Table of Contents
Usual | Usual - pseudohyperplastic carcinoma | Verrucous | Verrucous - carcinoma cuniculatum | Papillary | SarcomatoidCite this page: Chaux A, Cubilla AL. HPV independent squamous cell carcinoma (usual, verrucous, papillary, sarcomatoid). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/penscrotumHPVindependentSCC.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Usual - pseudohyperplastic carcinoma
Definition / general
Epidemiology
Sites
Clinical features
Treatment
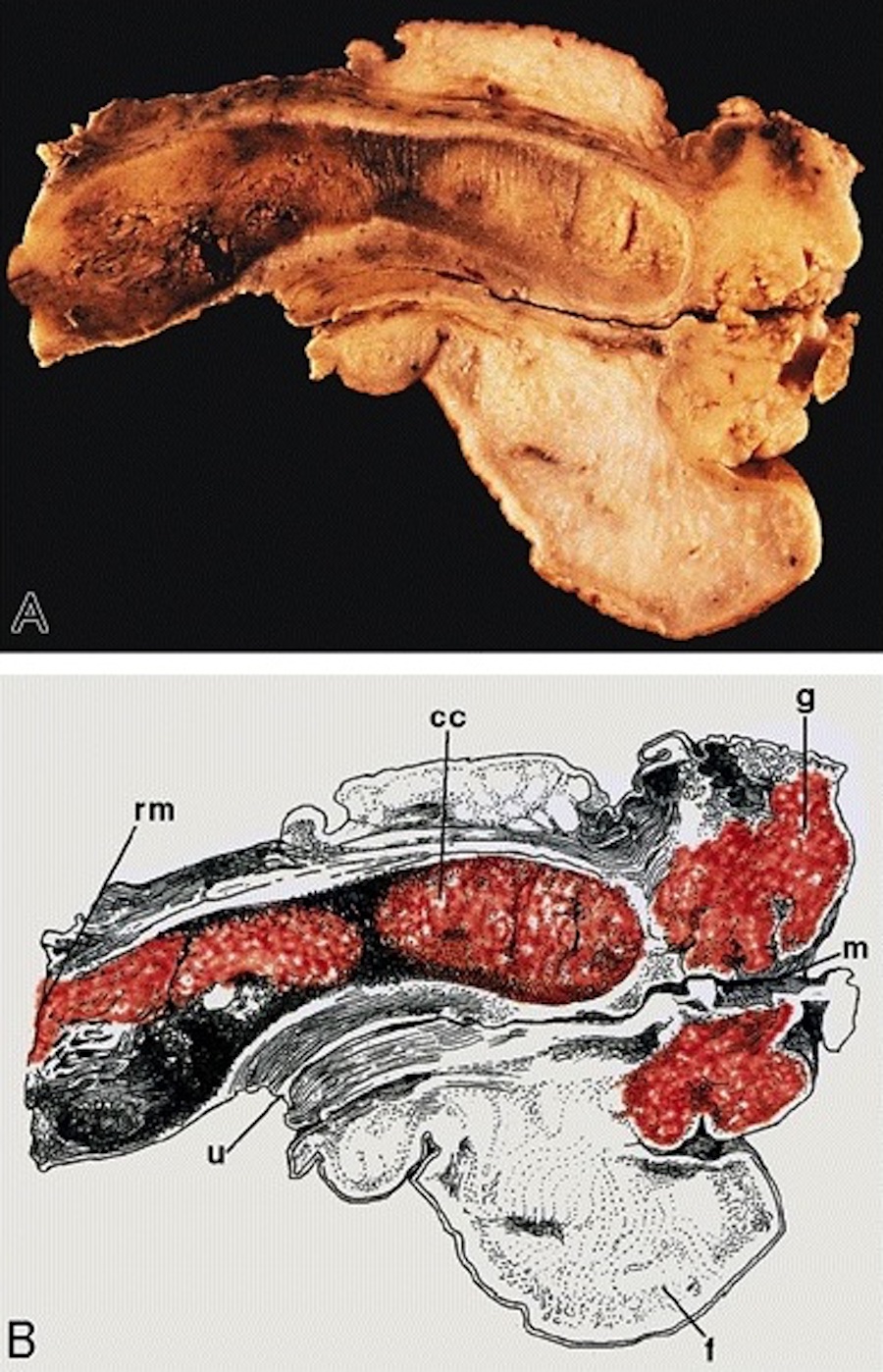
Gross description
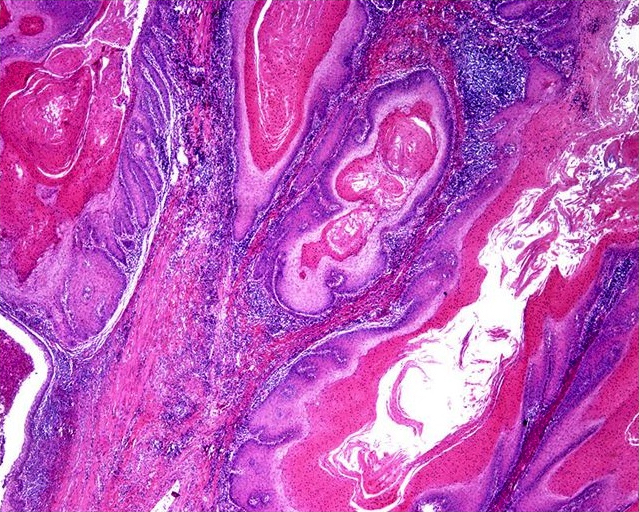
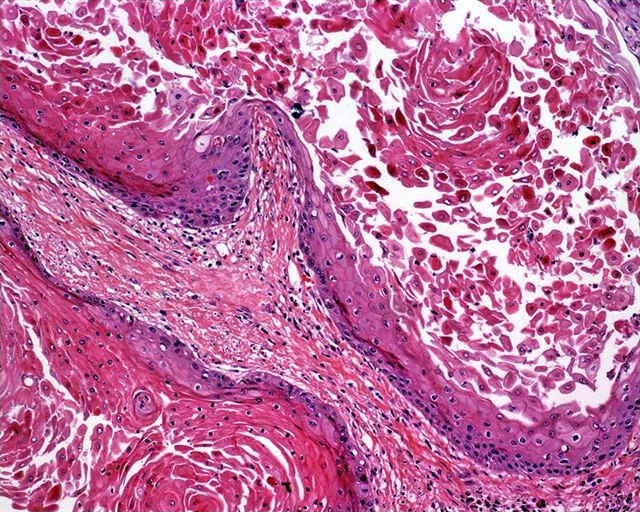
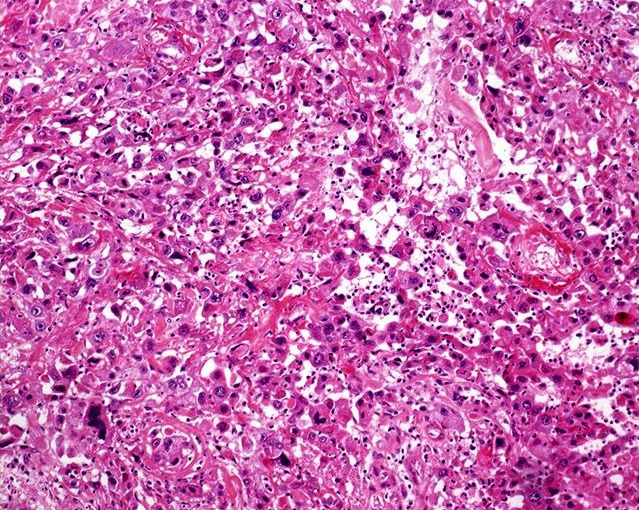
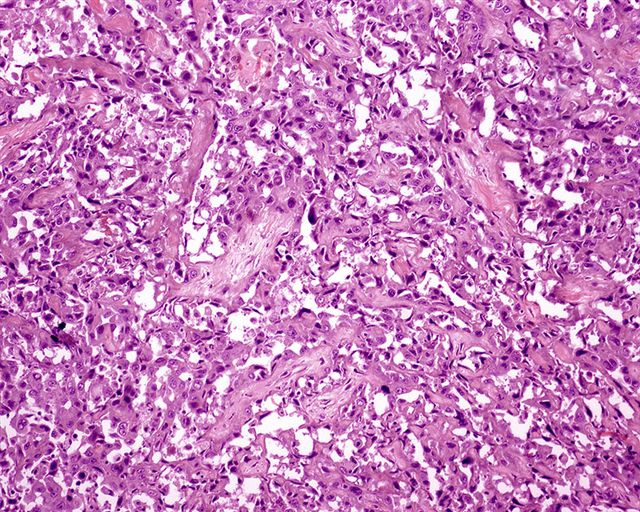
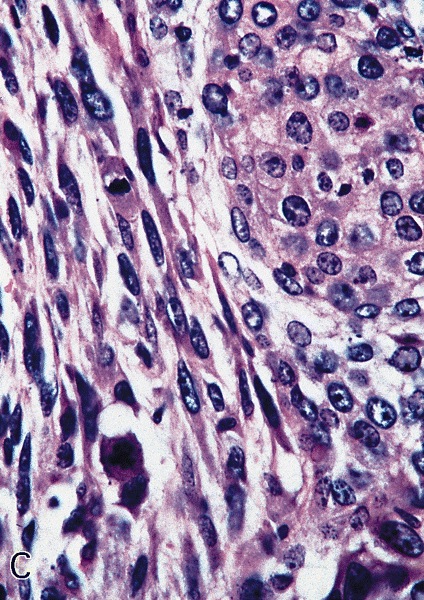
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Alcides Chaux, M.D. and Antonio Cubilla, M.D.
