Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Turashvili G. Clear cell carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorclearcell.html. Accessed September 15th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Malignant epithelial tumor composed of clear, eosinophilic or hobnail cells with tubulocystic, papillary and solid growth patterns
Essential features
- Admixture of tubulocystic, papillary and solid growth patterns comprised of cells with uniform nuclear atypia without brisk mitotic figures
- Usually positive for CK7, PAX8, napsin A and HNF1β and negative for ER, PR and WT1, with aberrant p53 expression in up to 24% of cases
- May be associated with endometriosis or Lynch syndrome
- Stage is the most important prognostic factor
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Accounts for 10 - 12% of ovarian carcinomas in North America (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2010;29:203, J Natl Cancer Inst 2019;111:60)
- Racial distribution in United States: 4.8% white, 3.1% black, 11.1% Asian (Gynecol Oncol 2011;121:407)
- Higher incidence in Asia (up to 27% in Japan) (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2014;40:338, Gynecol Oncol 2019;153:589)
- Mean age is 55 - 56 years (Gynecol Oncol 2008;109:370, J Pathol Clin Res 2018;4:250)
- Increased risk associated with:
- Endometriosis, including endometriotic cysts (50 - 74%) (Lancet Oncol 2012;13:385, Int J Gynecol Cancer 2012;22:1310)
- Less frequently, Lynch syndrome (Eur J Cancer 2016;55:65, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1029, Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1173, Clin Cancer Res 2019;25:3962, Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2008;1:502)
- Mismatch repair (MMR) deficiency in 6 - 43.75% of cases
- Younger patients
- 10% develop endometriosis associated carcinomas, including clear cell carcinoma
- Family history of ovarian cancer in a first degree relative (PLoS One 2018;13:e0205000)
- Decreased risk associated with:
