Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Magliocca K, Martinez A. Odontoameloblastoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillaodontoameloblastoma.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Odontoameloblastoma (OA) is / was viewed as an extremely rare mixed odontogenic tumor with both epithelial and mesenchymal components
- Epithelial component represented by ameloblastoma
- Mesenchymal component - a compound or complex odontoma
- Not considered an entity in the current 4th edition WHO (El-Naggar: WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours, 4th Edition, 2017)
Essential features
- Odontoameloblastoma (OA) is no longer considered an entity in the current 4th edition WHO (El-Naggar: WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours, 4th Edition, 2017)
Terminology
- Odontoblastoma
- Adamant-odontoma
- Calcified mixed odontogenic tumor
- Soft and calcified odontoma
- Ameloblastic odontoma
Epidemiology
- Wide age range (2 - 50 years) with mean age of ~20 years (Oral Oncol 2002;38:800)
- Slight male predilection
Sites
- Molar / premolar region of maxilla or mandible
Clinical features
- Swelling, dull pain, delayed eruption of teeth, bone expansion
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis dependent on clinical, radiologic and pathologic correlation
Radiology description
- Radiolucent lesion that can be destructive
- Contains calcified structures resembling mature dental tissue
Prognostic factors
- Known to recur after curettage
- No long term prognostic data, given so few cases
Case reports
- 11 year old Japanese boy with a painless and large mass of the right maxillary region (J Med Case Rep 2015;9:278)
- 12 year old Caucasian girl referred for occasional pain and gingival swelling (Med Oral 2004;9:340)
- 12 year old boy with mass in upper jaw (Case of the Week #367)
- 17 year old girl with odontoameloblastoma resembling a fibro-osseous lesion (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2015;19:251)
- 47 year old man with a chief complaint of rapidly growing swelling on the back side of the anterior lower jaw for 3 months (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2011;15:60)
Treatment
- Suggested to treat similarly to ameloblastoma
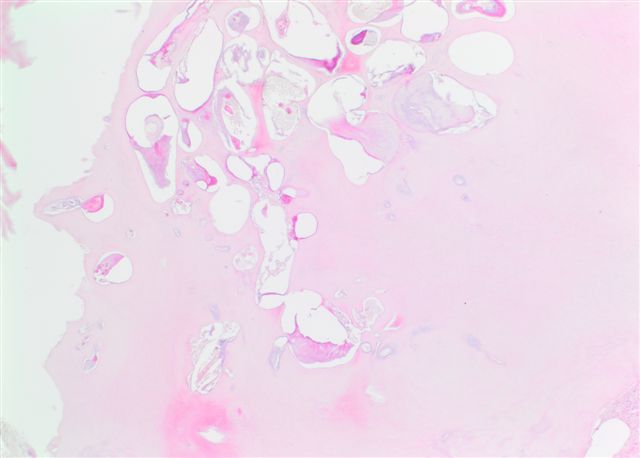
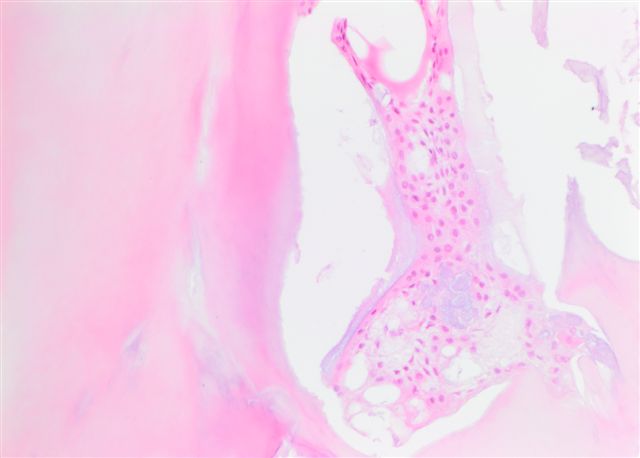
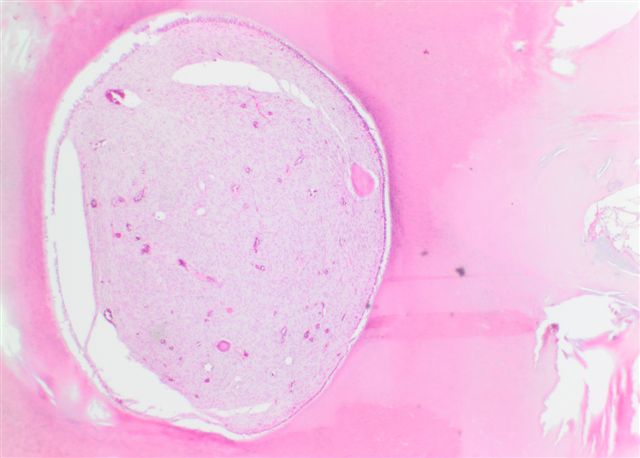
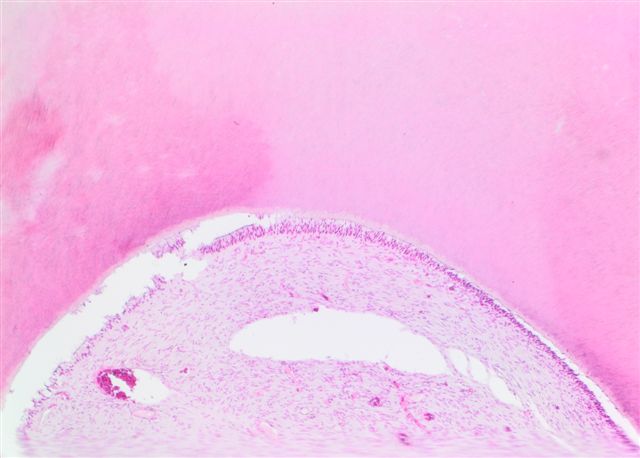
Microscopic (histologic) description
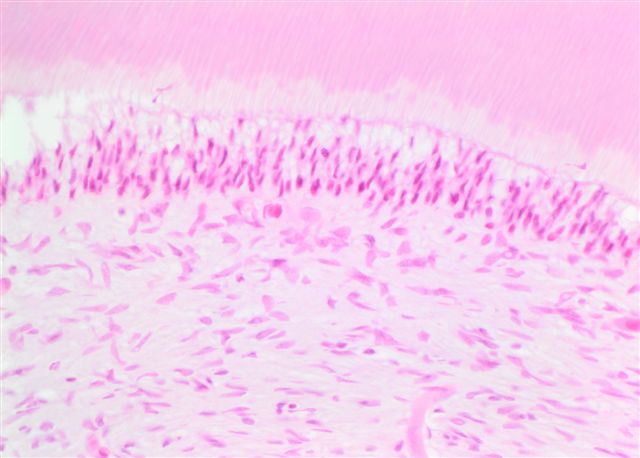
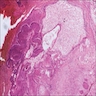
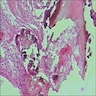
- Proliferating odontogenic epithelium portion identical to that of an ameloblastoma with peripheral palisading, reverse polarization and stellate reticulum
- Generally presenting as plexiform or follicular pattern
- This epithelial portion appears intermingled with dental tissues of variable degrees of maturity
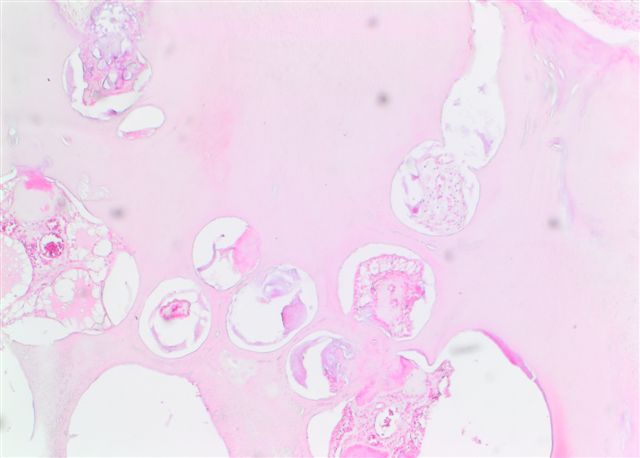
- Can show resemblance to the developing rudimentary teeth, as in a compound odontoma
- Can also show conglomerate masses of enamel, dentin and cementum, as seen in complex odontoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Ameloblastic fibroma
- Composed of odontogenic epithelial component strands, cords and islands that may exhibit peripheral palisading, reverse polarization and stellate reticulum
- Primitive appearing stroma that is delicate and lobular in appearance
- Should not have the mesenchymal (odontoma) component
- Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
- Has soft tissue component that is similar to ameloblastic fibroma
- Also contains a calcifying component composed of enamel and dentin structures
- Ameloblastoma
- Same histologic epithelial features with peripheral palisading, reverse polarization and stellate reticulum
- Should not have mixed mesenchymal component (odontoma)
- Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor (CCOT)
- Benign cystic tumor of odontogenic origin, also known as Gorlin cyst or calcifying odontogenic cyst
- Can have ameloblastic features: columnar or cuboidal basal cells with lumen lined by tissue resembling stellate reticulum
- Will have ghost cells or anucleate epithelial cells
- Can also have dentinoid materal resembling odontoma in around 20% of cases
- Odontoma
- Compound odontoma: cluster of denticles of varying sizes
- Complex odontoma: conglomerate of dentin admixed with enamel matrix