Molecular / cytogenetics description
Differential diagnosis
- Nonverruciform, highly differentiated invasive tumor resembling pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia
Epidemiology
- Affects elderly patients (mean age 69 years)
- ~12 cases have been reported
Sites
- Preferentially involves inner mucosa of foreskin
- Tends to be multicentric
Clinical features
- Good prognosis
- Usually no recurrence after excision
- Negative inguinal nodes
Treatment
- Circumcision or partial penectomy
- Groin dissection is not needed in absence of clinically evident metastatic disease
Gross description
- Often multicentric
- Typically flat or slightly elevated, white and granular, 2 cm
Microscopic (histologic) description
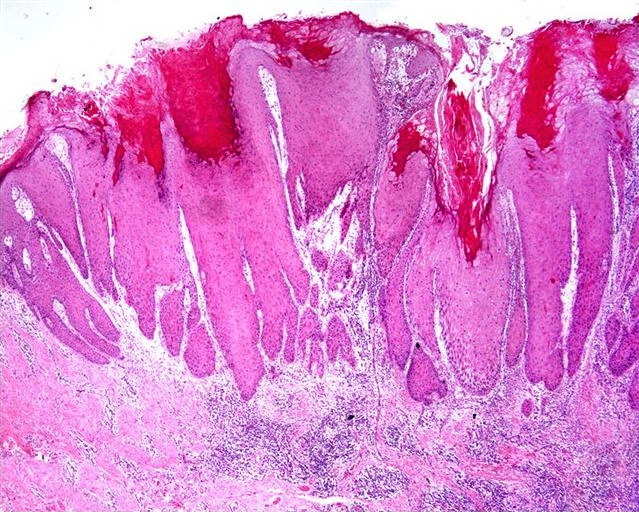
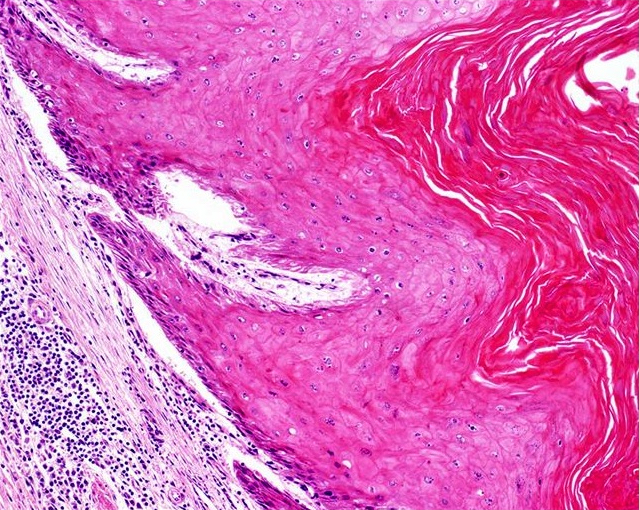
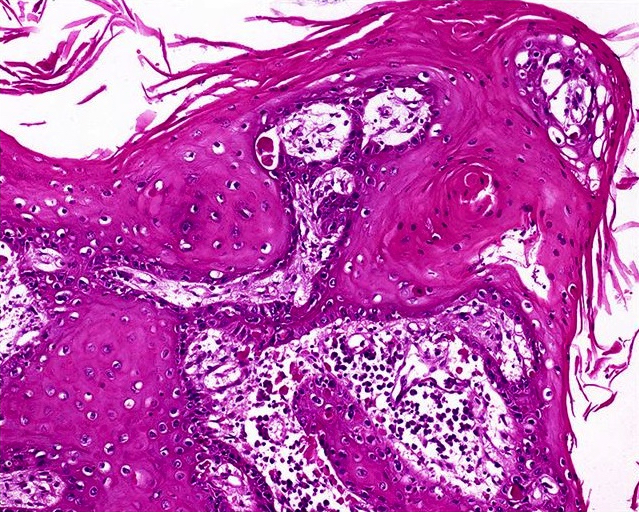
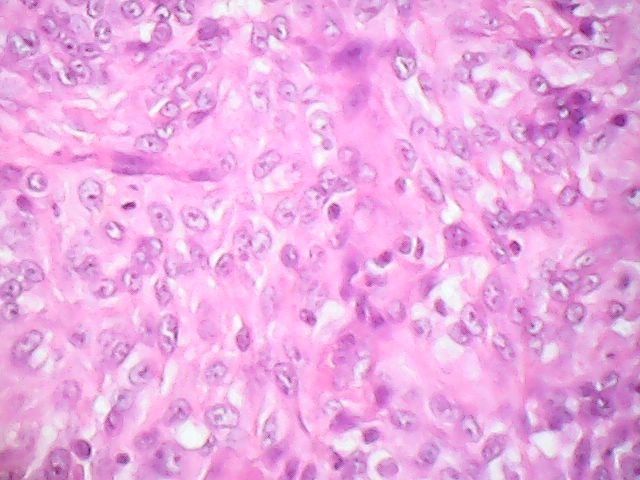
- Nonverruciform, highly differentiated and downward proliferation of keratinizing nests of squamous cells with minimal atypia
- Squamous pearls in almost all cases
- Most nests are orderly and surrounded by reactive fibrous stroma with variable inflammatory cells
- Tumor cells have eosinophilic cytoplasm with distinct intercellular bridges
- Definite invasion with irregular stromal interface is present but may need additional sections to identify
- Frequent extension beyond lamina propria
- Adjacent squamous epithelium exhibits squamous hyperplasia and differentiated penile intraepithelial lesion
- Well developed lichen sclerosus is almost always present (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:895)
- Peripheral palisading is not evident
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Alcides Chaux, M.D. and Antonio Cubilla, M.D.
