Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Chen Wongworawat Y, Fisher KE. FOXO1. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/molecularFOXO1.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- FOXO1 (forkhead box O1) gene is located on chromosome 13q14.11
- It is comprised of 3 exons, 2 of which are protein coding (NM_002015.4) and was known previously as FKHR (forkhead) (HGNC: Symbol Report for TMEM266 [Accessed 26 October 2023])
- FOXO1 protein, encoded by the FOXO1 gene, belongs to the forkhead (FH) family of transcription factors
- 4 human FOXO proteins, FOXO1 / FOXO3 / FOXO4 / FOXO6, share a conserved DNA binding domain called the FH domain that binds specific double stranded DNA sites; namely, the DAF-16 binding element (DBE) and the insulin responsive element (IRE)
- FH family proteins regulate the expression of target genes involved in cellular homeostasis, maintaining tissue structure and function and coordinate the response to environmental challenges
- They also play roles in senescence, autophagy and stem cell maintenance (Trends Pharmacol Sci 2022;43:1070)
Essential features
- Translocation t(2;13)(q35;q14) yields PAX3::FOXO1 fusion transcripts reported in a majority (60%) of alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas (ARMS)
- Translocation t(1;13)(p36;q14) yields PAX7::FOXO1 fusion transcripts reported in a subset (20%) of ARMS
