Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Kommoss FKF, Tessier-Cloutier B. Small cell carcinoma of ovary, hypercalcemic type. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorsmallcellhyper.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Small cell carcinoma of the ovary, hypercalcemic type (SCCOHT) is a rare and highly aggressive ovarian malignancy defined by an inactivating mutation of the SMARCA4 gene, that occurs in young women and is commonly associated with hypercalcemia
Essential features
- Small cell neoplasm with undifferentiated morphology (monomorphic, discohesive and mitotically active) with or without follicle-like spaces, rhabdoid morphology or large cell component
- Loss of nuclear SMARCA4 / BRG1 immunohistochemical expression (> 93% of cases)
Terminology
- SMARCA4 deficient carcinoma of ovary
- Malignant rhabdoid tumor of the ovary
- This lesion is unrelated to small cell neuroendocrine (pulmonary) carcinoma, which refers to a neuroendocrine neoplasm of the ovary
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8044/3 - small cell carcinoma, intermediate cell
- ICD-11: 2C73.0Y & XH8ZR8 - other specified carcinomas of ovary & small cell carcinoma, hypercalcemic type
Epidemiology
- Adolescent and young adult women (median: 25 years) (Gynecol Oncol 2016;141:454, Nat Genet 2014;46:427)
- Cases associated with germline mutations may occur in younger patients (Gynecol Oncol 2016;141:454, Nat Genet 2014;46:427)
- Very rare cases reported in postmenopausal women
Sites
- Ovary
Pathophysiology
- Inactivating mutation (germline or somatic) of the SMARCA4 gene, a core subunit of the SWI / SNF complex, drives oncogenesis (Gynecol Oncol 2016;141:454)
