Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Morrison A. Inflammatory collateral cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillaparadental.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Inflammatory odontogenic cyst occurring at the crown or root of a partially or fully erupted tooth
- Includes paradental cyst and buccal bifurcation cyst
- Is a term applied to a spectrum of clinicoradiographic entities - see terminology
Terminology
- Reduced enamel epithelium (REE): ameloblastic and epithelial cells from the outer enamel that overly an unerrupted tooth, as the REE degenerates the underlying tooth is exposed
- Crevicular epithelium: epithelium lining the inner aspect of the gingival sulcus
- Epithelial rests of Malassez: discrete clusters of residual cells from Hertwig epithelial root sheath
- Inflammatory odontogenic cysts: distinguished from developmental odontogenic cysts by their association with inflammation
- Clinicoradiographic variants include:
- Apical radicular cyst
- Lateral radicular cyst
- Residual cyst
- Paradental cyst
- Clinicoradiographic variants include:
- Buccal bifurcation cyst (BBC):
- Aka paradental cyst, juvenile paradental cyst or mandibular infected buccal cyst
- Occurs along the buccal root surface of partially erupted mandibular molar of children and young adults
- Affected tooth is vital
- Paradental cyst:
- After excluding cysts occurring along the lateral / buccal surface of a partially impacted mandibular molar of a young individual, the term paradental cyst also refers to a variant of the dentigerous cyst with an inflammatory, rather than developmental pathogenesis
- The two most common scenarios include vital (non-necrotic) teeth:
- A dentigerous cyst that develops around the crown of an unerupted permanent tooth as a result of periapical inflammation from an overlying primary tooth
- A partially erupted mandibular third molar that develops an inflamed cystlike lesion along the distal aspect associated with inflammation or recurrent pericoronitis
- These are often called dentigerous cyst, as it is impossible to determine histopathologically whether the inflammatory component is primary or secondary in nature
Epidemiology
- 1 - 5% of odontogenic cysts
Sites
- Buccal >> Mesial surface
- Erupted or partially erupted teeth
- Molars >> premolars > cuspids
- 3rd molar (wisdom teeth) >> 1st / 2nd molars
- Mandibular teeth >> Maxillary teeth
- ~24% of paradental cysts in 1st or 2nd molars are bilateral
