Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Bantumilli S, Maygarden S. Hairy polyp. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/nasalhairypolyp.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign nasopharyngeal lesion
- Polypoid lesion containing both ectodermal and mesodermal components
Essential features
- Polypoidal lesions are often pedunculated with bigerminal origin
- Congenital, usually presents in newborns
- Comprised of only ectoderm and mesodermal cell lines; no endoderm
- Skin covered polypoid mass with mesoderm core
Terminology
- Not recommended: dermoid polyp, teratoid polyp, naso-oropharyngeal choristoma
ICD coding
- ICD-11: 2E90.6 - benign neoplasm of nasopharynx
Epidemiology
- Rare (1/40,000 live births) (Am J Case Rep 2021;22:e930200)
- Usually presents in neonates and young children
- F > M
Sites
- Lateral wall of nasopharynx (most common) (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e14305)
- Oropharynx, lip, tongue, palate, tonsillar areas and middle ear (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:232)
Pathophysiology
- Pathogenesis is unclear
- May be branchial arch anomaly or misdirected totipotent cells (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e14305)
- Closure failure of naso-oropharyngeal plates during organogenesis (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:232)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Varies based on extent, site and mobility of the lesion
- Spectrum ranges from asymptomatic to lethal presentation
- Presents as polyhydramnios prenatally in 20 - 30% of cases (Ear Nose Throat J 2022;101:NP68)
- Most common symptom is respiratory obstruction (Am J Case Rep 2021;22:e930200)
- Others include snoring, feeding difficulties, cyanosis, cough, stridor, dyspnea, vomiting and recurrent middle ear infections (BMJ Case Rep 2015;2015:bcr2015209825)
- Smaller polyps and polyps in nasopharynx and middle ear remain silent until adulthood
- Rare associations: branchial arch anomalies, cleft palate, choanal atresia or Dandy-Walker syndrome (Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2009;2:46, J Med Genet 1990;27:788)
- Autoamputation occurs infrequently (Radiol Case Rep 2021;16:1570)
