Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Practice question #1 | Practice answer #1 | Practice question #2 | Practice answer #2Cite this page: Collins V, Kalir T. Thecoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorthecoma.html. Accessed September 29th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Ovarian stromal neoplasm, almost always benign, composed of cells resembling theca cells
Essential features
- Almost always benign
- Usually occurs in postmenopausal women who present with uterine bleeding
- Histology shows a predominant population of cells with ovoid to round nuclei and pale gray cytoplasm
- Reticulin stain and molecular testing for FOXL2 mutation help distinguish thecoma from adult granulosa cell tumor
Terminology
- Theca cell tumor
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8600/0 - thecoma, NOS
- ICD-10: D27 - benign neoplasm of ovary
- ICD-11: 2F32.Y & XH34A0 - other specified benign neoplasm of ovary & thecoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Uncommon
- Usually postmenopausal women
- Mean age = 59 years (Ann Diagn Pathol 2008;12:12)
- Age ranges from 16 to 81 (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1023)
Sites
- Ovary
Pathophysiology
- Molecular alterations, such as trisomy 12 and loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at the PTCH gene (see Molecular / cytogenetics description)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- May be discovered incidentally
- Most common symptom is postmenopausal bleeding (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1023)
- Symptoms can be related to mass: pelvic pain / pressure
- May present with estrogenic or androgenic manifestations
- Associated with endometrial hyperplasia and malignancy
Diagnosis
- Histologic examination
Laboratory
- Occasionally elevated serum inhibin A and inhibin B (Gynecol Oncol Rep 2020;34:100658, Gynecol Endocrinol 2016;32:872)
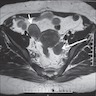
Radiology description
- Sonographic features:
- Adnexal hypoechoic mass with clear border and acoustic attenuation
- Minimal Doppler flow signal (J Ovarian Res 2016;9:81)
- Magnetic resonance imaging features:
- Isointense or slightly hyperintense
- Pelvic fluid accumulation (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e20358)
- Computed tomography features:
- Isodense or hypodense (J Comput Assist Tomogr 2012;36:46)
- Occasionally thecomas have positive F-FDG uptake on PET scan (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2017;43:599)
Prognostic factors
- Thecomas are almost always benign but may be associated with endometrial malignancy
Case reports
- 57 year old woman with postmenopausal bleeding and elevated serum inhibin B level (Gynecol Oncol Rep 2020;34:100658)
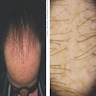
- 58 year old woman with progressive scalp hair loss (Skin Appendage Disord 2019;5:259)
- 61 year old woman with Meigs syndrome and elevated CA-125 level (J Menopausal Med 2015;21:56)
Treatment
- Oophorectomy if fertility sparing is desired
- Total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy is indicated in postmenopausal patients
- References: Gynecol Oncol 1994;55:S62, Acta Radiol Oncol 1980;19:241, Gynecol Oncol 1985;21:135
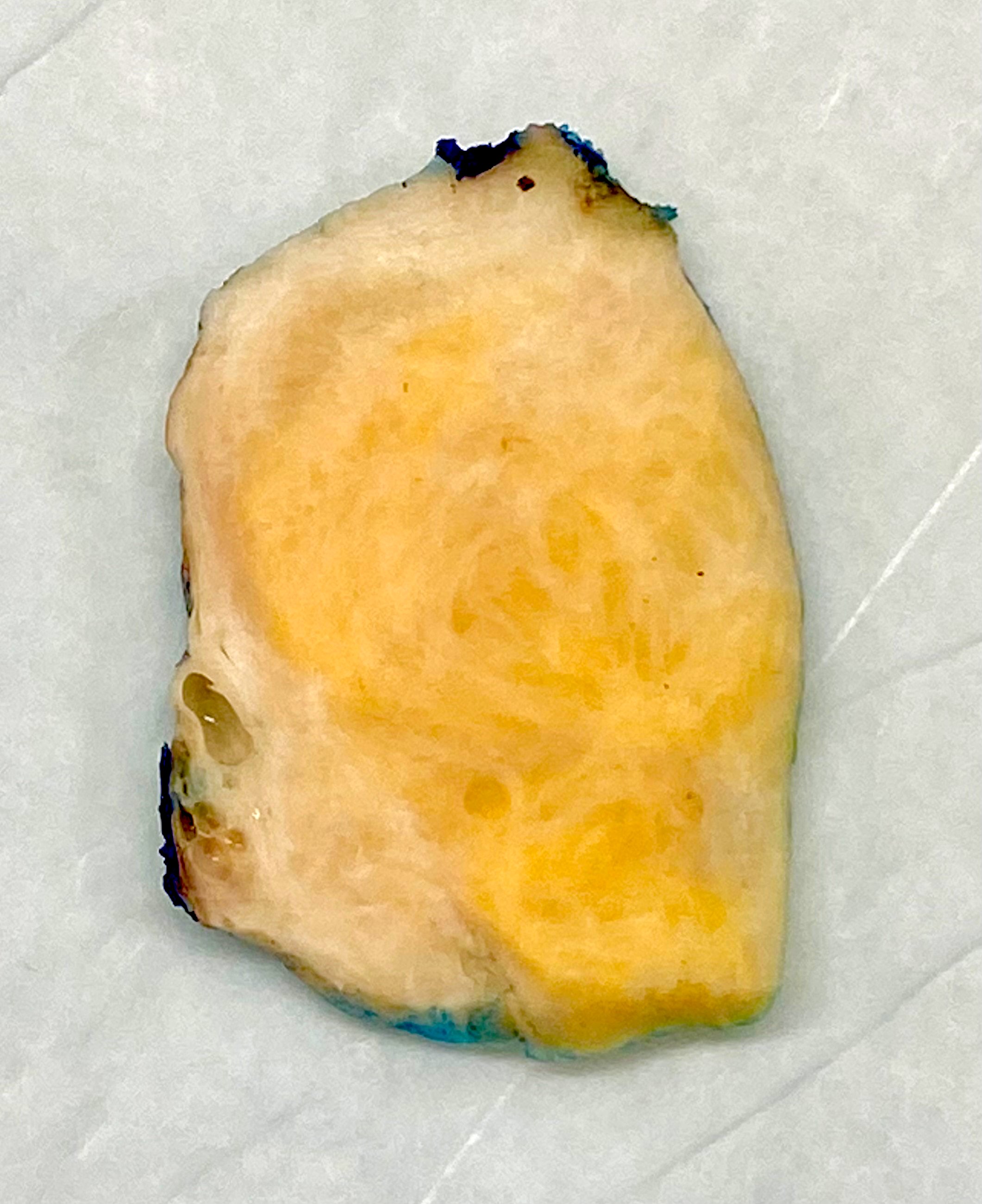
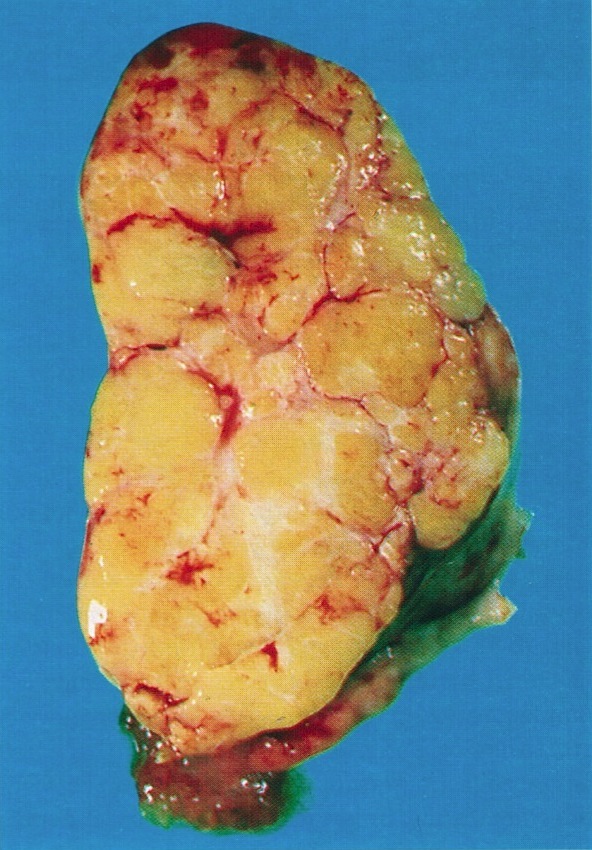
Gross description
- Usually unilateral
- Most are < 5 cm
- Solid, yellow and lobulated or white with focal yellow areas
- Occasionally cystic change and hemorrhage are present
