Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Laboratory | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Gupta N. Carcinosarcoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumormmt.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Aggressive tumor with malignant epithelial and sarcomatous components
- Most common in postmenopausal, low parity women
- Very poor prognosis; stage is best predictor and most patients present at advanced stage
Terminology
- Previously called malignant mixed mesodermal tumor, MMMT
Epidemiology
- Mostly postmenopausal females, peaks in sixth decade
Sites
- Uterus, cervix, fallopian tube (rare)
Pathophysiology
- Appear to have epithelial origin (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:317, Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:666)
Clinical features
- Abdominal mass, pain, vaginal bleeding
- Risk factors include advanced age, excess estrogen exposure, nulliparity, prior pelvic irradiation, tamoxifen use (Lancet 2000;356:881)
Laboratory
- No useful biochemical marker (Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 2006;18:20)
Radiology description
- Pelvic ultrasound and CT: heterogeneous pelvic mass containing solid parts with/without ascites
Case reports
- 52 year old woman (Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2010;49:87)
- 70 year old woman (Journal of Medical Cases 2010;1:55)
- Growing into an inguinal hernia sac (Surg Today 2003;33:797)
Treatment
- Surgical cytoreduction with adjuvant chemotherapy (Gynecol Oncol 2000;79:196)
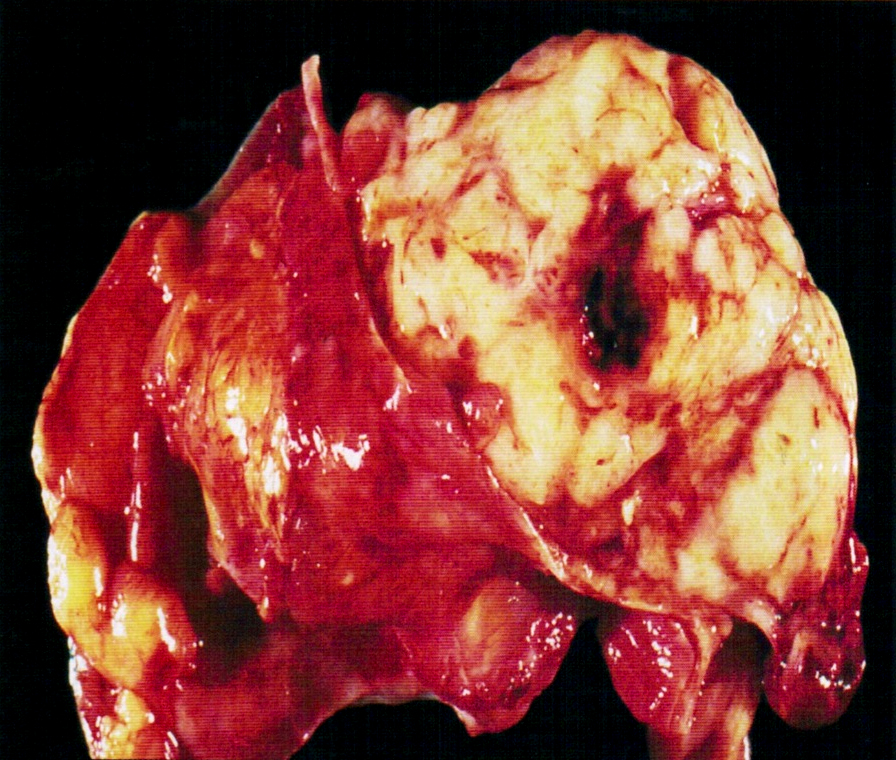
Gross description
- Soft and fleshy mass, often with bleeding and necrosis
Gross images
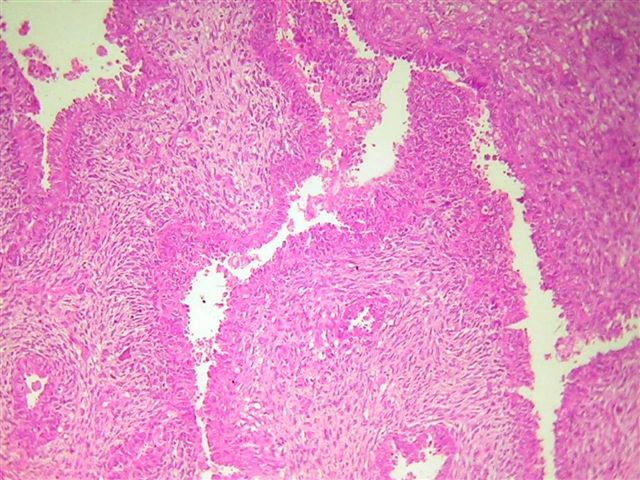
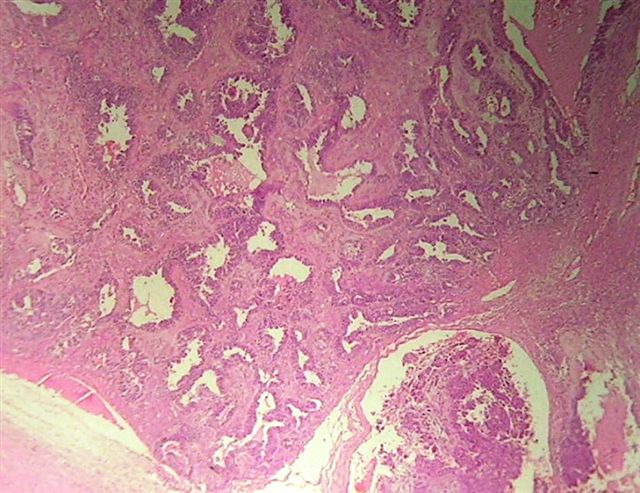
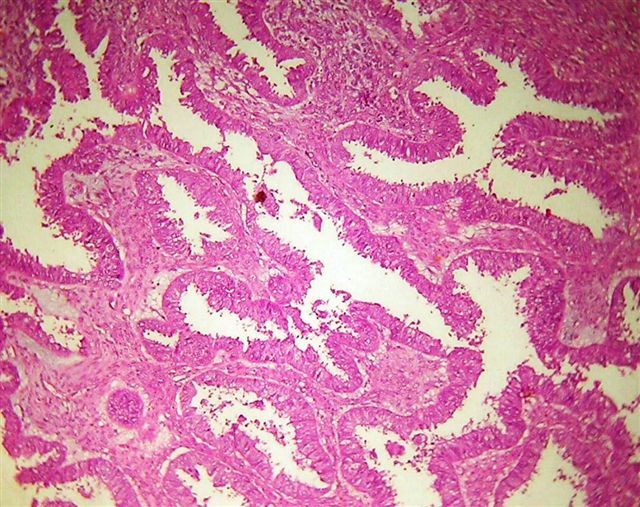
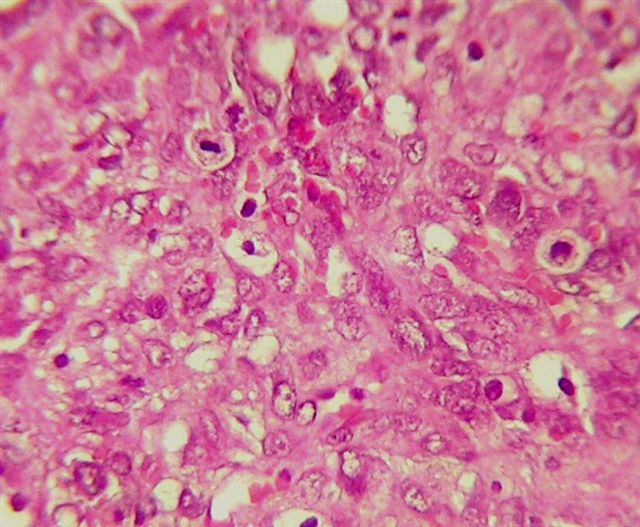
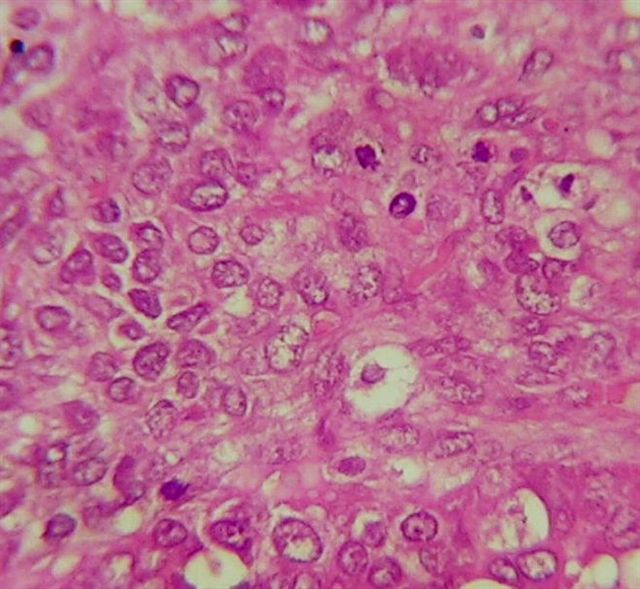
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Malignant epithelial and sarcomatous elements
- Sarcomatous element can be homologous (nonspecific malignant stroma) or heterologous (malignant elements of a different tissue type, particularly cartilage)
- Often contains cytoplasmic hyaline droplets containing alpha-1-antitrypsin (Hum Pathol 1982;13:930)
- Rarely trophoblastic tissue (Hum Pathol 1988;19:1235)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis