Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Roe CJ, Hanley K. Serous cystadenoma, adenofibroma and surface papilloma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorserousbenign.html. Accessed October 4th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign partially or completely cystic lesion measuring > 1 cm in size and composed of cells resembling fallopian tube epithelium or cuboidal nonciliated epithelium resembling ovarian surface epithelium
Essential features
- Benign; > 1 cm in size (< 1 cm signifies a cortical inclusion cyst); composed of cells resembling fallopian tube epithelium
- Presents over a broad age range and are generally asymptomatic
- Usually small, uni to multilocular cysts lined by a single layer of tall, columnar, ciliated cells
- Adenofibromas and cystadenofibromas are composed predominantly of fibrous stroma, with glands and cysts forming a minor component
Terminology
- Includes cystadenoma, cystadenofibroma, adenofibroma, papillary cystadenoma, papillary cystadenofibroma, papillary adenofibroma
- Term used depends on the relative amount of fibrous stroma but distinctions are often arbitrary
ICD coding
- ICD-11: 2F32.3 - serous ovarian cystadenoma
Epidemiology
- Patients present over a broad age range
- Most often found in adult women of reproductive age
Sites
- Ovary, less commonly fallopian tube
Pathophysiology
- DNA copy number changes may be seen in stromal fibromatous cells and epithelial cells (Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:7273, Lab Invest 2004;84:778)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Generally asymptomatic
- Symptoms related to an ovarian mass
- One of the more common ovarian tumors to undergo torsion
Diagnosis
- Cystectomy or oophorectomy
Laboratory
- CA-125 levels may be mildly elevated (rarely marked) (Arch Gynecol Obstet 2007;276:559)