- SWI / SNF complex is an important regulator of the chromatin remodeling process
Etiology
- Predisposition factor: rhabdoid tumor predisposition syndrome 2 (RTPS2)
- Exact cellular origin remains unknown
- Although SCCOHT was initially believed to be of epithelial origin, studies have suggested a primitive germ cell, neural or mesenchymal progenitor (Hum Pathol 1987;18:175, Histopathology 2017;70:1147, J Pathol 2017;242:371)
- Studies have shown distinct DNA methylation signatures in SCCOHT that are distinct from ovarian epithelial neoplasms (J Pathol 2022;257:140)
Clinical features
- Poor clinical outcome (Gynecol Oncol 2016;141:454)
- Most patients present at an advanced stage (Gynecol Oncol 2016;141:454)
- Nonspecific symptoms may include abdominal pain, distention and signs related to intestinal obstruction
- A minority of patients may show symptoms of hypercalcemia (N Engl J Med 2010;362:1031)
- Patients may harbor SMARCA4 germline mutation which is associated with the rhabdoid tumor predisposition syndrome 2 (RTPS2) and also predisposes for other undifferentiated malignancies such as atypical teratoid / rhabdoid tumors (ATRT) and other extracranial malignant rhabdoid tumors (OMIM: Rhabdoid Tumor Predisposition Syndrome 2; RTPS2 [Accessed 22 February 2023])
Diagnosis
- There are no established tests to screen for SCCOHT
- When clinical suspicion arises, abdominal ultrasound and computed tomography scans are useful adjuncts
- Definitive diagnosis requires biopsy
- All patients diagnosed with SCCOHT should be referred to clinical genetics services and offered testing for germline SMARCA4 pathogenic variants