- Late menarche (> 15 years), early menopause (< 40 years), tubal ligation, parity, hysterectomy, smoking, oral contraceptives (J Clin Oncol 2016;34:2888)
- Expression of the genetic susceptibility locus (HNF1β) via epigenetic mechanisms (Nat Commun 2013;4:1628)
Sites
- Ovary
- Any extraovarian site with endometriosis
Pathophysiology
- Genetic alterations due to various mutations (see Molecular / cytogenetics description)
Etiology
- Endometriosis (J Pathol 2018;245:265, Int J Gynecol Cancer 2012;22:1310)
- Mutation signatures: age related (40%) and APOBEC mediated (apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like (26%), a family of evolutionarily conserved cytidine deaminases) (Nat Genet 2017;49:856)
Clinical features
- Symptoms related to endometriosis or pelvic mass (Gynecol Oncol 2010;116:374)
- Most common ovarian epithelial neoplasm associated with paraneoplastic syndromes, such as hypercalcemia, thromboembolism, subacute cerebellar degeneration or bilateral diffuse uveal melanocytic proliferation (Onkologie 2009;32:517, Gynecol Oncol 2007;104:406, Semin Diagn Pathol 2019;36:246)
- May be incidental (asymptomatic)
Diagnosis
- Microscopic examination
Laboratory
- May be associated with mildly elevated CA-125 (usually ≤ 200 U/mL) (Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e10881)
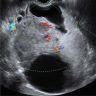
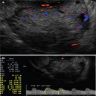
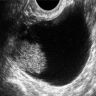
Radiology description
- Large unilocular, mainly cystic, smooth marginated mass with 1 or more solid nodular protrusions into the cavity on all imaging modalities
- High attenuated cystic portion on computed tomography (J Comput Assist Tomogr 2006;30:875)
- Variable T1 signal, depending on hemorrhagic components on magnetic resonance imaging
- Blood flow in solid nodules on Doppler ultrasound examination
- In postmenopausal women, ground glass appearance in a cyst ultrasonographically should be evaluated carefully to rule out a component of clear cell carcinoma (Ultrasonography 2015;34:173)
Prognostic factors