- ~20% of ARMS cases are negative for FOXO1 fusions (Molecules 2018;23:2798)
Terminology
- FOXO1 (forkhead box O1)
- PAX3 (paired box 3)
- PAX7 (paired box 7)
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS)
Pathophysiology
- PAX3 and PAX7 represent transcription factors that play essential roles in myogenesis (Semin Cell Dev Biol 2015;44:115)
- PAX3::FOXO1 and PAX7::FOXO1 chimeric proteins function as oncoproteins affecting growth, survival, differentiation and other pathways through activation of numerous downstream target genes such as MET, ALK, FGFR4, MYCN, IGF1R and MYOD1
- PAX3::FOXO1 fusion transcripts fuse the DNA binding domain of PAX3 with the transactivation domain of FOXO1; this fusion results in the generation of a novel transcription factor with altered transcriptional power, potentially altered transcriptional targets and altered posttranslational regulation (Cancer Lett 2008;270:10)
- In PAX7::FOXO1 expressing tumors, the fusion gene is present in increased copy numbers due to amplification of the genomic region containing the fusion gene (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012;51:662)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- PAX3::FOXO1 and PAX7::FOXO1 fusion transcripts are specific genetic changes associated with ARMS and detection of these fusion transcripts is considered a desirable diagnostic criterion for ARMS
