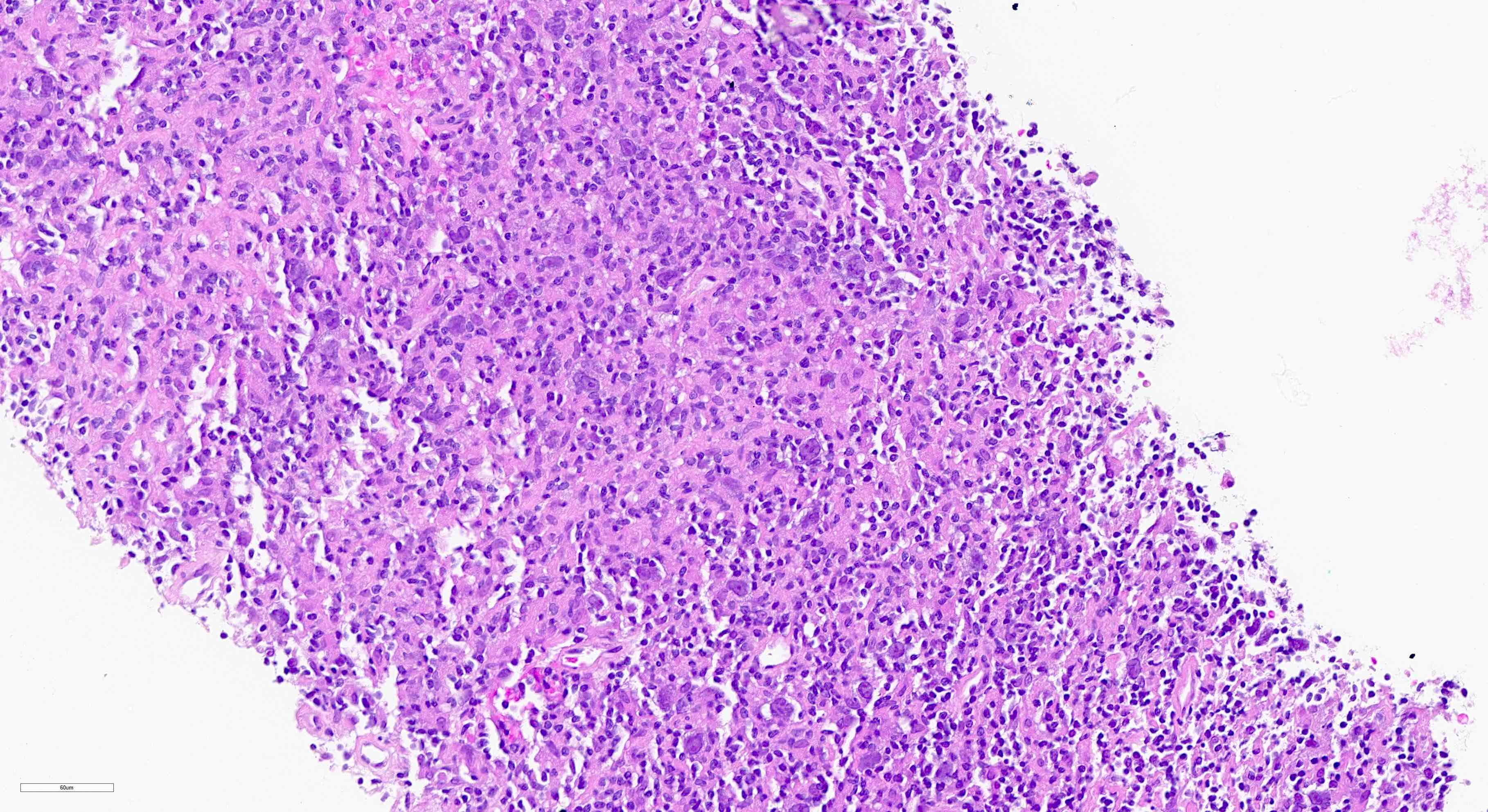
- Lymph node is either completely or partially effaced by lymphoma with a diffuse or vaguely nodular growth pattern (Virchows Arch 2011;459:557)
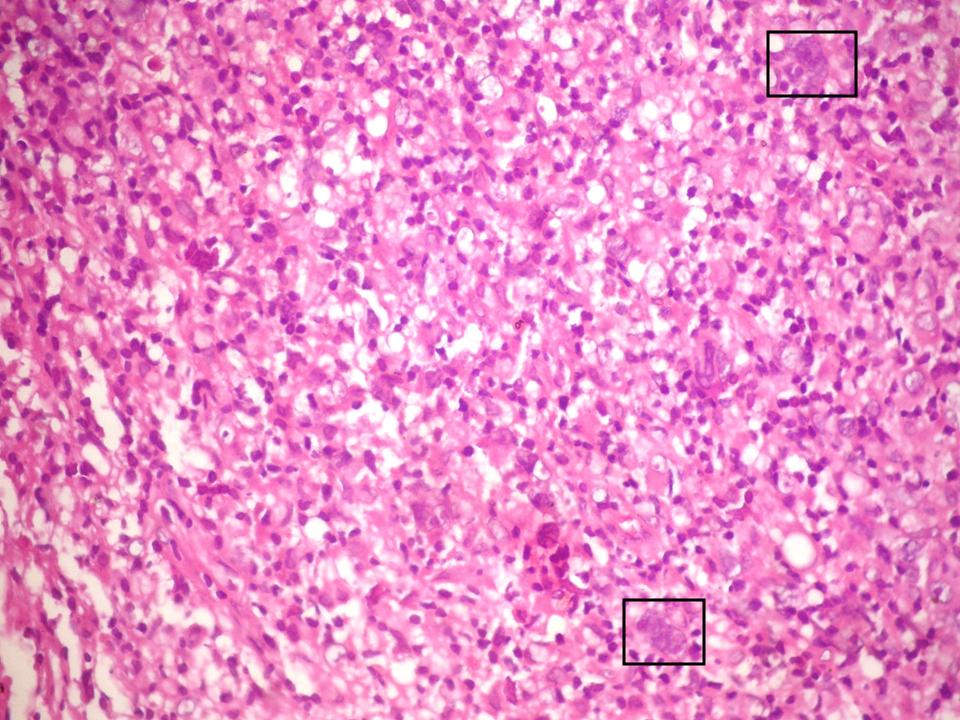
- Scattered single neoplastic large B cells (< 10% of all cells) among a background of small reactive T cells and histiocytes
- Near absence of small B lymphocytes in the background; no remnants of B cell follicles or clusters of small B lymphocytes
- Large numbers of plasma cells and eosinophils are usually not present (Virchows Arch 2011;459:557)
- Large neoplastic B cells are scattered and not seen in aggregates or sheets
- Large neoplastic B cells vary in appearance and can look similar to centroblasts, immunoblasts, Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells or lymphocyte predominant (LP) cells (Virchows Arch 2011;459:557)
- Diverse morphologic and immunophenotypic features (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1458)
- LP-like cells have polylobated and vesicular nuclei that look similar to kernels of popcorn and have been called popcorn cells
- Centroblast-like cells have oval / round nuclei with vesicular chromatin and small basophilic nucleoli adjacent to the nuclear membrane
- HRS-like (Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cell-like) cells are large multinucleated cells with pleomorphic nuclei with prominent eosinophilic or amphophilic round / central nucleoli, sometimes binucleated
- Neoplastic B cells are surrounded by clusters of bland nonepithelioid histiocytes that do not have grooved nuclei
- Necrosis can be present
- THRLBCL in the spleen can involve the white pulp with a micronodular pattern, sometimes in fibrosis
- Involvement of the liver can be seen within portal areas
- Bone marrow with THRLBCL can be paratrabecular or sinusoidal with a diffuse or nodular growth pattern
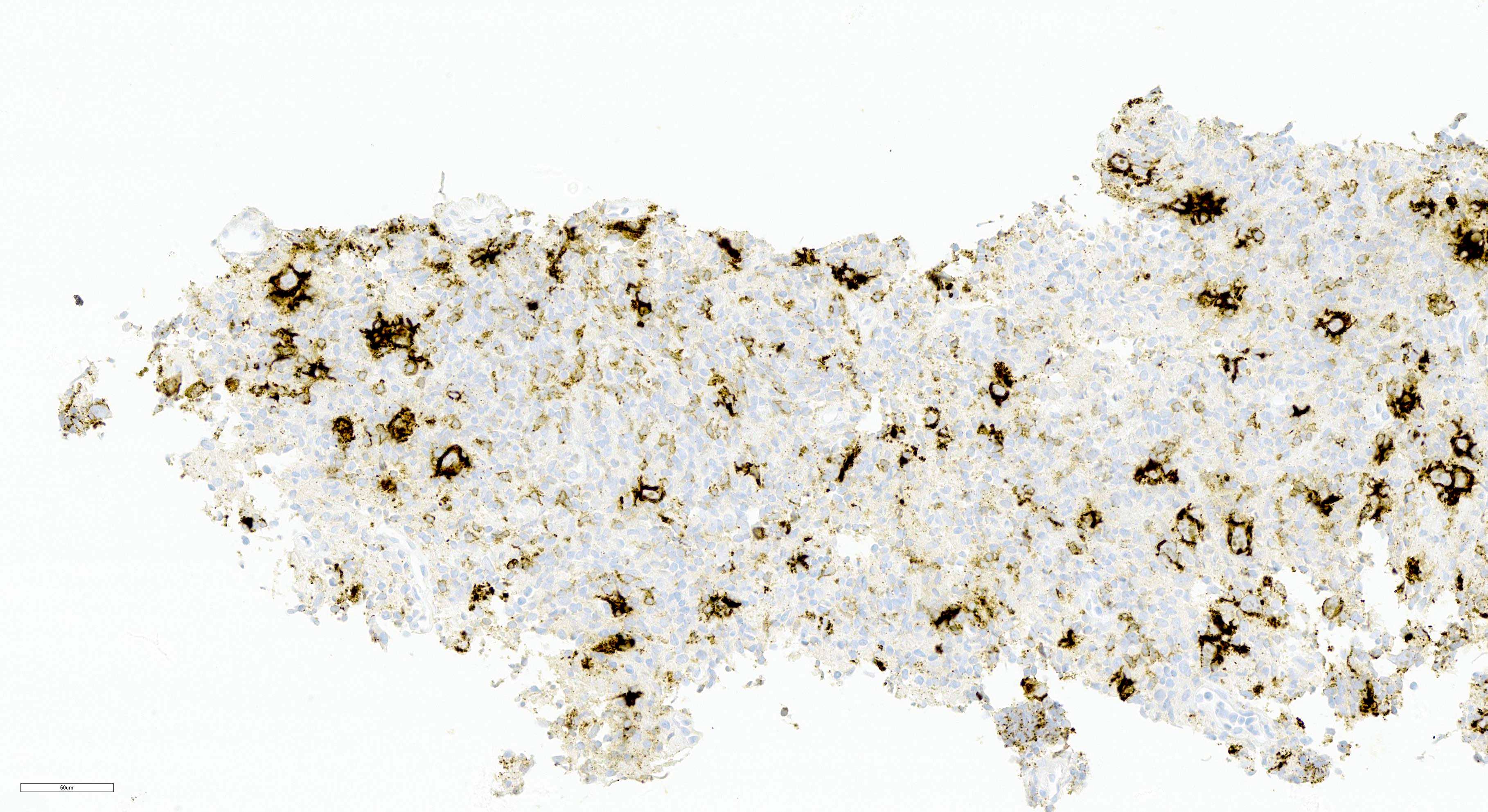
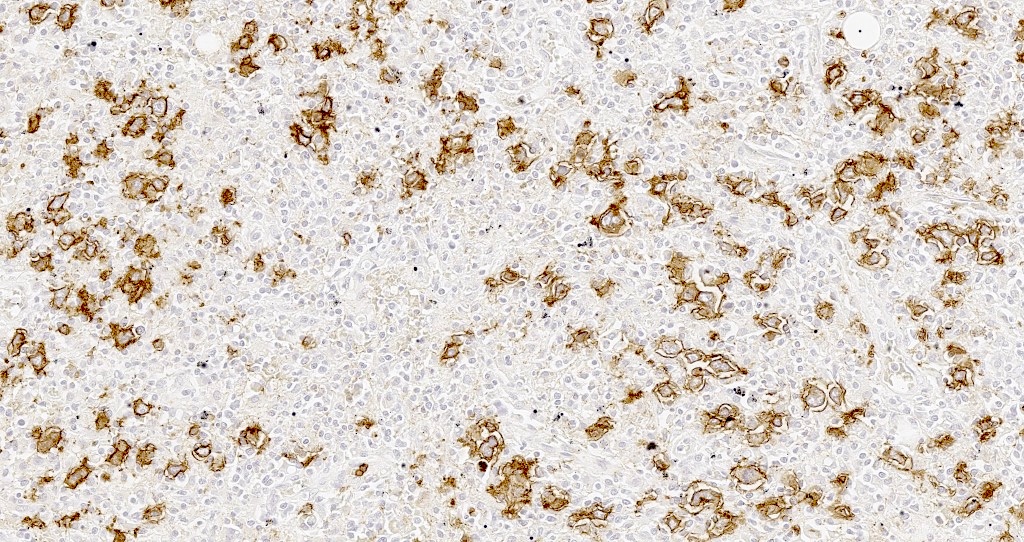
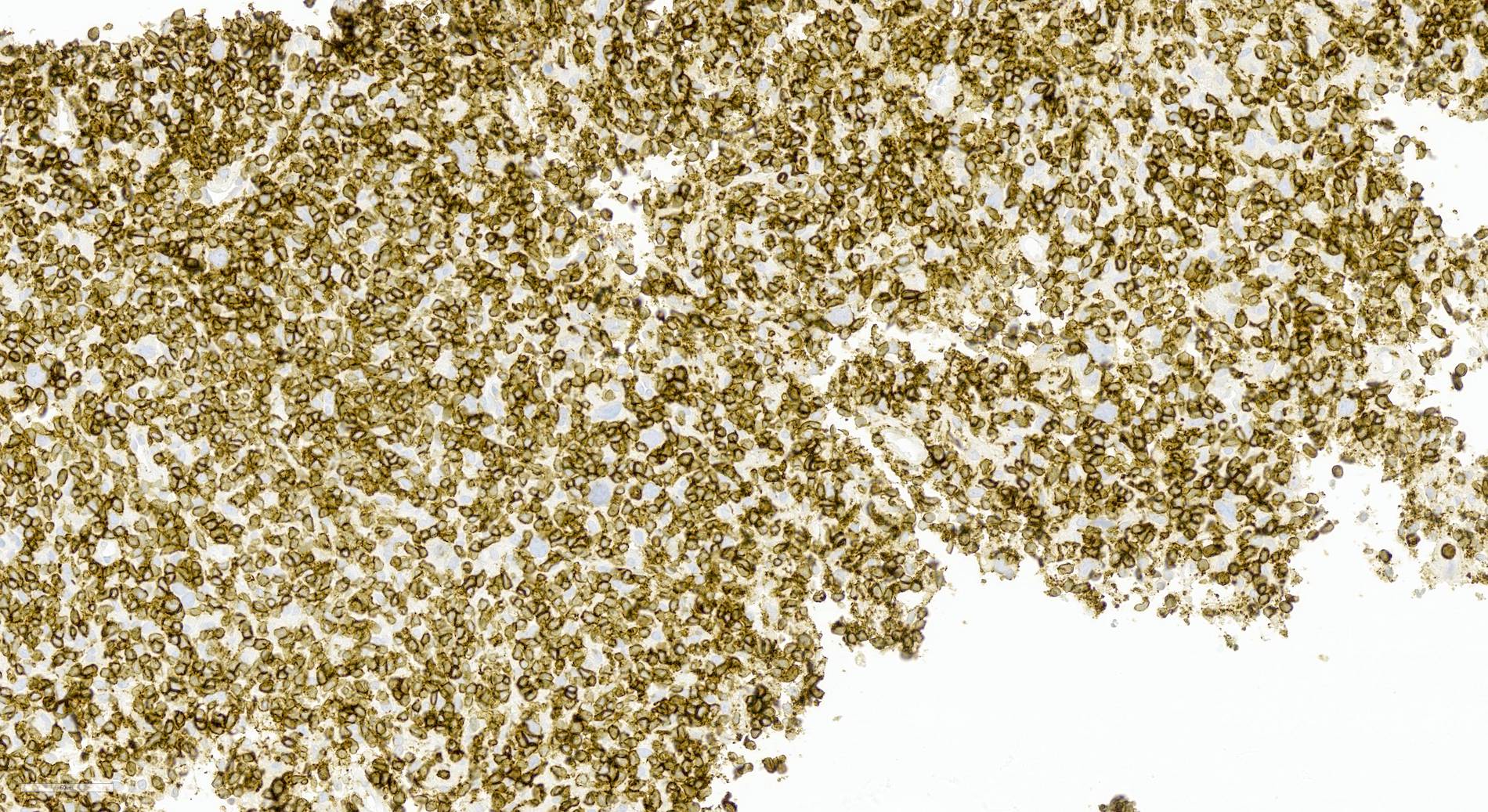
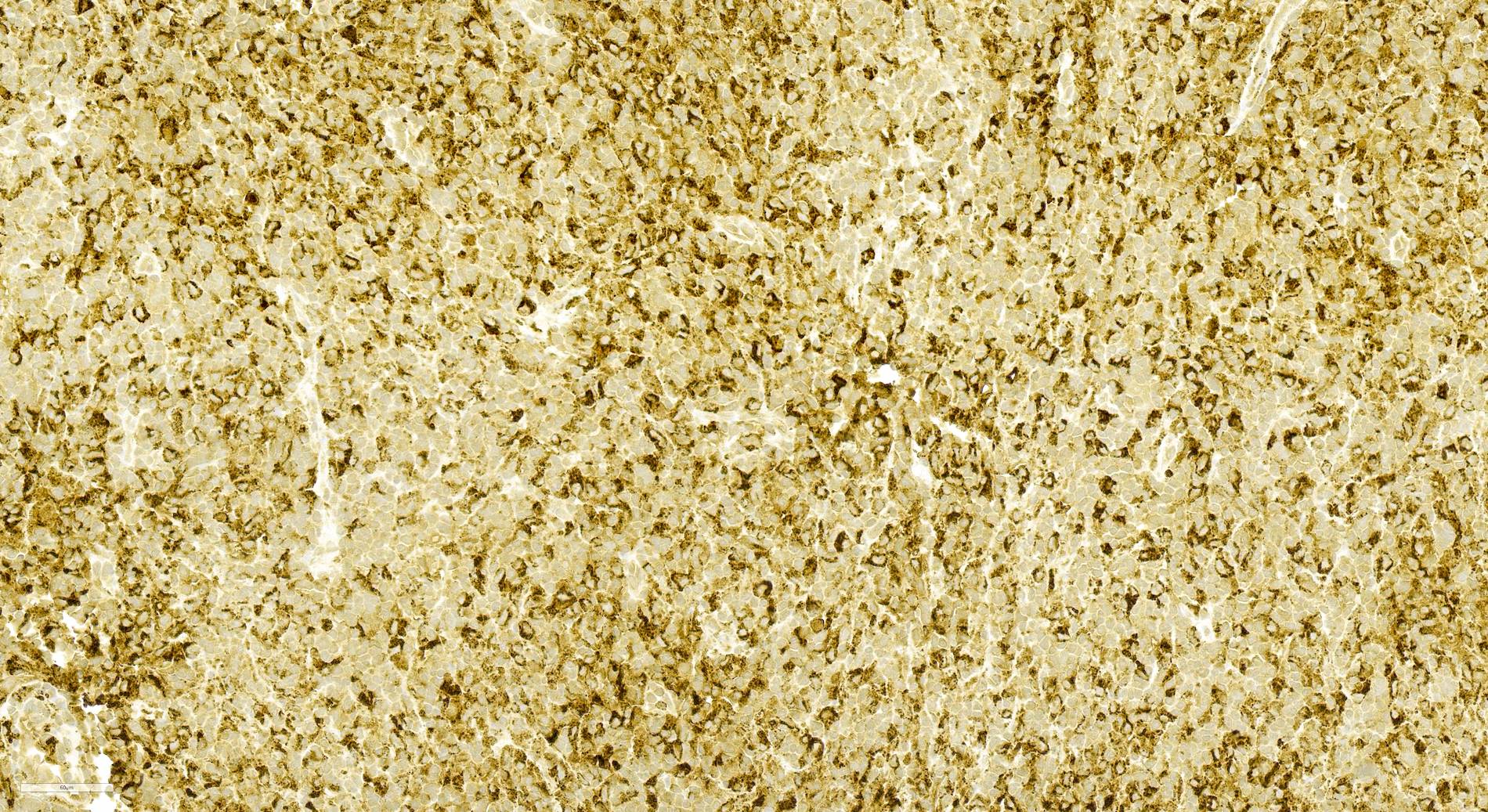
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Aaron Auerbach, M.D., M.P.H., Asmaa Gaber Abdou, M.D. and Nancy Youssef Asaad, M.D.
Contributed by Contributed by Mingyi Chen, M.D., Ph.D. (Case #317)
Cytology description
- Cytology specimens will contain relatively rare large atypical lymphocytes in a background of more numerous small mature lymphocytes and cytologically bland histiocytes
- Diagnosis of THRLBCL cannot be accurately made on cytologic specimens alone and requires a biopsy or excision as well as phenotyping by immunohistochemistry
- References: Blood 2022;140:1229, Leukemia 2022;36:1720
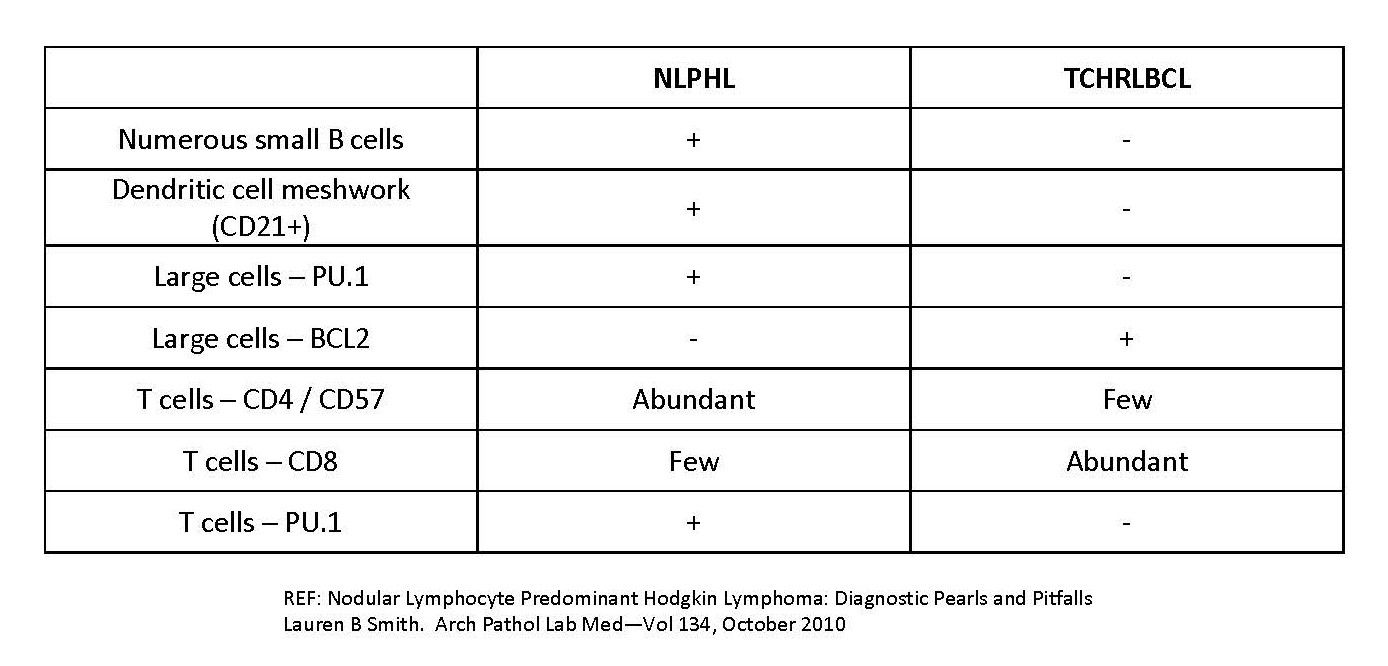
Positive stains
- Large B cells
- Reactive T cells: CD3, CD5, CD8, TIA1 (cytotoxic T cells)
- Reactive histiocytes: CD4, CD68, CD163, lysozyme
