Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Bárcena C, de Leval L. CHL lymphocyte rich. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomanonblrhl.html. Accessed September 18th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Subtype of classic Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) with Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells in a nodular or less commonly diffuse background of small lymphocytes (Blood 2022;140:1229, Leukemia 2022;36:1720)
Essential features
- B cell lymphoma derived from germinal center B cells
- Scattered HRS cells in a nodular or diffuse background of small lymphocytes without eosinophils and neutrophils
- Immunophenotype of HRS cells: PAX5+ (dim), CD30+, CD15 variable, CD20 variable
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Rare subtype of CHL that accounts for 5.8% of classic Hodgkin lymphoma (Cancer Med 2018;7:953)
- Most patients are adults (30 - 50 years)
- Male predominance (70%)
- EBV infection in 30 - 50% of cases; the virus is within the HRS cells and usually shows a type II latency pattern of infection
Sites
- Peripheral lymph nodes (most often cervical) are typically affected (Leuk Lymphoma 2019;60:3426)
- Mediastinal involvement (15%) and bulky disease are rare
Pathophysiology
- Pathophysiology is incompletely understood
- HRS cells derived from preapoptotic germinal center B cells with a disrupted B cell program (Leukemia 2021;35:968)
- HRS cells harbor monoclonal IGH rearrangements with somatic mutations of their Ig variable region genes and lack the capacity of Ig expression (Leukemia 2021;35:968)
- Genetic lesions that promote HRS cell proliferation, survival, immune evasion and interaction with their microenvironment, including alterations in NFκB and JAK / STAT signaling pathways (Leukemia 2021;35:968)
- EBV could play a crucial role by infecting HRS cells with crippled germinal center B cell receptor (BCR), rescuing them from apoptosis and thus inducing lymphomagenesis (Blood 2005;106:4339)
- EBV infection activates the NFκB pathway promoting survival and growth (Histopathology 2021;79:451)
Etiology
- Remains unknown
Clinical features
- Similar to those of nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (WHO 5) / nodular lymphocyte predominant B cell lymphoma (ICC), except that relapses are less frequent in lymphocyte rich CHL (LRCHL) (J Clin Oncol 1999;17:776)
- B symptoms are rare
- Most patients are diagnosed at stage I / II (J Clin Oncol 2005;23:5739)
Diagnosis
- Histopathological analysis of an excisional lymph node biopsy or tissue biopsy supplemented with ancillary techniques (immunohistochemistry, EBER ISH)
Laboratory