- At risk family member surveillance
- In patient's family members with germline SMARCA4 mutation, surveillance may include clinical examination and ultrasound, as well as whole body and CNS MRI
- Furthermore risk reducing bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (RRBSO) may be considered; however, the benefits of early detection using imaging and RRBSO remain unproven
- Guidelines are provided by the International SCCOHT Consortium (ISC) (Clin Cancer Res 2020;26:3908)
Laboratory
- Hypercalcemia can be detected in a majority of patients, likely from parathyroid hormone related peptide secretion by the tumor cells
- Most of these patients will not present with symptoms of hypercalcemia (N Engl J Med 2010;362:1031, Cancer 1994;73:1878, Gynecol Oncol 2016;141:454)
Prognostic factors
- Stage is the most important parameter (Gynecol Oncol 2016;141:454)
- FIGO stage I: 55% 5 year overall survival
- FIGO stage II: 40% 5 year overall survival
- FIGO stage III: 29% 5 year overall survival
- FIGO stage IV: 0% 5 year overall survival
- Favorable prognostic factors include
- Older patient age at diagnosis (> 40 years) (Gynecol Oncol 2016;141:454)
- Small tumor size (< 10 cm) and absence of large cell component (Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:1102)
Case reports
- 18 - 29 year old women with small cell carcinoma of the ovary of hypercalcemic type with responses to anti-PD1 immunotherapy (J Natl Cancer Inst 2018;110:787)
- 21 year old pregnant woman with small cell carcinoma of the ovary of hypercalcemic type (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e20387)
- 24 year old woman with an abdominal mass (Case Rep Oncol 2016;9:305)