- Necrosis is rare (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1023)
Gross images
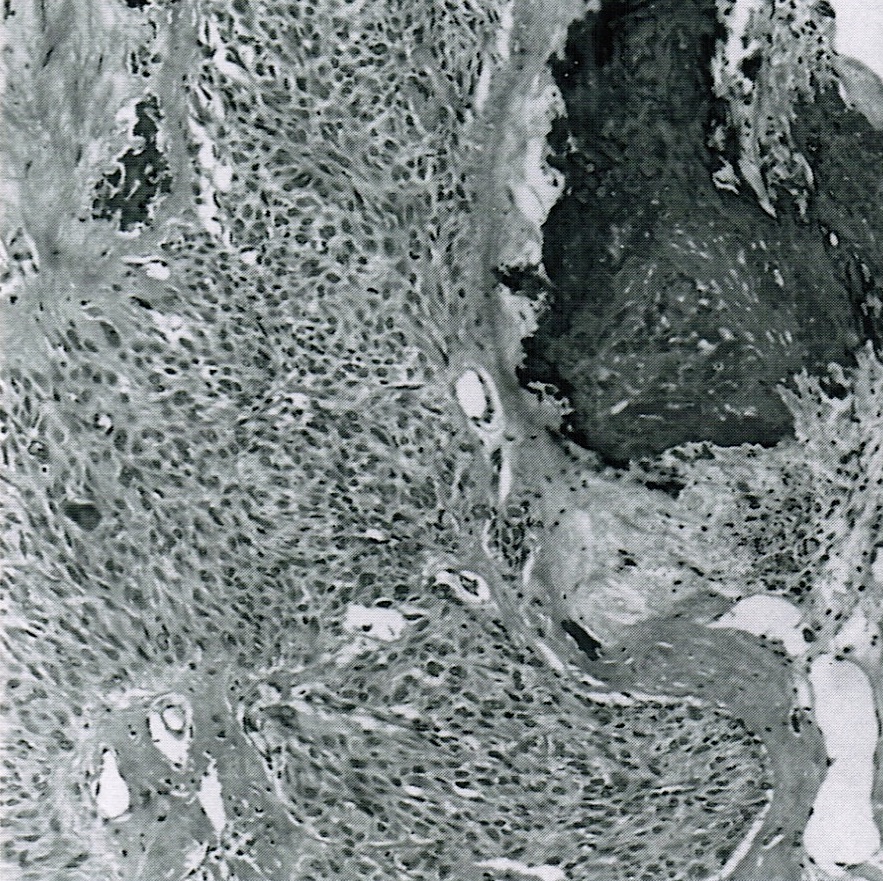
Frozen section description
- Sheets of oval to round cells with moderate to abundant pale gray cytoplasm
- Bilaterality should raise suspicion for metastasis
- Signet ring cells may be missed on frozen section and misinterpreted as fibrothecoma (Yeungnam Univ J Med 2019;36:163)
Frozen section images
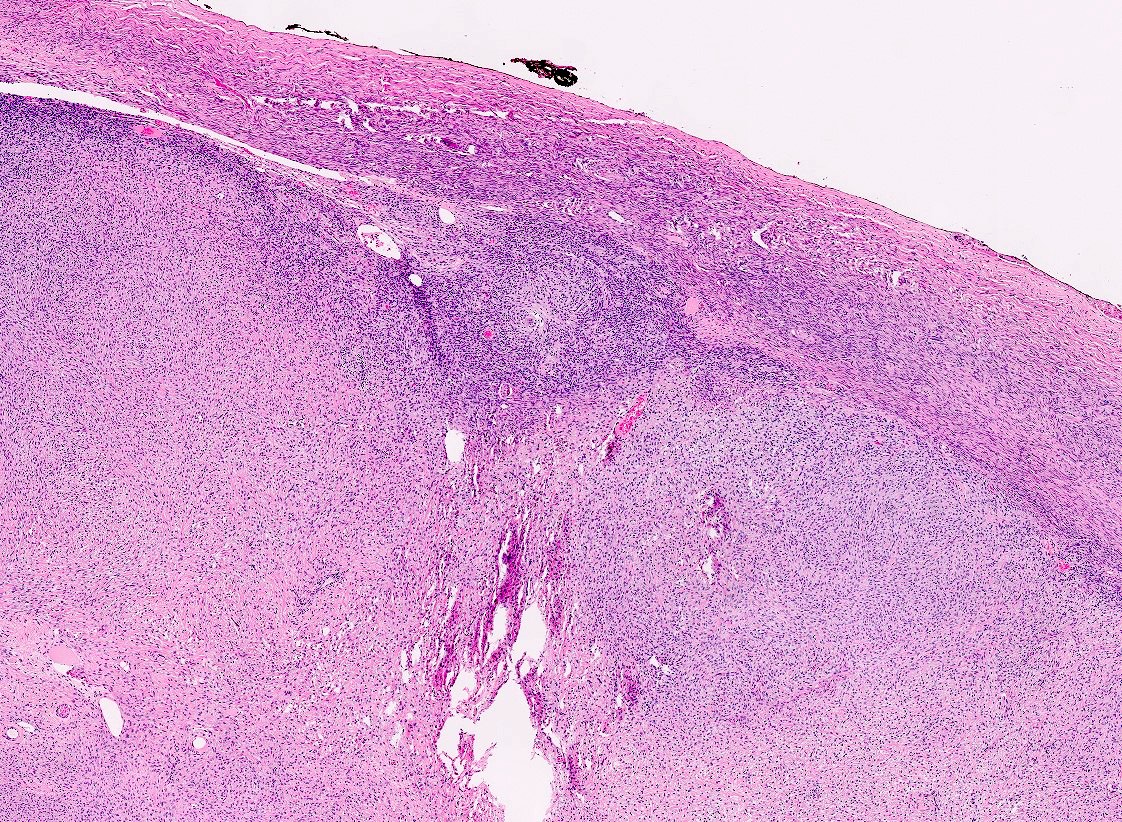
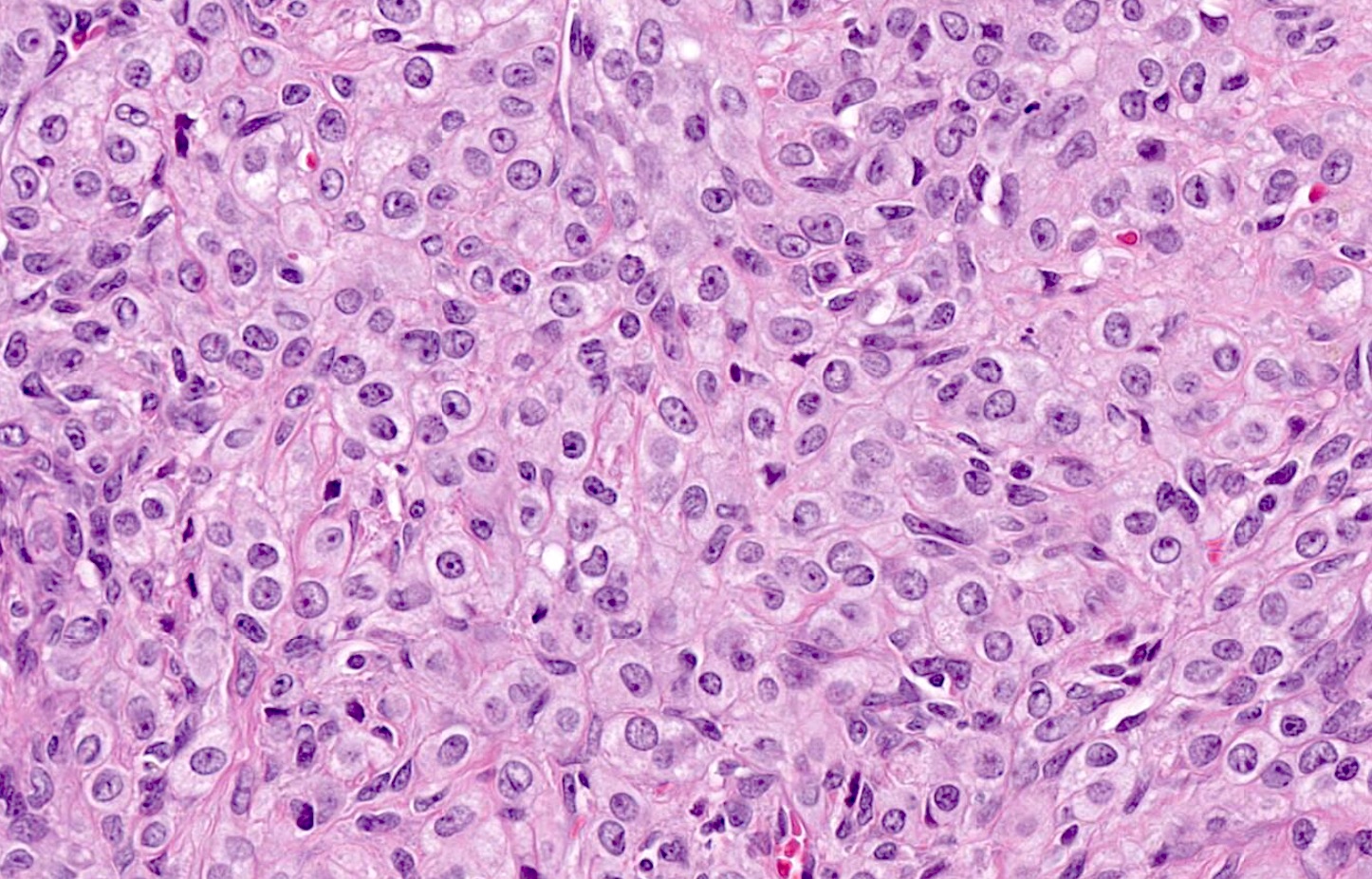
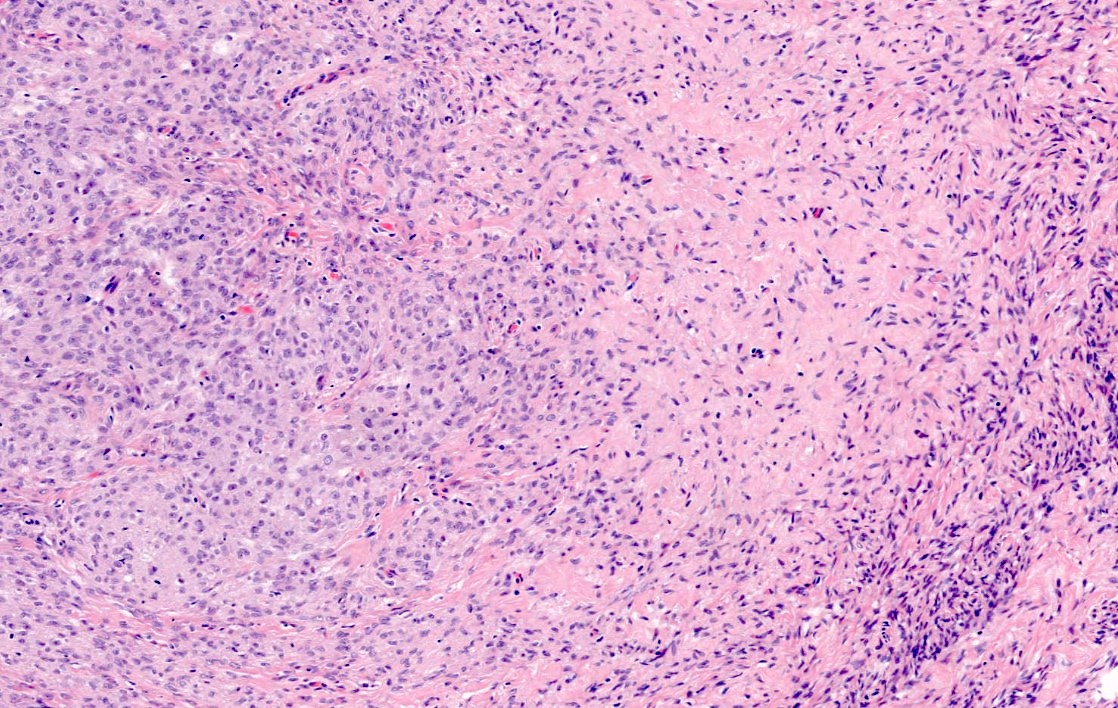
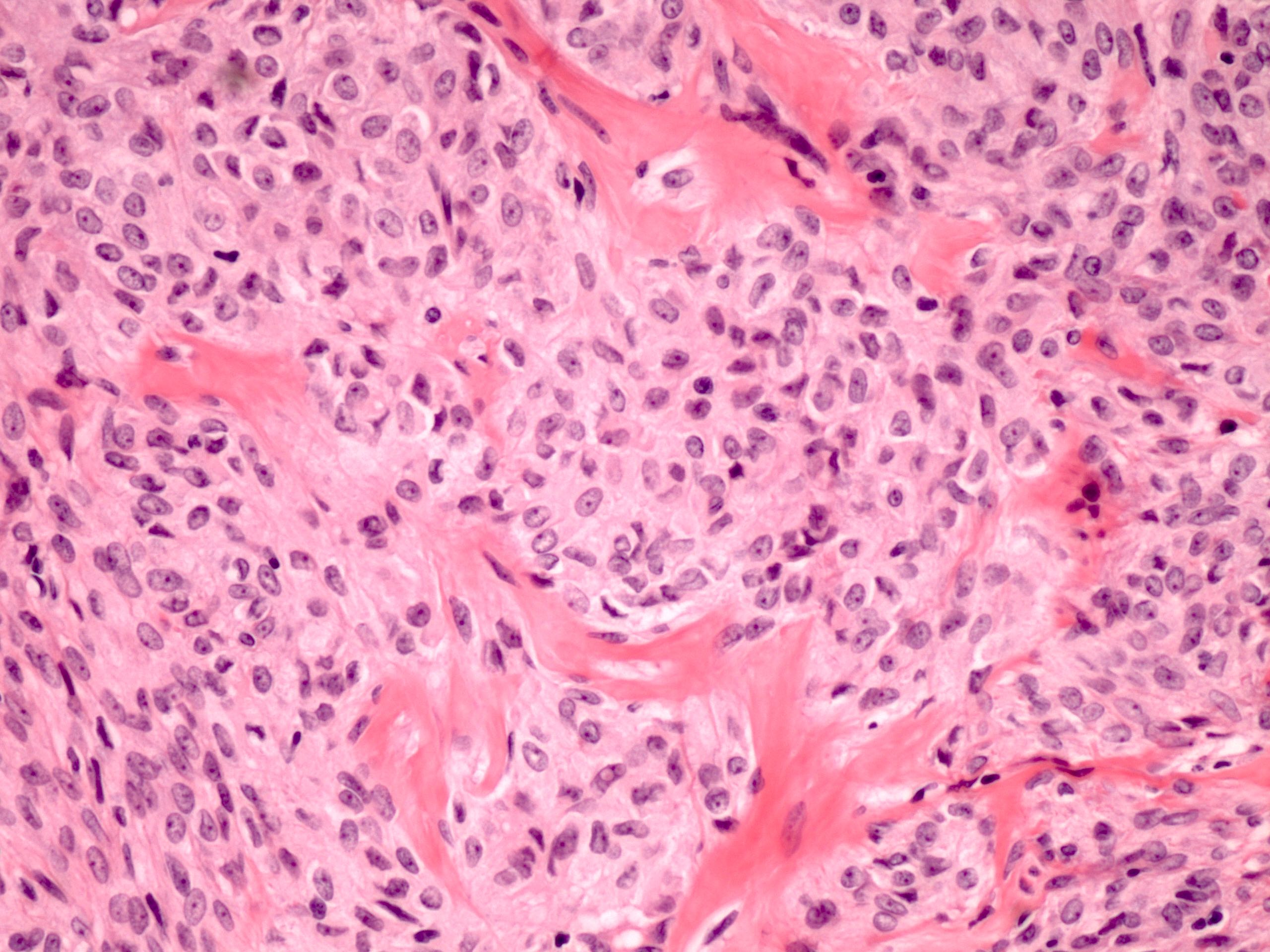
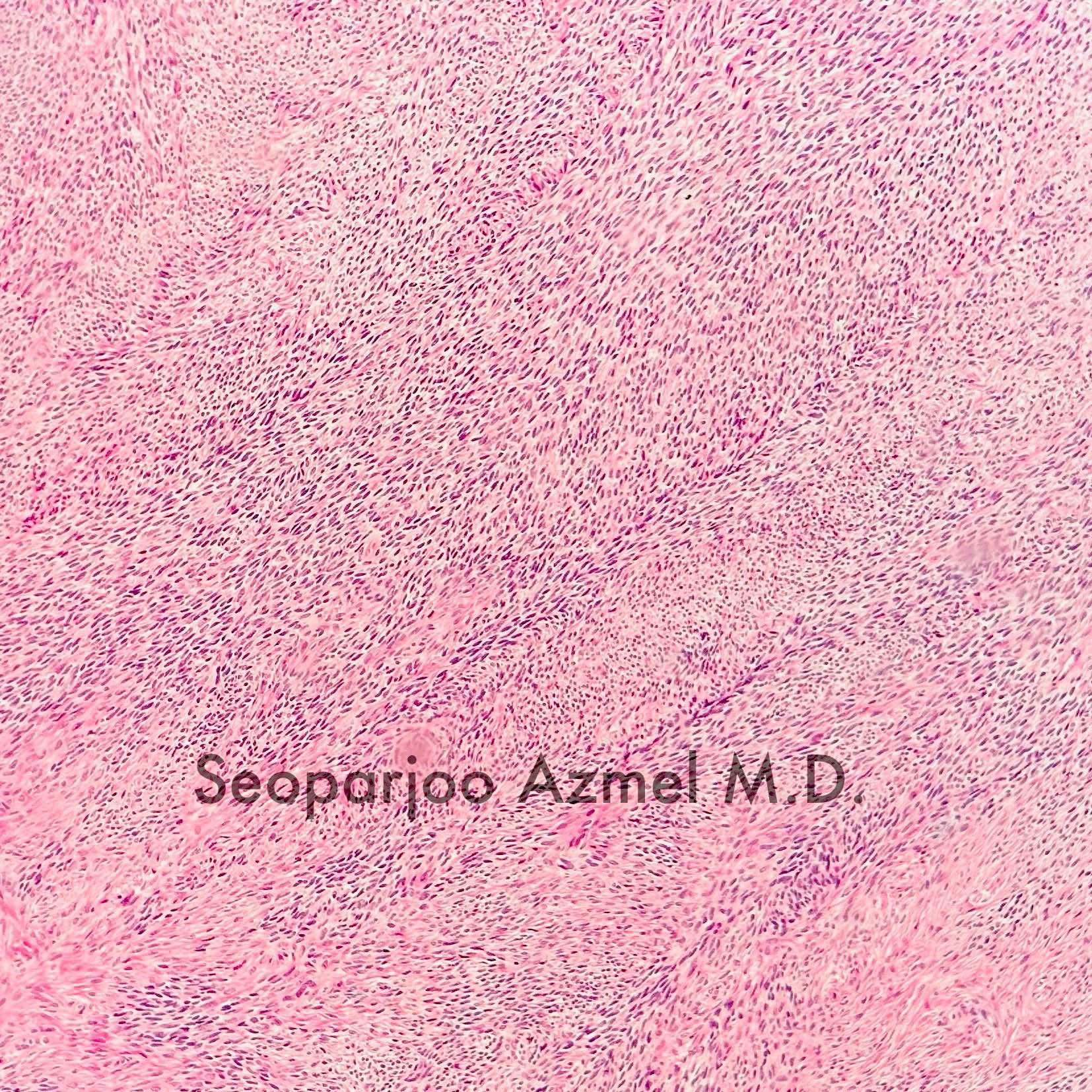
Microscopic (histologic) description
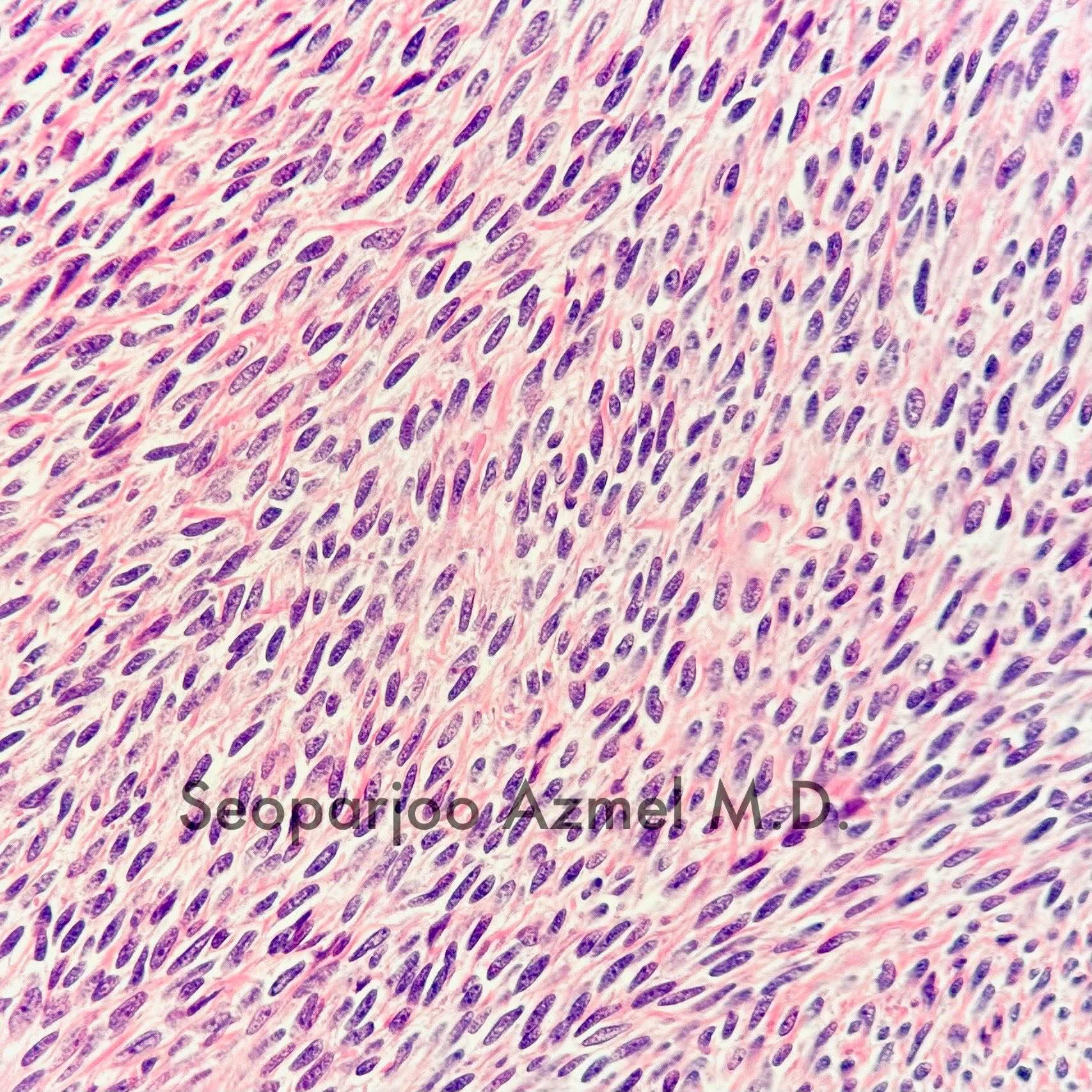
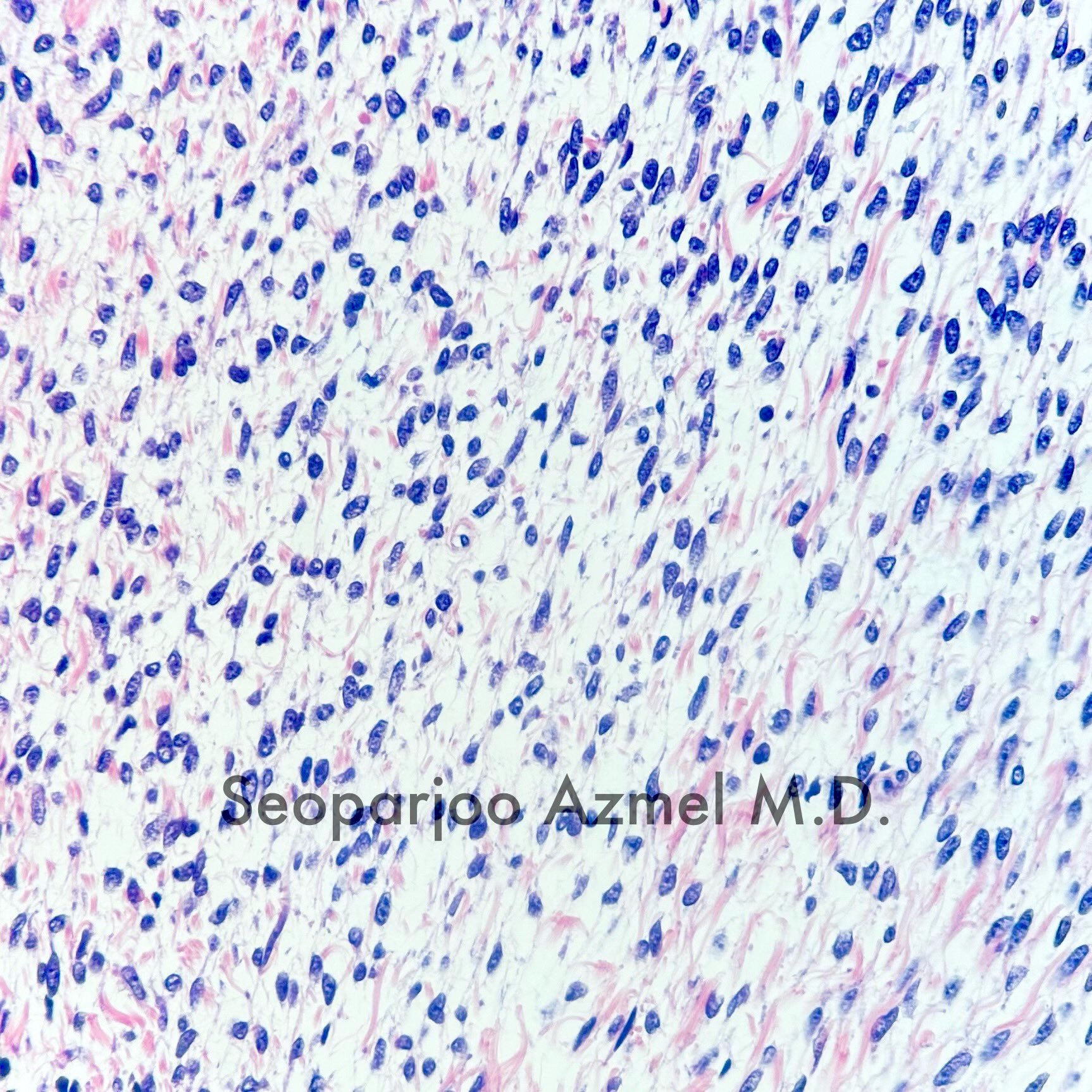
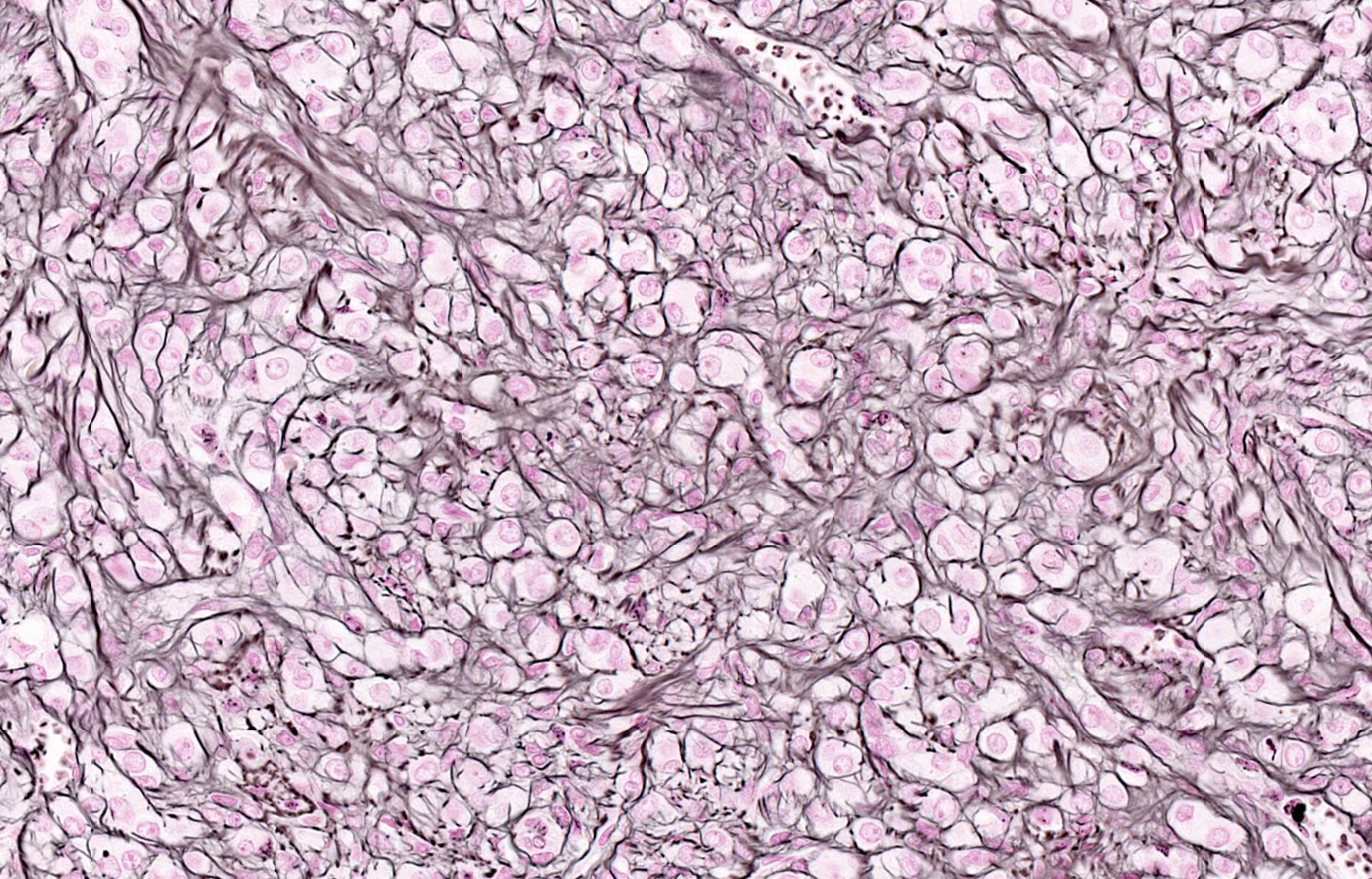
- Predominant population of cells showing ovoid to round nuclei and pale gray cytoplasm, which can be abundant
- Minor component of the tumor may have spindled nuclei, reflecting overlap between fibroma and thecoma
- Indistinct cell membranes impart a syncytial appearance
- Diffuse or nodular growth pattern
- Absent or minimal nuclear atypia
- Mitotic rate usually < 5/10 high power fields
- Hyaline plaques