- References: Pathology 2020;52:53, Int J Cancer 2013;133:2609
Negative stains
- Large B cells: CD15, CD30, CD138, IgD, EMA (~30%, associated with lymphocyte rich / LR-like cells), BCL2 (40%) (Virchows Arch 2011;459:557)
- Background small lymphocytes: IgD (mantle cell marker)
- No follicular dendritic cell (FDC) meshwork (CD21, CD23, CD35)
- T cells (CD3, CD57, PD-1) usually do not form rosettes around the neoplastic B cells
- EBV (otherwise defined as EBV+ DLBCL)
- References: Pathology 2020;52:53, Int J Cancer 2013;133:2609
Flow cytometry description
- Flow cytometry is typically not helpful due to the relative paucity of neoplastic B cells
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- IgH gene rearrangement studies can be detected by PCR, although the results may not show clonality due to the paucity of neoplastic B cells
- T cell receptor (TCR) gene rearrangement should not be detected
- References: Blood 2022;140:1229, Leukemia 2022;36:1720
Videos
NLPHL versus THRLBCL
Sample pathology report
- Lymph node, excision:
- T cell / histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: Histologic sections show a few cores of soft tissue involved by a diffuse proliferation of numerous small lymphocytes and histiocytes with occasional isolated large atypical cells scattered throughout the specimen. No significant plasma cell component or eosinophilia is appreciated. No normal appearing lymph node tissue is seen. No diffuse sheets of large atypical cells are identified.