- Negative prognostic factors:
- Advanced stage (most important) (Histopathology 2015;66:808, Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e10881)
- Most cases are FIGO stage I (BMC Cancer 2018;18:347, J Natl Cancer Inst 2019;111:60)
- Worse prognosis in stage IC disease compared with stage IA
- Overall 5 year cause specific survival of 66%, including 85% for stage I, 71% for stage II, 35% for stage III and 16% for stage IV (CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:284)
- Better prognosis than high grade serous carcinoma when confined to the pelvis but worse prognosis if advanced stage except for some MMR deficient tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:36)
- Positive lymph nodes (Histopathology 2015;66:808)
- Lymphovascular invasion
- Immunohistochemically, loss of ARID1A, aberrant p53 and block-like p16 staining, expression of IMP3, nuclear expression of beta catenin, fibroblast growth factor receptor 2, chromobox homolog 7 (CBX7), Emi1, CXCR4, HOXA10, glypican 3 and Rsf-1 (HBXAP) (Surg Pathol Clin 2019;12:529)
- Genetic alterations, including amplification of MET or MDM2 (in TP53 wild type cases), CCNE1 copy number gain, somatic copy number variations such as chr20q13.2 harboring the ZNF217 gene (Surg Pathol Clin 2019;12:529)
- Advanced stage (most important) (Histopathology 2015;66:808, Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e10881)
- Positive prognostic factors:
- PIK3CA mutations (Hum Pathol 2012;43:2197)
Case reports
- 28 year old woman with Cowden syndrome diagnosed with PTEN negative ovarian clear cell carcinoma (J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2019;17:7)
- 50 year old woman with cerebellar metastasis of ovarian clear cell carcinoma (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2020;39:68)
- 55 year old woman with primary diaphragmatic clear cell carcinoma associated with endometriosis (Gynecol Oncol Rep 2021;36:100733)
- 61 year old woman with bilateral breast metastases of ovarian clear cell carcinoma (Case Rep Oncol Med 2019;2019:8013913)