- Can be occasionally bilateral (Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 2017;83:117)
Diagnosis
- Ear, nose and throat (ENT) examination (Ear Nose Throat J 2022;101:NP68)
- Flexible endoscopy (Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2019;200:924)
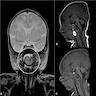
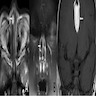
- CT or MRI to assess the extent of lesion and to exclude intracranial extension (Ear Nose Throat J 2022;101:NP105, BMJ Case Rep 2015;2015:bcr2015209825)
- Histopathological examination is confirmatory (Am J Case Rep 2021;22:e930200)
Laboratory
- No specific laboratory findings
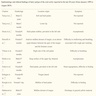
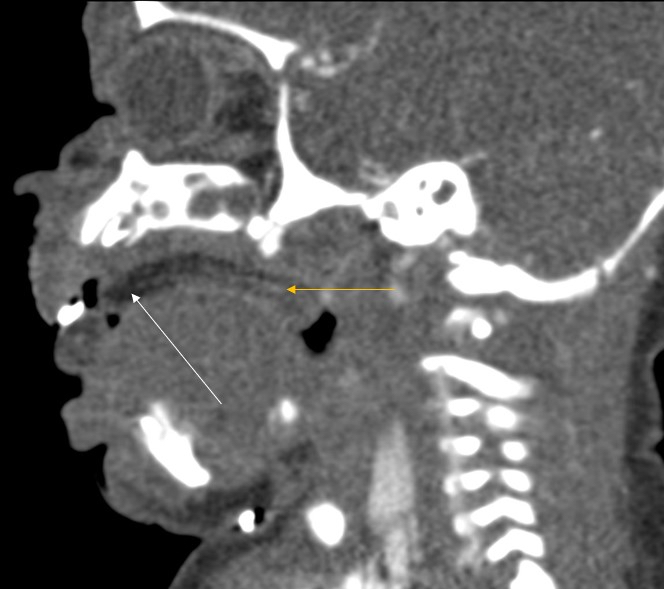
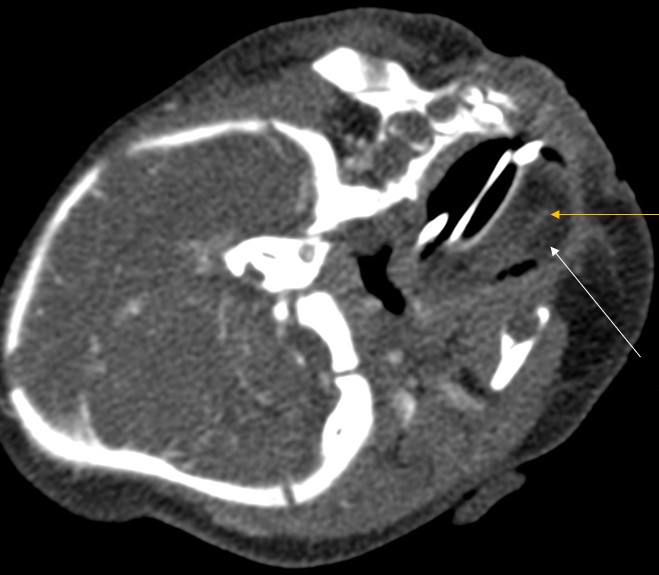
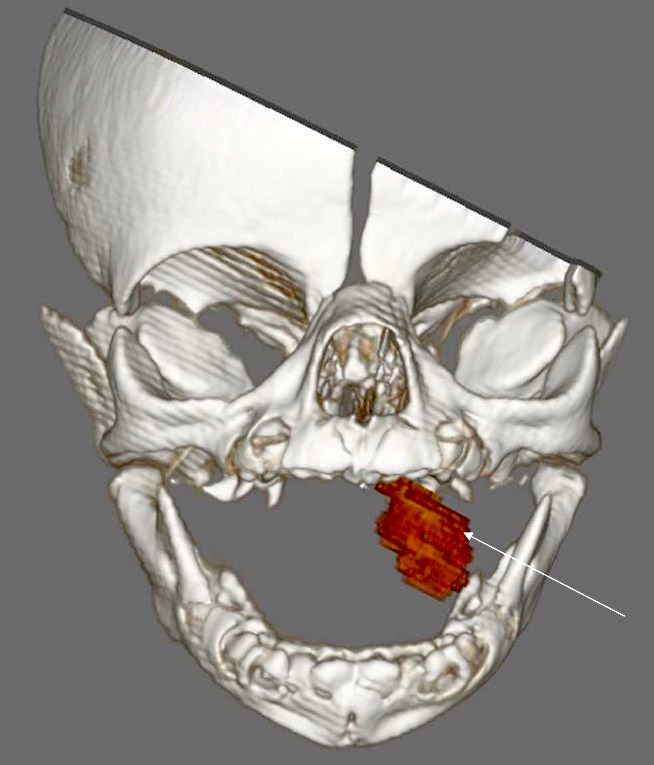
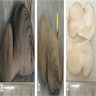
Radiology description
- CT findings: sausage shaped mass with fat attenuation (Diagnostics (Basel) 2023;13:1328)
- MRI: multilayered mass with hyperintense signal on both T1 and T2 with a linear internal low signal (Eurorad: Nasopharyngeal Hairy Polyp in an Infant with Apnoiec Spells [Accessed 6 September 2023])
