Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Tushir A, Napit AR, Mannan R. Adenocarcinoma-general. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/nasaladenocarcinoma.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Sinonasal adenocarcinoma (SNAC) is a relatively rare and heterogenous type of carcinoma of the sinonasal region (i.e., the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses) with glandular differentiation
- May originate from respiratory surface epithelium or the underlying seromucinous glands (Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:68)
Essential features
- Rare type of carcinoma originating from the sinonasal area (nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses)
- On histology, the tumor resembles adenocarcinoma that arises at other body locations
- Several histologic tumor subtypes are described
- Adequate surgical resection is the usual treatment but has poor prognosis
ICD coding
- ICD-O:
- ICD-11:
- 2C20.0 & XH0349 - adenocarcinoma of nasal cavity & adenocarcinoma, intestinal type
- 2C22.0 & XH0349 - adenocarcinoma of accessory sinuses & adenocarcinoma, intestinal type
- 2C20.0 & XH74S1 - adenocarcinoma of nasal cavity & adenocarcinoma, NOS
- 2C22.0 & XH74S1 - adenocarcinoma of paranasal sinuses & adenocarcinoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Second most common malignancy of the sinonasal region, after squamous cell carcinoma, comprising 10 - 20% of primary sinonasal malignancies (Acta Otolaryngol 2018;138:415)
- Average age of presentation is between 50 and 60 years (Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2014;11:460)