- 62 year old woman with ovarian clear cell carcinoma associated with low grade endometrial stromal sarcoma (Gynecol Obstet Invest 2020;85:371)
Treatment
- Hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, omentectomy and staging biopsies
- Adjuvant chemoradiation in some patients (Ann Oncol 2016;27:i50)
- Often platinum resistant (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:36)
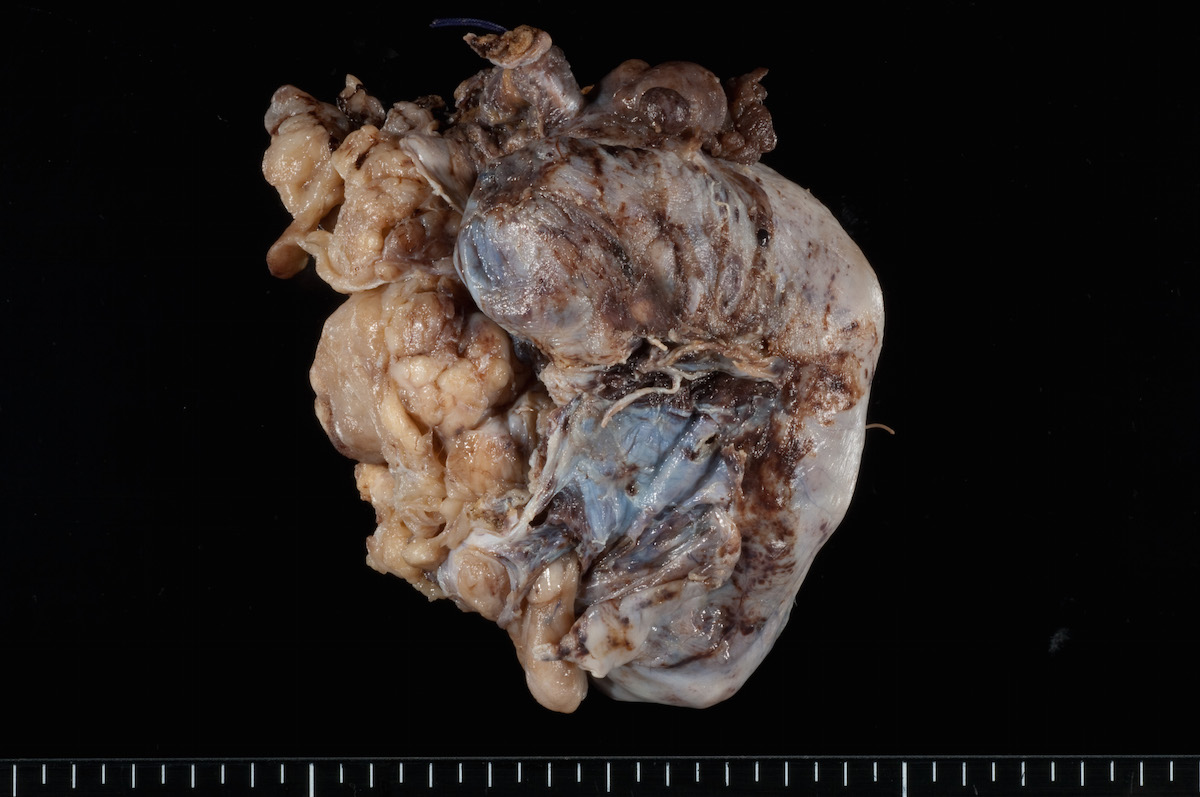
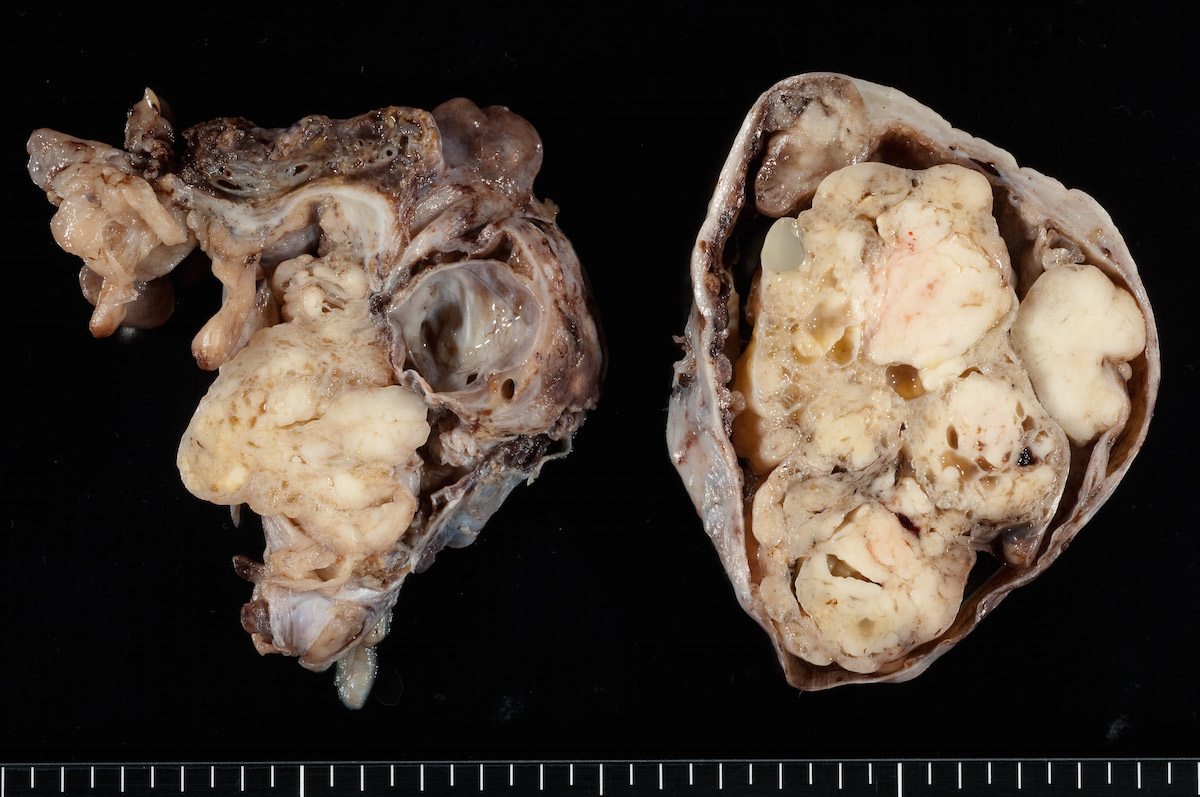
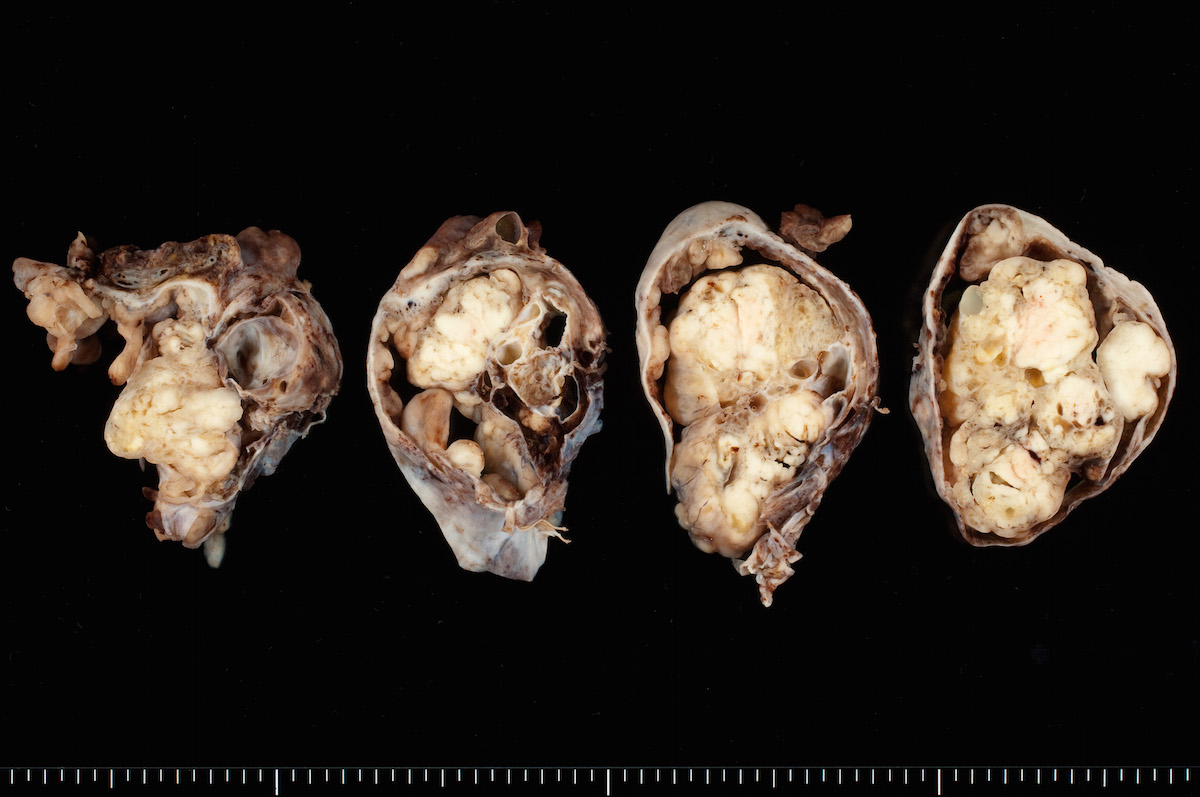
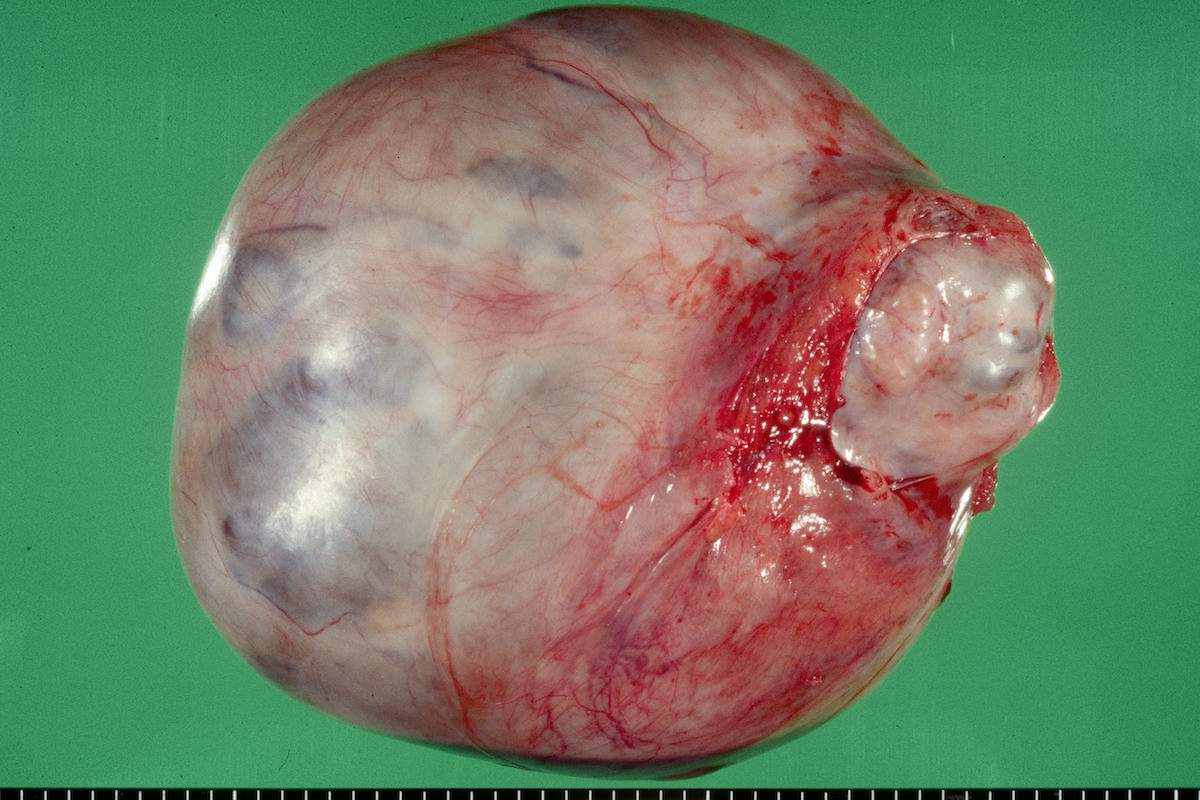
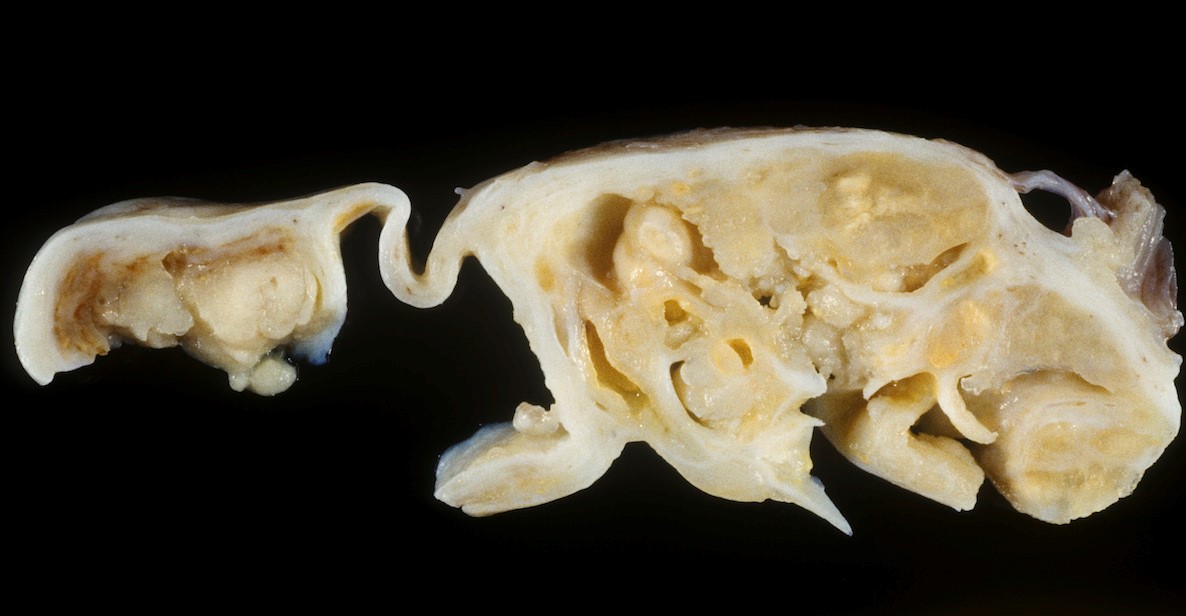
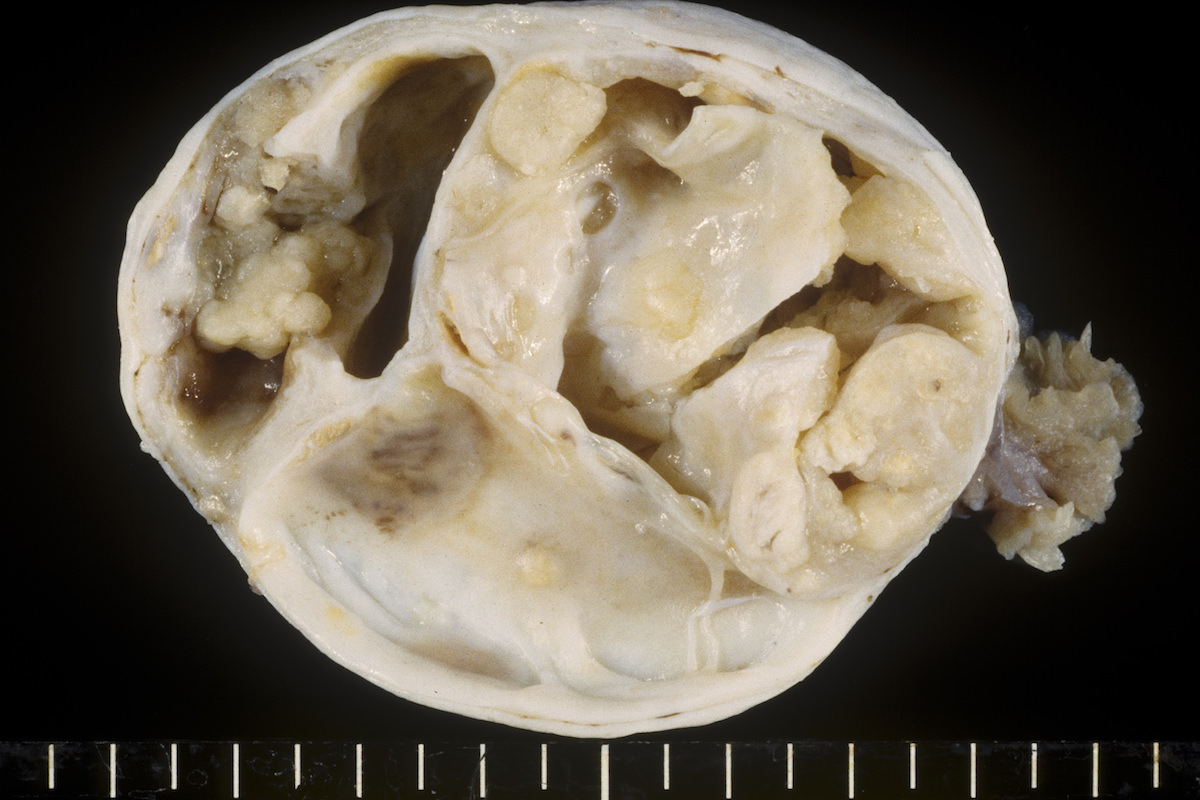
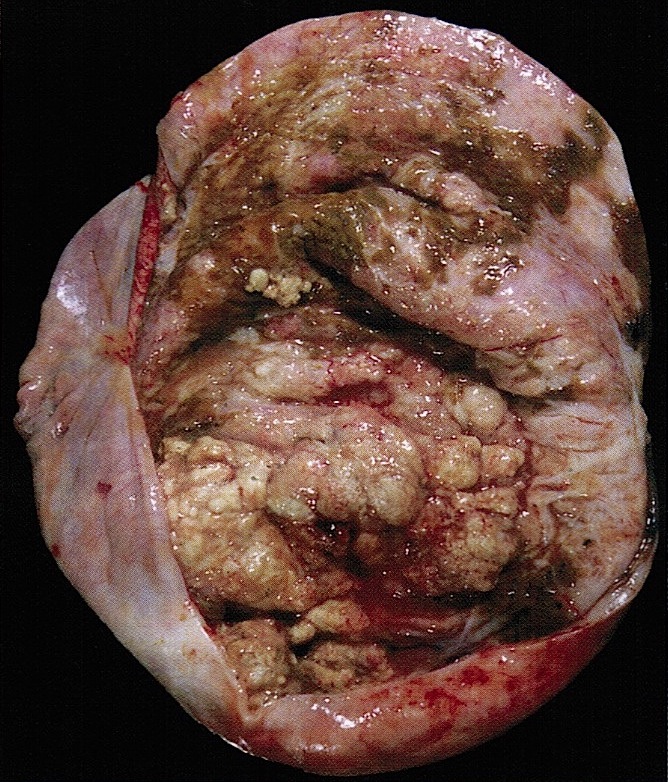
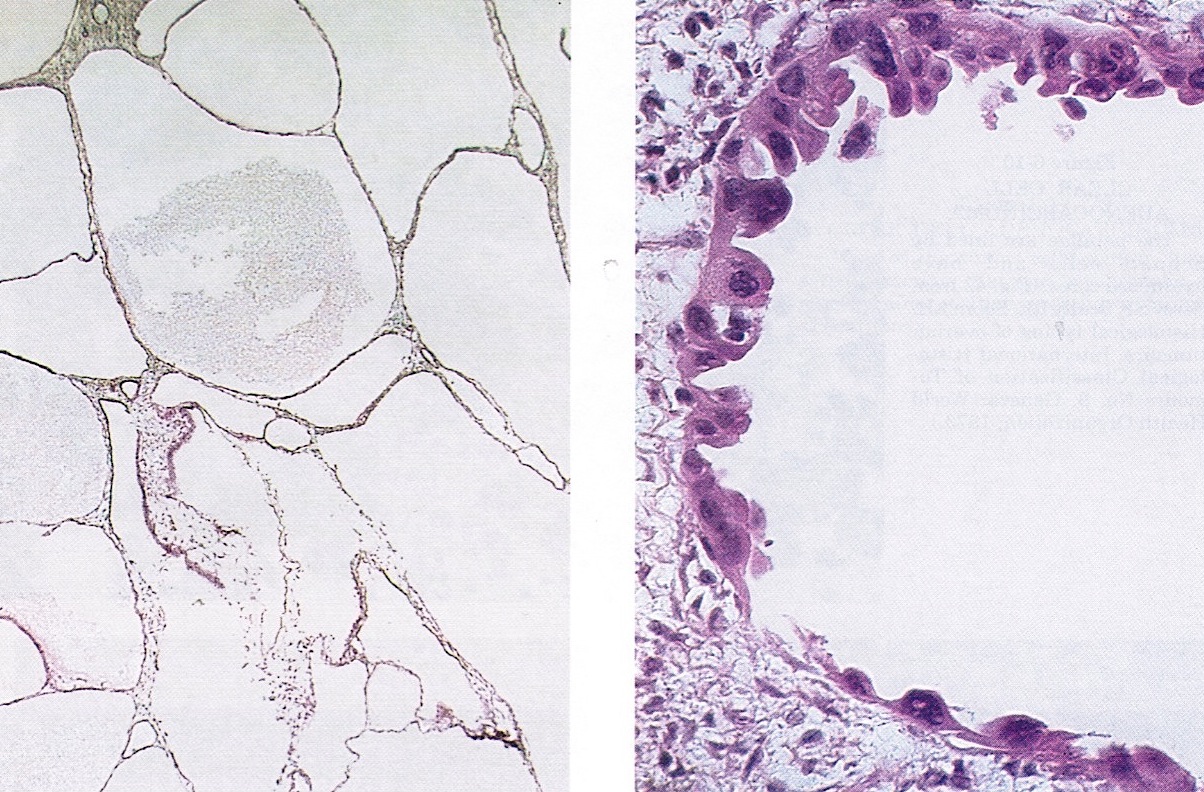
Gross description
- Usually unilateral
- Mean size 13 cm (range 0.8 - 35 cm) (Histopathology 2015;66:808)
- Variable appearance on cut surface:
- Mainly cystic, with fleshy nodules protruding into the cyst lumen
- Solid and cystic (spongy appearance due to small cysts)
- Solid (may be arising from clear cell adenofibroma or borderline clear cell tumor)
- Cyst may contain chocolate brown fluid
- Pale yellow to brown appearance
- Necrosis or hemorrhage
- Ovarian surface involvement in 11% of cases (Histopathology 2015;66:808)
Gross images
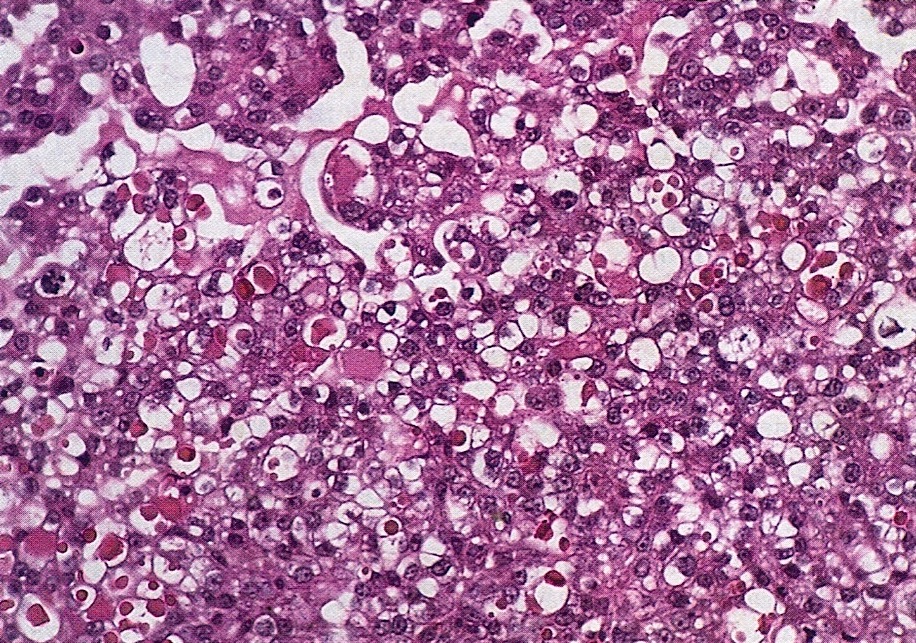
Frozen section description
- Admixure of characteristic tubulocystic, papillary and solid growth patterns
- Uniformly atypical cells with clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm, no brisk mitoses
Frozen section images
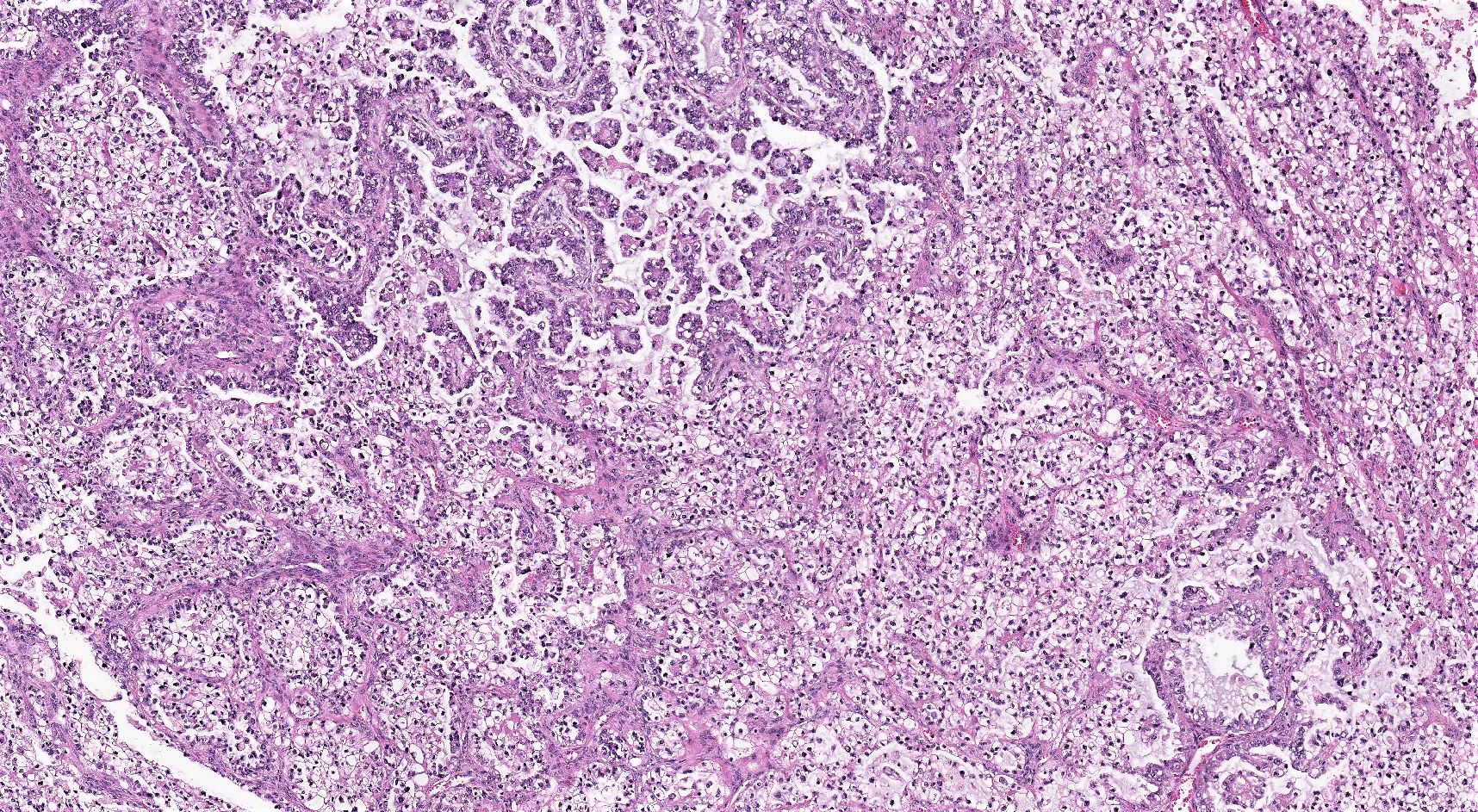
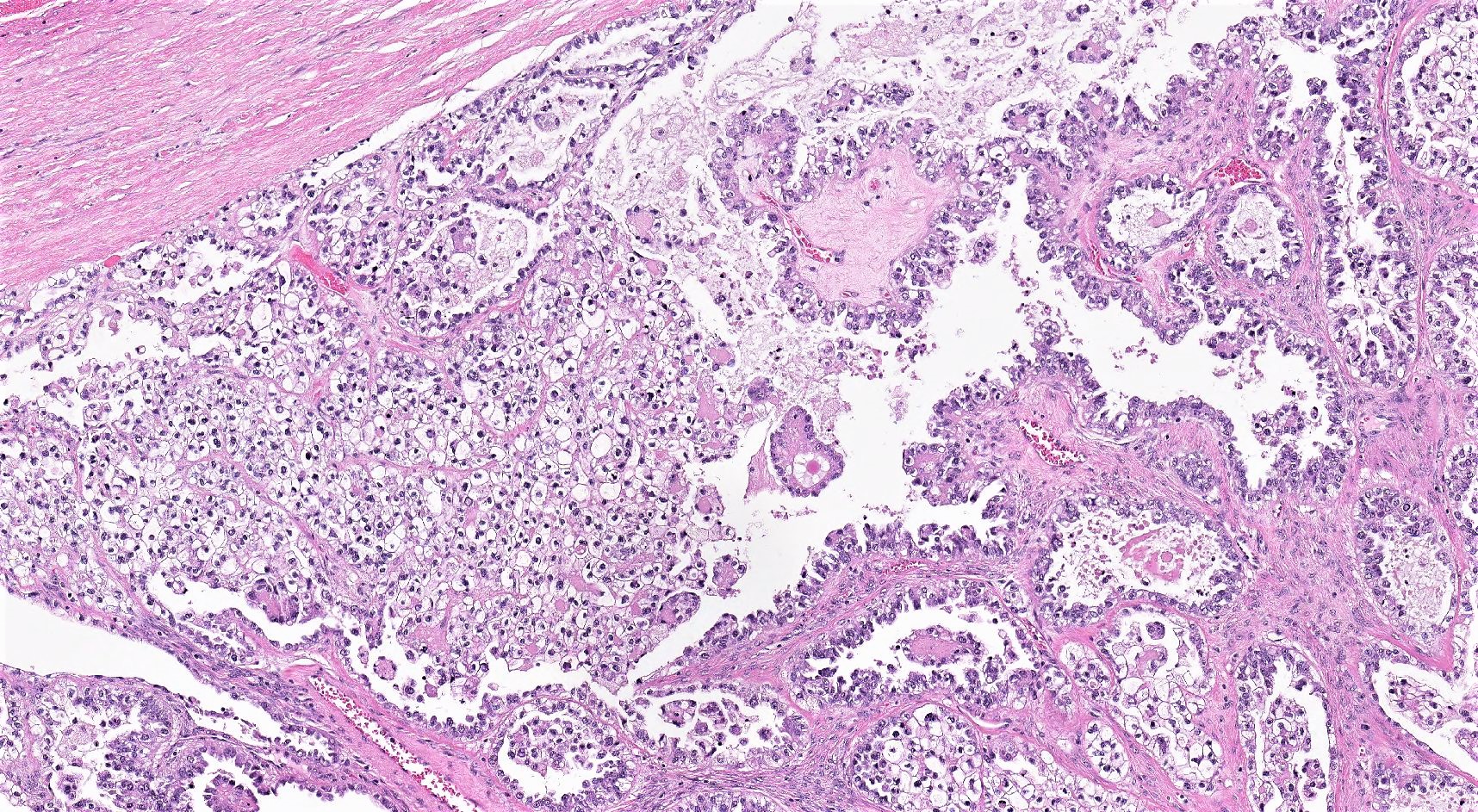
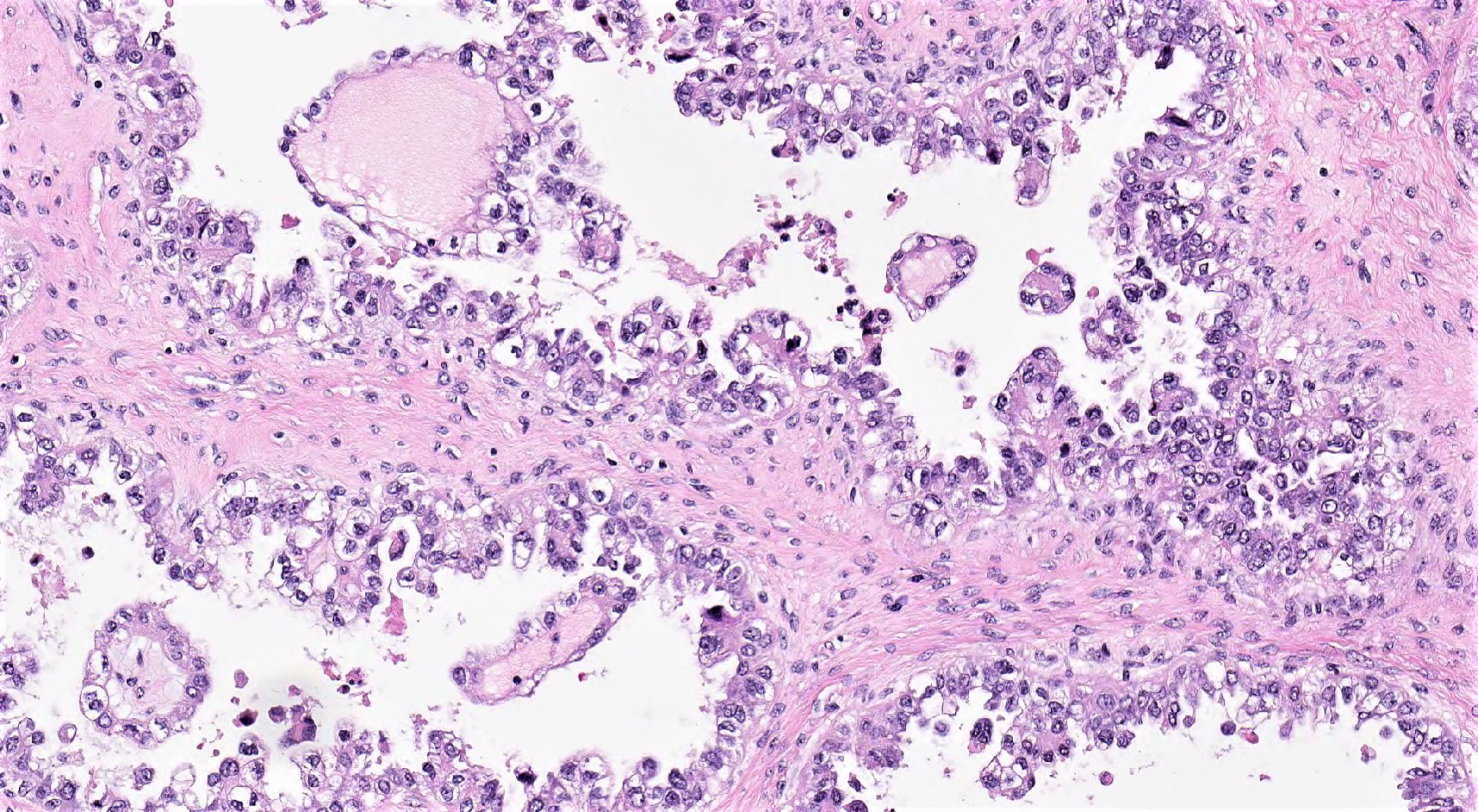
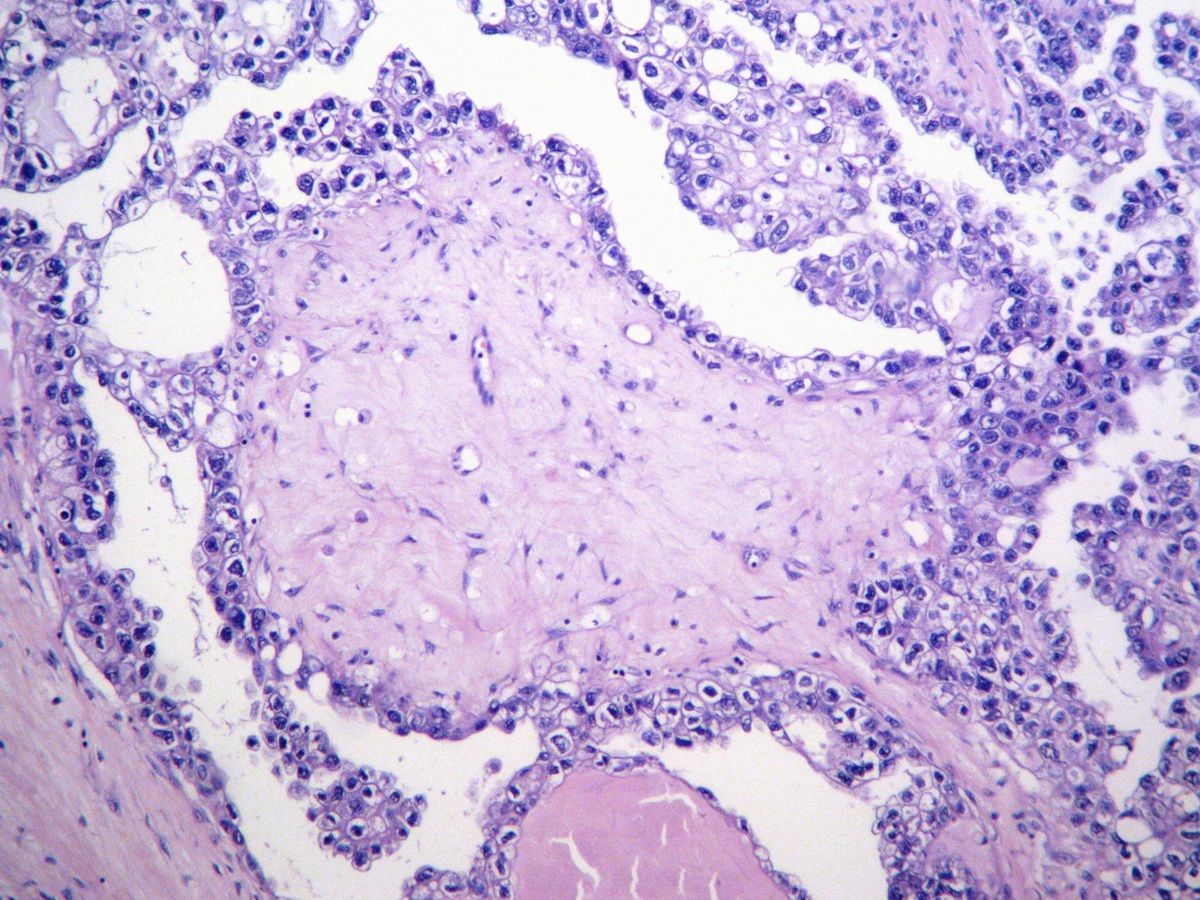
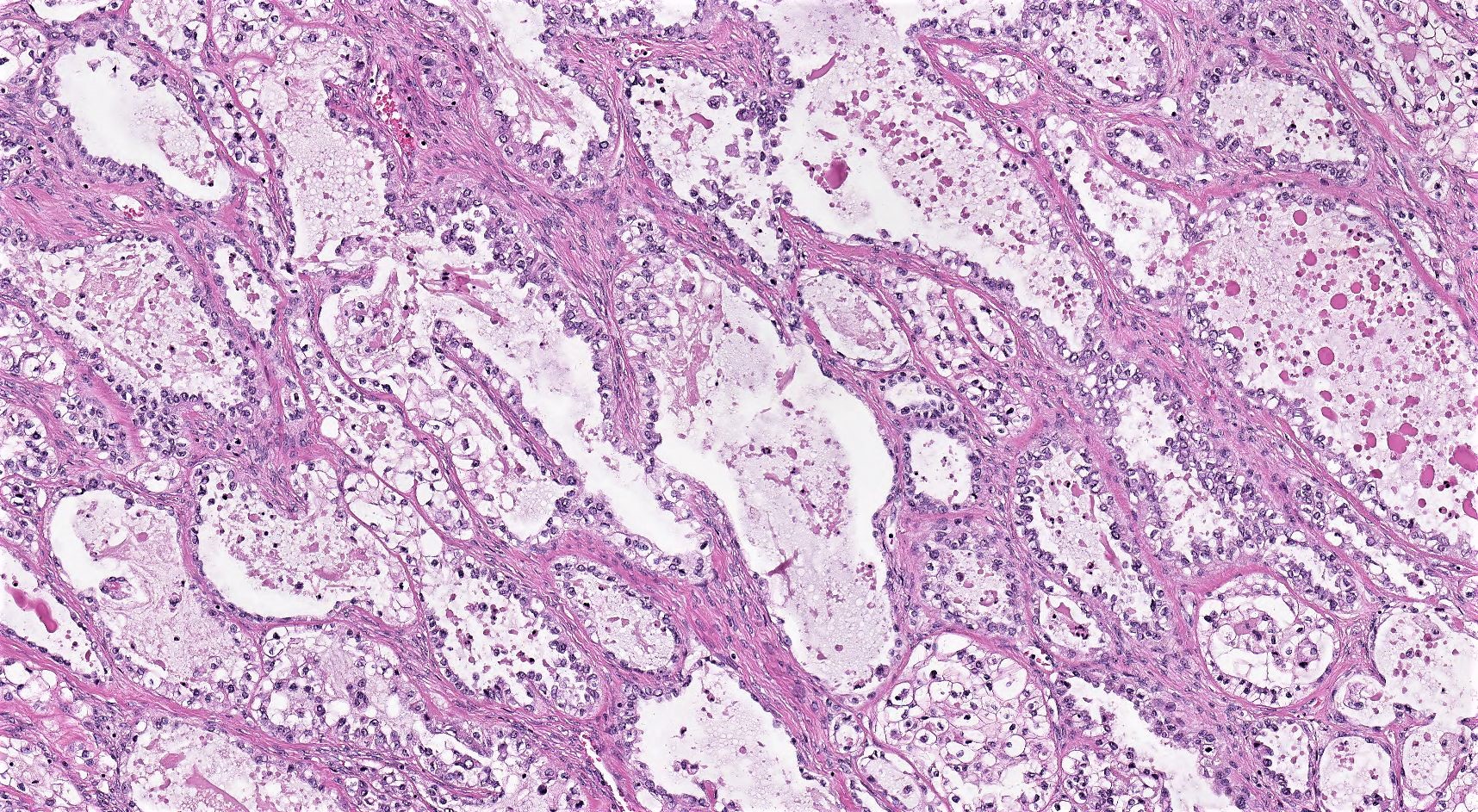
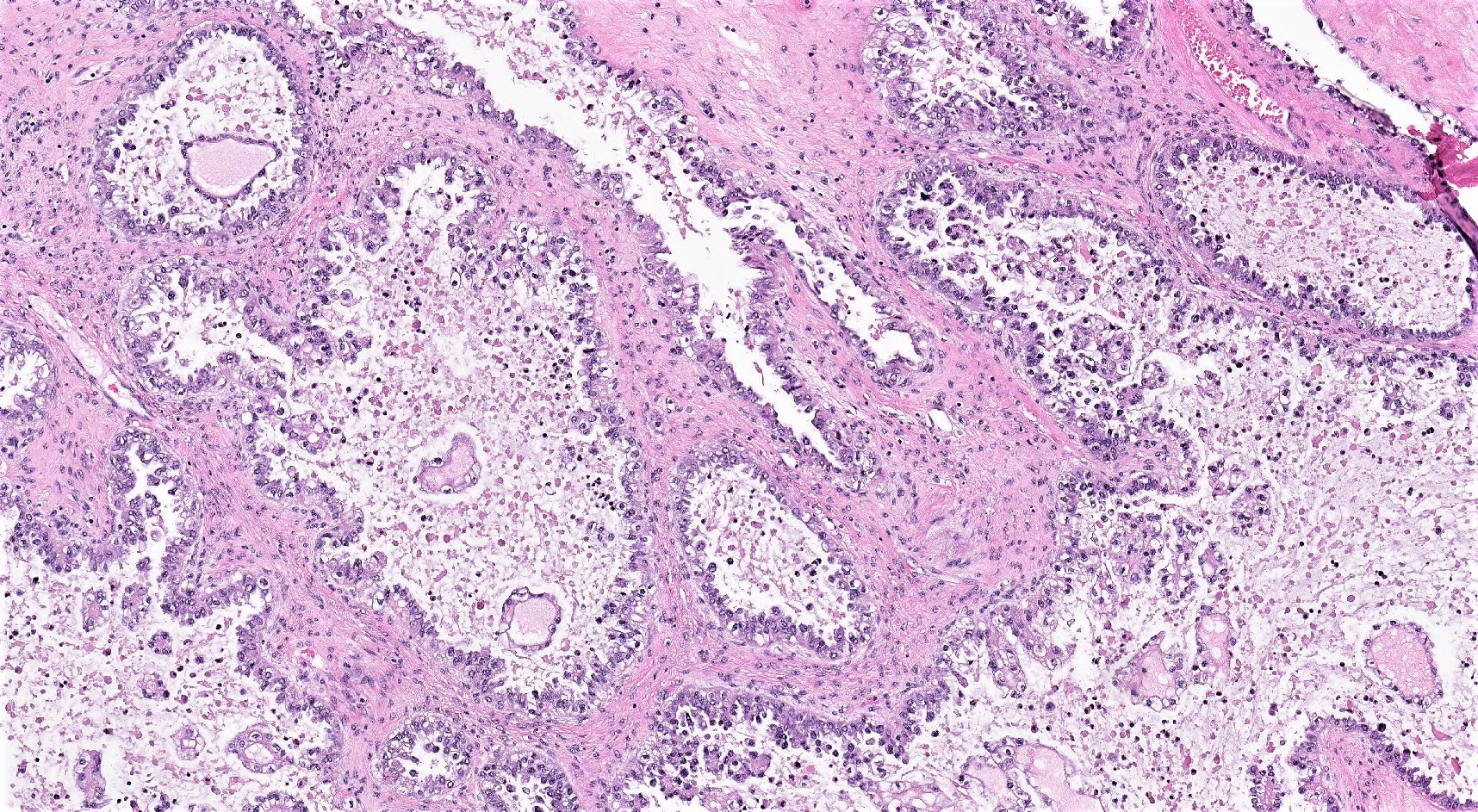
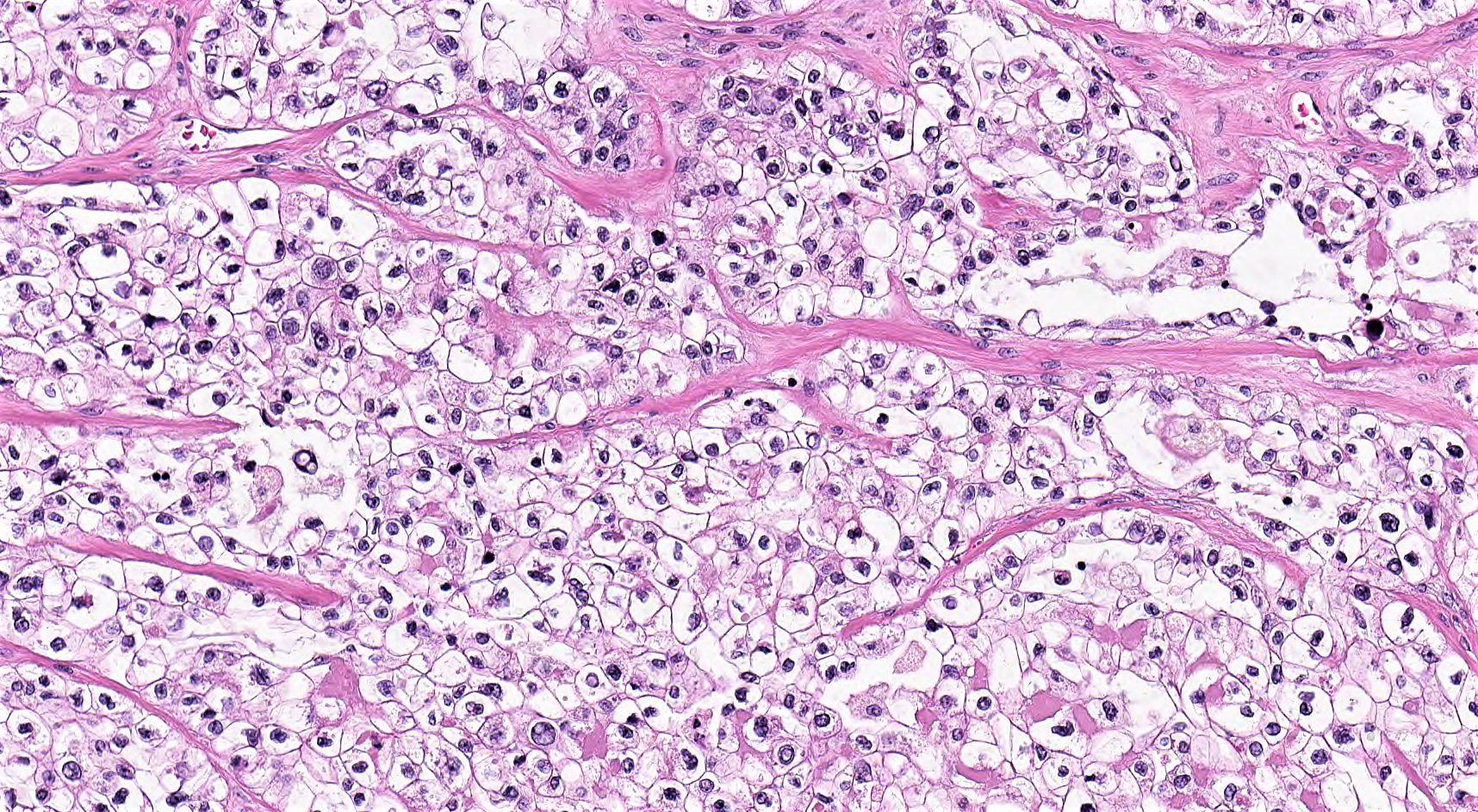
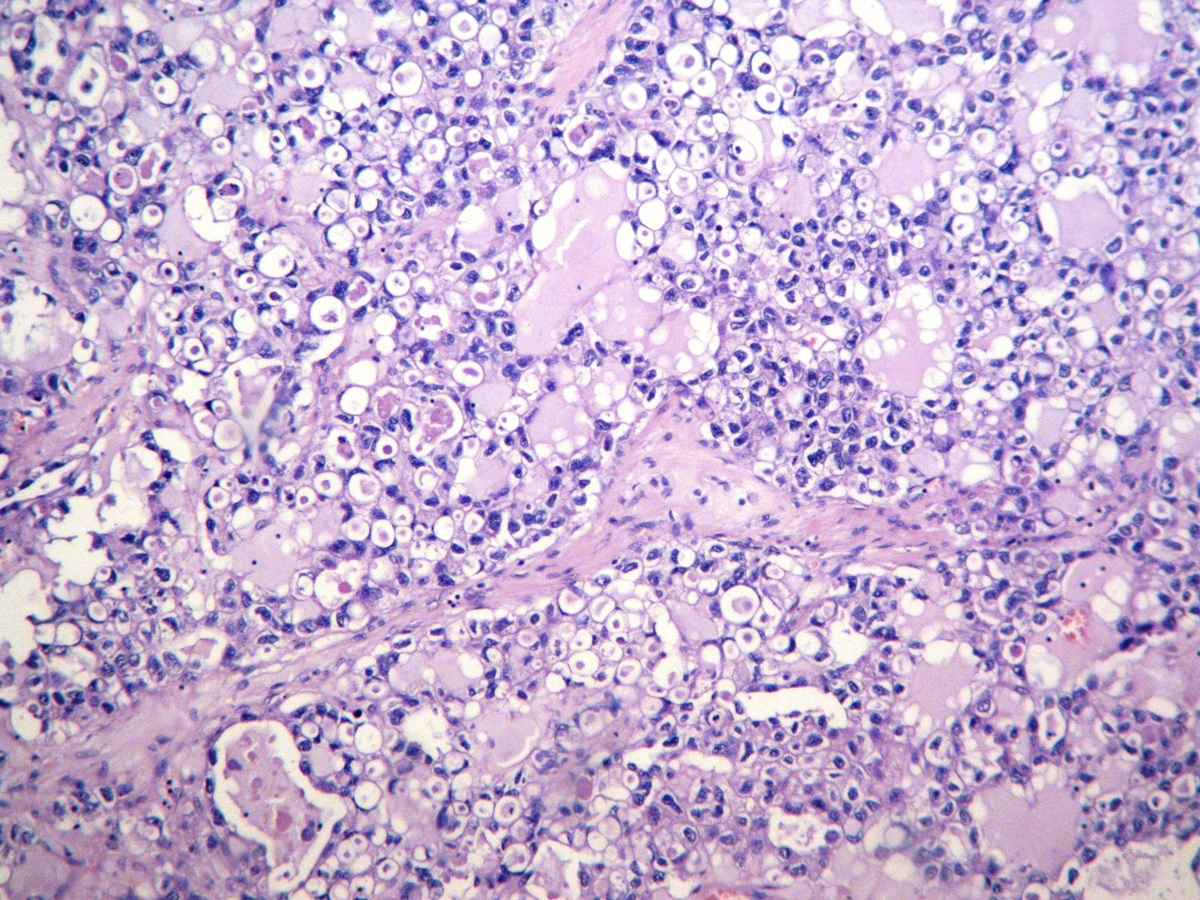
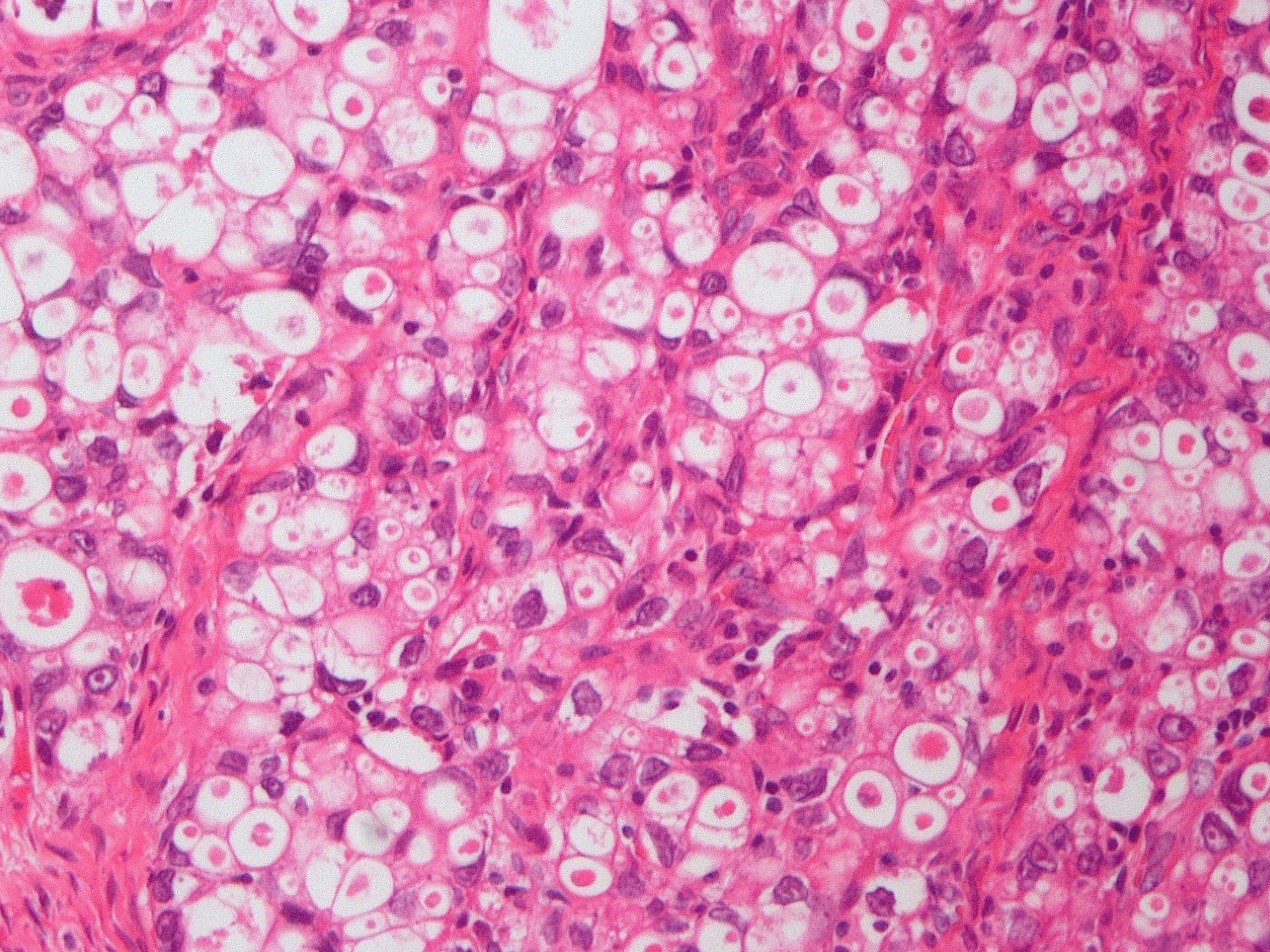
Microscopic (histologic) description
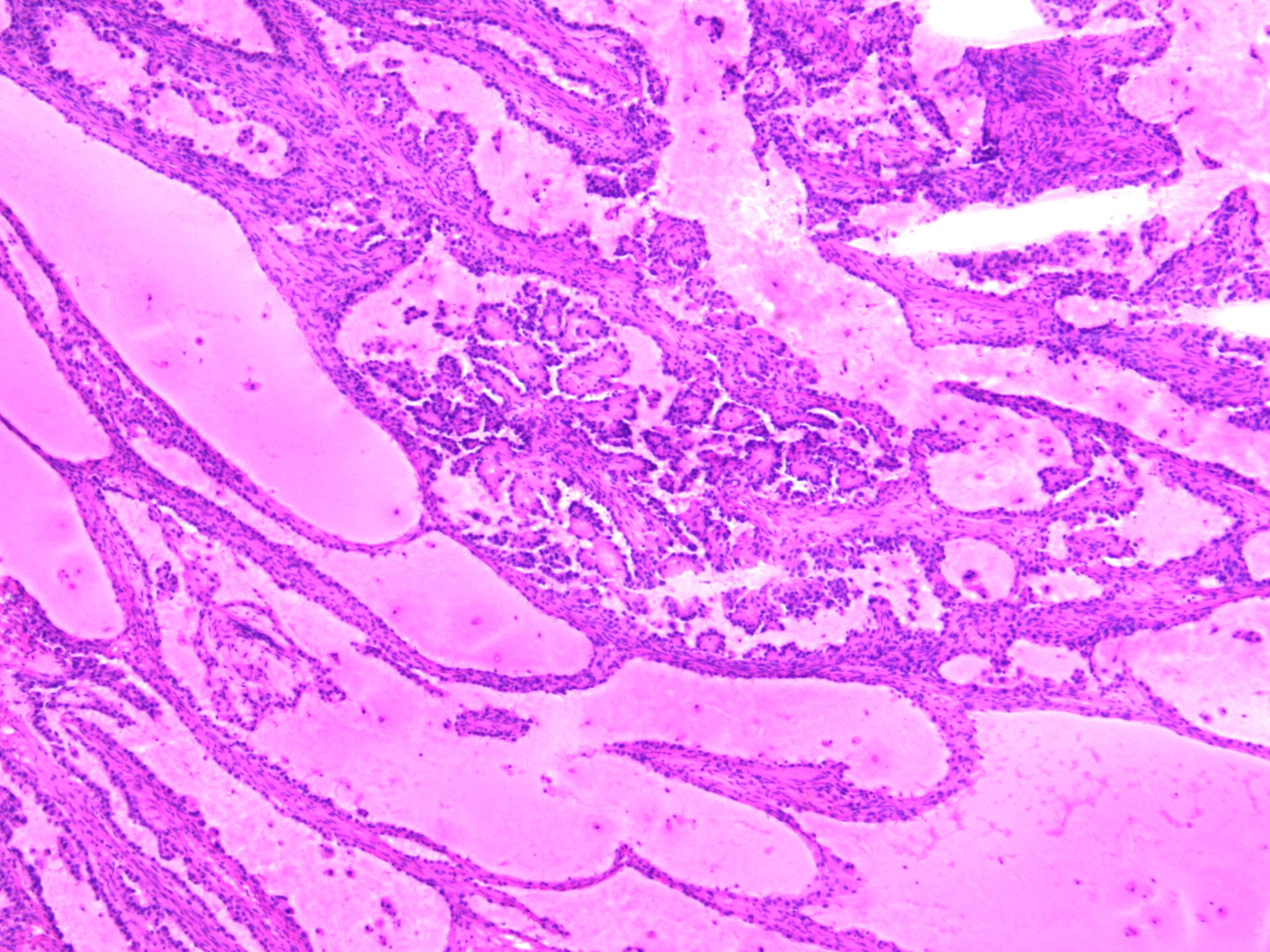
