Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Wakeman K, Mantilla J. Fibrous dysplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonefibrousdysplasia.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign fibro-osseous lesion that may involve one (monostotic) or multiple (polyostotic) bones
- Developmental disorder of bone resulting in the failure to form mature lamellar bone
- Mass forming developmental defect composed of woven bone and fibroblast-like spindle cells
- Caused by failure in bone maturation, with arrest as woven bone (see Pathophysiology)
- Associated clinical or syndromic manifestations (see Clinical features)
Essential features
- Slow growing expansion of bone, composed of a proliferation of irregular woven bone trabeculae lacking conspicuous osteoblastic rimming, within a background of fibrous tissue with cytologically bland spindle cells
- Intramedullary lesions without cortical destruction
- May be congenital or hereditary (but differs from cherubism)
Terminology
- Historically, osteitis fibrosa or generalized fibrocystic disease of bone (both terms not conventionally used)
- 2 basic clinical forms: monostotic and polyostotic
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Usually manifests during the first 3 decades of life
- M=F
- Monostotic forms are more common than polyostotic
- Polyostotic can be sporadic or occur in patients with germline GNAS1 mutations, which can lead to distinct clinical syndromes; McCune-Albright syndrome (endocrine abnormalities, café au lait spots) and Mazabraud syndrome (with soft tissue myxomas) (Dorfman and Czerniak: Bone Tumors, 2nd Edition, 2015, IARC: WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone, 4th Edition, 2014)
Sites
- Can affect any bone; however, involvement of the spine is very rare (J Orthop Case Rep 2014;4:73)
- Monostotic forms are more common in ribs, craniofacial bones (maxilla > mandible) and femur
- Polyostotic forms frequently affects lower extremities and pelvis
Pathophysiology
- Arrest in development of cortical bone, leading to lesions composed of irregular woven bone and immature fibroblast-like spindle cells