- The scattered large, atypical cells are B cells positive for CD20, CD45, CD79a, PAX5, OCT2, BCL6 and MUM1 and negative for CD3, CD4, CD5, CD8, CD10, CD15, CD21, CD23, CD30, CD68, PD-1, EMA, IgD and EBER ISH. The background small lymphocytes consist mostly of T cells positive for CD3, CD5 and CD45 with approximately equal numbers of CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells. The CD21 and CD23 stains are negative for follicular dendritic cell networks. The CD68 stain highlights numerous histiocytes, which show normal coexpression of CD4 and CD45. The Ki67 stain is positive in the large atypical B cells as well as in scattered background small lymphocytes and histiocytes.
- The morphologic findings together with the immunophenotype are in keeping with a diagnosis of T cell / histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma (THRLBCL). THRLBCL typically presents at an advanced Ann Arbor stage with frequent liver and spleen involvement.
Differential diagnosis
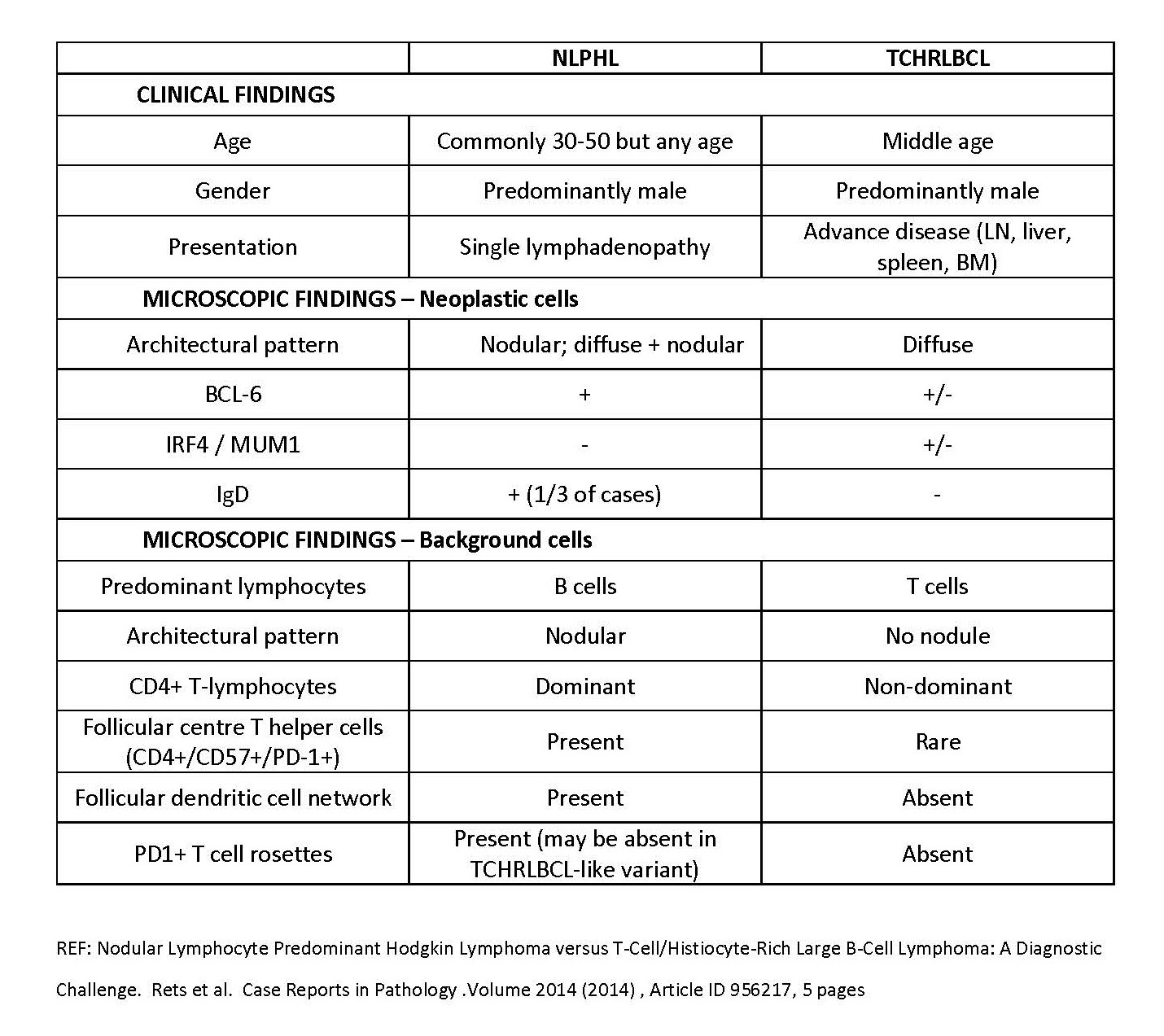
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL):
- Can be difficult to distinguish from THRLBCL, especially on small biopsy material (Pathology 2020;52:142)
- Clinical presentation is less aggressive in NLPHL, which usually presents at low stage (stage I - II), usually as a solitary mass