Treatment
- No established standard treatment
- Patients are usually treated by a combination of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation
- Treatment guidelines are provided by the International SCCOHT Consortium (ISC) (Clin Cancer Res 2020;26:3908)
- Following complete response to initial chemotherapy, high dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell rescue (HDC-aSCR) may be considered (Gynecol Oncol 2016;141:454)
- There is active research looking at epigenetic modulators, kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy as potential treatment alternatives
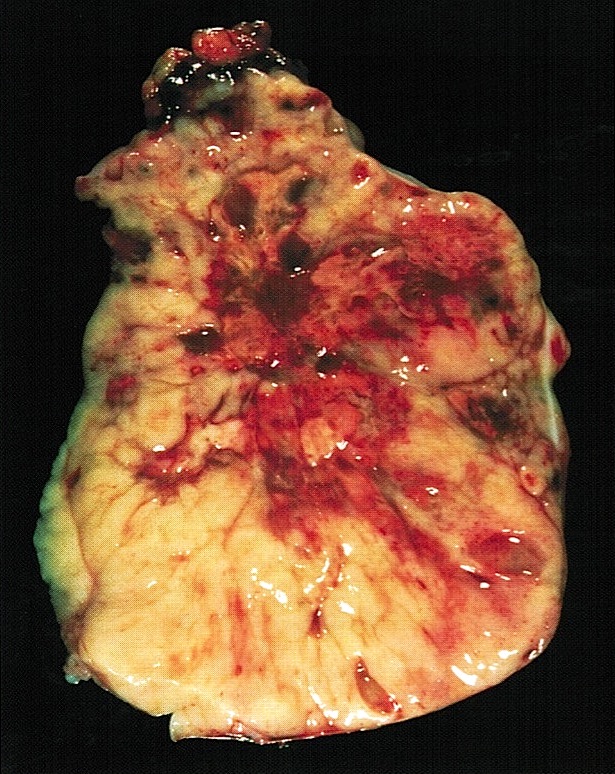
Gross description
- Unilateral (vast majority of cases), solid or cystic mass with lobulated or nodular surface
- Mean size of 15 cm (range: 6 - 26 cm)
- Fleshy and tan to white to gray cut surface
- Hemorrhage and necrosis are common
- Familial cases are more often bilateral (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1995;119:523, J Med Genet 1996;33:333)
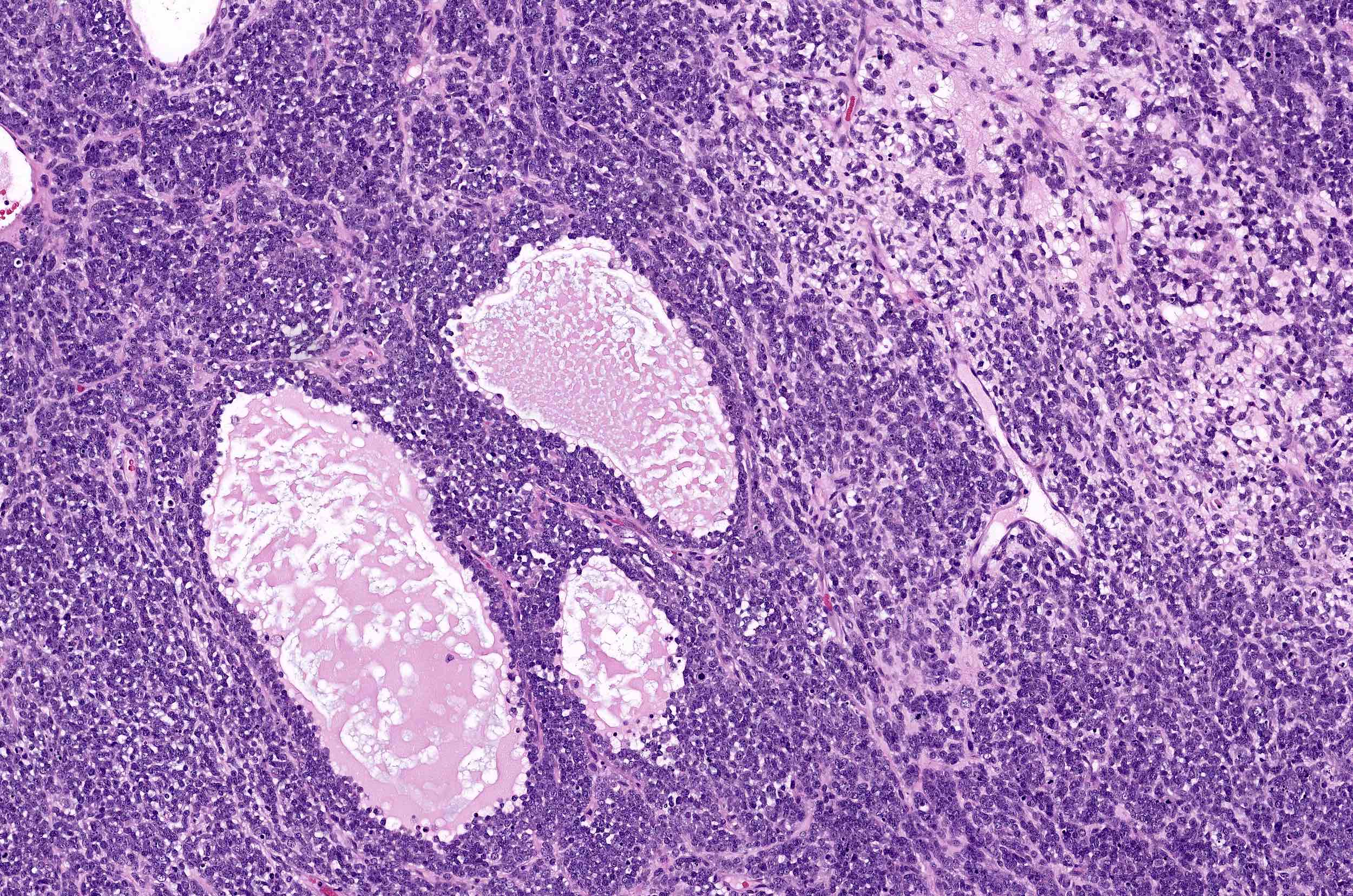
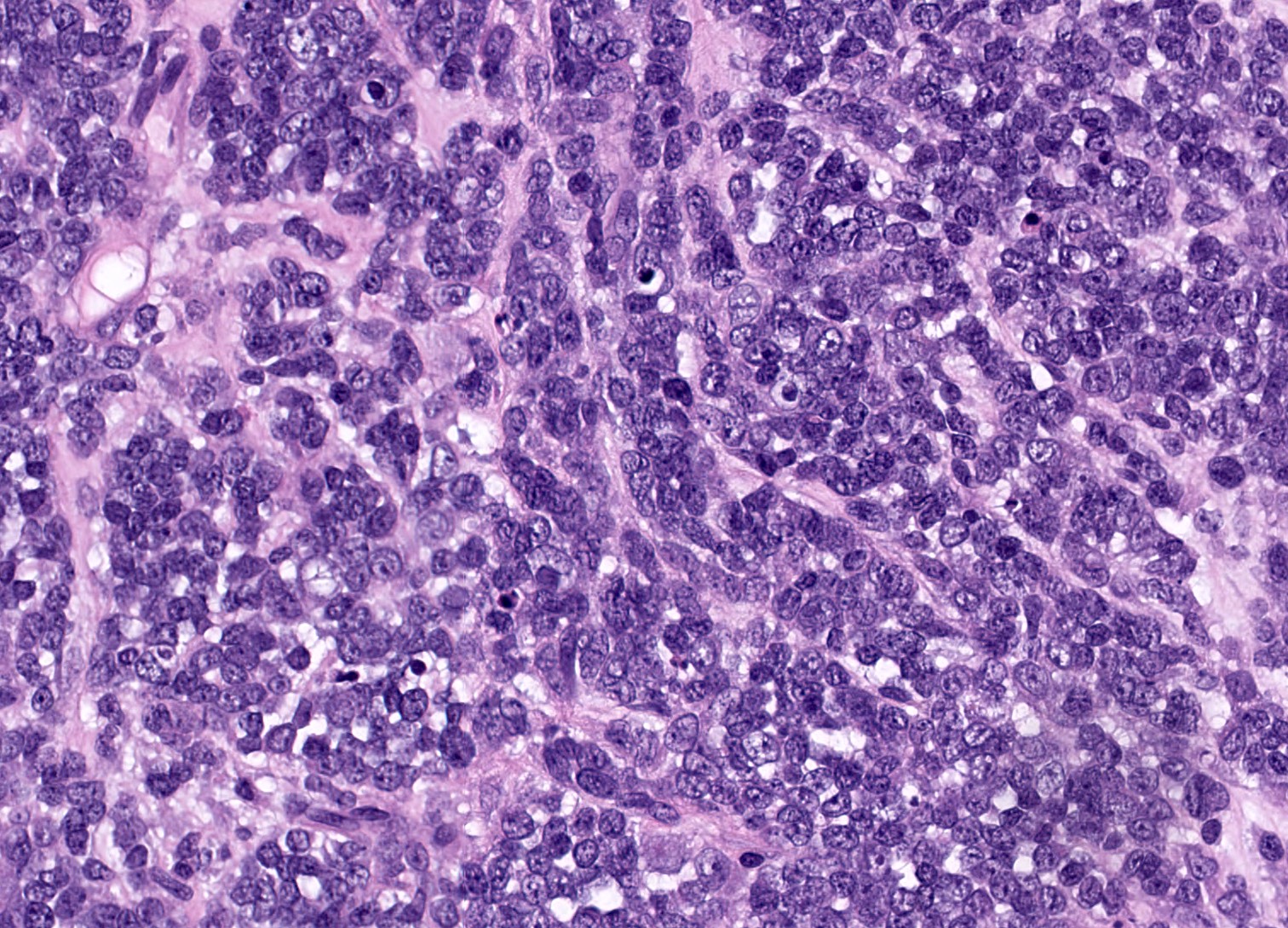
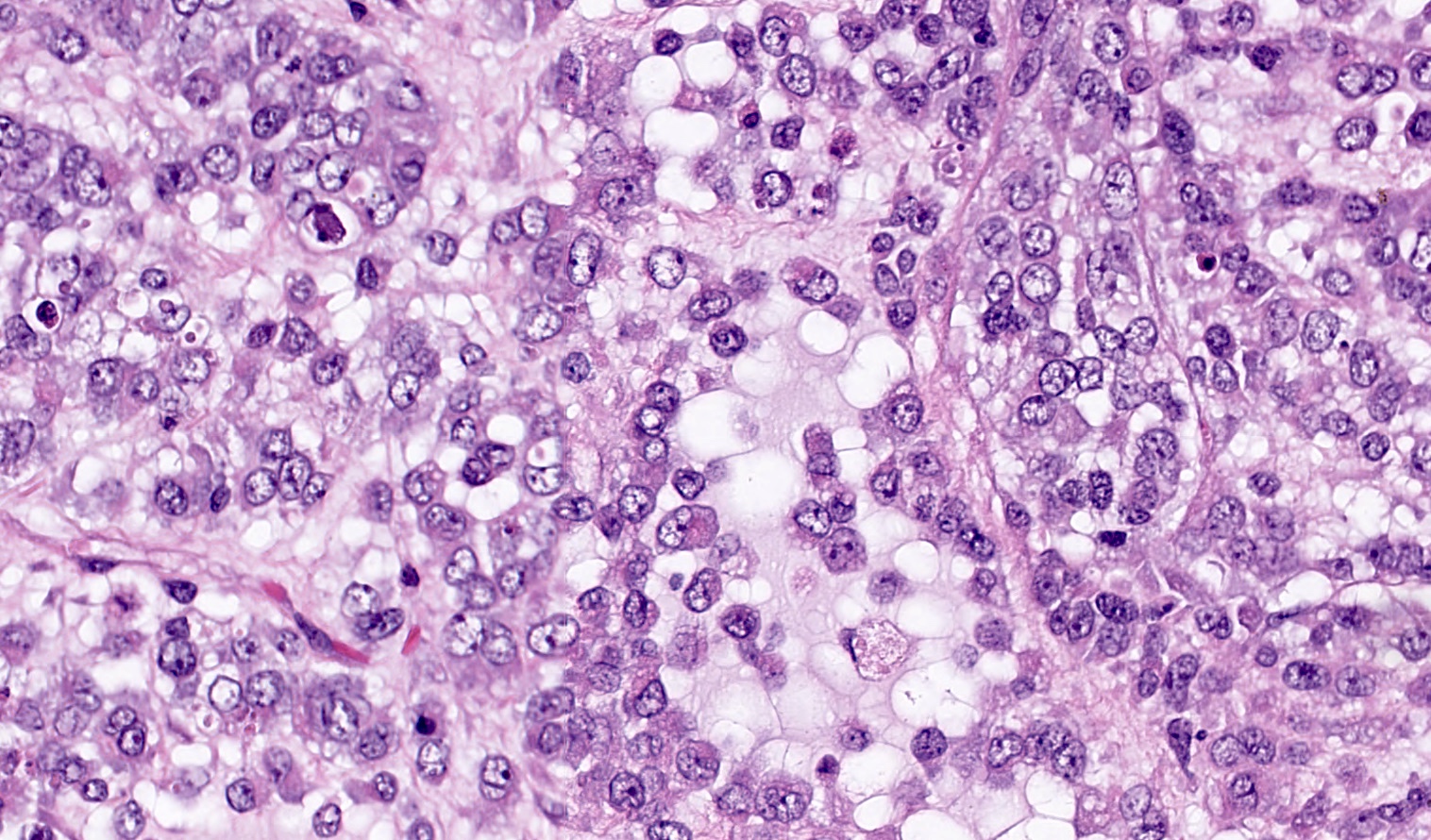
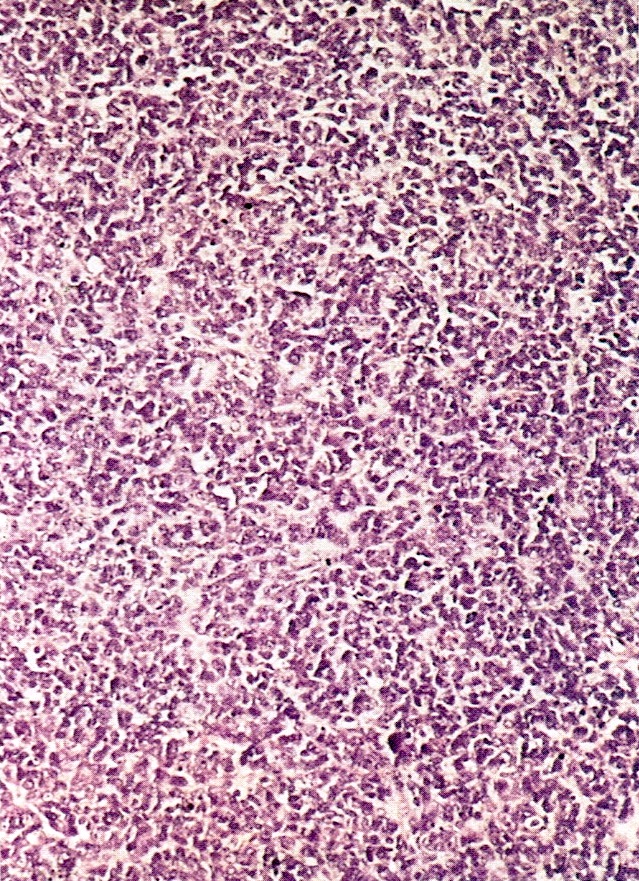
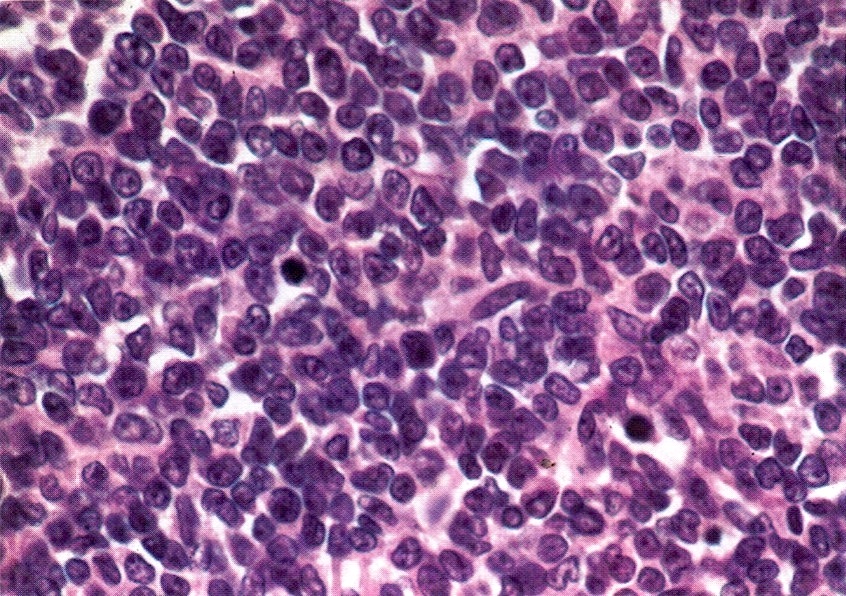
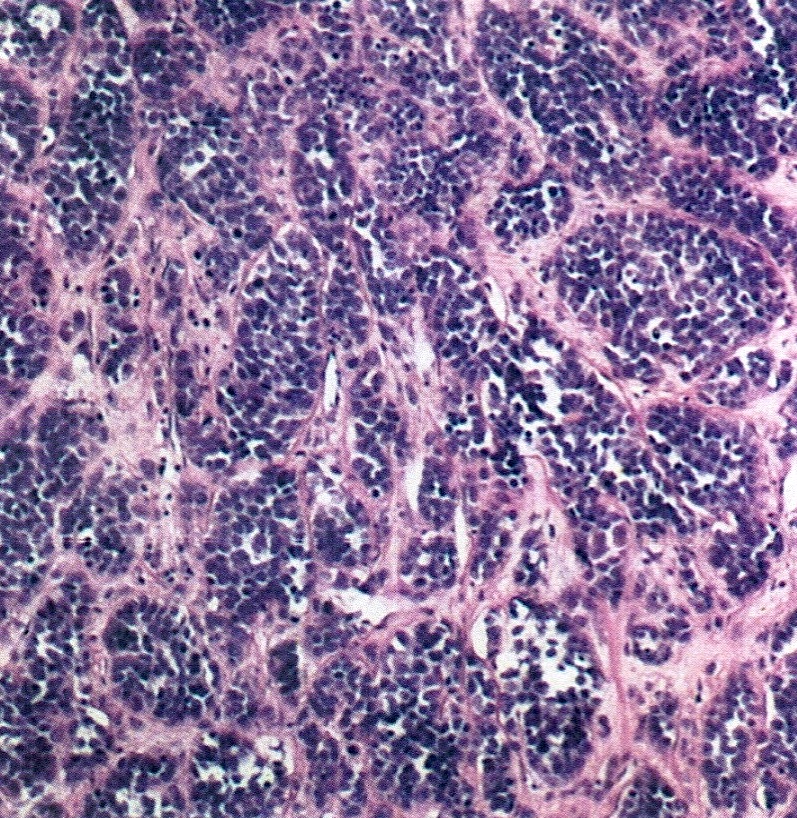
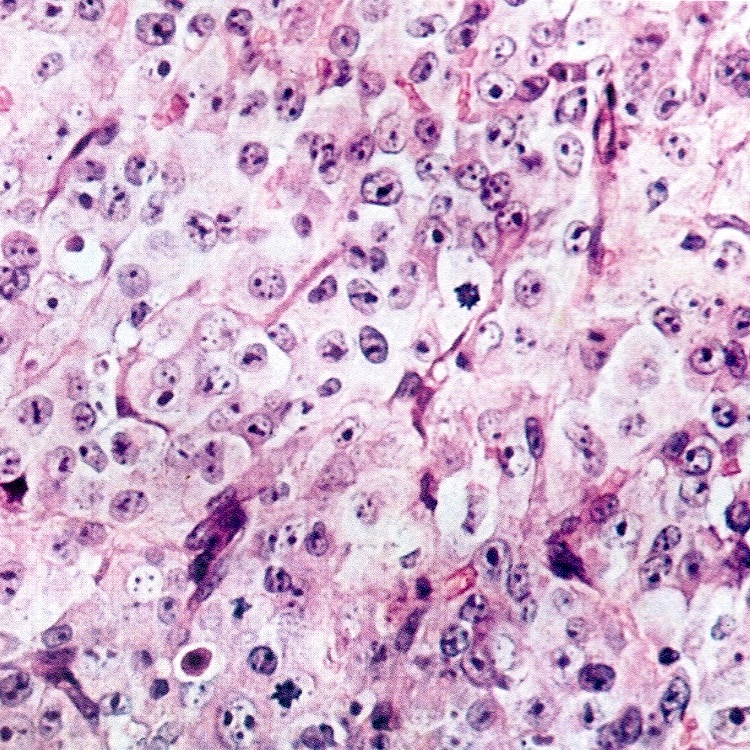
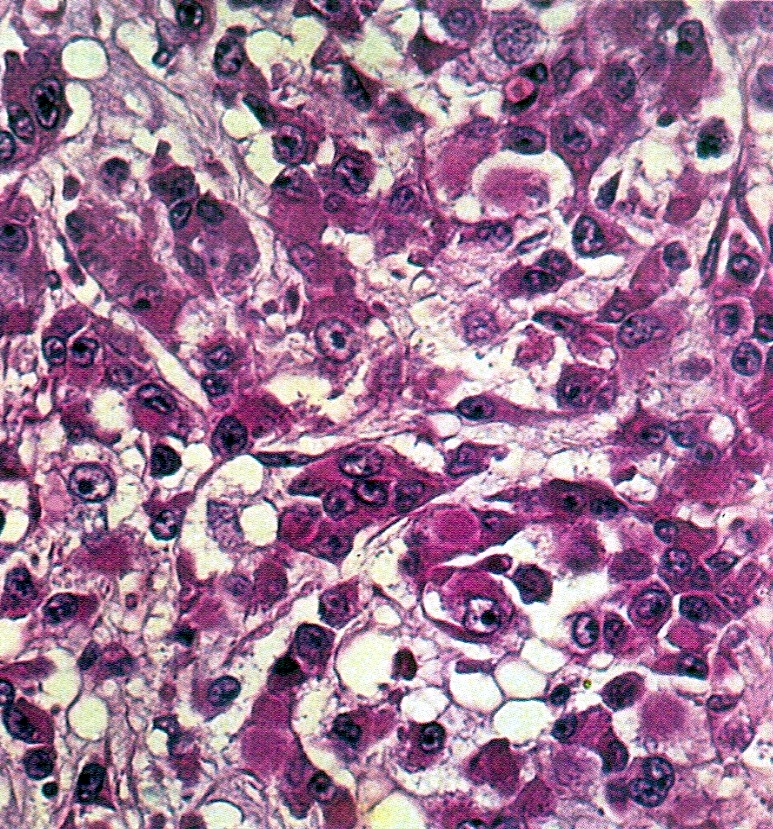
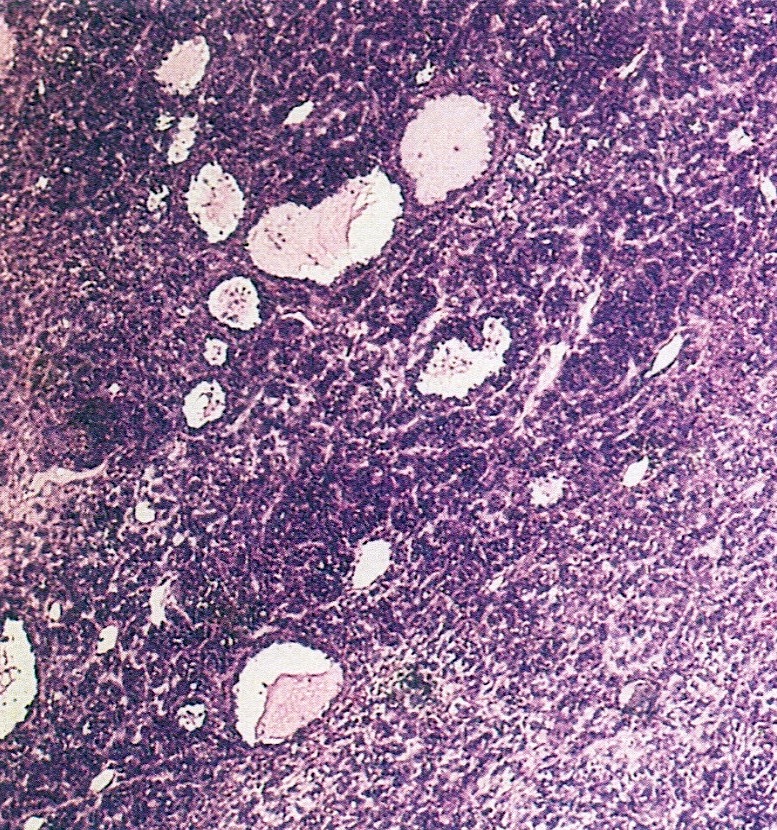
Microscopic (histologic) description
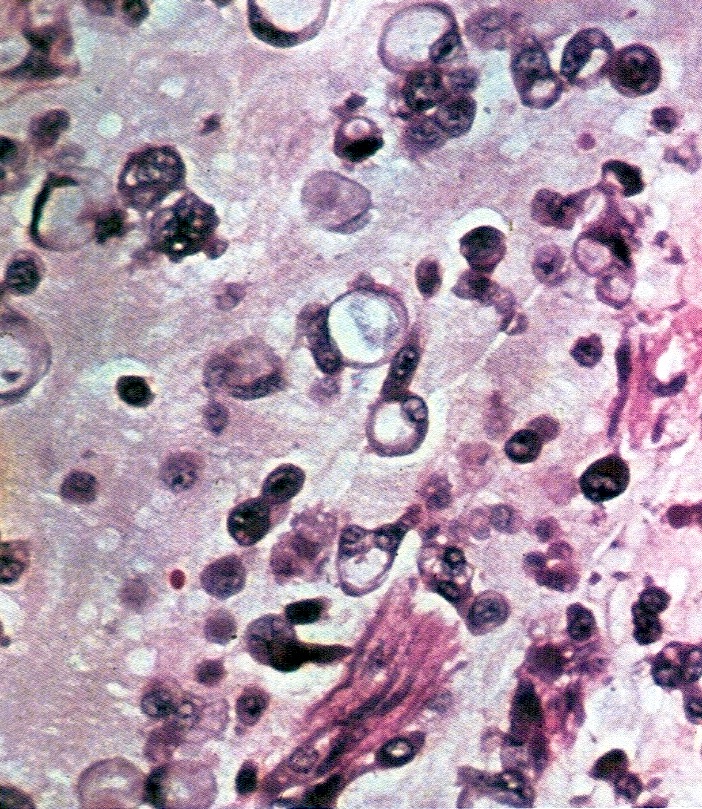
- Small round cells with scant cytoplasm, small nucleoli and brisk mitotic activity
- Diffuse growth of tightly packed cells, sometimes in a nested or corded architecture