- 3 classic growth patterns, frequently admixed but 1 pattern (usually papillary or tubulocystic) may predominate (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:36, Adv Anat Pathol 2012;19:296, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:656, Histopathology 2015;66:808):
- Papillary:
- Most frequent (70%)
- Usually small, round, simple, nonbranching papillae with fibrous / hyalinized, edematous / myxoid or empty (open tumor rings) stromal cores
- Lined by 1 - 2 layers of cuboidal, flattened or hobnail cells
- Micropapillary tufts may be seen
- Rarely irregular, broad papillae with or without hierarchical branching and micropapillae (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:269)
- Tubulocystic:
- Frequent (65%)
- Variably sized tubules and cysts, with or without intraluminal dense eosinophilic secretions and outpouchings
- Lined by a single layer of hobnail, cuboidal or flattened cells
- Often associated with an adenofibromatous background
- Solid:
- Least common (62%)
- Diffuse sheets or nested clusters of polyhedral cells separated by delicate septa exhibiting clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Papillary:
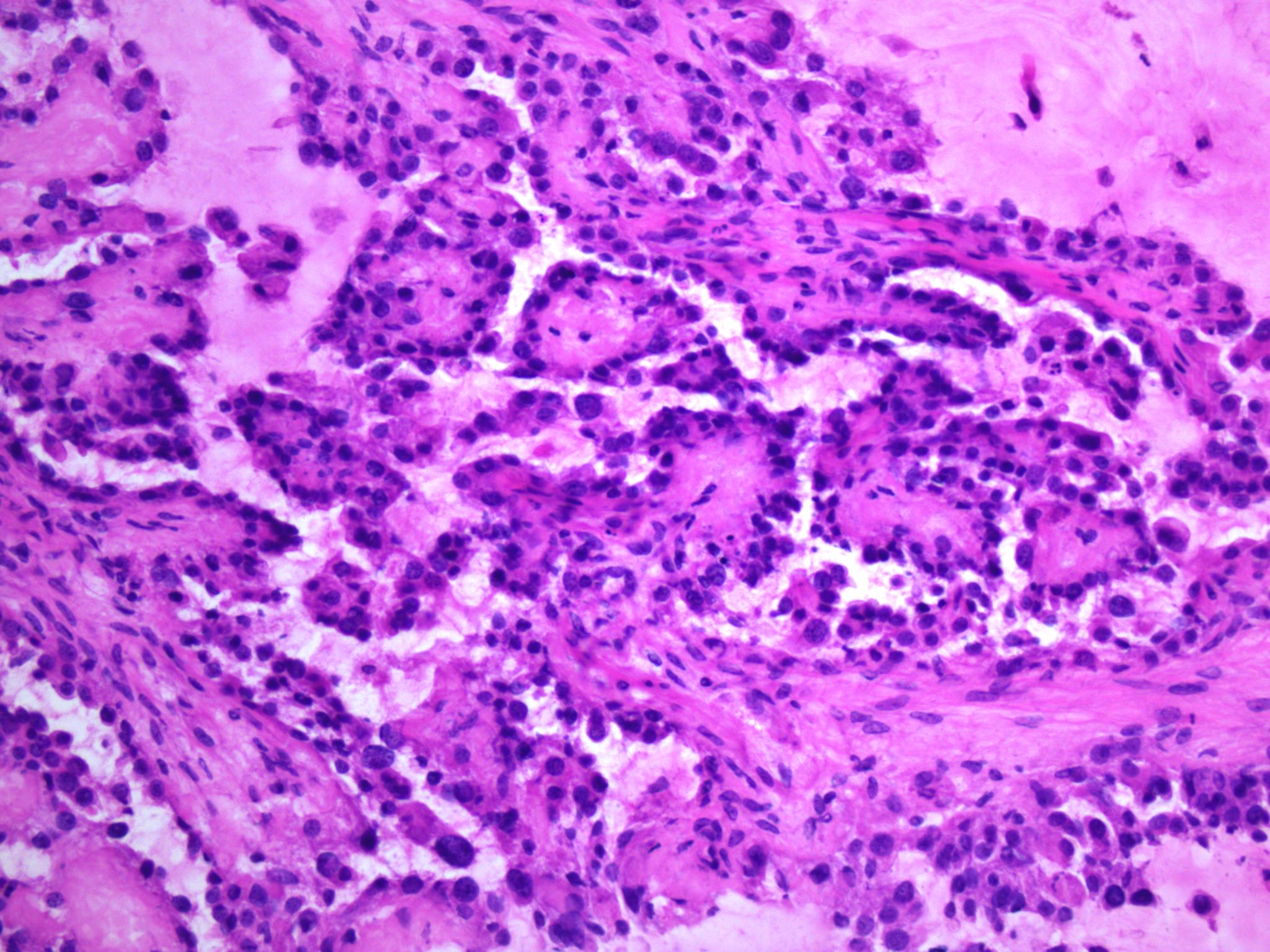
- General features:
- Low cuboidal, polyhedral, hobnail or flattened cells with uniform nuclear atypia, prominent nucleoli and variable mitotic activity (usually low at < 6 per 10 high power fields)
- Hobnail cells have hyperchromatic nuclei protruding into lumina of tubulocystic structures or lining papillae
- Focal nuclear pleomorphism may be present in 40%
- Eosinophilic hyaline globules (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:36, Adv Anat Pathol 2012;19:296)
- Nuclear pseudoinclusions
- Peritumoural or diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate may be present
- May be associated with clear cell adenofibroma, clear cell borderline tumor, endometriosis or endometrioid adenocarcinoma
- Not graded (high grade by definition)
