Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Gonzalez-Mancera M, Kitahara S. DLBCL-primary testicular. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomaprimarytesticular.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Large B cell lymphoma that is confined to and presumably arises in testis
- Recently classified under large B cell lymphomas (LBCL) of immune privileged sites in the most recent revision of the WHO, 5th edition; this is a new umbrella term that acknowledges common biological features of aggressive B cell lymphomas (Leukemia 2022 Jun 22 [Epub ahead of print])
- This new entity now combines the previous entity of primary DLBCL of CNS with DLBCL of the vitreoretina and testis that were previously included among DLBCL, NOS
- Recently considered a distinct entity by the International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms, closely related to primary DLBCL of the central nervous system on the basis of common clinical and molecular features (Blood 2022 Jun 2 [Epub ahead of print])
Essential features
- Comprises 80 - 90% of all primary testicular lymphomas with a mean age of presentation between 60 and 70 years of age
- Composed of large atypical lymphoid cells with a predominant centroblastic morphology that replace the testicular parenchyma
- Positive for pan B cell markers and typically positive for BCL6, MUM1 and BLC2
Terminology
- Primary DLBCL of testis
- Primary testicular lymphoma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Typically presents in adult men with a median age between 60 and 70 at diagnosis
- Most common testicular malignancy in men > 60 years of age
- Most common testicular malignancy to present with bilateral involvement
- Increased incidence in HIV positive men (Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:4049)
- HIV positive patients with primary testicular diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL PT) are younger (median age of 36)
Sites
- Most patients present with localized disease
- Approximately 20% of patients have advanced stage with spread to contralateral testis, CNS or other extranodal sites (J Clin Oncol 2009;27:5227)
Pathophysiology
- Evaluation of the cell of origin through IHC and gene expression profiling has demonstrated that DLBCL PT has a non-GCB phenotype in 60 - 96% of cases (Mod Pathol 2006;19:1521, J Pathol 2006;210:163)
- Characterized by deregulation of intercellular immune signaling mechanisms, including NFkB pathway activation (Blood 2016;127:869)