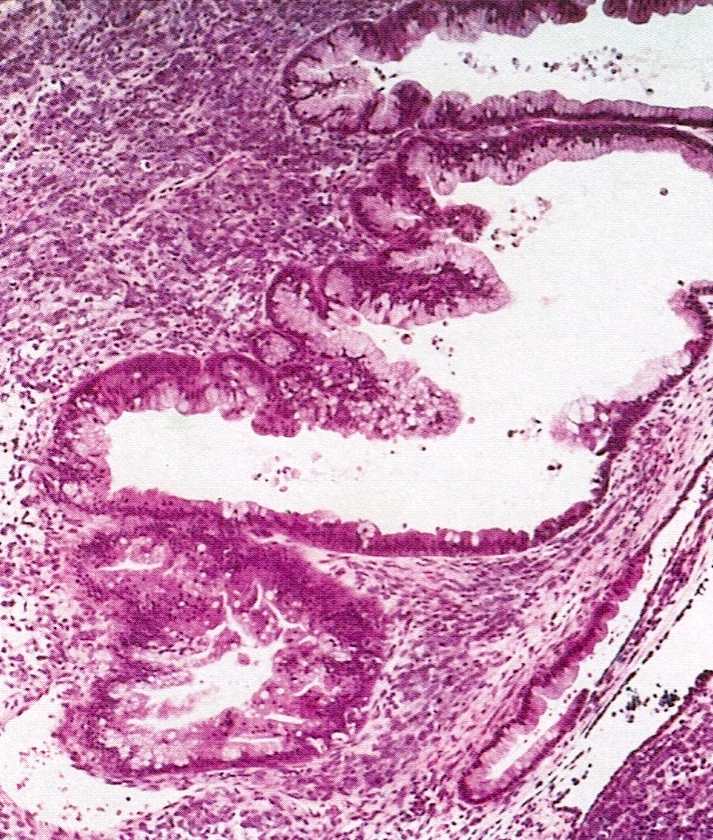
- Follicle-like spaces (80%), usually containing eosinophilic or basophilic fluid
- Necrosis seen in most tumors
- Focal myxoid stroma is common
- Most show a large cell component, often with rhabdoid features, of varying extent (if > 50% of the tumor, it is referred to as a small cell carcinoma of the ovary hypercalcemic, large cell variant)
- Intermixed mucinous glands are reported in some cases (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1995;119:523)
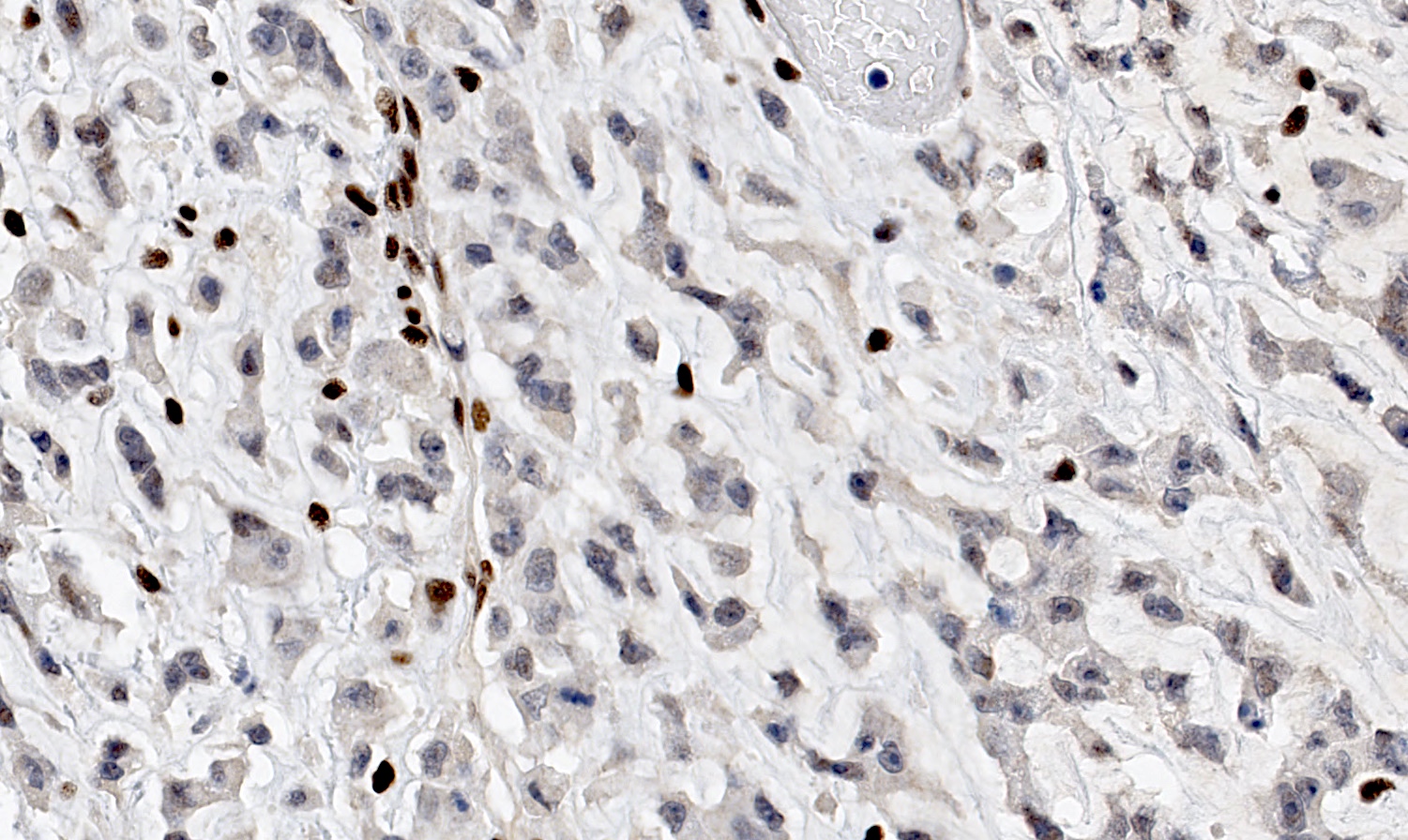
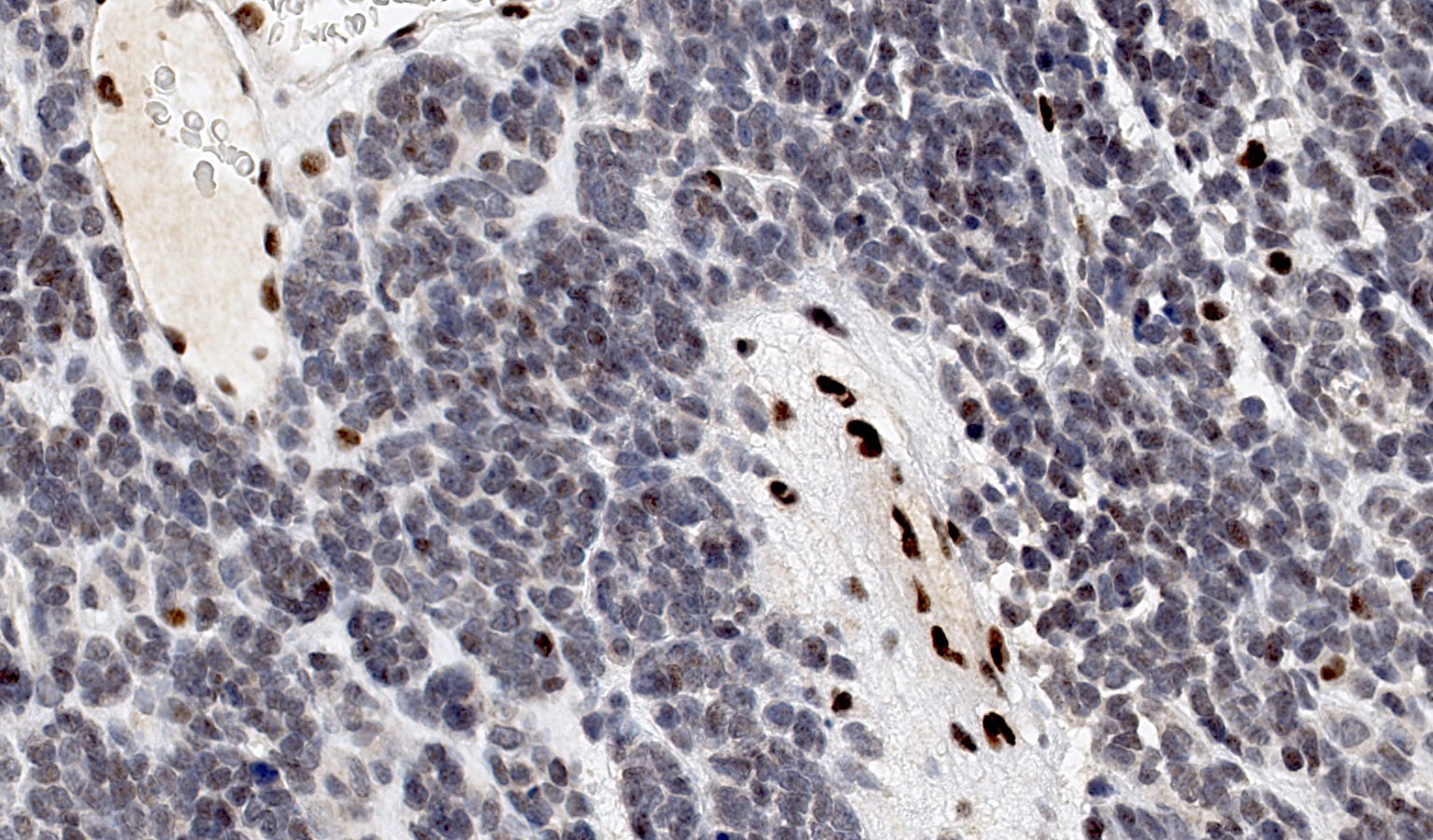
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Basile Tessier-Cloutier, M.D. and AFIP
Positive stains
- WT1 (86 - 93%) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:330, Histopathology 2007;51:305)
- CD10 (93%) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:330)
- Calretinin (73%) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:330)
- EMA (87%) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:330)
- AE1 / AE3 (60%) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:330)
- p53 wild type pattern (Histopathology 2023;83:154)
Negative stains
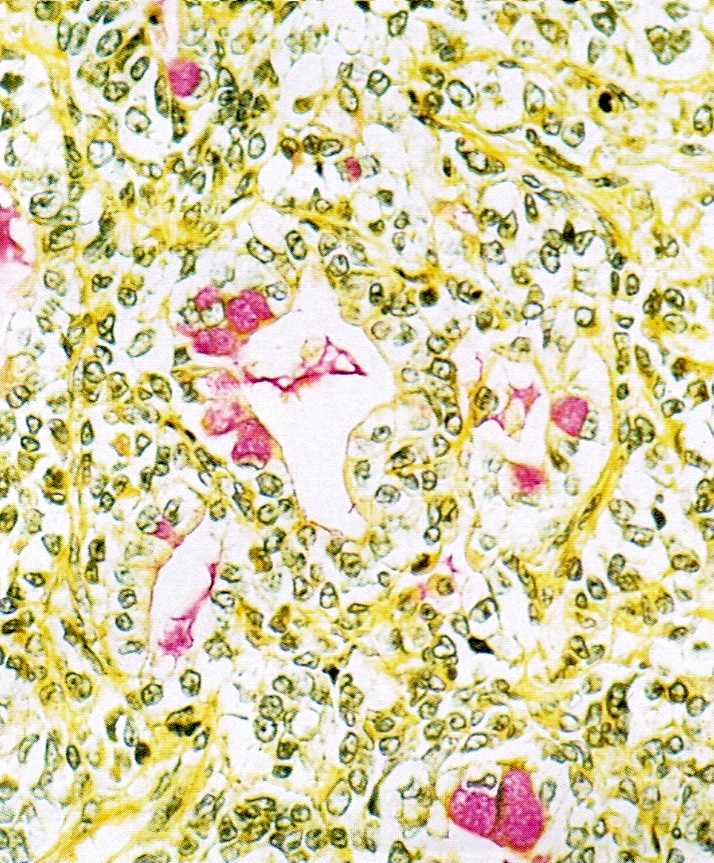
- Loss of nuclear SMARCA4 / BRG1 expression (Pol J Pathol 2013;64:238, Nat Genet 2014;46:427, Nat Genet 2014;46:438, Nat Genet 2014;46:424)
- Loss of nuclear SMARCA2 / BRM expression (J Pathol 2016;238:389)
- CAM5.2 (20%) (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:330)
- Inhibin (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:330)
- CD99 (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2004;23:330)
- TTF1 (Histopathology 2007;51:305)