- Recent therapeutic approaches are under development to target the PAX3::FOXO1 fusion oncoprotein by inhibiting the PAX3::FOXO1 modifying kinases (Molecules 2018;23:2798, Semin Cancer Biol 2018;50:115)
Uses by pathologists
- Translocation of the FOXO1 gene at 13q14 with PAX3 at 2q35 or less commonly PAX7 at 1p36 is a characteristic feature of ARMS
- Presence of PAX3::FOXO1 and PAX7::FOXO1 fusion genes is highly suggestive of ARMS in appropriate histopathologic settings
- FOXO1 fusions are absent in embryonal rhabdomyosarcomas (ERMS) and other histologic variants of ARMS
- Reference: J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2001;23:215
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis for patients with fusion positive ARMS is inferior to that for patients with fusion negative ARMS and ERMS (Adv Anat Pathol 2013;20:387)
- Prognosis for patients with PAX3::FOXO1 ARMS is inferior to that for patients with PAX7::FOXO1 ARMS (Cancer 2021;127:946, Pediatr Blood Cancer 2013;60:1411)
- Amplification of MYCN, CDK4 and MIR17HG has also been correlated with poor outcomes in ARMS (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002;33:310, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2009;48:661, Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:1463)
Microscopic (histologic) description
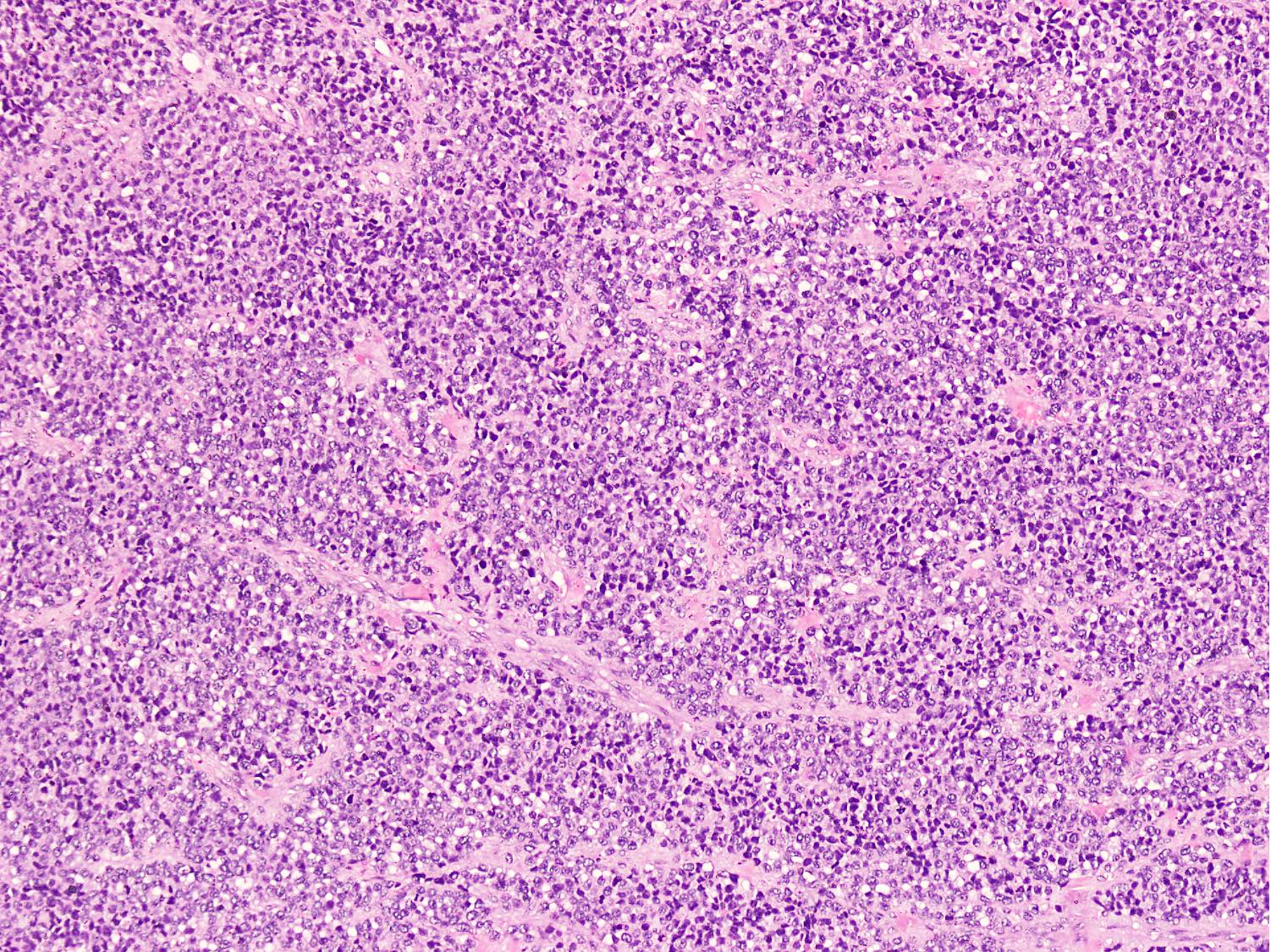
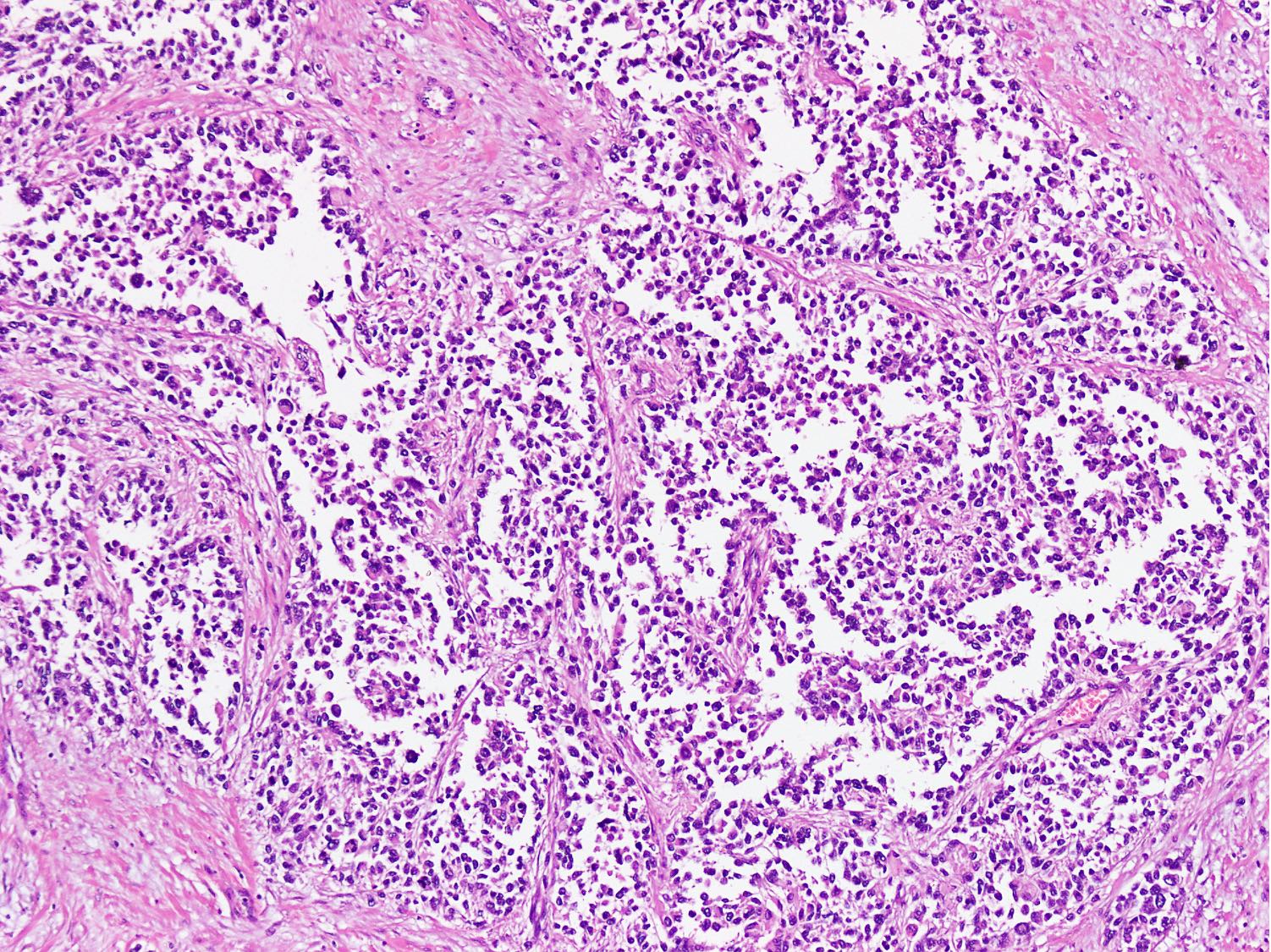
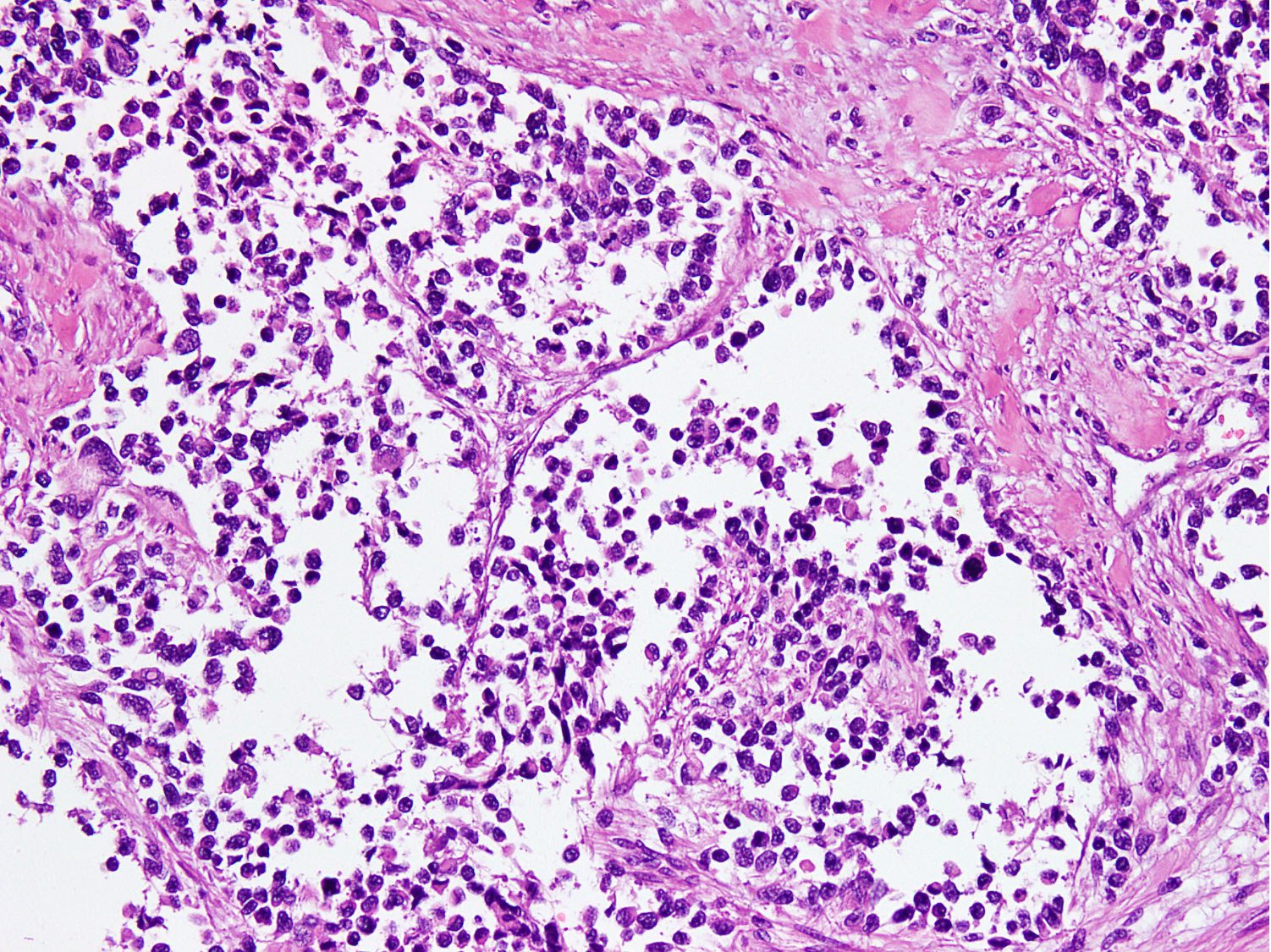
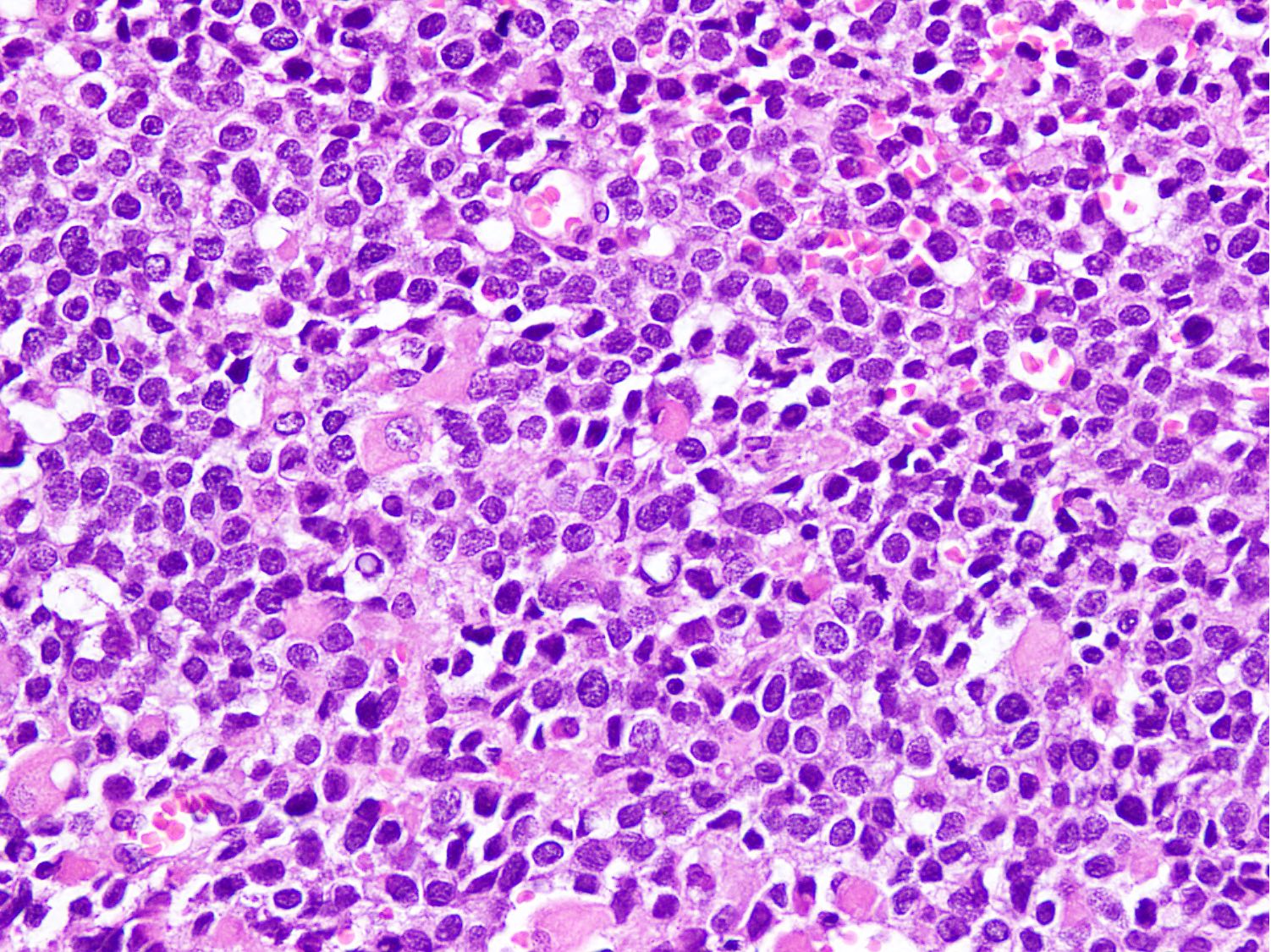
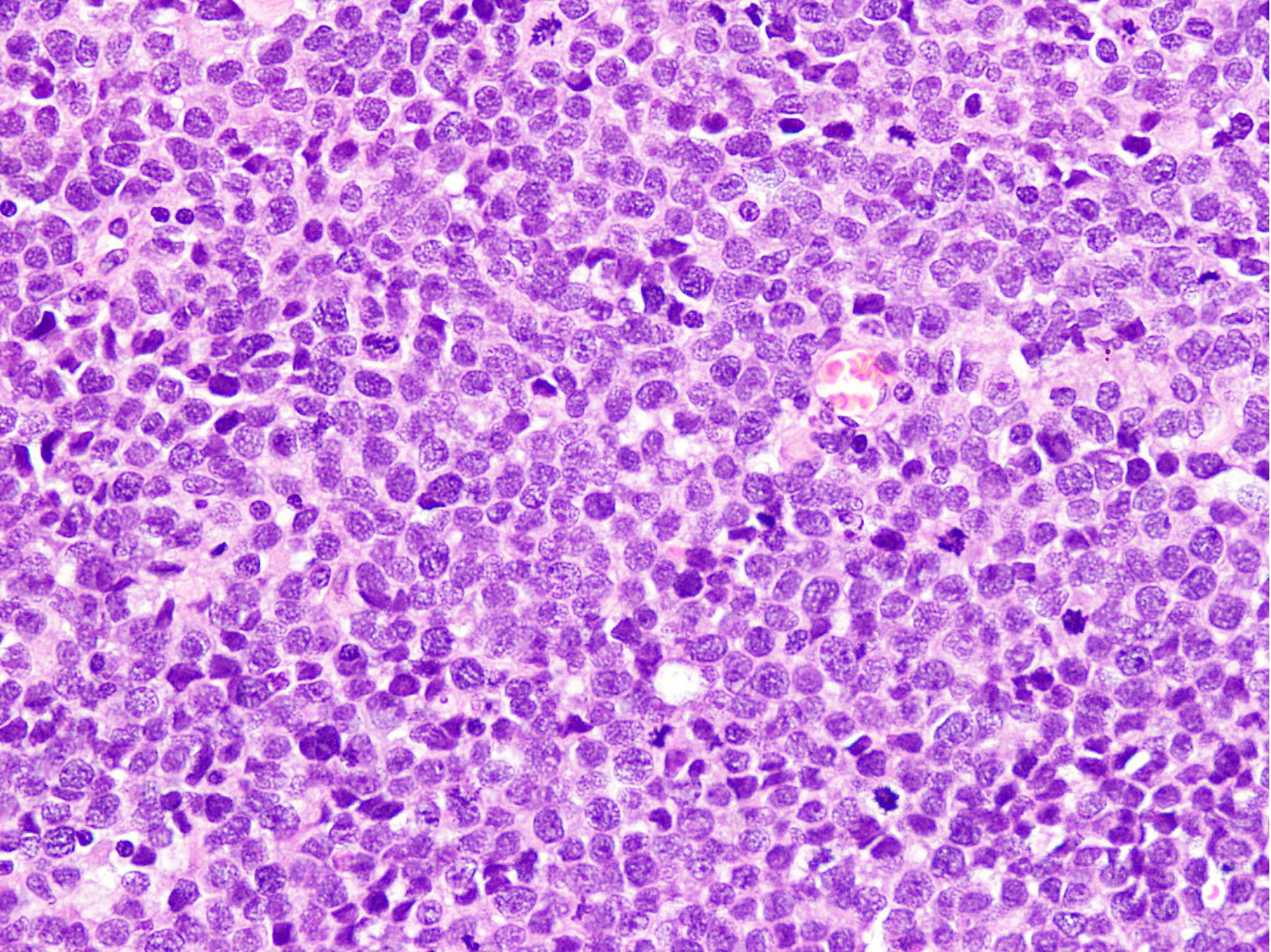
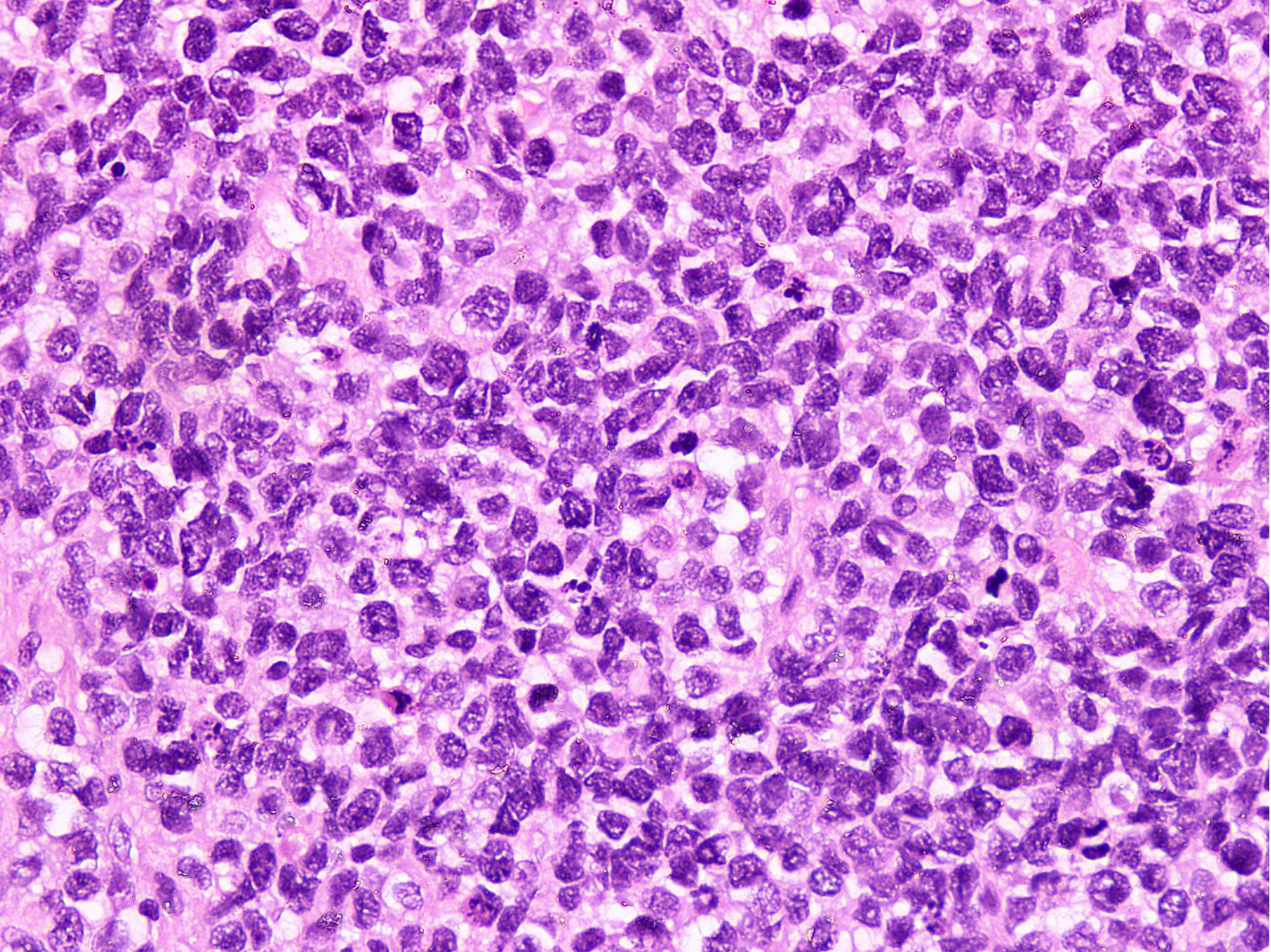
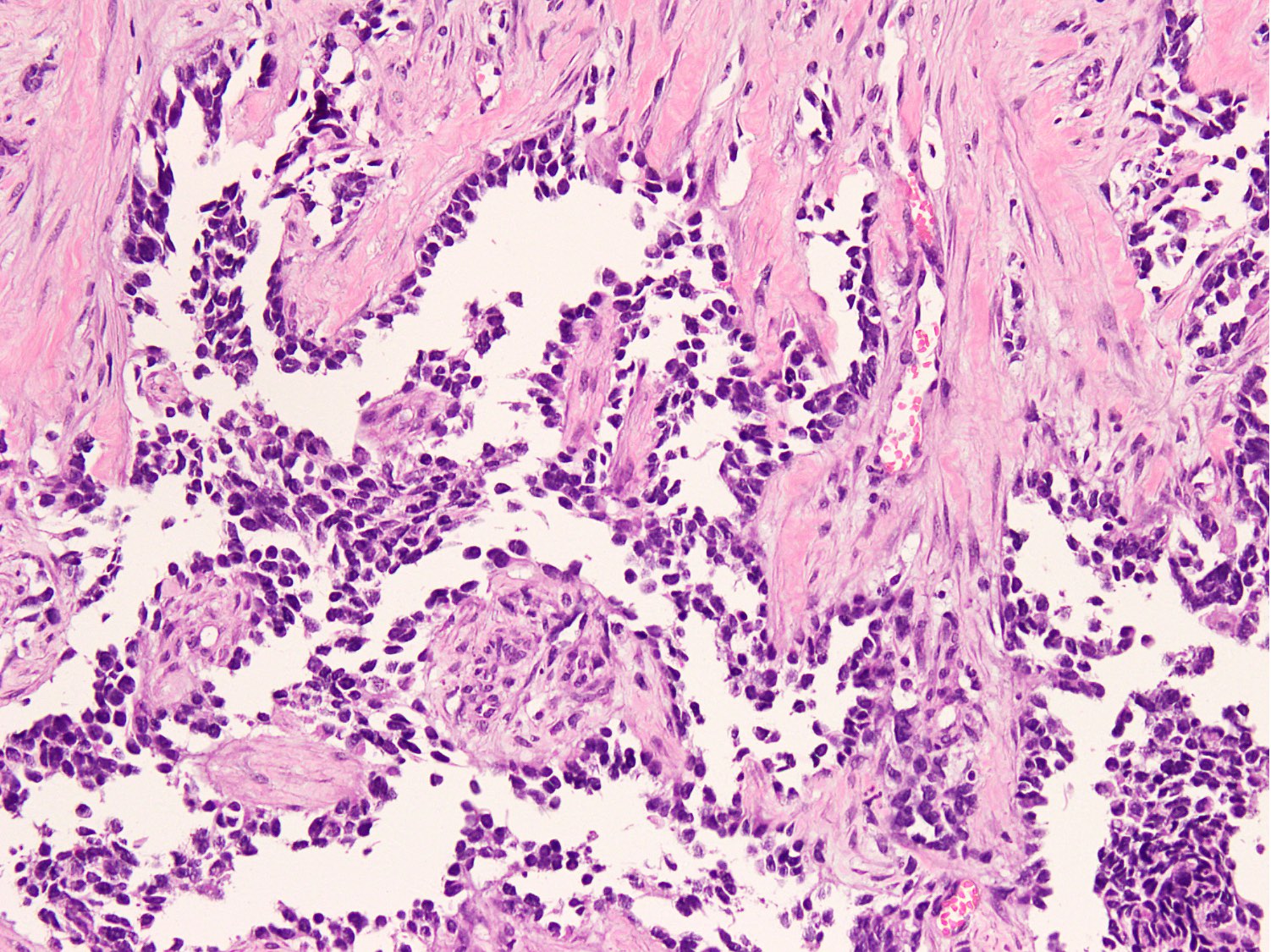
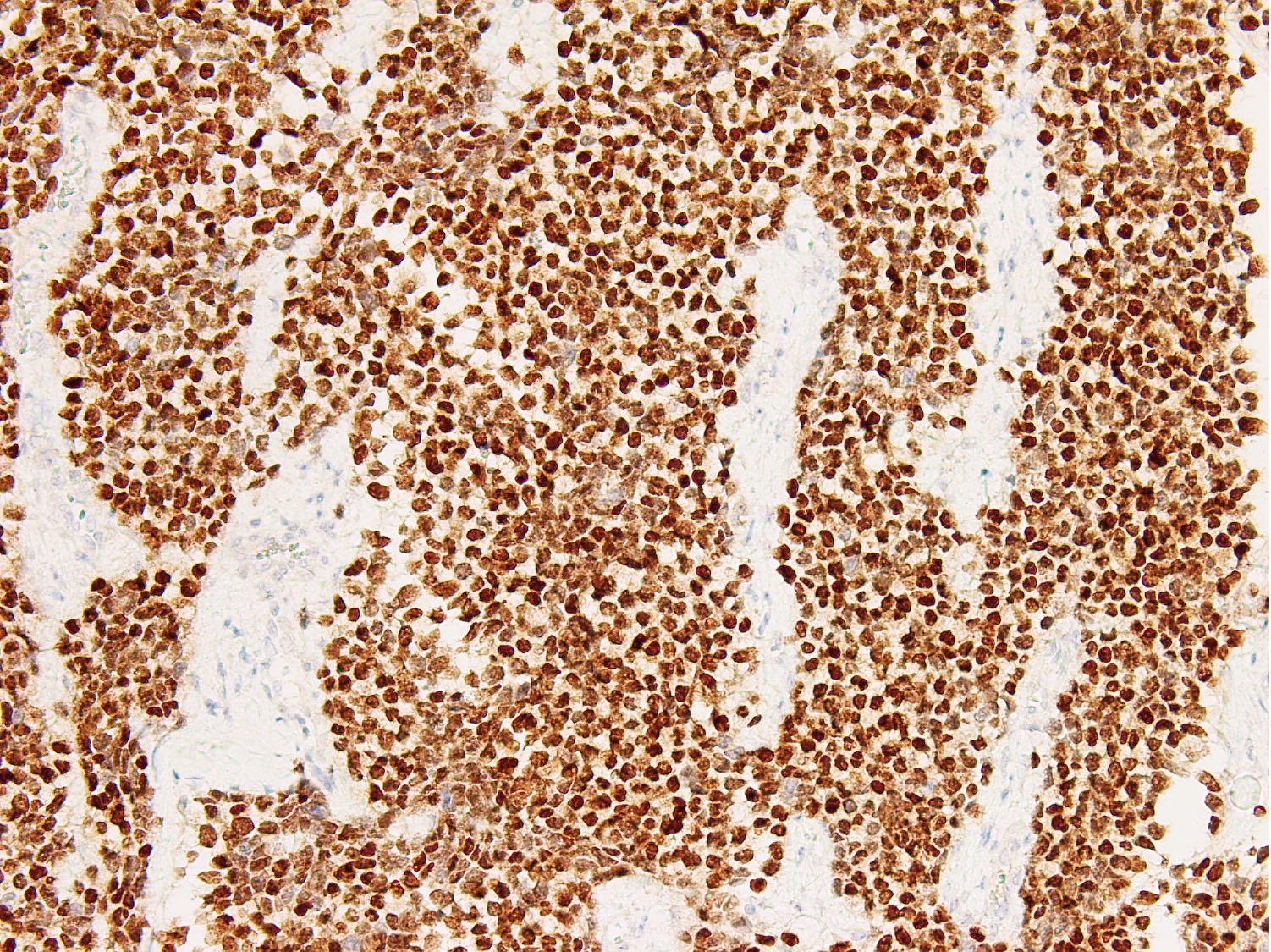
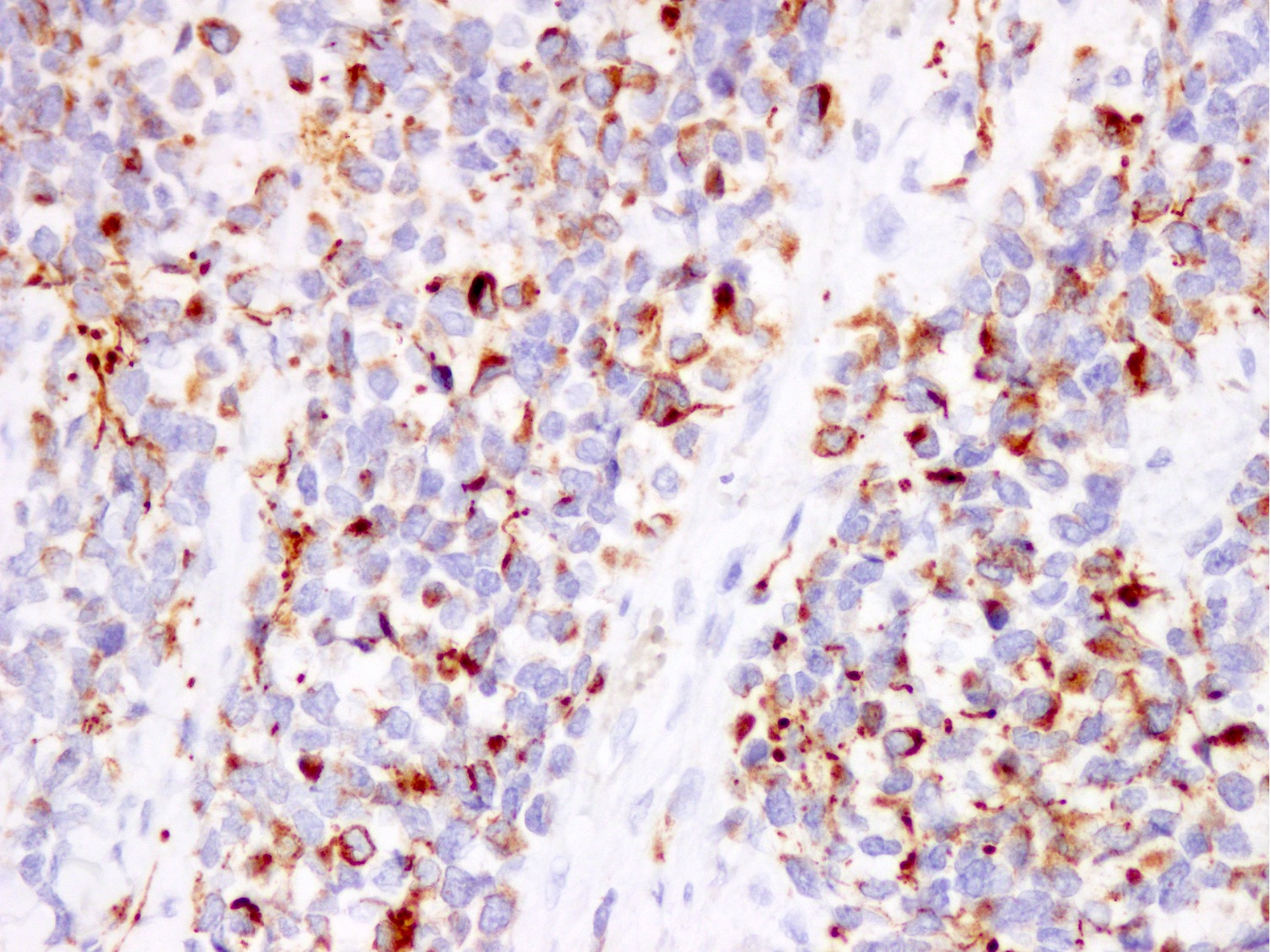
Microscopic (histologic) images
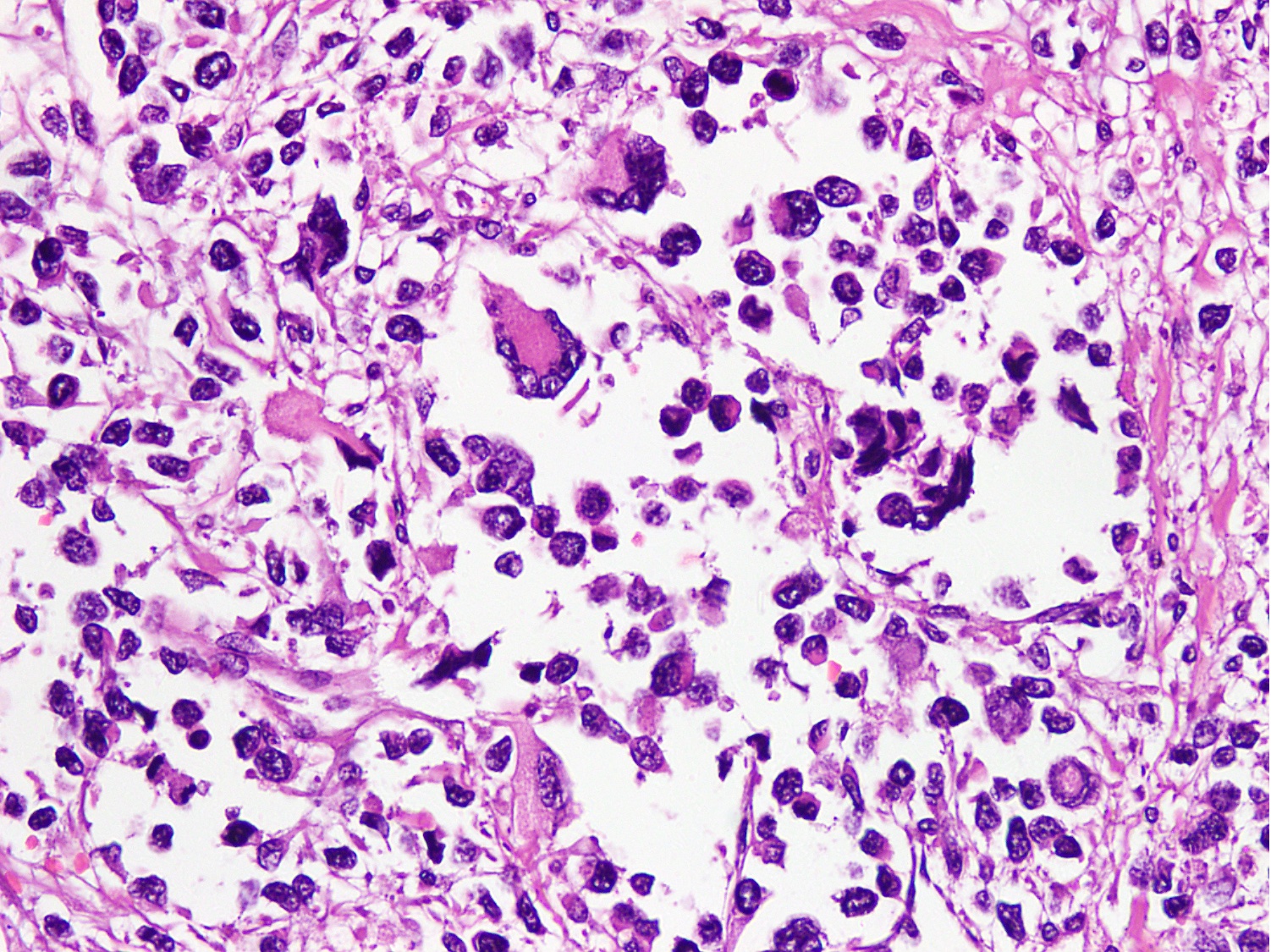
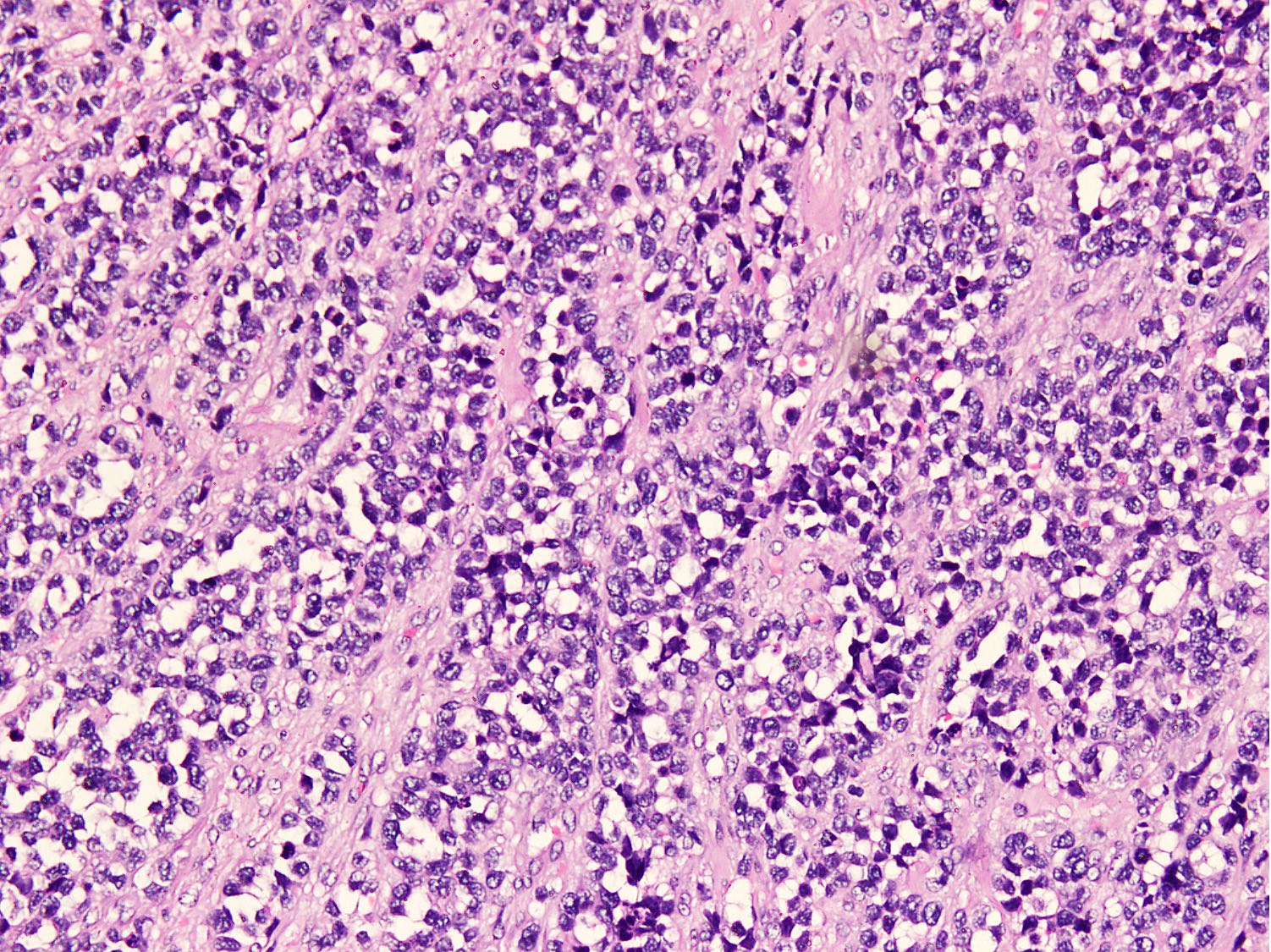
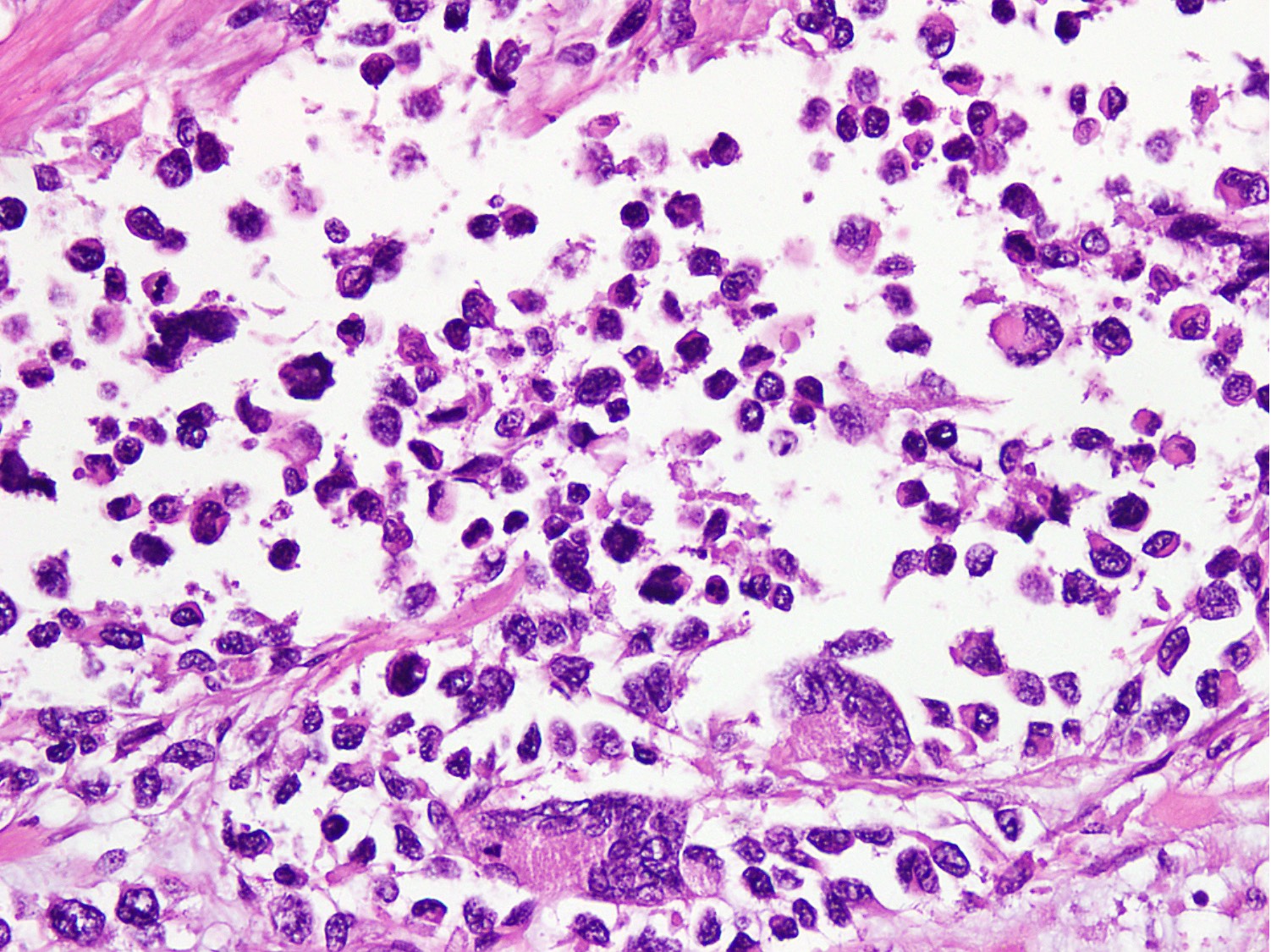
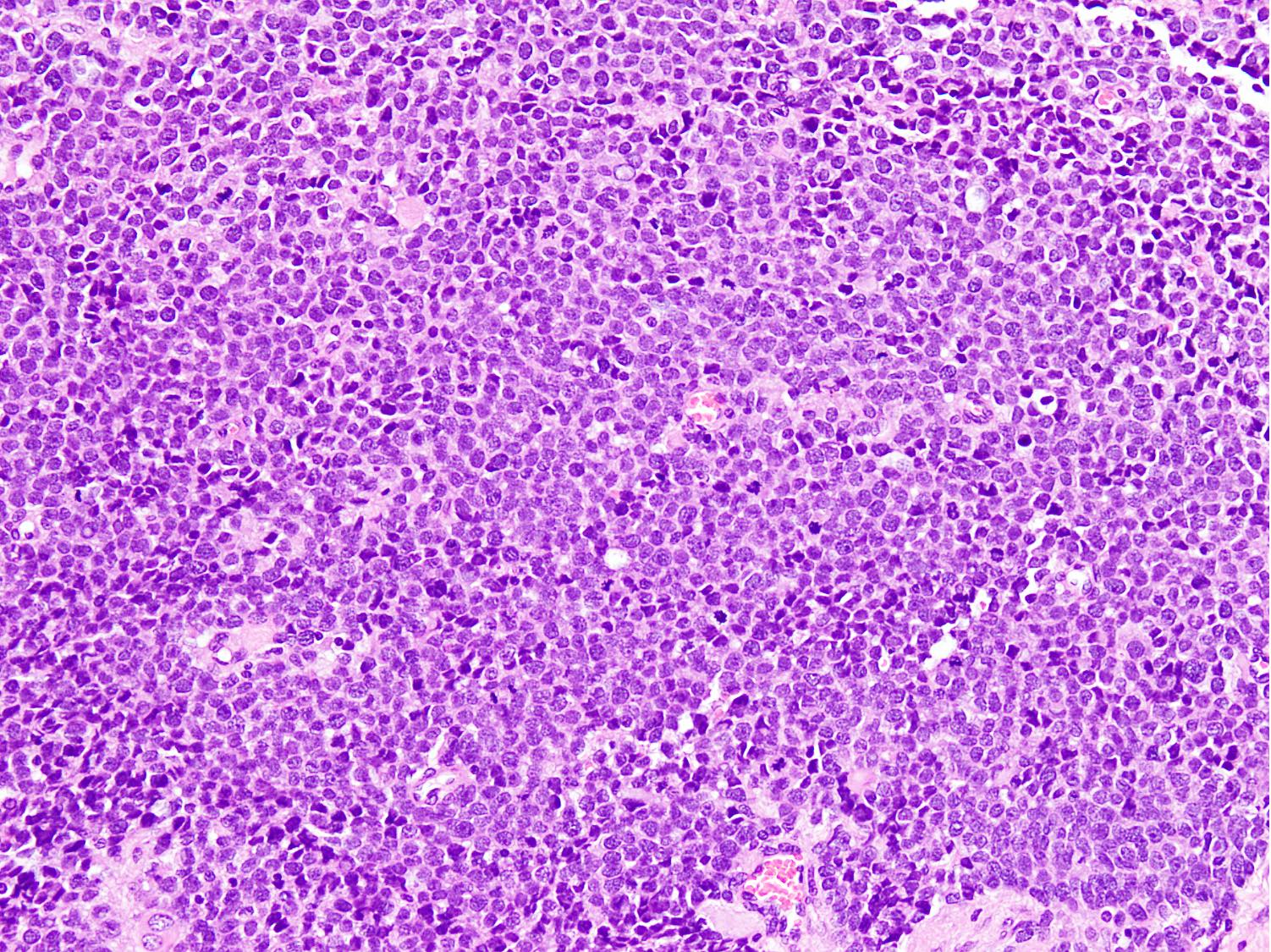
Contributed by Nasir Ud Din, M.B.B.S.