- Oncogenic toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling (via MYD88 activating mutations) and B cell receptor (BCR) signaling (via CD79b mutation) are central to the pathogenesis, leading to NFkB pathway activation
- Prosurvival signals through mutations in PIM1/2, CARD11 and TNFAIP3 further contribute to the dysregulation in NFkB signaling
- Mutations within genes mediating immune surveillance are also central to DLBCL PT pathogenesis
- Losses of the HLA class I and II loci are associated with reduced expression of major histocompatibility complexes (MHC)
- Gains and amplifications of the programmed death ligand (PDL) 1 (CD274) and 2 (CD273) loci, that increase protein expression and contribute to the evasion of an antitumor immune response
Etiology
- Unknown in immunocompetent patients
Clinical features
- Firm, painless testicular mass without preference for either side (Blood 2014;123:486)
- Median tumor size at presentation is 6 cm
- Systemic symptoms are infrequent, seen in approximately 25 - 40% of cases
- Fever, anorexia, night sweats, weight loss
- Most patients present with localized disease and about 20% present with advanced stage disease, including spread to contralateral testis, CNS or other extranodal sites
Diagnosis
- Imaging modalities that may assist in diagnosis include:
- Ultrasonography
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Biopsy of the involved testis or orchiectomy
- Secondary testicular involvement by systemic lymphoma should be excluded
- Reference: Ann Oncol 2016;27:v91
Laboratory
- Increased serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), increased serum B2 microglobulin and hypoalbuminemia have been associated with an adverse prognosis (J Clin Oncol 2003;21:20)
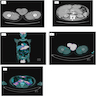
Radiology description
- Ultrasonography will show focal or diffuse areas of hypoechogenicity with hypervascularity in affected testis
- MRI allows simultaneous evaluation of both testes, paratesticular spaces and spermatic cord
Prognostic factors
- High relapse rate; recurrence most often occurs in the CNS or the contralateral testis (Br J Haematol 2017;176:210)
- Involvement / recurrence in the CNS is associated with a dismal prognosis; relapse in the CNS has been reported in up to 30% of the cases within 1 - 2 years from diagnosis
- Adverse prognostic factors for progression free survival include age > 70 years, advanced stage, B symptoms, involvement of extranodal sites other than testis and tumor diameter > 10 cm (J Clin Oncol 2009;27:5227, J Clin Oncol 2003;21:20, Leuk Lymphoma 2010;51:1217)
Case reports
- 47 year old man with right testicular swelling (Ann Clin Lab Sci 2010;40:75)
- 48 year old man with bilateral testicular masses (J Surg Case Rep 2021;2021:rjab431)
- 55 year old man with bilateral testicular enlargement and pain (Urol Case Rep 2021;38:101733)
- 16 patients ranging from 36 - 93 years old with various clinical presentations of DLBCL PT (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e19463)
Treatment
- Orchiectomy followed by immunochemotherapy (R-CHOP or R-CHOP-like regimen)
- Addition of CNS prophylaxis with CNS penetrating chemotherapy or intrathecal chemotherapy, as well as irradiation or excision of the contralateral testis, are highly recommended
- References: J Clin Oncol 2011;29:2766, Urol Oncol 2020;38:641.e1, Clin Lymphoma Myeloma 2009;9:386, Leukemia 2016;30:361
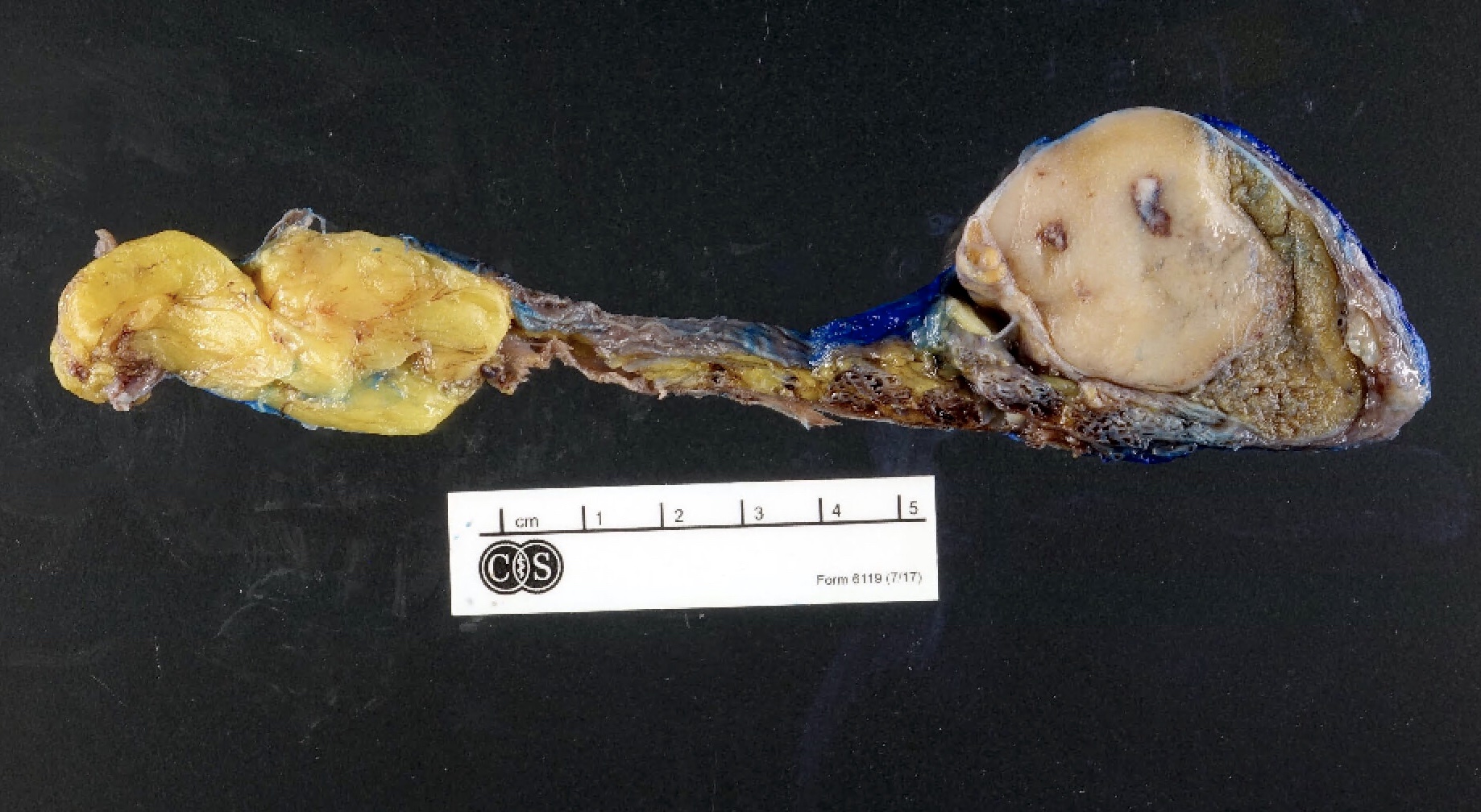
Gross description
- Enlarged testicle with a fleshy, diffuse or lobulated firm mass
- Cut surface is relatively homogeneous and bulging, with a tan-yellow color
- Often demonstrates a sharp demarcation from testicular parenchyma
- Reference: Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e19463
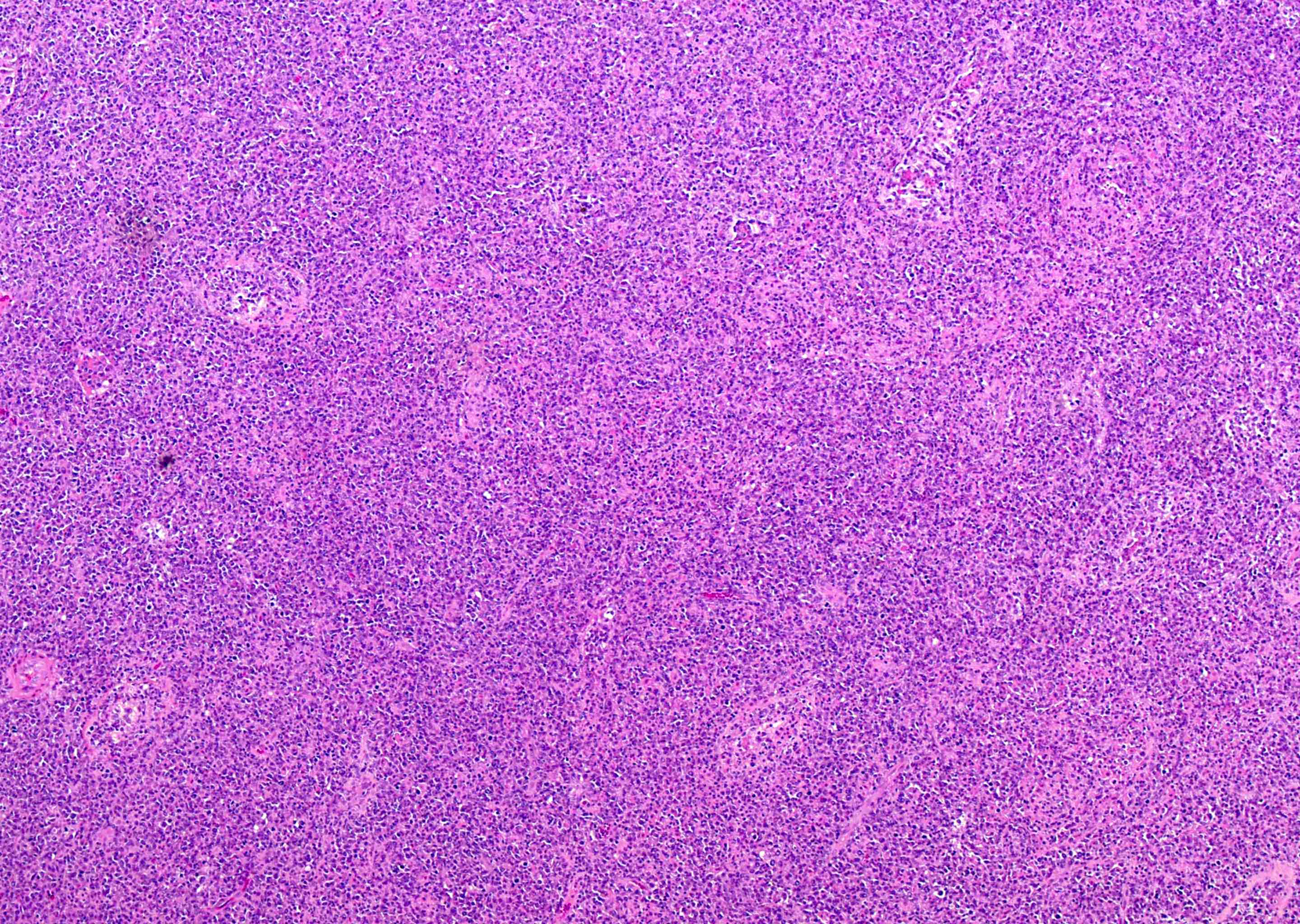
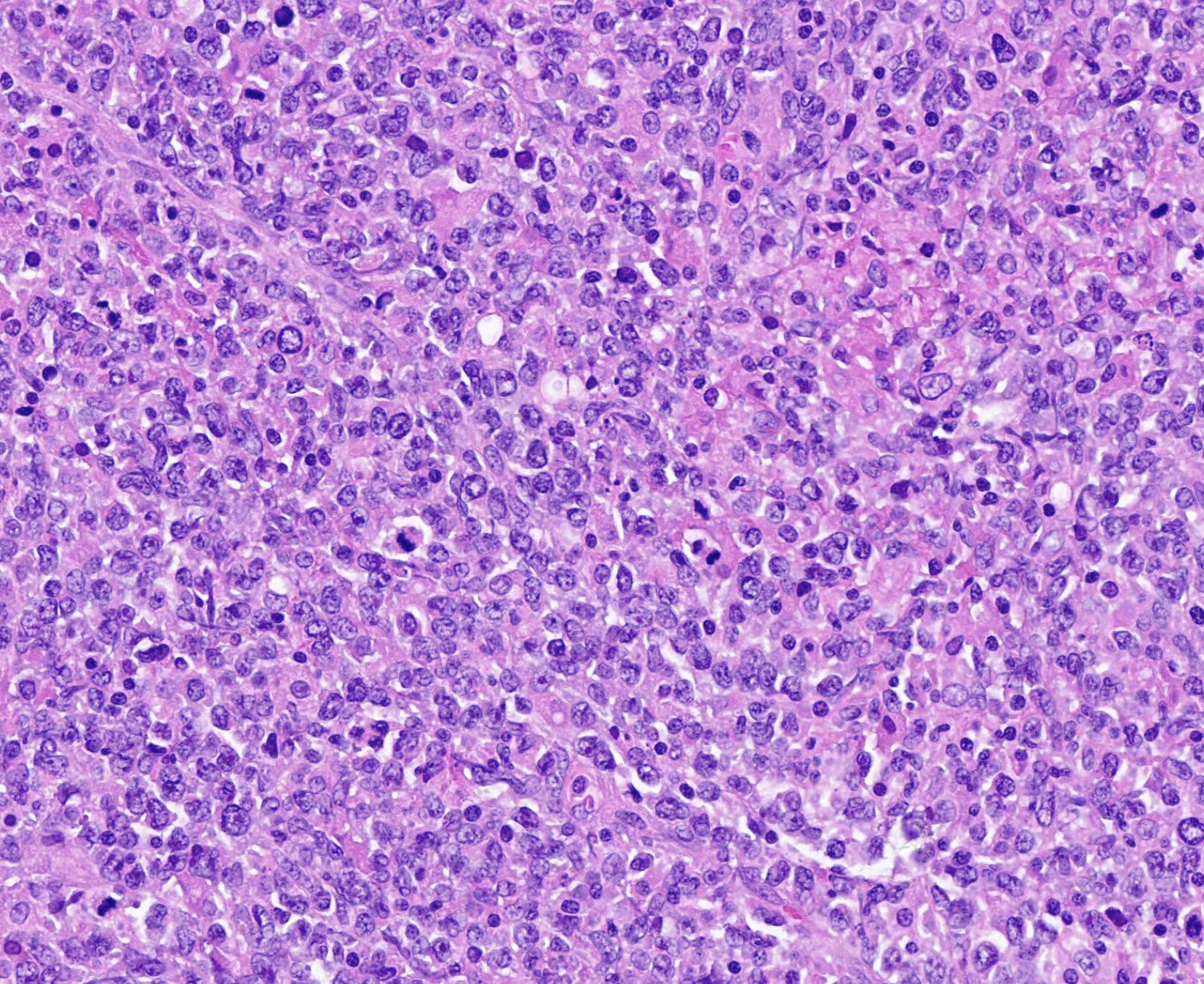
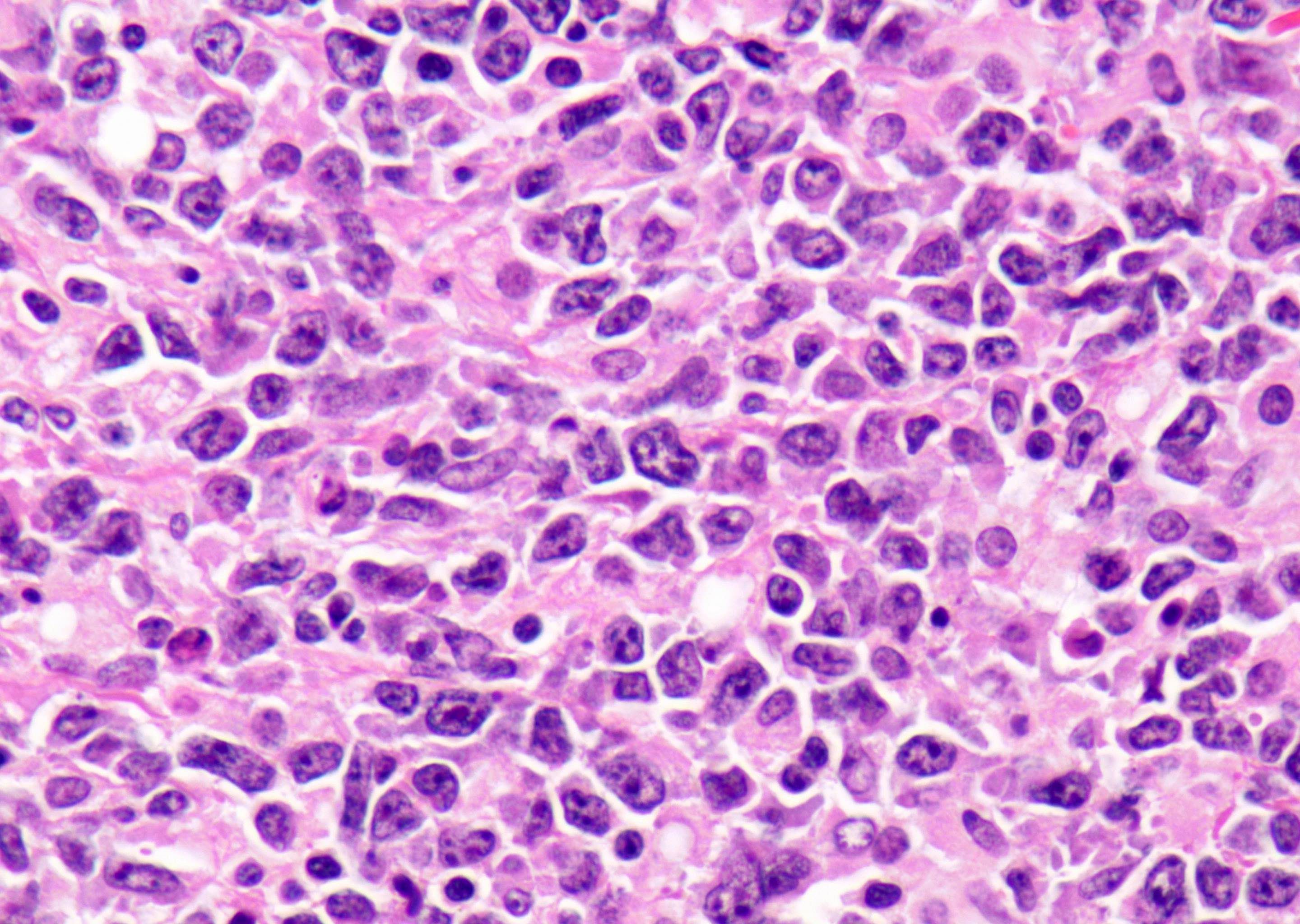
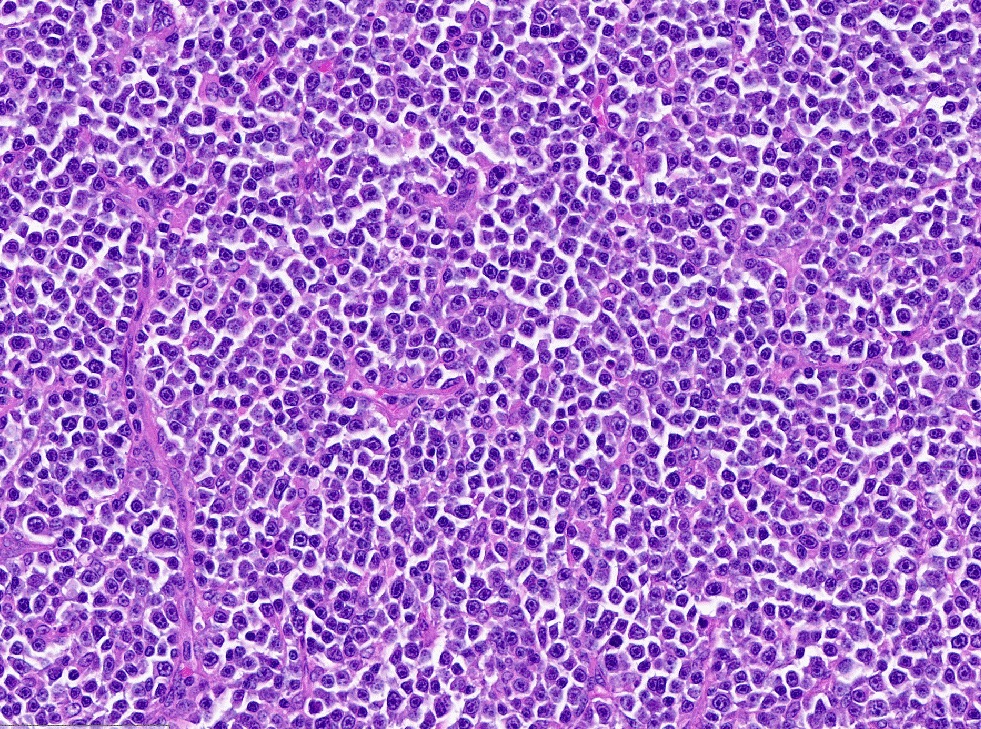
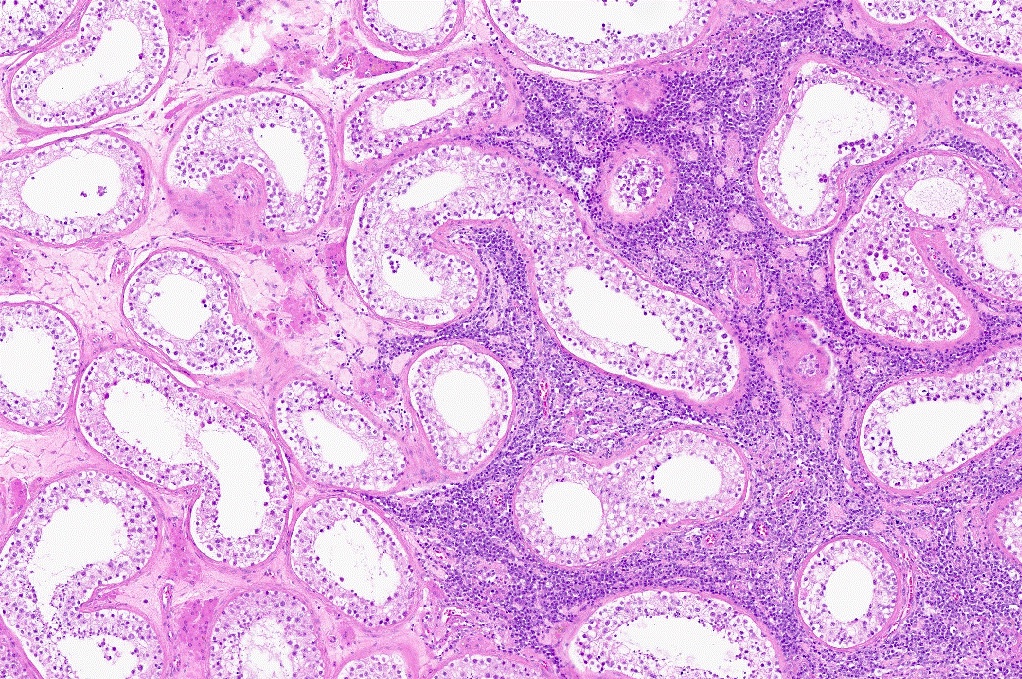
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Diffuse sheets of large lymphoma cells (Pathology 2020;52:53)
- Initially infiltrate between seminiferous tubules before total replacement of the parenchyma
- Lymphoma cells frequently invade and fill the seminiferous tubules
- Frequent mitotic figures can be seen (Hematol Oncol 2014;32:72)
- Necrosis is common
- Lymphoma cells show centroblastic morphology in most cases (90%) and less commonly, immunoblastic morphology (10%)
- Associated changes in the testis include spermatogenic arrest, interstitial fibrosis and tubular hyalinization
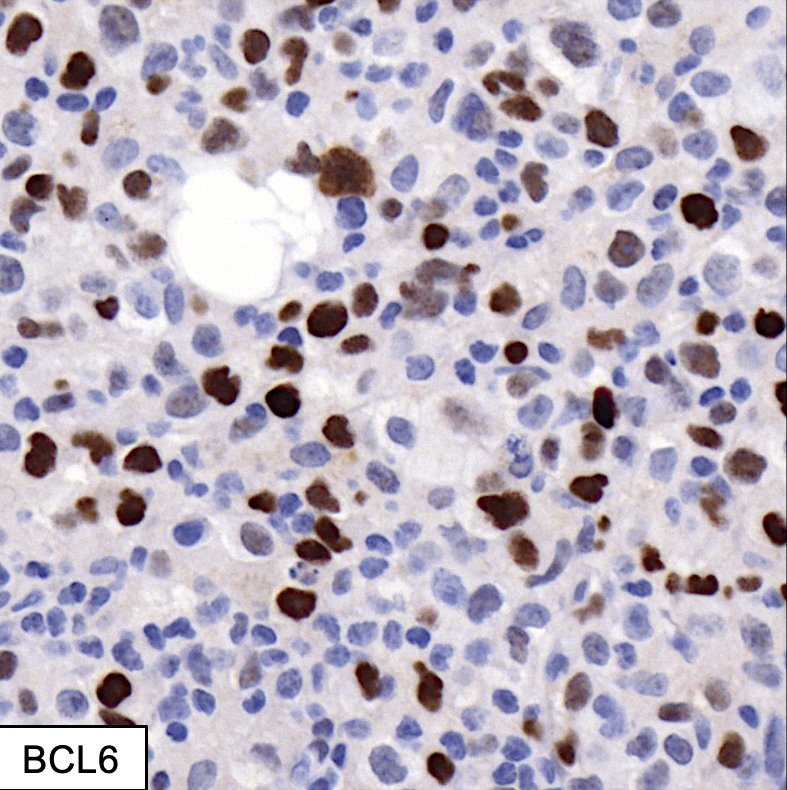
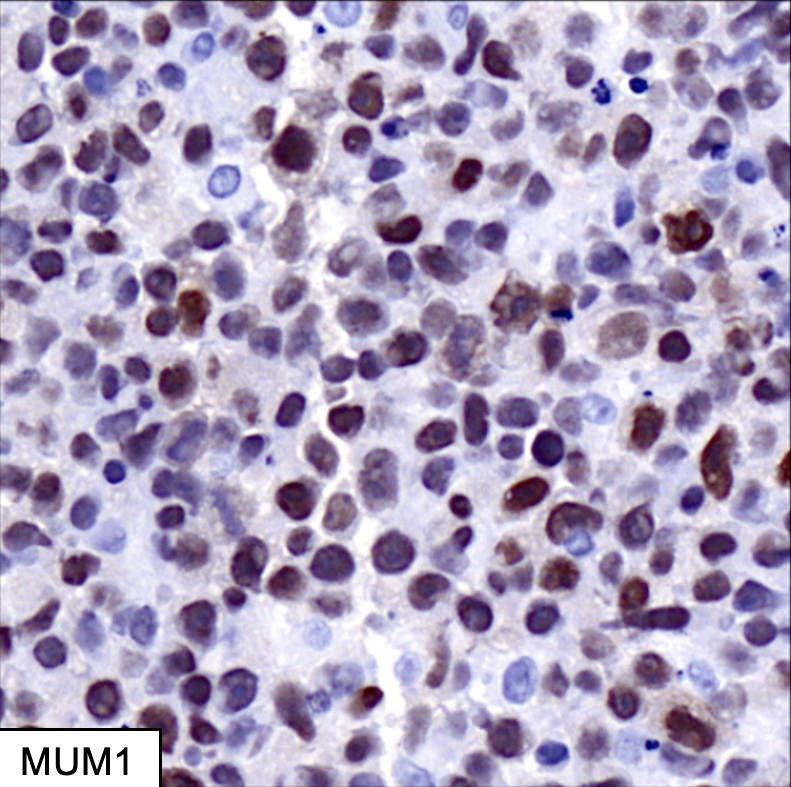
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
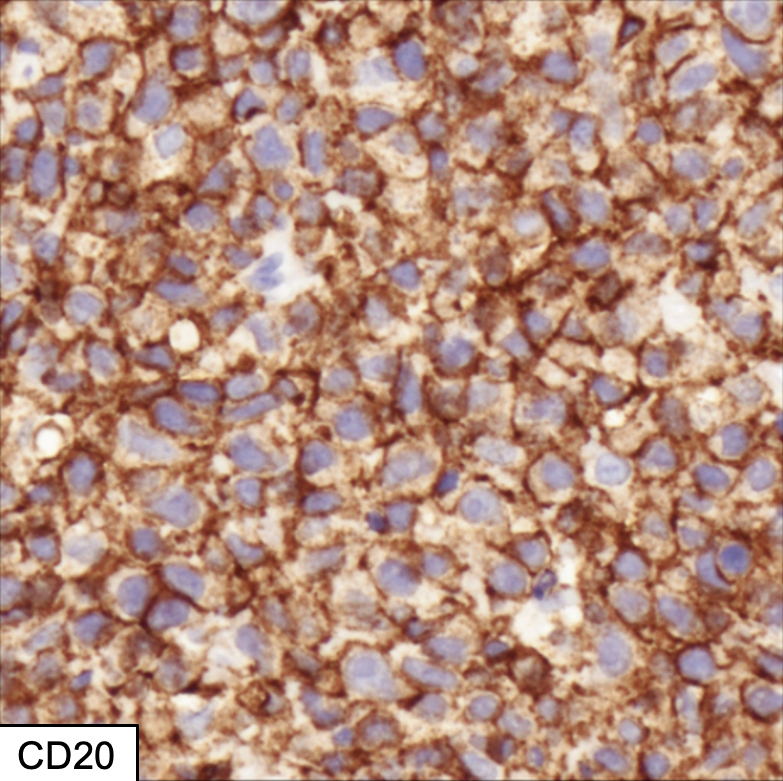
- Pan B cell antigens (CD19, CD20, CD79a, PAX5) (Leukemia 2016;30:361, Blood Rev 2018;32:249)
- BCL6 (75 - 90%), MUM1 (40 - 70%), CD10 (20 - 40%)
- TCL1 (~67%), FOXP1 (~80%)
- BCL2 (~75%), MYC (13%) (Hematol Oncol 2014;32:72)
- Double expressers have been reported in 13% of cases