- OCT3/4 (Histopathology 2007;51:305)
- Loss of nuclear SMARCB1 / INI1 staining has been reported in rare cases of SMARCA4 proficient tumors (J Pathol 2016;238:389)
- FOXL2
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Almost all SCCOHTs harbor inactivating somatic or germline mutations in SMARCA4 (Pol J Pathol 2013;64:238, Nat Genet 2014;46:427, Nat Genet 2014;46:438, Nat Genet 2014;46:424)
- SCCOHTs show SMARCA2 loss of expression likely due to transcriptional / posttranscriptional silencing (J Pathol 2016;238:389)
- SCCOHTs are chromosomally stable cancers (Orphanet J Rare Dis 2013;8:33, Oncotarget 2016;7:1732, J Pathol 2022;257:140)
- SCCOHTs harbor distinct DNA methylation profiles, which distinguish them from other SWI / SNF deficient cancers (Oncotarget 2016;7:1732, Acta Neuropathol 2021;141:291, J Pathol 2022;257:140)
Sample pathology report
- Ovary, oophorectomy:
- Small cell carcinoma of the ovary hypercalcemic type (see comment and synoptic report)
- Comment: Immunohistochemical tests for SMARCA4 / BRG1 and SMARCA2 / BRM show loss of expression. Small cell carcinoma of the ovary, hypercalcemic type (SCCOHT) can be associated with the rhabdoid tumor predisposition syndrome 2 (RTPS2); referral to medical genetics is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Undifferentiated and dedifferentiated carcinomas of the ovary:
- Older age (median: 53 years)
- May be associated with a differentiated ovarian carcinoma (dedifferentiated carcinoma)
- Mismatch repair deficiency is common
- Loss of nuclear expression of SMARCA4 / BRG1, SMARCB1 / INI1 or ARID1B
- Associated with other genetic alterations (PTEN, ARID1A, PIK3CA, KRAS, CTNNB1, NRAS, TP53)