- Oxyphilic variant of clear cell carcinoma is composed of tumor cells with variable amounts of clear to granular eosinophilic cytoplasm (oxyphil cells), especially in nested, solid or trabecular growths (Am J Surg Pathol 1987;11:661)
- Rare features:
- Multinucleated cells
- Psammoma bodies
- Diastase resistant intracytoplasmic material imparting a signet ring appearance (so called targetoid cells)
- Intraglandular cellular sloughing mimicking high grade serous carcinoma
- Uncommon growth patterns include glandular, nested, trabecular and reticular-like (myxoid stroma)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Gulisa Turashvili, M.D., Ph.D., Sonali Lanjewar, M.D., M.B.B.S., Semir Vranić, M.D., Ph.D. and AFIP
Cytology description
- Round to oval nuclei with fine chromatin
- Abundant, pale, finely granular to vacuolated cytoplasm and indistinct cytoplasmic membranes
- Hyaline extracellular material forming so called raspberry bodies or globule-like structures (Cytopathology 2016;27:427)
- Psammoma bodies in ascitic fluid (Acta Cytol 2000;44:1005)
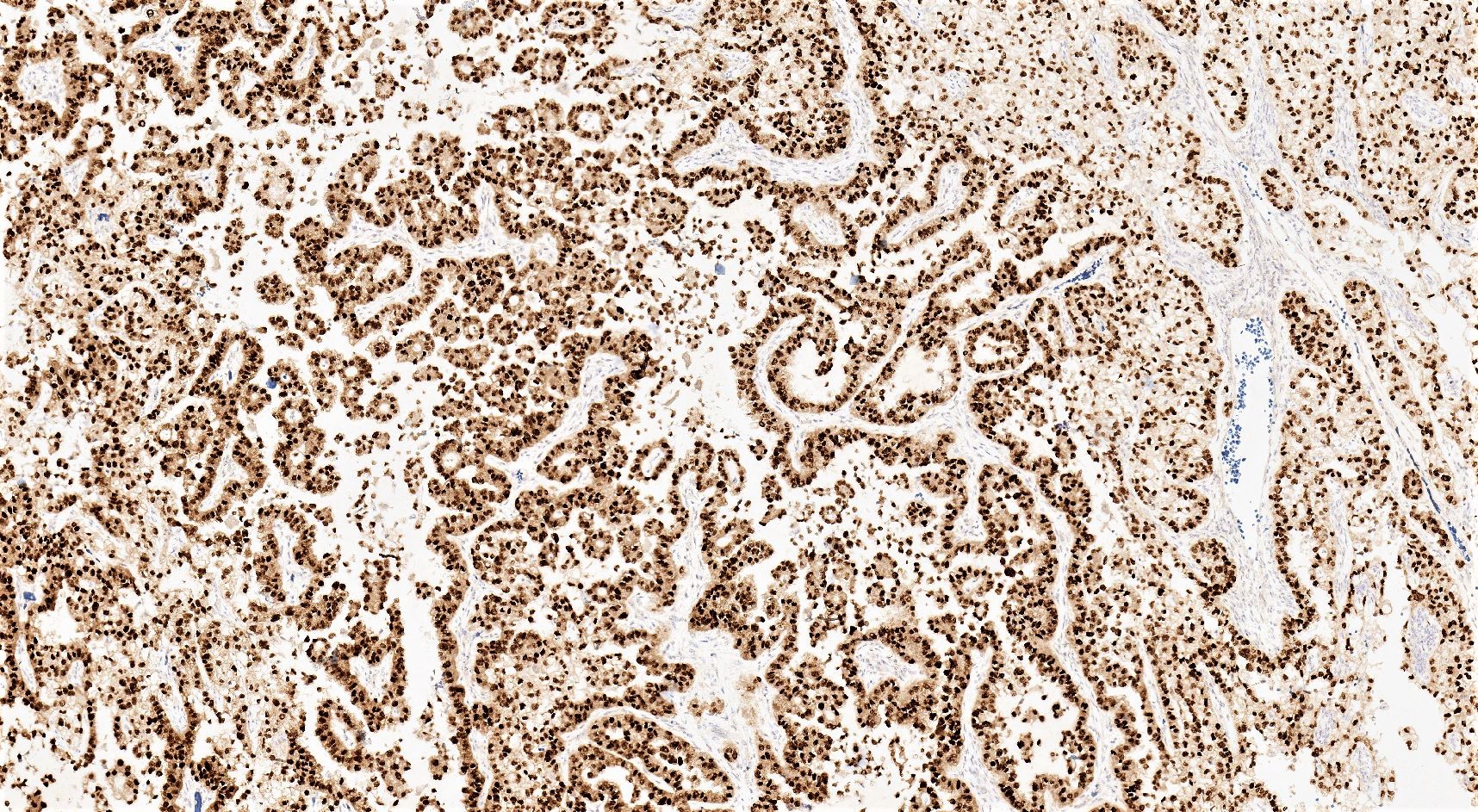
Positive stains
- CK7
- EMA
- PAX8
- HNF1β: sensitive but not specific (Mod Pathol 2006;19:83, Pathology 2015;47:105)
- Napsin A: specific with intermediate sensitivity (Mod Pathol 2015;28:111, Pathology 2015;47:105)
- AMACR: specific but not sensitive (Pathology 2015;47:105, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2020;28:593)
- p53: aberrant in 7 - 24% of cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1591, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:36)
- PAS positive diastase sensitive material (glycogen) in clear cells, diastase resistant intracytoplasmic material in targetoid cells
Negative stains
- ARID1A: loss of expression in 15 - 75% (Mod Pathol 2012;25:282, Int J Gynecol Cancer 2012;22:1310)
- MMR: loss of expression in 6 - 43.75% (not adjusted for age) (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:656, Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2008;1:502)
- WT1 (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2019;38:353)
