Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Mohamed KS, Al-Quran SZ. Myointimoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/penismyointimoma.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign myointimal proliferation with predilection to the corpus spongiosum of the glans penis
Essential features
- Benign mesenchymal neoplasm in the corpus spongiosum of the glans penis
- Intravascular proliferation of the vascular intimal cells
- Lesional cells stain with α smooth muscle actin but not desmin
Terminology
- Penile myointimoma
- Myointimoma of the penis
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9137/0 - myointimoma
Epidemiology
- Rare tumor with ~28 cases reported in the literature (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1622, Int J Surg Pathol 2022 Aug 9 [Epub ahead of print])
- Previously described as intravascular leiomyoma, leiomyomatosis, late stage intravascular fasciitis, leiomyoma of the glans penis, solitary cutaneous myofibroma of the glans penis (Cancer 1970;25:1431, J Urol 2000;164:791, Am J Dermatopathol 1996;18:317)
- Wide age range (2 - 74 years old) (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524, Actas Dermosifiliogr 2009;100:511)
Sites
- Corpus spongiosum of the glans penis
Pathophysiology
- Intravascular proliferation from the intimal cells of the inner layer of the corpus spongiosum vasculature in the glans penis (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524)
Etiology
- Mesenchymal tumor unrelated to the status of circumcision, history of trauma or the presence of disease (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524, Actas Dermosifiliogr 2009;100:511)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Small, distinct, nonmobile, firm, painless nodule on the glans penis (J Am Acad Dermatol 2005;53:1084)