Radiology description
- Typically anechoic with thin, smooth walls and posterior acoustic enhancement; unilocular cysts, thin walls, minimal septations and absence of papillary projections (Radiographics 2000;20:1445)
- Imaging modality: pelvic ultrasound or CT scan
Prognostic factors
- May recur after incomplete excision
Case reports
- 63 year old woman with ruptured benign serous ovarian cystadenoma mimicking ovarian malignancy with peritoneal carcinomatosis (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:1187)
- 64 year old woman with bilateral ovarian fibromas and concomitant unilateral serous cystadenoma (J Obstet Gynaecol 2019;39:1027)
- 65 year old woman with ovarian serous cystadenoma with ectopic adrenal tissue (Int J Surg Case Rep 2017;33:89)
Treatment
- Surgery (cystectomy or oophorectomy)
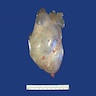
Gross description
- Cystadenoma:
- Usually 3 - 10 cm (but can be up to 30 cm), oval to round, smooth glistening surface
- Usually watery clear to pale yellow cyst fluid but can be viscous and mucoid
- Rarely papillary excrescences are seen on outer surface
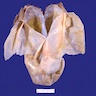
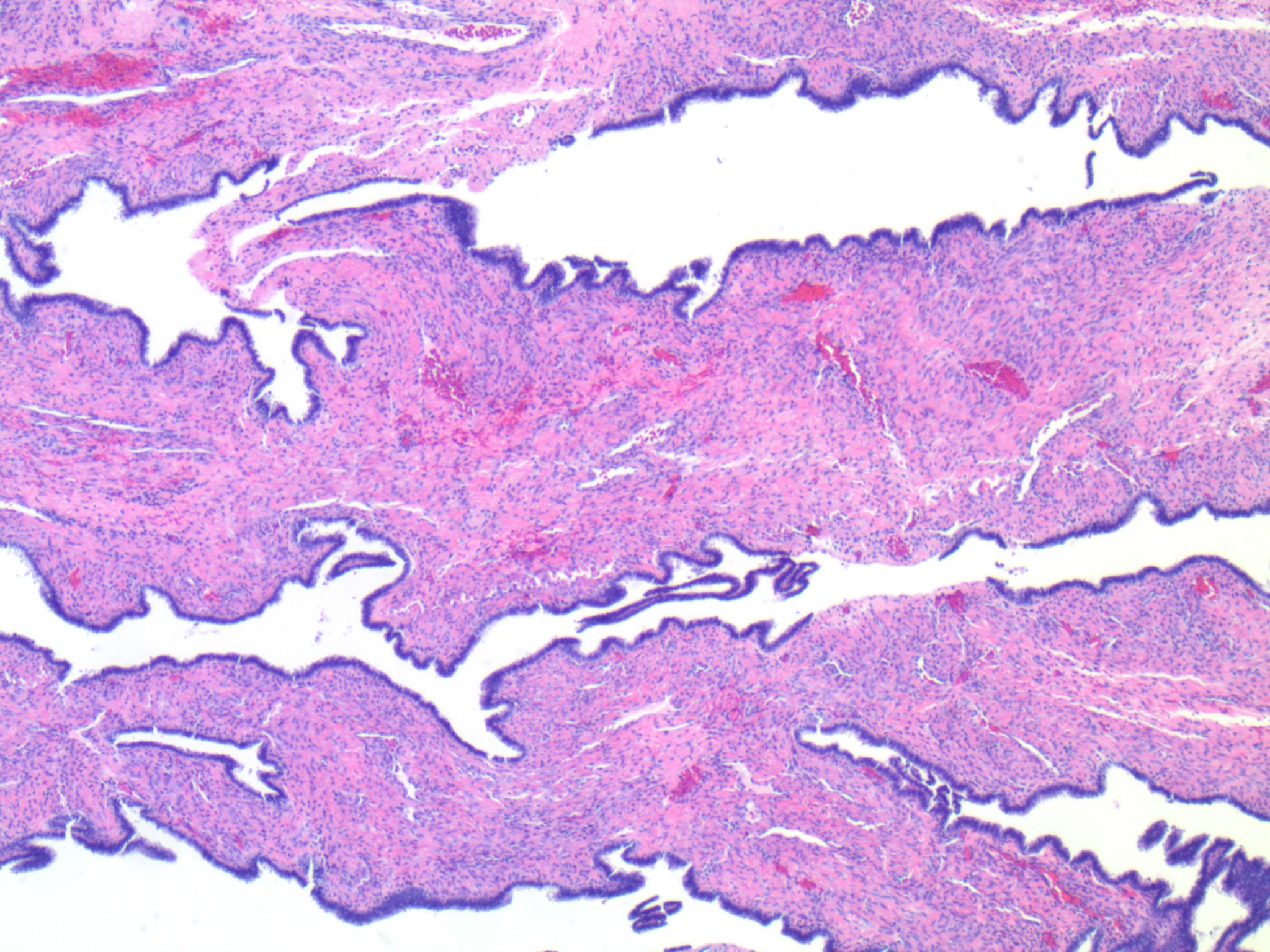
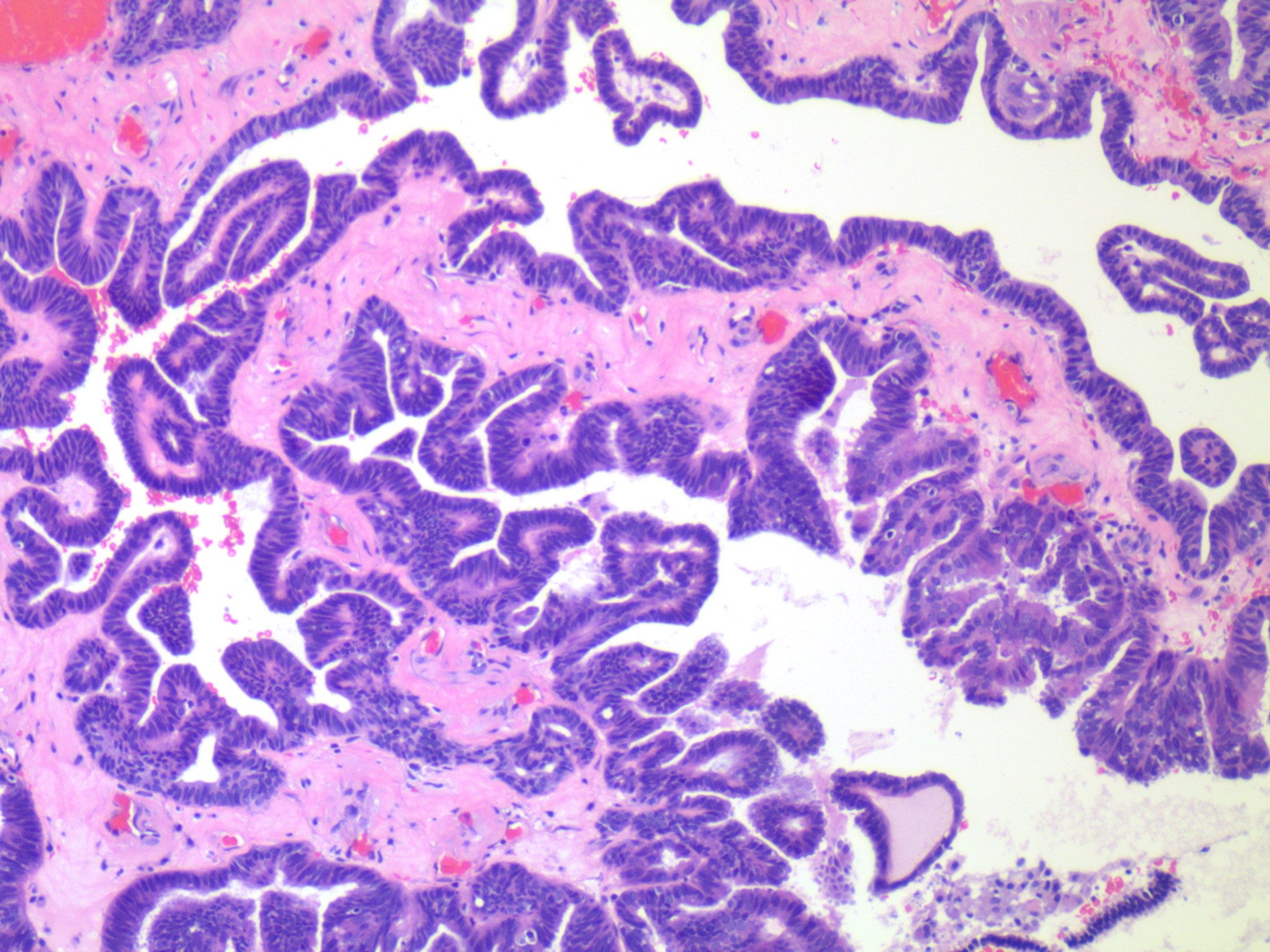
- Cystadenofibroma:
- Varies from solid areas with knobby papillae to firm confluent areas
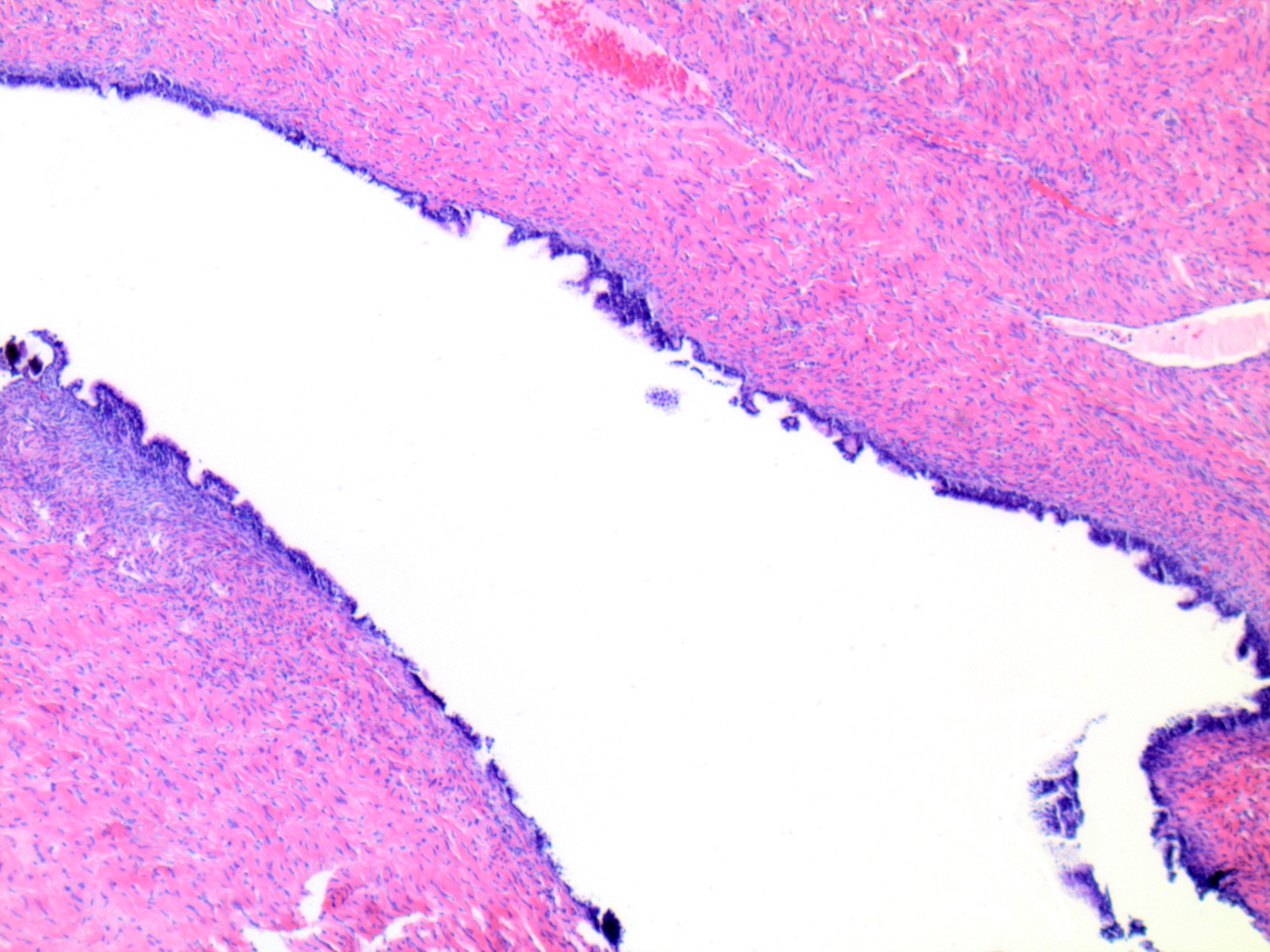
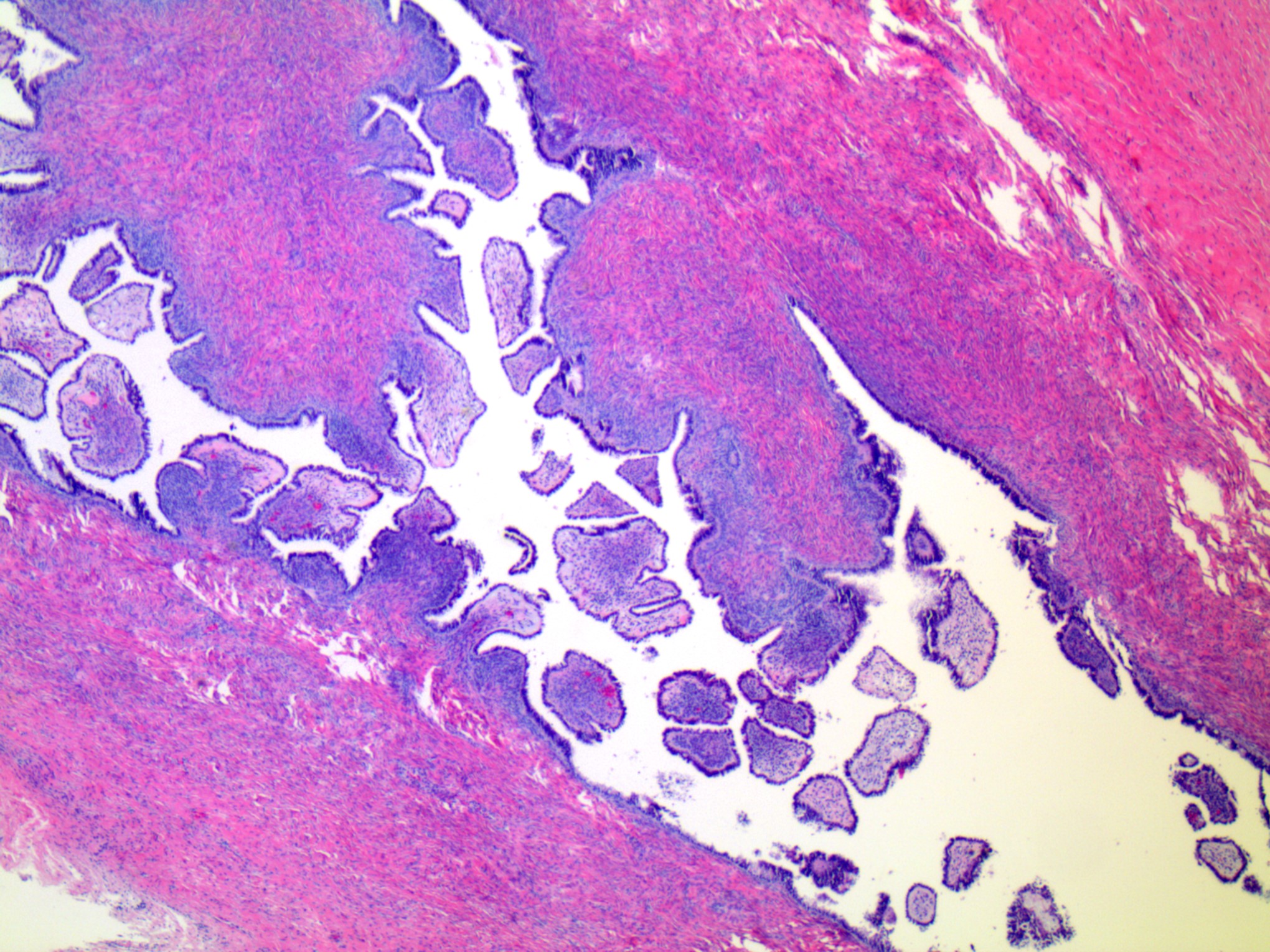
- Adenofibroma:
- Entirely solid with small cysts
- Reference: Kurman: Blaustein's Pathology of the Female Genital Tract (Springer Reference), 7th Edition, 2019
Frozen section description
- Uni or multiloculated cysts with single layer of cuboidal or columnar epithelium and simple papillary projections, if present
- Bland appearing fibrous stroma in varying amounts
- No invasion, architectural complexity or atypia