- Nonspecific findings: anemia, leukocytosis, lymphocytopenia, elevated C reactive protein (N Engl J Med 1998;339:1506)
Prognostic factors
- Approximately 90 - 95% of patients with early stage CHL and 80 - 85% with advanced stage CHL are cured (Am J Hematol 2020;95:978)
- Prognosis is slightly better than other CHL subtypes and similar to nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL), unless for the relapses, that are more common in NLPHL
- Treatment is individualized according to defined risk groups based on following prognostic factors
- Ann Arbor stage (most important predictor of outcome) (J Clin Oncol 2014;32:3059)
- Bulky (mediastinal) disease
- Extranodal involvement
- B symptoms
- International Prognostic Score (N Engl J Med 1998;339:1506)
Case reports
- 35 year old woman with a 2 month history of progressive cough and intermittent fever (Ann Hematol 2014;93:1073)
- 35 year old man with a 4 month history of supraclavicular and cervical lymphadenopathies (J Clin Exp Hematop 2015;55:23)
Treatment
- Intensive polychemotherapy (ABVD or BEACOPP) with or without radiotherapy (Am J Hematol 2020;95:978)
- For refractory cases: stem cell transplant, brentuximab vedotin, checkpoint inhibitors (N Engl J Med 2018;378:331)
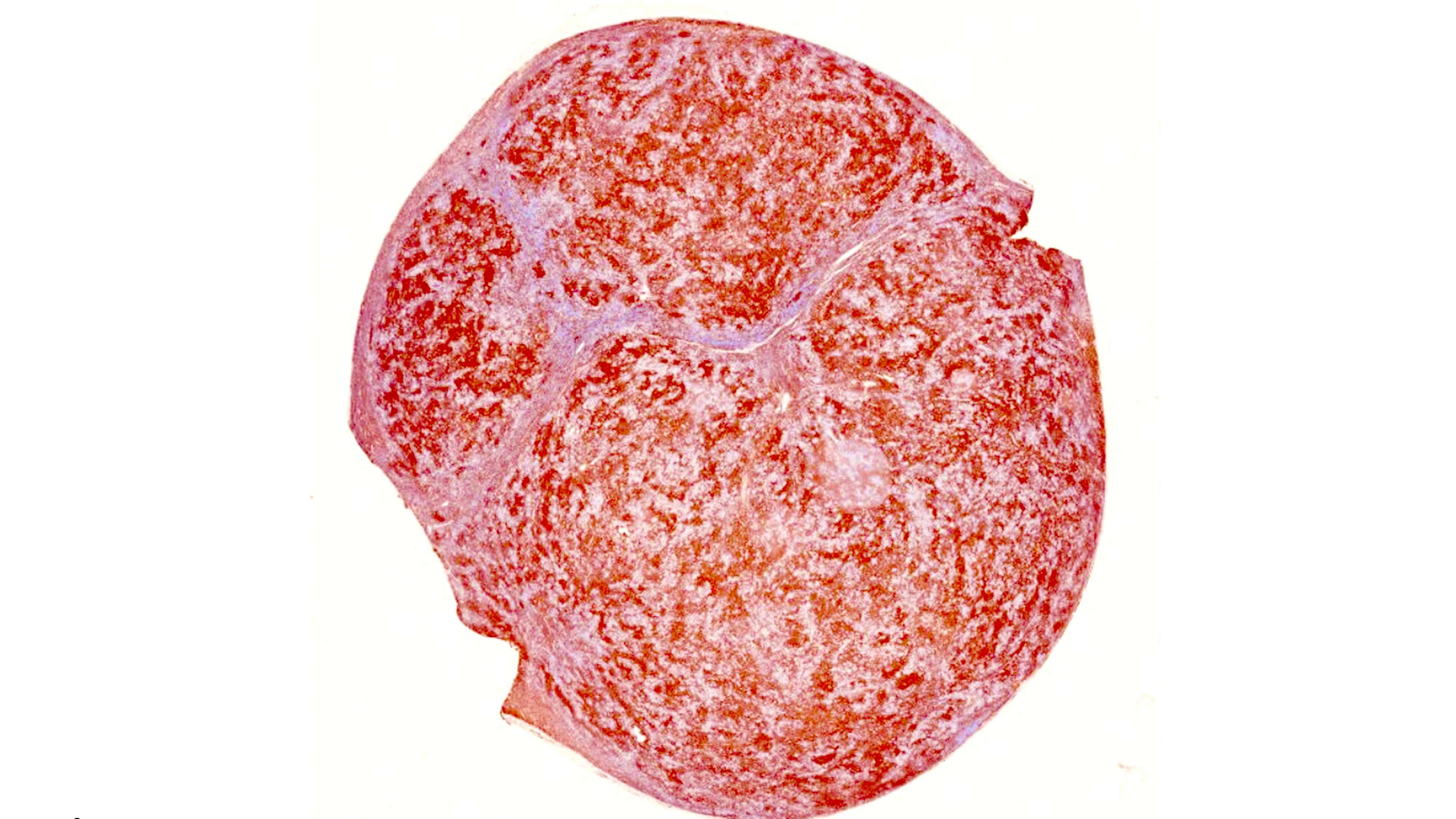
Gross description
- Involved lymph node is enlarged
- Vaguely nodular
- Fleshy appearance