- Contrast: variable stalk enhancement with no lesion enhancement on both CT and MRI
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis
- No recurrence or malignancy reported (Case Rep Otolaryngol 2013;2013:374681)
- Rarely may be life threatening due to bleeding, choking or autoamputation (Int J Otolaryngol 2022;11:75)
Case reports
- Newborn girl with severe respiratory distress due to hairy polyp of eustachian tube (Congenit Anom (Kyoto) 2015;55:158)
- Newborn boy with nasopharyngeal hairy polyp arising from eustachian tube (Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:213)
- Full term newborn boy with intermittent dyspnea and cyanosis due to hairy polyp (Pediatr Neonatol 2014;55:231)
- 2 day old preterm infant girl with oral mass (Case Rep Otolaryngol 2013;2013:374681)
- 15 month old boy with rare occurrence of 2 separate hairy polyps with meningothelial components (Case Rep Otolaryngol 2021;2021:1844244)
- 3 year old boy with respiratory distress due to nasopharyngeal hairy polyp from supratonsillar region (Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2015;19:90)
Treatment
- Surgical excision is curative (Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:213)
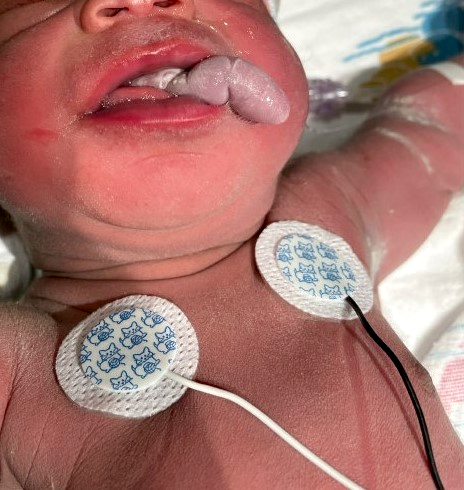
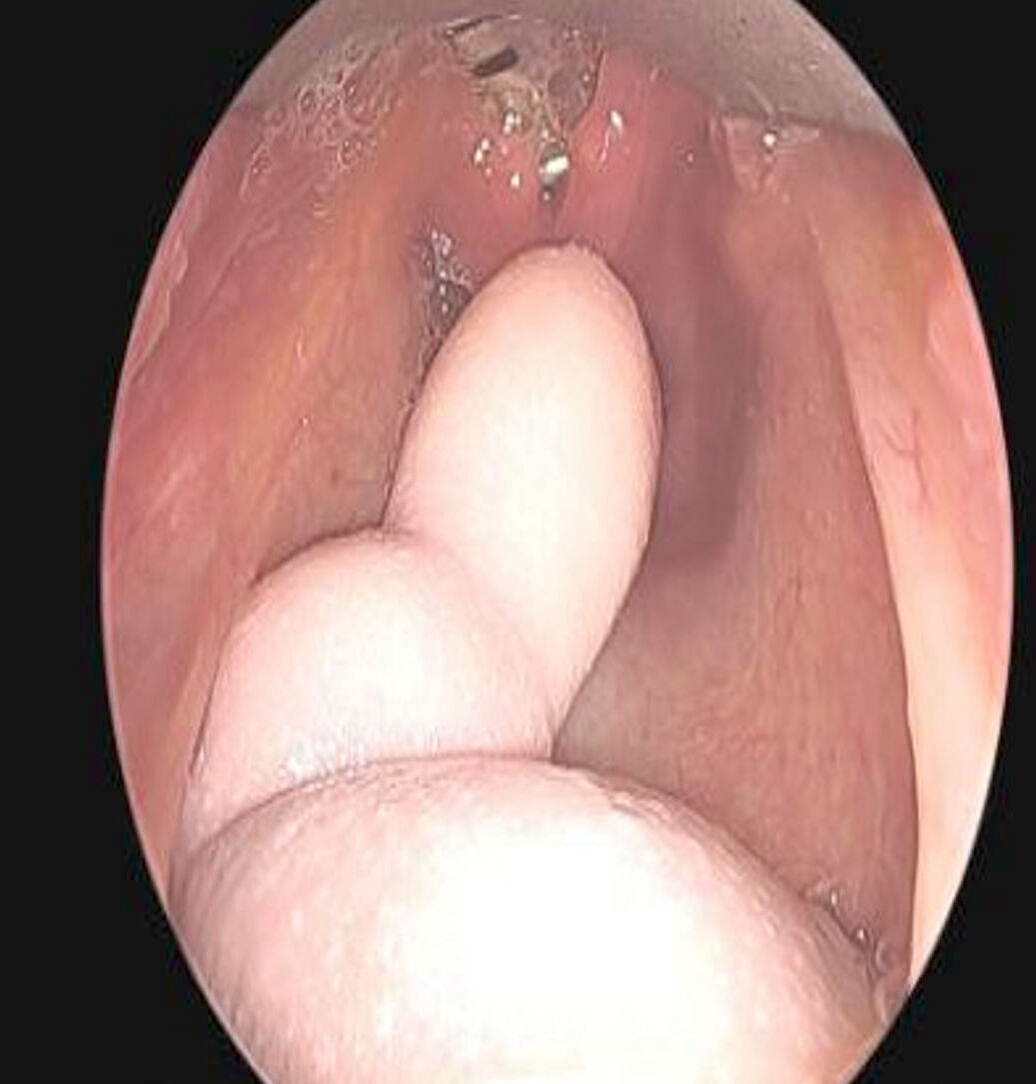
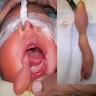
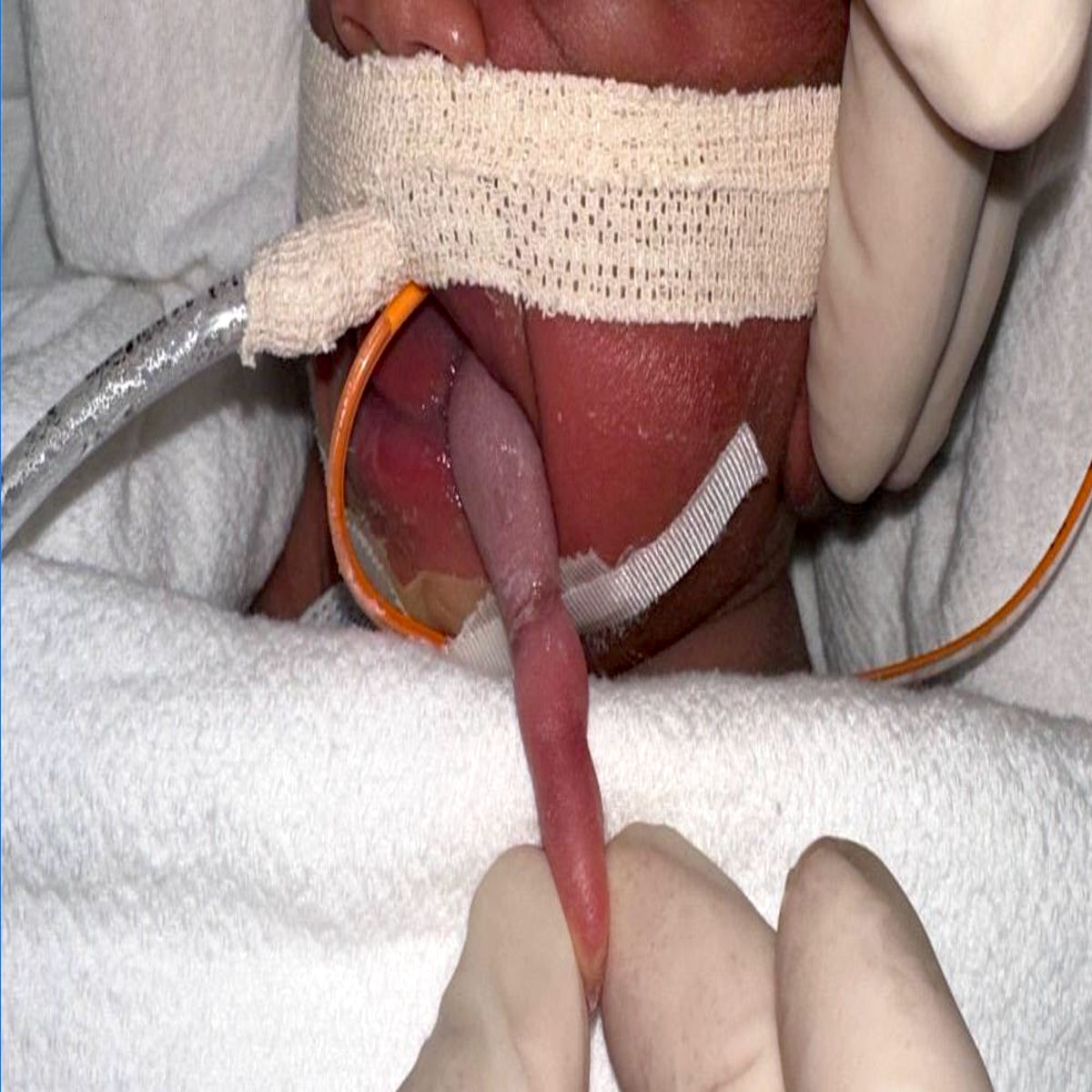
Clinical images
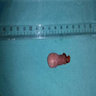
Gross description
- Grossly, skin covered polypoid and pedunculated / sessile lesion (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e14305)
- Hair growth on the external surface (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e14305)
- Cut surface: tan-yellow and mostly solid
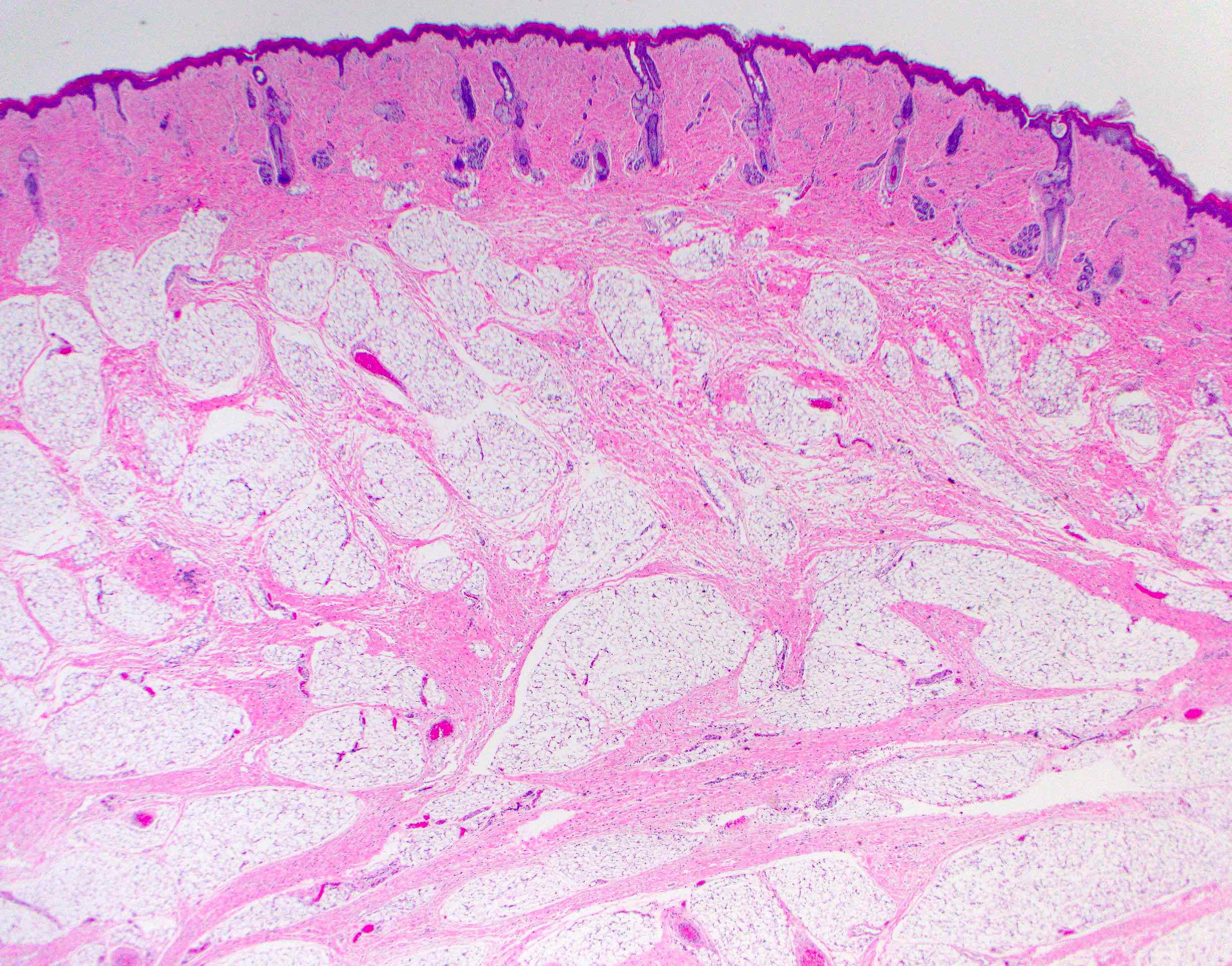
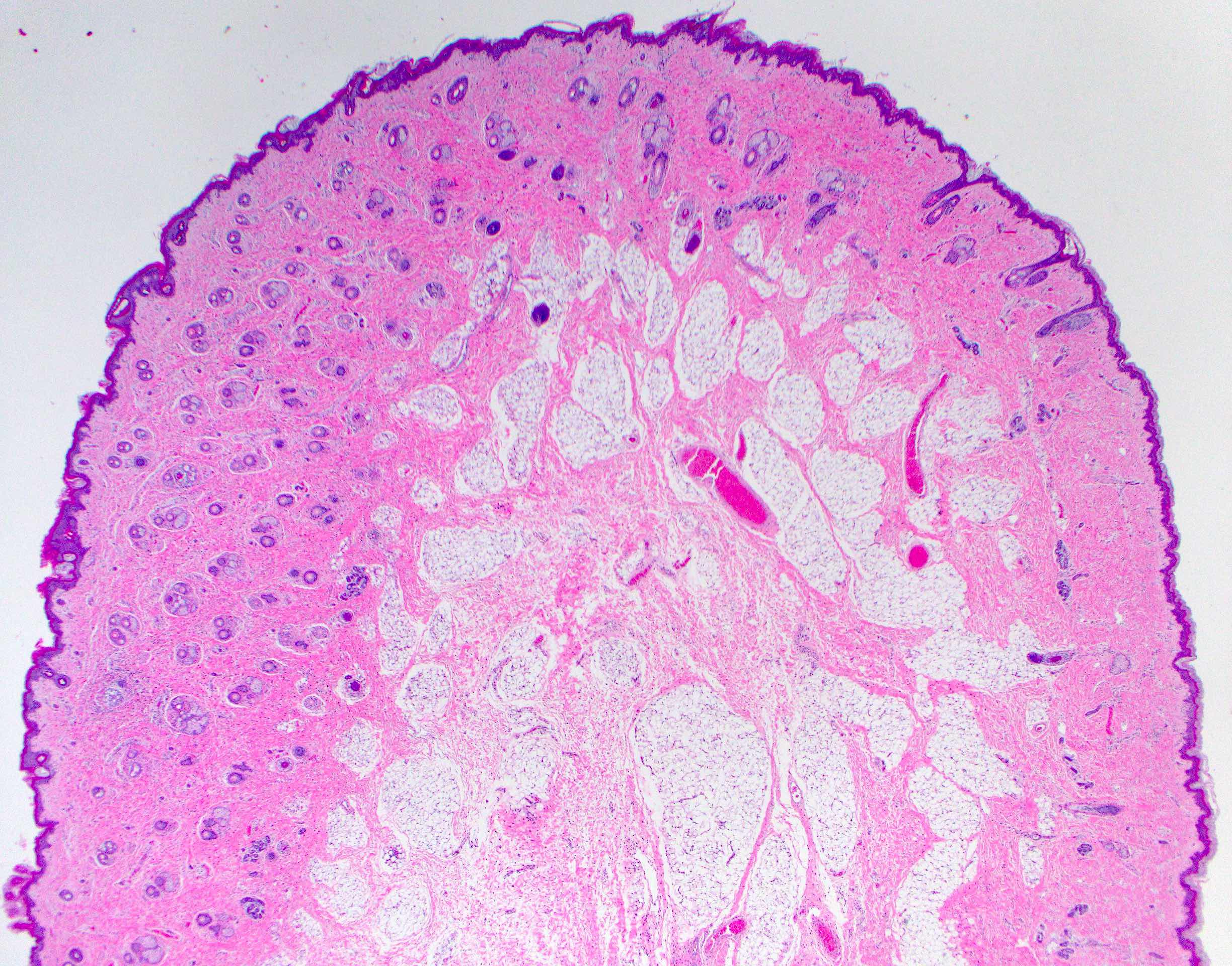
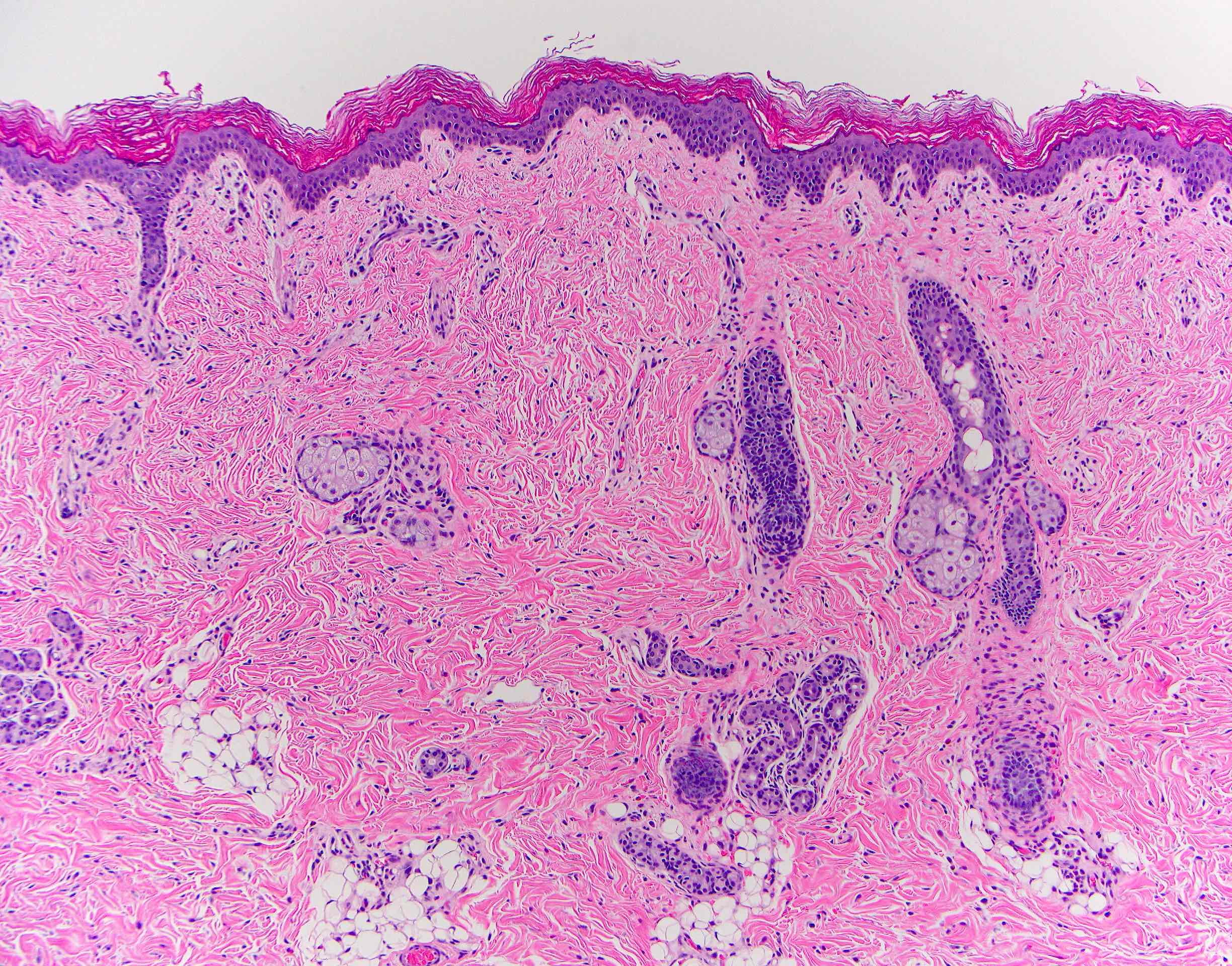
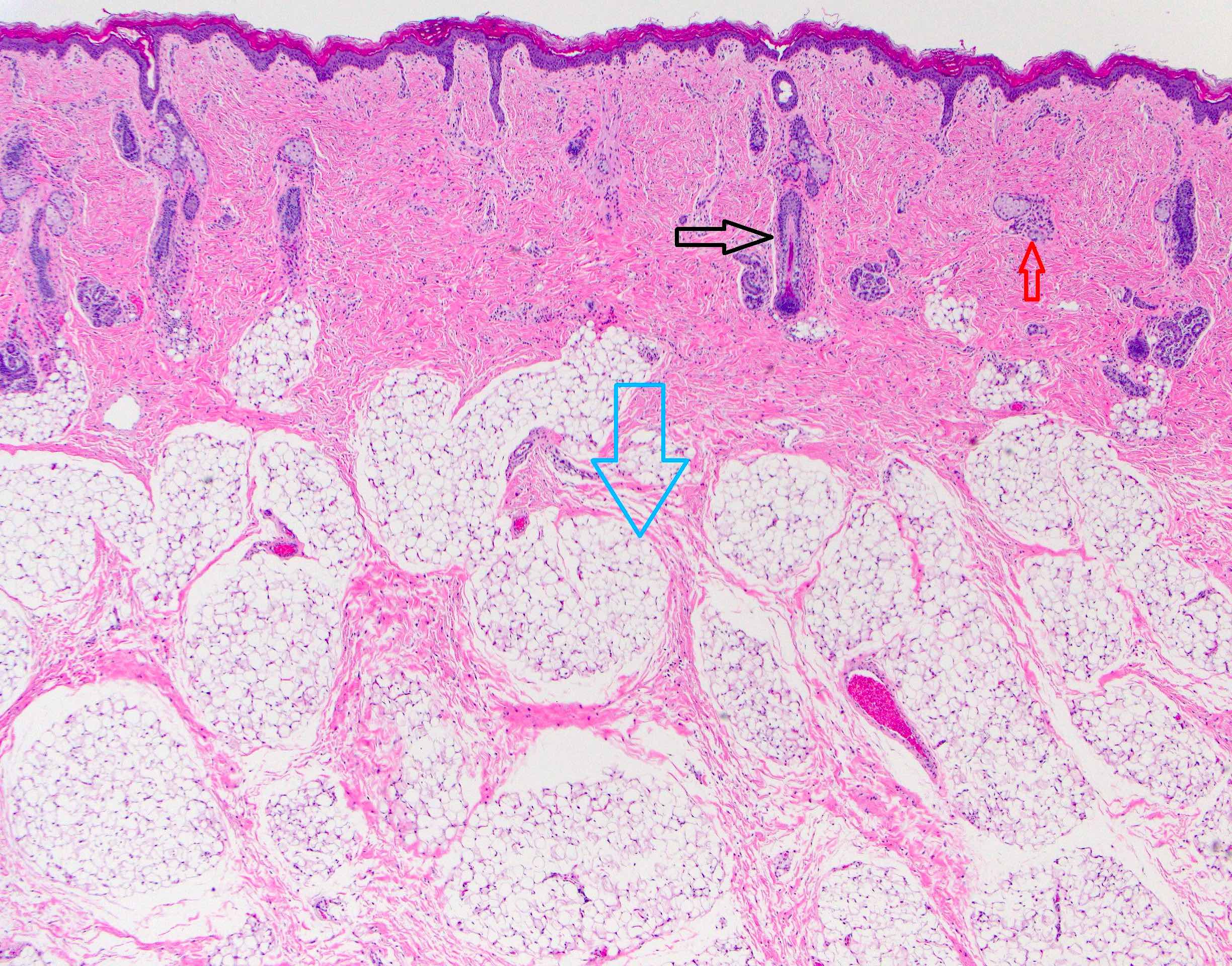
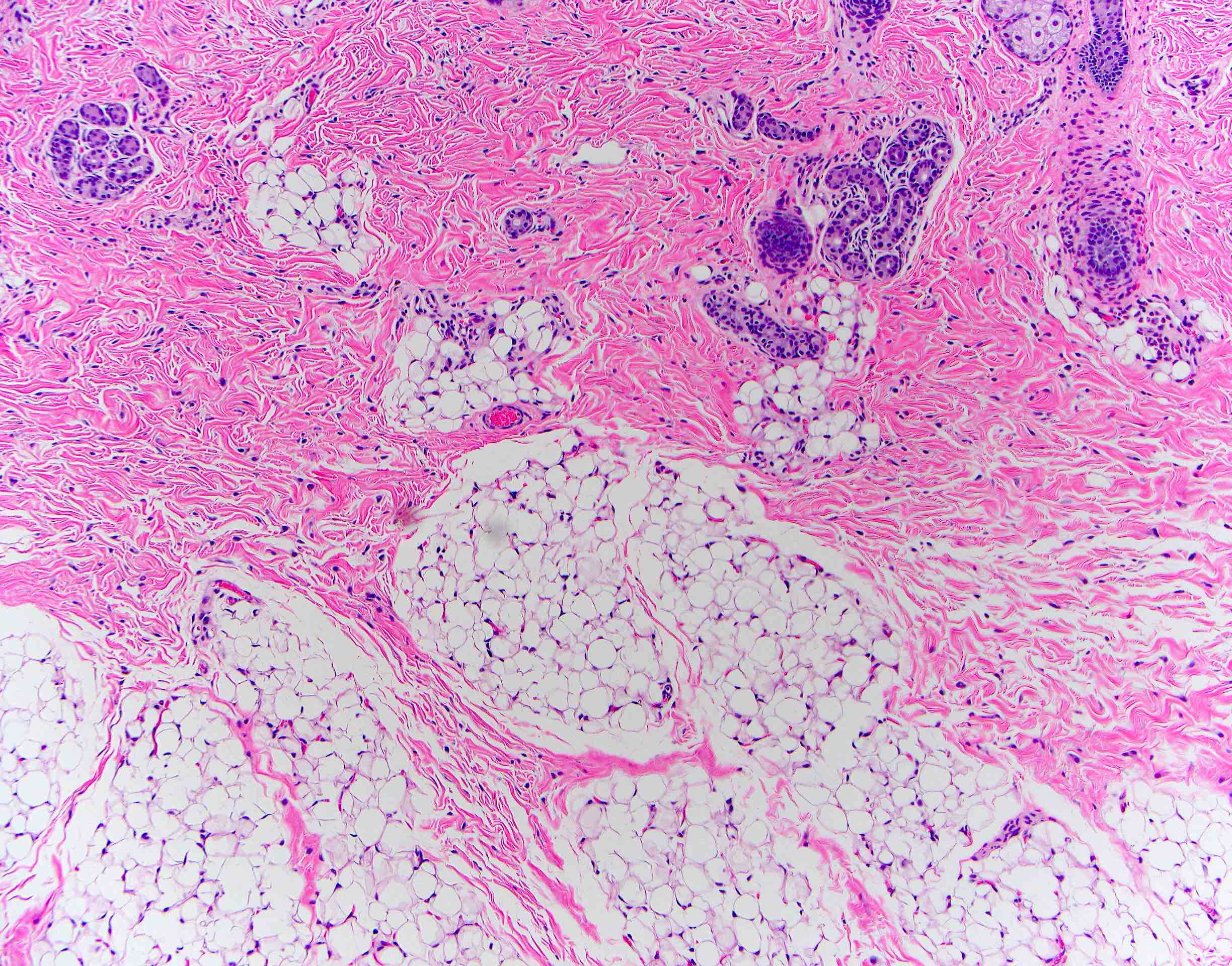
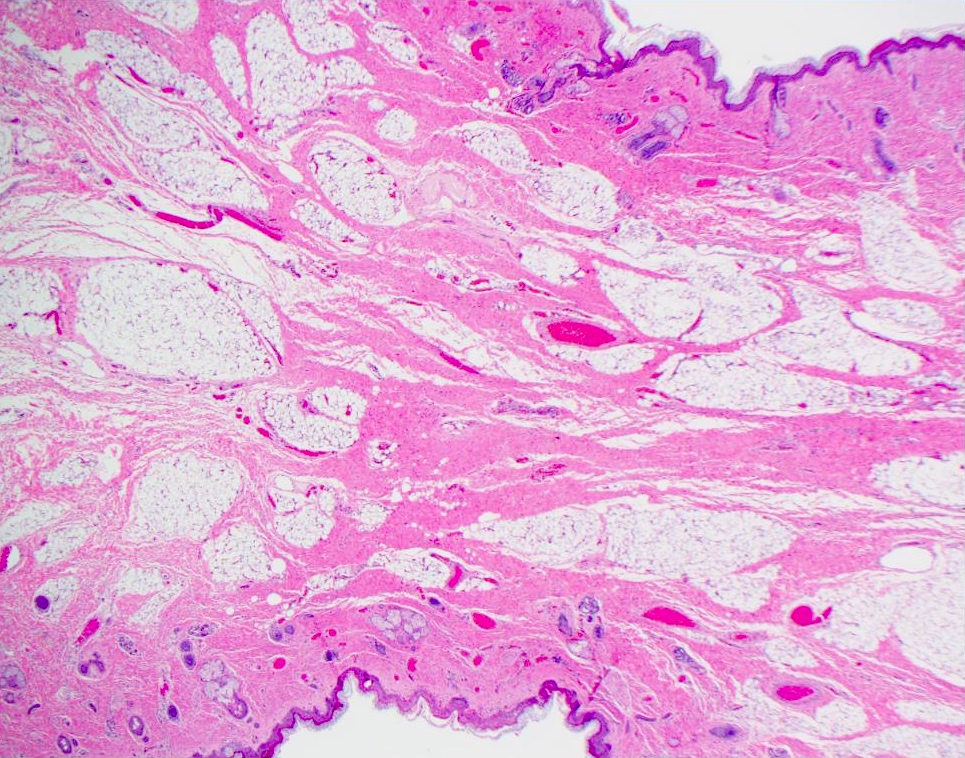
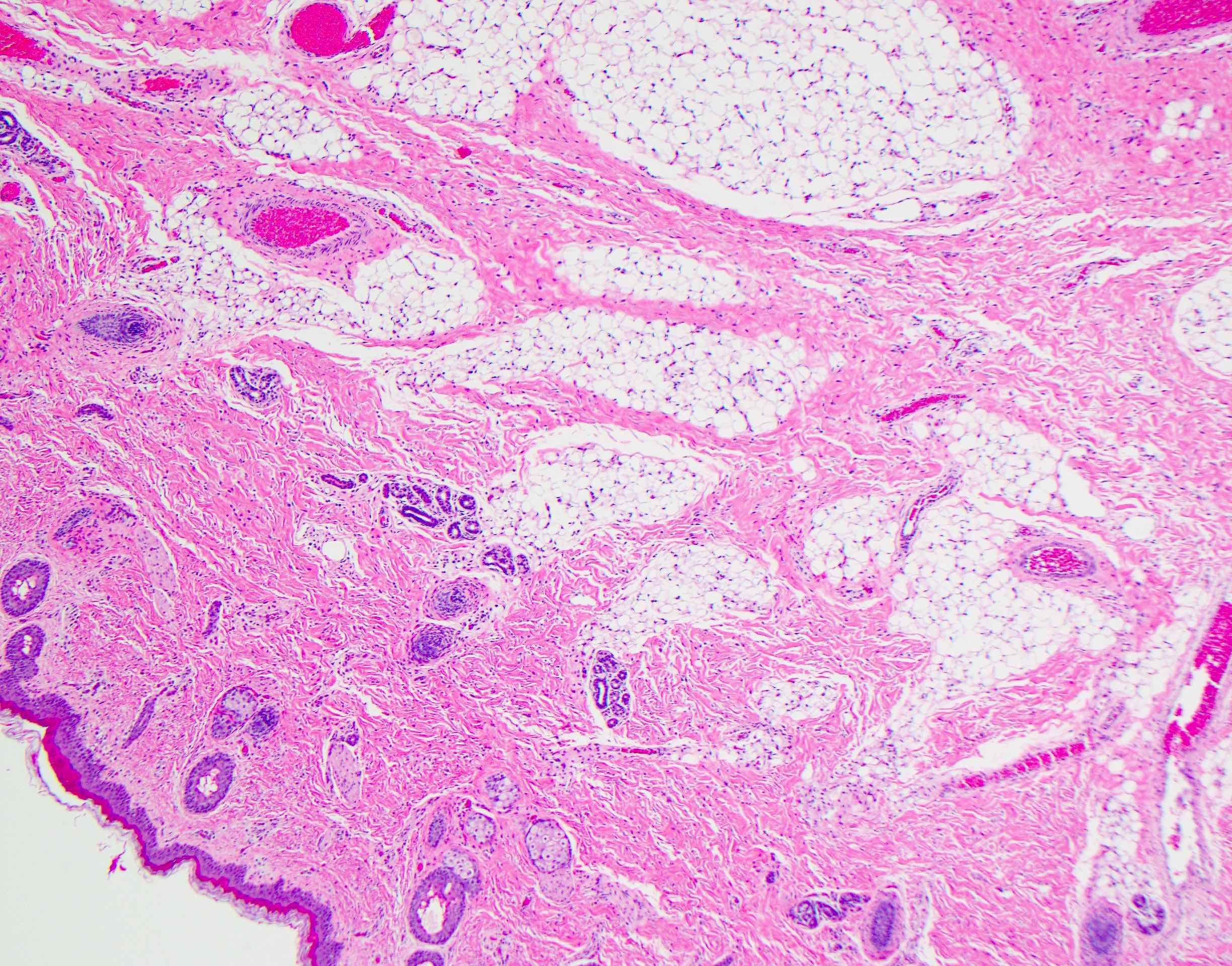
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Comprised of tissue derived from ectoderm and mesoderm