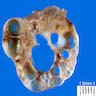
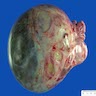
Microscopic (histologic) description
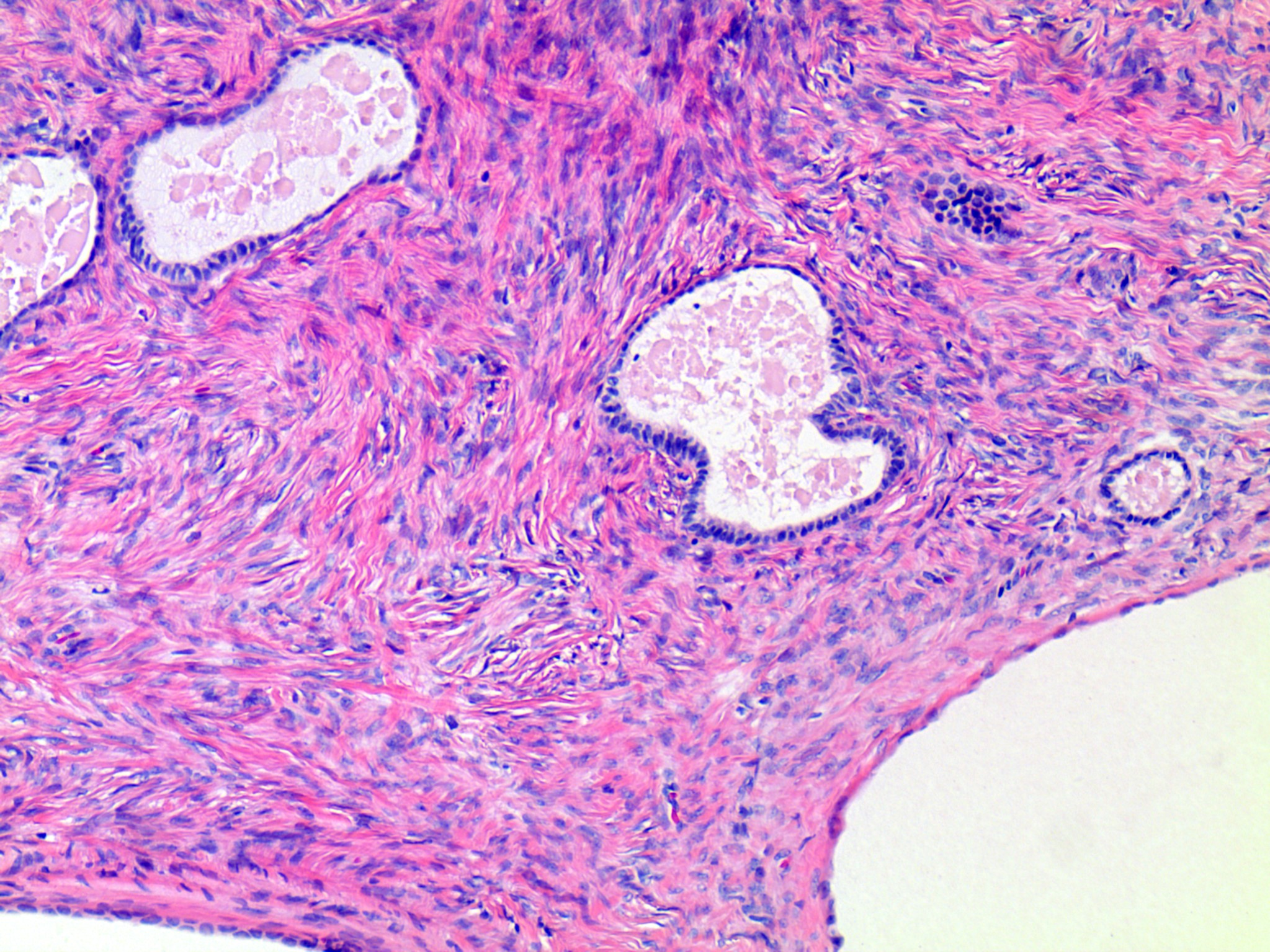
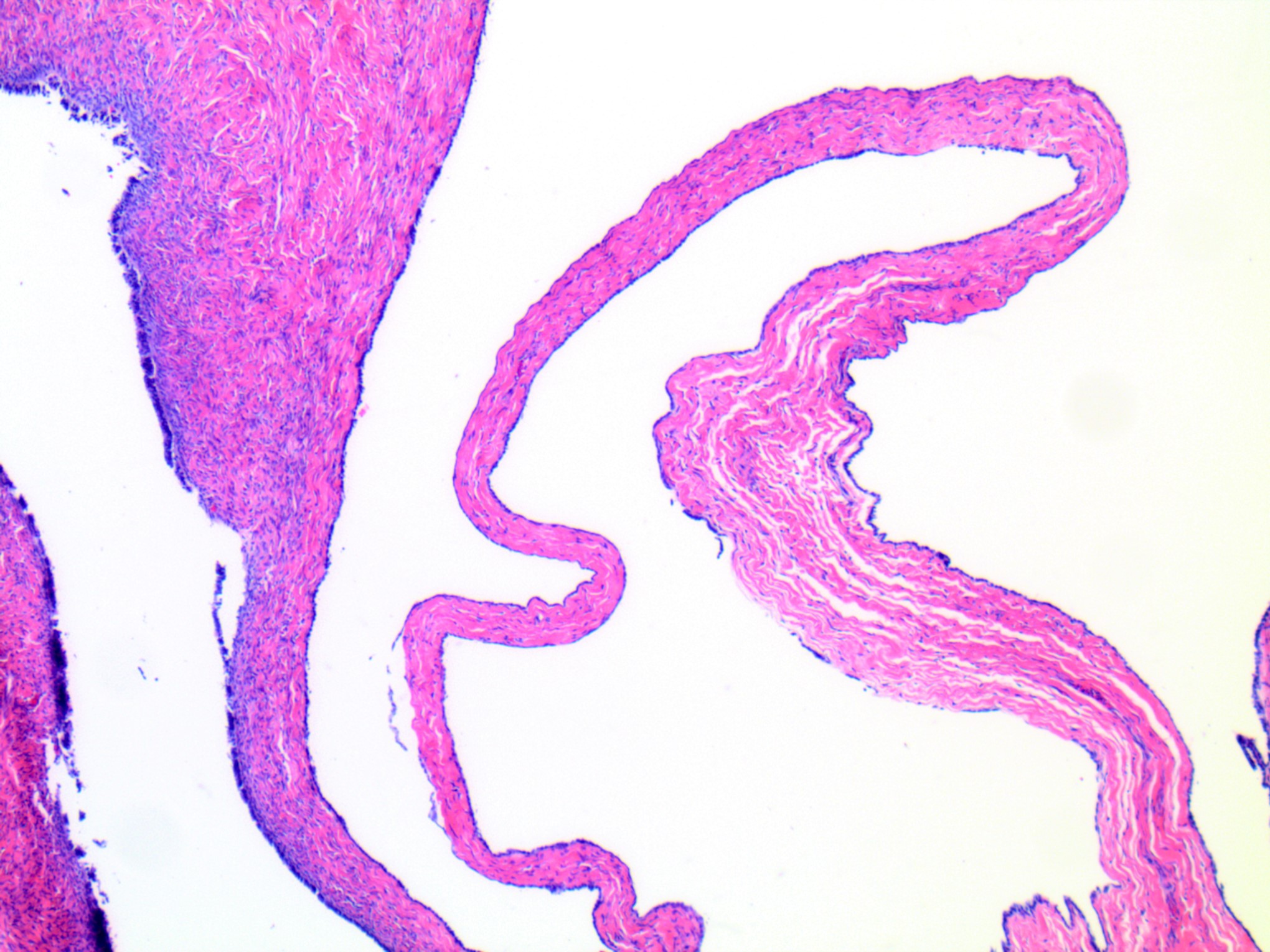
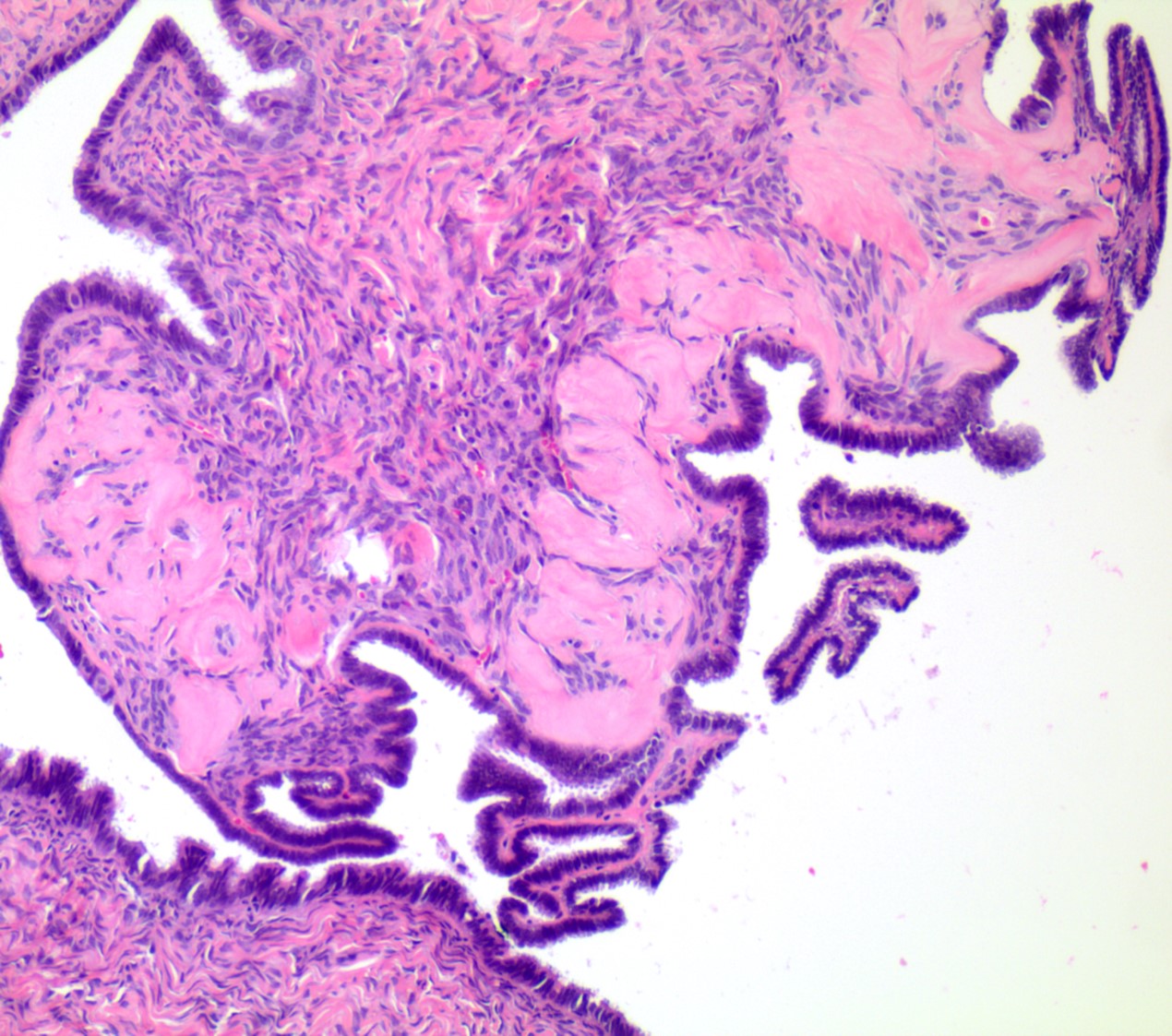
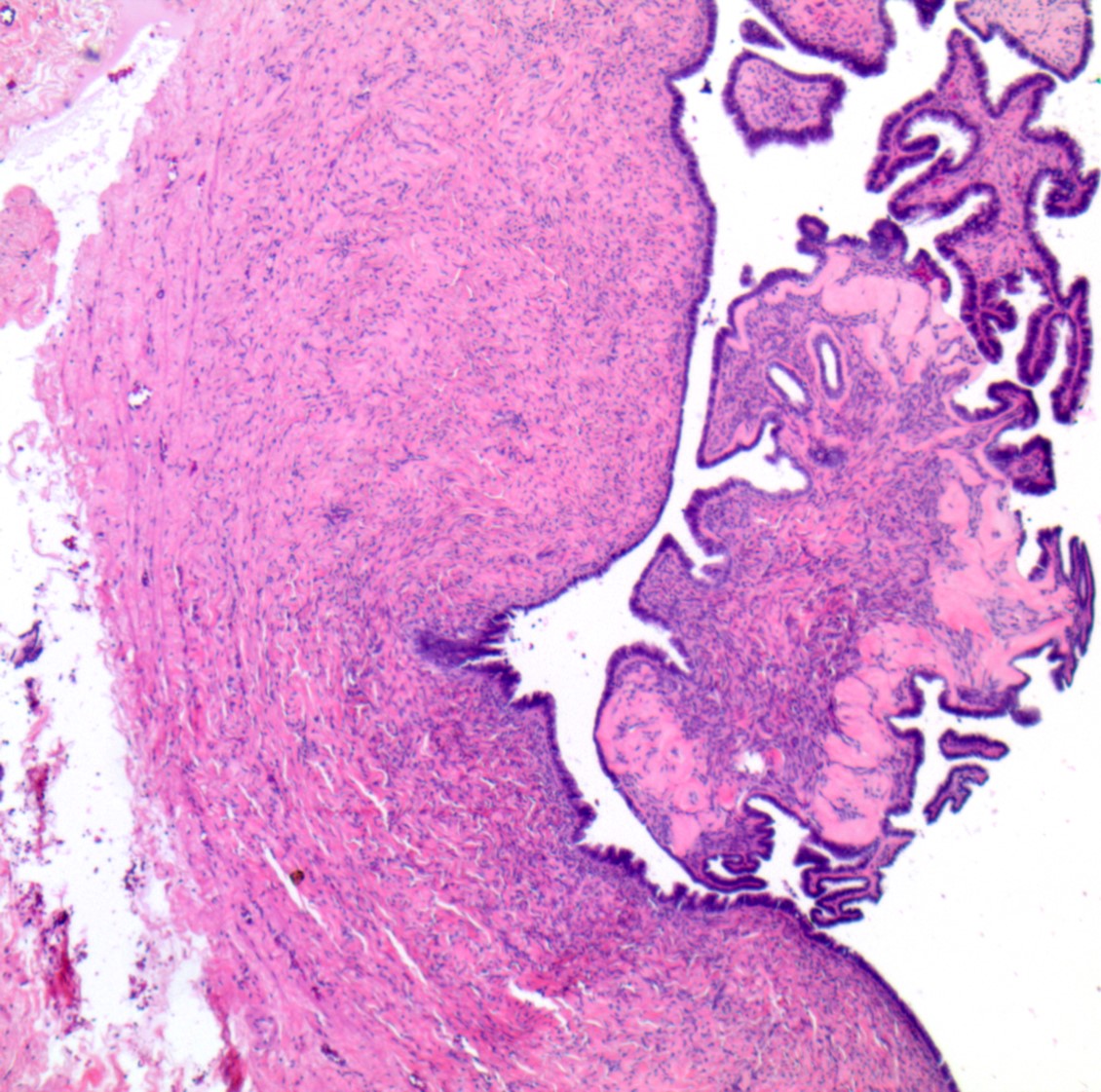
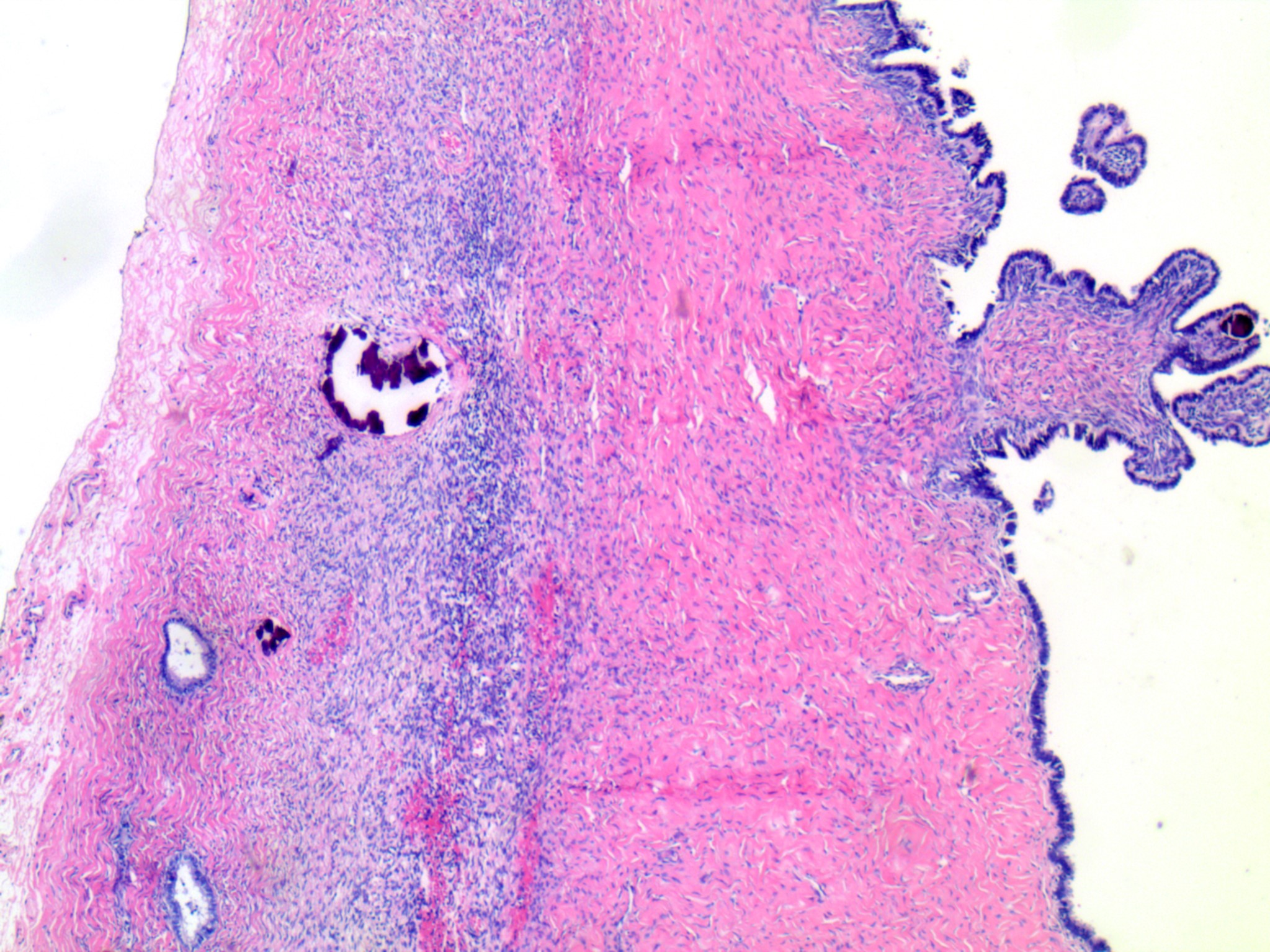
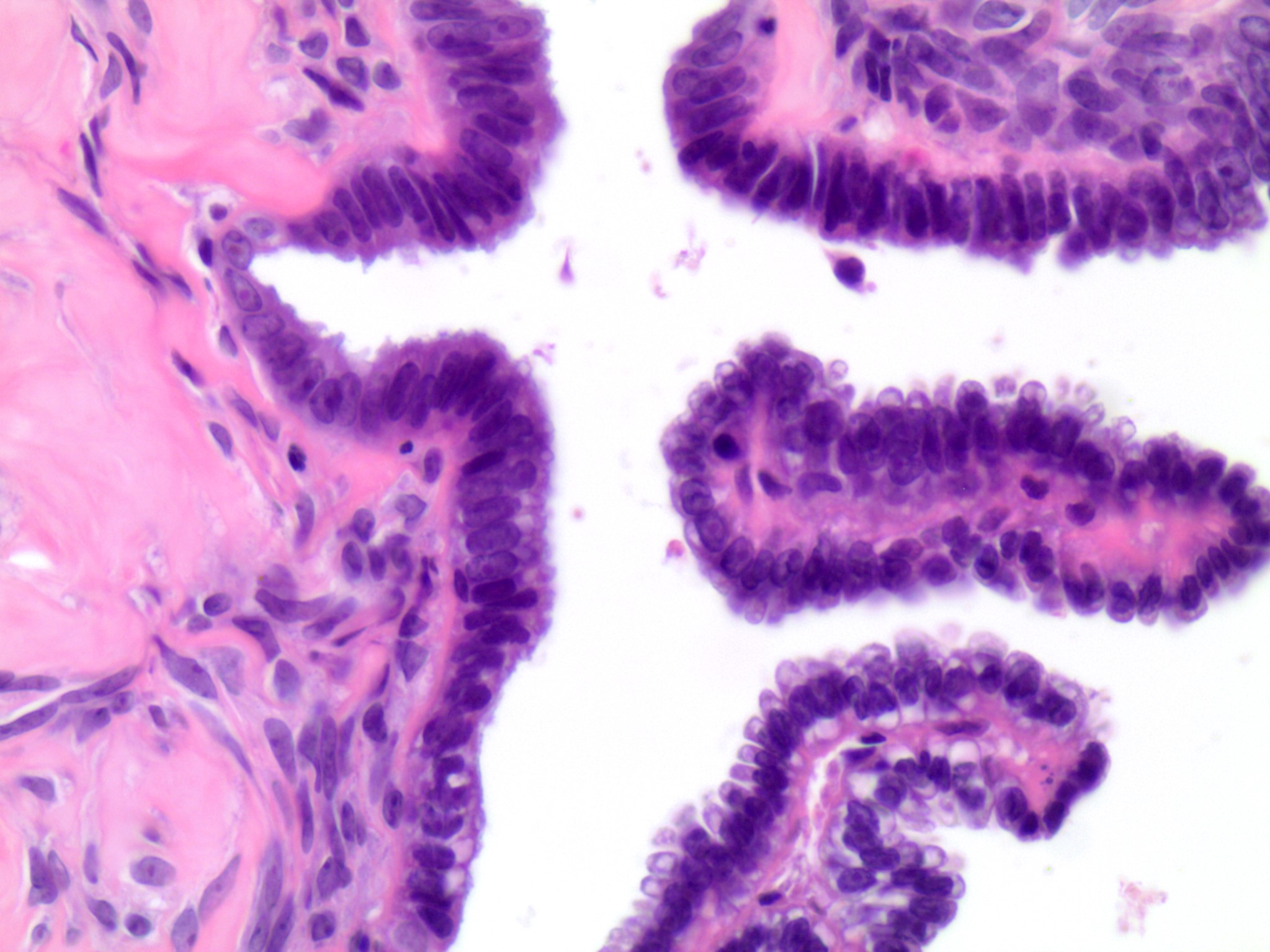
- Usually small, uni to multilocular cysts lined by a single layer of tall, columnar, ciliated cells resembling normal tubal epithelium or cuboidal nonciliated epithelium resembling ovarian surface epithelium
- Stroma contains spindle fibroblasts
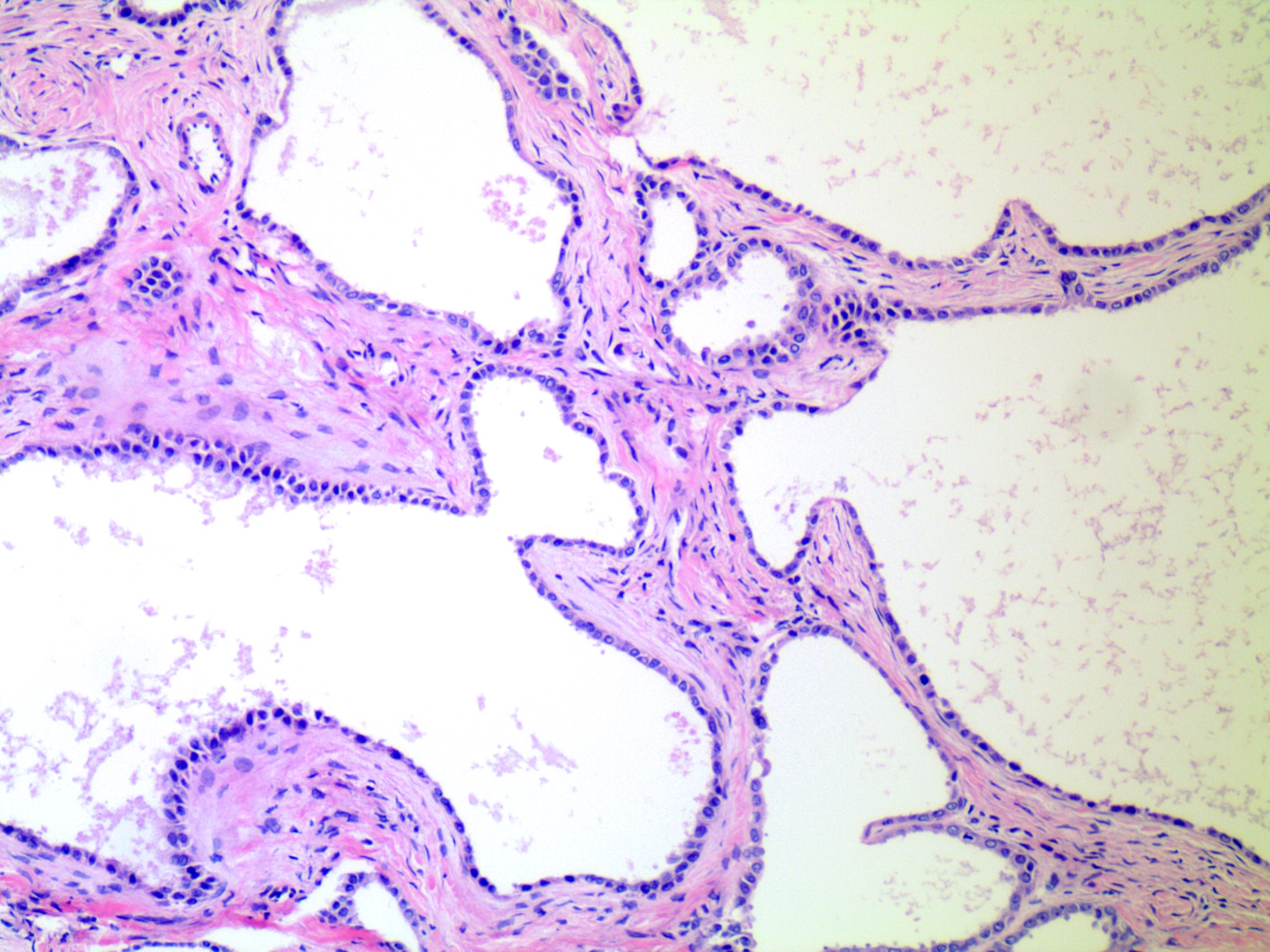
- If papillae are present, they are simple
- Adenofibromas and cystadenofibromas are composed predominantly of fibrous stroma, with glands and cysts forming a minor component
- If < 10% of the total tumor volume shows epithelial proliferation within the cysts that would otherwise qualify as serous borderline tumor, the tumor is designated as serous cystadenoma with focal epithelial proliferation