- Higher incidence in Europe compared to North America, while less is known about the incidence in Asia, Africa, Oceania and South America (J Neurooncol 2020;150:405)
- Higher incidence in men compared to women (up to 6:1 in ITAC), probably due to occupational hazards (Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2014;11:460)
Sites
- Intestinal type adenocarcinoma (ITAC) is most often localized in the ethmoid sinus (40%), followed by the nasal cavity (25%) and the maxillary antrum (20%)
- ITAC associated with wood dust exposure occurs predominantly in the ethmoid sinus, while sporadic ITAC often arises in the maxillary sinus
- Due to their aggressive nature, ITAC may spread to adjacent structures, including the orbit, the pterygopalatine fossa, the infratemporal fossa and the cranial cavity
- Low grade nonintestinal type adenocarcinomas are uncommon and occur mainly in the ethmoid sinus, the nasal cavity and the maxillary sinuses (Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:68)
Etiology
- Occupational exposure to wood dust (furniture), leather (shoe production), chromium and nickel
- Large particle dust from certain hardwoods (ebony, oak and beech) is thought to provide a 900 fold risk of developing adenocarcinoma (Am J Rhinol Allergy 2013;27:S35)
- Cumulative exposure time to wood dust in patients with ITAC has been 40 - 43 years (Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:68)
- < 5 years of exposure is still considered critical and the latency to tumor development is delayed (~40 years)
- Other significant etiologic associations include