- Classical NLPHL has an indolent clinical course, while THRLBCL is an advanced stage aggressive disease
- There are cases of NLPHL with a diffuse T cell rich THRLBCL-like morphology (pattern E) but unlike THRLBCL, these have evidence of residual follicular dendritic cell meshworks and a preponderance of follicular helper T cells, which form rosette-like structures around some of the large B cells
- Presence of nodularity in NLPHL distinguishes it from THRLBCL (Pathology 2020;52:142)
- Presence of numerous mantle zone B cells that are positive for CD20, CD23, IgD and TCL1 favors NLPHL over THRLBCL
- T cells positive for follicular helper T cell markers (e.g., CD4+, CD57+, PD-1+, ICOS+, CXCL13+, MUM1+, BCL6+, BOB1+), which form rosette-like structures around the neoplastic B cells favors NLPHL over THRLBCL
- Presence of expanded follicular dendritic cell meshwork positive for CD21, CD23 and CD35 favors NLPHL over THRLBCL (Pathology 2020;52:142)
- CD163+ histiocytes more frequent in THRLBCL than NLPHL
- EBV+ diffuse large B cell lymphoma:
- EBV+ DLBCL can have scattered malignant cells similar to THRLBCL and the tumor cells can look like centroblasts, immunoblasts, Reed-Sternberg cell-like or LP cells
- Presence of EBER+ large cells is diagnostic of EBV+ DLBCL as long as it does not fulfill the requirements of another lymphoma, such as classic Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL)
- EBER+ cells exclude a diagnosis of THRLBCL