- Gain of function mutations in GNAS (guanine nucleotide-binding protein / α-subunit), located in 20q13.2-3, lead to overexpression of Gsα protein and increased downstream adenyl cyclase activity (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:660)
- Activation of c-jun, c-fos and Wnt/β-catenin are associated with activation of Gsα protein
- Variable expression of GNAS mutations may explain the variability in clinical manifestations
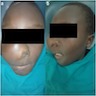
Clinical features
- Can be associated with McCune-Albright syndrome (endocrine abnormalities, café au lait spots) or Mazabraud syndrome (soft tissue myxomas)
- Transformation into sarcoma is extremely rare but has been reported, typically decades after initial diagnosis (J Formos Med Assoc 2004;103:711)
- Unilateral painless swelling of mandible or maxilla in men / women ages 25 - 35 years
Diagnosis
- Radiologic imaging (plain Xray films, CT scan) and biopsy
- Usually diagnosed by age 20 years
Laboratory
- Alkaline phosphatase can be elevated in certain cases, especially when tumor is growing
- Endocrine abnormalities (gonads, thyroid) can be seen in patients with McCune-Albright syndrome
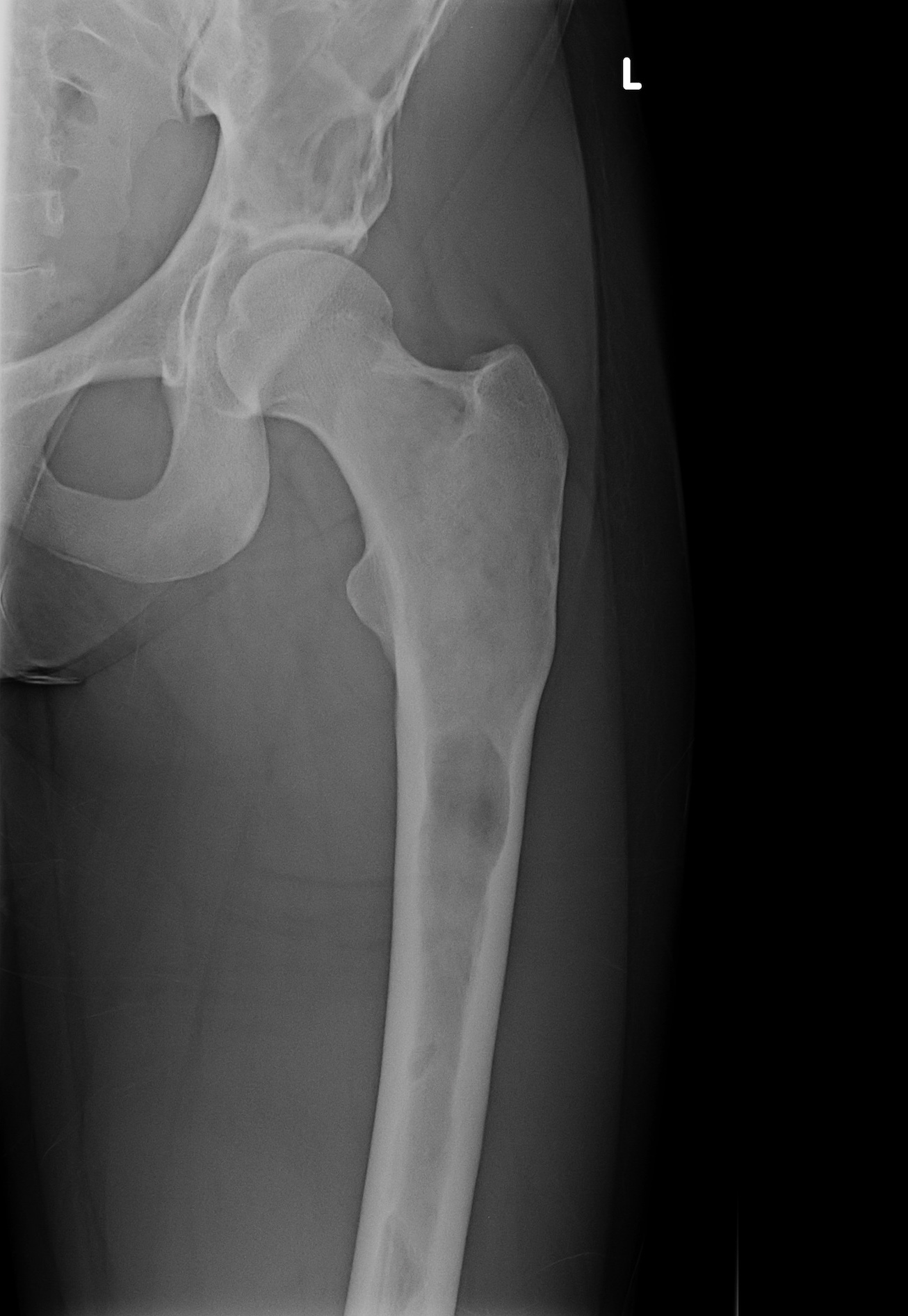
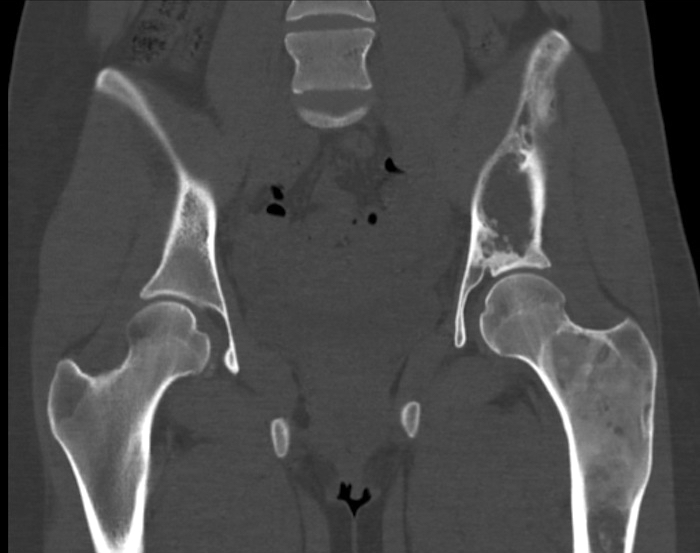
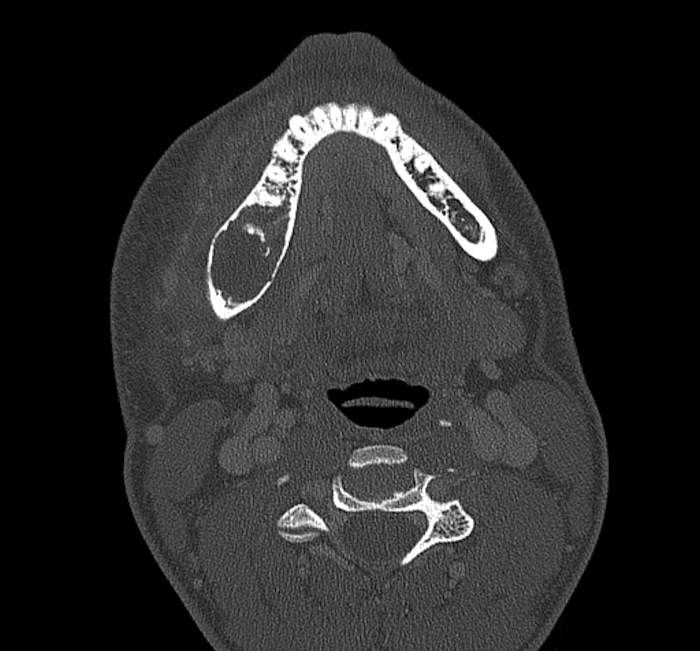
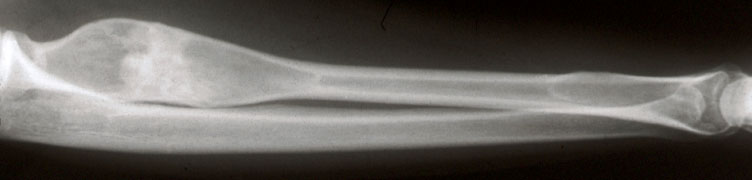
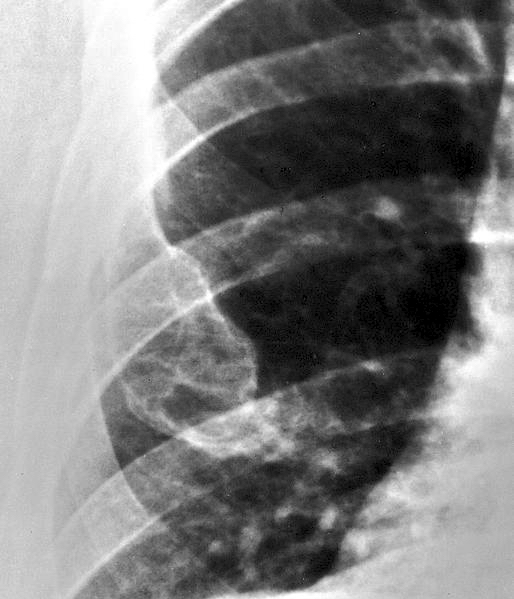
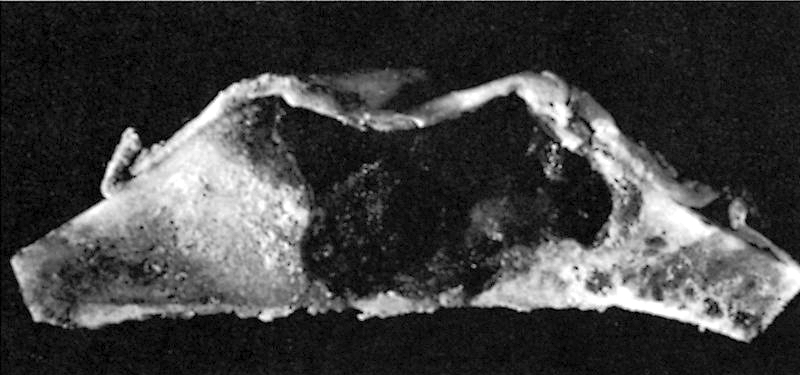
Radiology description
- Ill defined margins; diffusely radiopaque with ground glass image
- Single or multiple well circumscribed intramedullary lesions with a sclerotic rim
- May see cortical thinning as lesion expands
- Centered in metaphysis or diaphysis
- Radiolucent or ground glass appearance on Xray (Dorfman and Czerniak: Bone Tumors, 2nd Edition, 2015)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Unknown
Case reports
- 21 year old man with fibrous dysplasia in a lumbar vertebral body with secondary aneurysmal bone cyst-like change (Clin Pathol 2019;12:2632010X19861109)
- 30 year old man with fibrous dysplasia in the calcaneus (Foot Ankle Spec 2017;10:72)
- 62 year old man with angiosarcoma arising in fibrous dysplasia after radiation therapy (Oral Radiol 2019 Jul 31 [Epub ahead of print])