- Alcohol and cigarette smoking (Head Neck 2014;36:1490)
- Formaldehyde (Cancer Causes Control 2002;13:147)
- Leather dust (Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2004;24:199)
Clinical features
- Usually nonspecific clinical findings that mimic benign conditions, including rhinorrhea, nasal obstruction, epistaxis and hyposmia, highlight the importance of initial clinical suspicion
- Regional symptoms such as neck lumps, orbital changes (proptosis), diplopia, epiphora and cranial nerve dysfunction are relatively uncommon for most subtypes and are seen in advanced stage tumor (Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2014;11:460)
- Visible morphologic changes to hard palate mucosa or overlying skin are rarely seen (Am J Rhinol Allergy 2013;27:S35)
Diagnosis
- Often delayed due to location and nonspecific symptoms (Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2004;37:473)
- Most patients will undergo both computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to obtain precise anatomical details regarding the tumor localization and extension (staging), which are critical in determining operability or in planning radiotherapy (Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2014;11:460)
- Endoscopic guided biopsy under local anesthesia for histologic confirmation
- If a deep biopsy is required or if profuse bleeding is anticipated, the procedure is performed in an operating room under general anesthesia
- Nonintestinal type adenocarcinoma (non-ITAC) is a diagnosis of exclusion (J Neurooncol 2020;150:405)
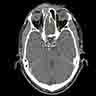