- Benign, rapidly growing lesions that remain stable for years, even after incomplete excision (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524)
Diagnosis
- Laboratory tests, including urine analysis and ultrasonic evaluation of the abdomen and the scrotum to exclude other potential causes (Pathol Int 2007;57:158, J Pediatr Surg Case Rep 2019;44:101189)
- Punch, incisional or excisional biopsy (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524)
Prognostic factors
- Benign outcome with no recurrence; spontaneous regression may occur (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1622, Int J Surg Pathol 2022 Aug 9 [Epub ahead of print)
Case reports
- 14 year old boy with a 1 cm nodule on the right side of his glans penis (J Cutan Pathol 2009;36:817)
- 49 year old man with a 12 month history of a palpable lesion involving the glans penis (Int J Impot Res 2021;33:583)
- 50 year old man with a nodule located in the glans penis (Pathol Int 2007;57:158)
Treatment
- Simple excision
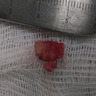
Gross description
- Firm white mass of 0.4 - 1.9 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1622, Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524, J Am Acad Dermatol 2005;53:1084)
Frozen section description
- Lesion may be present at margin of excision (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1622)
Microscopic (histologic) description
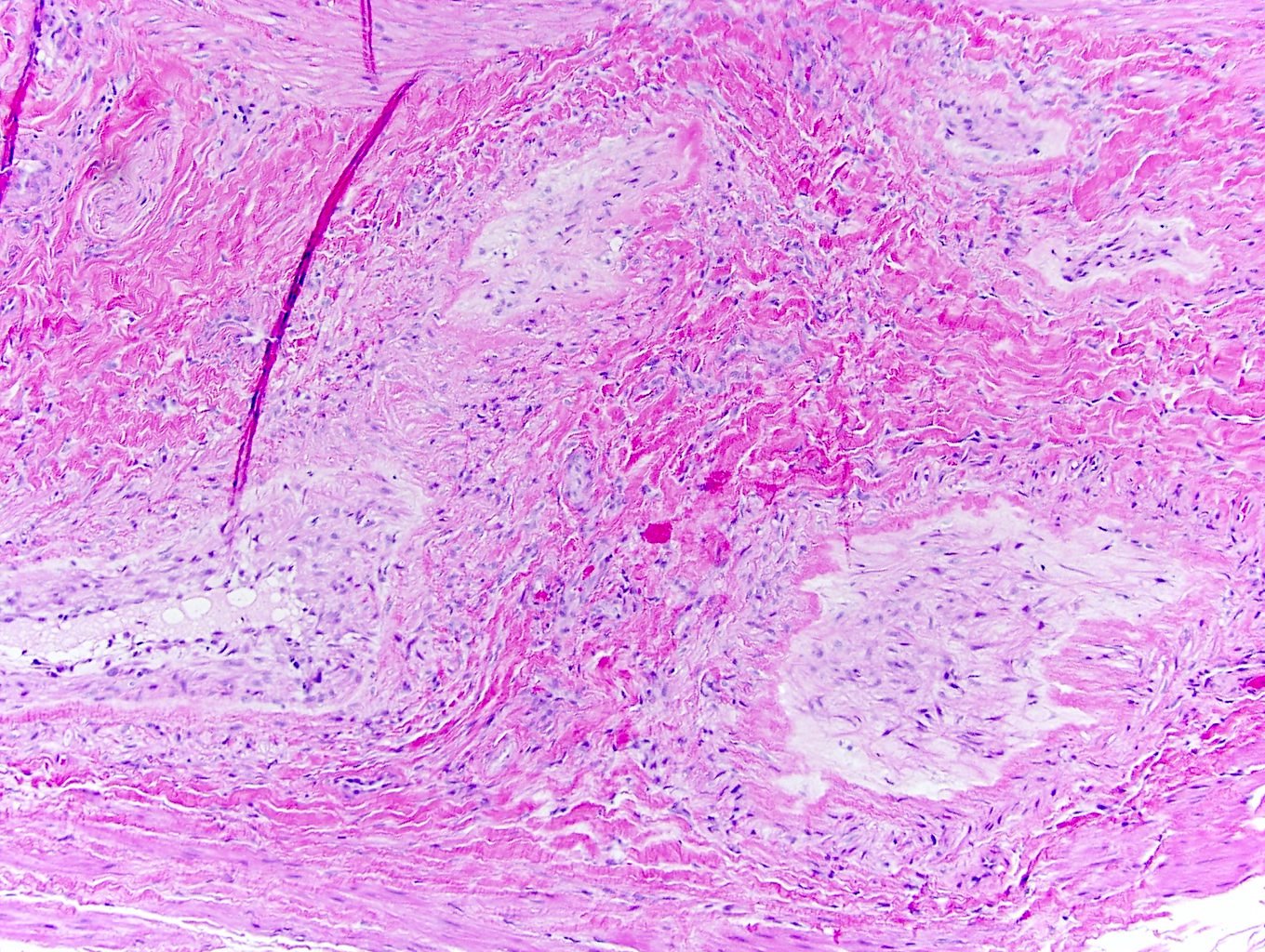
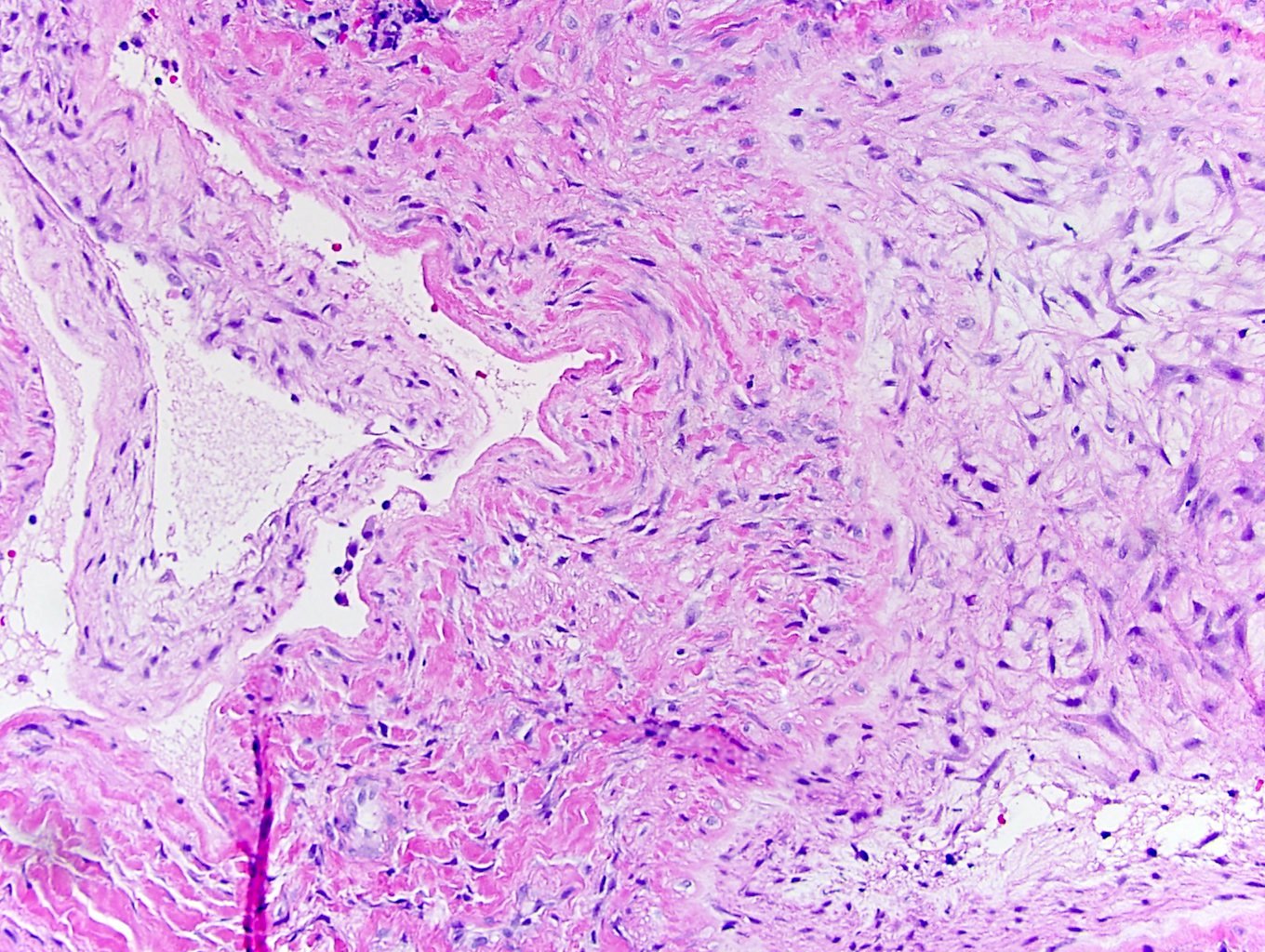
- Multinodular or plexiform pattern; composed of occlusive intravascular myointimal proliferation (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524)
- Nodules contain spindle or stellate shaped cells embedded in abundant fibromyxoid matrix or sometimes chondroid matrix (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1622)
- Cells have long eosinophilic cytoplasmic processes, blunt ended nuclei, fine chromatin and juxtanuclear vacuoles