- 62 year old woman with Mazabraud syndrome and malignant transformation into osteosarcoma (Case Rep Orthop 2019;2019:2638478)
- Case series, locally aggressive fibrous dysplasia mimicking malignancy (Clin Orthop Relat Res 2015;473:742)
Treatment
- No treatment since growth is self limited and responsive to pubertal hormonal changes
- Usually conservative / symptomatic management
- Surgery in cases with fracture or bony deformity
- Surgical recontouring performed if facial deformity, although may regrow in 25%
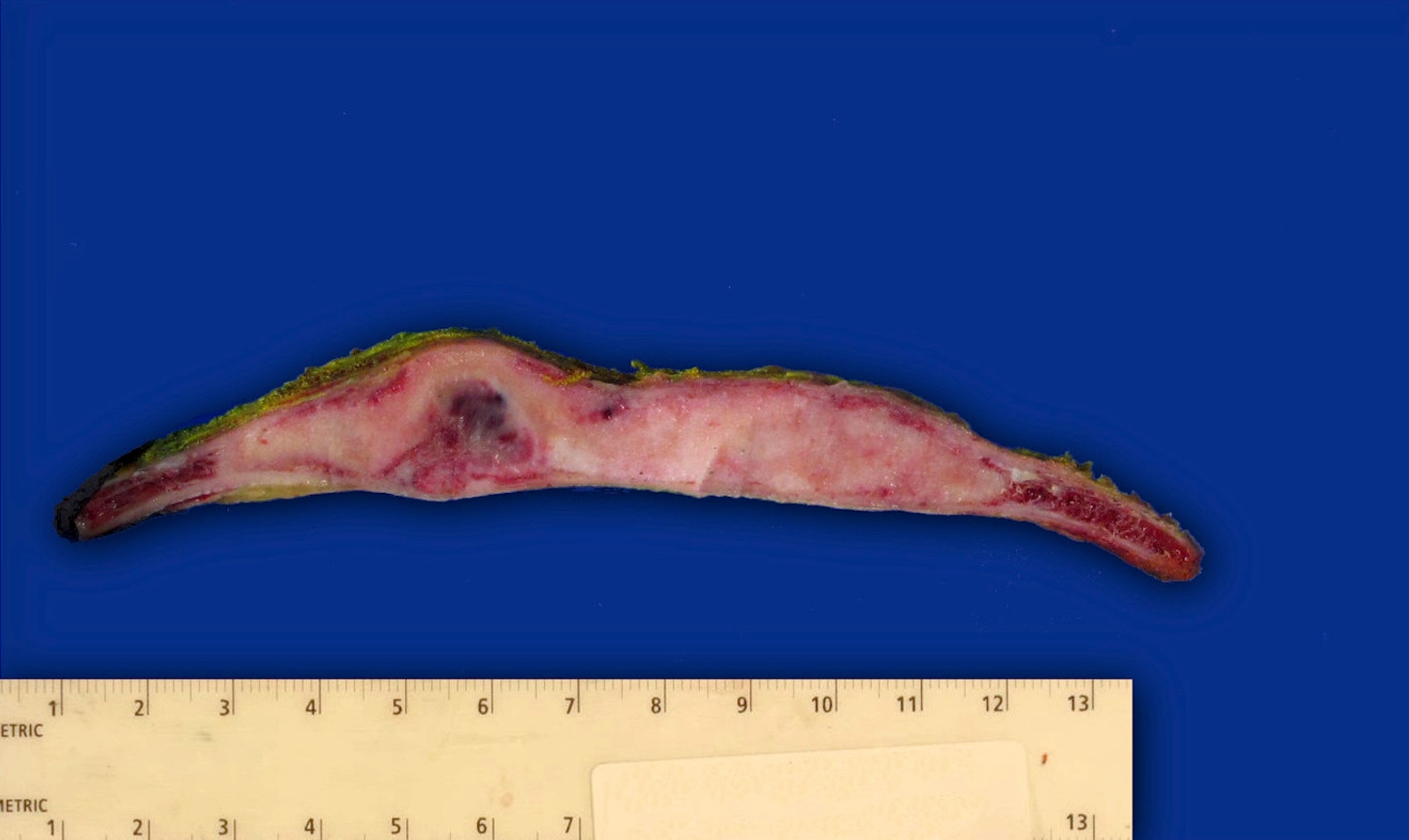
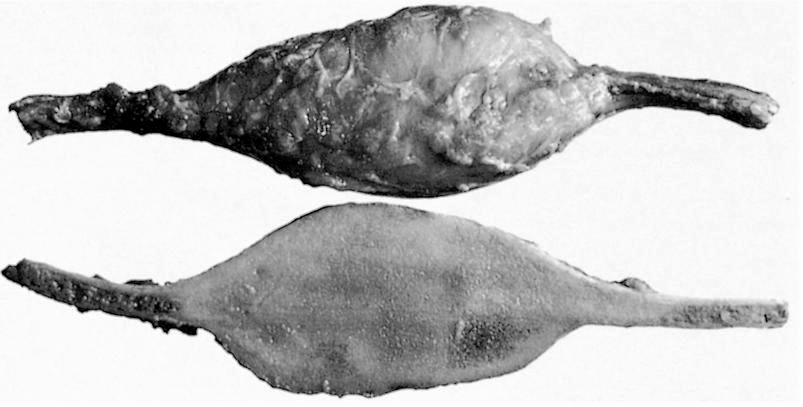
Gross description
- Well circumscribed lesion with a sclerotic rim centered within the cortex
- Cortex may be thinned as lesion expands
- Lesion itself may undergo aneurysmal bone cyst-like changes or cartilaginous metaplasia (Dorfman and Czerniak: Bone Tumors, 2nd Edition, 2015)
Gross images
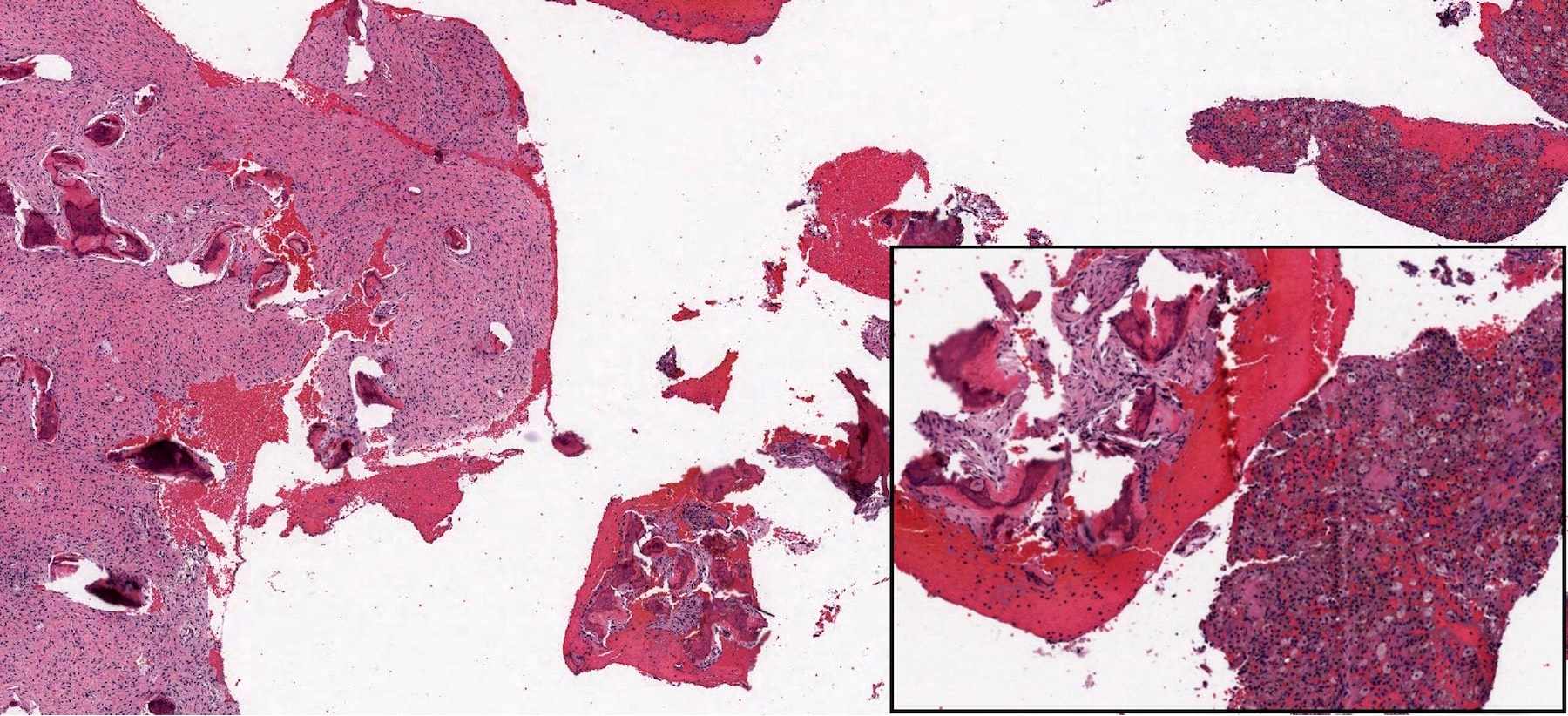
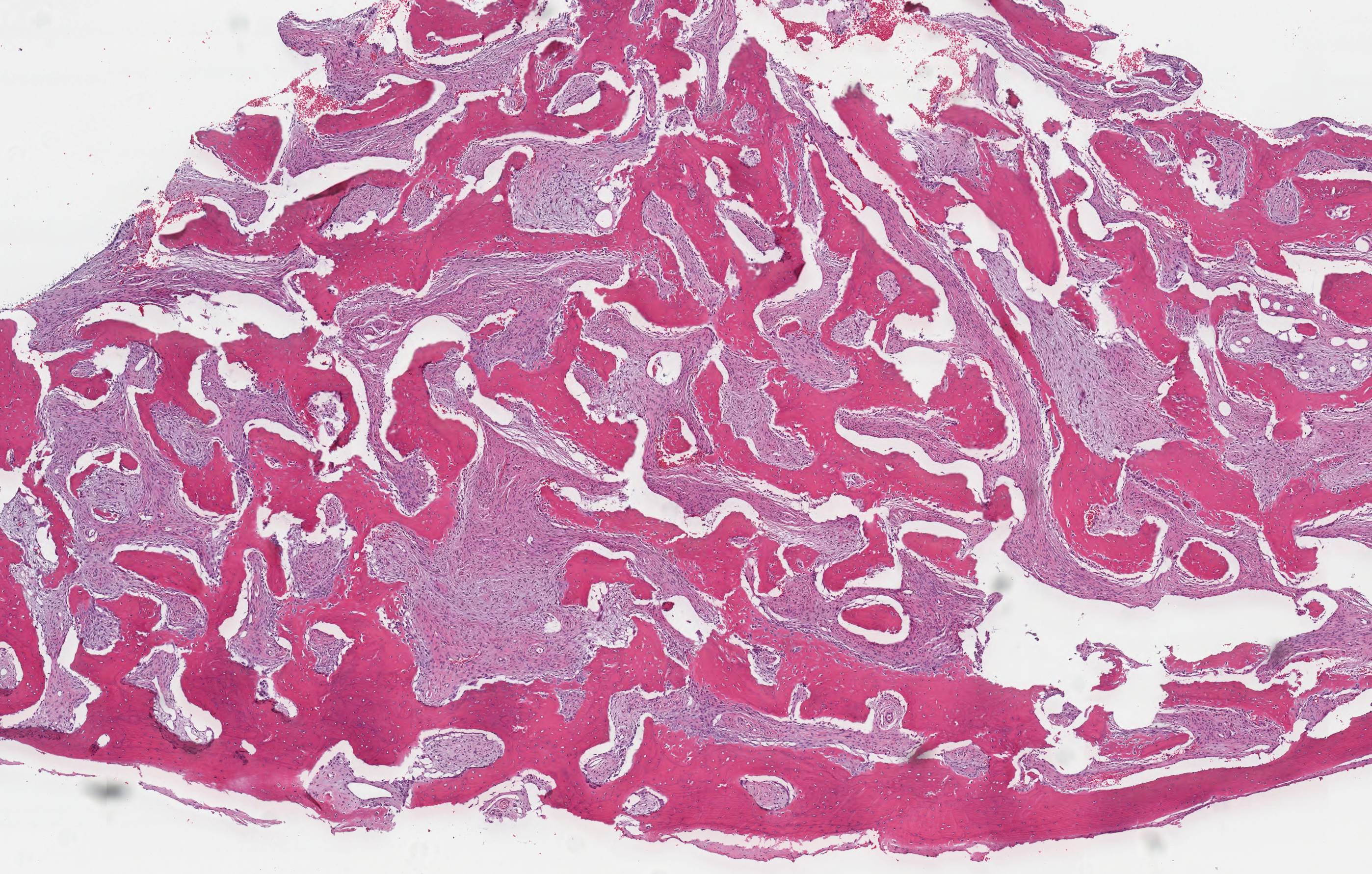
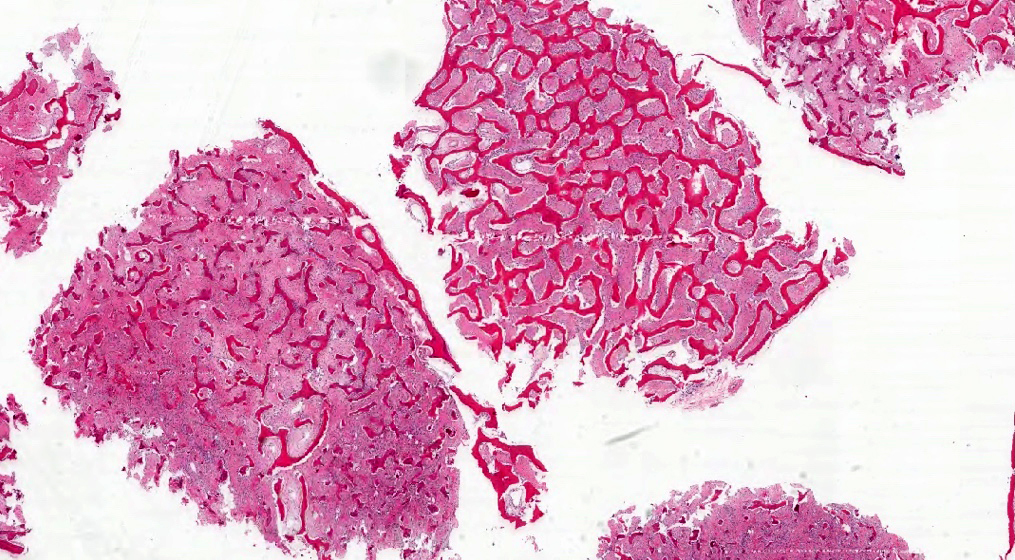