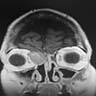
Radiology description
- Presents as an ill defined and heterogeneously enhancing mass in the sinonasal cavity or area in the base of the skull
- Bone involvement is shown by CT scan as an aggressive pattern of bone erosion invading surrounding structures
- Soft tissue details are seen in MRI findings
- PET CT scan defines the regional and distant metastasis; an efficient tool for tumor staging (Am J Rhinol Allergy 2013;27:S35)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- ITAC: usually advanced disease at presentation, poor prognosis with a 5 year survival rate of ~60% depending upon disease extent (local extension and metastasis) and histologic type
- Low grade non-ITAC: overall favorable outcome; usually localized but the possibility of localized recurrence, metastasis is unusual, death is rare
- High grade non-ITAC: poor prognosis (Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:68)
- High grade, signet ring cell morphology and local invasion have a worse prognosis
Case reports
- 26 year old man presented with 3 - 4 months of epistaxis, bilateral nasal obstruction, hyposmia and headaches (Cureus 2021;13:e14285)
- 29 year old woman was referred for a posterior choanal mass (Ear Nose Throat J 2022 Aug 10 [Epub ahead of print])
- 44 year old man, without exposure to wood dust, presented with left nasal discharge and obstruction and left sided headache (South Asian J Cancer 2020;9:183)
- 45 year old man who was a chronic smoker presented with an isolated retro-orbital headache, resistant to analgesics (Pan Afr Med J 2014;18:284)
- 81 year old man who was formerly a carpenter presented with unilateral deteriorating vision (Ugeskr Laeger 2018;180:V12170942)
- 84 year old male nonsmoker and nondrinker complained of nasal fullness (Ann Ital Chir 2016;87:S2239253X16025019)
Treatment
- Adequate surgical resection is the usual treatment
- Surgery followed by radiotherapy for advanced stage disease or if there is a possibility of recurrence
- Radiotherapy or combined chemoradiotherapy may be an alternative to definitive surgery for a nonsurgical candidate
- Reference: J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 2020;81:627
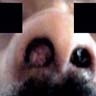
Clinical images
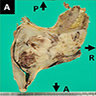
Gross description
- Polypoidal, fungating, nodular or papillary mass
- Usually friable, with ulceration and hemorrhage
- Rarely gelatinous or mucoid
- Reference: West Indian Med J 2014;63:678
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Per the WHO classification, based on the histologic characteristics, sinonasal adenocarcinoma is divided into
- Intestinal adenocarcinoma (ITAC)
- Nonintestinal adenocarcinoma (non-ITAC)
- Non-ITAC is subsequently classified into
- Low grade
- High grade (Acta Otolaryngol 2018;138:415)
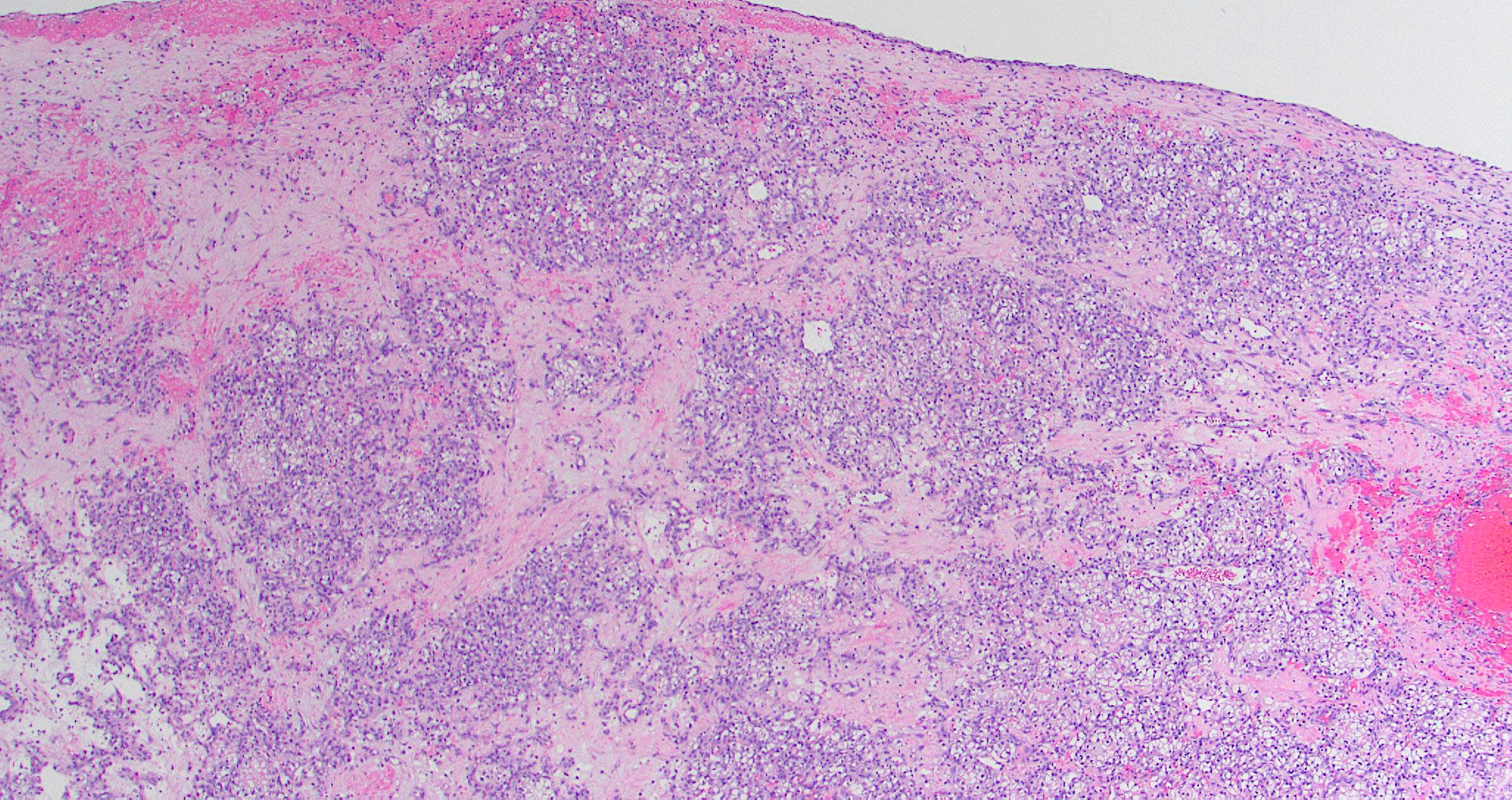
- Sinonasal renal cell-like adenocarcinoma (SRCLA) is a recently described (first case in 2002) subtype of low grade non-ITAC
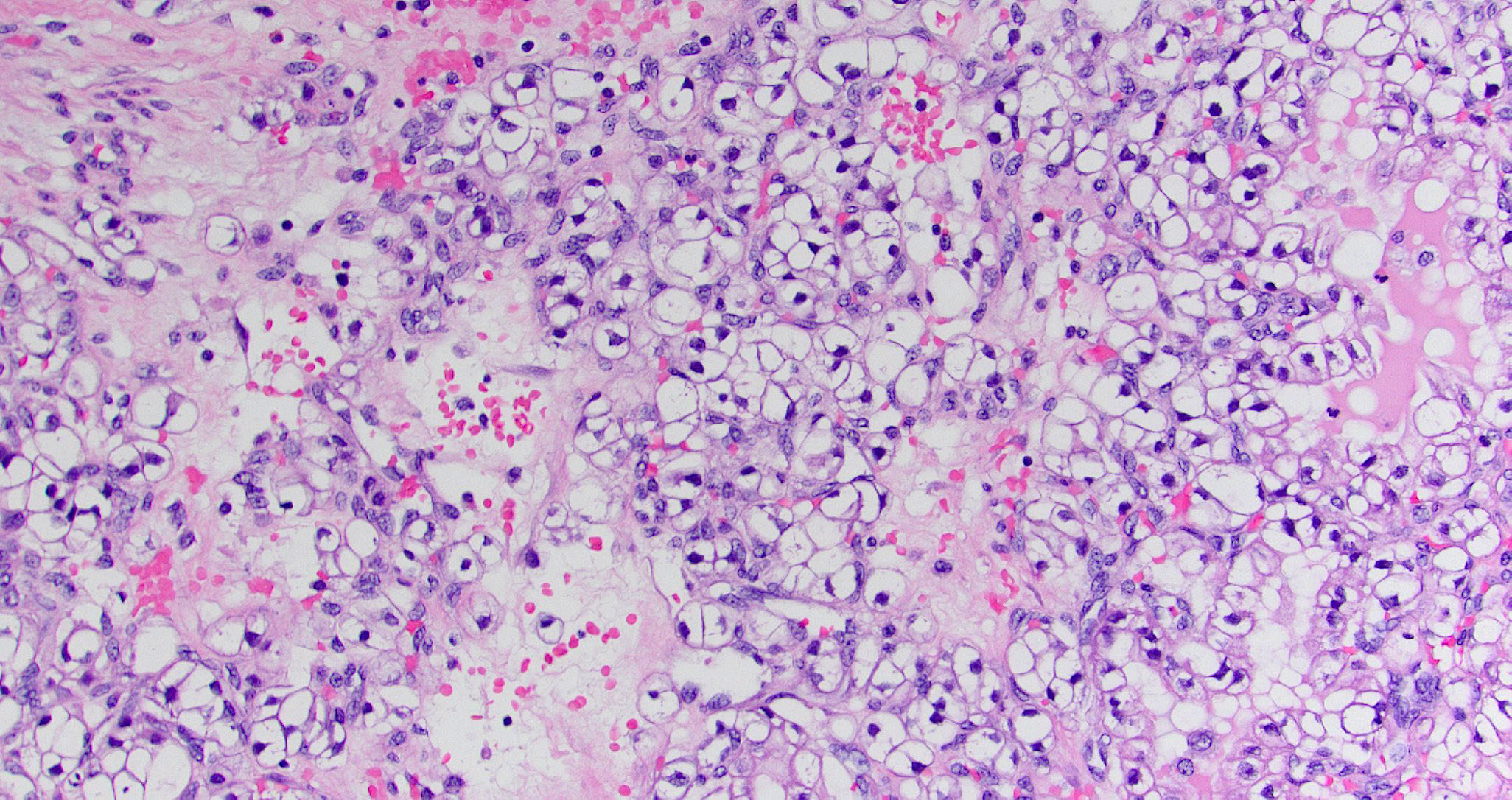
- SRCLA exhibits uniform, cuboidal to polyhedral glycogen rich cells with clear cytoplasm that lacks mucin production (Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:68)