- Cytoplasmic lipid vacuoles may be present but are not essential
- May show aggregates of cells with brightly eosinophilic cytoplasm (lutein cells)
- Calcification is more common in young patients (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1988;7:343)
- Uncommon features include keloid-like sclerosis, nuclear grooves, bizarre nuclear atypia (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1023)
- Rarely contains a minor component of sex cord elements (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1983;2:227)
- Malignant thecoma: very rare, diagnosis requires diffuse moderate to severe nuclear atypia and high mitotic rate (> 4/10 high power fields) (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:e15)
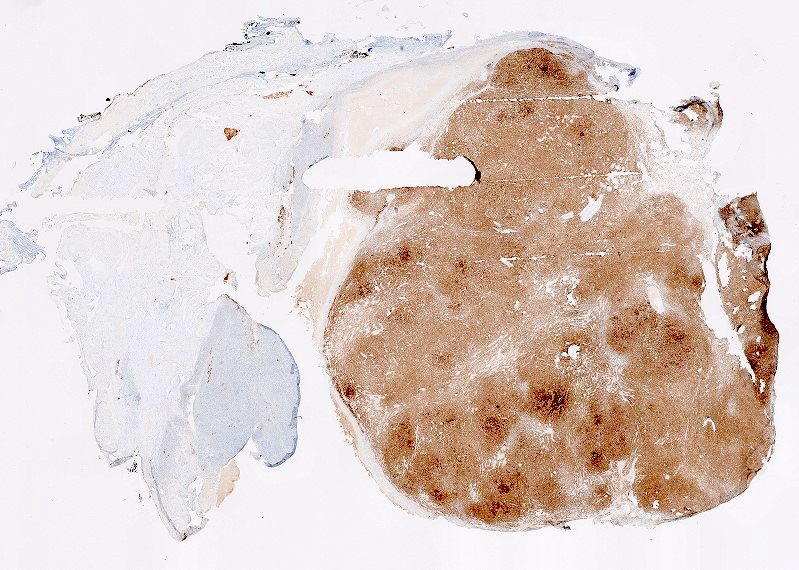
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Victoria Collins, M.D., Tamara Kalir, M.D., Ph.D., AFIP and @SeoparjooAzmel on Twitter
Positive stains
- Inhibin
- Calretinin
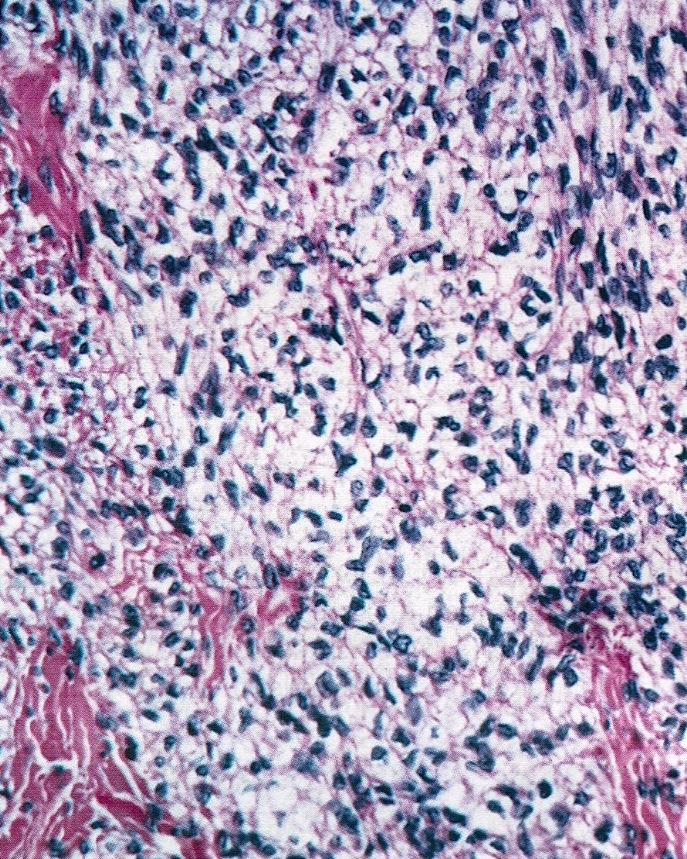
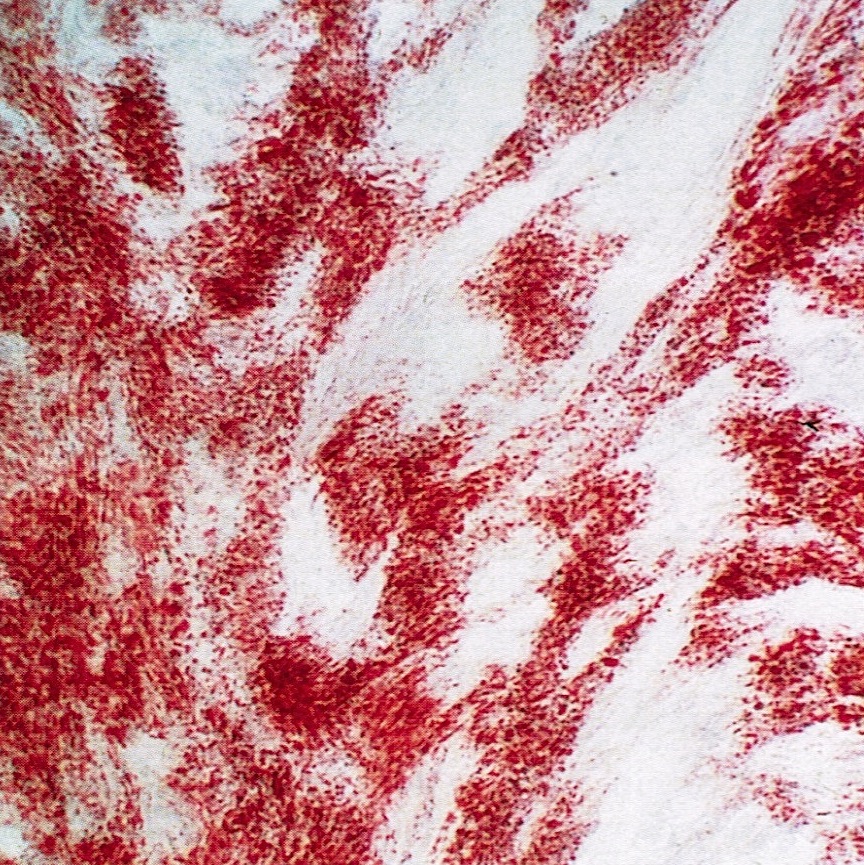
- Reticulin stain shows a pericellular pattern (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2018;37:305)
- SF1