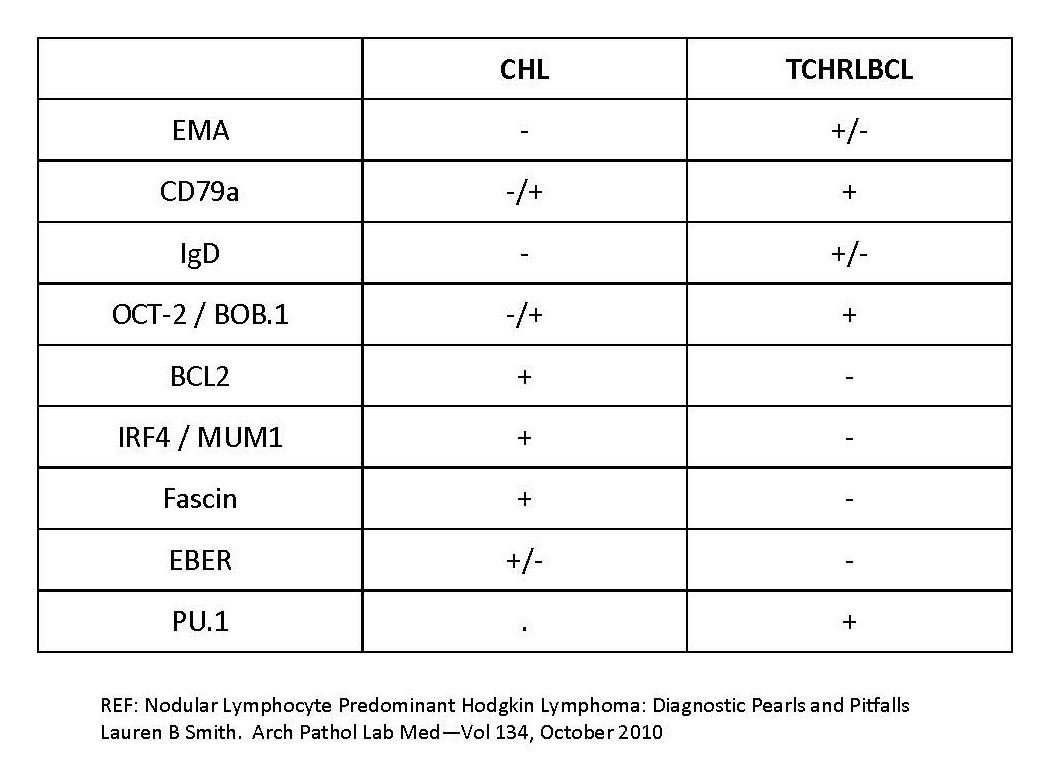
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma:
- Mixed cellularity CHL and lymphocyte depleted CHL often have ample reactive histiocytes, like THRLBCL
- Background cells often include eosinophils and neutrophils, unlike THRLBCL
- Bands of sclerosis in nodular sclerosing CHL are not seen in THRLBCL
- Neoplastic B cells are CD15+, CD30+, MUM1+ and CD45-, a phenotype different from THRLBCL
- CHL is often negative or only weakly positive in B cell markers like CD20 and PAX5, whereas these markers are strongly expressed in THRLBCL
- Peripheral T cell lymphoma:
- Will have numerous T cells similar to THRLBCL but the neoplastic tumor cells are the atypical T cells often present in aggregates
- Atypical cells will express 1 or more T cell markers
- CD30 can be expressed in a subset of patients, unlike THRLBCL
- Some cases will show a follicular helper T cell phenotype and express CD10, BCL6, PD-1 and ICOS
- T cell receptor gene rearrangements should be monoclonal
- Granulomatous lymphadenitis (GL):
- Can sometimes resemble THRLBCL, especially on small biopsy material
- Granulomatous lymphadenitis from infections can contain necrosis as well as neutrophils and special stains can be performed to look for microorganisms
- Sarcoidosis will typically show well formed variably confluent noncaseating granulomas with some multinucleated giant cells and can involve multiple different organs