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Detection of PAX3::FOXO1 or PAX7::FOXO1 fusion transcripts requires RNA based methods such as reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT PCR), target RNA next generation sequencing (NGS) or transcriptome sequencing (Front Cell Dev Biol 2023;11:1214262, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;113:13126, J Mol Diagn 2014;16:361)
- FOXO1 gene rearrangement can be assessed using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) (Diagn Mol Pathol 2009;18:138)
- t(2;13)(q35;q14) and t(1;13)(p36;q14) translocations can be detected using conventional karyotyping (G banding) (Virchows Arch 1997;431:83)
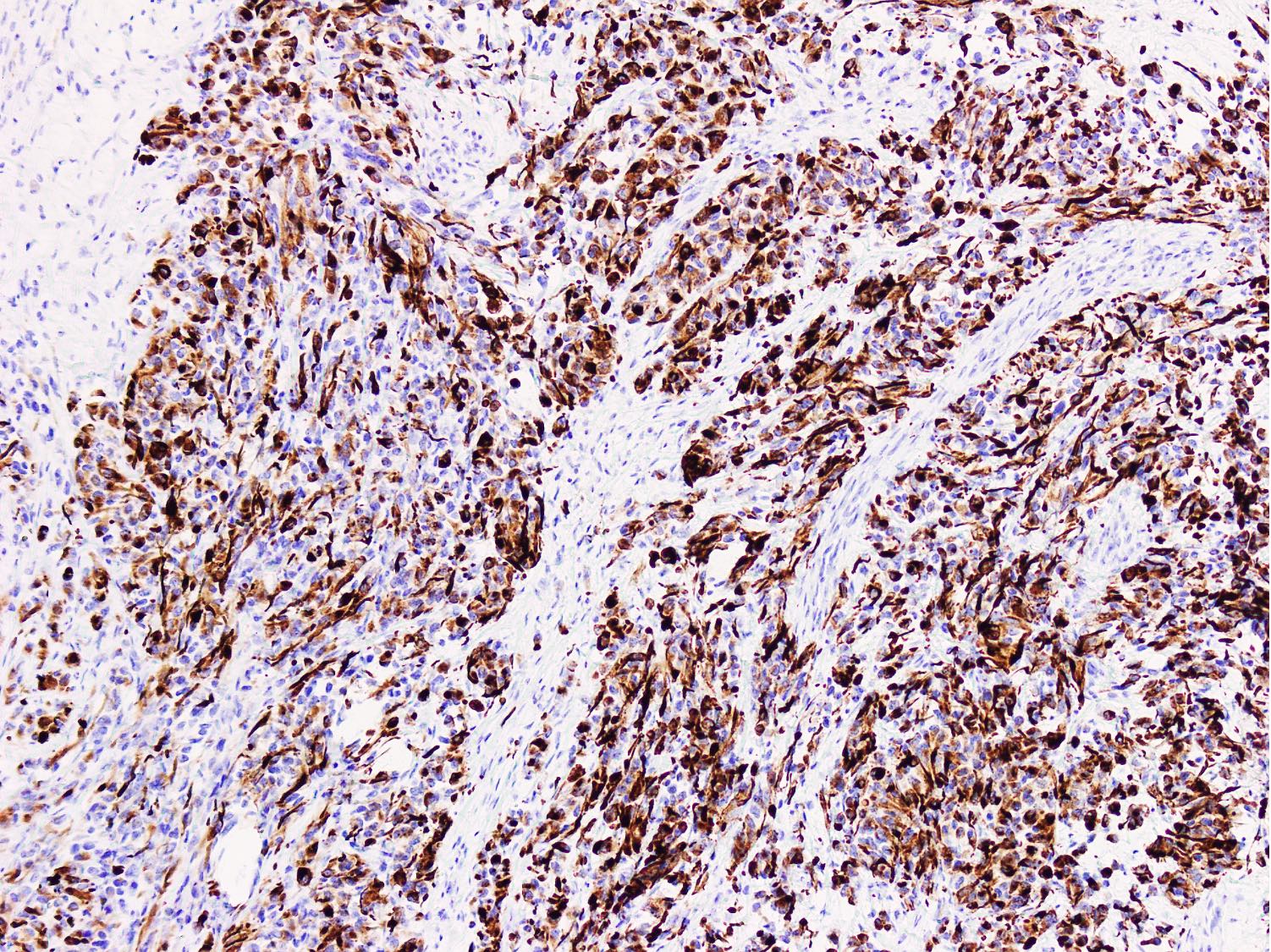
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue mass, neck, biopsy:
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, PAX3::FOXO1 positive (see comment)
- Comment: RT PCR testing confirmed the presence of PAX3::FOXO1 fusion transcripts.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 17 year old boy presented to clinic with a painless head and neck soft tissue mass. An MRI revealed a 2.5 cm mass with possible meningeal extension. Histopathologic examination revealed uniform round cells arranged in an alveolar pattern with strong nuclear immunoreactivity for myogenin. Which of the following molecular markers, if present, would indicate a more favorable prognosis?
- CDK4 amplification
- FGFR4 missense mutations
- MYCN amplification
- PAX3::FOXO1 fusion transcripts
- PAX7::FOXO1 fusion transcripts
Board review style answer #1
E.
PAX7::FOXO1 fusion transcripts. The clinical and histopathologic features support the diagnosis of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS). PAX3::FOXO1 and PAX7::FOXO1 fusion transcripts are specific genetic changes associated with ARMS and detection of these fusion transcripts is considered a desirable diagnostic criterion for ARMS. The presence of PAX7::FOX01 fusion transcripts indicates a more favorable prognosis Answer D is incorrect because patients with PAX7::FOXO1 ARMS have a more favorable prognosis compared to patients with PAX3::FOXO1 ARMS. Answers A and C are incorrect because MYCN and CDK4 amplification have been correlated with poor outcomes in ARMS. Answer B is incorrect because the prognostic impact of rare FGFR4 missense mutations in ARMS is not well established.
Comment Here
Reference: FOXO1
Comment Here
Reference: FOXO1
Board review style question #2
A 19 year old man presented with a rapidly growing mass in the left forearm. Histopathologic examination of the resected tumor specimen revealed uniform round cells arranged in an alveolar pattern with strong nuclear immunoreactivity for myogenin. Which of the following molecular markers is most commonly found in tumors with these histologic characteristics?
- CDK4 amplification
- MYCN amplification
- PAX3::FOXO1 fusion transcripts
- PAX7::FOXO1 fusion transcripts
- TP53 mutations
Board review style answer #2
C. PAX3::FOXO1 fusion transcripts.
The clinical and histopathologic features support the diagnosis of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS). ARMS is associated with specific genetic changes, including t(2;13)(q35;q14) PAX3::FOXO1 and t(1;13)(p36;q14) PAX7::FOXO1 fusion transcripts. PAX3::FOXO1 fusion transcripts are reported in a majority (60%) of ARMS cases. Answer D is incorrect because PAX7::FOXO1 fusion transcripts are reported in a subset (20%) of ARMS cases. ~20% of ARMS cases are negative for FOXO1 fusions. Answers A, B and E are incorrect because CDK4 amplification, MYCN amplification and TP53 mutation are less common.
Comment Here
Reference: FOXO1
Comment Here
Reference: FOXO1