- Reference: Leukemia 2022;36:1720
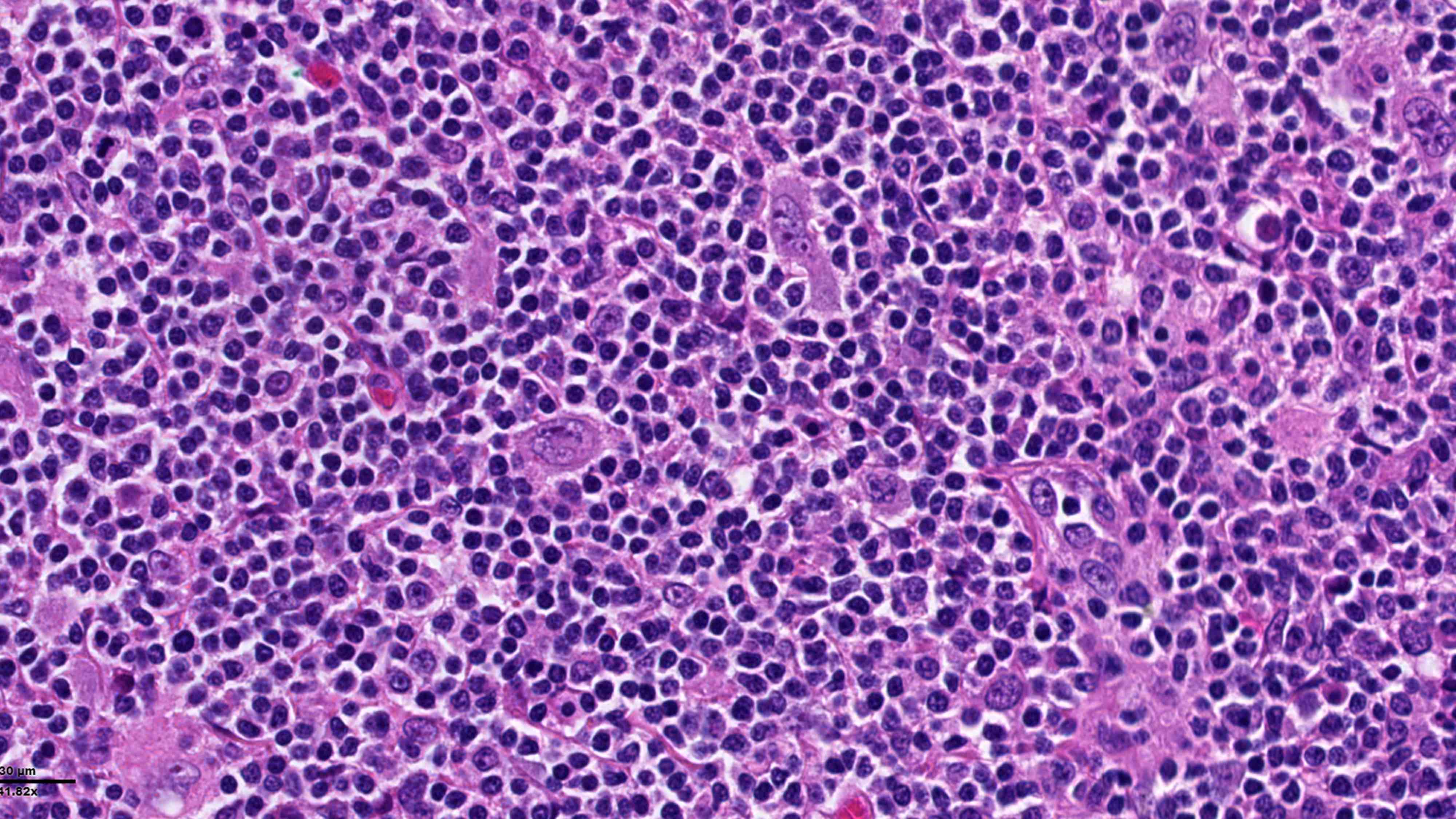
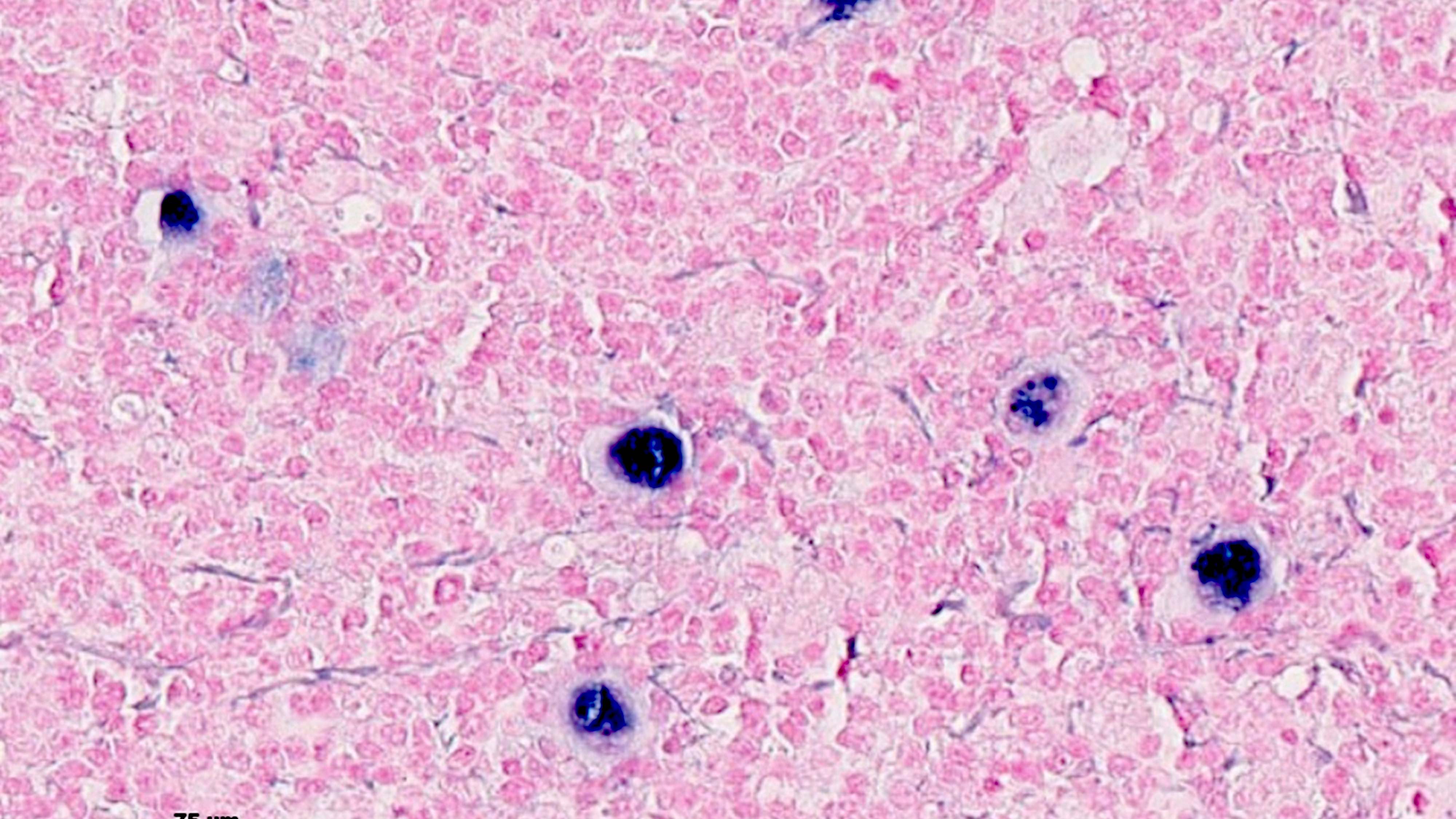
Microscopic (histologic) description
- 2 patterns of growth: nodular or less often, diffuse proliferation with numerous reactive small lymphocytes and scattered HRS cells (Leukemia 2022;36:1720)
- Neutrophils and eosinophils are absent from the nodules
- In lymphocyte rich classic Hodgkin lymphoma (LRCHL) nodular cases
- Nodules are composed of small lymphocytes and may contain eccentrically located germinal centers (small or regressed)
- Nodules contain dense meshwork of follicular dendritic cells (CD21+)
- HRS cells are within the nodules but outside of the germinal centers
- Some HRS cells resemble lymphocyte predominant cells (LP cells) or lacunar cells
- In LRCHL diffuse cases
- Small lymphocytes of the background can be intermingled with histiocytes with or without epithelioid morphology
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
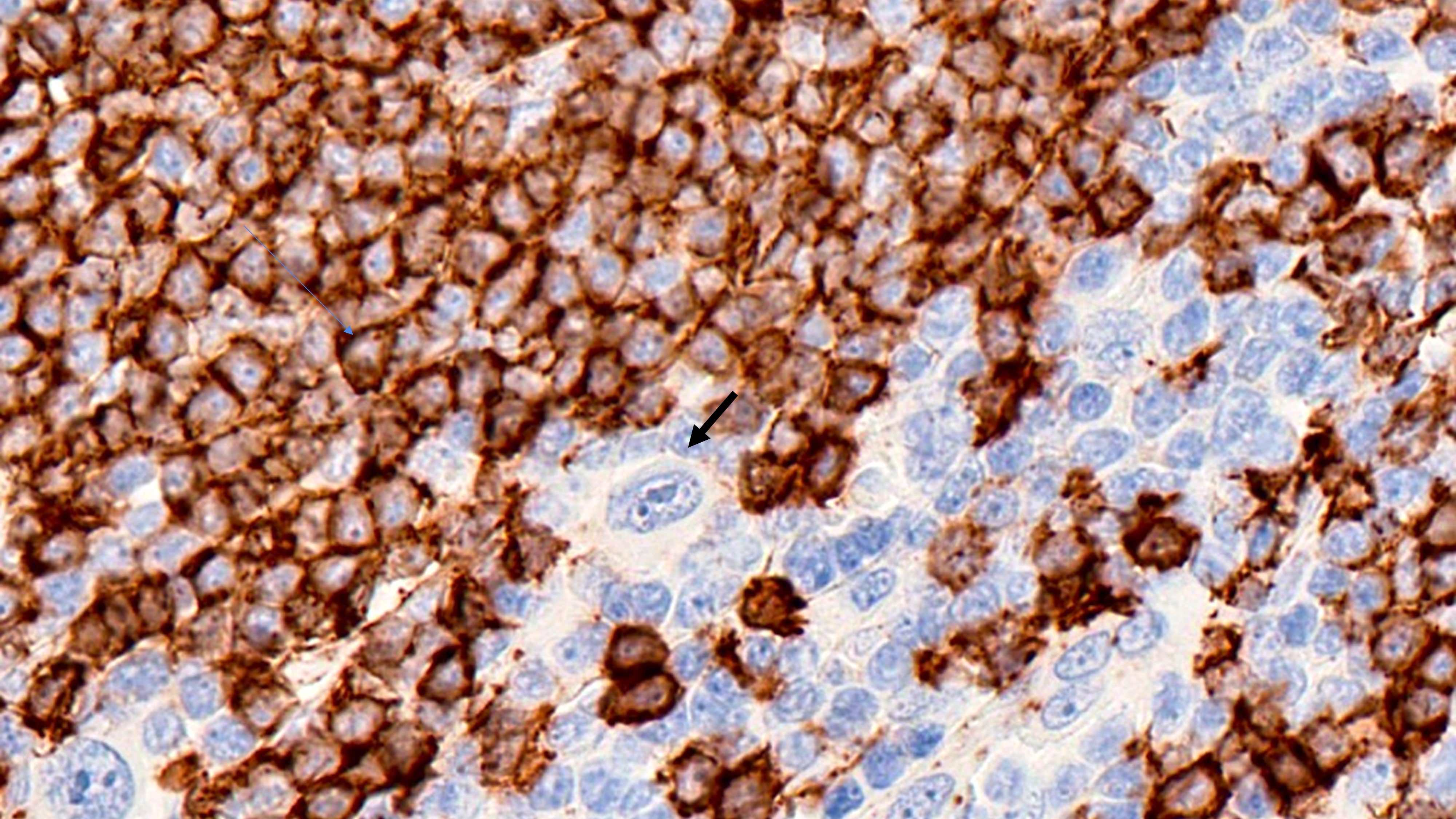
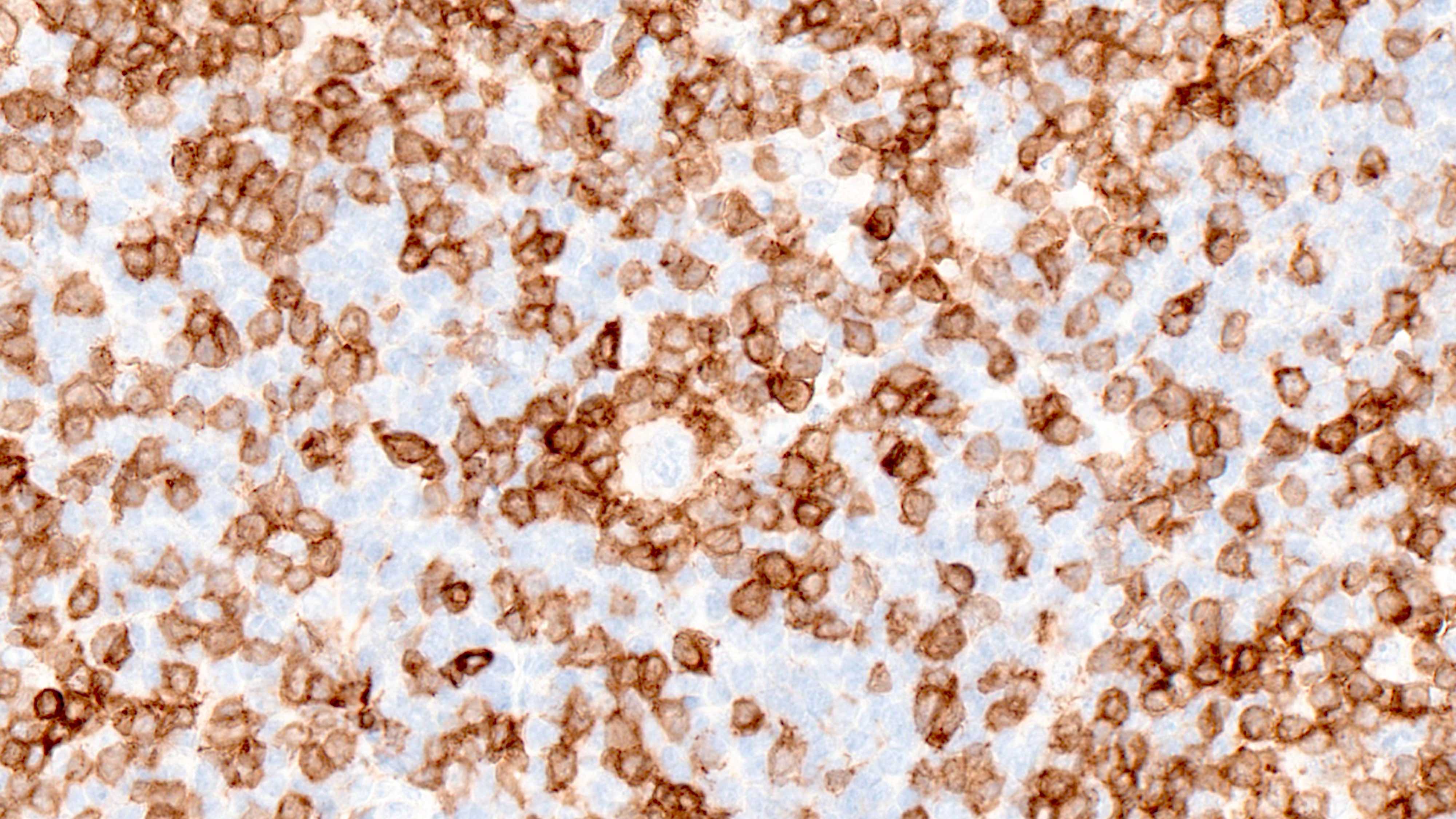
- Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells
- PAX5 (dim), CD30 (strong and uniform), CD15 variable (75% of cases), MUM1 (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;39:105)
- OCT2 (56%) and BOB1 (62%) are more frequently expressed than in other CHL subtypes (Mod Pathol 2009;22:1006)
- STAT6YE361 (nuclear or nuclear and cytoplasmic) (Mod Pathol 2020;33:834)
- GATA3 (67%) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:180, Blood 2010;116:4202, Am J Pathol 2005;166:127, J Clin Pathol 2007;60:1092)
- PDL1, PDL2 (Histopathology 2018;72:1156, Blood 2018;131:68)
- Fascin (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:16)
- EBV positive cases: EBV LMP1 variable, EBER
- Immunophenotype of the small lymphocytes in the background
- Background is composed of both B and T lymphocytes
- B cells are most prominent in LRCHL compared to other CHL subtypes
- B cells are IgM+, IgD+, corresponding to expanded mantle zones
- CD4+ T cells dominate the CHL microenvironment (Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2008;74:1, Blood 2004;103:1755, Lab Invest 2008;88:482)
- In 50% of LRCHL cases, HRS are surrounded by rosettes of T follicular helper cells (CD4+, PD-1+, CD57 variable) (Mod Pathol 2009;22:1006, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021;118:e2105822118)
Negative stains
- Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells
- Variable: CD20 (weak), CD79a (Leukemia 2022;36:1720)
- CD20 (31%) and BCL6 (36%) are more frequently expressed than in other CHL subtypes (Mod Pathol 2009;22:1006)
- BCL2 (Leukemia 2022;36:1720)
- CD45, ALK, EMA, CD23 (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2011;6:157, Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;40:72)
- Immunoglobulins, light and heavy chains, are negative (Leukemia 2022;36:1720)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Aneuploidy is seen in nearly all cases (Blood 1995;86:1464, Cancer Res 2006;66:10332, Cancers (Basel) 2018;10:91)
- High constitutive activity of the NFκB pathway is the hallmark of HRS cells which is essential for HRS cell survival (Semin Cancer Biol 2016;39:32)
- Mutations in members of the JAK / STAT signaling pathway, main mediator of cytokine signaling (Nat Genet 2014;46:329)
- Mutations in ITPKB, PI3K / AKT and MAP / ERK pathways (Leukemia 2020;34:151)
- Lesions in genes involved in immune evasion of HRS: PDL1, PDL2, B2M, CIITA, CD58 (Blood 2010;116:3268, J Clin Oncol 2016;34:2690)
- Mutations in additional genes: ARID1A, TNFRS14, XPO1 (Leukemia 2021;35:968)
Sample pathology report
- Lymph node, left neck, excision:
- Lymphocyte rich classic Hodgkin lymphoma (see comment)
- Comment: H&E stained sections display a lymph node with architectural effacement by a nodular proliferation of abundant small lymphocytes and scattered large atypical lymphoid cells. The neoplastic cells have monolobated / bilobated / multilobated nuclei, vesicular chromatin, prominent nucleoli and amphophilic cytoplasm, consistent with HRS cells.
- Immunophenotypically, the large atypical cells are positive for PAX5 (weak), OCT2, CD30 (strong), CD15, MUM1 and GATA3 and negative for CD20 and CD45.
- TFH markers reveal T cell rosettes around HRS cells.
Differential diagnosis
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL) / nodular lymphocyte predominant B cell lymphoma (NLPBCL) (Blood 2000;96:1889):
- T cell / histiocytic rich large B cell lymphoma (THRLBCL):
- Composed of a background rich in small lymphocytes and histiocytes with scattered large neoplastic B cells CD20+, BCL6+, CD30-, CD15-, EBER-
- Eosinophils, plasma cells and neutrophils are uncommon
- These characteristics argue against a diagnosis of CHL (Leukemia 2022;36:1720)
- B symptoms are more common
- Aggressive clinical course
- Small lymphocytic lymphoma / chronic lymphocytic leukemia:
- Follicular lymphoma:
- Nodal TFH T cell lymphoma:
- Scattered large B cells with an HRS-like morphology may be present
- HRS-like cells have a preserved B cell program (CD79a+, PAX5+, OCT2+, BOB1+, CD20 variable)
- Some cases harbor B cells with a HRS phenotype (CD30+, CD15 variable, EBV variable) in a background of TFH atypical cells
- Monoclonal T cell receptor gene rearrangement and NGS showing mutation of the hotspot RHOA (G17V) and IDH2 (R172) favor the diagnosis of nodal TFH (Histopathology 2014;64:171, Br J Haematol 2008;141:124)
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
D. CD45-, PAX5+, CD30+, CD15+. This is the characteristic immunophenotype of Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg cells. Answer A is incorrect because the large atypical cells of T cell / histiocytic rich large B cell lymphoma express this immunophenotype. Answer B is incorrect because this immunophenotype is characteristic of primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma. Answer C is incorrect because the LP cells in nodular lymphocyte Hodgkin lymphoma (WHO 5) / nodular lymphocyte predominant B cell lymphoma typically express this immunophenotype (ICC 2022). Answer E is incorrect because this immunophenotype is not specific. T cells could show this immunophenotype.
Comment Here
Reference: CHL lymphocyte rich
Comment Here
Reference: CHL lymphocyte rich
Practice question #2
What is the typical composition of the background of lymphocyte rich classic Hodgkin lymphoma (LRCHL) with nodular pattern?
- Small atypical B cells: CD20+, BCL2+, BCL6+, CD10+
- Small B cells: CD20+, CD5+, CD23+, LEF1+
- Small B cells IgD+ admixed with CD4+ PD-1+ T cells
- Small T cells, eosinophils, plasma cells and neutrophils
Practice answer #2
C. Small B cells IgD+ admixed with CD4+ PD-1+ T cells. The background is typically composed of B cells corresponding to expanded mantle zones (IgD+) admixed with CD4+, PD-1+ T cells, rosetting Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells. Answer B is incorrect because this is the characteristic composition of small lymphocytic lymphoma. Answer D is incorrect because this background is not specific but in the present of HRS cells it is diagnostic of mixed cellularity classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Answer A is incorrect because this is the characteristic composition of follicular lymphoma.
Comment Here
Reference: CHL lymphocyte rich
Comment Here
Reference: CHL lymphocyte rich