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- HPV- in analyzed cases
Differential diagnosis
- Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia:
- Regular nests, conspicuous peripheral palisading, scant stromal reaction, no extension beyond lamina propria and no cytological atypia
- Squamous cell carcinoma, usual type:
- Glans penis is preferential location, has irregular nests with moderately differentiated neoplastic cells
- The presence of broad areas of highly differentiated tumor is uncommon
- Verrucous carcinoma:
- Exophytic pattern of growth, broad pushing tumor base
Verrucous
Definition / general
Terminology
ICD coding
Epidemiology
Sites
Etiology
Clinical features
Treatment
Gross description
Gross images
AFIP images
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Alcides Chaux, M.D., Antonio Cubilla, M.D. and AFIP
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Verruciform, slow growing, extremely well differentiated variant of squamous cell carcinoma with low malignant potential
Terminology
- Also called Buschke-Löwenstein tumor
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8051/3 - verrucous carcinoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Represents 3 - 8% of all penile carcinomas and 12 - 38% of all verruciform tumors (Anal Quant Cytol Histol 2007;29:185)
- Median age 57 years
Sites
- Glans is the preferred site but there is occasionally extension to other compartments
- Tends to be multicentric in foreskin
Etiology
- Consistently HPV- or only rarely HPV+ when applying strict diagnostic criteria (Mod Pathol 1992;5:48, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:104)
Clinical features
- Many cases classified as verrucous carcinoma could be reclassified as other verruciform neoplasms
- Slow growing but may recur locally
- No inguinal nodal metastases and no death due to disease in pure verrucous carcinoma
Treatment
- Partial or total penectomy
- Possibly intra-arterial chemotherapy (Urology 2003;61:1216)
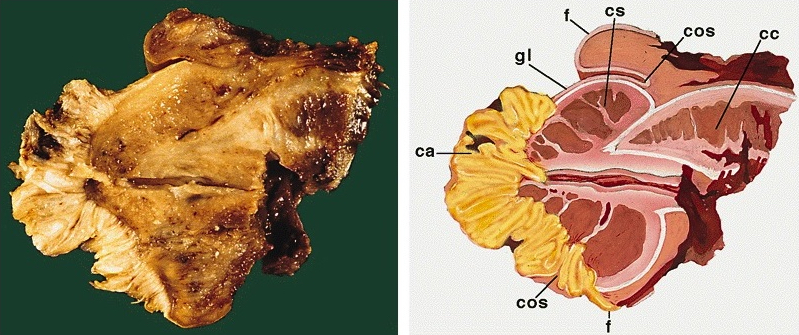
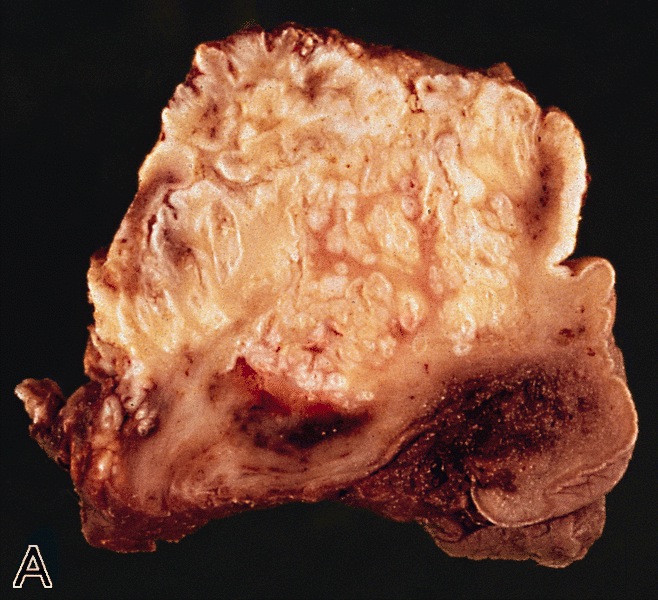
Gross description
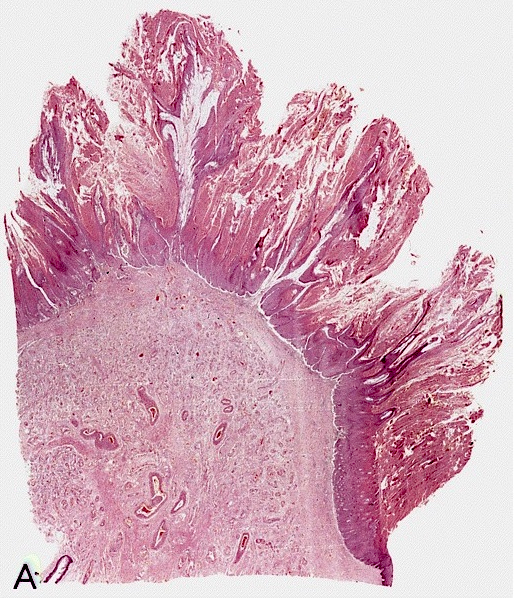