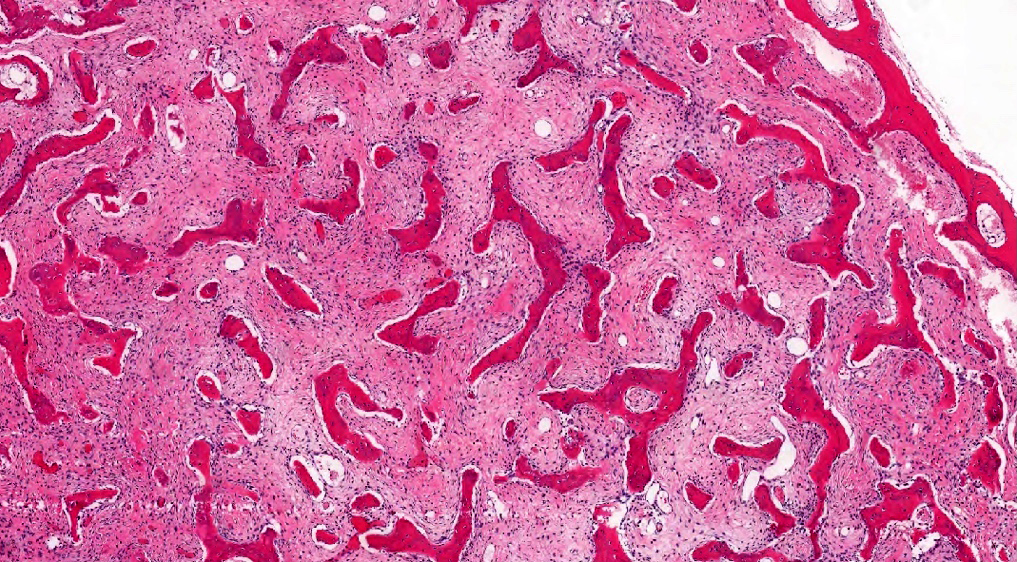
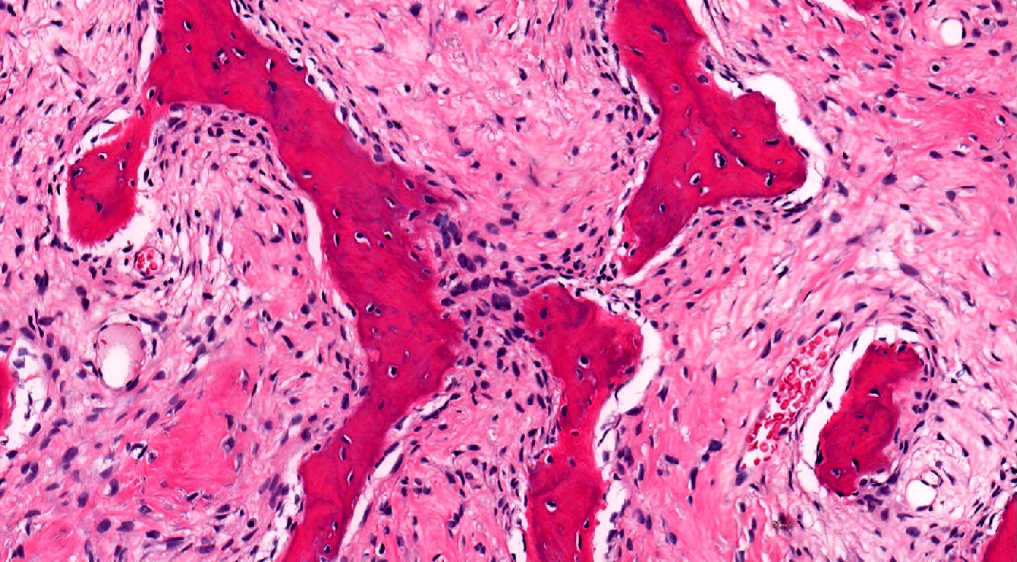
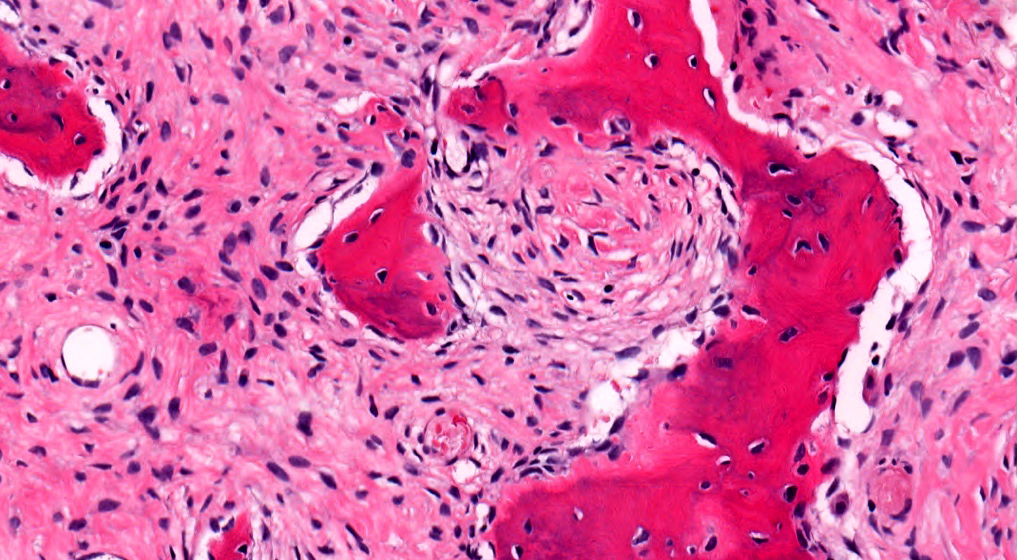
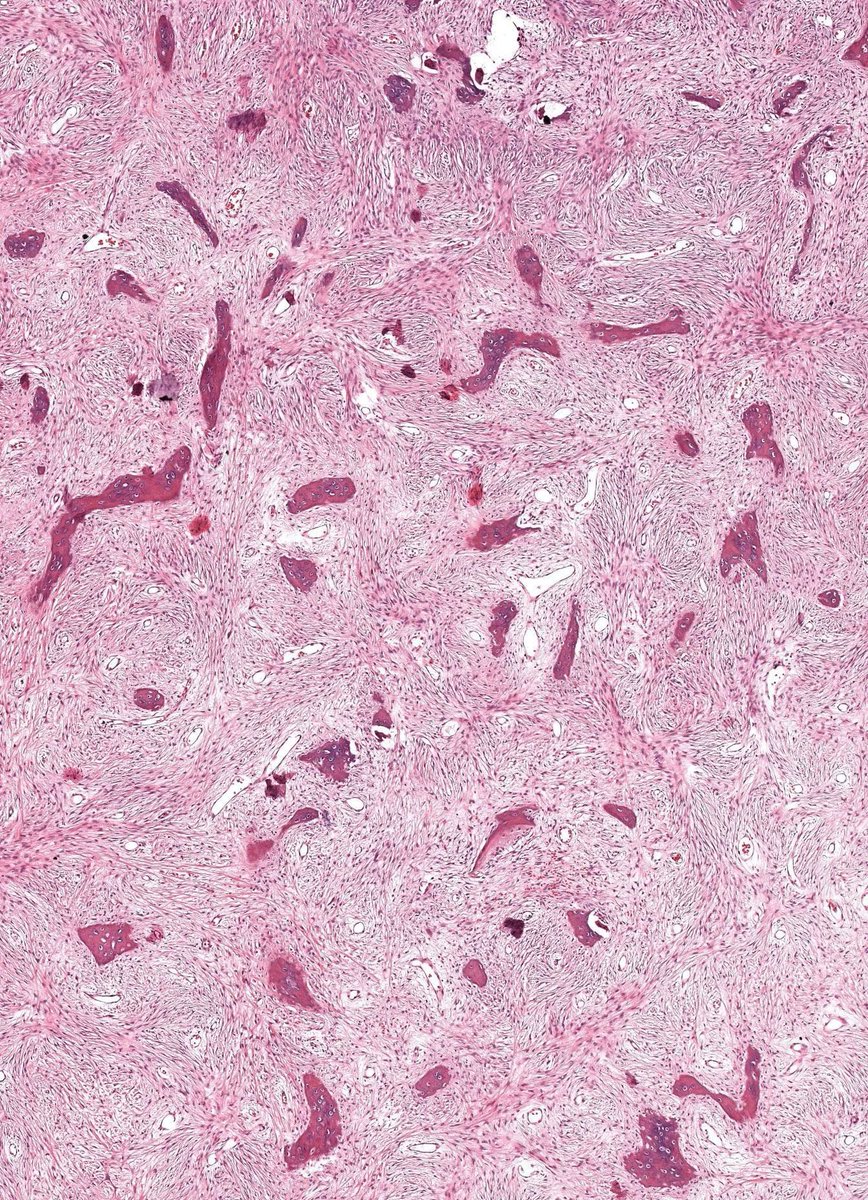
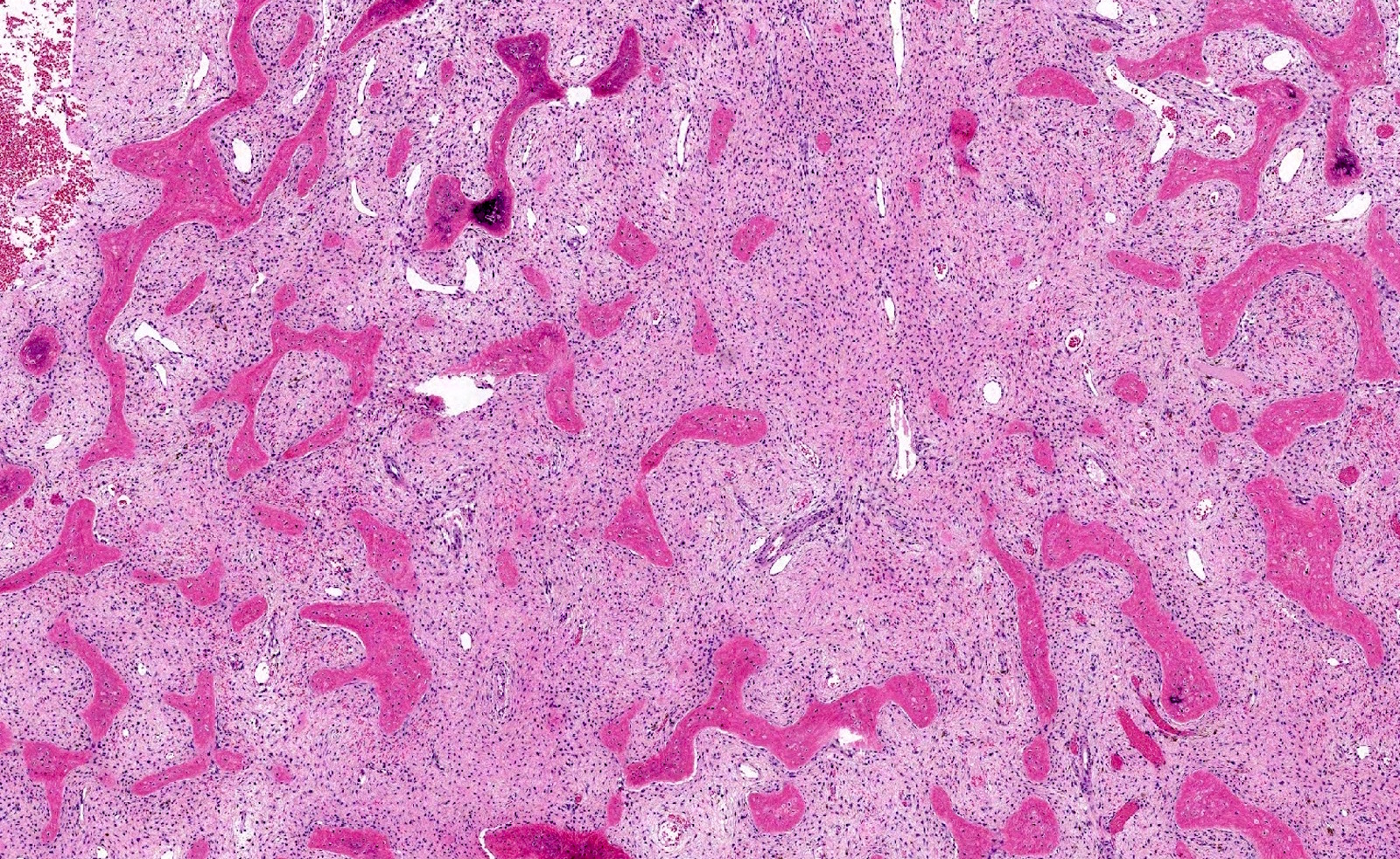
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Branching and anastomosing irregular trabeculae of woven bone ("C" and "S" shapes) with no conspicuous osteoblastic rimming
- No / rare osteoclasts
- Intervening fibrous stroma containing cytologically bland spindle cells, without prominent cytologic atypia
- Mitotic figures rare
- Stromal changes, including myxoid change and fatty metaplasia, may be seen in some cases (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2003;4:20)
- Secondary aneurysmal bone cyst-like changes may also be seen (Turk Patoloji Derg 2018;34:234)
- Fibrocartilaginous dysplasia: uncommon variant containing variable proportions of cartilaginous differentiation and enchondral ossification (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:924)