- Granulosa cell tumor, adult and juvenile:
- Prominent follicle-like spaces (juvenile)
- Small cells usually not present (juvenile)
- Prominent nuclear grooves (adult)
- Usually, no brisk mitotic activity of small cells (adult)
- Intact nuclear expression of SMARCA4 / BRG1 (J Pathol 2016;238:389)
- Positive for FOXL2
- Small cell carcinoma, pulmonary type (primary or metastatic):
- Usually lacks follicle-like spaces
- Positive for TTF1
- May show dot-like positivity for CK20
- Intact nuclear expression of SMARCA4 / BRG1 (J Pathol 2016;238:389)
- Dysgerminoma:
- Usually lacks follicle-like spaces
- Large, uniform cells with clear or eosinophilic cytoplasm and distinct membranes
- May show granulomatous reaction
- Positive for OCT4, PLAP, KIT and SALL4
- Intact nuclear expression of SMARCA4 / BRG1 (J Pathol 2016;238:389)
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma:
- Primitive neuroectodermal tumor (central type or peripheral type):
- Associated with ovarian teratoma (central type)
- Positive for FLI1 and GFAP
- EWSR1 rearrangement (peripheral type)
- Melanoma (primary or metastatic):
- May be associated with ovarian teratoma (primary)
- Often bilateral (metastatic)
- May show cytoplasmatic melanin pigment
- Intact nuclear expression of SMARCA4 / BRG1 (J Pathol 2016;238:389)
- Positive for S100, HMB45, MelanA
- Negative for cytokeratin and WT1
- Lymphoma:
- Lacks follicle-like spaces
- Negative for cytokeratin and WT1
- Positive for lymphoid markers (subtype specific)
Board review style question #1
A 27 year old woman presented with a 5 cm unilateral ovarian mass. SMARCA4 / BRG1 IHC image is provided above. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Dysgerminoma