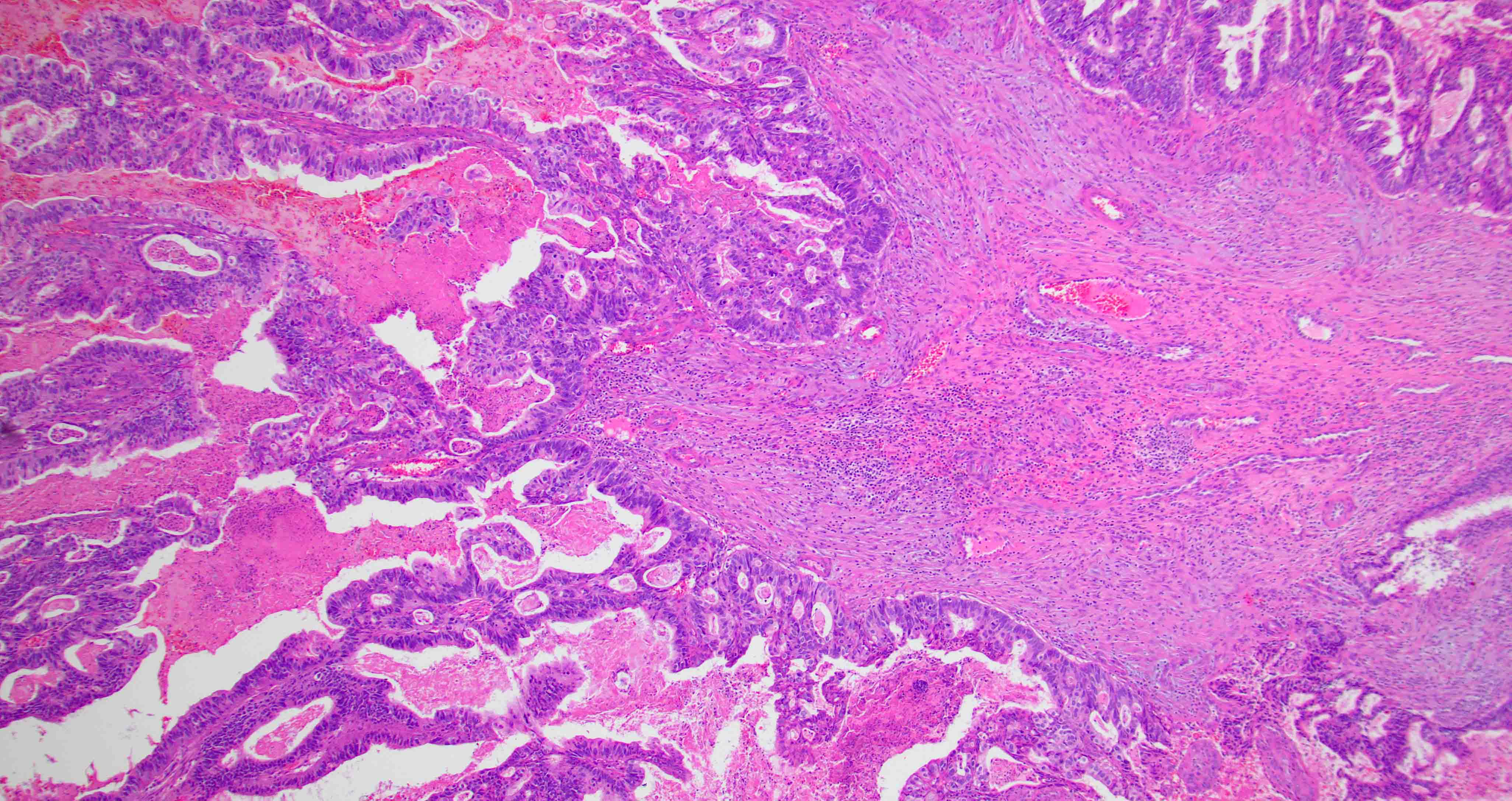
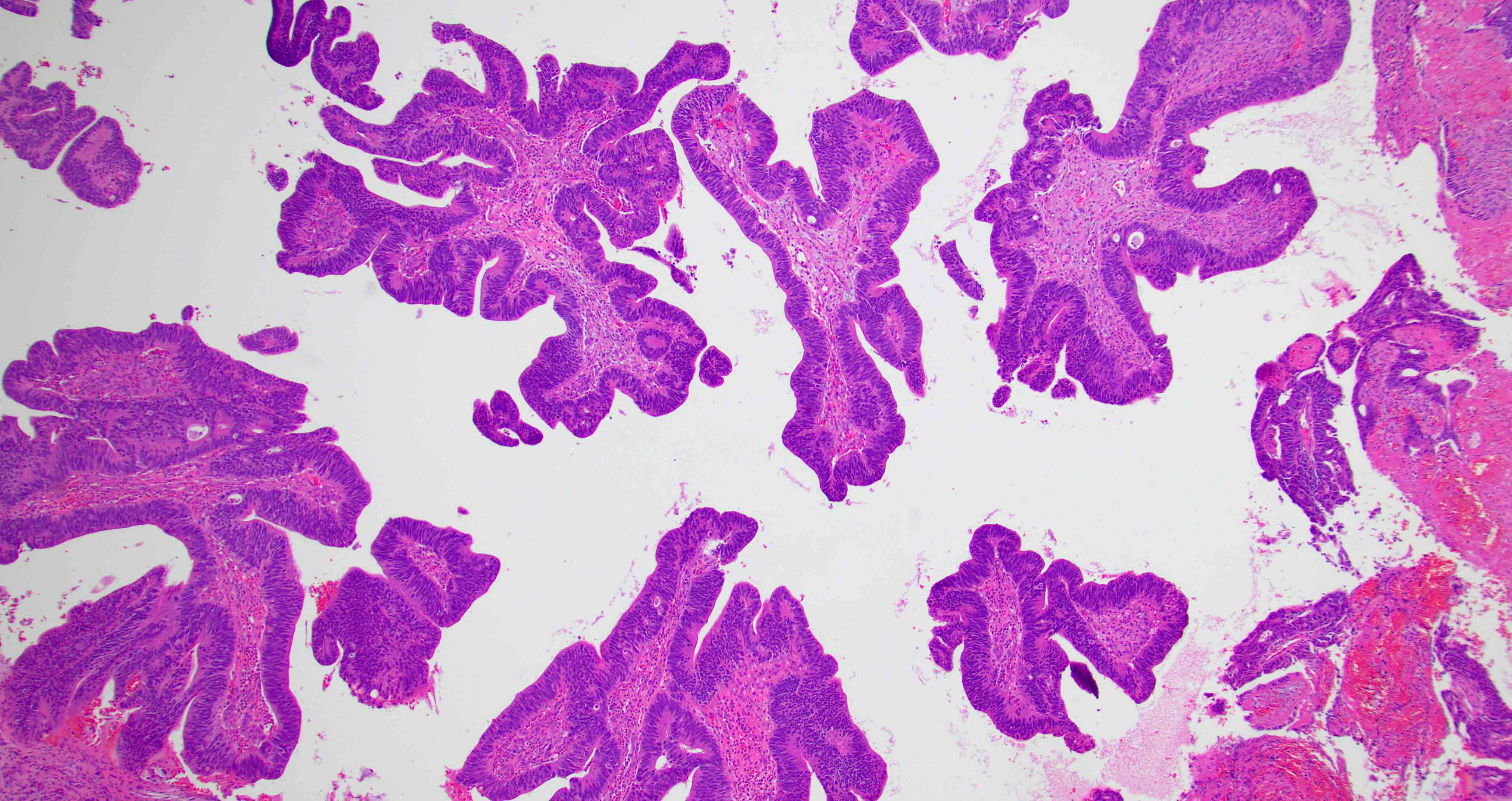
- ITAC displays glandular, tubular and trabecular architecture and few papillae and resembles a conventional colorectal adenocarcinoma
- Exclusion of metastasis from primary gastrointestinal tract tumor is required
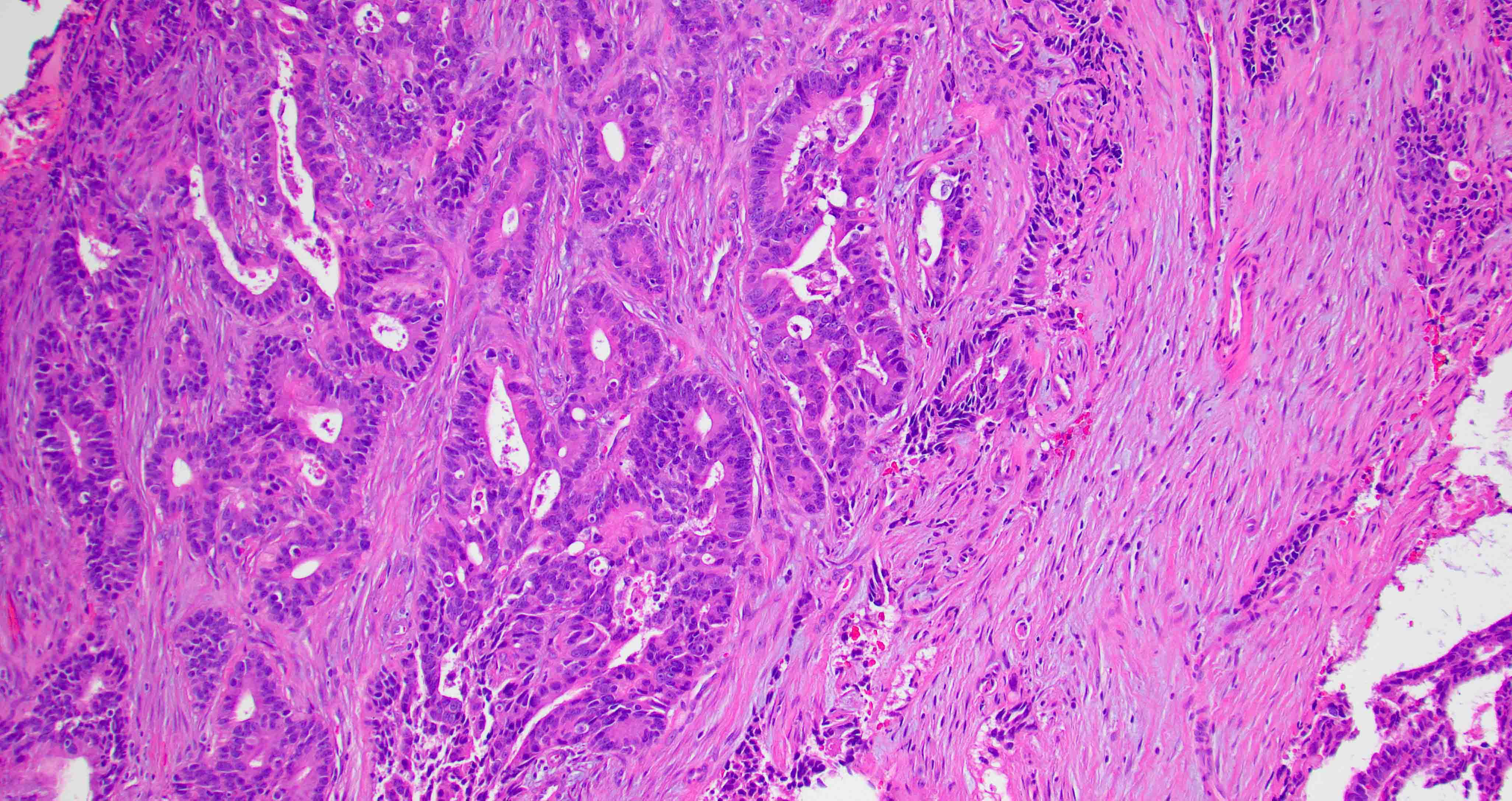
- Low grade non-ITAC can exhibit exophytic papillae, tubular or glandular, trabecular, cribriform, clear cell and mucinous patterns
- Papillae and glands are usually lined by a single layer of uniform columnar or cuboidal cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and slight cytologic aberrations
- High grade non-ITAC can display blastomatous, apocrine, mucinous, poorly differentiated patterns with pleomorphic nuclei with predominantly solid growth pattern
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Diana Bell, M.D.
Intestinal adenocarcinoma (ITAC)
Nonintestinal adenocarcinoma (non-ITAC)
Sinonasal renal cell-like adenocarcinoma
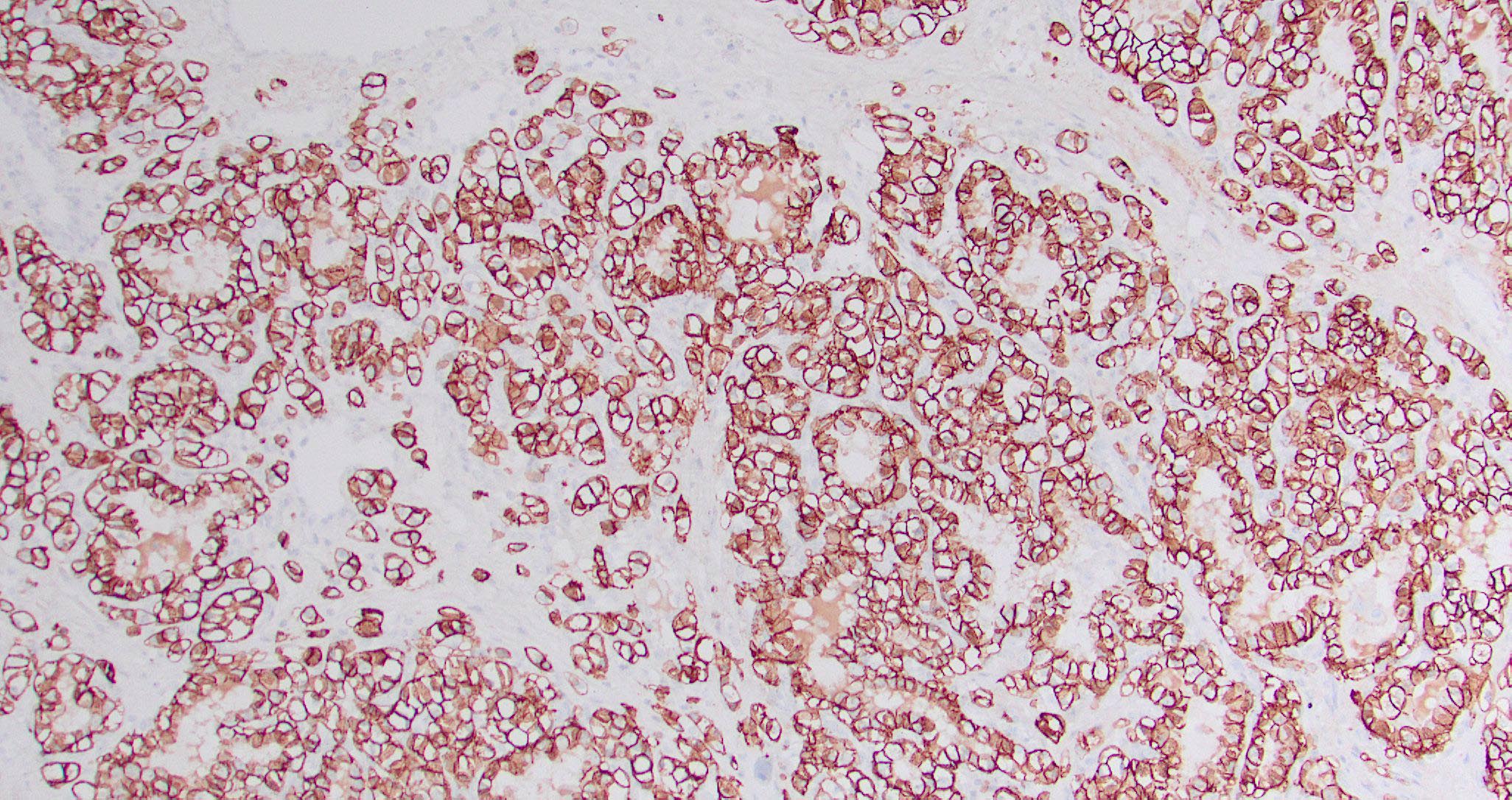
Positive stains
- Intestinal type adenocarcinoma
- Nonintestinal type adenocarcinoma
- Sinonasal renal cell-like adenocarcinoma
- Reference: Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:68
Negative stains
- Nonintestinal type adenocarcinoma
- Sinonasal renal cell-like adenocarcinoma
- Reference: Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:68
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Intestinal type adenocarcinoma
- EGFR mutation frequently observed (Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2012;35:443)
- KRAS and BRAF mutations infrequent or absent (Oral Oncol 2012;48:692, Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2012;35:443)
- TP53 mutation in 41% of cases (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2021;147:1019)
- BRAF mutation in < 10% of cases
- Tumors are microsatellite stable (MSS)
- Variable beta catenin expression with aberrant nuclear expression of beta catenin in > 30% of cases
- Sinonasal renal cell-like adenocarcinoma rarely shows BRAF mutation (Curr Oncol Rep 2022;24:55)
Videos
Sinonasal carcinoma: updated phenotype and molecular characterization
Malignant tumors of the paranasal sinuses by Dr. Nadir Ahmad
Sample pathology report
- Ethmoidal sinus, biopsy:
- Adenocarcinoma, morphologically consistent with intestinal type adenocarcinoma
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma of intestinal origin:
- Clinical history is critical and mandatory
- Histology, histochemistry and IHC of ITAC and gastrointestinal (GIT) adenocarcinoma are identical
- Metastatic renal cell carcinoma:
- Must be excluded clinically and radiologically
- Adenosquamous carcinoma:
- High grade neoplasm showing squamous and glandular features
- Salivary gland neoplasm:
- Seromucinous hamartomas:
- Submucosal epithelial proliferation of small glands, serous acini and tubules growing in clusters and lobules
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 66 year old man presented with a rapidly growing soft mass on his glabellar region for 4 months. He was on medication for hypertension and recently had normal endoscopy findings for gastrointestinal malignancy. The findings of the transcutaneous open biopsy are given in the image shown above. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Intestinal type adenocarcinoma
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma
- Mucocele
- Papillary rhinosinusitis
Board review style answer #1
A. Intestinal type adenocarcinoma. Microscopy is similar to colonic adenocarcinoma but the latest screening endoscopy of the colon was normal. Answer B is incorrect because despite having a morphology similar to primary intestinal adenocarcinoma, the patient's recent gastrointestinal endoscopy was normal. Answer C is incorrect because no epithelium lined cystic mass is seen. Answer D is incorrect because there is no inflammation with polyploidal structure.
Comment Here
Reference: Nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx - Adenocarcinoma-general
Comment Here
Reference: Nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx - Adenocarcinoma-general
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
B. Kidney. As microscopy has clear cell architecture, it is crucial to rule out clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Answer A is incorrect because clear cell colorectal carcinoma is an extremely rare entity. Answer C is incorrect because clear cell carcinoma of the lung secretes mucus, which is absent here. Answer D is incorrect because the prostate does not have presentation as well as diagnosis of prostate cancer.
Comment Here
Reference: Nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx - Adenocarcinoma-general
Comment Here
Reference: Nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx - Adenocarcinoma-general