Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1Cite this page: De Los Santos Y, Cai C. MGMT promoter hypermethylation. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/molecularmgmtpromoterhypermethylation.html. Accessed August 28th, 2025.
Definition / general
- O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) is a DNA repair protein encoded by the MGMT gene located on chromosome 10q26.3
- It removes alkyl groups from the O6 position of guanine in alkylated DNA, thus reversing the DNA damage induced by alkylating agents
- Methylation of the MGMT promoter silences MGMT, making the tumor cells more sensitive to treatment with alkylating agents such as temozolomide (TMZ) and nitrosourea based systemic therapy
Essential features
- Hypermethylation of the MGMT promoter has been shown to be a strong, independent prognostic biomarker in patients with malignant gliomas, particularly in elderly patients (Lancet Oncol 2012;13:707, Lancet Oncol 2012;13:916)
- There are 2 highly methylated regions in the CpG island in the MGMT promoter; most of the molecular assays in clinical use target these regions and calculate the percentage of methylated CpG sites (J Mol Diagn 2013;15:539)
- The most used cut off threshold for MGMT promoter hypermethylation is > 10% for IDH wild type glioblastomas; a higher threshold of 30% MGMT promoter methylation has been suggested for IDH mutant glioblastoma, WHO grade 4 (J Neurooncol 2016;128:333, Cancer Biol Med 2021;18:272)
- MGMT testing in low grade IDH mutant astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma has limited prognostication value (Sci Rep 2020;10:19758, Neurooncol Adv 2022;4:vdac030)
- So far, the utility of testing MGMT promoter methylation in nonglial cancer types has not been established
Terminology
- MGMT methylation
- O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase
Pathophysiology
- MGMT is a DNA repair protein that removes alkyl groups from the O6 position of guanine in alkylated DNA, thus antagonizing the lethal effects of alkylating agents on tumor cells (Love: Greenfield's Neuropathology, 9th Edition, 2015)
- Expression of MGMT is mainly regulated by epigenetic mechanisms; loss of MGMT protein expression is mainly due to methylation of the CpG island located in the MGMT promoter and only in rare cases due to gene deletion, mutation or rearrangement (Sci Rep 2018;8:6704)
- Hypermethylation of the MGMT promoter leads to decreased expression of MGMT protein, which makes glioma tumor cells more susceptible to alkylating agents (such as temozolomide) and therefore portends a better prognosis (N Engl J Med 2005;352:997)
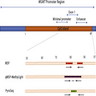
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- MGMT hypermethylation is associated with the phenomenon of pseudoprogression, in which early radiographic changes after treatment are indicative of treatment effect rather than tumor recurrence (Rodriguez: Biomarkers in Neoplastic Neuropathology, 1st Edition, 2016, J Clin Oncol 2008;26:2192)
- MGMT hypermethylation is a predictive marker for response to temozolomide, although some unmethylated tumors still respond (N Engl J Med 2000;343:1350)
- Per 2021 WHO CNS tumor classification, MGMT hypermethylation is frequently seen in IDH mutant astrocytomas (> 75%; associated with G CIMP), IDH wild type glioblastomas (40 - 50%), oligodendrogliomas (majority), high grade astrocytoma with piloid features (46%), diffuse hemispheric glioma H3 G34 mutant and primary diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the CNS (52%)
Interpretation
- Results are reported as MGMT promoter methylation positive versus negative or percentage of methylated CpG sites within the MGMT promoter region; a positive result predicts better response to temozolomide and thus better prognosis
- Cut off value of > 10% methylated DNA is generally accepted as positive for MGMT methylation in IDH wild type gliomas; however, patients in the > 30% methylated group relapse significantly later than patients with 10 - 30% methylated MGMT (J Neurooncol 2016;128:333)
- Therefore, percentage reporting is preferred
- Cut off of 30% has been suggested for IDH mutant, WHO grade 4 astrocytomas (Cancer Biol Med 2021;18:272)
Uses by pathologists
- 2022 National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines for CNS cancers recommend that MGMT promoter methylation testing be done on all high grade gliomas, WHO grade 3 and 4 (NCCN: Central Nervous System Cancers [Accessed 26 January 2023])
- MGMT testing is most helpful in predicting prognosis in IDH wild type glioblastoma in elderly patients; a cut off value of 10% is generally used (Lancet Oncol 2012;13:707, Lancet Oncol 2012;13:916)
- Cut off of 30% has been suggested for IDH mutant high grade astrocytoma, WHO grade 4 (Cancer Biol Med 2021;18:272)