- Reference: Kurman: Blaustein's Pathology of the Female Genital Tract (Springer Reference), 7th Edition, 2019
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Groups, strips or clusters of epithelial cells with small, bland, round to oval nuclei and variable cytoplasm with or without cilia
- Background cyst contents, including histiocytes and proteinaceous debris
- Cannot definitively diagnose on a cytology specimen; histologic examination is required for classification
Positive stains
Sample pathology report
- Right ovary, oophorectomy:
- Serous cystadenofibroma (3.3 cm)
- Left ovary, oophorectomy:
- Serous cystadenoma with focal epithelial proliferation (see comment)
- Comment: The 8.3 cm cystic ovarian mass was extensively sampled. Focal epithelial proliferation (small, noncomplex papillae) is noted, which represents less than 10% of sampled cyst wall. These finding represent a benign serous cystadenoma with focal epithelial proliferation.
Differential diagnosis
- Rete cyst / cystadenoma:
- Located in ovarian hilus, undulating epithelium, smooth muscle wall, cyst lining is a single layer of flat cuboidal cells
- Nests of Leydig cells may be present in the wall
- Paratubal Müllerian cyst (hydatid cyst of Morgagni):
- Paramesonephric cyst attached to fimbria, thin fallopian tube type epithelium with small epithelial plicae projecting into the lumen, may have smooth muscle in the wall
- Peritoneal cyst:
- Lined by mesothelial cells, often associated with ovarian surface adhesions
- Mesonephric cyst:
- Lined by cuboidal cells and usually surrounded by smooth muscle
- Mucinous cystadenoma:
- Lined by a single layer of mucin containing tall columnar epithelium
- Hydrosalpinx:
- Dilated fallopian tube lumen, lined by ciliated epithelium, attenuated or rare plicae, well developed smooth muscle in the wall
- Cortical / epithelial inclusion cyst:
- < 1 cm
- Lined by simple cuboidal to columnar epithelium with ciliated cells, sometimes admixed with nonciliated cells
- Serous borderline tumor:
- Epithelial proliferation with architectural complexity, including branching of irregularly shaped papillae
- Seromucinous cystadenoma:
- Lined by epithelium with 2 or more Müllerian cell types each accounting for at least 10% of the epithelium (Histopathology 2021;78:445)
- Frequently associated with endometriosis (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2021 Feb 11 [Epub ahead of print])
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
What feature distinguishes cystadenoma from cortical inclusion cyst?
- Epithelial lining
- Location
- Presence of psammoma bodies
- Relationship to ovarian serosa
- Size
Practice answer #2