- ER
- PR
- AFP: rarely positive
- Glypican 3: rarely positive
- OCT4: rarely positive
- SALL4
- CD10 (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2003;22:272)
- p16: block-like in 20% of cases
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Loss of function mutations in ARID1A, a tumor suppressor gene from the SWI / SNF chromatin remodelling complex (50%) (N Engl J Med 2010;363:1532, Science 2010;330:228)
- PIK3CA mutations (40%), often associated with ARID1A mutations (Cancer Res 2004;64:7678, Am J Pathol 2009;174:1597, Mod Pathol 2012;25:615, Int J Gynecol Cancer 2016;26:648)
- TERT promoter mutations (16%) (J Pathol 2014;232:473)
- KRAS mutations (10%) (Nat Genet 2017;49:856)
- TP53 mutations (< 10%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1591)
- DNA mismatch repair deficiency (up to 6%), most commonly germline mutations in MSH2 (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2012;31:524, Histopathology 2016;69:288, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1591, Clin Cancer Res 2019;25:3962, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:656)
- PTEN mutations (5%) (Cancer Res 2000;60:7052)
- Rarely MET, ARID1B, PIK3R1, SMARCA4 and SMARCD3 mutations
Sample pathology report
- Uterus with cervix, fallopian tubes and ovaries, total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy:
- Right ovary: clear cell carcinoma, positive for ovarian surface involvement (see synoptic report)
- Left ovary and fallopian tubes: benign
- Endometrium: inactive
- Myometrium: leiomyomata
- Uterine serosa and cervix: benign
Differential diagnosis
- Clear cell adenofibroma:
- Extremely rare
- Scattered tubulocystic structures lined by bland flat to low cuboidal cells, with clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm in a fibromatous background
- Associated with clear cell carcinoma in up to 33% of cases; therefore, extensive sampling is important to rule out clear cell carcinoma (J Cancer 2011;2:94)
- Borderline clear cell tumor:
- Very rare
- Growth pattern similar to clear cell adenofibroma but with cytologic atypia
- Lacks stromal invasion by back to back glands, papillary or solid architecture or solid growth within cysts
- Serous borderline tumor or low grade serous carcinoma:
- High grade serous carcinoma with clear cell features:
- Usually diagnosed at advanced stage
- May be associated with serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma
- Typical papillary growth pattern
- Lack of small rounded papillae and tubulocystic structures
- Greater cytologic atypia with brisk mitoses
- Usually shows aberrant p53 expression, diffuse WT1, patchy to diffuse ER and PR; lacks HNF1β and napsin A
- Panel of WT1, napsin A, HNF1β and ER recommended for distinction of clear cell carcinoma from high grade serous carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:14, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2016;35:430)
- Endometrioid carcinoma with clear cell features:
- Metastatic clear cell renal carcinoma:
- Prior history or concurrent renal mass
- Nested alveolar pattern with interalveolar stromal vascularity
- Composed of tumor cells with mostly clear cytoplasm
- Lack of tubulocystic architecture, small rounded papillae and hobnail cells
- Diffuse expression of RCC, carbonic anhydrase IX and CD10 and no reactivity for CK7, ER, PR, napsin A and AMACR (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:377)
- Dysgerminoma:
- Yolk sac tumor:
- Young patients
- Elevated serum α fetoprotein
- Variable growth patterns with brisk mitoses
- Schiller-Duval bodies may be seen
- Diffusely positive for SALL4, AFP and glypican 3
- Negative or focally positive for CK7 and EMA
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
- Which of the following is the most useful immunohistochemical panel for distinguishing between clear cell carcinoma and high grade carcinoma with clear cell features?
- ER, PR, WT1 and p53
- ER, PR, WT1 and SALL4
- PAX8, p16, napsin A and HNF1β
- WT1, ER, napsin A and HNF1β
- WT1, napsin A, p16 and SALL4
Practice answer #2