- Foci of degenerative changes appear as ghost cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524)
- No cytologic atypia, nuclear pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli or mitoses
- Residual smooth muscle bundles surrounding the tumor (Actas Dermosifiliogr 2009;100:511)
- Overlying skin may show slight hyperkeratosis (J Cutan Pathol 2009;36:817)
- No necrosis or significant inflammation
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Desmin (shows the residual native smooth muscle of the vessel walls)
- CD34 / CD31 / factor VIII related antigen (highlight the penetrating capillaries and the residual endothelial cells)
- S100 protein
- AE1 / AE3 (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524)
- Verhoeff-van Gieson elastic histochemical stain (demonstrates the meshwork of the elastic fibers surrounding the nodules) (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1524)
Sample pathology report
- Glans penis, excisional biopsy:
- Penile myointimoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show a plexiform vascular proliferation composed of spindle cells in a fibromyxoid background with occluded lumens. The neoplastic cells are α smooth muscle actin positive and desmin negative.
Differential diagnosis
- Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor:
- Not intravascular
- Common in extremities, trunk, head and neck
- Dimorphic population of cells:
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma:
- Myofibroma:
- Biphasic pattern of myoid nodules similar to myointimoma; however, there are hemangiopericytoma-like areas
- Can involve vessels but is not limited to intravascular lumina
- Intravascular fasciitis:
- May overlap
- Intralesional inflammatory cells, mucoid pools
- Nerve sheath tumor:
- Diffuse nuclear S100
- Leiomyoma:
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1