- Broad based white to gray exophytic neoplasm with a verruciform pattern of growth
- Invasion is usually limited to lamina propria or superficial corpus spongiosum
Gross images
AFIP images
Microscopic (histologic) description
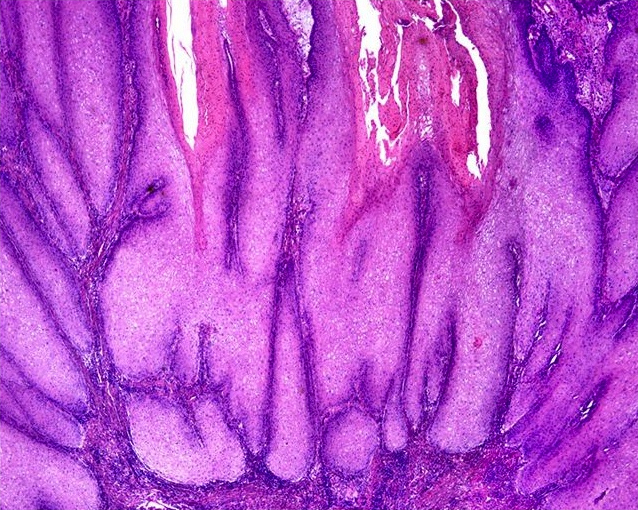
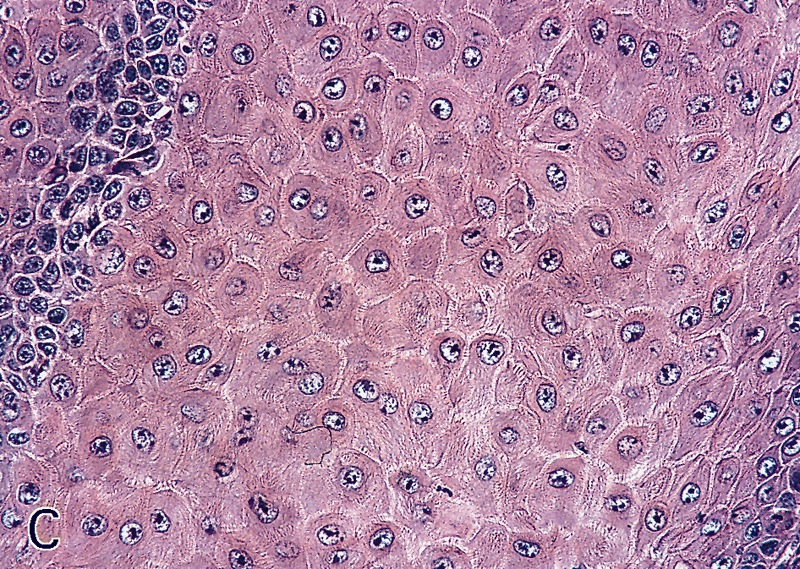
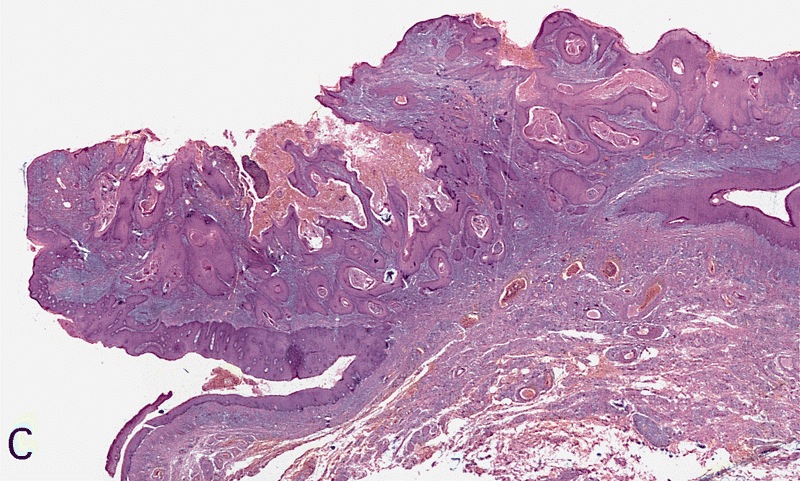
- Very well differentiated with prominent intercellular bridges, minimal atypia and rare mitotic figures
- Penetrates through lamina propria with broad base and pushing borders
- Hyperkeratotic and acanthotic papillae with keratin cysts
- Orthokeratosis more prominent than parakeratosis
- Tumor cells are polygonal squamous cells with glassy cytoplasm, central vesicular nuclei and intercellular edema; may have superficial vacuolated clear cells but no koilocytosis
- Dense inflammatory infiltrate may obscure tumor stroma boundary
- Intraepithelial abscess and crust formation is common
- Frequently associated with squamous hyperplasia and differentiated penile intraepithelial neoplasia
- Central fibrovascular cores are uncommon
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Alcides Chaux, M.D., Antonio Cubilla, M.D. and AFIP
Negative stains
- Low / negative p16 INK4a and Ki67 (Mod Pathol 2009;22:1160)
Differential diagnosis
- Giant condyloma:
- Conspicuous koilocytosis, prominent fibrovascular cores
- Hybrid verrucous carcinoma:
- Foci of usual squamous cell carcinoma intermingled with a typical verrucous carcinoma
- Papillary carcinoma:
- Invasive and jagged border, more atypia, irregular but usually evident fibrovascular cores
- Squamous hyperplasia:
- No atypia, no stromal reaction and no extension beyond lamina propria (in some cases distinction is not possible)
- Warty carcinoma:
- Koilocytotic change present, jagged tumor front, neoplastic cells with more pleomorphism, prominent fibrovascular cores and usually deeper invasion
Verrucous - carcinoma cuniculatum
Definition / general
Terminology
Epidemiology
Sites
Etiology
Clinical features
Case reports
Gross description
Gross images
Images hosted on other servers:
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Alcides Chaux, M.D. and Antonio Cubilla, M.D.