- Granulosa cell tumor, adult type
- Granulosa cell tumor, juvenile type
- Metastatic melanoma
- Small cell carcinoma of the ovary, hypercalcemic type
Board review style answer #1
E. Small cell carcinoma of the ovary, hypercalcemic type. The H&E image shows a solid and corded undifferentiated tumor with follicle-like spaces and focal myxoid stroma. The immunohistochemical test for SMARCA4 / BRG1 shows aberrant expression (loss of nuclear staining). The morphology and immunophenotype are consistent with the diagnosis of SCCOHT. All 4 other options may have some overlapping morphologic features with SCCOHT but retain SMARCA4 / BRG1 expression.
Comment Here
Reference: Small cell carcinoma of ovary, hypercalcemic type
Comment Here
Reference: Small cell carcinoma of ovary, hypercalcemic type
Board review style question #2
Which of the following immunohistochemical tests shows aberrant expression in small cell carcinoma of the ovary, hypercalcemic type (SCCOHT)?
- BAP1
- MDM2
- MLH1
- p53
- SMARCA4 / BRG1
Board review style answer #2
E. SMARCA4 / BRG1. SCCOHT is molecularly defined by inactivating SMARCA4 mutations, which are associated with SMARCA4 / BRG1 nuclear loss of expression. The other options are in other entities such as mesothelioma (BAP1 loss of expression), malignant Brenner tumor (MDM2 overexpression), ovarian undifferentiated and dedifferentiated carcinoma (MLH1 loss of expression) and high grade serous carcinoma (aberrant p53 expression).
Comment Here
Reference: Small cell carcinoma of ovary, hypercalcemic type
Comment Here
Reference: Small cell carcinoma of ovary, hypercalcemic type