- FOXL2 (Mod Pathol 2013;26:860)
- WT1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:354)
- CD56 (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:884)
- Vimentin
- Oil red O in lipid rich cells
- GLUT5 in FDG PET positive tumors (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2017;43:599)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Cytoplasmic lipid (Ultrastruct Pathol 1992;16:363)
- Type I cells: dispersed chromatin, basal lamina investment of each cell, coiled / branching rough endoplasmic reticulum, sparse smooth endoplasmic reticulum, irregular mitochondria
- Type II cells: degenerative changes, large round mitochondria with incomplete cristae and centers displaced by microfilaments (Hum Pathol 1984;15:153)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Trisomy 12 or tetrasomy 12 (Gynecol Oncol 1990;36:413, Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1993;71:180)
- Trisomy 4 (Gynecol Oncol 1992;45:66)
- Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at 9q22.3 (PTCH1) and 19p13.3 (Hum Pathol 2005;36:792)
- FOXL2 mutation has been reported in a subset of thecomas (3 out of 14 tumors in one series) (N Engl J Med 2009;360:2719)
- However these may represent misdiagnosed granulosa cell tumors (PLoS One 2009;4:e7988)
- Pericellular reticulin staining is 100% specific for absence of FOXL2 mutation (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2018;37:305)
Videos
Thecoma of ovary
Ovarian pathology
Sample pathology report
- Right ovary and fallopian tube, salpingo-oophorectomy:
- Ovarian thecoma
- Fallopian tube with no significant pathologic changes
Differential diagnosis
- Adult granulosa cell tumor:
- Reticulin stain shows nested pattern (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2019;38:143)
- Harbors FOXL2 mutation (Mod Pathol 2013;26:860, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2018;37:305)
- Fibroma:
- Intersecting bundles of spindle cells producing collagen
- A morphologic spectrum between fibroma and thecoma exists
- Indeterminate tumors have been called fibrothecoma
- Luteinized thecoma associated with sclerosing peritonitis:
- Younger age at presentation (median age: 28)
- Symptoms include abdominal pain, ascites and bowel obstruction
- Cutaneous involvement has been reported (Ann N Y Acad Sci 1985;448:231)
- Bland spindle cell proliferation circumferentially involving the ovarian cortex with sparing of the medulla
- Almost always bilateral (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1273)
- Sclerosing stromal tumor:
- Pseudolobular growth pattern with cellular nodules separated by dense collagenous or edematous connective tissue (Cancer 1973;31:664)
- Staghorn vessels
- Microcystic stromal tumor:
- Small, anastomosing cysts
- Inhibin-, calretinin-
- Nuclear beta catenin+
- Cyclin D1+
- CD10+ (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1420)
- Steroid cell tumor, NOS:
- FOXL2- (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:484)
- Polygonal cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Typically has a component of lipid rich cells (pale and vacuolated) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:1459)
- Leydig cell tumor:
- Tumor centered in ovarian hilus
- Cytoplasmic Reinke crystals
- Nuclei tend to cluster, forming eosinophilic nuclei free zones (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1989;8:299)
- Fibrinoid necrosis of blood vessel walls
Additional references
Practice question #1
Practice answer #1
Practice question #2
Practice answer #2