- Consists of keratinizing squamous epithelium with underlying adnexa which includes pilosebaceous units
- Mesoderm derivatives include fibroadipose tissue, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, seromucous glands and cartilage
- Meningothelial cells have been reported in literature occasionally (Case Rep Otolaryngol 2021;2021:1844244, Head Neck Pathol 2021;15:25)
- No endodermal elements are present
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Right oral cavity lesion, excision:
- Hairy polyp (see comment)
- Comment: Squamous epithelium with underlying adnexal structures, cartilage and fibroadipose tissue are present.
Differential diagnosis
- Teratoma (Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2015;53:188):
- Comprised of 3 germ layers
- Solid or cystic with mature and immature components
- Hamartoma:
- Disordered growth of cells or tissue in normal anatomical location
- Dermoid cyst (Ear Nose Throat J 2022;101:NP105):
- Consists of squamous epithelium with adnexal structures
- No other derivatives present
- Choristoma (Turk J Pediatr 2018;60:460, Eurorad: Nasopharyngeal Hairy Polyp in an Infant with Apnoiec Spells [Accessed 6 September 2023]):
- Histologically normal tissue in abnormal anatomical location
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 2 day old neonate presents with airway obstruction and oropharyngeal mass since birth. There are no underlying congenital deformities. Flexible endoscopy demonstrates a mass extending from the left torus tubarius into the oral cavity which is excised for histopathological examination. Microscopic examination displays epidermal squamous epithelium with underlying pilosebaceous units and mesenchymal core (depicted in the image above). What is the diagnosis?
- Dermoid cyst
- Hairy polyp
- Squamous papilloma
- Teratoma
Board review style answer #1
B. Hairy polyp. Hairy polyp is comprised of 2 germ layers, which are ectoderm and mesoderm derivatives. Answer D is incorrect because teratoma contains derivative from all 3 layers. Answer C is incorrect because squamous papillomas show finger-like projections with squamous epithelium and fibrovascular cores. Answer A is incorrect because it is a midline cyst with squamous epithelium and adnexal structures only.
Comment Here
Reference: Hairy polyp
Comment Here
Reference: Hairy polyp
Board review style question #2
A neonate presents with a finger-like polypoidal extension of soft tissue mass from oral cavity (depicted in the clinical picture above) with feeding difficulties and airway obstruction requiring intubation. The baby has had this lesion since birth. The microscopic examination shows keratinizing squamous epithelium with adnexal structures, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and cartilaginous core. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case?
- Hairy polyp
- Hamartoma
- Lipoma
- Teratoma
Board review style answer #2
A. Hairy polyp. Hairy polyps occur congenitally and are comprised of mesodermal core with ectodermal lining. Answer C is incorrect because lipomas contain mature adipose tissue. Answer D is incorrect because teratomas contain derivatives from all 3 germ layers. Answer B is incorrect because hamartomas have a haphazard growth of cells in a normal anatomical location.
Comment Here
Reference: Hairy polyp
Comment Here
Reference: Hairy polyp