- Reactive conditions (drugs, viral infection, autoimmune diseases):
Additional references
Practice question #1
The histologic image above is from an axillary lymph node biopsy taken from a 60 year old man with axillary lymphadenopathy. Which of the following features would favor a diagnosis of T cell / histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma (THRLBCL) over nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL)?
- Background CD21+ follicular dendritic cell networks
- CD30 and CD15 expression in the large cells
- Numerous CD4+, PD-1+ small T cells
- Similar histologic features involving bone marrow
- T cell rosettes around the large cells
Practice answer #1
D. Similar histologic features involving bone marrow. THRLBCL typically presents at a high stage with frequent bone marrow involvement. NLPHL, in contrast, usually presents at low stage with only rare bone marrow involvement. Answer A is incorrect because background CD21+ follicular dendritic cell networks are a feature of NLPHL, not THRLBCL. Answer B is incorrect because CD30 and CD15 expression is most frequently negative in the large cells of THRLBCL. Answer C is incorrect because numerous CD4+, PD-1+ small T cells are a feature of NLPHL, not THRLBCL. Answer E is incorrect because T cell rosettes of PD-1+ T cells are a feature of NLPHL, not THRLBCL.
Comment Here
Reference: T cell / histiocyte rich
Comment Here
Reference: T cell / histiocyte rich
Practice question #2
Which one of the following statements regarding T cell / histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma (THRLBCL) is true?
- Differential diagnosis of THRLBCL includes infection, peripheral T cell lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- Large cell component of THRLBCL is CD20+, OCT2+, BCL6+ and EBV+
- Peritumoral environment of THRLBCL contains prominent follicular dendritic cell networks and abundant reactive small B cells
- THRLBCL and NLPHL show similar clinical presentation and organ involvement
- THRLBCL typically shows T cell receptor gene rearrangements
Practice answer #2
A. Differential diagnosis of THRLBCL includes infection, peripheral T cell lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Answer B is incorrect because EBV is negative in THRLBCL and similar EBV+ cases would be defined as an EBV+ DLBCL. Answer C is incorrect because THRLBCL lacks follicular dendritic cell networks and has abundant small T cells. Answer D is incorrect because THRLBCL is a more aggressive disease than NLPHL. NLPHL often only presents as a single lymph node, whereas THRLBCL can present with more than one site of involvement. Answer E is incorrect because THRLBCL is a clonal B cell lymphoma and would not be expected to show T cell receptor gene rearrangements.
Comment Here
Reference: T cell / histiocyte rich
Comment Here
Reference: T cell / histiocyte rich