- Vast majority of WHO grade 2 - 3 IDH mutant astrocytomas or oligodendrogliomas are MGMT promoter hypermethylated due to the G CIMP status; MGMT testing in these tumors may not provide additional prognostication information (Int J Cancer 2012;131:1104, Acta Neuropathol 2012;124:547, Sci Rep 2020;10:19758, Neurooncol Adv 2022;4:vdac030)
- MGMT methylated, IDH wild type gliomas are typically treated with temozolomide with or without radiation, while MGMT nonmethylated gliomas are typically treated with radiation alone (Lancet Oncol 2012;13:707, Lancet Oncol 2012;13:916)
- MGMT testing is used for clinical trial enrollment criteria (Clin Cancer Res 2019;25:1809)
Prognostic factors
- MGMT methylation status correlates with longer progression free survival and overall survival in patients treated with temozolomide (N Engl J Med 2005;352:987)
- Even when treated with radiation alone, MGMT methylated glioblastoma showed a survival advantage compared to unmethylated tumors, suggesting a general advantage in survival (Neuro Oncol 2010;12:116)
- Elderly patients with MGMT methylated gliomas had longer survival when receiving temozolomide (either alone or with radiation) compared to radiation alone; patients with MGMT nonmethylated gliomas showed no survival benefit from temozolomide compared to radiation alone (Lancet Oncol 2012;13:707, Lancet Oncol 2012;13:916)
- Apart from malignant gliomas, the prognostic utility of MGMT promoter methylation has not been firmly established in other cancer types (PLoS One 2016;11:e0165509, Lung Cancer 2017;107:91)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- MGMT immunohistochemistry has not been proven to be a sensitive or specific indicator of promoter methylation status and is not routinely performed (Brain Pathol 2008;18:520)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- MGMT gene is located on chromosome 10q26.3
- In gliomas with chromosome 10 monosomy, which is commonly seen in IDH wild type gliomas, methylation of the remaining allele can result in complete blockage of DNA repair by MGMT, resulting in higher tumor cell susceptibility to temozolomide and better prognosis (Cancer Med 2020;9:6344)
- MGMT promoter methylation analysis can be performed on snap frozen tissue or formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissue (Methods 2010;52:248)
- Some preanalytical factors that can lead to false negatives include tumor purity of the sample, sampling and intratumoral epigenetic heterogeneity (Mol Cancer Res 2017;15:532, Neuro Oncol 2019;21:616)
- To avoid poor results, selection of tissue with the highest number of viable tumor cells is recommended
- Areas of necrosis or background nonneoplastic tissue should be avoided
- Percentage of neoplastic cells in the tissue should also be provided
- Most techniques include these steps: DNA extraction, bisulfite treatment and PCR amplification (J Mol Diagn 2013;15:539)
- Bisulfite treatment deaminates unmethylated cytosine into uracil but cannot deaminate methylated cytosines
- PCR amplification then converts deaminated uracil to thymine; this process allows separation of methylated from unmethylated transcripts
- 3 common methods for detection of MGMT methylation are (J Mol Diagn 2013;15:539):
- Methylation specific PCR (MSP)
- Quantitative real time PCR or MethyLight methylation specific quantitative real time PCR (MethyLight qMSP)
- Methylation specific sequencing, including pyrosequencing
- Whole genome DNA methylation array testing has emerged as a new diagnostic tool for accurate classification of CNS tumors; in addition to tumor types, it also reports MGMT promotor methylation status (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:71)
Sample pathology report
- Brain, parietal lobe, biopsy:
- MGMT promoter methylation present (see comment)
- Comment: Current data suggests that the presence of MGMT promoter methylation predicts response to alkylating chemotherapy (i.e., temozolomide) for patients with glioblastoma. Therefore, the presence of MGMT promoter methylation in this tumor specimen suggests that this patient may respond to such therapies. Additionally, the presence of MGMT promoter methylation is a favorable prognostic factor for patients with glioblastoma. The clinical significance of the MGMT promoter methylation status in other tumor types is not fully understood.
Additional references
Practice question #1
A 78 year old man with a peripherally enhancing lesion in the right parietal lobe is diagnosed with an IDH wild type CNS WHO grade 4 glioblastoma. MGMT promoter methylation portends which of the following?
- Longer progression free and overall survival
- Shorter progression free and overall survival
- Worse response to alkylating agents
- Worse response to radiotherapy
Practice answer #1
A. Longer progression free and overall survival
Comment Here
Reference: MGMT promoter hypermethylation
Comment Here
Reference: MGMT promoter hypermethylation