Pathophysiology
- Theorized to arise from one of the following, however, each can be debatable given the specified location of paradental cysts:
- Reduced enamel epithelium
- Epithelial rests of Malassez
- Crevicular epithelium
- Epithelial remnants of dental lamina
Clinical features
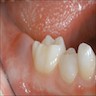
- Recurring periodontal inflammatory process (pericoronitis)
- Symptoms: discomfort, swelling, tenderness, pain
- Often Asymptomatic
Diagnosis
- Based on location, radiography, pathology, root vitality studies
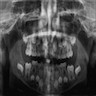
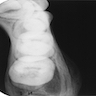
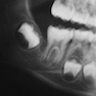
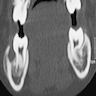
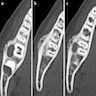
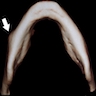
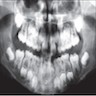
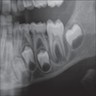
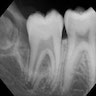
Radiology description
- Periosteal reaction common
- Onion skin deposition of bone appears as parallel opaque layers
Radiology images
Images hosted on other servers:
Prognostic factors
- Good prognosis
- No reports of recurrence to date
Case reports
- 8 year old boy with paradental cyst of first molar (J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent 2012;30:343)
- Two cases involving paradental cysts (J Periodontol 2006;77:1602)
- Paradental cyst mimicking a radicular cyst on the adjacent tooth (J Endod 2003;29:73)
Treatment
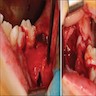
- Curettage
Clinical images
Gross description
- A cyst-like soft tissue (may or may not be intact) attached to the cementoenamel junction, or along the root of the tooth
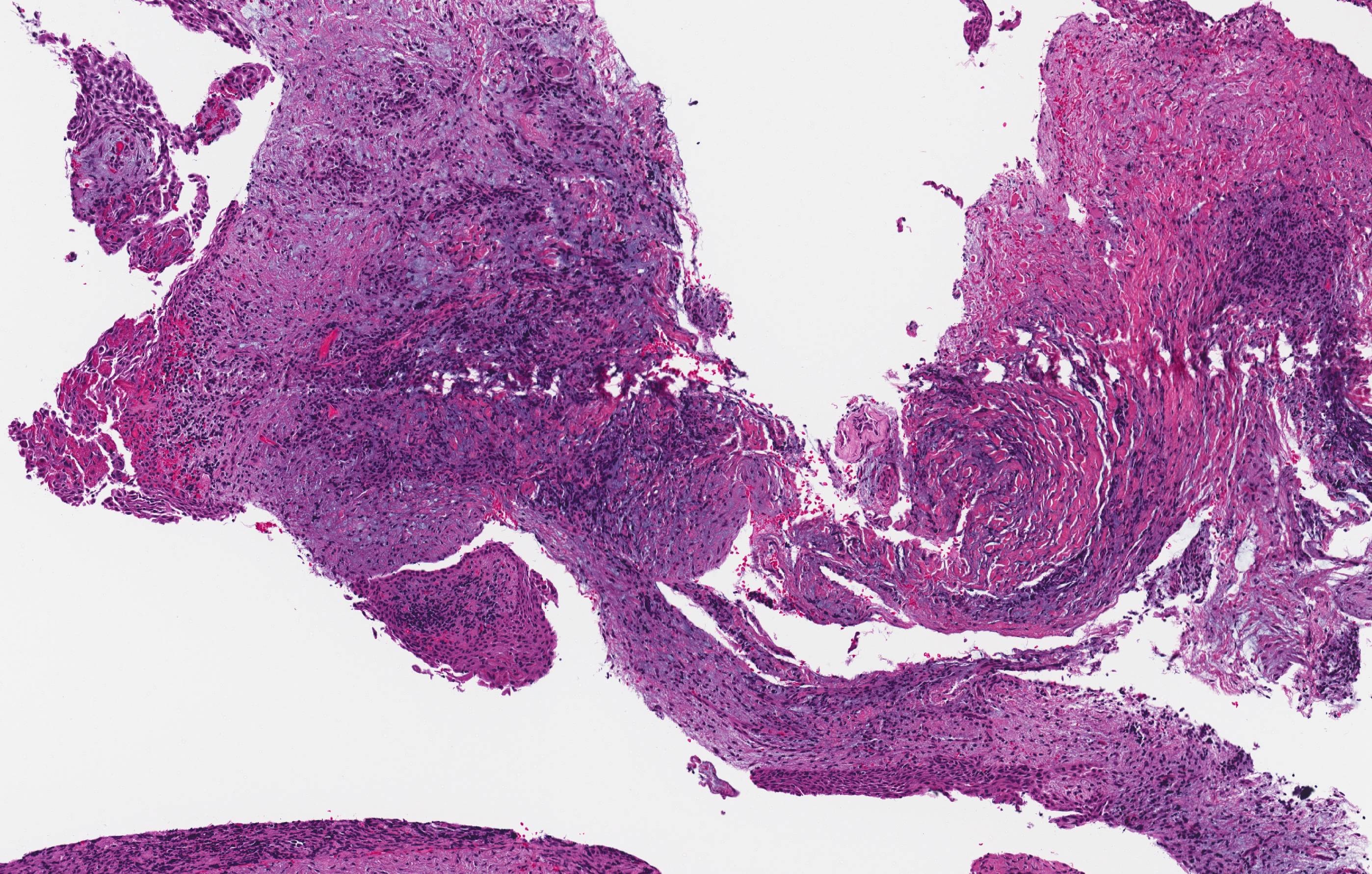
Microscopic (histologic) description
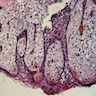
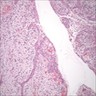
- The microscopic findings are not specific and cannot distinguish between the variants of inflammatory odontogenic cysts, or a markedly inflamed developmental dentigerous cyst
- Clinical and radiographic correlation essential
- Connective tissue wall
- Heavy mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrate
- Hyperplastic nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelium
- Often with hemosiderin pigment or cholesterol clefts
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Apical radicular cyst
- Dentigerous cyst, markedly inflamed
- Inflamed periodontal pocket / periodontal tissues
- Lateral radicular cyst
- Residual cyst
Additional references