Differential diagnosis
- Rare, low grade variant of verruciform penile carcinoma with deeply penetrating and burrowing pattern of growth
- More common in plantar surface of foot, first described in 1954 (Br J Surg 1954;42:245)
Terminology
- Cuniculatum: from cuniculus, rabbit's burrow (hole)
Epidemiology
- Elderly men
- Mean age 77 years (range 73 - 83 years)
Sites
- Glans and coronal sulcus frequently involved
- Multiple anatomical compartments usually affected
Etiology
- No evidence of HPV infection
Clinical features
- Slow growing
- Tumors may begin as small warts and slowly progress to larger tumors
- No reported cases with regional nodal metastasis or cancer related death
Case reports
- Series of seven cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:71)
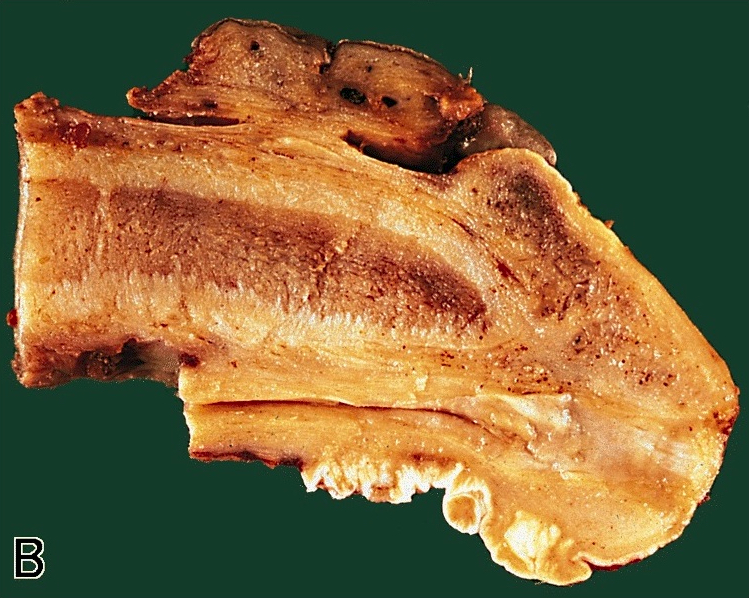
Gross description
- Verruciform pattern of growth
- Average size 6.3 cm (range 5 - 9 cm)
- Tumor invade deep erectile tissues with a burrowing pattern of growth on cut section
- Stroma tumor interface sharply delimited
- Presence of cyst-like and sinus structures
- Fistulae to preputial or shaft skin are common
Gross images
Images hosted on other servers:
Microscopic (histologic) description
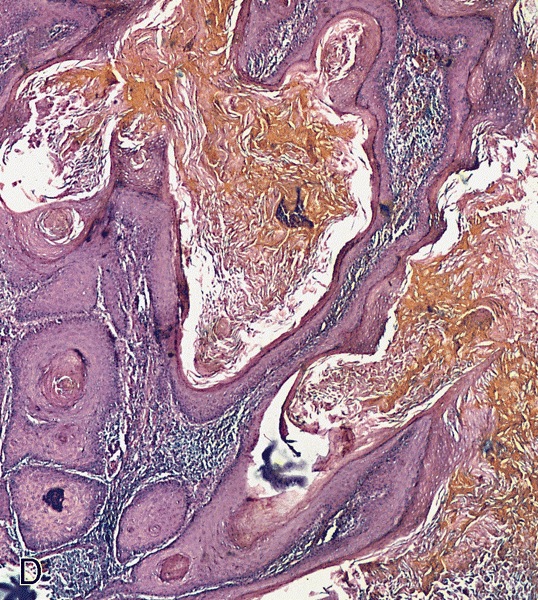
- Low grade keratinizing neoplastic nests resembling verrucous carcinoma
- Hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis and marked acanthosis
- Bulbous front of invasion
- Cyst-like and sinus lumina filled with hyperkeratotic material
- No / rare vascular and perineural invasion; no fibrovascular cores; no koilocytes
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Alcides Chaux, M.D. and Antonio Cubilla, M.D.