- OCT4 expression has been demonstrated in up to 18% of DLBCL PT and represents a potential diagnostic pitfall with germ cell tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:950)
- Ki67 ranges from 40 - 90% (mean of 70%) (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e19463)
Negative stains
- Pan T cell antigens
- Cyclin D1
- EBER ISH
- SALL4
- CD30
- Reference: Hematol Oncol 2014;32:72
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- IGH rearrangements in virtually all cases
- BCL2 and MYC rearrangements occur in 10% and 15% of cases, respectively; BCL6 rearrangement occurs in 40% (Leuk Lymphoma 2014;55:1410)
- Genetic analysis (Onco Targets Ther 2019;12:10165, Leukemia 2014;28:719):
- MYD88: amplifications, mutations and deletions (60 - 82%)
- CD79B: mutations and deletions (19 - 34%)
- NFKBIZ: copy number gain (42%)
- CDKN2A: copy number alterations (71%)
- CD274: rearrangements, copy number alterations, an increased protein expression (35%)
- CD273: rearrangements, copy number alterations, an increased protein expression (47%)
Sample pathology report
- Right testis, orchiectomy:
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, nongerminal center type (see comment)
- Comment: In the proper clinical circumstances, findings are consistent with primary diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the testis. Clinical correlation is required to exclude systemic or extratesticular primary disease.
Differential diagnosis
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A man presents with right testicular mass and undergoes orchiectomy. Microscopic findings reveal a diffuse process of large lymphoid cells replacing the testicular parenchyma (see image). In which age group is this entity most commonly seen?
- < 15 years
- 30 - 40 years
- 60 - 70 years
- Typically seen at any age
Board review style answer #1
C. 60 - 70 years. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the testis has a mean age of presentation of 60 - 70 years.
Comment Here
Reference: DLBCL-primary testicular
Comment Here
Reference: DLBCL-primary testicular
Board review style question #2
Which of the following stains would be expected to be negative in diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the testis?
- BCL2
- CD20
- EBER ISH
- MUM1
Board review style answer #2
C. EBER ISH. EBV infection has not been associated with diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the testis.
Comment Here
Reference: DLBCL-primary testicular
Comment Here
Reference: DLBCL-primary testicular