- Growing collagen (Sharpey's fibers) may form perpendicular to the sites of bone formation but are not essential for diagnosis (Oral Dis 2017;23:697)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- SATB2, expressed in bone forming lesions, may be expressed in up to 89% of cases (Histopathology 2013;63:36)
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Postzygotic somatic mutations in GNAS; typically gain of function single nucleotide substitutions (Sci Rep 2017;7:2836, Molecules 2017;22:E1874, Hum Pathol 2012;43:1234)
Sample pathology report
- Right tibia, biopsy:
- Benign fibro-osseous proliferation, consistent with fibrous dysplasia
Differential diagnosis
- Parosteal and low grade central osteosarcoma:
- Destructive, slow growing lesion on imaging
- Can histologically mimic
- MDM2 amplification is typically present
- Osteofibrous dysplasia:
- Similar irregular bone trabeculae
- Osteoblastic rimming is prominent
- Liposclerosing myxofibrous tumor (LSMFT):
- Can have significant clinical and morphologic overlap
- Also characterized by activation of Protein G, suggesting that these lesions may be part of the same spectrum
- Typically located in the proximal femur
- Can have a variety of coexisting histologic patterns, including curvilinear trabeculae of woven bone (mimicker), interspersed with paucicellular myxofibrous tissue, ossification, adipose tissue and cartilage (Acta Ortop Mex 2015;29:191, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2016;140:473, Iowa Orthop J 2012;32:35)
Board review style question #1
- What is the underlying genetic mutation in patients with McCune-Albright syndrome?
- GNAS1
- p53
- PTH1R
- SDH
Board review style answer #1
A. Mutations in GNAS1 are seen in patients with McCune-Albright and Mazabraud syndrome
Comment Here
Reference: Fibrous dysplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Fibrous dysplasia
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
D. Woven bone trabeculae. The trabeculae in fibrous dysplasia are composed of woven bone with various phases of mineralization. Mature lamellar bone can be seen at the periphery but should not be part of the lesion itself.
Comment Here
Reference: Fibrous dysplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Fibrous dysplasia