Differential diagnosis
- Mixed (hybrid) usual verrucous carcinoma:
- Verrucous carcinoma with foci of usual squamous cell carcinoma typically located at tumor front, absence of a burrowing pattern of growth
- Verrucous carcinoma:
- Similar in the exophytic component, usually limited to lamina propria or superficial corpus spongiosum and absence of a burrowing pattern of growth
- Warty carcinoma:
- Condylomatous papillae with prominent fibrovascular cores, conspicuous koilocytosis and jagged tumor front
Papillary
Definition / general
ICD coding
Epidemiology
Sites
Etiology
Clinical features
Gross description
Gross images
AFIP images
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Alcides Chaux, M.D., Antonio Cubilla, M.D. and AFIP
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Slow growing, low grade verruciform variant of squamous cell carcinoma representing 5 - 15% of all penile carcinomas and 27 - 53% of all verruciform tumors (Anal Quant Cytol Histol 2007;29:185)
- Diagnosis is made after exclusion of other verruciform tumors
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8050/3 - papillary carcinoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Mean age 57 years (range 26 - 84 years)
Sites
- Usually involves glans, possibly with foreskin and coronal sulcus
Etiology
- Low HPV detection rate (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:104)
Clinical features
- Inguinal nodal metastases in 0 - 25% and local recurrence in 12% of all cases
- Low mortality rate (0 - 6%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:223)
Gross description
- Usually in glans but extension to coronal sulcus and inner foreskin is common
- Large gray-white exophytic destructive lesion
- Mean tumor size 5.5 cm (range 1 - 9 cm)
- Cut surface shows pearly white papillomatous tissue, poor demarcation between tumor and stroma
Gross images
AFIP images
Microscopic (histologic) description
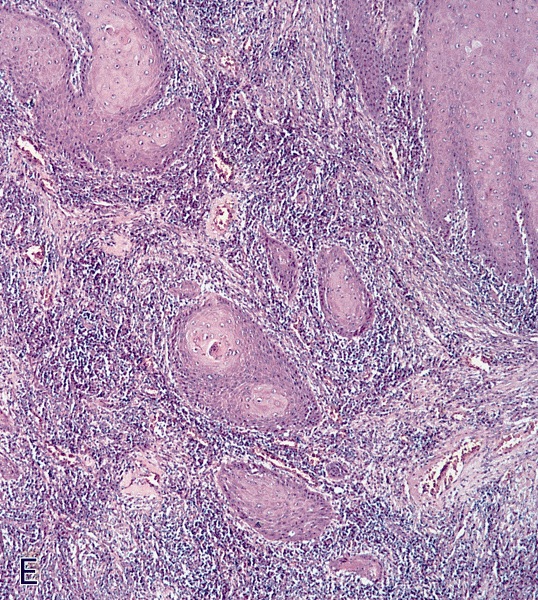
- Well differentiated papillary squamous neoplasm
- Prominent hyperkeratosis and acanthosis
- Complex papillae with irregular fibrovascular cores
- Irregular / infiltrative tumor base
- Frequent association with squamous hyperplasia (74%), differentiated penile intraepithelial neoplasia (46%) and lichen sclerosus (34%)
- May have keratin cysts and intraepithelial abscesses
- High grade foci are unusual
- No koilocytotic changes
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Alcides Chaux, M.D., Antonio Cubilla, M.D. and AFIP
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Squamous cell carcinoma, NOS:
- No prominent papillary features, most cases are moderately differentiated
- Squamous hyperplasia:
- No atypia, no stromal reaction and no extension beyond lamina propria
- Verrucous carcinoma:
- Inconspicuous fibrovascular cores, broad / bulbous boundary of tumor and stroma
- Warty carcinoma:
- Prominent fibrovascular cores, pleomorphic cells with koilocytotic changes
Sarcomatoid
Definition / general
Terminology
ICD coding
Epidemiology
Sites
Etiology
Clinical features
Case reports
Gross description
Gross images
AFIP images
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Alcides Chaux, M.D., Antonio Cubilla, M.D., Ajeeth Kumar, M.D., Eliz Thomas, M.D., Mythreye Karthikeyan, Ph.D. and AFIP
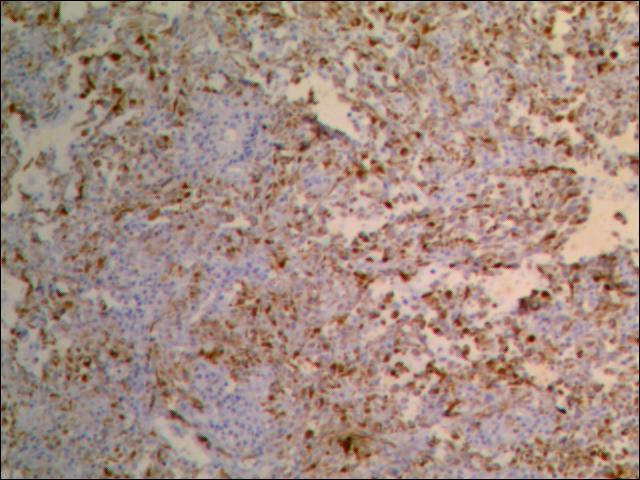
Positive stains
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Aggressive variant of penile squamous cell carcinomas composed mostly of anaplastic spindle cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1152)
Terminology
- Also called spindle cell carcinoma
- Rare tumors with distinct sarcoma and carcinoma components are called carcinosarcoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8074/3 - squamous cell carcinoma, sarcomatoid
Epidemiology
- Median age 59 years (range 28 - 81 years)
Sites
- Preferred site is glans but extension to coronal sulcus and foreskin is not unusual
Etiology
- May occur after radiation therapy; low HPV detection rate
Clinical features
- Represents 1 - 3% of all penile carcinomas (J Urol 2004;172:932)
- High mortality rate (40 - 75%)
- Inguinal nodal metastases in 75 - 89% and local recurrence in 67% of all cases
Case reports
- 50 year old man with 3 cm tumor of glans (Indian J Urol 2008;24:267)
Gross description
- Large gray-white or red polypoid or fungating mass with frequent ulceration and hemorrhage
- Mean tumor size 3 - 5 cm (up to 7 cm)
- Cut surface shows deep invasion of corpus spongiosum or corpora cavernosa
- Superficial or deep tumor satellite nodules
Gross images
AFIP images
Microscopic (histologic) description
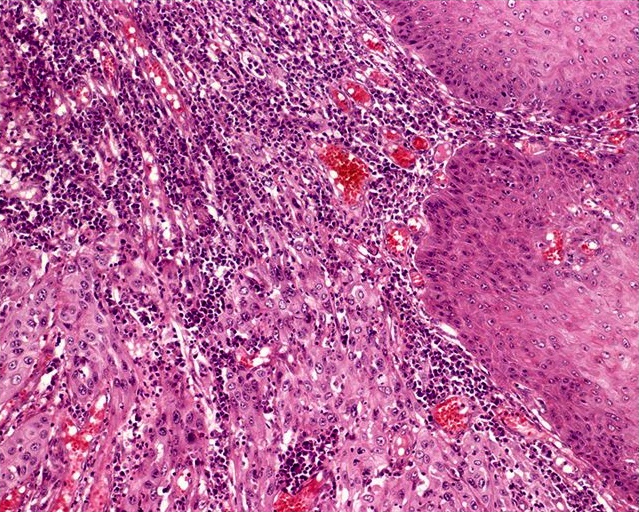
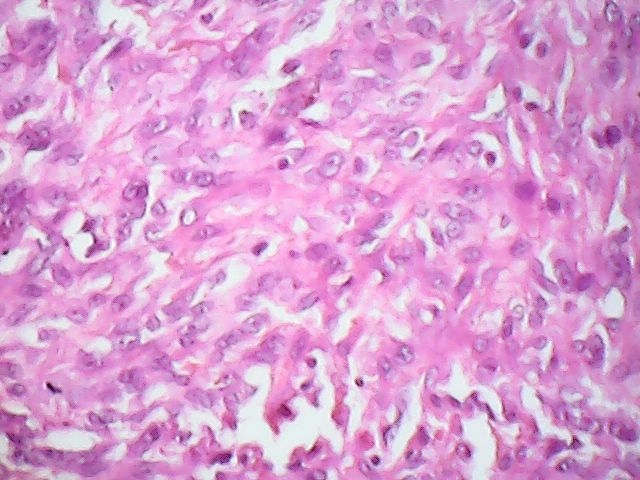
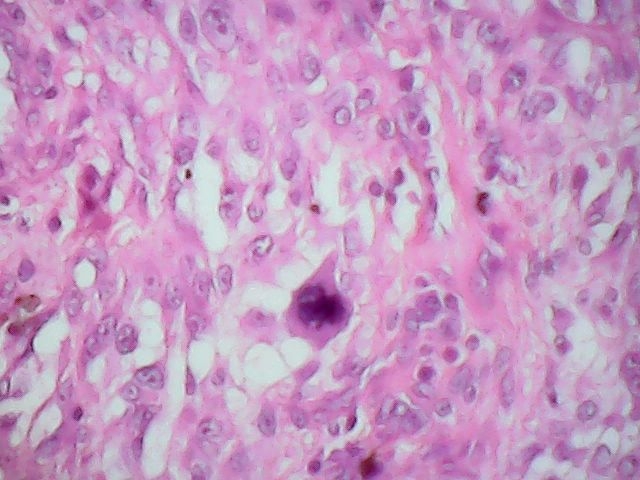
- Predominantly anaplastic spindle cells resembling fibrosarcoma or leiomyosarcoma
- Occasional giant or multinucleated malignant fibrohistocytoma-like cells
- Foci of usual squamous cell carcinoma present in most cases
- Prominent necrosis and mitotic activity
- Areas of myxoid, chondroid, osteosarcomatous or angiosarcomatous-like changes may be observed
- Penile intraepithelial neoplasia in adjacent mucosa is not uncommon
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Alcides Chaux, M.D., Antonio Cubilla, M.D., Ajeeth Kumar, M.D., Eliz Thomas, M.D., Mythreye Karthikeyan, Ph.D. and AFIP
Positive stains
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis